Abstract
Bacteria that utilize sunlight to supplement metabolic activity are now being described in a range of ecosystems. While it is likely that phototrophy provides an important competitive advantage, the contribution that these microorganisms make to the bioenergetics of polar marine ecosystems is unknown. In this minireview, we discuss recent advances in our understanding of phototrophic bacteria and highlight the need for future research.
1. Introduction
Microorganisms have been fundamentally important to the history and function of life on Earth. They have played a central role in the climatic, geological, and biological evolution of the planet [1]. They are found in every conceivable ecological niche, from the tropics to the poles, from underground mines and oil fields to the stratosphere and mountain ranges, from deserts to the Dead Sea and from hot springs to underwater hydrothermal vents [2,3,4,5]. Microbes dominate the flux of energy and biologically important chemical elements in the world’s oceans and, as a result, are estimated to be five to ten times the mass of all multicellular marine organisms [6]. Bacteria harbor a potential reservoir of useful genes for medicine and biotechnology, and unraveling their complex taxonomic diversity is considered the key to understanding the process of evolution [7,8].
Sea ice is one of the most seasonally dynamic ecosystems on Earth. An important driver of the global climate system, annual sea ice at polar latitudes influences both physical and biological processes; particularly in modulating the exchange of heat and moisture between the atmosphere and ocean, and restricting the penetration of solar radiation. Importantly, sea ice also provides a stable platform for the colonization and growth of marine microbes [9,10]. Although a range of microbial taxa are initially scavenged from the water column during ice formation, only some are able to adapt to the physicochemical variability that characterizes the brine inclusions and interstices of the ice matrix. The most conspicuous ice-bound organisms are microalgae and research efforts have historically focused on the composition, physiology, and ecology of the diatoms that dominate sea ice assemblages [11,12,13,14,15]. Sea ice algae contribute between 10%–28% of the total primary production in ice-covered regions of the Southern Ocean [10,16] and over 90% of this biogenic carbon is produced within first-year ice and approximately 60% during the austral spring (November-December) when the algal cells typically discolor the bottom 1–20 cm of the ice [16] (Figure 1). Microalgae provide a crucial source of winter nutrition for juvenile zooplankton such as the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba [17,18], and may provide inocula for bloom events at the receding ice edge in the austral summer [11,16,19,20].
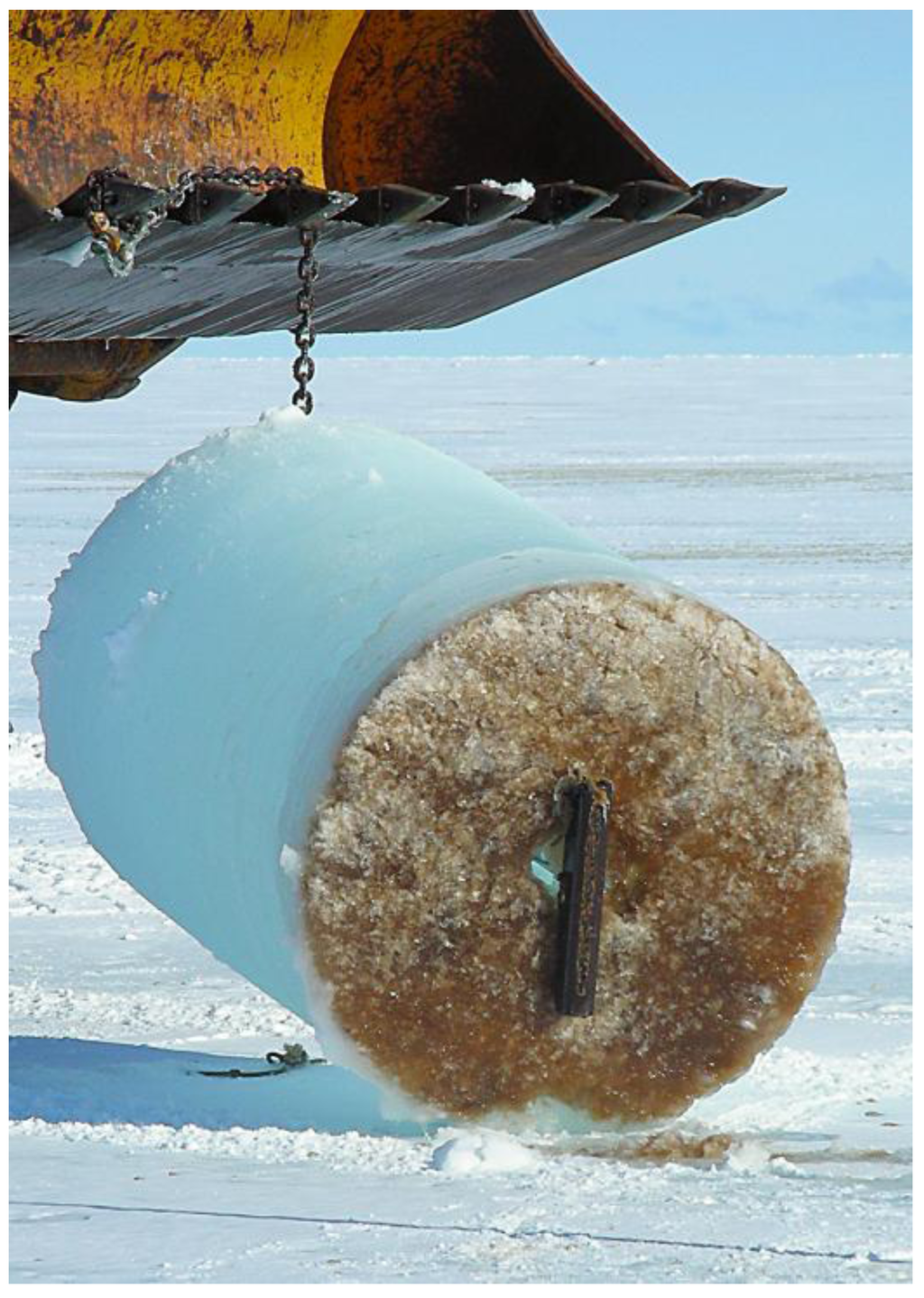

Figure 1.
Cross-section of sea ice. A distinct brown coloration is present at the bottom 20 cm of a 1 m diameter section of sea ice. This is due to the high concentration of bacteria and microalgae within the sea ice.
While bacteria are now recognized as a major biological component of the oceanic carbon cycle and ecosystem structure [21,22], an understanding of the phylogenetic diversity and functional capabilities of ice-associated bacteria remains fragmentary [23]. Evidence that bacteria actively grow within the ice dates back to only the 1980’s when Sullivan and Palmisano [24] observed large and morphologically distinct bacteria undergoing cell division in fast-ice within McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. This initial observation indicated an active heterotrophic community, and the subsequent microautoradiographic uptake of radiolabeled compounds such as 14C-L-serine, 3H-serine, 3H-glucose and 3H-thymidine confirmed community-level activity in the form of DNA synthesis [24,25]. More recent single-cell analyses, including the use of tetrazolium chloride (CTC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), have shown that ~80% of the bacteria present in the bottom of Antarctic sea ice have a probe-positive cellular rRNA content and >30% of the cells have an electron transport system that is capable of reducing CTC [26,27]. Most of these cells appear to be heterotrophic bacteria, which either live freely or attached to microalgae or detritus [28,29]. Molecular-based surveys of SSU rRNA gene diversity typically reveal psychrophilic and halotolerant members of the Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes (previously known as the Cytophaga-Flavobacteria-Bacteroides (CFB) cluster) and Gram-positive bacteria [23,28,30].
Following a decade of seminal research conducted within McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Sullivan [25] suggested that sea ice bacteria might play an important role in secondary microbial production mediated through the microbial loop and remineralisation and recycling of ice-associated organic matter (Figure 2). Sullivan [25] also postulated that these bacteria maintain a balance of oxygen concentration in the ice microenvironment through their respiration and may be involved in ice nucleation and early stages of sea ice formation although these ideas remain largely unsubstantiated.
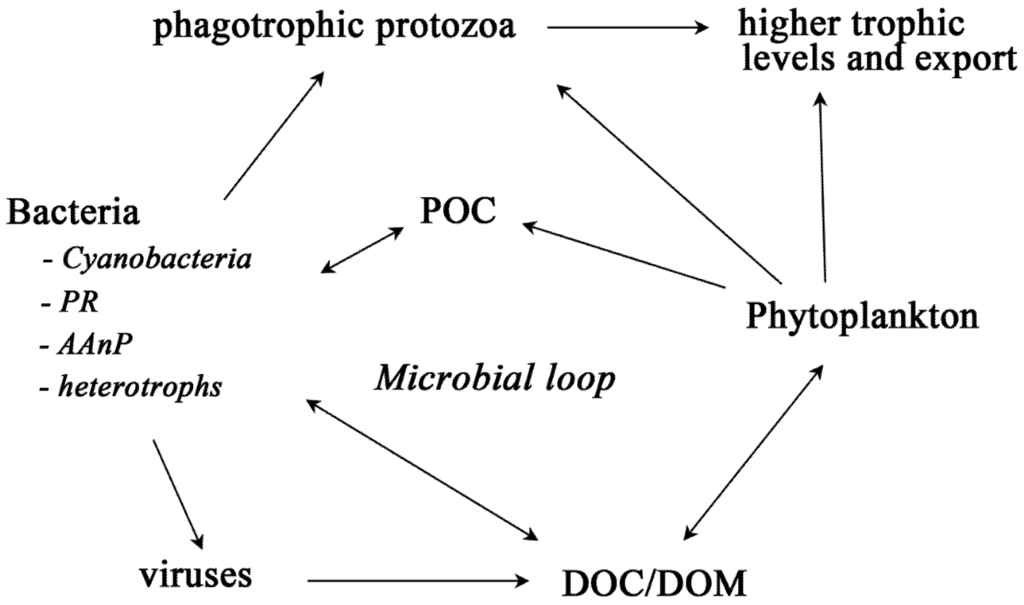
Figure 2.
Sea ice food web and the microbial loop. The microbial loop re-drawn and abridged from Azam et al. (1983) and Fenchel (2008). Only the bacteria discussed in this review are presented; the other bacteria are grouped as heterotrophs. AAnP = aerobic anaerobic phototroph, DOC = dissolved organic carbon, DOM = dissolved organic matter, POC = particulate organic carbon, PR = proteorhodopsins.
2. Bacteria with Light-Harvesting Capabilities
The energy to support life in the sea is ultimately derived from phototrophy in the euphotic zone [31]. The most significant contribution from prokaryotic life forms is from cyanobacteria, which utilize chlorophyll-based phototrophy and contribute 30% of all globally fixed carbon [32]. However, in recent years, non-cultivation-based studies of bacteria have led to the discovery of novel genes, proteins and phototrophic mechanisms that are rapidly gaining scientific interest [33,34,35,36,37]. In particular, widespread reports of bacteriochlorophyll (bchl) and proteorhodopsin (PR) in planktonic marine prokaryotes are challenging the assumption that chl-a is the only light-capturing pigment of ecological importance. It remains to be seen whether these metabolic pathways will require a significant revision of oceanic energy budgets [22,38], but alternative light-based metabolic strategies are now being described in aquatic ecosystems that range from the deep-sea biosphere to high-altitude glaciers [39,40].
2.1. Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria colonize a variety of polar terrestrial ecospheres including rocks, glaciers, ice shelves, streams, ponds and lakes [41,42,43,44,45]. Phototrophs in these environments are generally psychrotolerant and exhibit an assortment of cold-protection mechanisms and slow growth rates to endure freeze-thaw cycles. The intracellular accumulation of salts to sustain osmotic balance, variation in DNA repair mechanisms and the use of photo-complexes are additional strategies that terrestrial cyanobacteria employ in extreme cold environments [44,46,47]. Picocyanobacteria such as Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus are the most abundant phototropic cells in the World’s oceans [48]. Despite this significant contribution to primary production, these cells are small, 0.5–1.5 µm and, in the case of Prochlorococcus, remained undetected until 1986 when they were discovered using flow cytometry [49]. Importantly, the abundance of marine cyanobacteria decreases rapidly south of latitude 40° [50,51,52] and this has been attributed to eco-physiological factors such as temperature, salinity and nutrient requirements [44].
Considering their prevalence in cold terrestrial environments, the apparent absence of cyanobacteria within sea ice is, however, unexpected. Interestingly, Synechococcus was detected from coastal waters off East Antarctica in 1989 using microscopy and pigment chemistry [53] and a decade later, cyanobacterial-like pigments (phycoerythrin and phycocyanin) were detected for the first time within the ice matrix using flow cytometry [54]. Pigment-based confirmation is questionable however as phycoerythrin and phycocyanin are also present in other algae including Cryptophytes which are common during Antarctic coastal blooms [54]. To potentially validate these earlier findings, a multi-method molecular analysis was recently carried out on fast-ice cores extracted from sites spanning 300 km in the Ross Sea region of Antarctica [55]. Clone libraries were constructed from the 16S rDNA gene, the internal transcribed sequence (ITS) region and the cyanobacterial core RNA polymerase (rpoC). Analysis of all sections of extracted ice did not reveal the presence of Synechococcus sp., Prochlorococcus sp., or any other marine cyanobacteria-related species. Additional screening was carried out using ligation detection reaction-based microarray, which can detect as little as 1 fmol of DNA [56]. Data from the ITS and microarray analysis of these sea ice samples showed close affiliation to the freshwater cyanobacteria Phormidium sp. and Cylindrospermopsis sp., respectively [55], but the closest Antarctic relative was an uncultured cyanobacteria clone from the nearby meromictic Lake Fryxell [42]. Aerobiology studies conducted in the Antarctic [57,58] and the Arctic [59] suggested that much of the biological material present in the air originates locally. Harding et al. [59] observed that >47% of the operational taxonomic units (OTUs) in Arctic snow samples were from previously reported local cyanobacteria [45,60]. Given that Terra Nova Bay is situated in a katabatic wind cross-zone [61], it is likely that the cyanobacterial propagules identified by Koh et al. [55] were wind-transported from nearby freshwater ponds or terrestrial soil and incorporated into the ice during seasonal formation. Despite earlier anecdotal findings, molecular-based evidence now confirms that cyanobacteria do not play a significant role in sea ice ecosystem dynamics.
2.2. Bacteriochlorophyll
Phototropic metabolism is a feature of four other eubacterial phyla (i.e., Proteobacteria, Chlorobi, Chloroflexi and Firmicutes). Unlike cyanobacteria, these phototrophs utilize the most ancient form of photosynthesis: anoxygenic photosynthesis [62]. This pathway is important for nitrogen-fixation, and cells with bacteriochlorophyll (bchl) also play an important role in the microbial loop [63,64]. The presence of highly diverse anoxygenic phototrophic bacterial communities in marine environments now suggests that non-chlorophyll-a phototrophy may be a more common life history strategy than previously realized. For example, the Proteobacteria contain the largest group of anoxyphototrophs [65], which were thought to be strictly anaerobic until three decades ago when the first aerobic representative was identified [66]. In both aerobic and anaerobic taxa, bchl-a is the primary light-harvesting pigment and absorbs red light at 770 to 880 nm and blue light at ~385nm [67,68,69]. This provides a useful contrast to the chlorophyll-a present in cyanobacteria and algae, which absorbs at 430 nm and 665 nm (Figure 3).
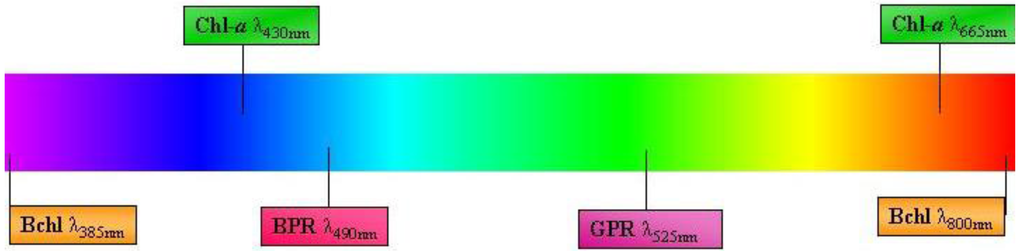
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of light pigments/proteins of sea ice phototrophic bacteria. Bchl = bacteriochlorophyll; Chl-a = Chlorophyll-a; BPR = Blue proteorhodopsin; GPR = Green proteorhodopsin. Diagram not drawn to scale.
The aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic (AAnP) bacteria are a diverse group of prokaryotes with respect to their functionality, physiology, and morphology [69]. These are obligate aerobes with unusually high concentrations of carotenoids, low cellular contents of bchl-a and a distinct lack of the light-harvesting complex II [38,39]. In the anaerobic phototrophic bacteria (AnPB), the puf operon coding for the bchl is repressed by both oxygen and high light [70]. However, in the AAnP, the expression of the puf operon is not limited by oxygen, but it is still repressed by strong light [37,71,72]. Despite these physiological differences, both AnPB and AAnPs have a similar photosynthetic apparatus and similar electron carriers and structural polypeptides [73]. The close correlation between AAnPs and oxygenic phototrophs in the euphotic zone may indicate that these cells contribute to a light-controlled component of the microbial redox cycle [38]. Several molecular studies based on the genes of the puf operon have been carried out in tropical, temperate and polar marine environments [74,75,76,77,78,79] and these organisms have been estimated to account for up to 10% of the energy production in the upper layers of the water column [38,80] in most temperate and tropical oceans.
There is some evidence to suggest that AAnP bacteria are absent at high latitudes [81] and are genetically distinct from their freshwater counterparts [82,83]. However, positive pufM [64,73] clonal sequences were detected from extracted DNA and messenger RNA transcripts from the lower sections of Antarctic annual fast-ice as well as the underlying water column [84]. All clones grouped with the cultured α-Proteobacteria [39,74]. No β- and δ-Proteobacteria AAnPs were detected in the sea ice, matching the observations of Karr et al. [82] at Lake Fryxell. In fact, all the sea ice and seawater clones were likely α-Proteobacteria Roseobacter-clade affiliated [84], which could constitute ~20% of the Southern Ocean bacterial community [85,86], given that Roseobacter denitrificans is able to illicit specific defence systems against photo-oxidative stress [87]. More importantly, their presence in RNA extracts indicates that bacteria within the sea ice are actively expressing the gene for bchl synthesis.
AAnPs may constitute only ~0.05% of the prokaryotic abundance in the Western Antarctic waters [80], however the ease with which AAnPs were found within sea ice suggests that their relative proportion may be higher in ice-associated microbial communities. Results obtained by quantitative PCR suggest that Bchl OTUs may comprise up to 10% of the sea ice bacterial community [88], although further work is clearly needed to ascertain the ecological significance of this metabolic pathway.
2.3. Proteorhodopsin
The discovery of phototrophic energy generated via proteorhodopsin (PR) was a major finding in microbial ecology [89]. PRs are retinal binding bacterial integral membrane proteins that belong to the microbial rhodopsin super-family of proteins and function as light-driven proton pumps [89,90]. Unlike Bchl, PR cells do not generate cellular reducing power through NADPH, however ATP is produced upon light stimulation without the evolution of oxygen or fixation of inorganic carbon. Since the first reported PR sequence was obtained in 2000 [89], many other PR-bearing bacteria have been identified in environments ranging from freshwater lakes to the deep marine biosphere [91,92,93,94,95,96]. PR genes appear to be abundant in the genomes of oceanic bacteria [95], accounting for 13% of the prokaryotic community in the Mediterranean Sea and Red Sea and 70% in the Sargasso Sea [94,95,97,98]. Importantly, in vitro studies have demonstrated proton pumping and increased growth rates of PR-bearing bacteria under illuminated conditions [99,100,101,102]. Recently, PR in Candidatus Pelagibacter ubique was reported to play a critical role in a cellular response that maintains cell function during periods of carbon starvation [102]. These observations suggest that harvesting light energy via PR may be important in marine environments [103], but again the ecological significance of this metabolic pathway is currently unknown.
Sea ice bacteria that express the PR gene were described for the first time in 2010 [104]. PR-bearing representatives from the classes α-Proteobacteria, γ-Proteobacteria and Flavobacteria were present throughout the fast-ice in the Ross Sea region of Antarctica. Complementary DNA (cDNA) generated from RNA samples suggested that PR bacteria were metabolically active at the time of sampling. The bulk of the positive cDNA samples were collected from the middle and bottom part of the ice matrix, which possibly indicates that PR bacteria favor the lower light intensity and relatively stable temperatures found in the bottom half of the ice. Essentially, as light penetrates deeper into the ice matrix, the more energetic blue light predominates [105]. A stratified distribution of different forms of PR-bacteria in marine waters has been observed previously [106,107], and this has been attributed to a single-residue switch mechanism whereby the presence of leucine or glutamine at amino acid position 105 determines whether the protein absorbs in the green or blue wavelength [106]. Koh et al. [104] found both blue-absorbing (BPR) and green-absorbing (GPR) forms, but BPR were found primarily in the middle of the ice where red and green wavelengths of the solar spectrum are relatively low [105]. Conversely, GPR appear to be distributed throughout the ice, but their highest concentrations were at the ice/water interface [104], where, due to the presence of eukaryotic chl-a, the only available light is green.
3. Future Research and the Significance of Light-Harvesting Pigments for Antarctic Sea Ice
Research-to-date has confirmed that some of the bacteria present in Antarctic sea ice are capable of phototrophic metabolism, most likely as a supplement to an otherwise heterotrophic lifestyle. A mechanistic understanding of the diversity, ecophysiology, and functionality of marine photoheterotrophs is therefore a worthy goal, but one that is extremely challenging [108].
Logistic and weather constraints are the primary reasons that polar studies are conducted during the summer months. As a result, insight into ice-associated light-harvesting bacteria has thus far come from cores extracted during the austral summer. In the future, it will be particularly important to contrast the light-driven energy flux with the metabolic processes and activity level that take place during the dark polar winter. Only a handful of over-winter studies have been reported in the more accessible Arctic [78,109,110], however microorganisms are more active during summer months compared with winter.
Next generation pyrosequencing [111,112], microfluidics [113] and microarray analysis [114,115,116] are rapidly changing the way microbial communities are studied. These high-throughput methods could be employed to elucidate more phototrophic bacteria from Antarctic sea ice and accurately determine their in situ distribution and abundance. Techniques such as catalyzed reporter deposition (CARD)-FISH [117] and quantitative PCR [80,118] will enable functional gene expression to be quantified at the single-cell level of resolution. In addition, metatranscriptomics and proteomics would provide a valuable tool with which to link in situ expression dynamics with environmental stress [99,119,120]. Coupled with the chromatin immune-precipitation (ChIP) procedure, it is now possible to characterize both the genome-wide location and function of novel energy-binding proteins [120,121,122].
4. Concluding Remarks
Sea ice represents one of the most ephemeral habitats on Earth and the ice-associated microbial communities are integral to the energy base of the Southern Ocean ecosystem. The specific physiological roles and adaptive strategies of phototrophic bacteria within this ecosystem have yet to be elucidated; however, the future looks promising given the expanding range of technologies that may be used to explore the bioenergetics of light-harvesting pathways. There is also a growing need to quantify the resilience of sea ice microbes to increased environmental stress and to provide a real-time biological response to climate change. Considering the variety of genetic, physiological and environmental contexts in which light-harvesting bacteria are found, the diversity observed to date may reflect only a subset of the organisms present and more light-dependent adaptive strategies are likely to exist in the microbial world. The combined sequencing of cultivated and uncultivated organisms will undoubtedly reveal more microbial groups with known, or even novel, photosynthetic abilities.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant VICX0706 from the New Zealand Foundation of Research Science and Technology and Victoria University of Wellington Faculty Strategic Research Grants 103167/2585 and 96429/2661.
References
- Xu, J. Microbial ecology in the age of genomics and metagenomics: Concepts, tools, and recent advances. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 1713–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, K.; Imhoff, F.; Staley, T.; Deming, J.W. Phylogenetic diversity of numerically important Arctic sea-ice bacteria cultured at subzero temperature. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.L.; Pérez, A.; Garcia-Pichel, F. The prokaryotic diversity of biological soil crusts in the Sonoran Desert (Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, AZ). FEMS Microb. Ecol. 2005, 54, 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- McCliment, E.A.; Voglesonger, K.M.; O’Day, P.A.; Dunn, E.E.; Holloway, J.R.; Cary, S.C. Colonization of nascent, deep-sea hydrothermal vents by a novel Archaeal and Nanoarchaeal assemblage. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, R.M.; Wood, S.A.; Grzymski, J.J.; McDonald, I.R.; Cary, S.C. Microbial biodiversity of thermophilic communities in hot mineral soils of Tramway Ridge, Mount Erebus, Antarctica. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.R.; Williams, P.J.I.; Azam, F.; Hobbie, J.E. The microbial loop. Oceanography 2007, 20, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, N.R. A molecular view of microbial diversity and the biosphere. Science 1997, 276, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrós-Alió, C. Marine microbial diversity: Can it be determined? Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Delille, D. Marine bacterioplankton at the Weddell Sea ice edge, distribution of psychrophilic and psychrotrophic populations. Polar Biol. 1992, 12, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, L.; Ackley, S.F.; Dieckmann, G.S.; Gulliksen, B.; Horner, R.; Hoshiai, T.; Melnikov, I.A.; Reeburgh, W.S.; Spindler, M.; Sullivan, C.W. Ecology of sea ice biota. 2. Global significance. Polar Biol. 1992, 12, 429–444. [Google Scholar]
- Kottmeier, S.T.; Sullivan, C.W. Sea ice microbial communities (SIMCO) 9. Effects of temperature and salinity on rates of metabolism and growth of autotrophs and heterotrophs. Polar Biol. 1988, 8, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMinn, A.; Ashworth, C.; Ryan, K.G. In situ net primary productivity of an Antarctic fast ice bottom algal community. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 21, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.G.; McMinn, A.; Mitchell, K.A.; Trenerry, L. Mycosporine-like amino acids in Antarctic sea ice algae, and their response to UVB radiation. Z. Naturforsch. C 2002, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, K.G.; Cowie, R.O.M.; Liggins, E.; McNaughtan, D.; Martin, A.; Davy, S.K. The short-term effect of irradiance on the photosynthetic properties of Antarctic fast-ice microalgal communities. J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.G.; Tay, M.L.; Martin, A.; McMinn, A.; Davy, S.K. Chlorophyll fluorescence imaging analysis of the responses of Antarctic bottom-ice algae to light and salinity during melting. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 399, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.R.; Thomas, D.N. Large scale importance of sea ice biology in the Southern Ocean. Antarct. Sci. 2004, 16, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, K.L. Overwintering development, growth, and feeding of larval Euphausia superba in the Antarctic marginal ice zone. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 1564–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottmeier, S.T.; Sullivan, C.W. Bacterial biomass and production in pack ice of Antarctic marginal ice edge zones. Deep-Sea Res. 1990, 37, 1311–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesenhagen, H.C.; Detmer, A.E.; de Wall, J.; Weber, A.; Gradinger, R.R.; Jochem, F.J. How are Antarctic planktonic microbial food webs and algal blooms affected by melting of sea ice? Microcosm simulations. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, M.P. The contribution of sea ice algae to Antarctic marine primary production. Am. Zool. 2001, 41, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delille, D.; Rosiers, C. Seasonal changes of Antarctic marine bacterioplankton and sea ice bacterial assemblages. Polar Biol. 1996, 16, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, F.; Worden, A.Z. Microbes, molecules, and marine ecosystems. Science 2004, 303, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.E.; Grzymski, J.J. Diversity and genomics of Antarctic marine micro-organisms. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2007, 362, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.W.; Palmisano, A.C. Sea ice microbial communities: distribution, abundance, and diversity of ice bacteria in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, in 1980. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 47, 788–795. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, C.W. Reciprocal interactions of the organisms and their environmen. In Sea Ice Biota; Horner, R., Ed.; Boca Raton Chemical Rubber Company: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 160–171. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Hall, J.A.; O’Toole, R.; Davy, S.K.; Ryan, K.G. High single-cell metabolic activity in Antarctic sea ice bacteria. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 52, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Hall, J.A.; Ryan, K.G. Low salinity and high-level UV-B radiation reduce single-cell activity in Antarctic sea ice bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7570–7573. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.V.; Bowman, J.P. A molecular phylogenetic survey of sea-ice microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 35, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, K.; Krembs, C.; Deming, J.W.; Stierle, A.; Eicken, H. A microscopic approach to investigate bacteria under in situ conditions in sea-ice samples. Ann. Glaciol. 2001, 33, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, G.; Giuliano, L.; D’Auria, G.; Smedile, F.; Azzaro, M.; de Domenico, M.; Yakimov, M.M. Study of bacterial communities in Antarctic coastal waters by a combination of 16S rRNA and 16S rDNA sequencing. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2150–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, D.M. Microbial oceanography: Paradigms, processes and promise. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bhargava, P.; Rai, L.C. Molecular approaches towards assessment of cyanobacterial biodiversity. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 4284–4298. [Google Scholar]
- Madigan, M.T. Anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria from extreme environments. Photosynth. Res. 2003, 76, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyi, J.K. Bacteriorhodopsin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 665–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, D.A.; Frigaard, N.-U. Prokaryotic photosynthesis and phototrophy illuminated. Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J.A.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Stingl, U. Proteorhodopsins: An array of physiological roles? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 488–494. [Google Scholar]
- Yurkov, V.; Csotonyi, J.T. New light on aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs. In The Purple Phototrophic Bacteria; Hunter, C.N., Daldal, F., Thurnauer, M.C., Beatty, J.T., Eds.; Springer Science: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 31–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kolber, Z.S.; Gerald, F.; Lang, A.S.; Beatty, J.T.; Blankenship, R.E.; VanDover, C.L.; Vetriani, C.; Koblizek, M.; Rathgeber, C.; Falkowski, P.G. Contribution of aerobic photoheterotrophic bacteria to the carbon cycle in the ocean. Science 2001, 292, 2492–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Rathgeber, C.; Beattyc, J.T.; Yurkov, V. Aerobic phototrophic bacteria: New evidence for the diversity, ecological importance and applied potential of this previously overlooked group. Photosynth. Res. 2004, 81, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, H.; Yu, B.; Lv, G.; Deng, S.; Wu, Y.; Dai, M.; Jiao, N. Abundance and diversity of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria in saline lakes on the Tibetan plateau. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, I.; Schwarz, A.-M.J. Absorption and utilization of irradiance by cyanobacterial mats in two ice-covered antarctic lakes with contrasting light climates. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taton, A.; Grubisic, S.; Brambilla, E.; de Wit, R.; Wilmotte, A. Cyanobacterial diversity in natural and artificial microbial mats of Lake Fryxell (McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica): A morphological and molecular approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Hawes, I.; Mountfort, D.; Hitzfeld, B.; Dietrich, D.R.; Burns, B.P.; Neilan, B.A. Diversity within cyanobacterial mat communities in variable salinity meltwater ponds of McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, W.F. Cold tolerance in cyanobacteria and life in the cryosphere. In Cellular Origin and Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology; Seckbach, J., Ed.; Springer Science: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 289–301. [Google Scholar]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Lovejoy, C.; Vincent, W.F. Global distribution of cyanobacterial ecotypes in the cold biosphere. ISME J. 2010, 4, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.P.Y.; Vincent, W.F. Strategies of thermal adaptation by high-latitude cyanobacteria. New Phytol. 1999, 142, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Zakhia, F.; Jungblut, A.-D.; Taton, A.; Vincent, W.F.; Wilmotte, A. Cyanobacteria in cold ecosystems. In Psychrophiles: From Biodiversity to Biotechnology; Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Marx, J.-C., Gerday, C., Eds.; Springer Science: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Partensky, F.; Hess, W.R.; Vaulot, D. Prochlorococcus, a marine photosynthetic prokaryote of global significance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 106–127. [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm, S.W.; Olson, R.J.; Zettler, E.R.; Goericke, R.; Waterbury, J.B.; Welschmeyer, N.A. A novel free-living prochlorophyte abundant in the oceanic euphotic zone. Nature 1988, 334, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.S.; Haugen, E.M. The distribution and abundance of phototrophic ultraplankton in the North-Atlantic. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1985, 30, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, H.J.; Davidson, A.T.; Wright, S.W. The distribution and abundance of chroococcoid cyanobacteria in the Southern Ocean. Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol. 1987, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, W.F. Cyanobacterial dominance in the polar regions. In The Ecology of Cyanobacteria; Whitton, B.A., Potts, M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 2000; pp. 321–340. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, T.D.; Marchant, H.J. The seasonal occurrence of chroococcoid cyanobacteria at an Antarctic coastal site. Polar Biol. 1989, 9, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, C.; Moro, I.; La Rocca, N.; Dalla Valle, L.; Masiero, L.; Rascio, N.; Dalla Vecchia, F. Ecological, physiological and biomolecular surveys on microalgae from Ross Sea (Antarctica). Ital. J. Zool. 2000, 67, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, E.Y.; Cowie, R.O.M.; Simpson, A.M.; O’Toole, R.; Ryan, K.G. The origin of cyanobacteria in Antarctic sea ice: Marine or freshwater? Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2012, 4, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, B.; Rizzi, E.; Frosini, A.; Sivonen, K.; Rajaniemi, P.; Rantala, A.; Mugnai, M.A.; Ventura, S.; Wilmotte, A.; Boutte, C. Development of a universal microarray based on the ligation detection reaction and 16S rRNA gene polymorphism to target diversity of cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 7161–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.A.; McCartney, H.A.; Lachlan-Cope, T.A.; Pearce, D.A. A preliminary study of airborne microbial biodiversity over peninsular Antarctica. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 50, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, D.A.; Bridge, P.D.; Hughes, K.A.; Sattler, B.; Psenner, R.; Russell, N.J. Microorganisms in the atmosphere over Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, T.; Jungblut, A.D.; Lovejoy, C.; Vincent, W.F. Microbes in high Arctic snow and implications for the cold biosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3234–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottos, E.M.; Vincent, W.F.; Greer, C.W.; Whyte, L.G. Prokaryotic diversity of arctic ice shelf microbial mats. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.J.; Turner, J. Katabatic wind propagation over the western Ross Sea observed using ERS-1 scatterometer data. Antarct. Sci. 1997, 9, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, J.; Blankenship, R.E. The evolutionary development of the protein complement of photosystem 2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004, 1655, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Smith, D.C.; Hollibaugh, J.T. The role of the microbial loop in Antarctic pelagic ecosystems. Polar Res. 1991, 10, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, L.A.; Carey, J.; Madigan, M.T. Photosynthetic and phylogenetic primers for detection of anoxygenic phototrophs in natural environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2922–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Rainey, F.A.; Ward-Rainey, N. Anoxygenic phototrophy across the phylogenetic spectrum: Current understanding and future perspectives. Arch. Microbiol. 1996, 166, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, T.; Simidu, U.; Taga, N. Distribution of aerobic bacteria which contain bacteriochlorophyll a. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 38, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kolber, Z.S.; van Dover, C.L.; Niederman, R.A.; Falkowski, P.G. Bacterial photosynthesis in surface waters of the open ocean. Nature 2000, 407, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkov, W.; Beatty, J.T. Aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 695–724. [Google Scholar]
- Goericke, R. Bacteriochlorophyll a in the ocean: is anoxygenic bacterial photosynthesis important? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, J.; Klug, G. Regulation of bacterial photosynthesis genes by oxygen and light. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 179, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Shimada, H.; Ohta, H.; Masuda, T.; Shioi, Y.Z.; Takamiya, K. Expression of the puf operon in an aerobic photosynthetic bacterium, Roseobacter denitrificans. Plant Cell Physiol. 1996, 37, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Nagashima, K.V.P.; Shimada, K.; Matsuura, K. Transcriptional control of expression of genes for photosynthetic reaction center and light-harvesting proteins in the purple bacterium Rhodovulum sulfidophilum. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutin, N.; Beja, O. Putative novel photosynthetic reaction centre organizations in marine aerobic anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria: Insights from metagenomics and environmental genomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjà, O.; Suzuki, M.T.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Nelson, W.C.; Preston, C.M.; Hamada, T.; Eisen, J.A.; Fraser, C.M.; DeLong, E.F. Unsuspected diversity among marine aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs. Nature 2002, 415, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K.; Esat, T.M.; Potter, E.K. Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years. Nature 2002, 419, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, A.; Sabehi, G.; Koblizek, M.; Massana, R.; Beja, O. Roseobacter-like bacteria in Red and Mediterranean Sea aerobic anoxygenic photosynthetic populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutin, N.; Suzuki, M.T.; Beja, O. Novel primers reveal wider diversity among marine aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8958–8962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Photoheterotrophic microbes in the Arctic Ocean in summer and winter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4958–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.Z.; Zhang, F.; Hong, N. Significant roles of bacteriochlorophylla supplemental to chlorophylla in the ocean. ISME J. 2010, 4, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbach, M.S.; Fuhrman, J.A. Wide-ranging abundances of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria in the world ocean revealed by epifluorescence microscopy and quantitative PCR. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, M.T.; Michelou, V.K.; Nemcek, N.; DiTullio, G.; Kirchman, D.L. Carbon cycling by microbes influenced by light in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 50, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, E.A.; Sattley, W.M.; Jung, D.O.; Madigan, M.T.; Achenbach, L.A. Remarkable diversity of phototrophic purple bacteria in a permanently frozen Antarctic lake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4910–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, N.N.; Greer, C.W.; Andersen, D.T.; Tille, S.; Lacrampe-Couloume, G.; Lollar, B.S.; Whyte, L.G. Heterotrophic and autotrophic microbial populations in cold perennial springs of the high Arctic. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6898–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.Y.; Phua, W.; Ryan, K.G. Aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria in Antarctic sea ice and seawater. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebel, H.A.; Brinkhoff, T.; Zwisler, W.; Selje, N.; Simon, M. Distribution of Roseobacter RCA and SAR11 lineages and distinct bacterial communities from the subtropics to the Southern Ocean. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2164–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebel, H.A.; Kalhoefer, D.; Lemke, A.; Thole, S.; Gahl-Janssen, R.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Distribution of Roseobacter RCA and SAR11 lineages in the North Sea and characteristics of an abundant RCA isolate. ISME J. 2011, 5, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoff, B.A.; Glaeser, J.; Nuss, A.M.; Zobawa, M.; Lottspeich, F.; Klug, G. Anoxygenic photosynthesis and photooxidative stress: A particular challenge for Roseobacter. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.O.M.; Maas, E.W.; Ryan, K.G. Archaeal diversity revealed in Antarctic sea ice. Antarct. Sci. 2011, 23, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béja, O.; Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V.; Suzuki, M.T.; Hadd, A.; Nguyen, L.P.; Jovanovich, S.B.; Gates, C.M.; Feldman, R.A.; Spudich, J.L. Bacterial rhodopsin: Evidence for a new type of phototrophy in the sea. Science 2000, 289, 1902–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Beja, O.; Spudich, E.N.; Spudich, J.L.; Leclerc, M.; Delong, E.F. Proteorhodopsin phototrophy in the ocean. Nature 2001, 411, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamna-Ismaeel, N.; Sabehi, G.; Sharon, I.; Witzel, K.P.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K.; Barkay, T.; Stomp, M.; Huisman, J.; Beja, O. Widespread distribution of proteorhodopsins in freshwater and brackish ecosystems. ISME J. 2008, 2, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, J.R.; Christianson, L.M.; Béjà, O.; Suzuki, M.T.; Karl, D.M.; Heidelberg, J.; DeLong, E.F. Proteorhodopsin genes are distributed among divergent marine bacterial taxa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 12830–12835. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni, S.J.; Bibbs, L.; Cho, J.C.; Stapels, M.D.; Desiderio, R.; Vergin, K.L.; Rappé, M.S.; Laney, S.; Wilhelm, L.J.; Tripp, H.J. Proteorhodopsin in the ubiquitous marine bacterium SAR11. Nature 2005, 438, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.J.; Waidner, L.A.; Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Abundant proteorhodopsin genes in the North Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Sutton, G.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Williamson, S.; Yooseph, S.; Wu, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Remington, K. The Sorcerer II global ocean sampling expedition: Northwest Atlantic through Eastern Tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, F.; Jiao, N. Genetic diversity and abundance of Flavobacterial proteorhodopsin in China Seas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabehi, G.; Loy, A.; Jung, K.H.; Partha, R.; Spudich, J.L.; Isaacson, T.; Hirschberg, J.; Wagner, M.; Béjà, O. New insights into metabolic properties of marine bacteria encoding proteorhodopsins. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e273. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, J.C.; Remington, K.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Halpern, A.L.; Rusch, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Wu, D.; Paulsen, I.; Nelson, K.E.; Nelson, W. Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 2004, 304, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Poretsky, R.S.; Bano, N.; Buchan, A.; LeCleir, G.; Kleikemper, J.; Pickering, M.; Pate, W.M.; Moran, M.A.; Hollibaugh, J.T. Analysis of microbial gene transcripts in environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4121–4126. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Consarnau, L.; González, J.M.; Coll-Lladó, M.; Gourdon, P.; Pascher, T.; Neutze, R.; Pedrós-Alió, C.; Pinhassi, J. Light stimulates growth of proteorhodopsin-containing marine Flavobacteria. Nature 2007, 445, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelou, V.K.; Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Light-stimulated bacterial production and amino acid assimilation by cyanobacteria and other microbes in the North Atlantic Ocean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5539–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindler, L.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Smith, D.P.; Chan, F.; Giovannoni, S.J. Energy starved Candidatus Pelagibacter ubique substitutes light-mediated ATP production for endogenous carbon respiration. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19725. [Google Scholar]
- Eiler, A. Evidence for the ubiquity of mixotrophic bacteria in the upper ocean: Implications and consequence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7431–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.Y.; Atamna-Ismaeel, N.; Martin, A.; Cowie, R.O.M.; Beja, O.; Davy, S.K.; Maas, E.W.; Ryan, K.G. Proteorhodopsin-bearing bacteria in Antarctic sea ice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5918–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, R.G.; Trodahl, H.J. Scattering and absorption of visible light by sea ice. Nature 1987, 326, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, D.; Wang, W.; Sabehi, G.; Aravind, L.; Post, A.F.; Massana, R.; Spudich, E.N.; Spudich, J.L.; Béjà, O. Diversification and spectral tuning in marine proteorhodopsins. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabehi, G.; Kirkup, B.C.; Rozenberg, M.; Stambler, N.; Polz, M.F.; Beja, O. Adaptation and spectral tuning in divergent marine proteorhodopsins from the eastern Mediterranean and the Sargasso Seas. ISME J. 2007, 1, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.F.; Beja, O. The light-driven proton pump proteorhodopsin enhances bacterial survival during tough times. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrado, R.; Lovejoy, C.; Massana, R.; Vincent, W.F. Microbial food web responses to light and nutrients beneath the coastal Arctic Ocean sea ice during the winter-spring transition. J. Mar. Sys. 2008, 74, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.E.; Rocap, G.; Deming, J.W. Persistence of bacterial and archaeal communities in sea ice through an Arctic winter. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.M.D.; Johnson, J.; Busam, D.; Feldblyum, T.; Ferriera, S.; Friedman, R.; Halpern, A.; Khouri, H.; Kravitz, S.A.; Lauro, F.M. A Sanger/pyrosequencing hybrid approach for the generation of high-quality draft assemblies of marine microbial genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2006, 103, 11240–11245. [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg, J.M.; Leamon, J.H. The development and impact of 454 sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanauskas, R.; Sieracki, M.E. Matching phylogeny and metabolism in the uncultured marine bacteria, one cell at a time. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 9052–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, T.J.; Wickham, G.S.; Schadt, C.W.; He, Z.; Zhou, J. Microarray applications in microbial ecology research. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.; Bik, E.M.; Eisen, M.B.; Eckburg, P.B.; Sana, T.R.; Wolber, P.K.; Relman, D.A.; Brown, P.O. Rapid quantitative profiling of complex microbial populations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.; Brodie, E.; Moberg, J.; Zubieta, I.; Piceno, Y.; Andersen, G. High-density universal 16S rRNA microarray analysis reveals broader diversity than typical clone library when sampling the environment. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 371–383. [Google Scholar]
- Pernthaler, A.; Amann, R. Simultaneous fluorescence in situ hybridization of mRNA and rRNA in environmental bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5426–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Osborn, A.M. Advantages and limitations of quantitative PCR (Q-PCR)-based approaches in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias-Lopez, J.; Shi, Y.; Tyson, G.W.; Coleman, M.L.; Schuster, S.C.; Chisholm, S.W.; DeLong, E.F. Microbial community gene expression in ocean surface waters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105, 3805–3810. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, F.; Nie, L. Integrating multiple “omics” analysis for microbial biology: Application and methodologies. Microbiology 2010, 156, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, C.D.; Raffaelle, M.; Allen, T.E.; Kanin, E.I.; Landick, R.; Ansari, A.Z.; Palsson, B.Ø. Immobilization of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and location of binding sites by use of chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarrays. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 6166–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, E.; Kurokawa, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Ogasawara, N.; Oshima, T. Differential binding profiles of StpA in wild-type and hns mutant cells: A comparative analysis of cooperative partners by chromatin immunoprecipitation-microarray analysis. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2388–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).