Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase—Associated Ribonuclease H Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HIV-1 RT RNase H Structure and Activity
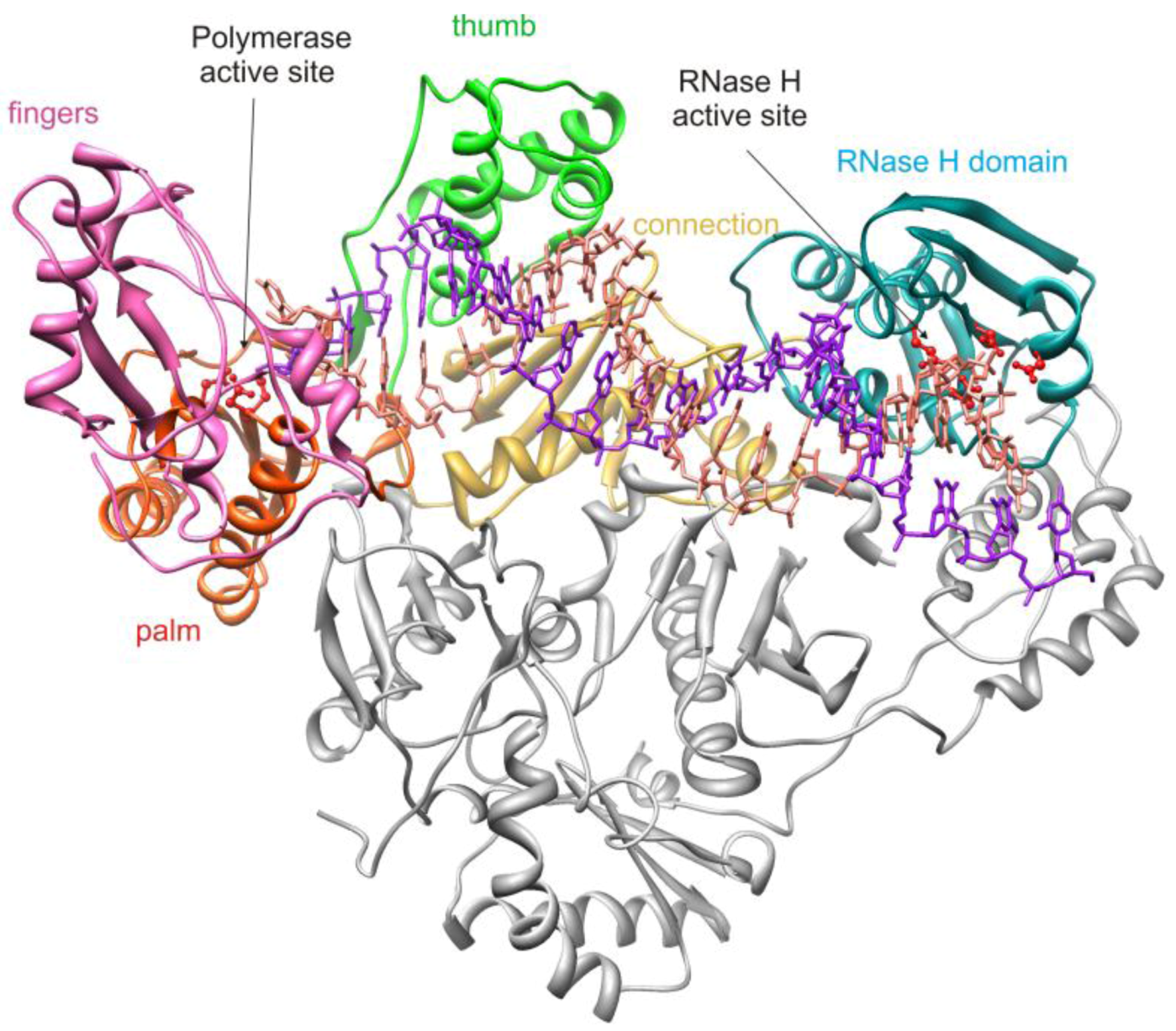
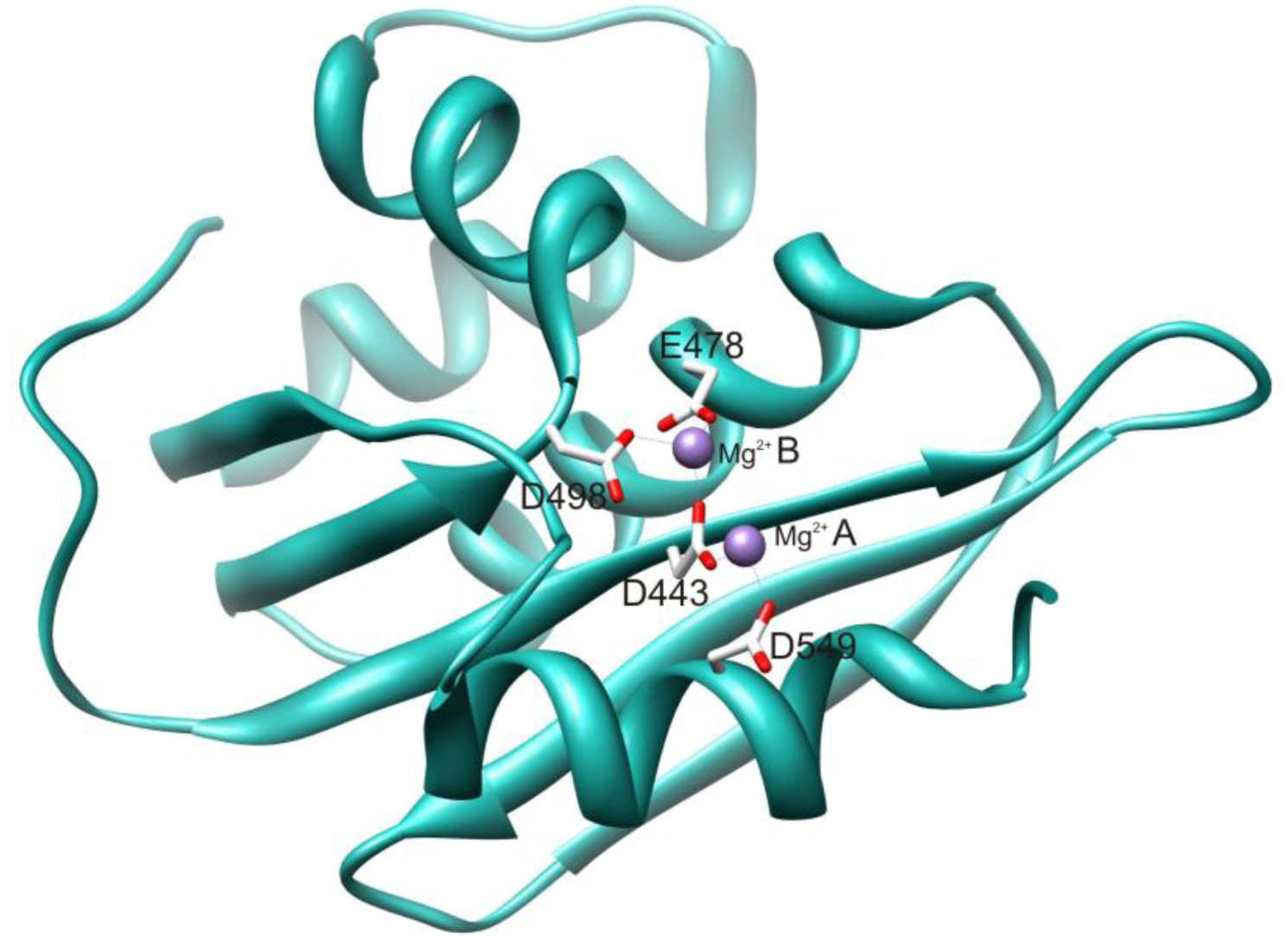
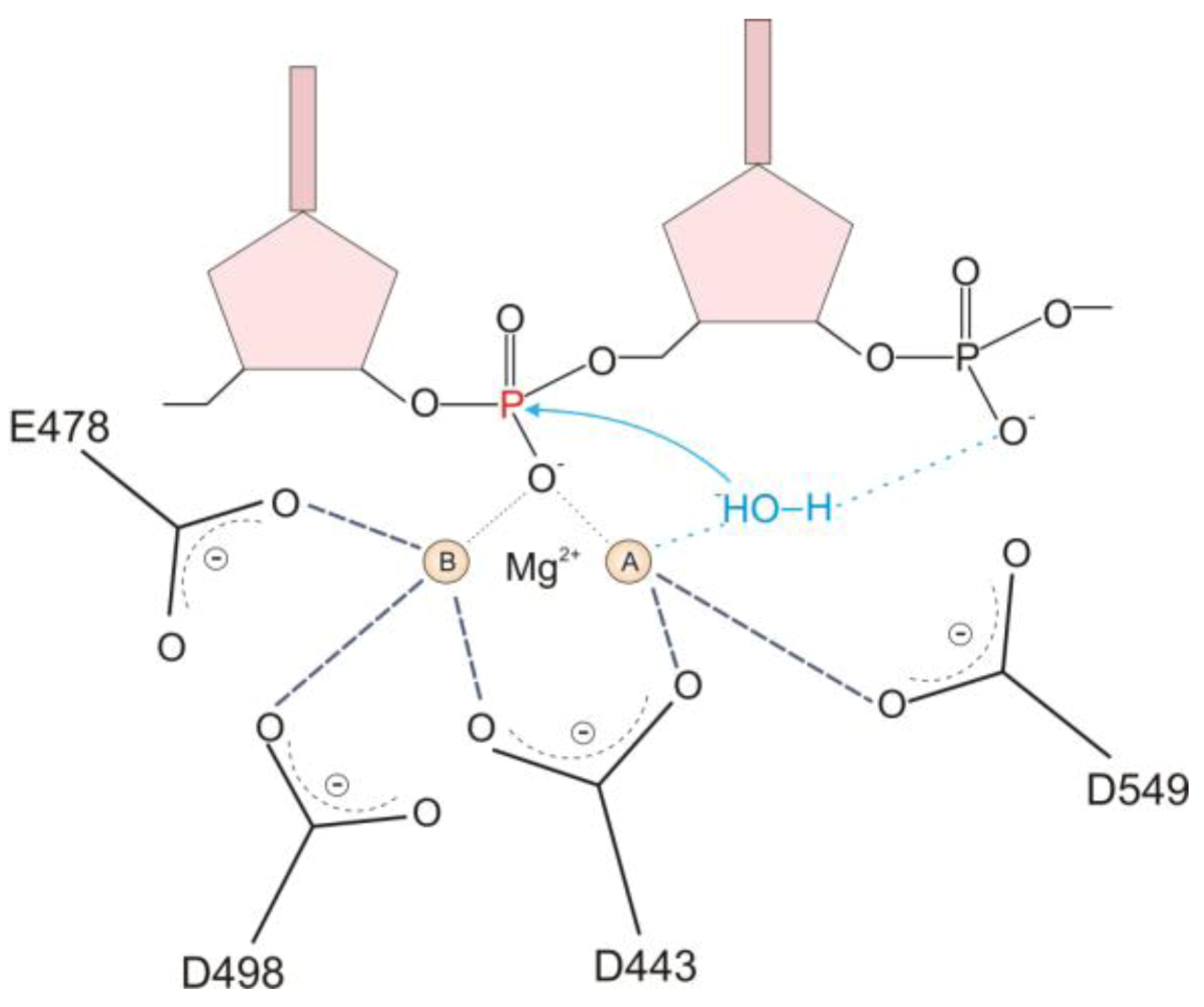
2.1. HIV-1 RT RNase H Catalytic Mechanism
2.2. RNase H Hydrolytic Activity during Reverse Transcription
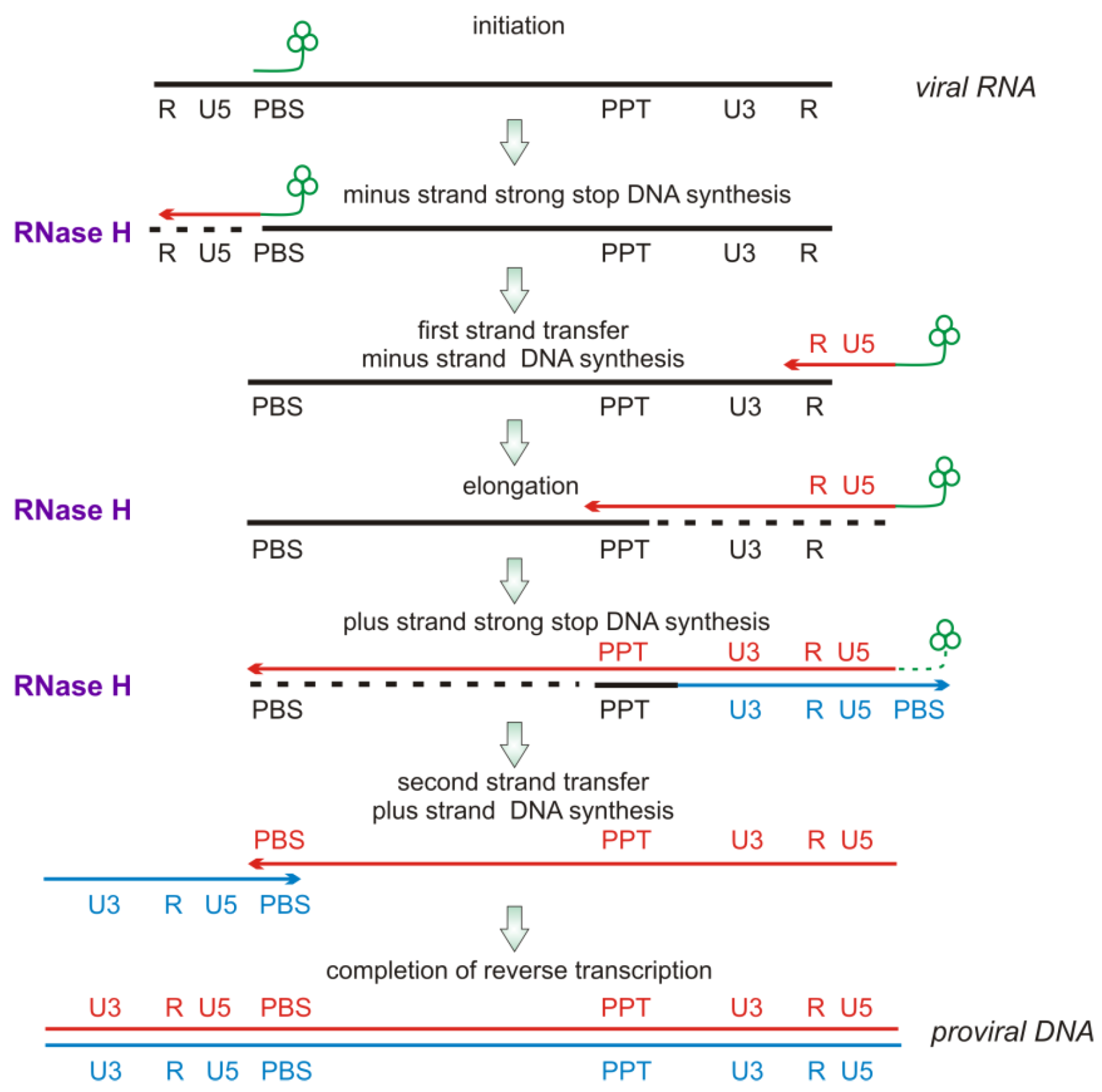
2.3. Modes of RNase H Hydrolysis
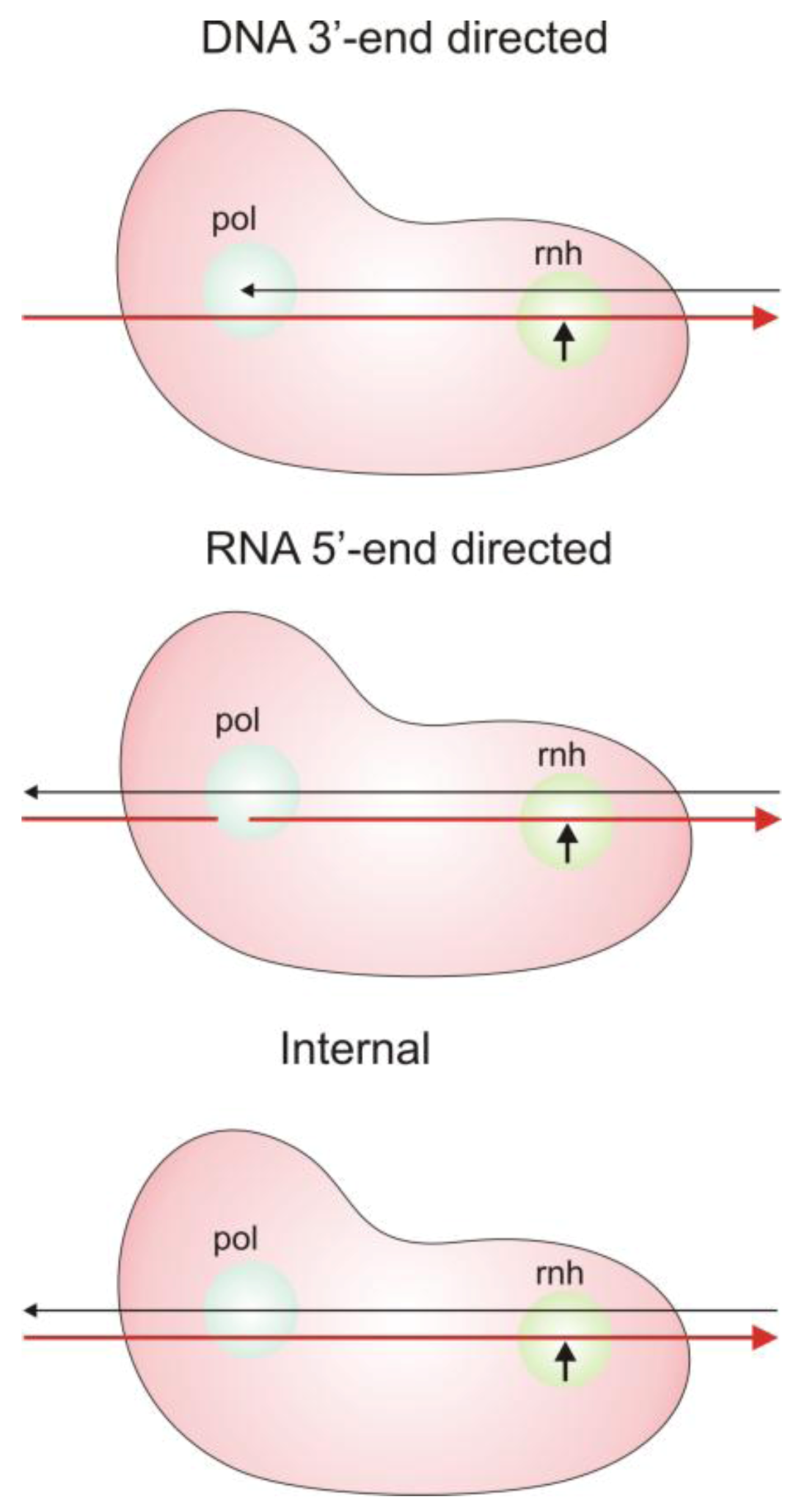
3. Inhibitors of HIV-1 RT RNase H
3.1. Active Site-directed RNase H Inhibitors (Table 1)
| Pharmacophore | Example | IC50 (µM) | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNase H | RT pol | IN | HIV | |||
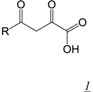 | 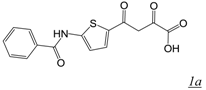 | 3.2 | Not active | 1.9 | Not active | [22] |
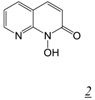 | 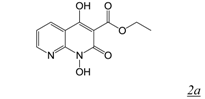 | 0.11 | Not active | No report | 2.8 | [31] |
 | 0.045 | 13 | 24 | 0.2 | [32] | |
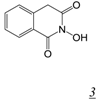 | 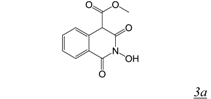 | 0.06 | > 50 | 4.9 | 13.4 | [36] |
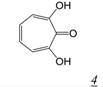 | 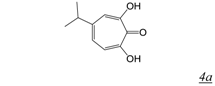 | 0.2 | Not active | No report | Not active | [37] |
 | 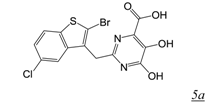 | 0.17 | No report | No report | No report | [39] |
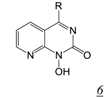 | 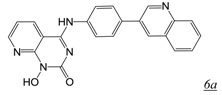 | 0.003 | No report | 0.4 | 0.01 | [41,42] |

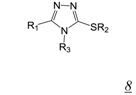
3.2. Allosteric RNase H Inhibitors (Table 2)
| Pharmacophore | Example | IC50 (µM) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNase H | RT pol | HIV | |||
 |  | 1.9 | Not active | 3.7 | [47] |
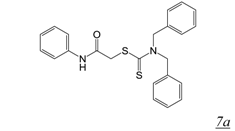
 | 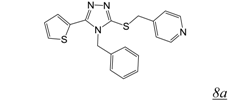 | 0.2 | 11.6 | 4.0 | [47] |
 | 0.8 | 4.5 | 0.2 | [48] | |
 | 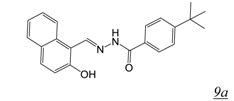 | 3.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 | [51] |
 | 0.5 | Not active | 5.5 | [52] | |
 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 2.5 | [54] | |
 | 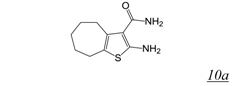 | 2.0 | Not active | Not active | [55] |
4. Conclusions
4.2. Future Efforts
Acknowledgments
References
- Ilina, T.; Parniak, M.A. Inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Adv. Pharmacol. 2008, 56, 121–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochmans, D. Novel HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Virus Res. 2008, 134, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chopra, R.; Verdine, G.L.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. Science 1998, 282, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Das, K.; Tantillo, C.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Ding, J.; Whitcomb, J.M.; Boyer, P.L.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Crystal structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in complex with a polypurine tract RNA:DNA. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Marchand, B.; Das, K.; Himmel, D.H.; Parniak, M.A.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Structure and Function of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase: Molecular Mechanism of Polymerization Inhibition. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 693–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.F.; Hostomska, Z.; Hostomsky, Z.; Jordan, S.R.; Matthews, D.A. Crystal Structure of the Ribonuclease H Domain of HIV- I Reverse Transcriptase. Science 1991, 252, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Julias, J.G.; McWilliams, M.J.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Arnold, E.; Hughes, S.H. Mutations in the RNase H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase affect the initiation of DNA synthesis and the specificity of RNase H cleavage in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9515–9520. [Google Scholar]
- Julias, J.G.; McWilliams, M.J.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Alvord, W.G.; Arnold, E.; Hughes, S.H. Mutation of amino acids in the connection domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase that contact the template-primer affects RNase H activity. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8548–8554. [Google Scholar]
- Rausch, J.W.; Lener, D.; Miller, J.T.; Julias, J.G.; Hughes, S.H.; Le Grice, S.F. Altering the RNase H primer grip of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase modifies cleavage specificity. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 4856–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arion, D.; Sluis-Cremer, N.; Min, K.L.; Abram, M.E.; Fletcher, R.S.; Parniak, M.A. Mutational analysis of Tyr-501 of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Effects on ribonuclease H activity and inhibition of this activity by N-acylhydrazones. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams, M.J.; Julias, J.G.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Alvord, W.G.; Arnold, E.; Hughes, S.H. Combining mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with mutations in the HIV-1 polypurine tract affects RNase H cleavages involved in PPT utilization. Virology 2006, 348, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoux, J.J. Roles of ribonuclease H in reverse transcription. In Reverse Transcriptase; Skalka, A.M., Goff, S.P., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, S.J.; Champoux, J.J. RNase H activity: Structure, specificity, and function in reverse transcription. Virus Res. 2008, 134, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kati, W.M.; Johnson, K.A.; Jerva, L.F.; Anderson, K.S. Mechanism and fidelity of HIV reverse transcriptase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 25988–25997. [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano, J.J.; Mallaber, L.M.; Fay, P.J.; Bambara, R.A. Determinants of the RNase H cleavage specificity of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 4330–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furfine, E.S.; Reardon, J.E. Reverse transcriptase. RNase H from the human immunodeficiency virus. Relationship of the DNA polymerase and RNA hydrolysis activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Ilina, T.; Van Ry, A.; Nagy, E.; Parniak, M.A. Mutations in HIV-1 RT RNase H domain reducing RT-associated RNase H activity have no impact on resistance to the nucleoside RT inhibitors. 2012; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, R.S.; Syed, K.; Mithani, S.; Dmitrienko, G.I.; Parniak, M.A. Carboxanilide derivative nonnucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase interact with different mechanistic forms of the enzyme. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 4036–4042. [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda, D.J.; Felock, P.; Witmer, M.; Wolfe, A.; Stillmock, K.; Grobler, J.A.; Espeseth, A.; Gabryelski, L.; Schleif, W.; Blau, C.; Miller, M.D. Inhibitors of strand transfer that prevent integration and inhibit HIV-1 replication in cells. Science 2000, 287, 646–650. [Google Scholar]
- Grobler, J.A.; Stillmock, K.; Hu, B.; Witmer, M.; Felock, P.; Espeseth, A.; Wolfe, A.; Egbertson, M.; Bourgeois, M.; Melamed, J.; Wai, J.S.; Young, S.; Vacca, J.; Hazuda, D. Diketo acid inhibitor mechanism and HIV-1 integrase: implications for metal binding in the active site of phosphotransferase enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6661–6666. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw-Reid, C.A.; Munshi, V.; Graham, P.; Wolfe, A.; Witmer, M.; Danzeisen, R.; Olsen, D.B.; Carroll, S.S.; Embrey, M.; Wai, J.S.; Miller, M.D.; Cole, J.L.; Hazuda, D.J. Inhibition of HIV-1 ribonuclease H by a novel diketo acid, 4-[5-benzoylamino)thien-2-yl]-2,4-dioxobutanoic Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2777–2780. [Google Scholar]
- Parniak, M.A.; Min, K.L.; Budihas, S.R.; Le Grice, S.F.; Beutler, J.A. A fluorescence-based high-throughput screening assay for inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H activity. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 322, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Parniak, M.A.; Min, K.L. Substrate for assaying ribonuclease H activity. Patent US7186520, 6 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Parniak, M.A.; Min, K.L. Method of identifying or characterizing a compound that modulates ribonuclease H activity. US Patent 7,439,035, 21 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Klumpp, K.; Mirzadegan, T. Recent progress in the design of small molecule inhibitors of HIV RNase H. Curr. Pharm. Drug 2006, 12, 1909–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P.; De Clercq, E. Recent advances in the research of HIV-1 RNase H inhibitors. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, E.; Di Santo, R. HIV-1 RT-associated RNase H function inhibitors: Recent advances in drug development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, E.; Esposito, F.; Badas, R.; Di Santo, R.; Costi, R.; La Colla, P. 6-[1-(4-Fluorophenyl)methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)]-2,4-dioxo-5-hexenoic acid ethyl ester a novel diketo acid derivative which selectively inhibits the HIV-1 viral replication in cell culture and the ribonuclease H activity in vitro. Antiv. Res. 2005, 65, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda, D.J.; Anthony, N.J.; Gomez, R.P.; Jolly, S.M.; Wai, J.S.; Zhuang, L.; Fisher, T.E.; Embrey, M.; Guare, J.P., Jr.; Egbertson, M.S.; Vacca, J.P.; Huff, J.R.; Felock, P.J.; Witmer, M.V.; Stillmock, K.A.; Danovich, R.; Grobler, J.; Miller, M.D.; Espeseth, A.S.; Jin, L.; Chen, I.W.; Lin, J.H.; Kassahun, K.; Ellis, J.D.; Wong, B.K.; Xu, W.; Pearson, P.G.; Schleif, W.A.; Cortese, R.; Emini, E.; Summa, V.; Holloway, M.K.; Young, S.D. A naphthyridine carboxamide provides evidence for discordant resistance between mechanistically identical inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11233–11238. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.P.; Yan, Y.; Prasad, S.; Smith, R.F.; Daniels, C.L.; Abeywickrema, P.D.; Reid, J.C.; Loughran, H.M.; Kornienko, M.; Sharma, S.; Grobler, J.A.; Xu, B.; Sardana, V.; Allison, T.J.; Williams, P.D.; Darke, P.L.; Hazuda, D.J.; Munshi, S. Structural Basis for the Inhibition of RNase H Activity of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase by RNase H Active Site-Directed Inhibitors. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7625–7633. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.D.; Staas, D.D.; Venkatraman, S.; Loughran, H.M.; Ruzek, R.D.; Booth, T.M.; Lyle, T.A.; Wai, J.S.; Vacca, J.P.; Feuston, B.P.; Ecto, L.T.; Flynn, J.A.; DiStefano, D.J.; Hazuda, D.J.; Bahnck, C.M.; Himmelberger, A.L.; Dornadula, G.; Hrin, R.C.; Stillmock, K.A.; Witmer, M.V.; Miller, M.D.; Grobler, J.A. Potent and selective HIV-1 ribonuclease H inhibitors based on a 1-hydroxy-1,8-naphthyridin-2(1H)-one scaffold. Biooganic. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6754–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, K.; Hang, J.Q.; Rajendran, S.; Yang, Y.; Derosier, A.; Wong Kai In, P.; Overton, H.; Parkes, K.E.B.; Cammack, N.; Martin, J.A. Two-metal ion mechanism of RNA cleavage by HIV RNase H and mechanism-based design of selective HIV RNase H inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Research 2003, 31, 6852–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.Q.; Rajendran, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wong Kai In, P.; Overton, H.; Parkes, K.E.B.; Cammack, N.; Martin, J.A.; Klumpp, K. Activity of the isolated HIV RNase H domain and specific inhibition by N-hydroxyimides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2006, 317, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Billamboz, M.; Bailly, F.; Barreca, M.L.; De Luca, L.; Mouscadet, J.F.; Calmels, C.; Andreola, M.L.; Witvrouw, M.; Christ, F.; Debyser, Z.; Cotelle, P. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a series of 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-diones as dual inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase and the reverse transcriptase RNase H domain. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7717–7730. [Google Scholar]
- Billamboz, M.; Bailly, F.; Lion, C.; Touati, N.; Vezin, H.; Calmels, C.; Androla, M.-L.; Christ, F.; Debyser, Z.; Cotelle, P. Magnesium chelating 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-diones, as inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase and/or the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase ribonuclease H domain: Discovery of a novel selective inhibitor of the ribonuclease H function. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budihas, S.R.; Gorshkova, I.; Gaidamakov, S.; Wamiru, A.; Bona, M.K.; Parniak, M.A.; Crouch, R.J.; McMahon, J.B.; Beutler, J.A.; Le Grice, S.F.J. Selective inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H activity by hydroxylated tropolones. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Himmel, D.M.; Meagley, K.A.; Pauly, T.A.; Bauman, J.D.; Das, K.; Dharia, C.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Ryan, K.; Hickey, M.J.; Love, R.A.; Hughes, S.H.; Bergqvist, S.; Arnold, E. Structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with the inhibitor β-thujaplicinol bound at the RNase H active site. Structure 2009, 17, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschberg, T.A.; Balakrishnan, M.; Squires, N.H.; Barnes, T.; Brendza, K.M.; Chen, X.; Eisenberg, E.J.; Jin, W.; Kutty, N.; Leavitt, S.; Liclican, A.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Mak, J.; Perry, J.K.; Wang, M.; Watkins, W.J.; Lansdon, E.B. Nase H active site inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase: Design, biochemical activity, and structural information. J. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 52, 5781–5784. [Google Scholar]
- Lansdon, E.B.; Liu, Q.; Leavitt, S.A.; Balakrishnan, M.; Perry, J.K.; Lancaster-Moyer, C.; Kutty, N.; Liu, X.; Squires, N.H.; Watkins, W.J.; Kirschberg, T.A. Structural and binding analysis of pyrimidinol carboxylic acid and N-hydroxy quinazolinedione HIV RNase H inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2905–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerondelis, P.; Johns, B.A. The development of novel pyrido-pyrimidinone antiretrovirals with selective activity against HIV ribonuclease H. In Proceedings of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories Conference on Retroviruses, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, NY, USA, 21–26 May 2012.
- Johns, B.A.; Vethuisen, E.J. Therapeutic compounds. Patent WO 2011/07547 A1, 23 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Felts, A.K.; Labarge, K.; Bauman, J.D.; Patel, D.V.; Himmel, D.M.; Arnold, E.; Parniak, M.A.; Levy, R.M. Identification of alternative binding sites for inhibitors of HIV-1 ribonuclease H through comparative analysis of virtual enrichment studies. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1986–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, R.H.; Dykes, C.; Gerondelis, P.; Lloyd, A.; Fay, P.; Reichman, R.C.; Bambara, R.A.; Demeter, L.M. Mutants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase resistant to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors demonstrate altered rates of RNase H cleavage that correlate with HIV-1 replication fitness in cell culture. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8390–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, R.H.; Wisniewski, M.; Bambara, R.A.; Demeter, L.M. The Y181C mutant of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase resistant to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors alters the size distribution of RNase H cleavages. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cammack, N.; Mirzadegan, T.; Klumpp, K. Substrate-dependent inhibition or stimulation of HIV RNase H activity by non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2007, 352, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Grandi, M.; Olson, M.; Prashad, A.S.; Bebernitz, G.; Luckay, A.; Mullen, S.; Hu, Y.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Pitts, K.; O'Connell, J. Small molecule inhibitors of HIV RT Ribonuclease H. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Ilina, T.; Van Ry, A.; Nagy, E.; Parniak, M.A. 1,2,4-Triazole Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Ribonuclease H Activity. Unpublished work, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschberg, T.A.; Balakrishnan, M.; Huang, W.; Hluhanich, R.; Kutty, N.; Liclican, A.C.; McColl, D.J.; Squires, N.H.; Lansdon, E.B. Triazole derivatives as non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase-structure-activity relationships and crystallographic analysis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Cichero, E.; Buffa, L.; Fossa, P. 3,4,5-Trisubstituted-1,2,4–4H-triazoles as WT and Y188L mutant HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Docking-based CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses. J. Mol. Model. 2011, 17, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Fletcher, R.S.; Barnard, J.; Arion, D.; Motakis, D.; Dmitrienko, G.I.; Parniak, M.A. Inhibition of the ribonuclease H and DNA polymerase activities of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by N-(4-tert-butylbenzoyl)-2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde hydrazone. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmel, D.M.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Dharmasena, S.; Hossain, M.M.; McCoy-Simandle, K.; Ilina, T.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Knight, J.L.; Julias, J.G.; Clark, P.K.; Krogh-Jespersen, K.; Levy, R.M.; Hughes, S.H.; Parniak, M.A.; Arnold, E. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase structure with RNase H inhibitor dihydroxy benzoyl naphthyl hydrazone bound at a novel site. ACS Chem. Biol. 2006, 1, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, T.V.; Hossain, M.; Parniak, M.A. Mutations in the p51 thumb subdomain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) provide resistance to acylhydrazone inhibitors of RT ribonuclease activity. In Proceedings of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories Conference on Retroviruses, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 May 2008.
- Gong, Q.; Menon, L.; Ilina, T.; Miller, L.G.; Ahn, J.; Parniak, M.A.; Ishima, R. Interaction of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase ribonuclease H with an acylhydrazone inhibitor. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 77, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, M.T.; Menon, L.; Myshakina, N.S.; Ahn, J.; Parniak, M.A.; Ishima, R. Structural basis for the allosteric inhibitor interaction on the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase RNase H domain. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendeler, M.; Lee, H.-F.; Bermingham, A.; Miller, J.T.; Chertov, O.; Bona, M.K.; Baichoo, N.S.; Ehtesham, M.; Beutler, J.A.; O'Keefe, B.R.; Gotte, M.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Le Grice, S.F.J. Vinylogous ureas as a novel class of reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 635–644. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Wendeler, M.; Rausch, J.W.; Beilhartz, G.; Gotte, M.; O'Keefe, B.R.; Bermingham, A.; Beutler, J.A.; Liu, S.; Zhuang, X.; Le Grice, S.F.J. Structure-activity analysis of vinylogous urea inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus-encoded ribonuclease H. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3913–3921. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Miller, J.T.; Johnson, B.C.; Hughes, S.H.; Le Grice, S.F. Mutagenesis of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase p51 subunit defines residues contributing to vinylogous urea inhibition of ribonuclease H activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4066–4075. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolenko, G.N.; Palmer, S.; Maldarelli, F.; Mellors, J.W.; Coffin, J.M.; Pathak, V.K. Mechanism for nucleoside analog-mediated abrogation of HIV-1 replication: balance between RNase H activity and nucleotide excision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2093–2098. [Google Scholar]
- Ilina, T.V.; Parniak, M.A. Novel RNA/DNA Substrates for the Characterization of Ribonuclease H Activity. In Proceedings of 10th Annual Symposium on Antiviral Drug Resistance: Targets and Mechanisms, Richmond, VA, USA, 15–18 November 2009.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilina, T.; LaBarge, K.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Ishima, R.; Parniak, M.A. Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase—Associated Ribonuclease H Activity. Biology 2012, 1, 521-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1030521
Ilina T, LaBarge K, Sarafianos SG, Ishima R, Parniak MA. Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase—Associated Ribonuclease H Activity. Biology. 2012; 1(3):521-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1030521
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlina, Tatiana, Krystal LaBarge, Stefan G. Sarafianos, Rieko Ishima, and Michael A. Parniak. 2012. "Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase—Associated Ribonuclease H Activity" Biology 1, no. 3: 521-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1030521
APA StyleIlina, T., LaBarge, K., Sarafianos, S. G., Ishima, R., & Parniak, M. A. (2012). Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase—Associated Ribonuclease H Activity. Biology, 1(3), 521-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1030521





