HIV-1 Resistant CDK2-Knockdown Macrophage-Like Cells Generated from 293T Cell-Derived Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Stable CDK2 Knockdown in 293T Cells Inhibits HIV-1 Transcription
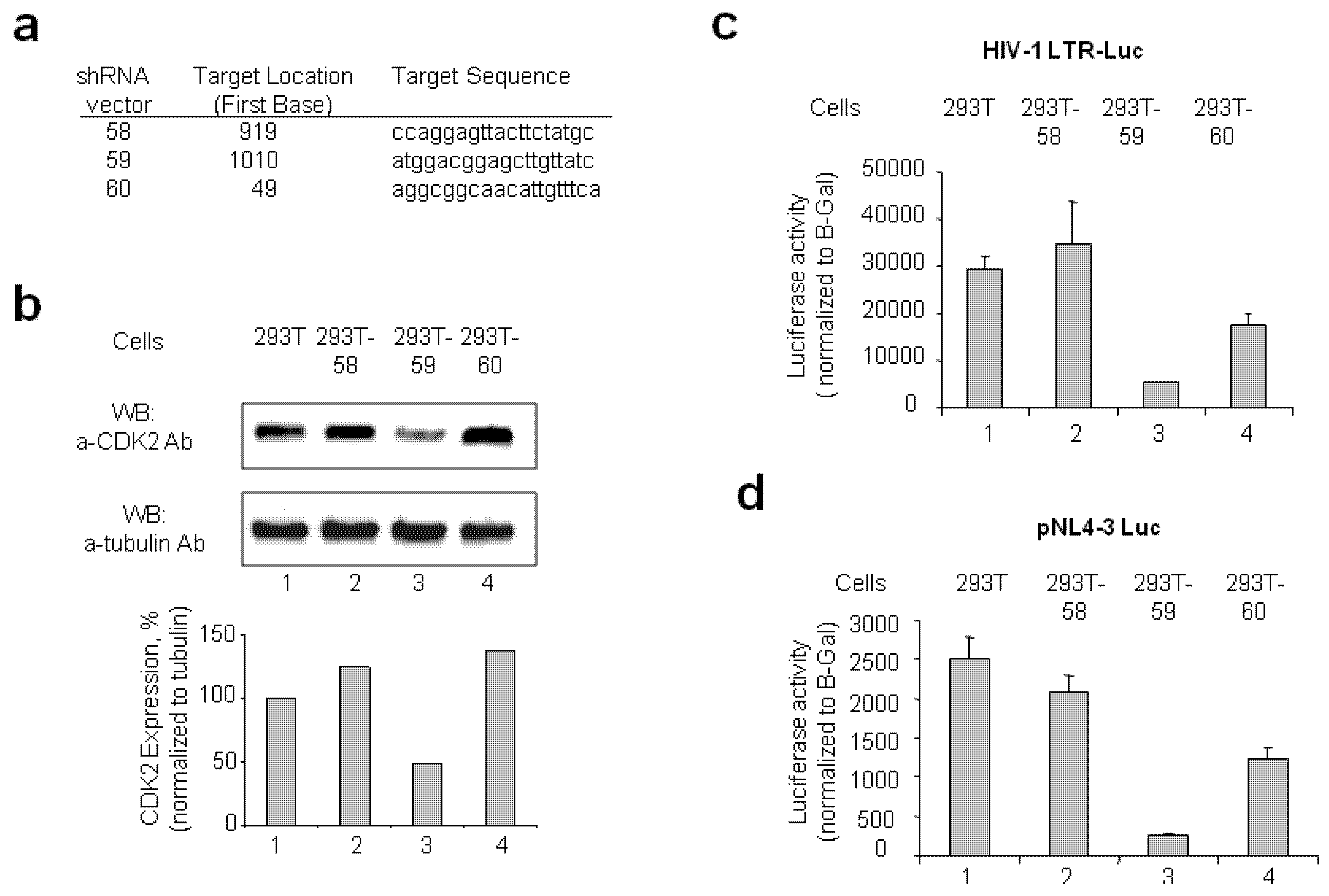
2.1.2. Reprogramming of 293T and CDK2 KD 293T Cells into iPSCs

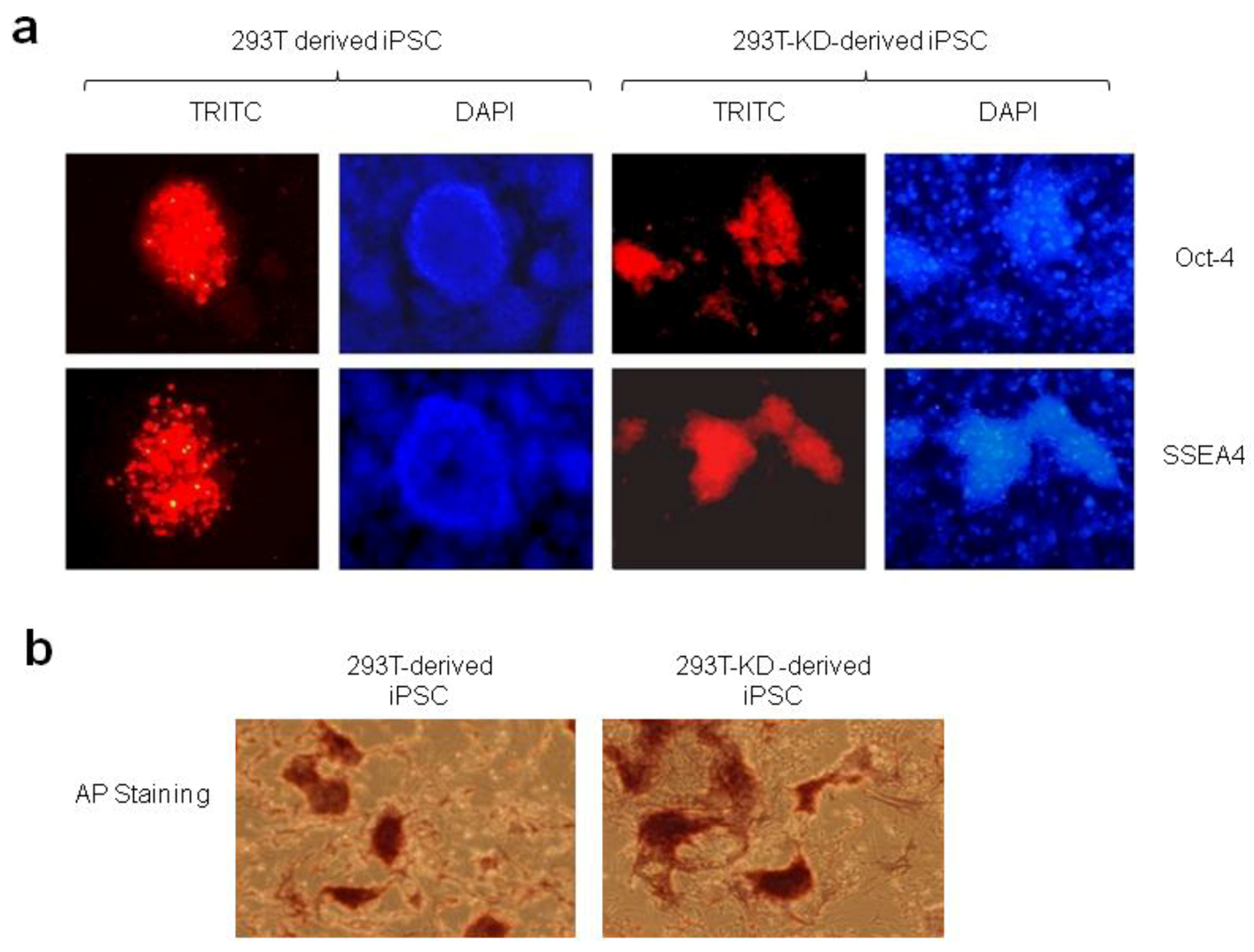
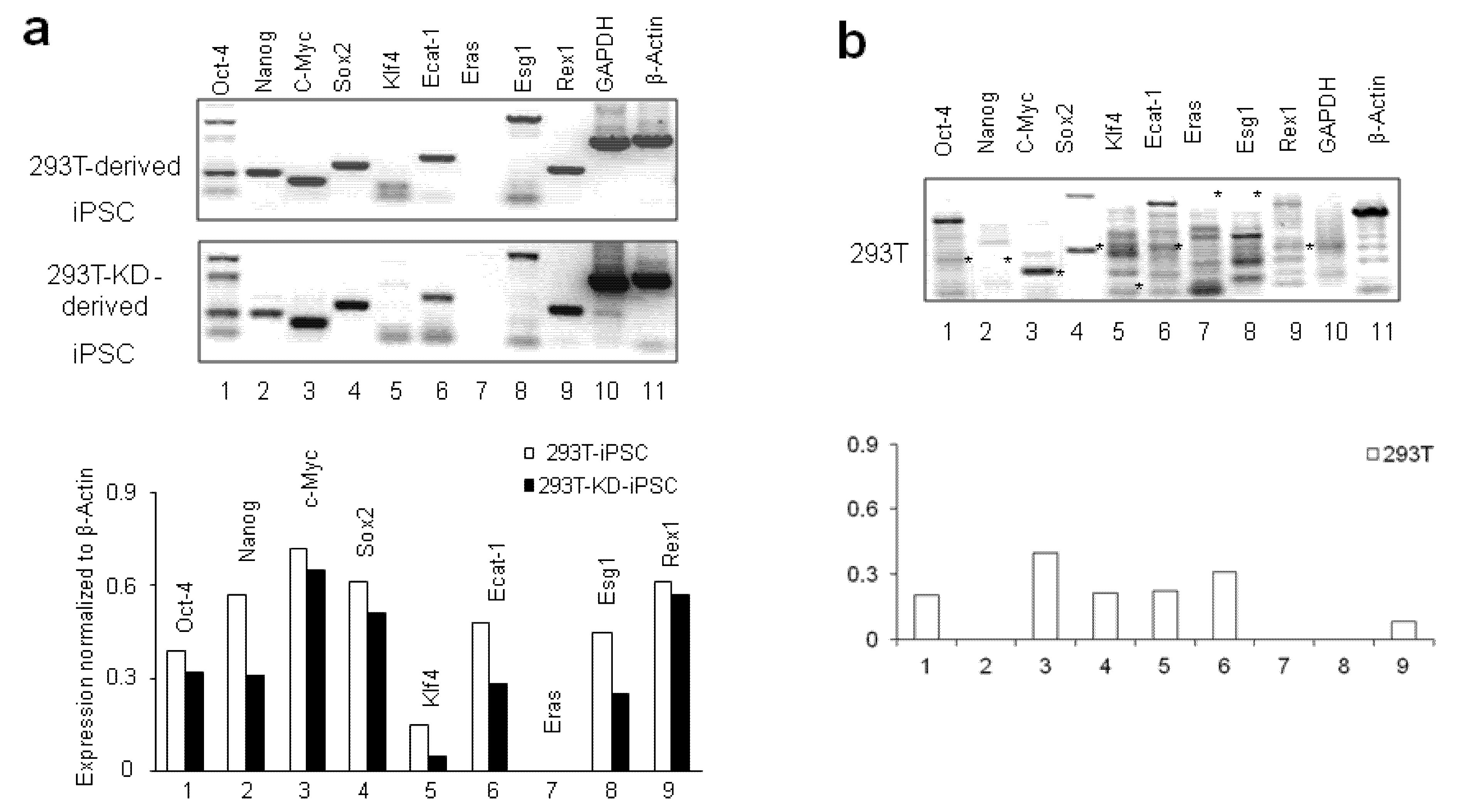
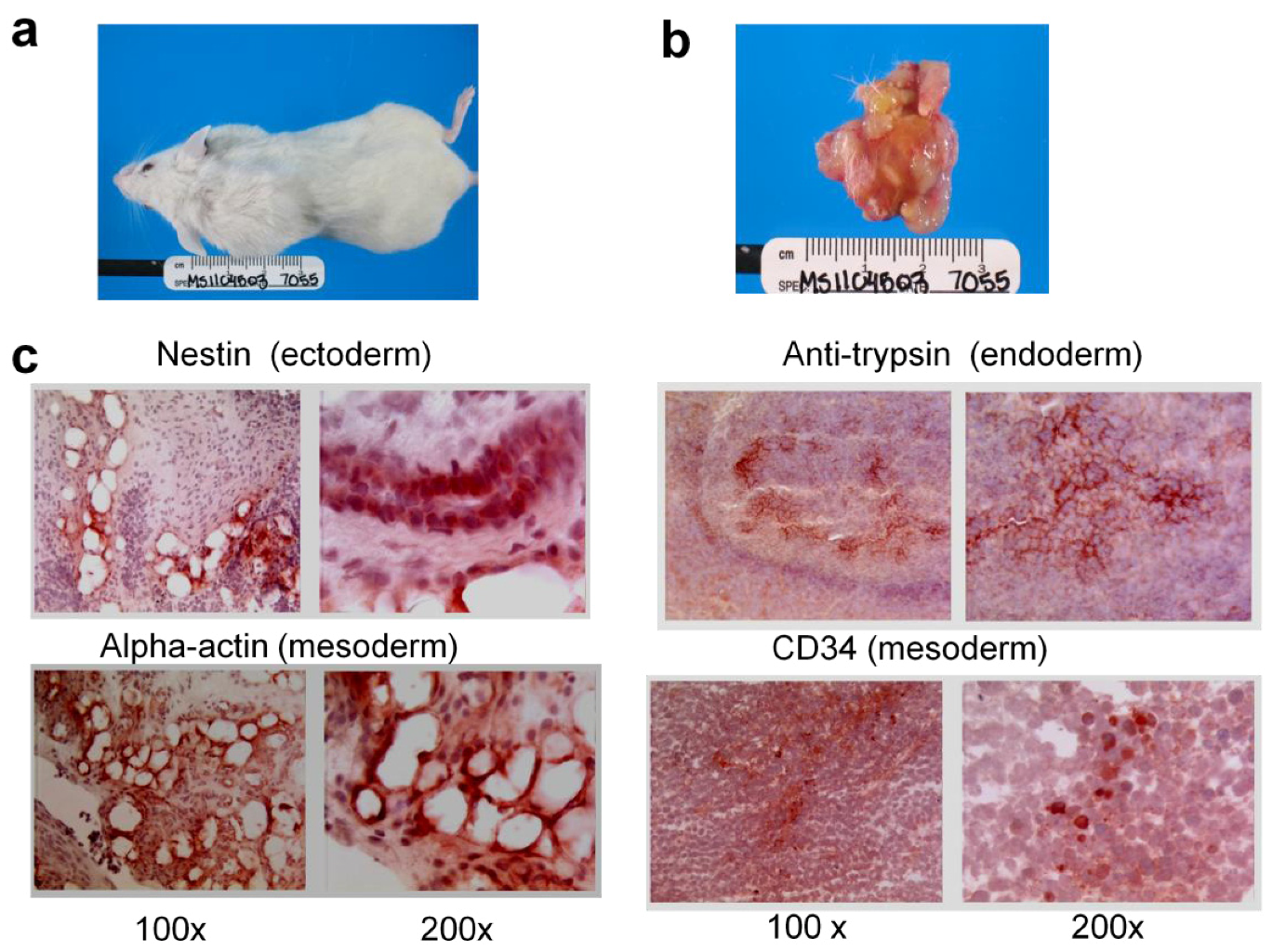
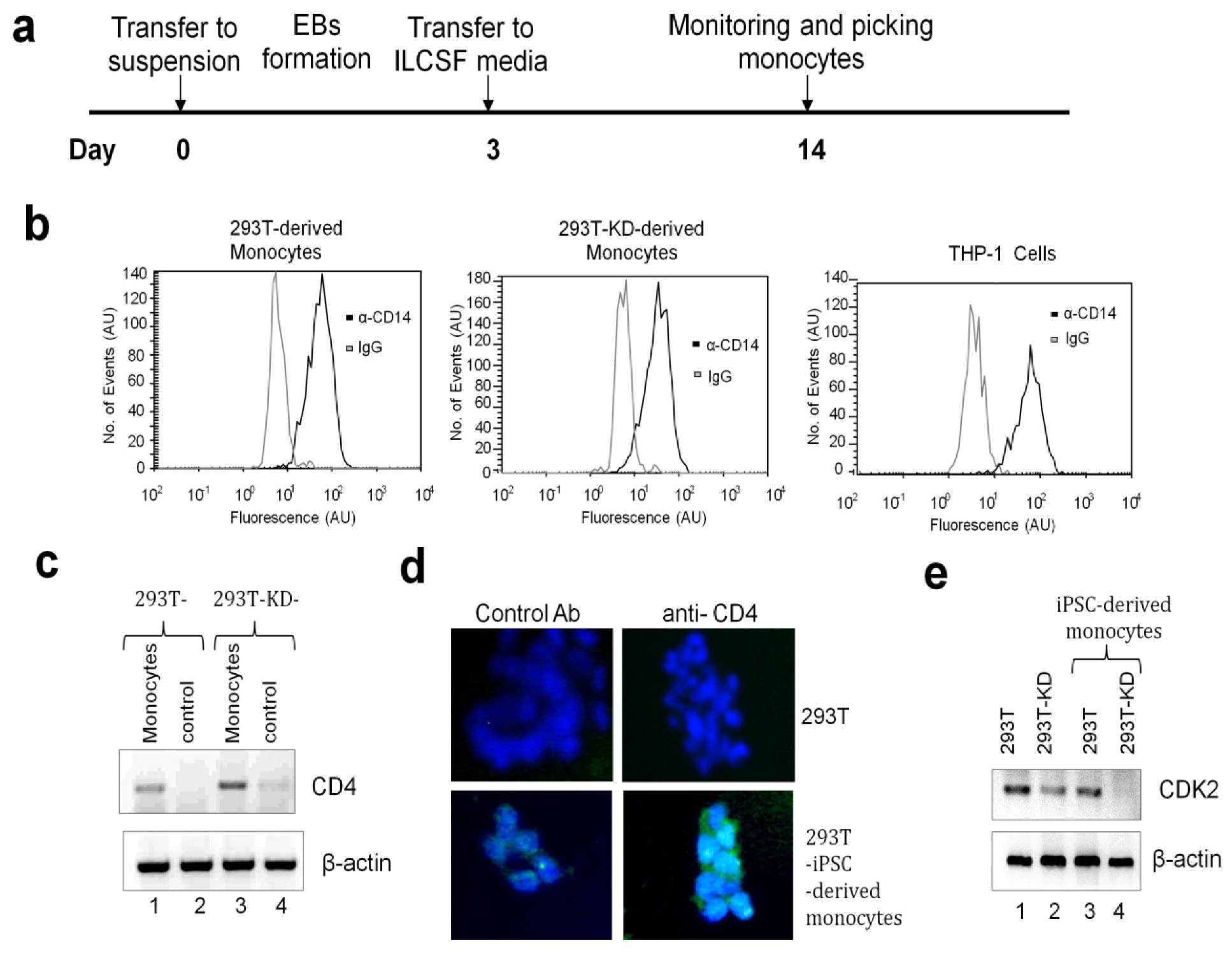
2.1.3. Differentiation of iPSCs into Monocytes
2.1.4. Differentiation of iPSCs-derived Monocytes into Macrophage-like Cells
2.2. Discussion

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Plasmids
3.3. Luciferase Assays
3.4. Stable CDK2-knock-down Cell Line
3.5. Conversion of 293T Cells into iPSC.
3.6. Tumor Formation
3.7. Differentiation of iPSC into Monocytes
3.8. Differentiation of Monocytes into Macrophage-like Cells
3.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
3.10. Immunocytochemistry of Tumor Sections
3.11. RT-PCR
3.12. Flow Cytometry
3.13. Cytokine and Chemokine Secretion
3.14. Infection of Macrophage-like Cells with HIV-1
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Schwartz, R.E.; Trehan, K.; Andrus, L.; Sheahan, T.P.; Ploss, A.; Duncan, S.A.; Rice, C.M.; Bhatia, S.N. Modeling hepatitis C virus infection using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2544–2548. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Takayama, K.; Kondoh, M.; Sakurai, F.; Tani, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Matsuura, Y.; Mizuguchi, H.; Yagi, K. Use of human hepatocyte-like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells as a model for hepatocytes in hepatitis C virus infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 416, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.; Breit, S.N. Variables in the isolation and culture of human monocytes that are of particular relevance to studies of HIV. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 56, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.; Taylor, P.R. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 953–964. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.L.; Yeap, W.H.; Tai, J.J.; Ong, S.M.; Dang, T.M.; Wong, S.C. The three human monocyte subsets: Implications for health and disease. Immunol. Res. 2012, 53, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkord, E.; Williams, P.E.; Kynaston, H.; Rowbottom, A.W. Human monocyte isolation methods influence cytokine production from in vitro generated dendritic cells. Immunology 2005, 114, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clanchy, F.I.; Hamilton, J.A. Proliferative monocyte frequency is associated with circulating monocyte prevalence. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, e175–e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.S.; Bandi, S.; Kaufman, D.S.; Akkina, R. Derivation of normal macrophages from human embryonic stem (hES) cells for applications in HIV gene therapy. Retrovirology 2006, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Vodyanik, M.A.; Smuga-Otto, K.; Antosiewicz-Bourget, J.; Frane, J.L.; Tian, S.; Nie, J.; Jonsdottir, G.A.; Ruotti, V.; Stewart, R.; Slukvin, I.I.; Thomson, J.A. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 2007, 318, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Mali, P.; Ye, Z.; Hommond, H.H.; Yu, X.; Lin, J.; Chen, G.; Zou, J.; Cheng, L. Improved efficiency and pace of generating induced pluripotent stem cells from human adult and fetal fibroblasts. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, K.; Tsuneto, M.; Melchers, F. Experimental limitations using reprogrammed cells for hematopoietic differentiation. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, J.M.; Liu, S.; Figueroa, M.E.; Kulalert, W.; Eminli, S.; Tan, K.Y.; Apostolou, E.; Stadtfeld, M.; Li, Y.; Shioda, T.; et al. Cell type of origin influences the molecular and functional properties of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 848–855. [Google Scholar]
- Bru, T.; Clarke, C.; McGrew, M.J.; Sang, H.M.; Wilmut, I.; Blow, J.J. Rapid induction of pluripotency genes after exposure of human somatic cells to mouse ES cell extracts. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Ammosova, T.; Pumfery, A.; Kashanchi, F.; Nekhai, S. HIV-1 Tat interaction with RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain (CTD) and a dynamic association with CDK2 induce CTD phosphorylation and transcription from HIV-1 promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33922–33929. [Google Scholar]
- Nekhai, S.; Zhou, M.; Fernandez, A.; Lane, W.S.; Lamb, N.J.; Brady, J.; Kumar, A. HIV-1 Tat-associated RNA polymerase C-terminal domain kinase, CDK2, phosphorylates CDK7 and stimulates Tat-mediated transcription. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Ammosova, T.; Berro, R.; Kashanchi, F.; Nekhai, S. RNA interference directed to CDK2 inhibits HIV-1 transcription. Virology 2005, 341, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debebe, Z.; Ammosova, T.; Breuer, D.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Karla, P.K.; Kumar, K.; Jerebtsova, M.; Ray, P.; Kashanchi, F.; et al. Iron chelators of the di-2-pyridylketone thiosemicarbazone and 2-benzoylpyridine thiosemicarbazone series inhibit HIV-1 transcription: Identification of novel cellular targets—iron, cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2, and CDK9. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Debebe, Z.; Ammosova, T.; Jerebtsova, M.; Kurantsin-Mills, J.; Niu, X.; Charles, S.; Richardson, D.R.; Ray, P.E.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Nekhai, S. Iron chelators ICL670 and 311 inhibit HIV-1 transcription. Virology 2007, 367, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbottah, E.; de La Fuente, C.; Nekhai, S.; Barnett, A.; Gianella-Borradori, A.; Pumfery, A.; Kashanchi, F. Antiviral activity of CYC202 in HIV-1-infected cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 3029–3042. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, A.; Gautier, M.; Callebaut, I.; Bontoux, M.; Jeanpierre, E.; Pontarotti, P.; Monget, P. Atypical structure and phylogenomic evolution of the new eutherian oocyte- and embryo-expressed KHDC1/DPPA5/ECAT1/OOEP gene family. Genomics 2007, 90, 583–594. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Kishi, Y.; Masuda, S.; Shibata, H.; Takeuchi, K.; Komura, M.; Iwanaka, T.; Muramatsu, S.; Kondo, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S.; Hanazono, Y. ERas is expressed in primate embryonic stem cells but not related to tumorigenesis. Cell Transpl. 2009, 18, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, H.; Itakura, K.; Maruyama, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Yamanaka, S. Identification and targeted disruption of the mouse gene encoding ESG1 (PH34/ECAT2/DPPA5). BMC Dev. Biol. 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Kim, H.; Ekram, M.B.; Yu, S.; Faulk, C.; Kim, J. Rex1/Zfp42 as an epigenetic regulator for genomic imprinting. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.R.; Cowley, S.; Martinez, F.O.; Shaw, M.; Minger, S.L.; James, W. Homogeneous monocytes and macrophages from human embryonic stem cells following coculture-free differentiation in M-CSF and IL-3. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulford, K.A.; Sipos, A.; Cordell, J.L.; Stross, W.P.; Mason, D.Y. Distribution of the CD68 macrophage/myeloid associated antigen. Int. Immunol. 1990, 2, 973–980. [Google Scholar]
- Kambal, A.; Mitchell, G.; Cary, W.; Gruenloh, W.; Jung, Y.; Kalomoiris, S.; Nacey, C.; McGee, J.; Lindsey, M.; Fury, B.; Bauer, G.; Nolta, J.A.; Anderson, J.S. Generation of HIV-1 resistant and functional macrophages from hematopoietic stem cell-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Mol. Ther. 2010, 19, 584–593. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkeaw, K.; Horio, Y.; Mizuochi, C.; Ogawa, M.; Sugiyama, D. Variation in hematopoietic potential of induced pluripotent stem cell lines. Stem Cell Rev. 2011, 6, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Stadtfeld, M.; Hochedlinger, K. Induced pluripotency: History, mechanisms, and applications. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2239–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, T.J.; Macnaughton, T.B.; Gowans, E.J. The development and characterisation of a SV40 T-antigen positive cell line of human hepatic origin. J. Virol. Methods 1997, 65, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neganova, I.; Zhang, X.; Atkinson, S.; Lako, M. Expression and functional analysis of G1 to S regulatory components reveals an important role for CDK2 in cell cycle regulation in human embryonic stem cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Jun Koh, Y.; Jeon, J.; Cho, Y.H.; Jang, M.J.; Kang, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, C.; Sook Cho, Y.; Chung, H.M.; Young Koh, G.; Han, Y.M. Efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional CD34+ progenitor cells by combined modulation of the MEK/ERK and BMP4 signaling pathways. Blood 2010, 116, 5762–5772. [Google Scholar]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Dunn, A.R. Development of functional macrophages from embryonal stem cells in vitro. Exp. Hematol. 1995, 23, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K.J.; Fabunmi, R.P.; Andersson, L.P.; Freeman, M.W. In vitro-differentiated embryonic stem cell macrophages: A model system for studying atherosclerosis-associated macrophage functions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindmark, H.; Rosengren, B.; Hurt-Camejo, E.; Bruder, C.E. Gene expression profiling shows that macrophages derived from mouse embryonic stem cells is an improved in vitro model for studies of vascular disease. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 300, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Odegaard, J.I.; Vats, D.; Zhang, L.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.; Smith, K.L.; Sykes, D.B.; Kamps, M.P.; Chawla, A. Quantitative expansion of ES cell-derived myeloid progenitors capable of differentiating into macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, M.R.; Gasson, J.C.; Paz, H. Modified ES / OP9 co-culture protocol provides enhanced characterization of hematopoietic progeny. J. Vis. Exp. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, C. Pseudotyping human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) by the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus targets HIV-1 entry to an endocytic pathway and suppresses both the requirement for Nef and the sensitivity to cyclosporin A. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5871–5877. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Gonzalo, M.; Carretero, M.; Rullas, J.; Lara-Pezzi, E.; Aramburu, J.; Berkhout, B.; Alcami, J.; Lopez-Cabrera, M. The hepatitis B virus X protein induces HIV-1 replication and transcription in synergy with T-cell activation signals: Functional roles of NF-kappaB/NF-AT and SP1-binding sites in the HIV-1 long terminal repeat promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35435–35443. [Google Scholar]
- Scaccabarozzi, A.; Arosio, P.; Weiss, G.; Valenti, L.; Dongiovanni, P.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Mattioli, M.; Levi, S.; Fiorelli, G.; Fargion, S. Relationship between TNF-alpha and iron metabolism in differentiating human monocytic THP-1 cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 110, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jerebtsova, M.; Kumari, N.; Xu, M.; Melo, G.B.A.d.; Niu, X.; Jeang, K.-T.; Nekhai, S. HIV-1 Resistant CDK2-Knockdown Macrophage-Like Cells Generated from 293T Cell-Derived Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Biology 2012, 1, 175-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1020175
Jerebtsova M, Kumari N, Xu M, Melo GBAd, Niu X, Jeang K-T, Nekhai S. HIV-1 Resistant CDK2-Knockdown Macrophage-Like Cells Generated from 293T Cell-Derived Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Biology. 2012; 1(2):175-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1020175
Chicago/Turabian StyleJerebtsova, Marina, Namita Kumari, Min Xu, Gustavo Brito Alvim de Melo, Xiaomei Niu, Kuan-Teh Jeang, and Sergei Nekhai. 2012. "HIV-1 Resistant CDK2-Knockdown Macrophage-Like Cells Generated from 293T Cell-Derived Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells" Biology 1, no. 2: 175-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1020175
APA StyleJerebtsova, M., Kumari, N., Xu, M., Melo, G. B. A. d., Niu, X., Jeang, K.-T., & Nekhai, S. (2012). HIV-1 Resistant CDK2-Knockdown Macrophage-Like Cells Generated from 293T Cell-Derived Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Biology, 1(2), 175-195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1020175




