Abstract
The study of rare objects requires the use of mobile non-invasive methods such as a portable X-ray fluorescence instrument (pXRF), but this involves an analysis from the outer surface, while the depth analyzed depends on the element measured and, in addition, the material can be very heterogeneous at different scales. The concept of elemental composition, therefore, has no “absolute” meaning for painted enamel decorations. This work evaluates this concept by comparing the pXRF measurements made with different configuration procedures, allowing to evaluate the consequences on the variability of the XRF signals, and discusses the contents of certain chemical elements. For this, two shards from the Qianlong period are analyzed, a shard of blue and white (underglazed) porcelain and a fragment of an ‘imperial’ bowl with painted enamel decoration (huafalang). The variability of measurements is compared for visually appearing homogeneous or heterogeneous areas.
1. Introduction
Enameling makes it possible to produce colorful objects with sophisticated and almost unalterable decoration. Painted enamels are the most sophisticated type of enameled decoration: numerous glass layers with various thicknesses, ranging from a few microns to a few hundreds of microns and colored with a variety of coloring agents (ions, metal nanoparticles or pigments), are deposited on a metal, glass or ceramic substrate. Painted enamels flourished in Europe during the second part of the 17th century and were given as gift to Chinese emperors by European missionaries, kings and ambassadors. European missionaries then contributed to develop the production of painted enamels in China [1,2,3]. The porcelains intended for the Emperors of China attested by their marks are considered great masterpieces of the Arts of Fire and have been among the most appreciated objects for several centuries [1,2,3]. Copies, or fakes, have therefore been made for a long time [4]. The Emperor Kangxi occupies a special place in the evolution of ‘Chinese’ taste [5]. The Manchu Dynasty, opened to foreign cultures, showed an interest in realistic painting that decorated the gifts offered by Europeans as well as Tibetan objects with multicolored decoration. This led Kangxi to ask the Jesuits, whom he installed at Court for their skills in astronomy and mathematics, to set up in the French Church Beitang, close to the Forbidden City [6], a workshop to produce glass, porcelain and metal objects decorated with enamels similar to those made in Europe. The archives of the Forbidden City as well as the correspondence of the Jesuits (Fathers Fontenay, Gerbillon, Ripa, de Mailla, …) report the arrival of European missionaries who were experts in painting (e.g., Fathers Castiglione and Gravereau) and also of a dozen collaborators with the expertise of enameling as well as the importation of ingredients and documentation [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Chinese records indicate that the palette went from a few to several dozen colors [9]. It is considered that this occurred because of the interest of Emperor Kangxi for the enameled objects given as gifts [16,17,18,19,20]. The Emperor requested that his workshops were able to manufacture such objects. Indeed, while the French enamellers of the middle of the 17th century were able to produce realistic works in enamel comparable to those of oil paintings due to a wide palette of opaque and intimately mixable colors [21], Chinese artisans only had a reduced number of transparent colors, allowing for decorations to be made which were analogous to watercolor. With the exception of the pioneering works of Zhang [22] and Kingery [23], it is only recently that the decoration of imperial objects has been made the subject of in-depth analysis [11,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. This also contributed to reviving analyses of porcelain and enameled metal objects intended for the ‘ordinary’ Chinese market and of objects, in particular emblazoned objects, produced for export to Europe (armorial porcelains, ‘porcelaines de commande’) [33,34,35,36]. Our objective is to assess the reliability of the portable X-ray fluorescence measurements carried out on site with the constraints imposed by the rarity and value of the artifacts, which not only exclude any sampling but also any contact with the instruments and limit the manipulation of these objects.
In fact, shards of artifacts with an imperial mark are rare, even rarer than intact artifacts. About 400 pieces of porcelain bearing the imperial mark are kept at the Palace Museum in Taipei, which preserves a large part of the imperial collections. This number makes it possible to estimate the number of imperial ceramics of the first reigns of the Qing Dynasty at less than (a few) thousand(s). Imperial bowl fragments from the Qianlong reign (from the same bowl or from similar bowls) have been analyzed by a few teams [24,25,26,27]. One of these fragments is used in this work to comprehend the variability of pXRF measurements. Although mobile devices for both Raman microspectroscopy [37,38,39,40] and X-ray fluorescence [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] have been marketed for more than 20 years, their use, indeed, has long been limited in archaeometric studies and often their disadvantages precluded their use. The growing practical and administrative constraints concerning the movement of rare objects to a laboratory has led to the development of new methodologies that do not require the movement of objects from their place of conservation. The weaknesses, inherent in the analysis solely of the outer surface without the possibility of visualizing the stratigraphy as is possible on a cross-section of a shard, are now well established [48]: the main one is due to the variable penetration/absorption of the X-ray photons according to their energy, which for a silicate matrix leads to the fact that the light elements are measured at the surface layer (a few µm thick), the transition metals at a depth close to the thickness of the enamel (~100–200 µm) and the heavy elements at a depth up to one millimeter. The measurement of the latter is therefore strongly ‘polluted’ by the contribution of the paste or the substrate, while that of the light elements can be disturbed by surface corrosion [48,49]. In this work, we compare the measurements made at different points on the top surface and on the section of two shards from the Qianlong reign that have already been analyzed by SEM-EDS and Raman microspectroscopy [24,36]. We will try to establish the intrinsic variability of the studies of such pieces to be able to discuss the perfectly non-invasive analyses made on the masterpieces of the Qing Dynasty.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
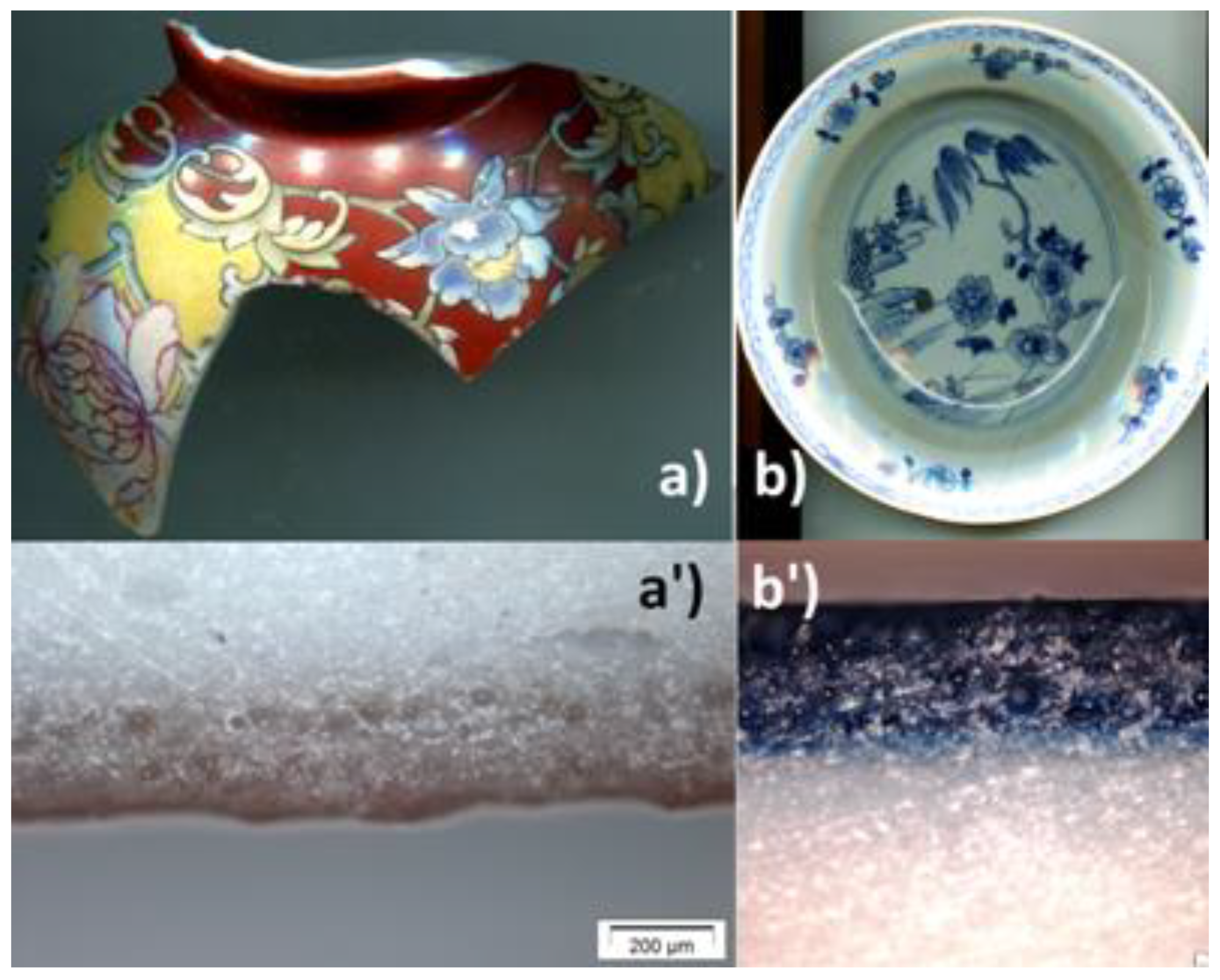
Figure 1 shows the two samples investigated in this work: (i) A fragment of an imperial bowl with a falangcai decoration of flowers on a red background dating from the Qianlong Dynasty (here after called QL), of which other fragments bear the imperial mark [26] which has already been analyzed. Cut pieces of the fragment have been analyzed by SEM-EDS and Raman microspectroscopy [24]. (ii) A fragment cut from a dish decorated in blue and white underglaze representing a willow tree (called ww), analyzed by SEM-EDS and Raman microspectroscopy previously [36]. No specific treatment was applied to sample except standard washing with water and drying in the open air.
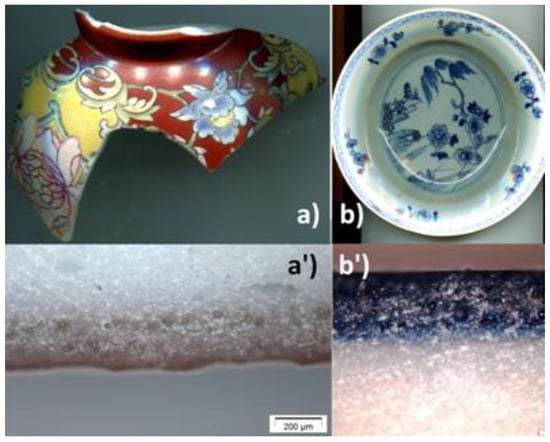
Figure 1.
Fragment of an imperial porcelain bowl (QL) with falangcai enamels (a) and corresponding cross-section (a’), and the dish with blue and white underglaze decoration (ww) (b) and its cross-section (b’), both objects being from the Qianlong reign period.
2.2. Experimental
X-ray fluorescence analysis was performed on site using an ELIO instrument (Bruker, AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). The pXRF instrument included a microfocus X-ray tube system with Rh anode (max voltage of 50 kV, max current of 0.2 mA for a maximal power of 4 W and a ~1 mm2 collimator) with an energy resolution of <140 eV for Mn Kα. The working distance was ~1.4 cm. We measured the Diorite DR-N geostandard from the ANRT (Association Nationale de la Recherche Technique [50,51]) to control the calibration performance of the instrument. Depending on the object, the measurement was carried out by positioning the instrument on the top or on the side. To ensure the reproducibility of the measurement geometry, a perfect perpendicularity of the excitation beam to the measured area is essential.
Measurements were carried out in the point mode with an acquisition time of 150 s, using a tube voltage of 50 kV and a current of 80 μA. No filter was used between the X-ray tube and the sample. The analysis depth during the measurement of the enamel (i.e., a silicate matrix), estimated from the Beer–Lambert law (analysis depth, defined as the thickness of the top layer from which comes 90% of the fluorescence) [49], was close to 6 µm at Si Kα, 170 µm at Cu Kα, 300 µm at Au Lα and 3 mm at Sn Kα. Within the energy resolution of our pXRF instrument, the Fe Kβ peak, which may refer to the red pigment, and the Co Kα peak corresponding to the blue color are located in the same energy range.
We undertook the analyses following two procedures (Table 1). The first one was conducted by fixing the spectrometer on a rack with micrometric displacements on a bench top. This enabled us to obtain perfectly stable measurement geometry. In this configuration, we sought to place the sample under the beam so that the analyzed surface was perpendicular to the beam, i.e., horizontal. The position of the spectrometer thus fixed the working distance and was adjusted by placing the sample on a laboratory lifting platform to place it as close as possible to the optimal focus.

Table 1.
Area analyzed and corresponding analysis number for each of the analytical configurations and samples. Details on the measured spots are given as Supplementary Materials (Figure S1).
Since we worked with two shards of different shapes, we also had to place them on the platform in two different ways. The shard of the falangcai bowl (QL) features a closed shape and therefore has a relatively pronounced convex outer surface. The sample was stuck on a piece of hard-plastic foam in which an incision was made (Figure 2a). Alternatively, we stabilized and orientated it in a box filled with glass mini-beads (or silica sand) to obtain the most horizontal surface possible, which could prove to be complex for certain zones, in particular those located at the extremities of the shard. The shard from the blue and white plate (ww), on the other hand, has a very flat shape, which allowed us to lay it directly on the lifting platform. Once the working distance was set for this sample, we moved it in the X and Y directions to move from one zone to be analyzed to the next, always respecting the perpendicularity and the position in the Z axis, and thus preserving the focus of the beam (Figure 2c). These configurations corresponded to the analyses conducted on both the glaze and the enamels of the two samples. The analyses on the body were conducted on the cross-section.
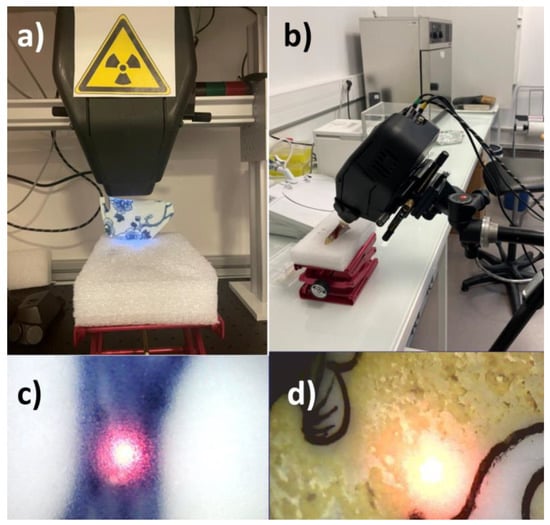
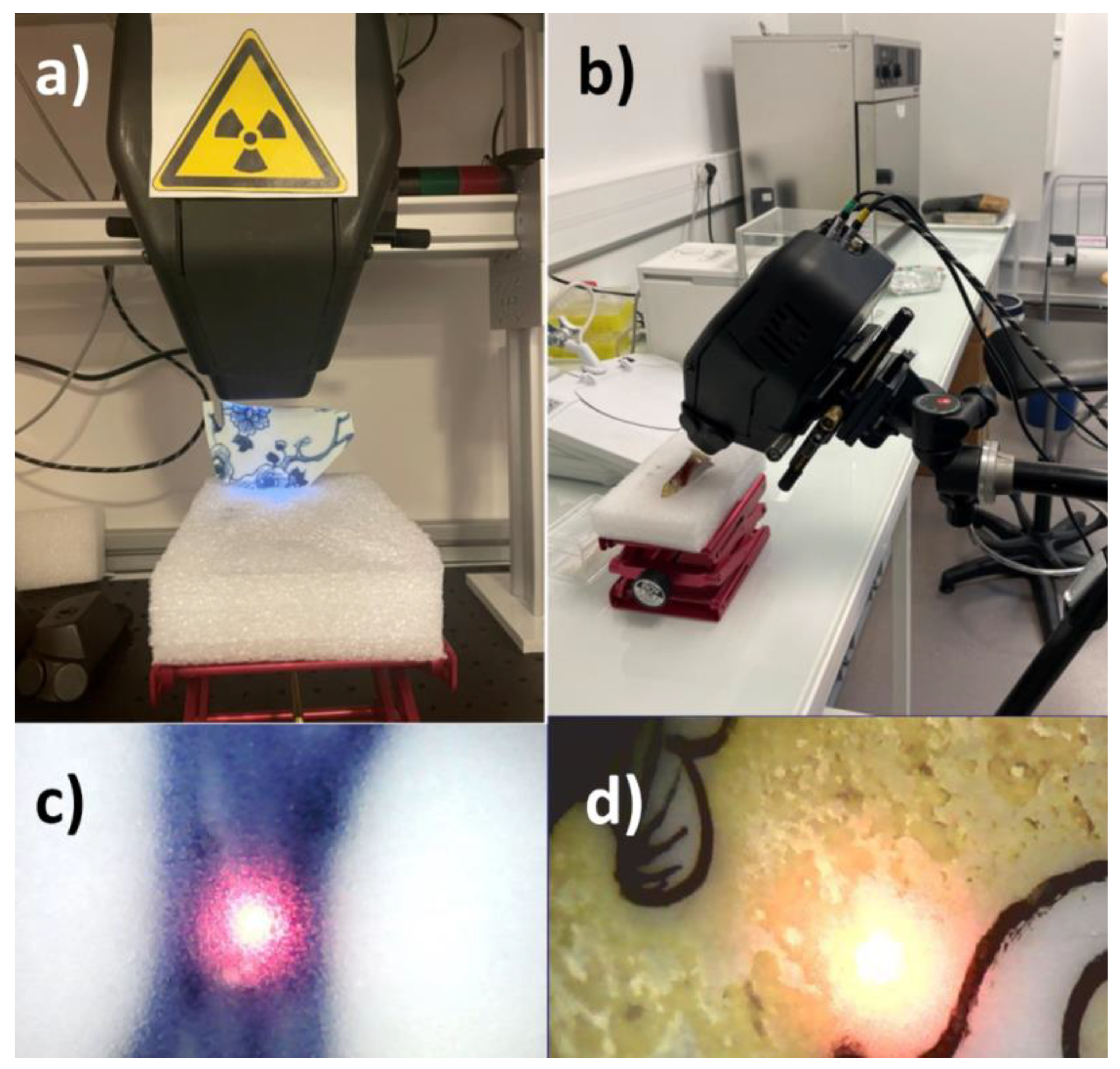
Figure 2.
The two measurement configurations: (a) vertical instrument fixed to a movable support placed on a bench; (b) use of a tripod; (c,d) example of focus showing a ‘good’ focus on a flat perpendicular area (support on a bench) and a ‘less good focus’, elongated, on a convex surface close to another colored area. Note the heterogeneity of the yellow area. Center halo diameter ~ ×1.2 mm.
The second procedure was only used for the QL sample because its closed form was precisely what presented the special challenge. In the second configuration, the spectrometer was fixed on a tripod designed as camera support, which made it possible to adjust its height as well as its orientation. It was indeed possible to direct the beam from vertical to horizontal. The shard was placed on the hard-plastic foam positioned on the lifting platform. It was oriented and stabilized through the positioning of other blocks on either side (Figure 2b). Once the sample was positioned, the spectrometer was oriented so as to present an excitation beam perpendicular to the analyzed surface and to respect a working distance that allowed a good focus. Figure 2d, for instance, illustrates a not well focused beam on a convex surface.
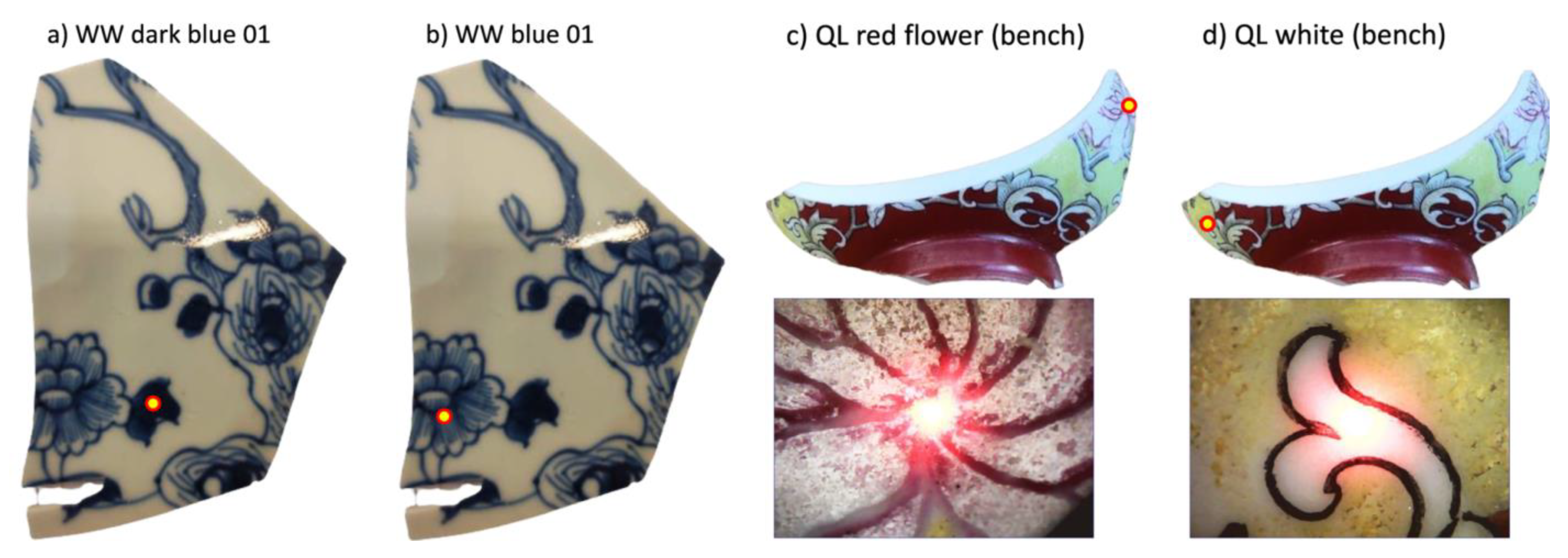
Notwithstanding the analysis configuration, the diameter of the beam spot (~1 mm) was such that it was sometimes impossible to analyze only a designated color, in particular concerning the QL shard. Some motifs painted with white enamels (Figure 3d) and others with red ones, such as the center of the flower (Figure 3c), were indeed smaller than the diameter of the beam. For this reason, adjacent colors will also contribute, namely, black lines, in the case of the analysis of the white patterns, and white areas in the case of the analyses of the red area representing the center of the flower. Note that for sample ww, we distinguished two levels of blue with dark and light (Figure 3a and Figure 3b, respectively). The difference was that the dark tone represents entirely blue areas and the less dark one represents areas marked by hatched blue patterns, which were therefore more influenced by the glaze. Concerning the analyses of the bodies conducted on the cross-sections of the two shards, their thickness was enough for the analysis beam not to interfere with the glaze applied on the surfaces.
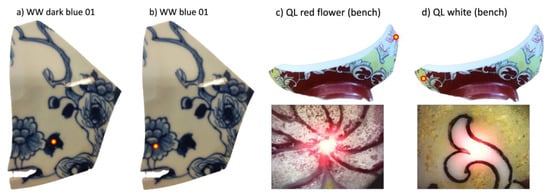
Figure 3.
Differences between the dark blue (a) and the blue (b) areas analyzed on sample ww. Red flower enamel (c) and white one (d) analyzed on sample QL (yellow dots: analyzed area).
2.3. XRF Data Processing
The procedure has already been described in previous papers [29,30,32]. After recording the raw data with ELIO, the recorded spectra files were analyzed through the Artax 7.4.0.0 (Bruker, AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany) software. For the data treatment process, the studied objects were considered as infinitely thick samples. Before evaluating the analysis data, all of the spectra were imported, and a new method file was created via the “Method Editor” of Artax for an applied voltage of 50 kV and current of 80 μA. The corresponding major (e.g., K, Ca), minor (e.g., Fe, Ti, Co) and trace elements (e.g., Ag, Bi, As) were added to the list of elements used to fit the experimental spectrum. For the correction, escape and background options were selected in the Method Editor, and 10 cycles of iteration were selected starting from 0.5 keV to 45 keV. The deconvolution method, Bayes, was applied to export the data table. The net area was calculated under the peak at the characteristic energy of each element selected for spectrum fitting, and the counts of the major, minor and trace elements were determined in the colored areas (white, red, yellow, blue and black). Before plotting the scatter diagrams, the net areas of each element were normalized by the number of XRF photons derived from the elastic peak of the X-ray tube of rhodium. An additional normalization with respect to the signal of Co was made for the comparison of certain elements. Then, these normalized data were plotted in the ternary scattering plots drawn for the interpretation and discussion of the results with the software Statistica 13.5.0.17 (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. XRF Fingerprint
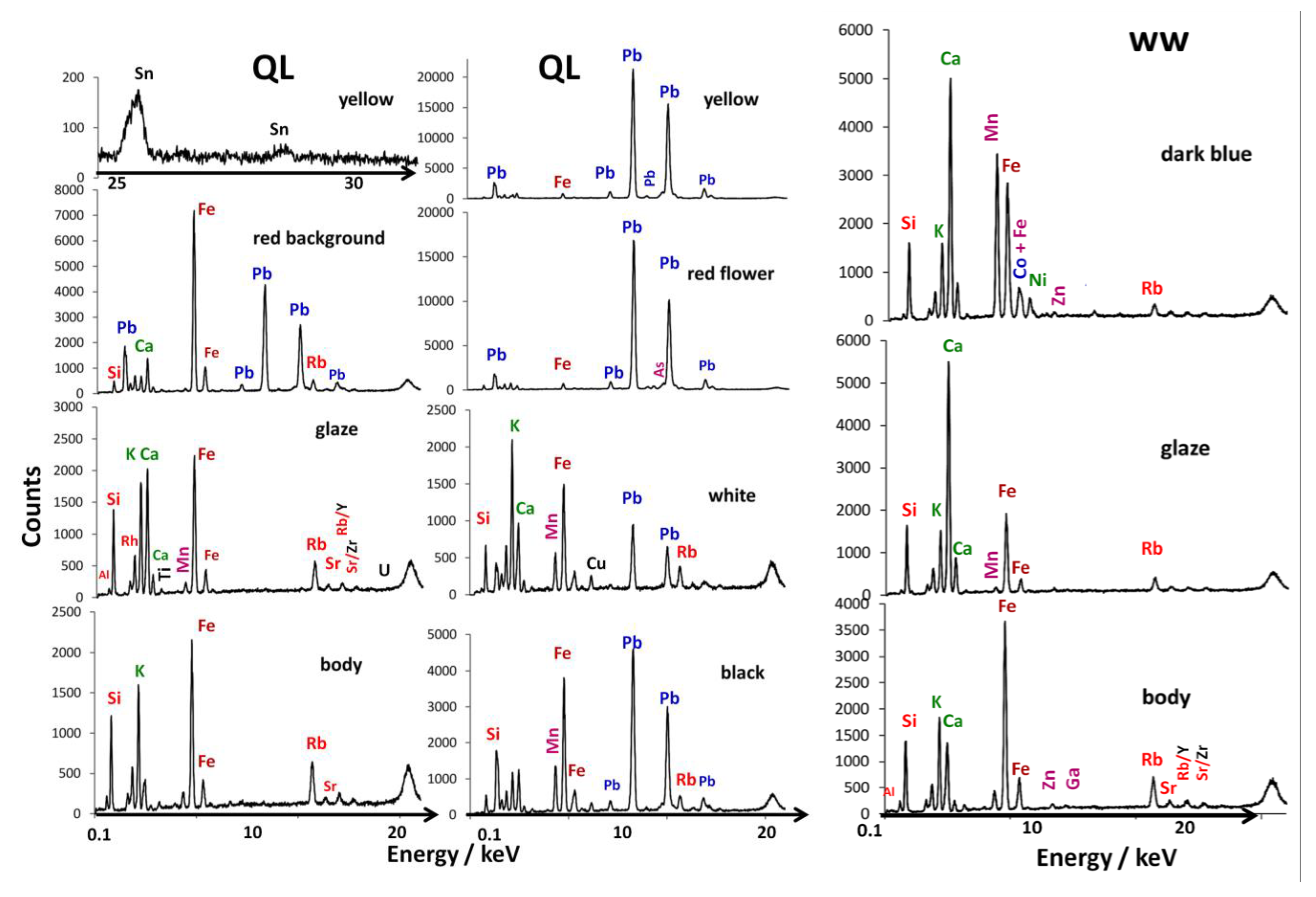
Figure 4 presents representative XRF spectra obtained on different parts of the fragments, the paste (body), the transparent glaze or blue-stained glaze and the enameled areas of different colors (red, yellow, white and black). All recorded spectra are shown in the Supplement Materials (Figure S1). The elements at the origin of the peaks are indicated. Note that sodium was detected in SEM-EDS [24], boron by Raman [52] and the triad of sodium, lithium and boron by PIGE [53], but was not detected by portable XRF (without having a vacuum or a light element atmosphere). The analysis points were taken at different zones on the surface and also on the section to be able to assess the variability of the material analyzed (for example, for the yellow regions of the falangcai bowl, we visually observed extra thicknesses at the darker yellow areas, and more or less dark blue areas on the second shard) and also the effects of disturbances coming from the surface measurements from the underlying layers or the mediocre quality of the focus due to the curvature of the analyzed zone. Table 1 lists the points of analysis. It should be remembered that the intensities of the XRF peaks are not directly proportional to the respective element contents, thus the peak of rubidium, an impurity of potassium (a few hundred ppm), is relatively much more intense than that of silicon, the major element (more than 50 wt%). The direct visual comparison of the spectra is therefore quantitatively relevant only peak-to-peak for measurement areas rather comparable in composition and thickness. It should indeed be remembered that because of the variable energies of the photons that are characteristic of the different transitions of the elements, which are absorbed differently by the sample matrix, the depths of explorations of heavy/light elements are very different [48,49]. The measurement of the light elements concerns the surface of the material (~a few µm) and the detection of the transition metals is roughly related to the thickness of the enamel (~200 µm), while the intensity of the peaks of the heavy elements (lead, tin, antimony, etc.) will be polluted by the contribution of the underglaze, glaze or paste layer, depending on the case. This is why, following the procedure described in references [30,32], we will compare the areas of the characteristic fluorescence peaks obtained after correction of the continuous background in ternary diagrams in order to evaluate the similarities and differences of the elemental ‘compositions’.
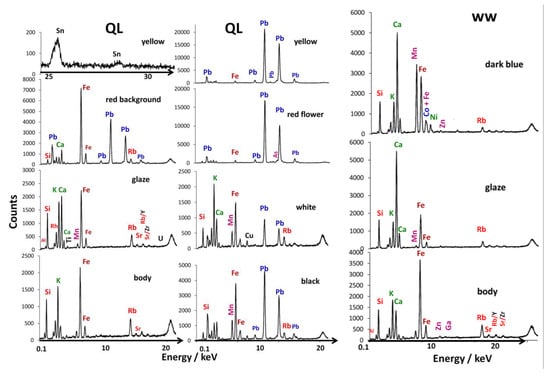
Figure 4.
Left and center, representative pXRF spectra recorded on the body section, the colorless glaze (surface), the red background and the different colored overglazes of the imperial bowl excavated fragment (QL, Figure 1a). Right, representative pXRF spectra recorded on the body section, the colorless glaze (surface) and the blue area of the blue and white cut fragment (Figure 1b, ww).
3.2. Silicate Matrix
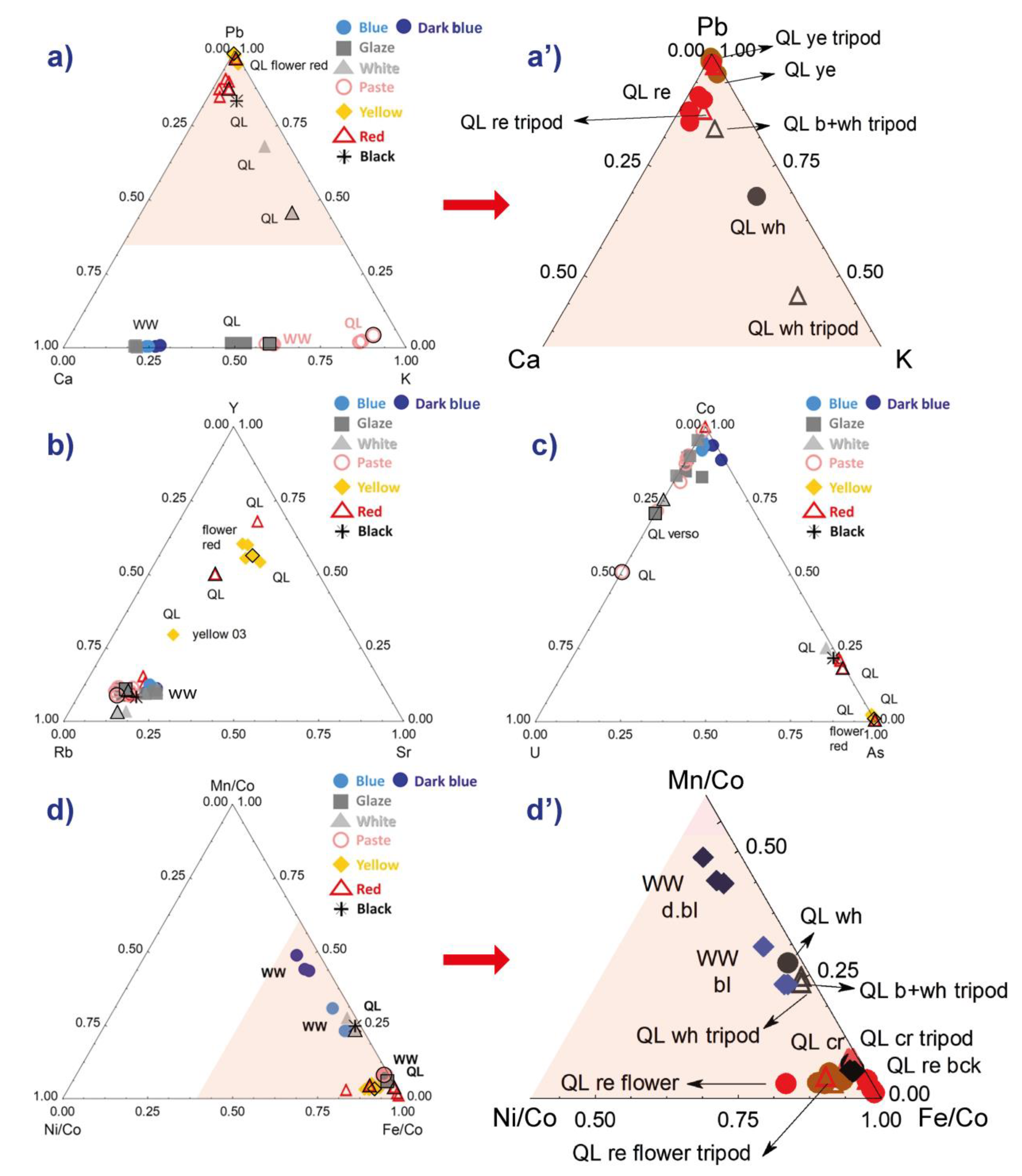
The comparison of the lead-calcium-potassium signals in Figure 5a,a’ show no dispersion of the data for the yellow areas of the bowl because of the high lead content of these zones. We see two clusters for the red, but the one that is rich in lead corresponds to the flower and not to the background.
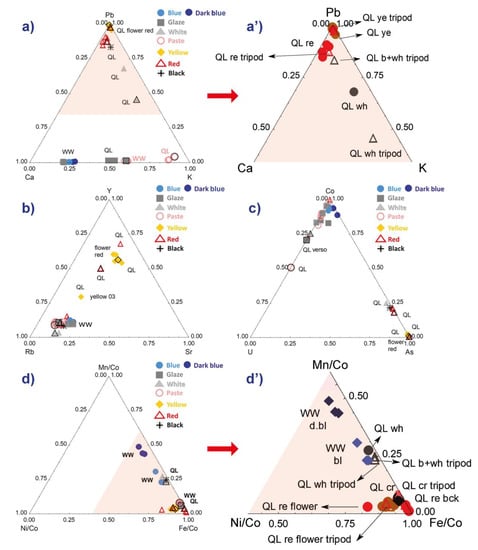
Figure 5.
Comparison of the characteristic signals (peak area) of elements of the silicate matrix of the enamel (a,a’) and those of the coloring or associated components (c,d’). A zoom of the diagrams (a,d) is given respectively in (a’,d’). In diagrams (d,d’), the signal of the elements associated with cobalt is normalized by the signal of cobalt for a better comparison. The color of the analyzed area is indicated (ye: yellow; b: blue; wh: white; re: red; bck: background) and the areas analyzed with the tripod are represented by a black outline in diagrams (a–d).
The measurements of these major elements are therefore little disturbed by the measurement configuration, except for the Ca and K contents of the glaze and the paste of the QL sample, the K/Ca ratios being higher for the analyses using the tripod. This is assigned to the variable thickness of the white enamel that determines the contribution of the lead-free substrate. The observation of a similar distribution for the blue zones of the second sample, for which only the bench setting has been used, shows that the heterogeneity within the specimen, both for the glaze and the paste, is the main cause of the distribution. The measurement error concerning the major elements is therefore very limited whatever the measurement configuration. A small dispersion distributed on a line parallel to the Pb-K side is observed for the overglaze white of the falangcai decoration. This difference between the two measurements might also have been influenced by the adjacent yellow area (much richer in Pb, for instance) analyzed at the same time.
Regarding the impurities associated with the raw materials of the silicate matrix and, in particular, fluxes, rubidium (associated with potassium) and strontium (associated with calcium), yttrium being assumed to be an impurity of the other raw materials (kaolin, pegmatite/feldspar or quartz), some dispersion is observed only for the red and yellow areas. Obviously, in painted enamel, the concentration of pigment is variable, hence the dispersion of the compositional data. Consideration of these clusters will therefore be relevant for the most minor or trace elements, i.e., areas colored by a pigment (pyrochlore for yellow and hematite for red [24]). The distribution on a line (e.g., Figure 5a,b) is again characteristic of the variable contribution of same two constituents.
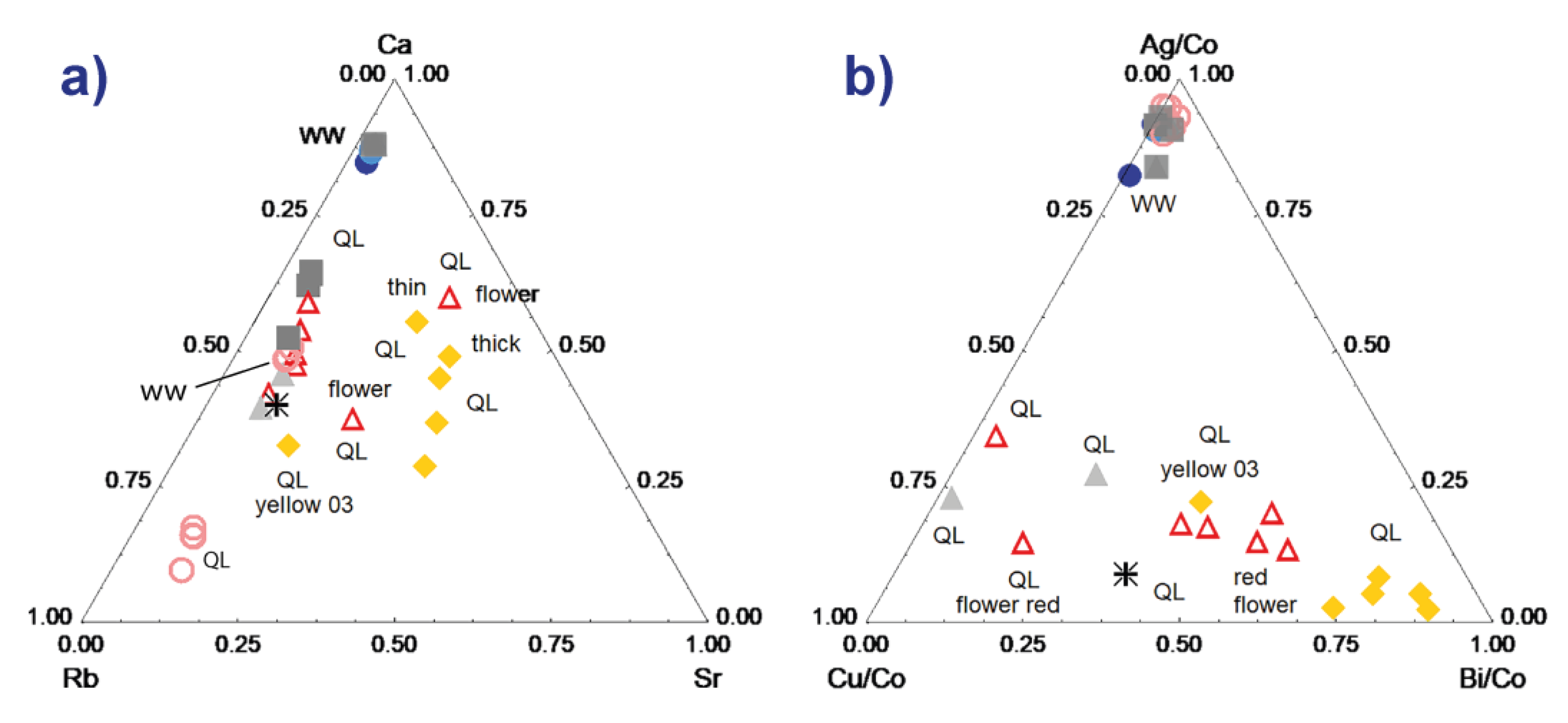
The maximum dispersions are observed for the ternary diagrams constructed with the peaks of medium or weak intensities. Figure 6a shows an example with the Ca-Rb-Sr diagram. We note a certain dispersion for the different measurements of the yellow zones, with the differentiation of the fine enamel measured on the surface due to the contribution of the glaze undercoat, which is richer in Ca. The same is true for the red zones, but the difference between the background and the flower (shift parallel to the Ca-Rb side) is obvious. We see that, even when the dispersion intrinsic to the measurement conditions is significant, the clustering effect is greater and the glazes belonging to the different techniques/decor therefore stand out. The data dispersion measured for the body gives an illustration of the ‘error’ measurement, the homogeneity of the paste being good for the area analyzed.
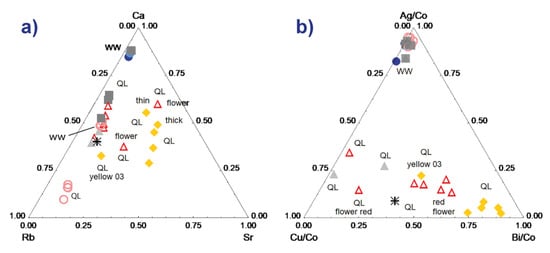
Figure 6.
Comparison of the characteristic signal (peak areas) of the elements Ca-Rb-Sr (a) and Ag-Cu-Bi normalized with respect to the signal of cobalt (b) for the different colored areas (see symbols in the previous figure) of the two analyzed samples.
3.3. Coloring and Associated Elements
The choice of the type of representation is effective for cobalt despite the low contents of this coloring agent due to its very strong coloring power: 0.1 to 0.5 wt% CoO is commonly observed [54]. Thus, the difference noted between a light blue and a dark blue colored area is weak, but the varied levels of arsenic are visualized (Figure 5c). It also well highlighted the presence of traces such as uranium (only visible with high magnification of the XRF spectrum intensity), whose peak is located in an energy zone without overlap with other signals. In Figure 5d,d’, the signals of the Mn, Fe and Ni elements associated with cobalt are better comparable after normalizing with respect to that of (weak) cobalt. Thus, in the sample representing a willow (ww), we see that two different ‘cobalts’ are used, one being richer in manganese—the manganese and iron contents are characteristics of Asian ores [54]—that is, the dark blue color. A grade choice is certainly made depending on the type of motif: full dark area vs. hatching. The presence of the same traces of nickel (Figure 5d,d’) leads to the distribution parallel to the Mn/Co-Fe/Co side.
Figure 6b is for normalized element data of which the peaks are low in intensity. The normalization is made with respect to the cobalt signal because the elements are associated with cobalt in the veins exploited in Europe [54,55]. Two groups are visible, the data from the red and yellow areas (plus the whites placed on yellow or red and the black) and the others (paste, colorless glaze). It appears that the Ag/Cu ratio is almost constant and that the bismuth content is variable. Bismuth can be an impurity of lead and therefore depends on both the lead content and the thickness of the enamel (this is a heavy element measured over a high thickness [49]). It is also volatile and diffuses widely during the firing, which accentuates the effects due to the variable thickness of the enamel. Nevertheless, the red flower is still very well distinguishable from the red background. The consideration of the specificities of each element in the enameling process is necessary for interpretation.
4. Discussion: Intrinsic Heterogeneity vs. Measurement Error
These results allow us to note certain differences in the measurements related to the geometries, whether they concern the nature/geometry of the analyzed surface of the shards or the layout of the analytical device, i.e., bench vs. tripod.
4.1. Effects of the Surface Geometry
Overall, we observe heterogeneity in the elemental fingerprint of the enamels. In Figure 5b (Rb-Y-Sr diagram), we observe indeed, for instance, a greater variability in the distribution of the data concerning the yellow enamels, according to visual examination (Figure 2d and Figure 3d). This is also the case for all the other enamels in the ternary diagrams of Figure 6. We can partly explain this variability as a result of the enamel thin layers being variable, in comparison with that of the glazes, which leads to an influence of the underneath layer(s)—covered glaze—during their analysis. We recall that the in-depth measurement for the Pb element reaches the order of millimeters in silicate matrixes [49]. The question of the technology used also arises from the fact that, unlike the application of a decoration painted under glaze as represented by the ww shard, the enameling technique is such that one can find a wide variety of shades and therefore of local compositions within an area of the “same” color.
We can make similar observations concerning the signal measured with the analyses of the red background of the QL shard, although the color looks homogeneous by eye examination. We suggest that the variability of the measurements could result from the convex shape of the analyzed surfaces that maximize the effect of the variable thickness, although we do not exclude the hypothesis that it could also be the consequence of the variable thickness of this red layer. We do not have similar variations for the analyses of the colorless glaze applied on the concave inner surface of the same shard, as well as for the analyses of the glazes of the ww shard which features a flat surface. By comparing the sections in Figure 1, we observe that the color is more homogeneous in the ww blue sample than in the QL red one. For the analyses of the porcelain bodies, which were conducted on a cross-section and therefore a flat surface and a layer of “unlimited” thickness, the distribution of the measurements is systematically the most homogeneous, whatever the sample. However, we cannot affirm that this is only due to the less complex geometry of the analyzed surfaces, since, unlike that of enamels, the composition of a porcelain paste is very homogeneous intrinsically.
In short, a kind of gradient in the quality of the analyses seems to emerge according to the combination of the surface, the material and the technology of the analyzed layer, which is, in the order of the quality of the analyses, porcelain body in cross-section, glaze applied on a flat surface and a concave one and glaze and enamels applied on a convex surface.
4.2. Tripod vs. Bench: The Case of Sample QL
We conducted the comparison of the two analytical configurations—bench and tripod—by systematically analyzing the same type of surface on the QL sample several times, namely, the paste, the glaze and the enamels for each distinct color. The idea is to see whether there are differences in the measured intensities that would not be due to the nature and the geometry of the surface analyzed. In this perspective, we note in the ternary diagrams presented in Figure 5 and Figure 6 that there is a difference between the results of the analyses made with the tripod and those obtained with the laboratory bench, especially concerning the paste and the glaze. For example, the intensities of Ca are lower for the paste and the glaze when they are measured with the tripod (Figure 5a,a’ (Ca-Pb-K diagram) and Figure 6a (Rb-Ca-Sr diagram)). With the colored enamels, whose signal values for Pb are all above 0.8 in Figure 5a’, the changes between the analytical configurations are not perceptible. This difference observed for the paste and for the glaze, according to the configuration of the analytical device, is also shown in Figure 5c (U-Co-As diagram) and Figure 6b (Cu/Co-Ag/Co-Bi/Co diagram) with lower Co/U and Ag/Cu ratios for the analyses with the tripod, respectively. Figure 5d’ shows that, for all types of layers (paste, glaze and enamel), there is systematically a slight loss of Ni intensities with the measurements using the tripod.
Concerning the quite important difference observed between the two compositions of the white enamel, this is not necessarily related to the analytical configuration varying from bench to tripod. We recall indeed that the dimensions of the analyzed white zones are smaller than the diameter of the beam spot (Figure 3d), so their analyses also accommodate integrated adjacent areas, namely, other colored enamels, which would further explain the large differences between the two analyses of the white enamel observed in Figure 5 and Figure 6. The same is true with the color of the red flower, of which the composition represents a mix between the white petals and the red stems of the flower (Figure 3c).
Table 2 shows, for each type of area of the QL sample where more than four analyses were conducted, the mean and the standard deviation calculated from the characteristic signals (peak area) of the elements used to create the ternary diagrams in Figure 5 and Figure 6. The difference calculated between the maximum and minimum signal measured on the same area is also mentioned. The data presented in the first rows correspond to the values calculated only from the bench measurements, while those in the second rows (marked with an asterisk) include both bench and tripod measurements (see Supplementary Materials for details of the calculations).

Table 2.
Means, differences between maximum and minimum and standard deviation calculated Figure 5 and Figure 6 (std = standard deviation). Details of calculations are given in Table S2 (Supplementary Materials).
For the paste and glaze, the differences calculated between the maximum and minimum intensities of the characteristic signals obtained from the ternary diagrams, as well as the standard deviations, are almost all higher when we combine bench measurements with tripod ones than when we only consider the values obtained with bench measurements without a tripod. This difference is systematically more than doubled. On the other hand, for the yellow enamel and the red background, the calculated data are rather similar between values measured only on the bench and values combining bench and tripod measurements. The standard deviations are sometimes even lower when we add the values obtained on the tripod to those obtained on the bench. This refers to our observation that the heterogeneity of the compositions of the colored enamels is such that the difference in the analytical methods—bench vs. tripod—does not seem to interfere in the distribution of the pXRF measurements of such types of layers.
The comparison of the two analytical configurations highlights the fact that, in general terms, the differences in composition, linked to one configuration or another, are especially observable when we analyze homogeneous zones, namely, the paste and the glaze in the present case. For the enamels, whose technology leads to the application of a material with a more heterogeneous composition at the microscopic scale and therefore a more pronounced variability of the compositions obtained on different areas of the same color, the results obtained from the analysis on a tripod do not attest to significant differences with those obtained on the laboratory bench.
5. Conclusions
The measurements conducted in different configurations lead to a dispersion of the data, which remains lower than that of glazes prepared and posed to obtain a different aesthetic effect concerning the coloring. However, it is essential to evaluate the effects of the contributions of the underlying layers (glaze, paste) for the elements whose measurement involves, according to the Beer–Lambert calculation [49], a depth of the order or greater than the supposed thickness of the enamel (knowledge of the thickness observed on comparable shards is therefore necessary). The method of visualizing data in the form of ternary diagrams of the signals of the characteristic elements allows the visualization of the element ratio or correlation underlining clusters that make sense and that can be discussed according to the parameters, such as the raw materials and their compositions, mixtures, thickness effects, etc. The dispersion observed on the measurement configurations in this work gives a view of the intrinsic dispersion.
Finally, we can conclude by mentioning that the data obtained with pXRF are in good agreement with those already obtained with SEM-EDS and Raman spectroscopy [24,36]. Indeed, for the QL sample, the SEM-EDS analysis carried out on spots of a few µm2 showed that the overglazes are lead-based and contain more calcium than the glaze [24], which is also shown in Figure 5a. Raman spectroscopy data confirmed this observation, since the spectra recorded on the different enamels from the top surface showed a peak ranging from ca. 930–990 cm−1, characteristic of depolymerized lead-rich silicate [24]. In the same way, the combination of EDS and Raman data allowed for the characterization of the presence of hematite (αFe2O3) in the red background, which is well confirmed with the main Fe peaks largely dominating in the pXRF spectra (Figure 4). The SEM-EDS and Raman spectroscopy results attested that the white color is associated with the presence of arsenic and a higher level of potassium. Of the enamels analyzed with pXRF, only the red flower clearly exhibits the As Kβ peak (Figure 4). Since the spot of the red flower analysis incorporates both the red flower core and the white petals (Figure 3c), we can then assume that the arsenic detection would be due to the white enamel used for the petals. Although for the yellow color no particular elements were clearly highlighted by SEM-EDS spectra, the Raman ones indicated the use of a lead pyrochlore, and probably of a lead-tin yellow [24]; this is confirmed by the presence of tin—and the absence of antimony which could have suggested the use of a lead antimony tin yellow—recorded in the yellow areas (Figure 4).
SEM-EDS analysis distinguished the glaze of the ww sample from other glazes of 18th century Chinese export/armorial porcelain by notably high calcium and low potassium contents [36], which seems to be well demonstrated by the ratio of the main Ca and K peaks of the pXRF spectra of the glaze and of the blue-painted underglaze decoration in Figure 4. Manganese, which may be associated with the cobalt-based blue pigment, was measured, with the highest manganese contents in the blue decoration [36], which is also observed in the ternary diagram in Figure 5d. This quite high manganese content, and arsenic not being detected with both methods (SEM-EDS and pXRF), seems to support the hypothesis of the use of a cobalt-based ore from an Asian source.
Although we are aware that the use of non-contact pXRF may have its limits in the detection of light elements, such as Na, for instance, whose role as a flux in a glassy matrix is no longer to be proven, the use of this method has nevertheless proved to be efficient for the accurate detection and distinction of transition metals, which allowed us to characterize the cobalt-based pigment used in the blue motifs of the ww sample. This method also allows good detection of tin (and potentially also antimony) to characterize the type of yellow pigment used by craftsmen, the lead-tin one in the case of the QL sample. Another advantage of the method presented in this article, compared to the analysis with SEM-EDS, is the possibility to observe precisely the color(s) of the area analyzed by the beam spot.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/colorants2010004/s1, Figure S1: Analyzed spots and corresponding XRF spectra. Table S1: XRF data. Table S2: Details of the calculations of the mean, standard deviation and difference obtained from the normalized areas of some element of QL sample.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C.; methodology, P.C. and G.S.F.; investigation, J.B., X.G., L.B.-G. and P.C.; resources, P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.C. and G.S.F.; writing—review and editing, P.C., G.S.F., J.B. and L.B.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research in France was partially funded by the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche ANR EnamelFC project—19-CE27-0019-02.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are given in Tables S1 and S2.
Acknowledgments
Mathieu Lebon (MNHN, Paris) is acknowledged for the availability of the XRF instrument and Nicolas Fournery (N. Fournery Gallery, Paris) for providing the ww shard. Edmund Lee (Royal Auction Laboratory, Hong-Kong) and Xiong-Lin Feng (Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing, China) are acknowledged for many discussions and help in selecting samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Finlay, R. 1. The Porcelain City: Jingdezhen in the Eighteenth Century. In The Pilgrim Art: Cultures of Porcelain in World History; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 17–46. ISBN 978-0-520-94538-8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, E.C. From the Imperial Court to the International Art Market: Jingdezhen Porcelain Production as Global Visual Culture. J. World Hist. 2012, 23, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, S. True Beauty of Form and Chaste Embellishment. Summer Palace Loot and Chinese Porcelain Collecting in Nineteenth-Century Britain. In Collecting and Displaying China’s “Summer Palace” in the West—The Yuanmingyuan in Britain and France, The Histories of Material Culture and Collecting, 1700–1950; Tythacott, L., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- Pierson, S. True or False? Defining the Fake in Chinese Porcelain. Les Cahiers de Framespa 2019, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalogue Porcelain with Painted Enamels of Qing Period; National Palace Museum: Taipei, Taiwan, 2013.
- Cai, H. Special Exhibition of Ch’ing Dynasty Enamelled Procelains of the Imperial Ateliers; National Palace Museum, Ed.; National Palace Museum: Taipei, Taiwan, 1992; ISBN 978-957-562-125-4. [Google Scholar]
- Landry-Deron, I. Les Mathématiciens Envoyés En Chine Par Louis XIV En 1685. Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 2001, 55, 423–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loehr, G. Missionary-Artists at the Manchu Court. Trans. Orient. Ceram. Soc. 1963, 34, 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, C.-F. Evidence of East-West Exchange in the Eighteenth Century: The Establishment of Painted Enamel Art at the Qing Court in the Reign of Emperor Kangxi. Natl. Palace Mus. Res. Q. 2017, 24, 45–94. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X. Europe-China-Europe: The Transmission of the Craft of Painted Enamel in the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries. In Goods from the East, 1600–1800 Trading Eurasia; Berg, M., Gottmann, F., Hodacs, H., Nierstrasz, C., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2015; pp. 92–106. [Google Scholar]
- Colomban, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B. Non-Invasive Raman Analyses of Chinese Huafalang and Related Porcelain Wares. Searching for Evidence for Innovative Pigment Technologies. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 12079–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Henderson, J.; Cui, J.; Chen, K. Glassmaking of the Qing Dynasty: A Review, New Data, and New Insights. Adv. Archaeomater. 2020, 1, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, E.B. Aspects of a Multi-Faceted Process: The Circulation of Enamel Wares between the Vatican and Kangxi’s Court. In Des Arts Diplomatiques. Les Cadeaux Diplomatiques Entre la Chine et l’Europe aux XVIIe-XVIIIe Siècles. Pratiques et Enjeux; Zhao, B., Landry-Deron, I., Simon, F., Eds.; Extrême-Orient, Extrême-Occident; Presses Universitaires de Vincennes: Vincennes, France, 2019; pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. Painted Enamel on Ceramics—The Encounter of Dutch and Chinese Pottery. Available online: https://www.aronson.com/painted-enamel-on-ceramic-the-encounter-of-dutch-and-chinese-pottery/ (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Bellemare, J. A New Palette: Reassessing the Development of Enamel Colors in Early Eighteenth-Century China. J. Glass Stud. 2022, 64, 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Treasures from Oversea Countries, Exhibition Catalogue of Kulangsu Gallery of Foreign Artefacts from the Palace Museum Collection; Palace Museum (Ed.) Gugong Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kleutghen, K. Chinese Occidenterie: The Diversity of “Western” Objects in Eighteenth-Century China. Eighteenth-Century Stud. 2014, 47, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rochebrunne, M.L. Les Porcelaines de Sèvres Envoyées En Guise de Cadeaux Diplomatiques à l’empereur de Chine Par Les Souverains Français Dans La Seconde Moitié Du XVIIIe Siècle. In Des Arts Diplomatiques. Les Cadeaux Diplomatiques Entre la Chine et l’Europe aux XVIIe-XVIIIe Siècles. Pratiques et Enjeux; Zhao, B., Landry-Deron, I., Simon, F., Eds.; Extrême-Orient, Extrême-Occident; Presses Universitaires de Vincennes: Vincennes, France, 2019; pp. 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Finlay, J. Henri Bertin and Louis XV’s Gifts to the Qianlong Emperor. In Des Arts Diplomatiques. Les Cadeaux Diplomatiques Entre la Chine et l’Europe aux XVIIe-XVIIIe Siècles. Pratiques et Enjeux; Zhao, B., Landry-Deron, I., Simon, F., Eds.; Extrême-Orient, Extrême-Occident; Presses Universitaires de Vincennes: Vincennes, France, 2019; pp. 93–112. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F. Presents and Tribute: Exploration of the Presents Given to the Qianlong Emperor by the British Macartney Embassy. In Des Arts Diplomatiques. Les Cadeaux Diplomatiques Entre la Chine et l’Europe aux XVIIe-XVIIIe Siècles. Pratiques et Enjeux; Zhao, B., Landry-Deron, I., Simon, F., Eds.; Extrême-Orient, Extrême-Occident; Presses Universitaires de Vincennes: Vincennes, France, 2019; pp. 143–172. [Google Scholar]
- Colomban, P.; Kırmızı, B.; Gougeon, C.; Gironda, M.; Cardinal, C. Pigments and Glassy Matrix of the 17th–18th Century Enamelled French Watches: A Non-Invasive on-Site Raman and PXRF Study. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. The Origin and Development of Traditional Chinese Glazes and Decorative Ceramics Color. In Ancient Technology to Modern Science; Kingery, W.D., Ed.; The American Ceramic Society: Colombus, OH, USA, 1985; Volume 1, pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kingery, W.D.; Vandiver, P.B. The Eighteenth-Century Change in Technology and Style from the Famille-Verte Palette to the Famille-Rose Palette. In Technology and Style; Kingery, W.D., Ed.; Ceramics and Civilization; The American Ceramic Society: Colombus, OH, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 363–381. [Google Scholar]
- Colomban, P.; Ambrosi, F.; Ngo, A.T.; Lu, T.A.; Feng, X.L.; Chen, S.; Choi, C.L. Comparative Analysis of Wucai Chinese Porcelains Using Mobile and Fixed Raman Microspectrometers. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 14244–14256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ji, L.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Sciau, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, C. Study of Arsenic in Famille Rose Porcelain from the Imperial Palace of Qing Dynasty, Beijing, China. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, X.; Kang, B.; Wang, G.; Qu, L.; Lei, Y. Non-Destructive Analysis and Deterioration Study of a Decorated Famille Rose Porcelain Bowl of Qianlong Reign from the Forbidden City. Stud. Conserv. 2019, 64, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sciau, P.; Zhu, J.; Ji, L.; Shan, Y.; Song, G. Microscopic Analysis of Overglaze Green Pigment on Chinese famille rose Porcelain from the Imperial Palace. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomban, P.; Kırmızı, B.; Zhao, B.; Clais, J.B.; Yang, Y.; Droguet, V. Investigation of the Pigments and Glassy Matrix of Painted Enamelled Qing Dynasty Chinese Porcelains by Noninvasive On-Site Raman Microspectrometry. Heritage 2020, 3, 915–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P.; Gironda, M.; Vangu, D.; Kırmızı, B.; Zhao, B.; Cochet, V. The Technology Transfer from Europe to China in the 17th–18th Centuries: Non-Invasive On-Site XRF and Raman Analyses of Chinese Qing Dynasty Enameled Masterpieces Made Using European Ingredients/Recipes. Materials 2021, 14, 7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P.; Simsek Franci, G.; Gironda, M.; d’Abrigeon, P.; Schumacher, A.C. PXRF Data Evaluation Methodology for On-Site Analysis of Precious Artifacts: Cobalt Used in the Blue Decoration of Qing Dynasty Overglazed Porcelain Enameled at Customs District (Guangzhou), Jingdezhen and Zaobanchu (Beijing) Workshops. Heritage 2022, 5, 1752–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P. The Discovery and Comparison of the Manufacturing Secrets of Enamelled Masterpieces. Orientations 2022, 53, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Colomban, P.; Gironda, M.; Simsek Franci, G.; d’Abrigeon, P. Distinguishing Genuine Imperial Qing Dynasty Porcelain from Ancient Replicas by On-Site Non-Invasive XRF and Raman Spectroscopy. Materials 2022, 15, 5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pevenage, J.; Lauwers, D.; Herremans, D.; Verhaeven, E.; Vekemans, B.; De Clercq, W.; Vincze, L.; Moens, L.; Vandenabeele, P. A Combined Spectroscopic Study on Chinese Porcelain Containing Ruan-Cai Colours. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, R.; Freestone, I.C.; Shortland, A.J. European Cobalt Sources Identified in the Production of Chinese famille rose Porcelain. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 80, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, D.E.; Braekmans, D.; Domoney, K.; Shortland, A. The Composition and Technology of Polychrome Enamels on Chinese Ruby-Backed Plates Identified Through Nondestructive Micro-X-ray Fluorescence. X-ray Spectrom. 2020, 49, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P.; Ngo, A.T.; Fournery, N. Non-Invasive Raman Analysis of 18th Century Chinese Export/Armorial Overglazed Porcelain: Identification of the Different Enameling Techniques. Heritage 2022, 5, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P. On-Site Raman Identification and Dating of Ancient Glasses: A Review of Procedures and Tools. J. Cult. Herit. 2008, 9, e55–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P. The On-site/Remote Raman Analysis with Mobile Instruments: A Review of Drawbacks and Success in Cultural Heritage Studies and Other Associated Fields. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P. On-Site Raman Study of Artwork: Procedure and Illustrative Examples. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P.; Milande, V.; Le Bihan, L. On-Site Raman Analysis of Iznik Pottery Glazes and Pigments. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackley, M.S. Is There Reliability and Validity in Portable X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (PXRF)? SAA Archaeol. Rec. 2010, 10, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Liritzis, I.; Zacharias, N. Portable XRF of Archaeological Artifacts: Current Research, Potentials and Limitations. In X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (XRF) in Geoarchaeology; Schackley, M.S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 109–142. [Google Scholar]
- Goodale, N.; Bailey, D.G.; Jones, G.T.; Prescott, C.; Scholz, E.; Stagliano, N.; Lewis, C. PXRF: A Study of Inter-Instrument Performance. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Q.H.; Fu, Q.; Gan, F.X.; Xiong, Z.M. Application of a Portable XRF Spectrometer for Classification of Potash Glass Beads Unearthed from Tombs of Han Dynasty in Guangxi, China: Application of PXRF for Potash Glass Found in Guangxi, China. X-ray Spectrom. 2013, 42, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, N.; Grave, P. Effects of Elevated Levels of Lead in Ceramics on Provenancing Studies Using Non-Destructive PXRF: A Case Study in Byzantine Cypriot Glazed Ceramics: Effects of Elevated Levels of Lead in Ceramics on Non-Destructive PXRF. X-ray Spectrom. 2013, 42, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, E. Validity of “off-the-Shelf” Handheld Portable XRF for Sourcing Near Eastern Obsidian Chip Debris. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Niziolek, L.C.; Feinman, G.M. Sourcing Qingbai Porcelains from the Java Sea Shipwreck: Compositional Analysis Using Portable XRF. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2019, 103, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirsar Arlı, B.; Simsek Franci, G.; Kaya, Ş.; Arli, H.; Colomban, P. Portable X-ray Fluorescence (p-XRF) Uncertainty Estimation for Glazed Ceramic Analysis: Case of Iznik Tiles. Heritage 2020, 3, 1302–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRUKER Information Depth. Available online: https://xrfcheck.bruker.com/InfoDepth (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Govindaraju, K. Report (1967–1981) on Four ANRT Rock Reference Samples: Diorite DR-N, Serpentine UB-N, Bauxite BX-N and Disthene DT-N. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 1982, 6, 91–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, K. 1995 Working Values with Confidence Limits for Twenty-Six CRPG, ANRT and IWG-GIT Geostandards. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 1995, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, P. Full Spectral Range Raman Signatures Related to Changes in Enameling Technologies from the 18th to the 20th Century: Guidelines, Effectiveness and Limitations of the Raman Analysis. Materials 2022, 15, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlot, J.; Bellot-Gurlet, L.; Lemasson, Q.; Pichon, L.; Colomban, P. Bore/Lithium-based flux in 18th Century Chinese porcelain enamels: PIXE/PIGE study. In Proceedings of the 18th ECerS Conf., Lyon, France, 2–6 July 2023. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Colomban, P.; Kırmızı, B.; Simsek Franci, G. Cobalt and Associated Impurities in Blue (and Green) Glass, Glaze and Enamel: Relationships between Raw Materials, Processing, Composition, Phases and International Trade. Minerals 2021, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissin, S.A. Five-Element (Ni-Co-As-Ag-Bi) Veins. Geosci. Can. 1992, 19, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).