Azaphilones Pigments from the Fungus Penicillium hirayamae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Fungal Materials
2.3. Extraction and Isolation
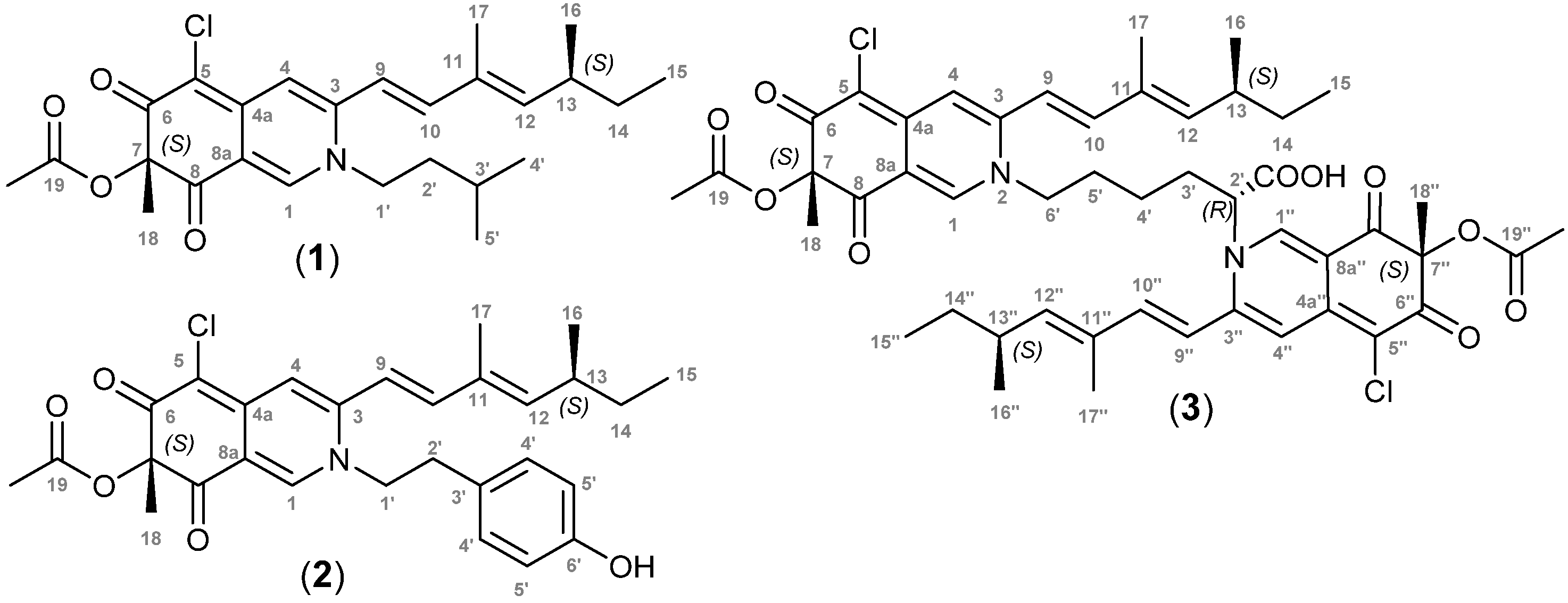
2.4. Penazaphilone J (1)
2.5. Penazaphilone K (2)
2.6. Penazaphilone L (3)
2.7. Computational Details
2.8. Biological Activities
2.8.1. Cytotoxic Activities
2.8.2. Antimicrobial Assay
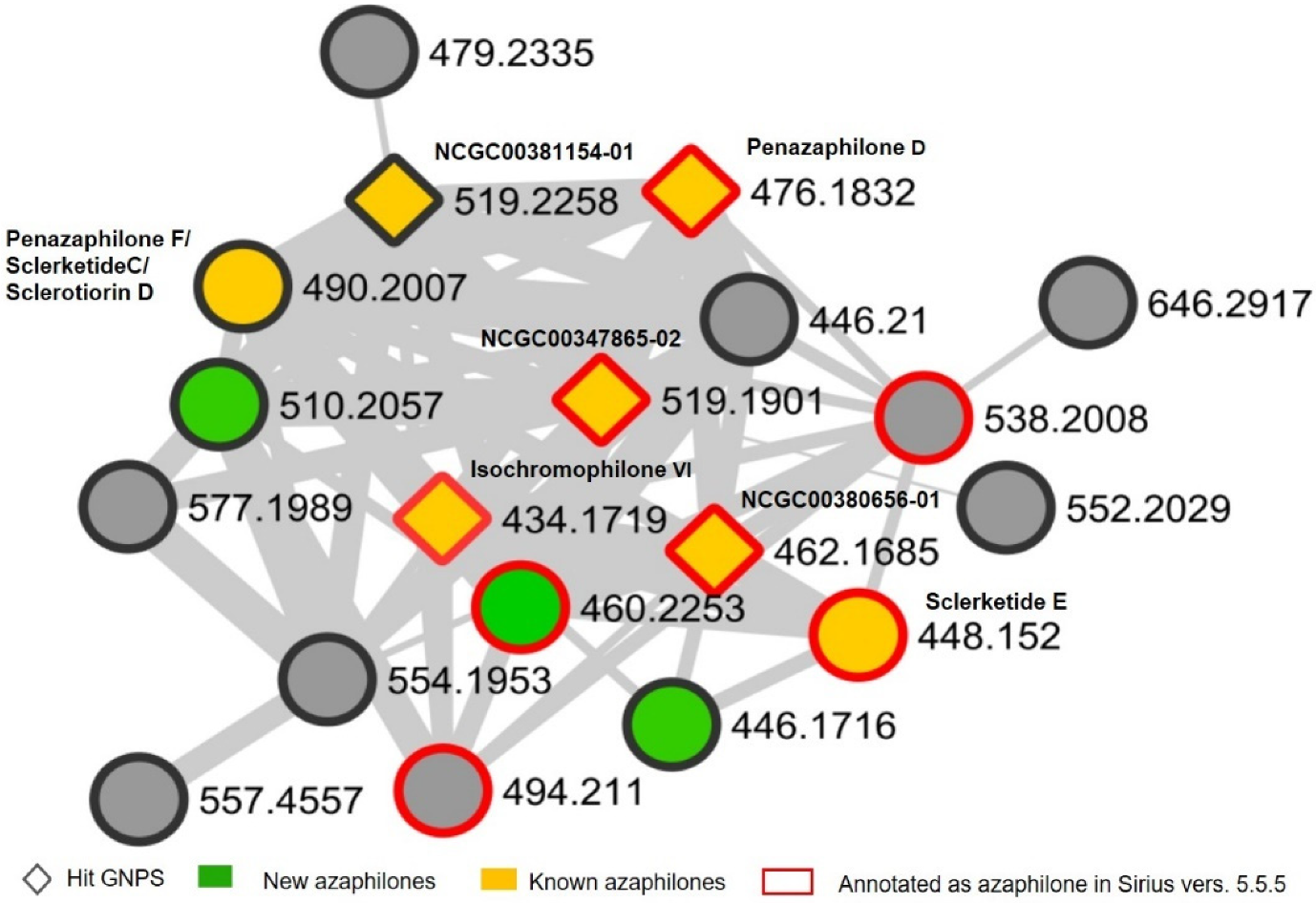
3. Results
| (1) a | (2) b | (3) a | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos. | δH | Mult. J (Hz) | δC | δH | Mult. J (Hz) | δC | δH | Mult. J (Hz) | δC |
| 1 | 7.93 | (s) | 143.0 | 7.99 | (s) | 142.7 | 7.88 | (s) | 143.1 |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | - | - | 149.9 | - | - | 149.2 | - | - | 149.9 |
| 4 | 7.02 | (s) | 111.4 | 6.92 | (s) | 109.6 | 6.99 | (s) | 111.1 |
| 5 | - | - | 100.6 | - | - | 99.0 | - | - | 100.8 |
| 6 | - | - | 184.1 | - | - | 182.2 | - | - | 184.2 |
| 7 | - | - | 86.3 | - | - | 84.9 | - | - | 86.2 |
| 8 | - | - | 194.5 | - | - | 192.9 | - | - | 194.4 |
| 9 | 6.33 | (d) 15.5 | 116.5 | 6.39 | (d) 15.5 | 116.1 | 6.24 | (d) 15.5 | 116.3 |
| 10 | 7.08 | (dd) 15.5; 0.8 | 145.4 | 7.09 | (d) 15.4 | 143.8 | 7.03 | (d) 14.8 | 145.5 |
| 11 | - | - | 133.4 | - | - | 132.3 | - | - | 133.4 |
| 12 | 5.75 | (d) 9.7 | 148.1 | 5.85 | (d) 9.7 | 146.5 | 5.76 | (d) 9.7 | 148.4 |
| 13 | 2.53 | (m) | 35.6 | 2.48 | (m) | 34.3 | 2.50 | (m) | 35.6 |
| 14 | 1.45 1.32 | (m) | 30.8 | 1.43 1.30 | (m) | 29.5 | 1.43 1.31 | (m) | 30.8 |
| 15 | 0.87 | (t) 7.4 | 12.2 | 0.85 | (t) 7.4 | 11.8 | 0.87/0.86 * | (t) 6.3 | 12.3 |
| 16 | 1.01 | (d) 6.7 | 20.5 | 0.98 | (d) 6.6 | 20.2 | 1.00/0.98 * | (d) 6.7 | 20.5 |
| 17 | 1.88 | (d) 1.2 | 12.8 | 1.86 | (d) 1.2 | 12.4 | 1.82 | (m) | 12.8 |
| 18 | 1.44 | (s) | 23.7 | 1.37 | (s) | 23.1 | 1.44 | (s) | 23.7 |
| 4a | - | - | 146.2 | - | - | 144.5 | - | - | 146.2 |
| 8a | - | - | 115.6 | - | - | 113.6 | - | - | 115.5 |
| 4a″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 145.3 |
| 8a″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 115.7 |
| 1′ | 3.99 | (m) | 53.7 | 4.37 4.25 | (ddd) 5.6; 8.2; 14.5 m | 54.8 | - | - | 171.0 |
| 2′ | 1.64 | (m) | 39.5 | 2.86 2.82 | (ddd) 5.6; 8.2; 14.5 m | 34.7 | 4.95 | (m) | 63.7 |
| 3′ | 1.66 | (m) | 26.6 | - | - | 126.7 | 2.27 2.05 | (m) | 31.9 |
| 4′ | 0.95 | (d) 6.3 | 22.5 | 6.96 | (d) 8.5 | 129.9 | 1.36 1.31 | (m) | 23.2 |
| 5′ | 0.95 | (d) 6.3 | 22.5 | 6.66 | (d) 8.5 | 115.4 | 1.71 | (m) | 30.1 |
| 6′ | - | - | - | - | - | 156.3 | 3.93 | (m) | 54.5 |
| 1″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 7.86 | (s) | 140.4 |
| 2″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 151.0 |
| 4″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6.88 | (s) | 111.8 |
| 5″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 102.1 |
| 6″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 184.7 |
| 7″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 86.2 |
| 8″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 194.1 |
| 9″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6.23 | (d) 15.4 | 116.7 |
| 10″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6.90 | (d) 15.3 | 145.9 |
| 11″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 133.4 |
| 12″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.68 | (d) 9.7 | 148.0 |
| 13″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.50 | (m) | 35.6 |
| 14″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.41 1.30 | (m) | 30.8 |
| 15″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.87/0.86 * | (t) 7.4 | 12.3 |
| 16″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00/0.98 * | (d) 6.6 | 20.5 |
| 17″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.82 | (m) | 12.9 |
| 18″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.42 | (s) | 23.7 |
| OCOCH3 | 2.07 | (s) | 20.5 | 2.06 | (s) | 20.1 | 2.06/2.07 * | (s) | 20.5 |
| OCOCH3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.06/2.07 * | (s) | 20.5 |
| 19 | - | - | 170.7 | - | - | 169.1 | - | - | 170.7 |
| 19″ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 170.8 |
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novais, C.; Molina, A.K.; Abreu, R.M.V.; Santo-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.; Pereira, C.; Barros, L. Natural Food Colorants and Preservatives: A Review, a Demand, and a Challenge. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2789–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, D.; Toth, G.; Humpf, H.U. New monascus metabolites with a pyridine structure in red fermented rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5493–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.M.; Yang, S.X.; Qin, J.C. Azaphilones: Chemistry and biology. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4755–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Feng, Y.; Molnar, I.; Chen, F. Nature and nurture: Confluence of pathway determinism with metabolic and chemical serendipity diversifies Monascus azaphilone pigments. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavesi, C.; Flon, V.; Mann, S.; Leleu, S.; Prado, S.; Franck, X. Biosynthesis of azaphilones: A review. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, T.; Ye, G.; Qiu, L.; Long, Y. New azaphilones from mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium sclerotiorin SCNU-F0040. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 37, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, N.; Shiomi, K.; Tomoda, H.; Tabata, N.; Yang, D.J.; Masuma, R.; Kawakubo, T.; Omura, S. Isochromophilones III-VI, inhibitors of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase produced by Penicillium multicolor FO-3216. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.L.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yang, T.; Yao, C.; Wu, L.W.; Li, G.Y. Azaphilone Alkaloids with Anti-inflammatory Activity from Fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum cib-411. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. C.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dillard, C.; Borde, C.; Mohammad, A.; Puchois, V.; Jourdren, L.; Larsen, A.K.; Sabbah, M.; Maréchal, V.; Escargueil, A.E.; Pramil, E. Expression Pattern of Purinergic Signaling Components in Colorectal Cancer Cells and Differential Cellular Outcomes Induced by Extracellular ATP and Adenosine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, T.; Berchel, M.; Le Hir, S.; Fraix, A.; Salaün, J.Y.; Férec, C.; Lehn, P.; Jaffrès, P.A.; Montier, T. Arsonium-containing lipophosphoramides, poly-functional nano-carriers for simultaneous antibacterial action and eukaryotic cell transfection. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youf, R.; Nasir, A.; Müller, M.; Thétiot, F.; Haute, T.; Ghanem, R.; Jonas, U.; Schönherr, H.; Lemercier, G.; Montier, T.; et al. Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complexes for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy: Prospects for Application in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Airways. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, T.; Lemercier, G.; Chevreux, S.; Tücking, K.S.; Ravel, J.; Thétiot, F.; Jonas, U.; Schönherr, H.; Montier, T. Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complexes as Photosensitizers for Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy: A Structure-Activity Study on Clinical Bacterial Strains. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udagawa, S. Penicillium hirayamae. J. Agric. Sci. Tokyo Nogyo Daigaku. 1959, 5, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Udagawa, S. (-)-Sclerotiorin, A Major Metabolite of Penicillium hirayamae Udagawa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1963, 11, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.W.; Whalley, W.B. The chemistry of fungi. Part LXIII. Rubrorotiorin, a metabolite of Penicillium hirayamae Udagawa. J. Chem. Soc. C 1971, 21, 3575–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, R.R.; Holzapfel, C.W.; Ferreira, N.P.; Marsh, J.J. The structure and biogenesis of desoxyverrucarin E, a metabolite of Eupenicillium hirayamae. Phytochemistry 1974, 13, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Color Market Size. Trend Research Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/food-color-market-2621 (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Morales-Oyervides, L.; Ruiz-Sánchez, J.P.; Oliveira, J.C.; Sousa-Gallagher, M.J.; Méndez-Zavala, A.; Giuffrida, D.; Dufossé, L.; Montañez, J. Biotechnological approaches for the production of natural colorants by Talaromyces/Penicillium: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, L.P.S.; Gomes, D.C.; Cardoso, P.G.; Takahashi, J.A. Recent Findings in Azaphilone Pigments. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufossé, L. Red colourants from filamentous fungi: Are they ready for the food industry? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 69, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tao, H.; Chen, W.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y. Recent advances in the chemistry and biology of azaphilones. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10197–10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapari, S.A.S.; Thrane, U.; Meyer, A.S. Fungal polyketide azaphilone pigments as future natural food colorants? Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavesi, C.; Flon, V.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Pramil, E.; Escargueil, A.; Nasir, A.; Montier, T.; Franck, X.; Prado, S. Azaphilones Pigments from the Fungus Penicillium hirayamae. Colorants 2023, 2, 31-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants2010003
Pavesi C, Flon V, Genta-Jouve G, Pramil E, Escargueil A, Nasir A, Montier T, Franck X, Prado S. Azaphilones Pigments from the Fungus Penicillium hirayamae. Colorants. 2023; 2(1):31-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants2010003
Chicago/Turabian StylePavesi, Coralie, Victor Flon, Grégory Genta-Jouve, Elodie Pramil, Alexandre Escargueil, Adeel Nasir, Tristan Montier, Xavier Franck, and Soizic Prado. 2023. "Azaphilones Pigments from the Fungus Penicillium hirayamae" Colorants 2, no. 1: 31-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants2010003
APA StylePavesi, C., Flon, V., Genta-Jouve, G., Pramil, E., Escargueil, A., Nasir, A., Montier, T., Franck, X., & Prado, S. (2023). Azaphilones Pigments from the Fungus Penicillium hirayamae. Colorants, 2(1), 31-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants2010003










