Abstract
This research examines the possibilities of regulating the structure of cellulose precursor fibers spun from solutions in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide when replacing aqueous coagulation baths with thermodynamically softer alcohol baths at different temperatures. The fibers were spun by the dry jet–wet method in isobutanol coagulation baths with a temperature of 25 °C and 70 °C. The study of the phase state of the solvent–coagulant system using viscometry and point cloud methods revealed the temperature-concentration regions of the single-phase and two-phase states of the system. Using elemental analysis, DSC (differential scanning calorimetry) and XRD (X-ray diffraction) methods, it was shown that just spun fibers, due to the presence of a residual amount of solvent and coagulant in them, regardless of the temperature of the precipitator, have an amorphous structure. Additional washing with water completely washed away the solvent and coagulant as well, however, the structure of cellulose changes slightly, turning into a defective amorphous-crystalline one. A relationship was found between the phase composition, structure, and properties of just spun fibers and precursors washed with water. Thus, the loss of structural ordering of both just spun and washed cellulose fibers leads to a decrease in strength characteristics and an increase in deformation. The thermal behavior of the fibers is determined by their phase composition. Fibers just spun into hot alcohol containing a coagulant and traces of solvent acquire thermal stability up to 330 °C. During the pyrolysis of the obtained precursors up to 1000 °C, the value of the carbon yield doubles. The amorphized structure of the obtained fibers allows us to consider it as a model when analyzing the transformation of the structure of precursors during thermolysis.
1. Introduction
The estimated total annual production capacity of all carbon fibers (CF) in the world in 2014 is 104,600 t (in 2017 136,500 t). Growing demand for CF stimulated an active growth in their production and an annual increase in capacity by 10% until 2020 [1].
The main advantages of carbon fibers are high flexibility, tensile strength and stiffness, adsorption, thermal stability, low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), etc. Due to these properties, CF and composites based on them are widely used in various industrial sectors. For example, in construction, CF are used for external reinforcement of load-bearing structures. In aviation, automotive, and green energy (wind turbines) industries, CF are used to produce low weight parts. In the nuclear industry, CF are not interchangeable in the construction of reactors, as insulation, where the key properties are resistant to high temperatures and pressure and radioactive radiation [2,3,4].
High modulus and cord fibers are used, as a rule, as cellulosic precursors of CF. Such cellulosic fibers are produced on an industrial scale by an environmentally hazardous viscose process. The exception is Hyosung Company (Seoul, South Korea). They use an environmentally friendly NMMO process for obtaining new Lyocell cord fibers (hydrated cellulose fibers classified as Lyocell fibers by the international committee BISFA (Bureau International pour la Standardisation des Fibres Artificielles), Brussels, Belgium) [5]. In this process, N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) is used as a direct solvent of cellulose. The production of Lyocell cord fibers proceeds according to two processes. The traditional process includes the preliminary stage of slurry preparation (cellulose suspension in an aqueous solution of NMMO) and the process of direct interaction of NMMO monohydrate (water content 13.3%) with cellulose under conditions of heating and intensive mixing [6,7]. It should be noted that three crystalline hydrates of NMMO have been identified and their dissolving ability increases with decreasing water content in them [8]. The second process in many respects intersects with the original “solid-phase” method [9,10], in which a solvent with a water content of 13.3% or less is used, which increases significantly the concentration of polymer in the solution, up to 45%. Orcel® fibers obtained through solid-phase presolutions (“solid-phase” method), characterized by high crystallinity and orientation, which provide them with high mechanical properties (strength and Young’s modulus) [11].
The main properties that carbon fibers obtained from cellulose precursors must have in order to create general-purpose structural materials are high strength and stiffness, a controlled coefficient of thermal expansion and a high thermal conductivity. Existing cellulose-based CF are produced only with viscose precursors. The existing new NMMO process, alternatively to viscose, is applied for textile and cord fiber production. The work on the creation of CF based on Lyocell precursors is mainly at the research stage. In this regard, it is extremely important to analyze the state and level of data known from the literature on the structural features of Lyocell precursors, their properties and thermolysis conditions.
The structure of potential precursor fibers is defined already at the stage of obtaining solutions and is further determined by the conditions of their formation [12]. Thus, a change in the nature of the coagulation bath affects not only the structure of the formed material, but also the morphology of the obtained samples [13,14]. For cellulose solutions in NMMO, such transformations are described in detail for coagulation into aqueous solutions of NMMO [15,16,17] and alcohols [18,19,20]. Along with a change in the chemical composition of the baths, their temperature was also varied in [18,21], which made it possible to change the structure of the spun fibers. It is important to note that if the formed film (fiber) after coagulation into alcohol passes through a second bath with a different liquid, its structure and properties change [21,22].
When producing CF, cellulose precursors are subjected to heat treatment up to 1500 or 2400 °C (higher temperatures make it possible to improve the special properties of CF) [23]. To increase the values of the carbon yield and achieve good mechanical characteristics of the obtained CF, as in the case of viscose precursors, it is proposed to impregnate Lyocell fibers with pyrolysis catalysts and flame retardants [24]. Traditional impregnations are ammonium phosphates, zinc and calcium chlorides, Lewis acids, etc. [25]. Silicon-based compounds became an alternative to these impregnations [26,27,28], interest to which arose already in the mid-70s. Thus, in [29,30], the importance of using silicon-containing compounds in the process of obtaining CF from cellulose precursors was noted, which made it possible to obtain graphitized fibers with a mechanical strength of more than 1 GPa.
An important parameter of the CF is the coefficient of thermal expansion. The values of CTE depend not only on the type of precursor, but also on the method and conditions of its thermal processing into the CF. For precursors obtained in the absence of orientation during thermolysis, the maximum CTE values are realized in the direction of the fiber axis and the minimum in the transverse direction. The anisotropic structure realized when the samples are drawn during thermolysis leads to a change in these values to the opposite [31]. The achievement of high mechanical characteristics of CF is associated with solving a number of issues: the choice of a precursor [32], the conditions of spinning, structural and morphological properties, and ending with the modes of thermal processing in CF [33]. Though the effective interconnection of these problems has not yet been identified, numerous results of studies of the mechanical characteristics of CF presented in the literature can be divided into two groups. The first group includes papers with unsatisfactory strength characteristics of CF [24], and the second presents conflicting results. In one of the first papers devoted to the production of CF from Lyocell fibers, strength values equal to 1 GPa, and elastic modulus values of 100 GPa were achieved [34]. Such high mechanical values are ambiguously correlated with X-ray diffraction data: in diffractograms, the angular position of the 002 reflection maximum does not reach 25° (2θ), and its intensity is very low. In [35], the mechanical properties of CF obtained from viscose and Lyocell precursors are compared after impregnation with the same flame retardants and carbonization in the same temperature–time regime. The strength of Lyocell fibers is almost two times higher compared to viscose precursors, while the crystallinity for Lyocell is 40% higher than that of viscose fibers. After heat treatment of these precursors under the same conditions, the difference between the strength values of CF is leveled [35]. Therefore, we can conclude that the strength and high crystallinity of the precursors are not limiting structural parameters that determine the high strength properties of CF.
The above data set one of the most actual and most important tasks in the problem of creating high-strength CF based on Lyocell fiber—searching for the ways of directional regulation of the structure of cellulose fiber precursors. In this regard, the aim of this research is to study the structural and morphological features of Lyocell precursors obtained from solutions in NMMO. When replacing water precipitation baths with more thermodynamically soft alcohol precipitation baths at different temperatures, were studied their mechanical and thermal properties and the relationship between the structure of the obtained precursors and properties were established.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
For fiber spinning, 16% cellulose solutions in NMMO were prepared based on the solid-state activation technique [36]. Sulfate pulp (Baikal Pulp and Paper Mill, Baykalsk, Russia) was preliminarily crushed and sieved in order to isolate a powder fraction with a particle size of up to 200 microns.
The degree of polymerization of cellulose was 600, the moisture content was ~8%, and the mass content of α-cellulose in the dry residue was ~94%. N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (Demochem, Shanghai, China) was used as a solvent. The water content in NMMO was ~7% (Tm ~ 120 °C). Propyl gallate (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) was added to the system to suppress destruction processes in an amount of 0.5%. Just spun fibers were coagulated in distilled water or isobutyl alcohol (IBA; Component-Reagent, Moscow, Russia).
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Rheological Measurements
Temperature viscosity scans for the NMMO–IBA system were carried out on a rotational rheometer Kinexus-pro+ (Malvern Panalytic Ltd, Malvern, UK). For measurements, an operating unit plane–plane with a diameter of 50 mm was used. Tests were conducted under the steady-state flow in the regime of fixed shear rate (1 s−1). The testing temperature was varied within 10–140 °C [21].
2.2.2. Fibers Spinning
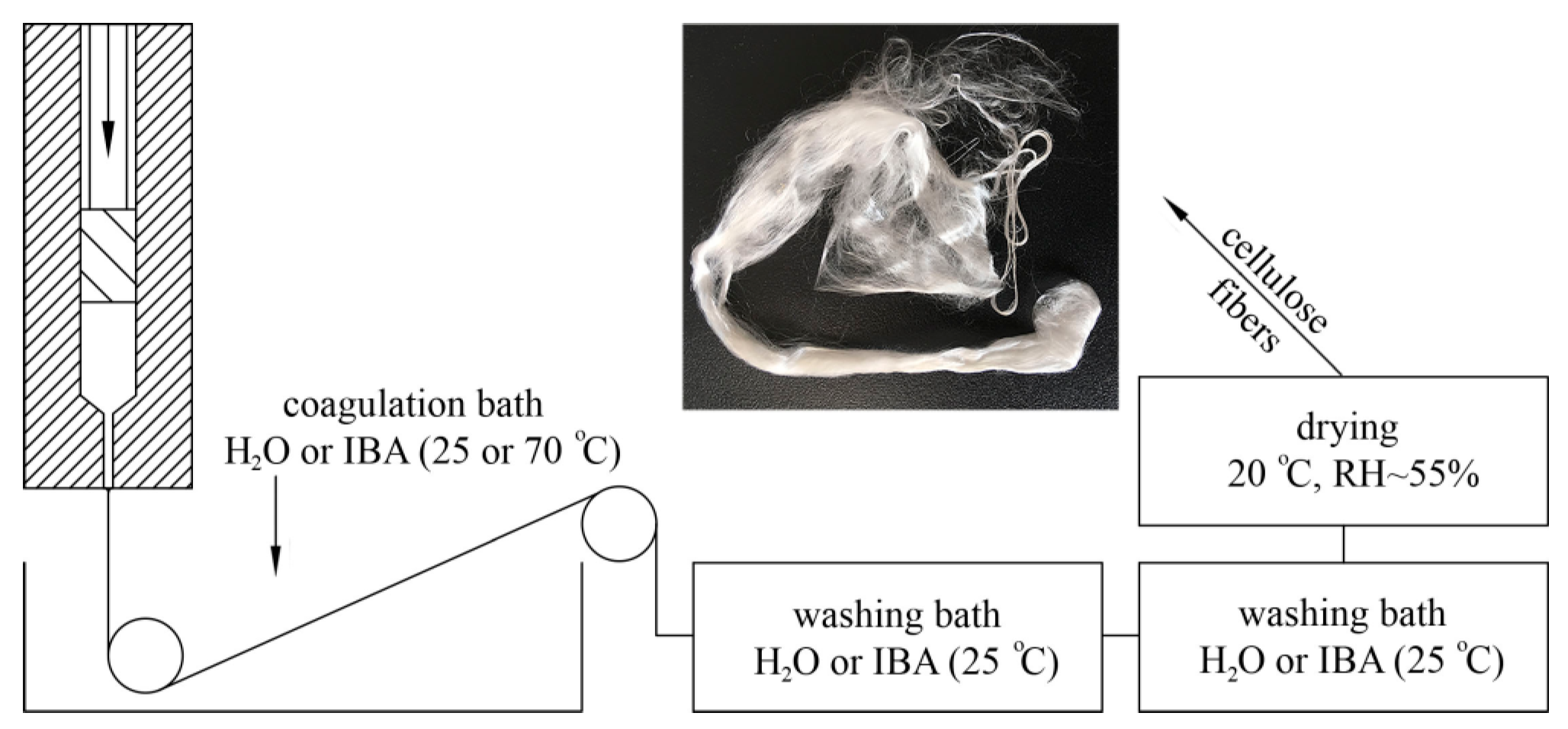
The fibers were spun on a capillary viscometer Rheoscope 1000 (CEAST, Torino, Italy) using a spinneret with channel geometry d = 0.5 mm, l/d = 10 at T = 120 °C (Figure 1). The spinning fibers, passing through a precipitation bath with water (T = 25 °C) or alcohol with various temperatures, were wound on a drum. The fiber spinning, both in room temperature alcohol and heated to 70 °C, was stable. Then, the fibers spun into alcohol were placed in IBA at room temperature (1 L volume). After 24 h, the samples were transferred to a bath with new alcohol or water for an equal time interval (the procedure was repeated twice). At the last stage, the fibers were dried in a free state under room conditions to constant weight.

Figure 1.
A scheme of the dry jet–wet fiber spinning process for cellulose– N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) solution.
2.2.3. Thermal Characterization
The phase composition of the alcohol–solvent system was qualitatively evaluated using the cloud point method during successive heating and cooling with fixing the temperatures of the appearance of the crystalline phase [37].
The thermal behavior of the fibers was investigated using a TGA/DSC1 thermal analysis instrument (Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland). The measurements were performed in alumina crucibles with a volume of 150 μL in the temperature range from 30 to 1000 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min. The inert gas flow rate (argon) was 100 cm3/min [23].
Differential scanning calorimetry data were obtained on a DSC 823e instrument (Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland) in the temperature range 25–350 °C (heating rate 10 °C/min) in aluminum crucibles with a volume of 40 μL and in an argon atmosphere (gas flow rate 70 mL/min) [23].
2.2.4. Fibers’ Carbonization
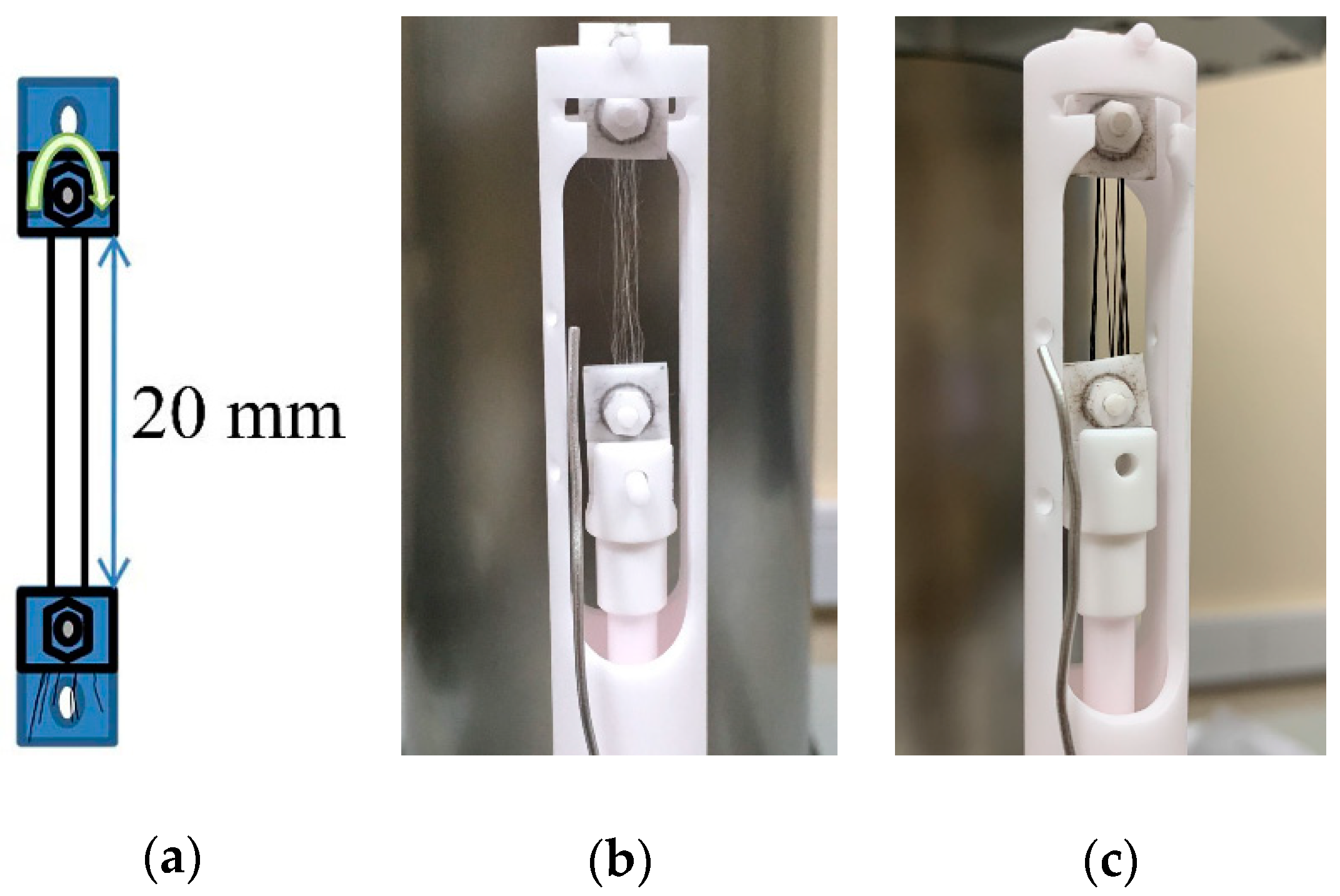
Fibers’ carbonization was carried out on a TMA 402 F1 Hyperion instrument (Netzsch, Selb, Germany). The precursor sample thread to fold in two was fixed in standard corundum clamps (~100 monofilaments; Figure 2). To prepare the tensioned samples, an alignment clamping device was used to fix the distance between corundum clamps of 20 mm. The sample was placed in a holder for tensile analysis and a constant tension force of 50 mN was set. The total inert gas (argon) flow rate was 70 mL/min when heated up to 300 °C inclusive and 100 mL/min at temperatures above 300 °C. The fiber was linearly heated up to 300 °C at a rate of 1.5 °C/min, followed by isothermal annealing for 2 h, then heated at a speed of 20 °C/min to 1200 °C.

Figure 2.
The pattern of fixing the sample in the clamps (a) and photographs of fibers fixed in the clamps (before (b) and after carbonization (c)).
2.2.5. Structural and Morphological Characterization
The structures of the precursors and the CF were studied by X-ray diffractometry on a Rigaku Rotaflex D/MAX-RC (Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) setup equipped with a rotating copper anode (the operating mode of the X-ray source was 50 kV, 100 mA, the characteristic radiation wavelength was λ = 0.1542 nm, a horizontal goniometer, and a scintillation detector). X-ray survey was carried out in the “reflection” and “transmission” geometry according to the Bragg–Brentano scheme in the continuous θ–2θ scanning mode in the angular range of 3–45° and the scanning step was 0.04° at room temperature. To obtain diffractograms of the fibers, parallel bundles of their fragments (~100 pieces) were used in the vertical or horizontal directions relative to the axis of the goniometer [21,34].
The degree of crystallinity was calculated by Ruland’s method [38]. The diffraction patterns were smoothed according to the Savitzky–Golay method at 15 points [39], the background line was approximated by a linear function and subtracted from the smoothed diffraction patterns. Deconvolution of the diffraction patterns obtained in this way was carried out in the MDI Jade 6.5 program (www.materialsdata.com) using the symmetric Pearson VII functions.
The degree of crystallinity was calculated by the formula:
where Aam is the total area corresponding to the amorphous component of the samples, Acr is the total area of peaks corresponding to the crystalline component of the samples. The amorphous component corresponded to wide diffuse maxima with angular positions of 16 and 26 degrees on a 2θ scale.
The morphology of the surface and cross-sectional cleavages of dried cellulose fibers was studied by low-voltage scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using a FEI Scios microscope (Hillsboro, OR, USA) at an accelerating voltage of less than 1 kV in the secondary electron mode. To obtain SEM microphotographs of cross-sections, cellulose precursors were preliminarily cooled in liquid nitrogen and then using a simple mechanical action on the fibers with a scalpel, cleavages were obtained [40].
Raman scattering was measured on a LabRAM HR Evolution Raman spectrometer (Horiba Scientific, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with 532 nm laser excitation at room temperature. Raman spectra were obtained in the continuous scanning mode. The focusing conditions of the exciting radiation were selected individually for each sample [41].
2.2.6. Mechanical Testing
The effect of type and temperature of coagulation bath on the mechanical properties of cellulose fibers, such as the tensile strength, elongation at break, and modulus, were determined according to the Russian standard GOST 10213.2-2002, 26171-2001, 10213.0-2002, 10213.4-2002. The mechanical properties of the fibers were evaluated on a universal machine for stretching Instron 1122 (Instron, Norwood, MA, USA), equipped with pneumatic clamps. The diameter of the fibers was measured using a Biomed-6PO optical microscope (Biomed, Moscow, Russia). A loading rate of 10 mm/min was used for all samples and a working length of 10 mm [42].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polarization Microscopy and Rheology
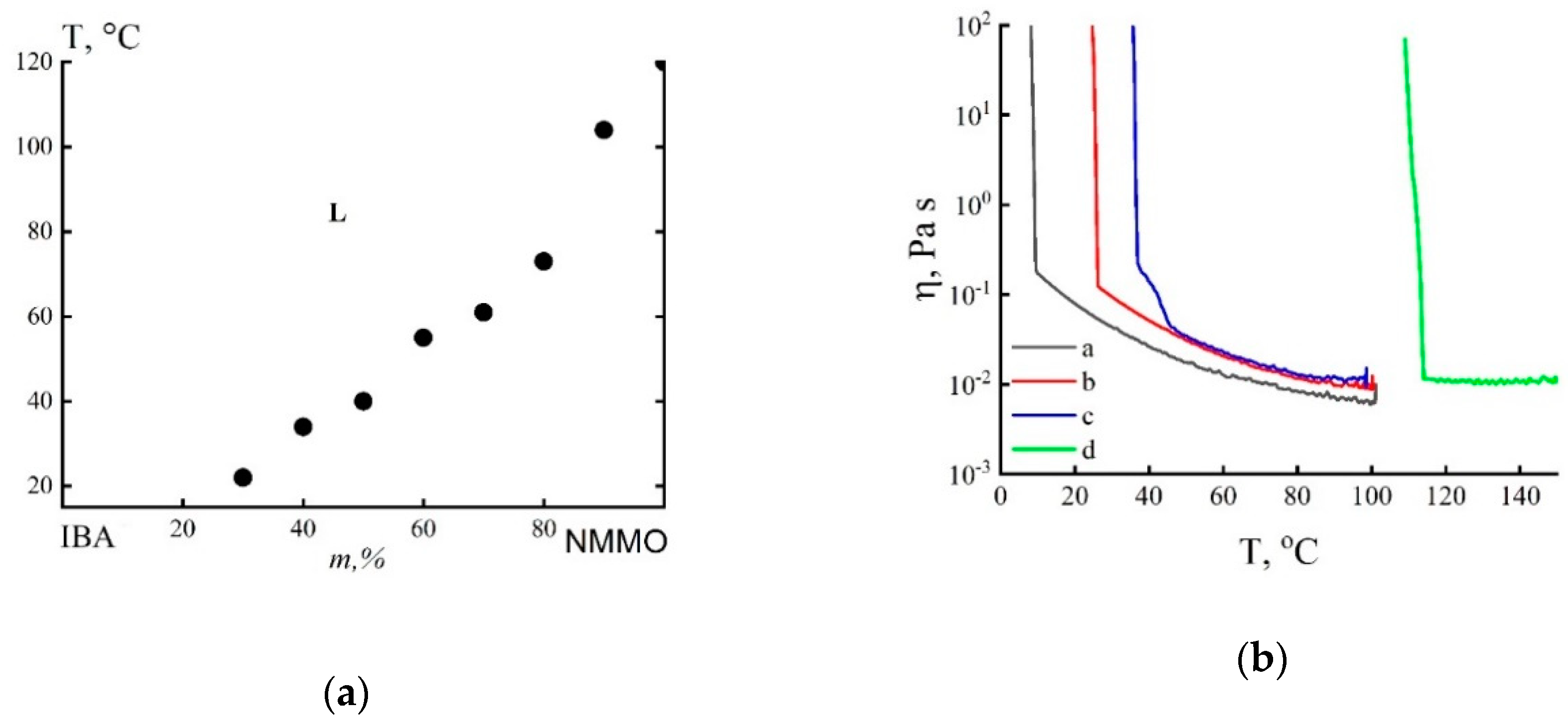
Using the methods of polarization microscopy and visual observation of the turbidity of the system, the phase state diagram of the IBA–high melting NMMO system was constructed, shown in Figure 3a.

Figure 3.
State diagram of the NMMO–isobutyl alcohol (IBA) system (a) and temperature dependences of viscosity (b) for the NMMO–IBA system with the ratio of components: 70/30 (a), 90/10 (b), 95/5 (c) and 100% NMMO (d).
Above the “liquidus” line, the system is in a liquid state (L); below it, crystallization of NMMO occurs, with the formation of a two-phase system, where crystals of NMMO or its adduct with IBA can be present in the liquid phase. The results correlate with the data described in [21,37], where NMMO monohydrate (Tm = ~78 °C) was used as a solvent. The only difference is that in IBA at 20 °C 30% of NMMO and 60% of monohydrate are dissolved, which is probably due to the different water content in the samples of various crystalline hydrates of NMMO [8,21,37].
Figure 3b shows the temperature dependences of viscosity for the NMMO–IBA system with different component ratios. As can be seen from Figure 3b, the temperature dependences of viscosity are also the same as the system based on alcohol and NMMO monohydrate [21]. The nature of the dependences changes slightly, the crystallization rate increases. NMMO crystallizes immediately after passing the melting point. When cooling mixed systems from high temperatures, where the systems are in a single-phase state, in contrast to systems with NMMO monohydrate, the viscosity immediately begins to increase. It is associated with both temperature changes in viscosity and nucleation of a higher melting crystalline hydrate. Reaching a certain critical temperature, a sharp jump in viscosity occurs, i.e., the systems stop flowing and become crystalline. Due to nontightness of the working unit during rheological tests, i.e., the phase composition of the system during the experiment is not constant; certain transition points cannot be considered as points of equilibrium phase transitions. However, the obtained results undoubtedly testify to the general nature of phase transformations [21].
3.2. Structure and Morphology of the Solvent and Precursors
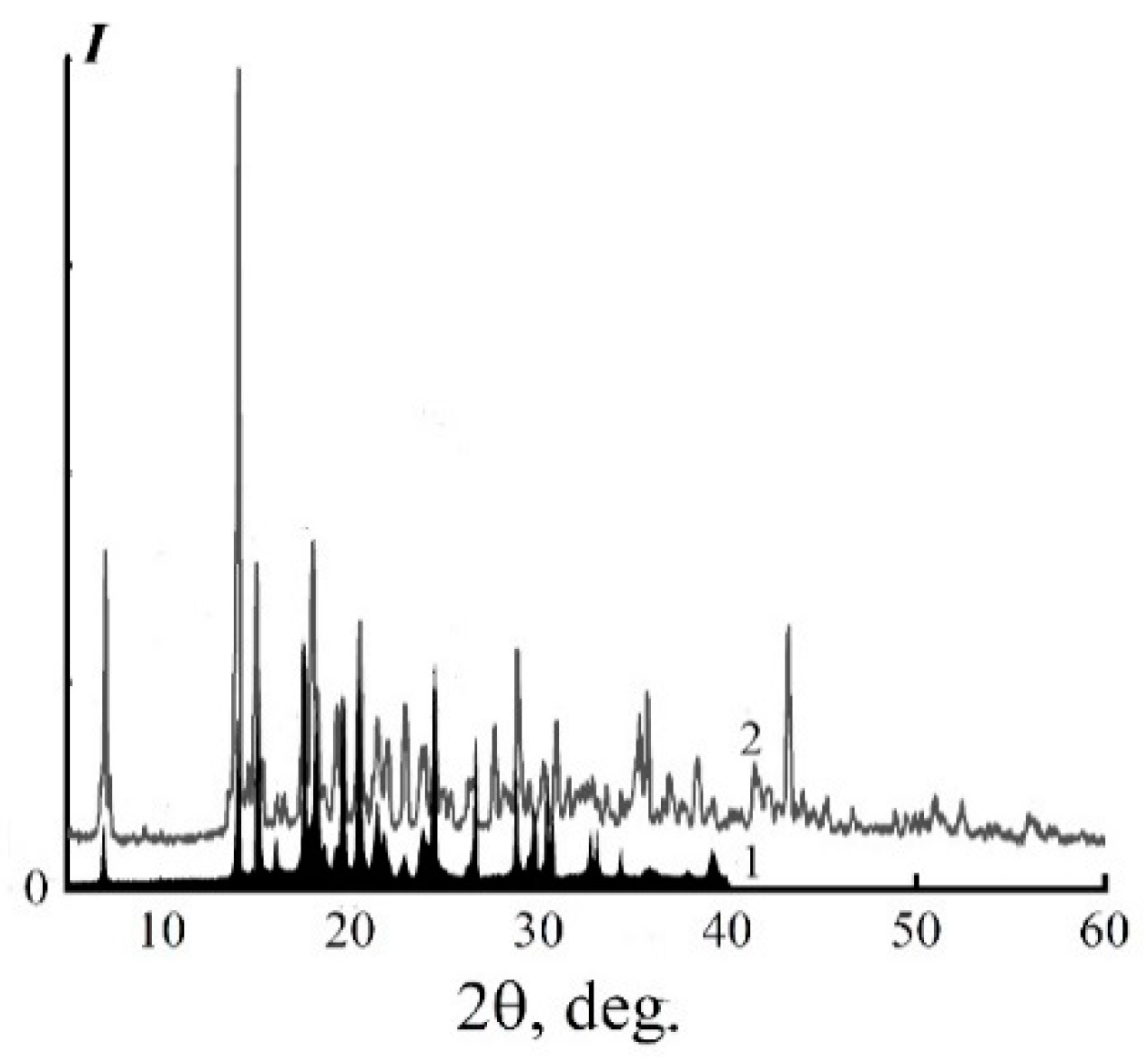
The formation of the crystalline phase was fixed using optical and X-ray diffraction methods (Figure 4). A mixed system (80% NMMO–20% IBA) in the field of crossed polaroids at room temperature is anisotropic.

Figure 4.
X-ray diffraction patterns of NMMO (1) and systems of 80% NMMO–20% IBA (2).
Numerous narrow peaks characteristic of crystalline compounds are observed in the obtained diffraction pattern. The angular position of these reflections, as can be seen in Figure 4 (Curve 1), differs from 2θ for NMMO (Curve 2) [43]. This indicates the formation by the molecules of IBA with NMMO of the additive compound, crystallosolvates [37].
The results of rheological, optical, and X-ray diffraction studies of the NMMO–IBA system were used as the basis for the formation of cellulose solutions into isobutanol precipitation baths with various temperatures.
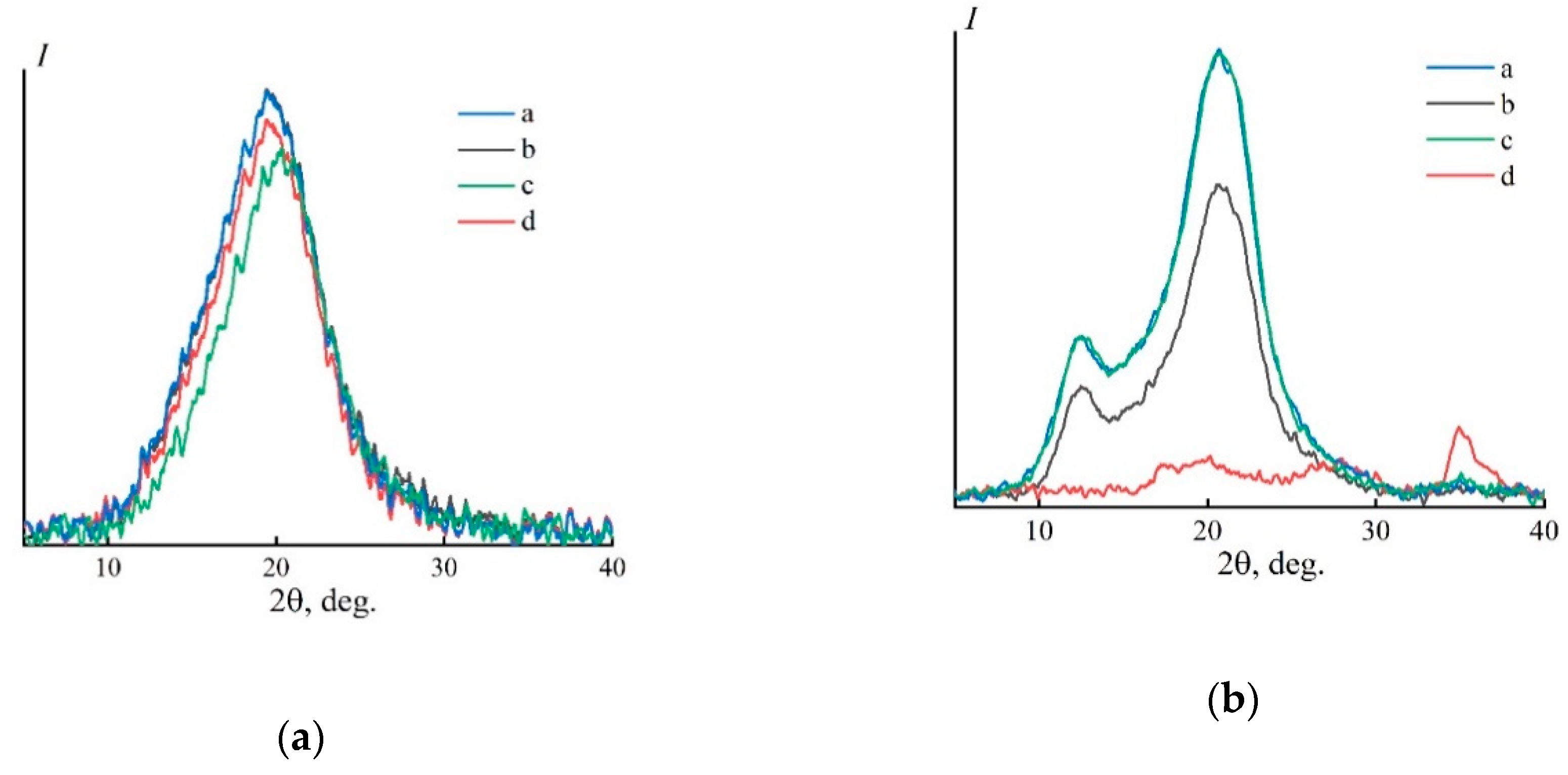
The fibers were spun using the dry jet–wet method in isobutanol precipitation baths at 25 °C and 70 °C. The diffractograms of the fibers formed into a “cold” IBA are shown in Figure 5a.

Figure 5.
Equatorial (a,c) and meridional (b,d) diffraction patterns for cellulose fibers obtained through isobutanol baths (25 °C) and dried under room conditions (a) and equatorial (a,c) and meridional (b,d) diffraction patterns for cellulose fibers obtained through isobutanol baths (25 °C), washed in water, and dried (b). Geometry of scanning—“reflection” (a,b) and “transmission” (c,d).
On the equatorial diffraction pattern recorded in transmission geometry, one wide reflection is observed in the region of 2θ 10–27°. Such a curve almost completely coincides with the diffraction pattern of cellulose solutions in NMMO [44]. The mass transfer processes upon contact of a thermodynamically mild alcohol precipitant with NMMO at room temperature are so slow that a solvent remains in the freshly just obtained fibers [45], which slows down the processes of traditional structural transformations.
Accordingly, an amorphous structure of the sample is formed, similar to the structure of the solution. To remove residual amounts of NMMO and IBA completely, the fiber was subjected to additional washing with water and subsequent drying. The diffractograms of the washed fibers are shown in Figure 5b. Two reflections appear in the equatorial diffractogram in the range 2θ ~ 12.3° and ~ 20.5°, which are specific to polymorph II [42,46]. The large half-width and poor resolution of the reflections indicate the formed imperfect layer order in the fibers and the presence of a considerable fraction of the amorphous phase.
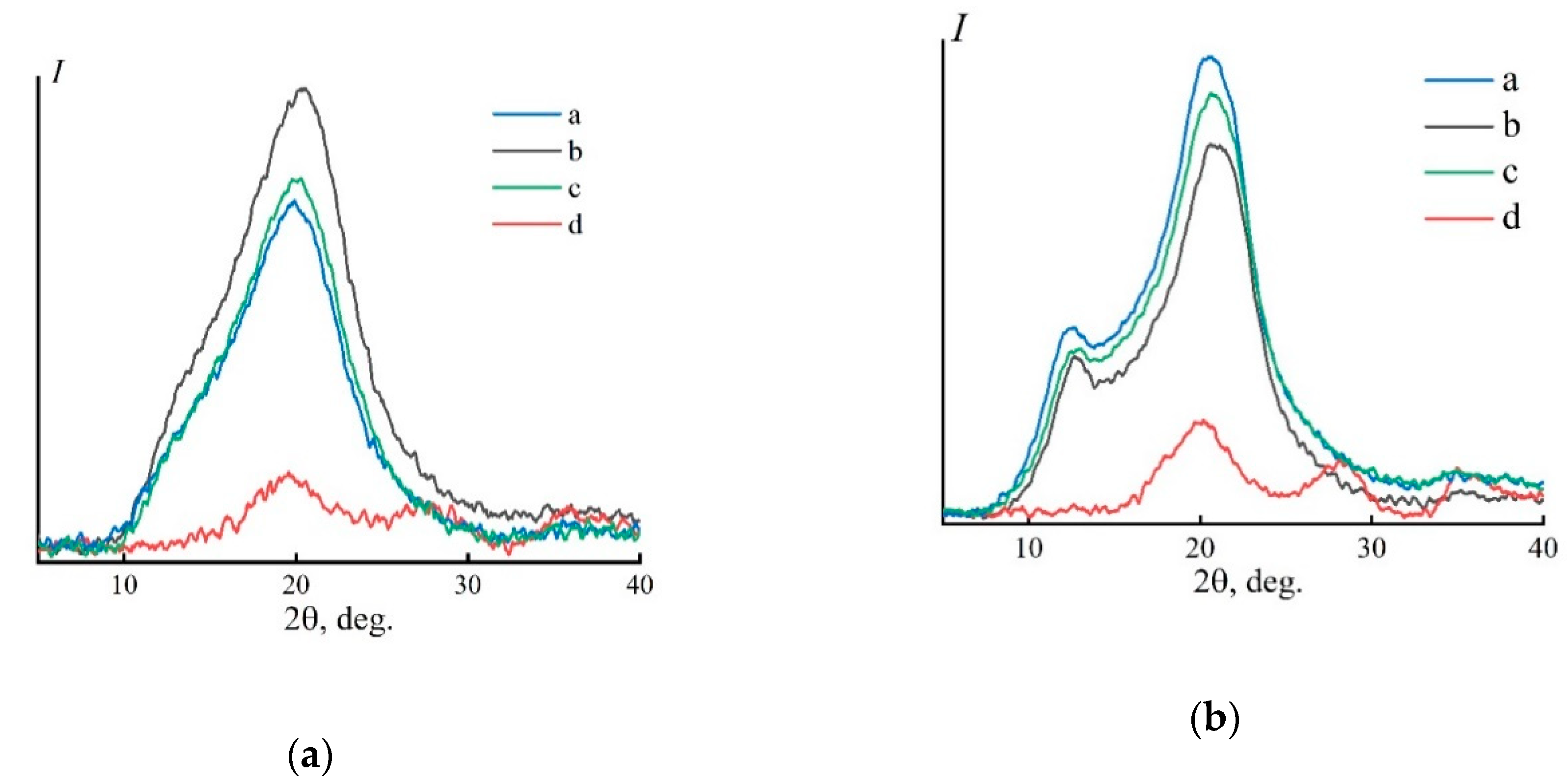
Increasing the temperature of the precipitant up to 70 °C should increase the mass transfer processes and contribute to the formation of a different structure (Figure 6a).

Figure 6.
Equatorial (a,c) and meridional (b,d) diffraction patterns for cellulose fibers obtained through isobutanol baths (70 °C) and dried (a) and equatorial (a,c) and meridional (b,d) diffraction patterns for cellulose fibers obtained through isobutanol baths (70 °C), washed in water, and dried (b). Geometry of scanning—“reflection” (a,b) and “transmission” (c,d).
In contrast to the equatorial diffraction patterns obtained during the coagulation of the fibers in IBA (25 °C), when the fibers are precipitated in hot alcohol, the appearance of the wide amorphous reflex of ~20° changes on the left branch a shoulder appears in the region 2θ ~ 12.5°. The meridional diffraction pattern also indicates the appearance of a certain ordering along the fiber axis. Therefore, an increase in the rate of interdiffusion upon contact of the solvent with a hot precipitation bath under conditions of orientational drawing leads to the appearance of some interlayer periodicity in the sample (Plane 101) [47].
The diffraction patterns of the fibers obtained by precipitation in isobutanol baths (70 °C), which are then washed in water and dried, are shown in Figure 6b. The nature of the diffraction patterns of the washed and dried fibers in water is almost the same as of the diffraction patterns obtained for fibers from IBA (25 °C). It is important to note that some ordering of cellulose revealed when coagulating cellulose fibers in hot alcohol, does not accelerate the processes of structural transformations at the washing stage, but significantly slows them down. The ordering contributes to an even larger fraction of the amorphous phase in the sample.
Based on the obtained diffraction patterns, for fibers spun into water and IBA at 25 and 70 °C, then washed in water and dried, the degree of crystallinity (CI) was calculated by Ruland’s method, shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The crystallinity index of the fibers formed into water and IBA at 25 °C and 70 °C, then washed in water and dried.
Replacing an aqueous precipitation bath with an alcohol bath leads to a decrease in the crystallinity index. A further transition to hot alcohol baths leads to a further decrease in ordering, by almost 20%, compared to samples spun in water.
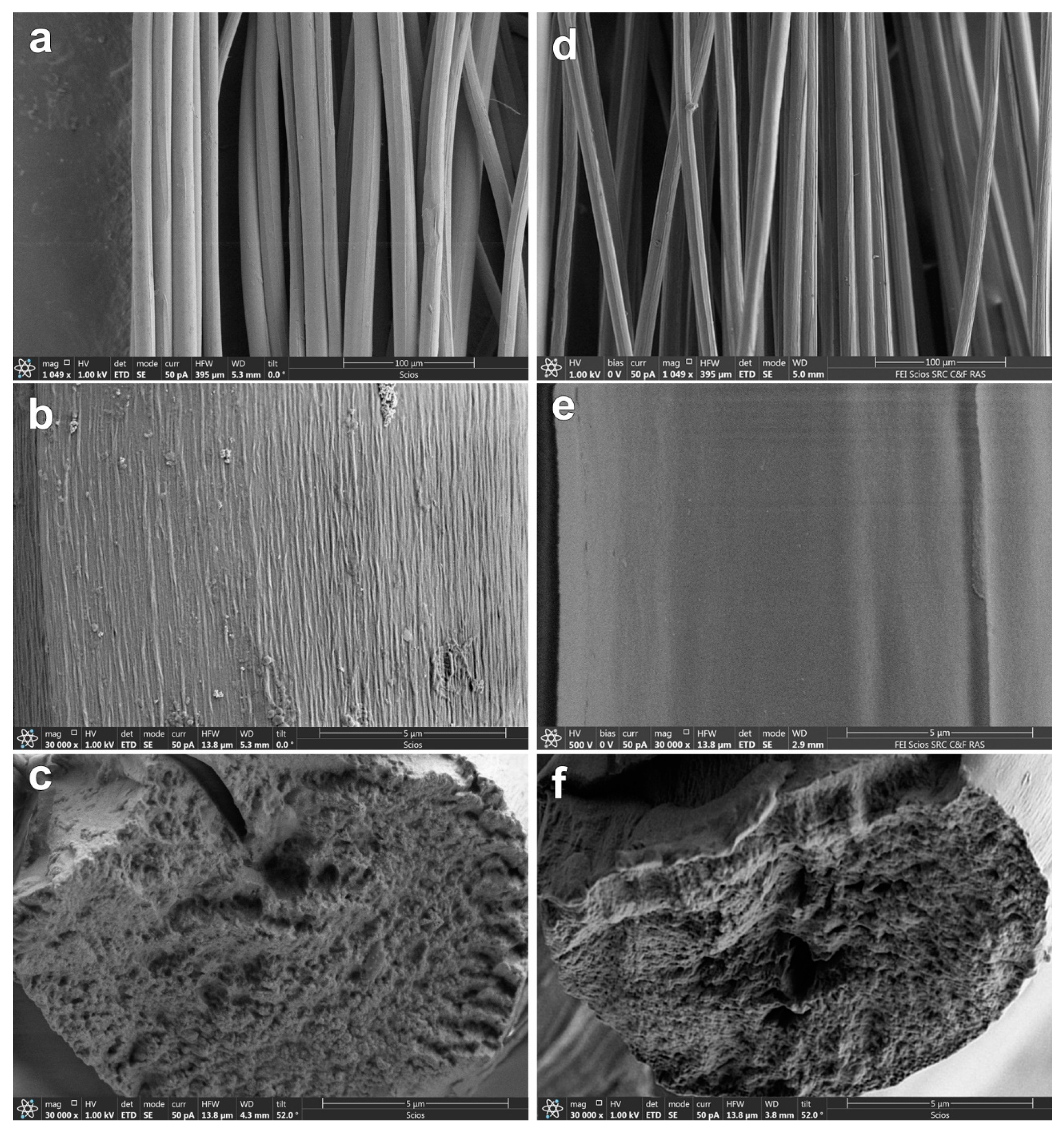
Microphotographs of the surface and transverse cleavage of fibers coagulated in alcohol at various temperatures and washed with water and dried are presented in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
SEM micrographs of cellulose fibers after precipitation into isobutanol T = 25 °C (a–c) and T = 70 °C (d–f) and washing in water: cross-section (c,f) and surface (a,b,d,e).
Lyocell fibers, unlike viscose fibers, have a cross-sectional shape close to a circle [48]. When precipitated into alcohol, the cross-sectional surface of the obtained fibers has a similar shape, with a furrowed texture on the surface of the fiber. This feature, most likely, is associated with uneven contraction of the fiber, in which vacuoles and numerous pores were formed during the deposition process [18,19,20,21]. If deposition in IBA (25 °C) is small, but frequent furrows are formed, then during hot deposition, the size of irregularities increases with a decrease in their number. The average fiber diameter is 14–20 microns.
3.3. Mechanical Properties
Structural and morphological features of the formed cellulose precursors predetermine their mechanical properties (Table 2).

Table 2.
Mechanical properties of fibers obtained through various precipitation baths.
Thus, fibers spun into water have the highest crystallinity and, accordingly, have the highest strength and stiffness; elongation for them does not exceed 11%. In the case of precipitation into alcohol (25 °C) and almost complete amorphization of the sample, the values of strength and elastic modulus sharply decrease, while the relative elongation doubles [20,22]. After washing the fibers spun in cold alcohol and amorphization of the sample, the values of strength and modulus increased. Though these values were lower the values of the fibers spun in water. Strength is more than 50% and elongation is 12% lower. Fibers coagulated in hot alcohol and washed further with water have the most defective structure. The strength and modulus values in such fibers fall almost twice, and the deformation properties remain at the level of fibers obtained in IBA (25 °C).
3.4. Thermal Behavior
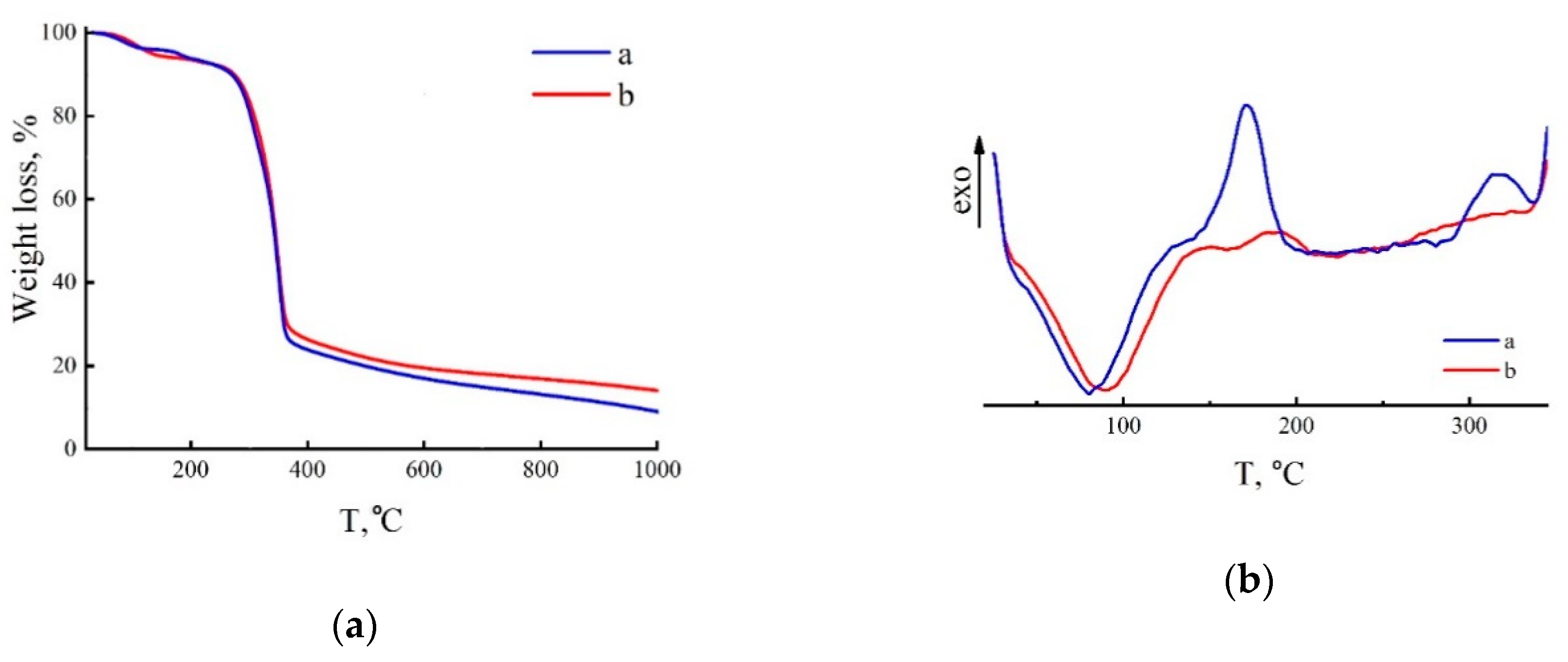
In order to identify the effect of structural disordering of the obtained cellulose precursors on the features of their thermal behavior, thermal studies were carried out using the TGA (Figure 8a and Figure 9a) and DSC (Figure 8b and Figure 9b).

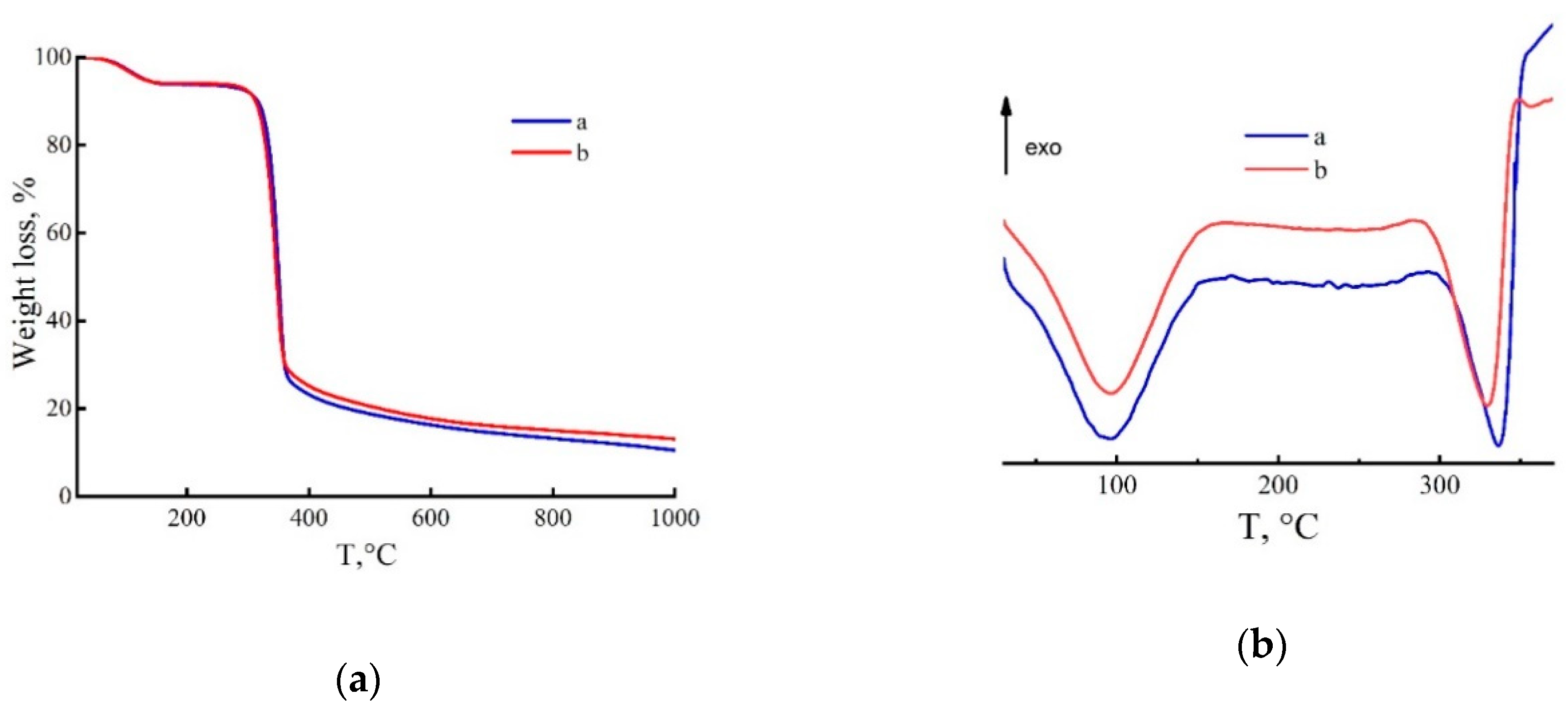
Figure 8.
TGA (a) and DSC (b) curves of fibers coagulated in IBA at 25 °C (a) and 70 °C (b), washing in alcohol and drying.

Figure 9.
TGA curves (a) and thermograms (b) of cellulose fibers spun into IBA at 25 °C (a) and 70 °C (b), water washing and drying.
When the fibers are spun in the IBA (25 °C), the TGA curve has an atypical course for cellulose precursors. Namely, it is possible to distinguish four areas of sample weight reduction on it. In the first section (up to 105 °C), the mass loss is 3.6%, then in the range of 160–250 °C the mass is reduced to 91.6%. The pyrolysis of cellulose to 365 °C is accompanied by a drop in residue to 26.6%. Heat treatment up to 1000 °C leads to a carbon yield of 7.7%. When using IBA with a temperature of 70 °C, the TGA curve takes the form traditional for cellulose fibers [49], and the carbon yield when heated to 1000 °C increases to 13.4%. The correlation of TGA curves with DSC thermograms (Figure 8b) allows us to understand more deeply what happens to the samples during heat treatment. The first endo effect of the curve in Figure 8b (Curve a; IBA at 25 °C), associated with the loss of water and IBA, is observed from 30 to 130 °C. Upon further heating in the range of 140–210 °C, an exo effect with a high thermal value of 925.7 mJ associated with the residual solvent in the fibers and its destruction, is observed. The exo effect in the region of 290–313 °C of cellulose is caused by the reactions of dehydration and structural rearrangements of cellulose [50,51]. The endo effect traditional for cellulose in the region of 250 °C, caused by cellulose degradation processes, is not observed in the thermogram. A DSC thermogram of fibers spun into hot alcohol has a different character. The first endo peak has the same nature and similar thermal effects in value [52]. The small exo peak of NMMO decomposition is shifted toward higher temperatures. The exothermic processes of dehydration and structural transformations that occur during further heating of the sample are weakly expressed in the thermogram by extended area. Amorphization of the structure of fibers spun into cold alcohol is due to the presence of a solvent and a precipitant. On contact with alcohol, a small amount of solvent in the form of a solvate with IBA remains in the fibers [21]. At the same time, the sample is not only restructured, but also demonstrates great thermal stability. This is a very important aspect that requires further detailed research.
Water washing of the fibers coagulated in alcohol at 25 or 70 °C, and their subsequent drying, fundamentally changes the thermal behavior of the fibers. The exo-effects associated with the presence of an unwashed solvent and precipitant in the samples disappear [52] and only two endo peaks are present, with a maximum at 94 °C and 334 °C (Figure 9b). The first is due to the removal of water, and the second is due to the structural transformations of the actual cellulose [53,54].
In the case of coagulation of fibers in IBA at 25 or 70 °C and their further washing with water and drying, the course of TGA curves is almost the same (Figure 9a). The values of the carbon yield at 1000 °C for the studied samples are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The carbon yield of the fibers formed into various precipitation baths, followed by washing with water, when heated to 1000 °C.
Summing up the revealed features of the structure and thermal behavior of the obtained precursors, the conclusion suggests itself that amorphization leads to an increase in the carbon yield during their carbonization. The seemingly illogical nature of this conclusion nevertheless fits into the emerging concept regarding the nature of the structural ordering of cellulose precursors most favorable for the formation of CF. It consists of structural homogeneity of the system, which makes it possible to approximate the activation energies of the thermolysis reactions of ordered and disordered regions. This can be achieved either by reducing the length of crystalline and amorphous regions or by their high orientation. This is especially important for amorphous sites. The results obtained fit this concept. Amorphization and restructurization of the obtained precursors lead to an increase in the carbon yield, although, due to their low crystallinity, they are characterized by low strength values.
3.5. Structure of the Carbon Fibers
Carbonization of all formed cellulose precursors was carried out under identical conditions up to 1200 °C. The diffraction patterns of the obtained CF are presented in Figure 10a.

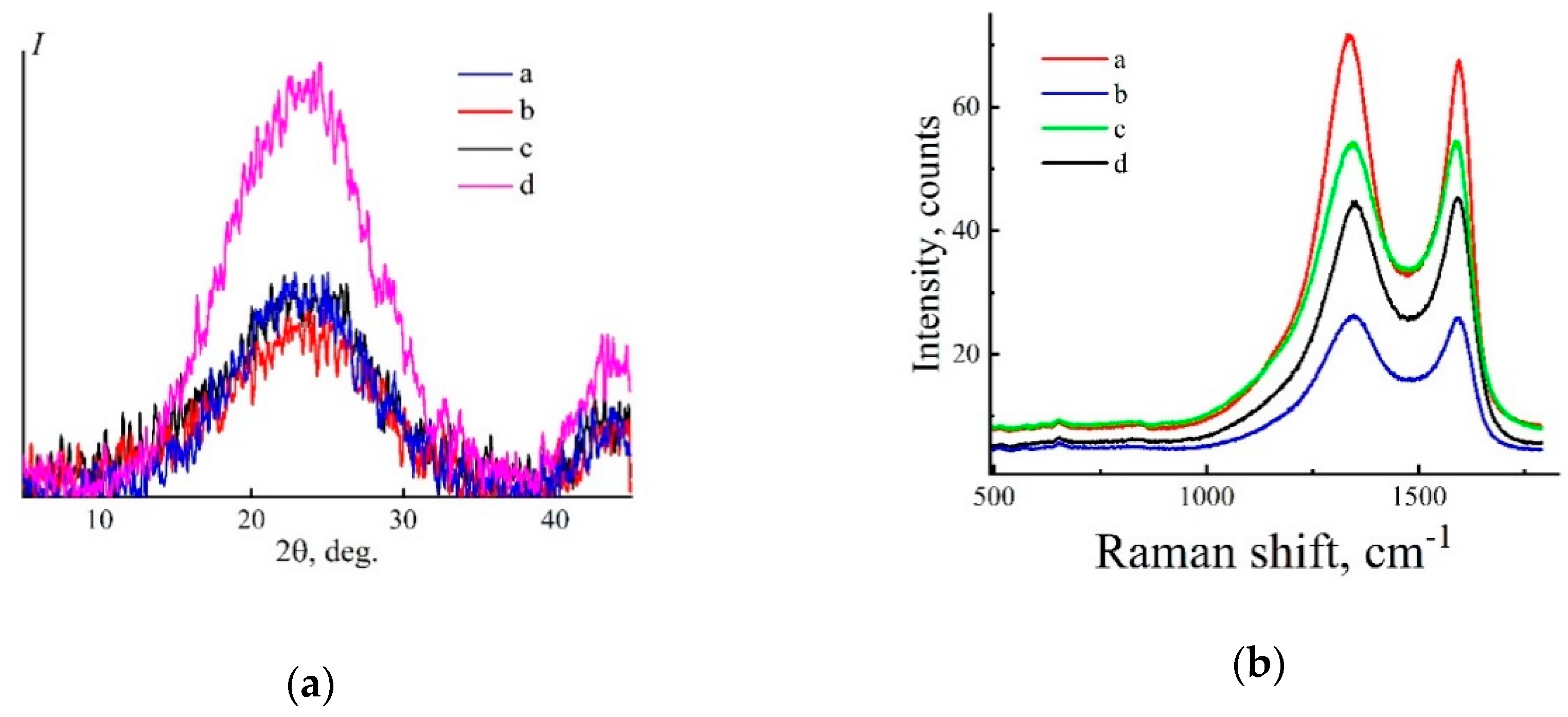
Figure 10.
Equatorial diffraction patterns (a) and Raman spectra (b) of carbon fibers (CF) obtained through water (a), isobutanol baths (25 (b) and 70 °C (c)), washed in water and dried, as well as from an industrial sample of Lyocell fibers (d) after heating up to 1200 °C.
The diffraction patterns of thermolized Lyocell precursors are characterized by the same angular positions of wide reflections in the range of 2θ ~ 23.5° and 43°, corresponding to the planes 002 and 100. Such an angular position of the reflections [55] indicates the amorphous nature of carbon.
The formed carbon structure on the Raman spectra is displayed by characteristic D and G peaks (Figure 10b). In the spectra of each of the four samples, two broad characteristic peaks with positions of ~1350 and 1590 cm−1 are observed; their different intensities are due to the background of the preparation of these samples for shooting. As can be seen from Figure 10b, despite the varying degree of structural ordering of the initial precursors, the spectra obtained do not have significant differences and indicate the nanocrystalline (very close to amorphous) structure (with the crystal size less than 2 nm) of all CF samples [41,56,57]. Apparently, the lack of pretreatment of the precursors, as well as the conditions for their thermolysis, overlap the significance and contribution of the primary structure of the precursors to the properties of CF obtained on their basis. The revealed regularities once again confirm the complexity and multifactorial nature of the problem of creating high-strength CF based on cellulose fibers. It can be solved only by combining the efforts of both the creators of cellulose precursors and the developers of their thermolysis processes.
4. Conclusions
Changes in the composition and temperature of the precipitation bath allow to vary the structure of the resulting fibers. However, precipitation into alcohol without additional washing with water of the samples does not exclude the residual amount of solvent and precipitant in the fibers, which leads to an amorphous structure of the samples. Only subsequent washing with water of the fibers spun into alcohol allows the solvent and IBA to be completely removed from the fibers. Moreover, as shown by X-ray diffraction data, the structural ordering of the samples is restored only partially. The samples have a pronounced amorphized structure, which leads to an increase in the carbon yield during fiber thermolysis, as evidenced by studies of the thermal behavior of the fibers by the TGA method. The CF annealed up to 1200 °C without pretreatment, regardless of the precursor structure, have the same amorphous structure, according to studies performed by X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. Structure is the most important factor in the process of obtaining precursors and processing them into CF. Conditions for their processing are also the quality factor of CF, namely the use of additional chemical reagents, pyrolysis catalysts and flame retardants, and temperature–time regimes.
Author Contributions
I.S.M. and L.K.G. provided the idea for this study, proposed the experiments and wrote the paper; Y.V.G., N.A.A., A.K.B., and I.S.L. analyzed the data; G.L.K., I.S.M., and G.A.S. analyzed the data and reviewed the paper; M.I.V., Y.V.G., and A.K.B. produced the samples; M.I.V. prepared the solutions; I.S.M. spun fibers; G.A.S. performed the determination of thermal properties; N.A.A., I.S.L., T.V.E., and E.D.O. performed the structural experiments; I.S.M. and L.K.G. edited the final paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out within the State Program of TIPS RAS using the equipment of the CCU “Analytical Center for the Problems of Deep Processing of Oil and Petrochemicals” of TIPS RAS.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Holmes, M. Global carbon fibre market remains on upward trend. Reinf. Plast. 2014, 58, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiuddin, M.; Abdel-Sayed, G.; Hearn, N. Effects of Pitch-Based Short Carbon Fibers on the Workability, Unit Weight, and Air Content of Mortar Composite. Fibers 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Gomes, R.; Pina, L.; Pereira, C.; Reichmann, O.; Teti, D.; Correia, N.; Rocha, N. Highly Conductive Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Electronic Box: Out-Of-Autoclave Manufacturing for Space Applications. Fibers 2018, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulis, S.; Konstantopoulos, G.; Koumoulos, E.P.; Charitidis, C.A. Impact of Alternative Stabilization Strategies for the Production of PAN-Based Carbon Fibers with High Performance. Fibers 2020, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.H.; Choi, S.M.; Wang, Y.S.; Kim, S.R.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, T.J.; Han, S.J. Lyocell Multifilament. U.S. Patent 6902804, 25 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kruger, R. Cellulosic filament yarn from the NMMO process. Lenzinger Ber. 1994, 4, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.W.; Kwon, S.Y.; Jeon, O.H.; OH, Y.S.; Jeong, J.C.; Kim, W.C.; Chung, I.; Lee, J.W. Lyocell Filament Fiber and Cellulose Based Tire Cord. Patent WO 2009031868, 8 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Golova, L.K.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Papkov, S.P. Mechanism of dissolution of cellulose in non-aqueous dissolving systems. Rev. Polym. Sci. U.S.S.R. 1986, 28, 1995–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golova, L.K. Processing of cellulose via highly concentrated “solid solutions”. Fibre Chem. 1996, 28, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golova, L.K.; Romanov, V.V.; Lunina, O.B.; Platonov, V.A.; Papkov, S.P.; Khorozova, O.D.; Yakshin, V.V.; Belasheva, T.P.; Sokira, A.N. The Method of Obtaining the Solution for Forming Fibers. Patent RF 1645308, 30 April 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Golova, L.K. New Cellulose Fiber Lyocell. Rus. J. Gen. Chem. 2002, XLVI, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Serkov, A.T. Theory of Man-made Fibre Spinning; Khimiya: Moscow, Russia, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kulichikhin, V.G.; Skvortsov, I.Y.; Mironova, M.I.; Ozerin, A.N.; Kurkin, T.S.; Berkovich, A.K.; Frenkin, E.I.; Malkin, A.Y. From Polyacrylonitrile, its Solutions, and Filaments to Carbon Fibers II. Spinning PAN-Precursors and their Thermal Treatment. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsov, I.Y.; Kalugina, A.D.; Litvinova, E.G.; Malkin, A.Y.; Khotimskiy, V.S.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Fibers spinning from poly(trimethylsilylpropyne) solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.V.; Baksheev, I.P.; Finger, G.G.; Sokolovskii, B.M.; Kop’ev, M.A. State and prospects of development in the manufacture of hydrocellulose fibres based on new technologies. Fibre Chem. 1991, 23, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, I.S.; Golova, L.K.; Kuznetsova, L.K.; Antonov, S.V.; Kotsyuk, A.V.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Influence of Precipitation and Conditioning Baths on the Structure, Morphology, and Properties of Cellulose Films. Fibre Chem. 2016, 48, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.V.; Kruchinin, N.P.; Lunina, O.B.; Milkova, L.P.; Trifonova, N.P.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Effect of precipitation conditions on the properties of yarns obtained from solutions of cellulose in methylmorpholine oxide. Fibre Chem. 1986, 17, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.V.; Sokira, A.N.; Lunina, O.B.; Iovleva, M.M. Morphological features of the structure of fibres prepared from solutions of cellulose in methylmorpholine oxide. Fibre Chem. 1988, 20, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banduryan, S.I.; Iovleva, M.M.; Belousov, Y.Y.; Ivanova, N.A. Structure formation in solutions of cellulose in n-methylmorpholine n-oxide and during its precipitation. Fibre Chem. 1985, 16, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.P.; Weigel, P.; Purz, H.J.; Ganster, J. Structure formation of regenerated cellulose materials from NMMO-solutions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, I.S.; Golova, L.K.; Vinogradov, M.I.; Mironova, M.V.; Levin, I.S.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Shandryuk, G.A.; Arkharova, N.A.; Kulichikhin, V.G. The Role of Isobutanol as a Precipitant of Cellulose Films Formed from N-Methylmorpholine N-Oxide Solutions: Phase State and Structural and Morphological Features. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2019, 61, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.P.; Weigel, P.; Purz, H.J. Formation of lyocell-type fibres with skin-core structure. Lenzinger Ber. 1998, 78, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Chernenko, D.N. Development and Research of the Technological Process for Producing Carbon Fabrics from Hydrated Cellulose Fibers. Ph.D. Thesis, NIIgrafit, Moscow, Russia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, N.; Setty, M.; Blight, S.; Tadros, R.; Ma, Y.; Sixta, H.; Hummel, M. Cellulose-Derived Carbon Fibers Produced via a Continuous Carbonization Process: Investigating Precursor Choice and Carbonization Conditions. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 2517–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanlı, A.G.; Windle, A.H. Carbon fibres from cellulosic precursors: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4236–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olri, P.; Plezantene, E.; Louison, S.; Paye, R. Carbonization of Cellulosic Fibrous Materials in the Presence of an Organosilicon Compound. Patent RF 2256013, 10 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov, M.E.; Trushnikov, A.M.; Yunitskaya, M.L. The Method of Obtaining Carbon Fiber Material. Patent RF 2045472, 9 April 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Trushnikov, A.M.; Kazakov, M.E.; Gridina, Y.F.; Vazheva, L.D.; Borisova, L.K. The Method of Obtaining Carbon Fiber Material. Patent RF 2047674, 10 November 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Konkin, A.A. Carbon and Other Heat-Resistant Fibrous Materials; Khimiya: Moscow, Russia, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Karasev, J.V.; Lazarev, M.N.; Motorin, S.V.; Ozolin, A.A. Method for Continuous Production of Carbon Fiber from Hydrated Cellulose in the form of a Unidirectional Tow. Patent RF 2429316, 20 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pradere, C.; Sauder, C. Transverse and longitudinal coefficient of thermal expansion of carbon fibers at high temperatures (300–2500 K). Carbon 2008, 46, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abroskin, A.A.; Eremyanov, O.G.; Chernenko, D.N.; Chernenko, N.M. The Method of Obtaining Lyocell Hydrate Cellulose Precursor Carbon Fiber Material. Patent RF 2669273, 17 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chernenko, D.N.; Beilina, N.Y.; Chernenko, N.M.; Elizarov, P.G. The Method for Carbonizing Viscose Fibrous Materials in the Process of Producing Carbon Fibers. Patent RF 2520982, 10 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Shao, H.; Hu, X. Lyocell fibers as the precursor of carbon fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Pan, D. A New Cellulose Based Carbon Fiber from a Lyocell Precursor. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Golova, L.K.; Borodina, O.E.; Kuznetsova, L.K.; Lyubova, T.A.; Krylova, T.B. The solid-phase MMO process. Fibre Chem. 2000, 32, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platonov, V.A.; Smolikov, V.V. Physicochemical Foundations of Production of Hydrated Cellulose Fibers by Nontraditional Methods; Papkov, S.P., Baksheeva, I.P., Eds.; VNIIVproekt: Mytishchi, Russia, 1989; p. 166. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orekhov, A.S.; Klechkovskaya, V.V.; Kononova, S.V. Low-voltage scanning electron microscopy of multilayer polymer systems. Crystallogr. Rep. 2017, 62, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Resonant Raman spectroscopy of disordered, amorphous, and diamondlike carbon. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. 2001, 64, 075414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, I.S.; Golova, L.K.; Kuznetsova, L.K.; Mironova, M.V.; Vinogradov, M.I.; Bermeshev, M.V.; Levin, I.S.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Composite Fibers from Cellulose Solutions with Additives of Bis (Trimethylsilyl) Acetylene and Alkoxysilanes: Rheology, Structure and Properties. Fibre Chem. 2019, 51, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golova, L.; Makarov, I.; Kuznetsova, L.; Plotnikova, E.; Kulichikhin, V. Structure—Properties Interrelationships in Multicomponent Solutions Based on Cellulose and Fibers Spun Therefrom. In Book Cellulose: Fundamental Aspects. Book 1; Van De Ven, T.G.M., Ed.; InTech Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 377. [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, I.S. Structure and Properties of Multicomponent Solutions based on Cellulose and Formed from Them Fibers and Films. Ph.D. Thesis, TIPS RAS, Moscow, Russia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Romanov, V.V.; Lunina, O.B.; Milkova, L.P.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Deformation properties of yarns spun from solutions of cellulose in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide and selection of spinning conditions. Fibre Chem. 1989, 21, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.L. Biopolymers from Renewable Resources; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; p. 420. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, T.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, C. Physical, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of modified peanut protein isolate based films incorporating thymol. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Duan, C.; Hu, H.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Stavik, J.; Ni, Y. Regenerated cellulose by the lyocell process, a brief review of the process and properties. Bioresources 2018, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Goldhalm, G. TENCEL® Carbon Precursor. Lenzinger Ber. 2012, 90, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel. 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, H.B.; Nolte, M.W.; Beckham, G.T.; Shanks, B.H.; Broadbelt, L.J. The Alpha–Bet(a) of Glucose Pyrolysis: Computational and Experimental Investigations of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural and Levoglucosan Formation Reveal Implications for Cellulose Pyrolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalt, W.; Manner, J.; Firgo, H. Moulding Materials and Spinning Materials Containing Cellulose. U.S. Patent 5679146A, 14 September 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Hatakeyama, T.; Hatakeyama, H. Studies on Bound Water of Cellulose by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Text. Res. J. 1981, 51, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseneau, D.F. Competitive Reactions in the Thermal Decomposition of Cellulose. Can. J. Chem. 1971, 49, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Yun, Y.S.; Jin, H.J. Carbon nanofibers prepared by the carbonization of self-assembled cellulose nanocrystals. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. 2000, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dychalska, A.; Popielarski, P.; Franków, W.; Fabisiak, K.; Paprocki, K.; Szybowicz, M. Study of CVD diamond layers with amorphous carbon admixture by Raman scattering spectroscopy. Mater. Sci. 2015, 33, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).