In-Situ Vacuum Assisted Gas Stripping Recovery System for Ethanol Removal from a Column Bioreactor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
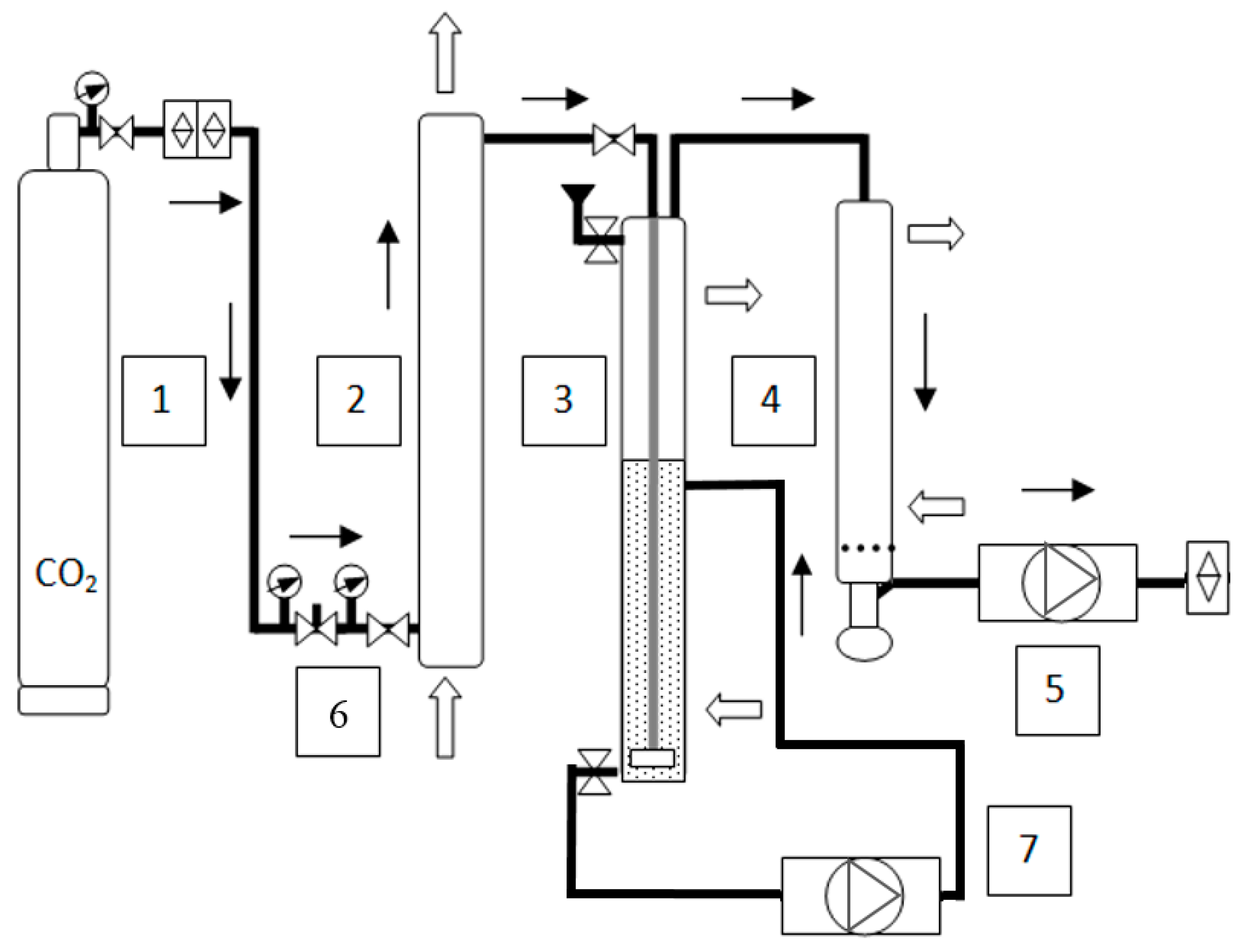
2.1. Column Bioreactor and In-Situ Gas Striping Vacuum Assisted Recovery System
2.2. Sugar Beet Pulp, Enzymes and Microorganisms
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
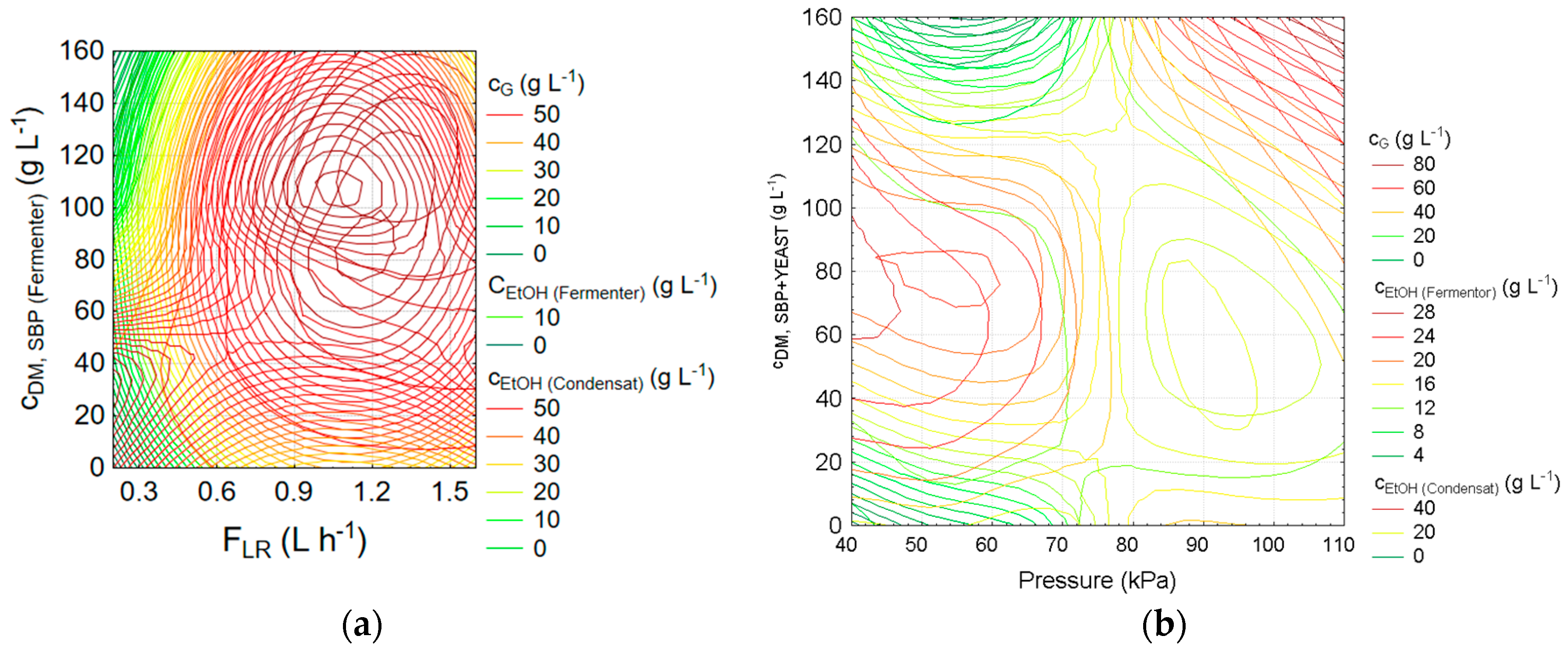
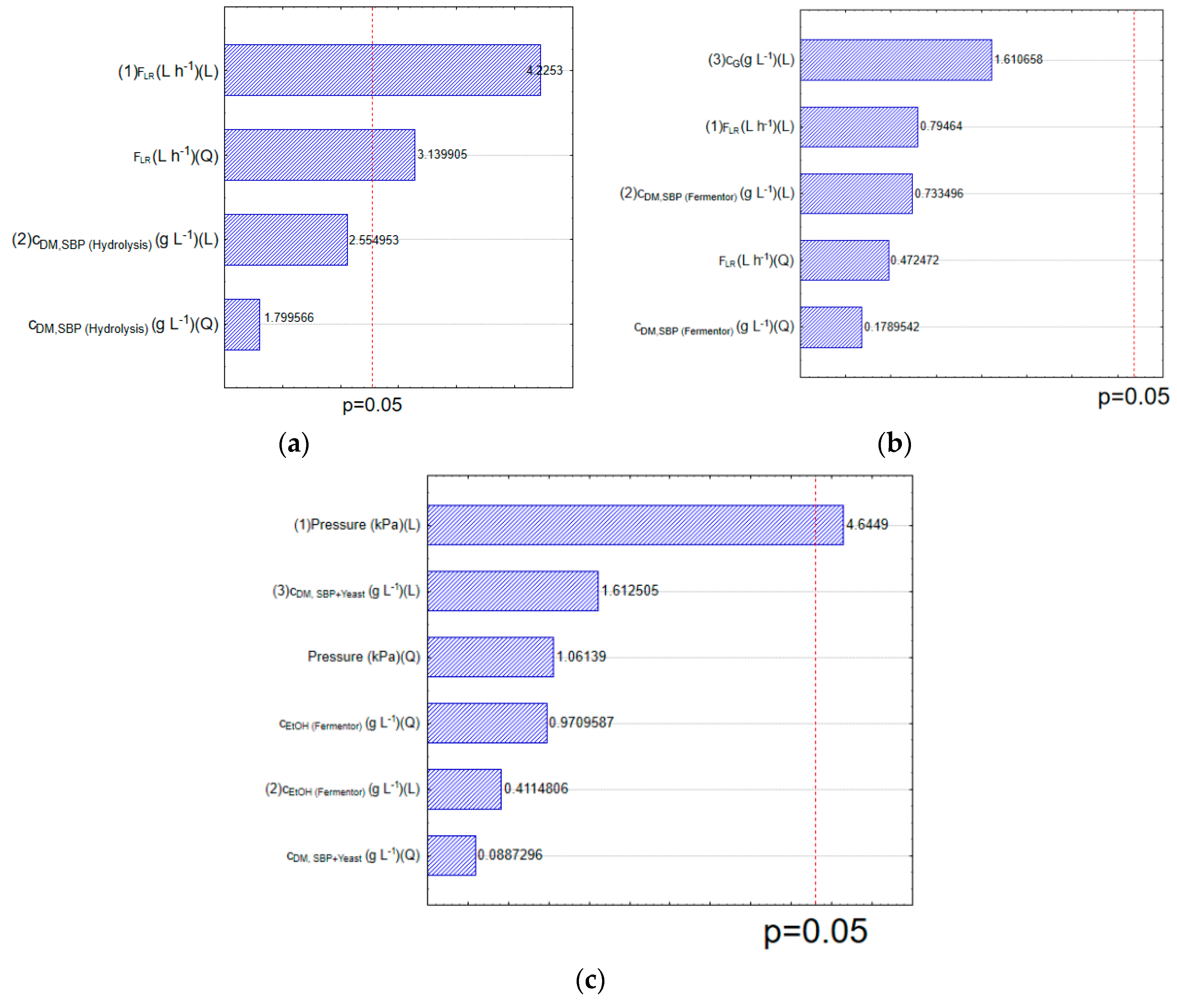
3.1. Evaluation of the Vacuum Assisted Gas Stripping for Ethanol Removal after SBP Hydrolysis and Fermentation
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Optimisation of Integrate Ethanol Production Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cG | hydrolyzed sugar concentration (g L−1) |
| cEtOH | concentration of ethanol (g L−1) |
| cDM SBP (Hydrolysis) | concentration of sugar beet pulp dry matter during hydrolysis (g L−1) |
| cEtOH (Fermenter) | concentration of ethanol in fermenter (g L−1) |
| cEtOH (Condensate) | concentration of ethanol in condensate (g L−1) |
| cDM SBP+YEAST | concentration of sugar beet pulp dry matter and yeast (g L−1) |
| FLR | recycling ratio (L h−1) |
| p | pressure (kPa) |
References
- Cysewski, G.R.; Wilke, C.R. Rapid ethanol fermentations using vacuum and cell recycle. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 19, 1125–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.L.D.H.; Rodrigues, M.I.; Maugeri, F. Dynamic modeling simulation and optimization of an extractive continuous alcoholic fermentation process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1999, 74, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Hsu, H.W. Analysis of gas stripping during ethanol fermentation-1 in a continuous stirred tank reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1990, 45, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugulis, A.J.; Axford, D.B.; McLellan, P.J. The economics of ethanol production by extractive fermentation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1991, 69, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M.; Morawski, A.W.; Tomaszewske, M. Ethanol production in membrane distillation bioreactor. Catalys. Today 2000, 56, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zeng, A.W. Ethanol production by strip-flash fermentation. Chem. Eng. 2008, 36, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mariano, A.P.; Mohammad, J.K.; Atala, D.I.P.; Filho, F.M.; Wolf Maciel, M.R.; Filho, R.M.; Stuart, P. Energy requirements for butanol recovery using the flash fermentation technology. Energy Fuel 2011, 25, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Blaschek, H.P. Recovery of butanol from fermentation broth by gas stripping. Renew. Energy 2001, 22, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, P.K.; Ghose, T.K.; Ghosh, P.; Chotani, G.K. Vapor liquid equilibrium behavior of aqueous ethanol solution during vacuum coupled simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1986, 28, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, P.K.; Liu, C.P.; Findley, M.E.; Liapis, A.I.; Siehr, D.J. Ethanol separation from water in a two-stage adsorption process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 1983, 13, 629–647. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, C.B.; Motoki, M.; Matsumura, M.; Kataoka, H.J. Simultaneous ethanol fermentation and stripping process coupled with rectification. Ferment. Bioeng. 1989, 68, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, F.; Kurantz, M.J.; Goldberg, N.; McAloon, A.J.; Craig, J.C., Jr. Dry-grind process for fuel ethanol by continuous fermentation and stripping. Biotechnol. Progr. 2000, 16, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeji, T.C.; Qureshi, N.; Blaschek, H.P. Production of acetone butanol (AB) from liquefied corn starch, a commercial substrate, using Clostridium beijerinckii coupled with product recovery by gas stripping. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 34, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, D.H. Effect of different types of gas in gas stripping ethanol fermentation (GSEF). Chin. J. Process. Eng. 2005, 5, 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez, M.A.; Velloso, A.A. Sistema de Fermentaçăo de Etanol (Ethanol Fermentation System). Brazilian Patent PI 0801209-1, 14 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, F.; Marquez, M.A.; Johnston, D.B.; Goldberg, N.M.; Hicks, K.B. Continuous high-solids corn liquefaction and fermentation with stripping of ethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4403–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrije, T.; Budde, M.; van der Wal, H.; Claassen, P.A.; López-Contreras, A.M. “In situ” removal of isopropanol, butanol and ethanol from fermentation broth by gas stripping. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Dai, S.H. A novel solid state fermentation coupled with gas stripping enhancing the sweet sorghum stalk conversion performance for bioethanol. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonego, J.L.S.; Lemos, D.A.; Pinto, C.E.M.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Badino, A.C. Extractive Fed-Batch Ethanol Fermentation with CO2 Stripping in a Bubble Column Bioreactor. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Sarks, C.; Bals, B.D.; Posawatz, N.; Gunawan, C.; Dale, B.E.; Balan, V. Toward high solids loading process for lignocellulosic biofuel production at a low cost. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andlar, M.; Rezić, I.; Oros, D.; Kracher, D.; Ludwig, R.; Rezić, T.; Šantek, B. Optimization of enzymatic sugar beet hydrolysis in a horizontal rotating tubular bioreactor. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 92, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracher, D.; Oros, D.; Yao, W.; Preims, M.; Rezić, I.; Haltrich, D.; Rezić, T.; Ludwig, R. Fungal secretomes enhance sugar beet pulp hydrolysis. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezić, T.; Oros, D.; Marković, I.; Kracher, D.; Ludwig, R.; Šantek, B. Integrated hydrolastion and fermentation of the sugar beet pulp to bioethanol. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oros, D. Development of Sustainable Processes for Bioethanol Production. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Food Technology and Biotechnology, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Analyt. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M.; Iavarone, A.T.; Marletta, M.A. Quantitative proteomic approach for cellulose degradation by Neurospora crassa. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4177–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Beeson, W.T.; Iavarone, A.T.; Sun, J.; Marletta, M.A.; Cate, J.H.D.; Glass, N.L. Systems analysis of plant cell wall degradation by the model filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22157–22162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fushinobu, S. Metalloproteins: A new face for biomass breakdown. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.-L.; An, G.H.; Yang, J.; Moon, Y.-H.; Yu, G.-D.; Ahn, J.-W. Bioethanol production from Miscanthus using thermotolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae mbc 2 isolated from the respiration-deficient mutants. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dheeran, P.; Singh, S.P.; Mishra, I.M.; Adhikari, D.K. Continuous ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate at high temperature with cell recycle and in-situ recovery of ethanol. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 138, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Linares, J.C.; Romero, I.; Cara, C.; Ruiz, E.; Castro, E.; Moya, M. Experimental study on ethanol production from hydrothermal pretreated rapeseed straw by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.A.; Ruiz, H.A.; Nogueira, C.C.; Santos, E.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Macedo, G.R. Comparison of delignified coconuts waste and cactus for fuel-ethanol production by the simultaneous and semi-simultaneous saccharification and fermentation strategies. Fuel 2014, 131, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narra, M.; James, P.; Balasubramanian, V. Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of delignified lignocellulosic biomass at high solid loadings by a newly isolated thermotolerant Kluyveromyces sp. for ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, A.; Kawamura, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Endo, T.; Rodriguez, M., Jr.; Mielenz, J.R. Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation and a consolidated bioprocessing for Hinoki cypress and Eucalyptus after fibrillation by steam and subsequent wet-disk milling. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonego, J.L.S.; Lemos, D.A.; Rodriguez, G.Y.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Badino, A.C. Extractive Batch Fermentation with CO2 Stripping for Ethanol Production in a Bubble Column Bioreactor: Experimental and Modeling. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7552–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.N.; Sutanto, S.; Huynh, L.H.; Ismadji, S.; Ju, Y.-H. Subcritical water and dilute acid pretreatments for bioethanol production from Melaleuca leucadendron shedding bark. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 78, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, F.; Lu, C.; Yang, S.-T.; Bai, F.-W. Two-stage in situ gas stripping for enhanced butanol fermentation and energy-saving product recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanares, P.; Negro, M.J.; Oliva, J.M.; S´aez, F.; Ballesteros, I.; Ballesteros, M.J. Different process configurations for bioethanol production from pretreated olive pruning biomass. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chu, D.; Huang, J.; Yu, Z.; Dai, G.; Bao, J. Simultaneous Saccharification and Ethanol Fermentation at High Corn Stover Solids Loading in a Helical Stirring Bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 105, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
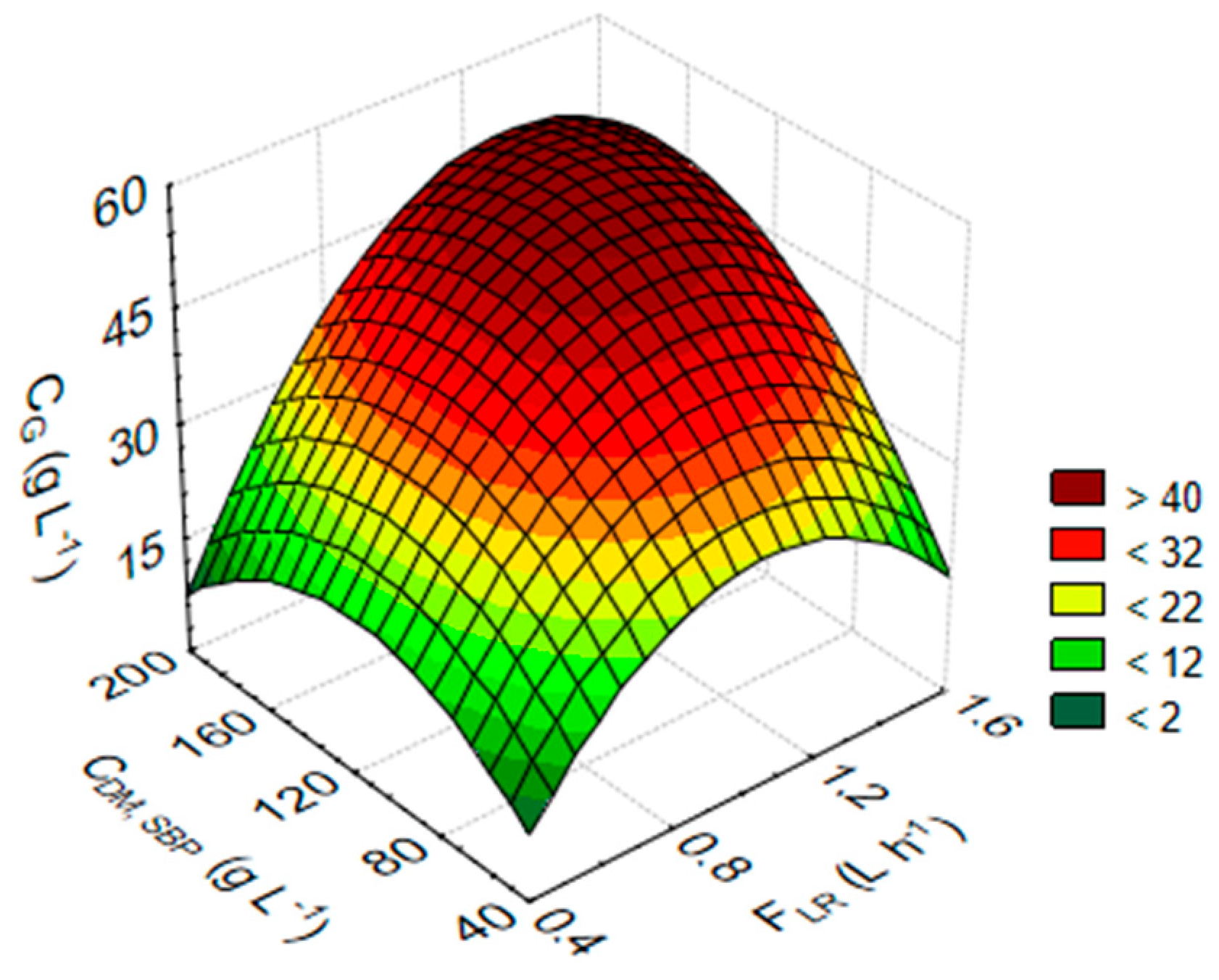
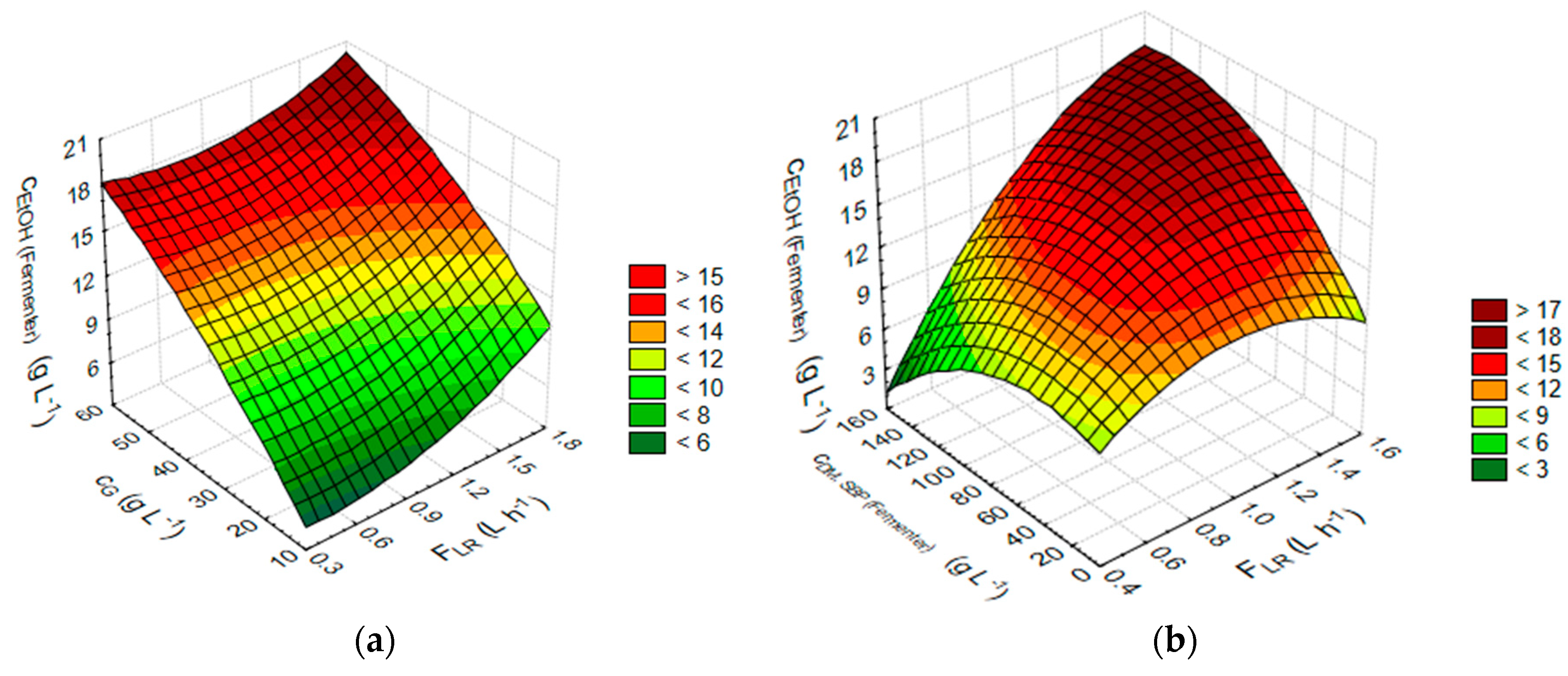
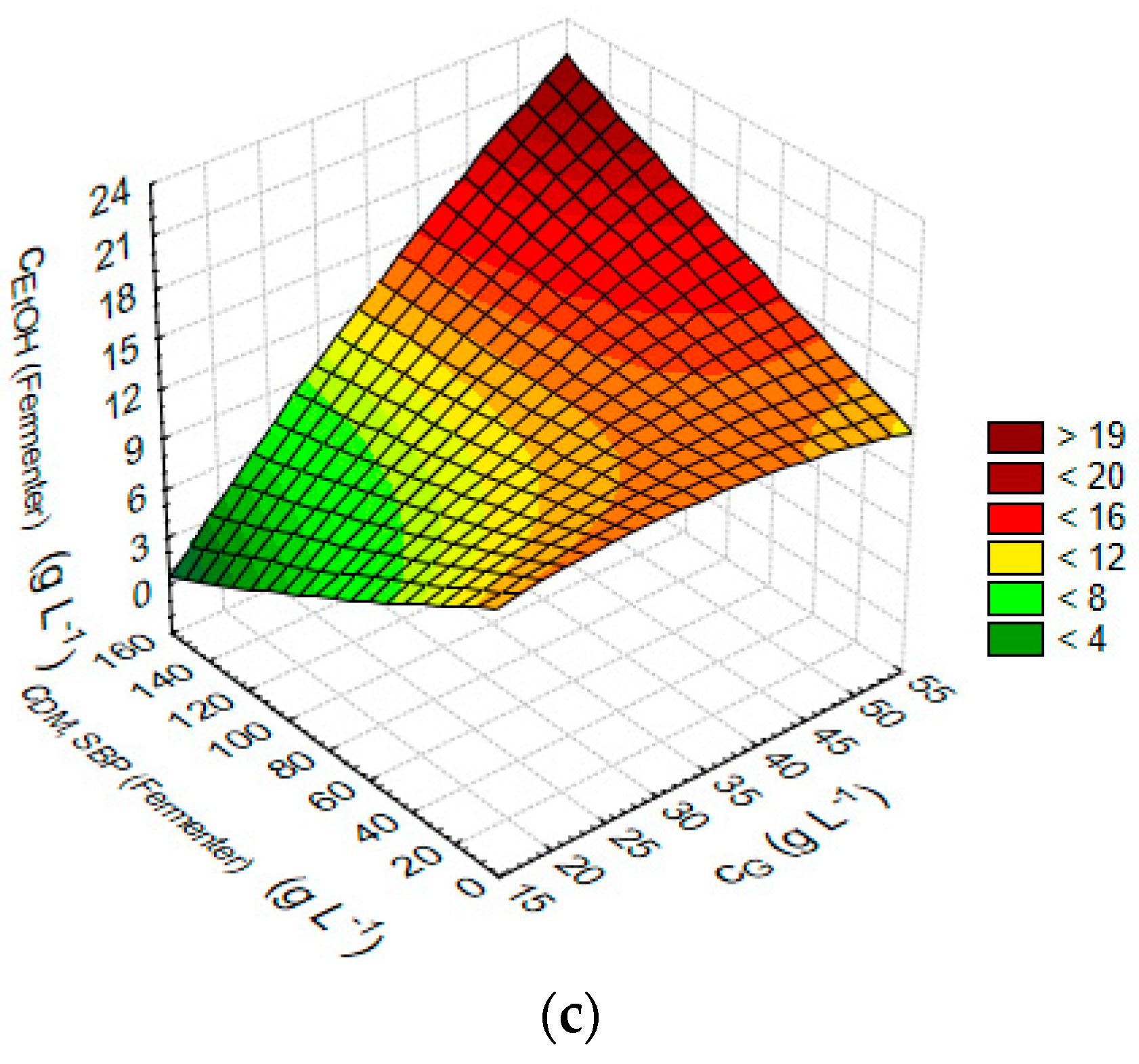


| Response | Model Equation |
|---|---|
| Hydrolysis step | |
| cG (g L−1) against FLR (L h−1) and cDM,SBP (Hydrolysis) (g L−1) | cG (g L−1) = −37.0244 + 95.9033 × x + 0.3898 × y − 48.7733 × x × x + 0.1716 × x × y − 0.0019 × y × y |
| Fermentation step | |
| cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) against FLR (L h−1) and cG (g L−1) | cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) = 1.0341 − 1.6724 × x + 0.4049 × y + 2.7967 × x × x − 0.0466 × x × y − 0.0017 × y × y |
| cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) against FLR (L h−1) and cDM,SBP (Fermenter) (g L−1) | cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) = 2.095 + 18.942 × x + 0.0064 × y − 9.4392 × x × x + 0.0899 × x × y − 0.0005 × y × y |
| cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) against cG (g L−1) and cDM,SBP (Fermenter) (g L−1) | cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) = 10.7033 + 0.1937 × x − 0.1385 × y 0.0032 × x × x + 0.0035 × x × y + 4.7931 × 10−5 × y × y |
| Vacuum-striping step | |
| cEtOH (Condensate) (g L−1) against cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) and Pressure (kPa) | cEtOH (Condensate) (g L−1) = 6.9934 + 4.1873 × x − 0.0298 × y − 0.0484 × x × x − 0.0014 × x × y + 1.9843 × 10−5 × y × y |
| cEtOH (Condensate) (g L−1) against cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) and cDM, SBP+yYeast (g L−1) | cEtOH (Condensate) (g L−1) = −156.5581 + 24.9372 × x+0.4586 × y − 0.8373 × x × x − 0.021 × x × y + 0.0006 × y × y |
| cEtOH (Condensate) (g L−1) against Pressure (kPa) and cDM, SBP+Yeast (g L−1) | cEtOH (Condensate) (g L−1) = 61.9621 − 0.1165 × x + 0.2763 × y + 7.2934 × 10−5 × x × x − 4.8328 × 10−6 × x × y − 0.0017 × y × y |
| Pressure (kPa) | mEtOH (Fermenter) (g) | mEtOH (Condensate) (g) | % EtOH |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 10.96 | 2.94 | 26.82 |
| 100 | 10.21 | 0.96 | 9.40 |
| 50 | 5.30 | 1.82 | 34.34 |
| 100 | 12.47 | 0.75 | 6.01 |
| 50 | 14.52 | 1.94 | 13.36 |
| 25 | 17.30 | 5.45 | 31.50 |
| 50 | 13.70 | 1.53 | 11.17 |
| 25 | 15.60 | 3.01 | 19.29 |
| 100 | 18.20 | 1.03 | 5.66 |
| Factors | Hydrolysis | Fermentation | Vacuum-Striping |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLR (L h−1) | 1.25 | 1.45 | - |
| cDM,SBP (g L−1) | 156 | 149 | 191 (out of range) |
| cG (g L−1) | 50.61 | 75.4 (out of the range) | - |
| cEtOH (Fermenter) (g L−1) | - | 13.2 | 15.5 |
| cEtOH (Condensate) (g L−1) | 62 | ||
| Pressure (kPa) | - | - | <20 (out of range) |
| Feedstock | Pretreatment Conditions | Fermentation Conditions | Strain | Theoretical Ethanol Yield (%) | Corresponding Ethanol Yield (g L−1) | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar beet pulp | Enzyme pretreatment with Ultrazym AFP-L (14.0 ± 0.1 g dm−3) and Neurospora crassa crude extract (0.1 mg protein per g of SBP) | Semi-solid fermentation in a column bioreactor at 30 °C and pH 4.5 for 24 h | Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y9 (ATCC® MYA-4941 | 97 | 62 | this study |
| Miscanthus | 1.5 M NaOH with stirring at 120 rpm and heated to 150 °C for 30 min | Liquid-state saccharification and fermentation at 42 °C with shaking at 150 rpm | Saccharomyces cerevisiae 7928 | 86.30 | 29.50 | [29] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | Acid hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse in two stages | Continuous fermentation with cell recycle system at a temperature of 50 °C and a pH of 5.0 | thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces sp. IIPE453 | 96 | 56.30 | [30] |
| Rapeseed straw | Liquid hot water pretreatment at 217 °C for 42 min | Liquid-state simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in an orbital shaker at 150 rpm | Saccharomyces cerevisiae, enzymes: Celluclast (NS50013) cellulases from Trichoderma reesei and β-glucosidase (NS50010) from Aspergillus niger | 66.60 | 17.20 | [31] |
| Sweet sorghum stalk | Sterilization at 121 °C for 15 min | Traditional static solid-state fermentation (TS-SSF) and gas stripping solid state fermentation (GS-SSF) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 77.5 | 27 | [18] |
| Coconut fibre | Sequential alkaline hydrogen peroxide (Alk-H2O2)–sodium hydroxide (NaOH) | Semi-simultaneous saccharification and fermentation at 30 °C for 40 h | Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia stipites and Zymomonas mobilis | 89.15 | 9.32 | [32] |
| Rice straw | Dilute acid pretreatment, then delignification with 0.5% NaOH at 121 °C for 30 min | Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation with agitation at 120 rpm for 72 h at 42 °C | Kluyveromyces sp. | 84.60 | 24.63 | [33] |
| Hinoki cypress | Steam treatment (150 °C for 2 h) with wet disk milling | Yeast-based simultaneous saccharification and fermentation at 58 °C with shaking at 125 rpm | S. cerevisiae D5A (ATCC 200062), C. thermocellum (ATCC27405) | 63.40 | - | [34] |
| Sugar cane molasses | Sterilization at 121 °C and 15 psig for 30 min | Extractive batch fermentation using CO2 as a stripping gas | commercial lyophilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 25% higher compared with to the conventional fermentation | 43.30 | [35] |
| Paper bark tree | Subcritical water at 180 °C for 30 min | Anaerobic condition in an orbital shaker (150 rpm, 37 °C) for 120 h | Ethanol Red® Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 91 | 24.70 | [36] |
| Fermentation P2 medium | Sterilization at 121 °C and 15 psig for 30 min | Integrated fermentation system with intermittent gas stripping (CO2 and H2) at 37 °C and pH 5.0 | Clostridium acetobutylicum JB200 (ATCC 55025) | 2 | 9.66 | [37] |
| Olive tree pruning | Liquid hot water pretreated at 210 °C with magnetic agitation | Liquid-state simultaneous saccharification and fermentation at 35 °C for 72 h and 150 rpm | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 50 | 31.10 | [38] |
| Corn stover | Steam explosion at 200 °C for 4 min | Semi-continuous liquid-state simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (37 °C for 60 h) | yeast mutant strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae DQ1 | 52.10 | 40.60 | [39] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andlar, M.; Oros, D.; Rezić, T.; Ludwig, R.; Šantek, B. In-Situ Vacuum Assisted Gas Stripping Recovery System for Ethanol Removal from a Column Bioreactor. Fibers 2018, 6, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040088
Andlar M, Oros D, Rezić T, Ludwig R, Šantek B. In-Situ Vacuum Assisted Gas Stripping Recovery System for Ethanol Removal from a Column Bioreactor. Fibers. 2018; 6(4):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040088
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndlar, Martina, Damir Oros, Tonči Rezić, Roland Ludwig, and Božidar Šantek. 2018. "In-Situ Vacuum Assisted Gas Stripping Recovery System for Ethanol Removal from a Column Bioreactor" Fibers 6, no. 4: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040088
APA StyleAndlar, M., Oros, D., Rezić, T., Ludwig, R., & Šantek, B. (2018). In-Situ Vacuum Assisted Gas Stripping Recovery System for Ethanol Removal from a Column Bioreactor. Fibers, 6(4), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040088







