Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Flax Cell Walls during Plant Development: The Relation between Performance and Cell Wall Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Culture Conditions
2.2. Sample Preparation Prior Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Peak Force Quantitative Nano-Mechanical (QNM) Measurements
2.3. AFM Peak Force QNM Measurements
2.4. Tensile Tests Performed on Extracted Elementary Fibers
2.5. Raman Spectroscopy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
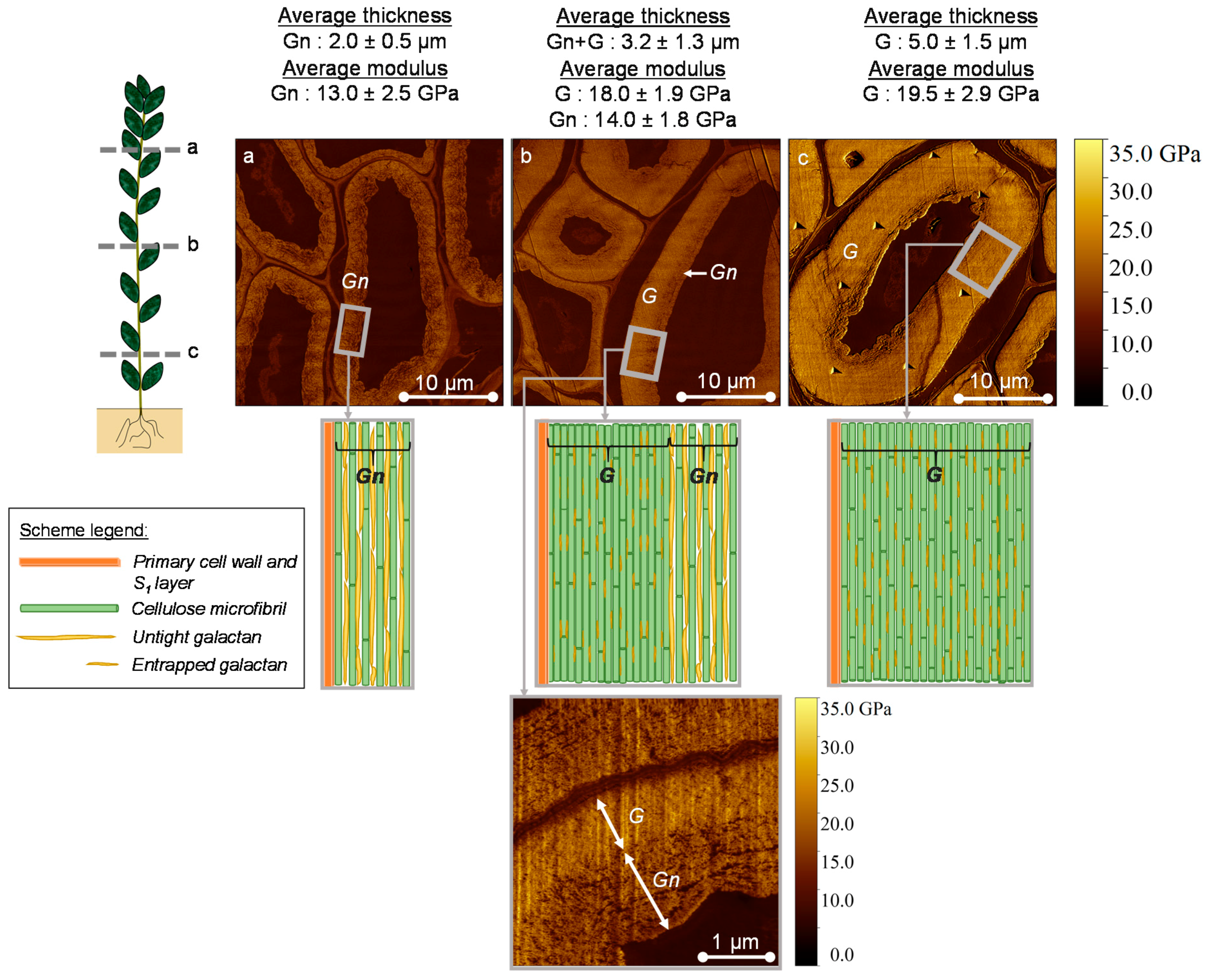
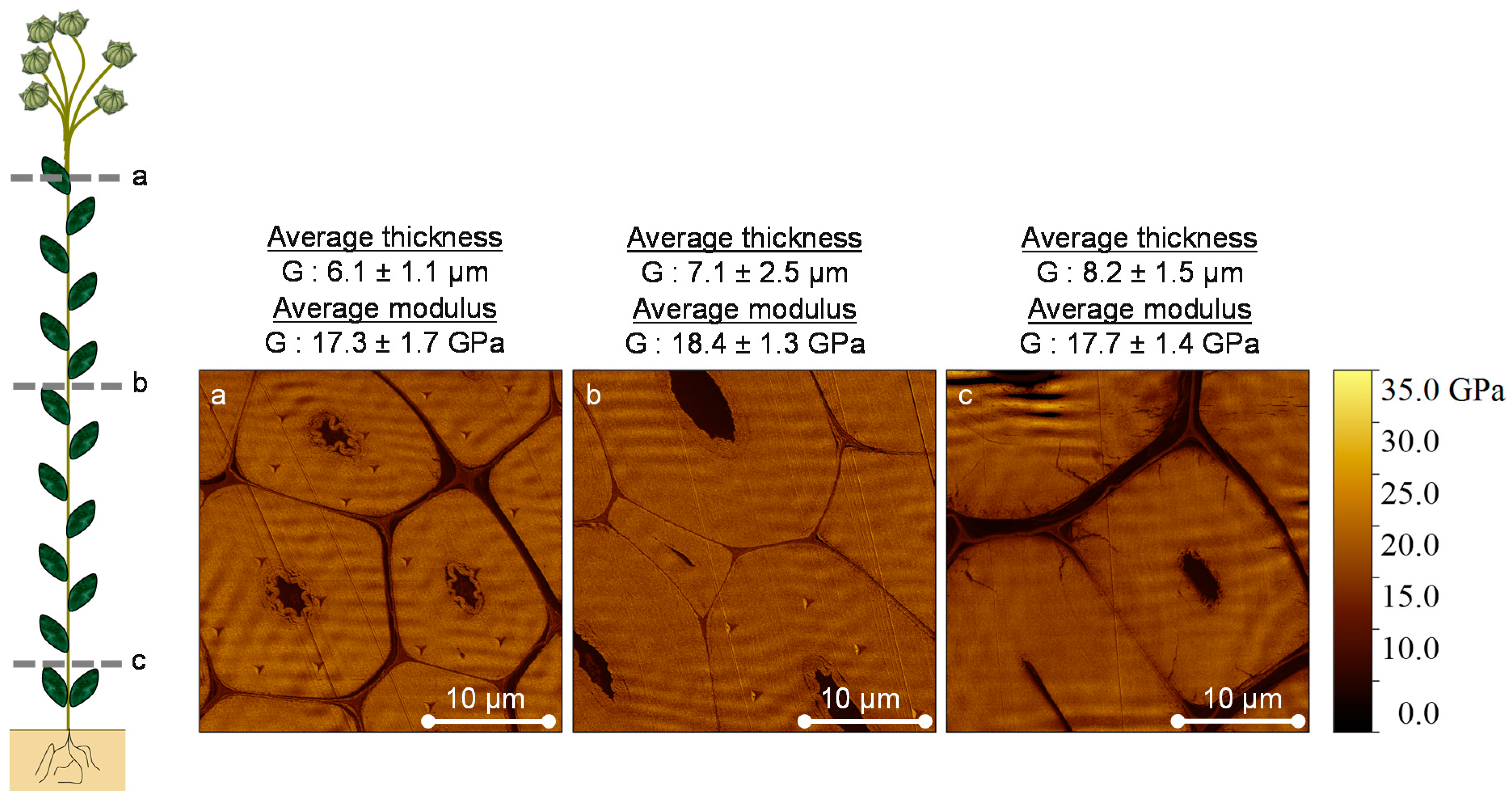
3.1. AFM Peak Force QNM Measurements
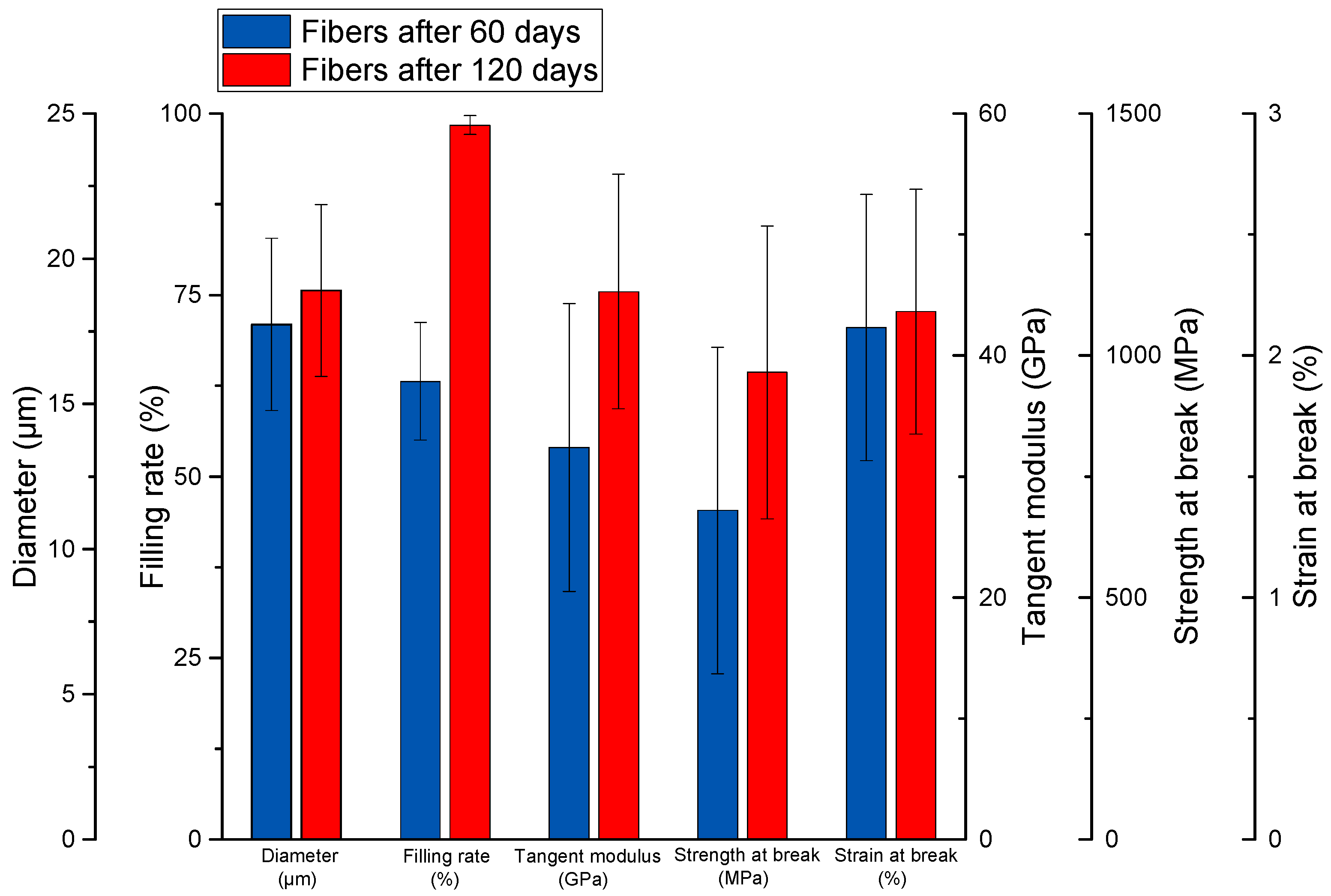
3.2. Tensile Tests Performed on Extracted Elementary Fibers
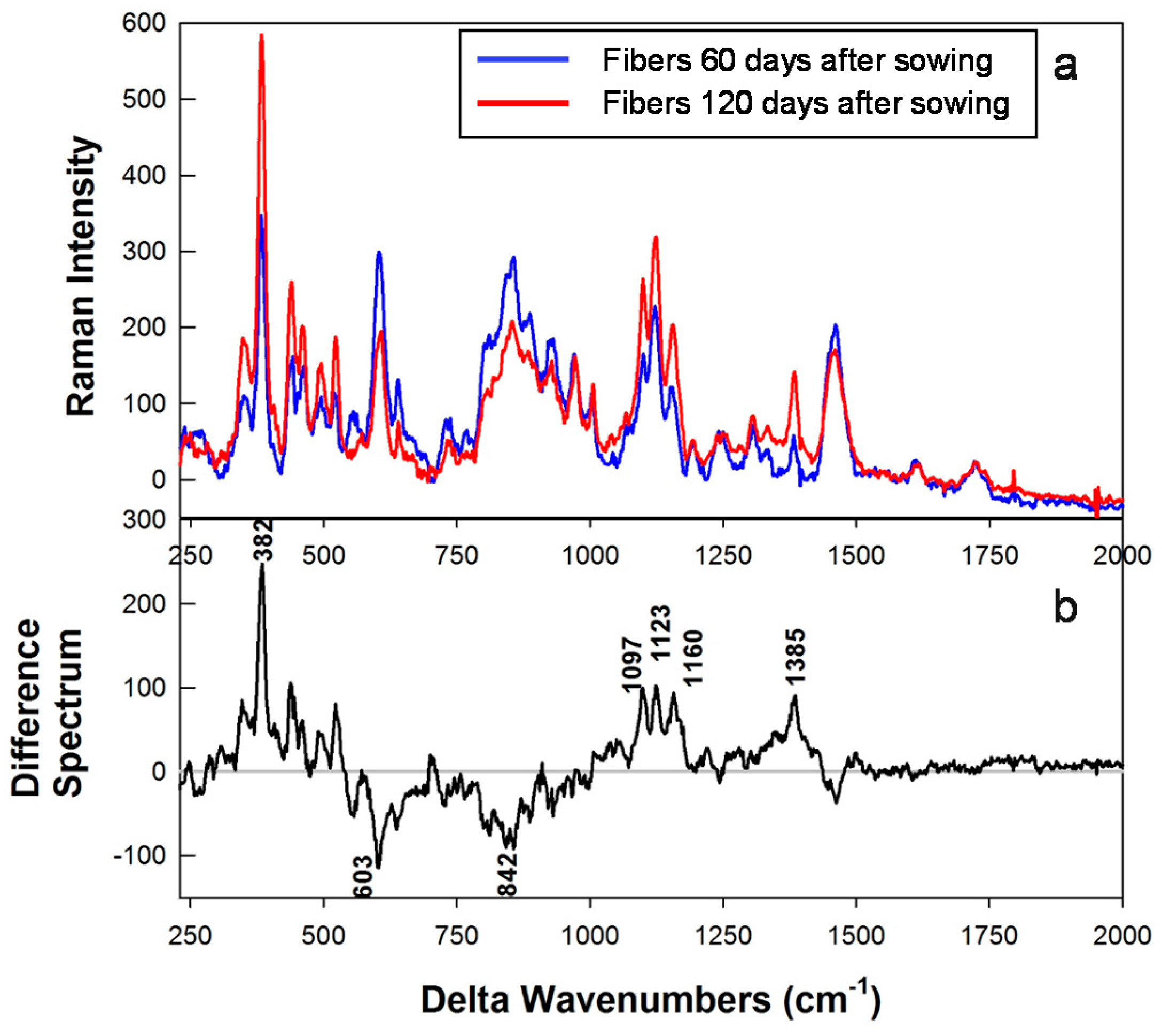
3.3. Raman Spectral Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kvavadze, E.; Bar-Yosef, O.; Belfer-Cohen, A.; Boaretto, E.; Jakeli, N.; Matskevich, Z.; Meshveliani, T. 30,000-year-old wild flax fibers. Science 2009, 325, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Bruyne, N.A. Plastic progress. Some further developments in the manufacture and use of synthetic materials for aircraft construction. Aircr. Eng. 1939, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Baley, C.; Bourmaud, A. Average tensile properties of French elementary flax fibers. Mater. Lett. 2014, 122, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snegireva, A.V.; Ageeva, M.V.; Amenitskii, S.I.; Chernova, T.E.; Ebskamp, M.; Gorshkova, T.A. Intrusive growth of sclerenchyma fibers. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 57, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikshina, P.; Chernova, T.; Chemikosova, S.B.; Ibragimova, N.N.; Mokshina, N.; Gorshkova, T.A. Cellulosic fibers: Role of matrix polysaccharides in structure and function. In Cellulose—Fundamental Aspects; InTechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 91–112. ISBN 978-953-51-1183-2. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, J.E.G.; Gorshkova, T.A. Cell walls and Fibers|Fiber formation. In Encyclopedia of Applied Plant Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, T.A.; Sal’nikov, V.V.; Chemikosova, S.B.; Ageeva, M.V.; Pavlencheva, N.V.; Van Dam, J.E.G. The snap point: A transition point in Linum usitatissimum bast fiber development. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2003, 18, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, F. Lin Fibre: Culture et Transformation; Arvalis-Institut du Végétal: Paris, France, 2013; ISBN 9782817901572. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, T.; Mokshina, N.; Chernova, T.; Ibragimova, N.; Salnikov, V.; Mikshina, P.; Tryfona, T.; Banasiak, A.; Immerzeel, P.; Dupree, P.; et al. Aspen tension wood fibers contain β-(1→4)-galactans and acidic arabinogalactans retained by cellulose microfibrils in gelatinous walls. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2048–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnould, O.; Arinero, R. Towards a better understanding of wood cell wall characterisation with contact resonance atomic force microscopy. Compos. Part A 2015, 74, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnould, O.; Siniscalco, D.; Bourmaud, A.; Le, A.; Baley, C. Better insight into the nano-mechanical properties of flax fibre cell walls. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 97, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, U.P. Raman imaging to investigate ultrastructure and composition of plant cell walls: Distribution of lignin and cellulose in black spruce wood (Picea mariana). Planta 2006, 224, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelsbach, D.S.; Akin, D.E. Near-infrared Fourier-transform Raman spectroscopy of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) stems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Farwell, D.W.; Webster, D. FT Raman microscopy of untreated natural plant fibres. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 1997, 1425, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsko, N.; Mueller, M. AFM of biological material embedded in epoxy resin. J. Struct. Biol. 2004, 146, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, S.; Cai, Z.; Young, T.M.; Du, G.; Li, Y. A novel sample preparation method to avoid influence of embedding medium during nano-indentation. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 110, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnerth, J.; Harper, D.; Lee, S.H.; Rials, T.G.; Gindl, W. Adhesive penetration of wood cell walls investigated by scanning thermal microscopy (SThM). Holzforschung 2008, 62, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L.; Bader, T.K.; De Borst, K. Nanoindentation of wood cell walls: Effects of sample preparation and indentation protocol. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clair, B.; Gril, J.; Baba, K.; Thibaut, B.; Sugiyama, J. Precautions for the structural analysis of the gelatinous layer in tension wood. IAWA J. 2005, 26, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, A.; Bader, T.; Hofstetter, K.; Eberhardsteiner, J. The relation between indentation modulus, microfibril angle, and elastic properties of wood cell walls. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudenhooft, C.; Bourmaud, A.; Baley, C. Varietal selection of flax over time: Evolution of plant architecture related to influence on the mechanical properties of fibers. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 97, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alméras, T.; Clair, B. Critical review on the mechanisms of maturation stress generation in trees. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roach, M.J.; Mokshina, N.Y.; Badhan, A.; Snegireva, A.V.; Hobson, N.; Deyholos, M.K.; Gorshkova, T.A. Development of Cellulosic Secondary Walls in Flax Fibers Requires b-Galactosidase. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorshkova, T.A.; Chemikosova, S.B.; Sal’nikov, V.V.; Pavlencheva, N.V.; Gur’janov, O.P.; Stolle-Smits, T.; Van Dam, J.E.G. Occurrence of cell-specific galactan is coinciding with bast fiber developmental transition in flax. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2004, 19, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Seymour, G.B.; Knox, J.P. Localization of Pectic Galactan in Tomato Cell Walls Using a Monoclonal Antibody Specific to (1/4)-b-D-Galactan. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanguy, M.; Bourmaud, A.; Baley, C. Plant cell walls to reinforce composite materials: Relationship between nanoindentation and tensile modulus. Mater. Lett. 2016, 167, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophe, F.; Séné, B.; Mccann, M.C.; Wilson, R.H.; Crinter, R. Fourier-Transform Raman and Fourier-Transform lnfrared Spectroscopy. Plant Physiol. 1994, 106, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlinger, N. New insights into plant cell walls by vibrational microspectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2017, 4928, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goudenhooft, C.; Siniscalco, D.; Arnould, O.; Bourmaud, A.; Sire, O.; Gorshkova, T.; Baley, C. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Flax Cell Walls during Plant Development: The Relation between Performance and Cell Wall Structure. Fibers 2018, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6010006
Goudenhooft C, Siniscalco D, Arnould O, Bourmaud A, Sire O, Gorshkova T, Baley C. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Flax Cell Walls during Plant Development: The Relation between Performance and Cell Wall Structure. Fibers. 2018; 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoudenhooft, Camille, David Siniscalco, Olivier Arnould, Alain Bourmaud, Olivier Sire, Tatyana Gorshkova, and Christophe Baley. 2018. "Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Flax Cell Walls during Plant Development: The Relation between Performance and Cell Wall Structure" Fibers 6, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6010006
APA StyleGoudenhooft, C., Siniscalco, D., Arnould, O., Bourmaud, A., Sire, O., Gorshkova, T., & Baley, C. (2018). Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Flax Cell Walls during Plant Development: The Relation between Performance and Cell Wall Structure. Fibers, 6(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6010006





