Abstract
Flax fibre bio-epoxy composites have not found many commercial uses in structural applications on account of their lack of cost efficiency and high susceptibility to environmental changes. Non-woven flax mats were subjected to alkali, acetylation, silane and enzymatic treatment, and then combined with untreated unidirectional (UD) flax fabrics to make hybrid flax bio-epoxy composites. Mechanical and environmental resistance (aging) tests were performed on the treated flax fibres. The glass transition temperature was detected at about 75 °C with little effect of treatments. Untreated composites were found to have a tensile strength of 180 MPa while no significant improvement was observed for any of the treatments, which are also not environmentally friendly. The amiopropyltriethoxysilane (APS) composites after Xenon aging, retained the tensile strength of 175 MPa and a modulus of 11.5 GPa, while untreated composites showed 35% reduction in elastic modulus.
1. Introduction
There are inherent environmental benefits associated with using natural fibre reinforced bio-resourced matrix composites due to them requiring less crude oil. Hence the environmental footprint of superlight electric vehicles could be reduced through the use of flax/bio-epoxy composites [1,2,3]. Their mechanical performance, together with the environmental benefits make bio-epoxy/flax composites suitable for load-bearing parts, such as vehicle body panels, crash elements, body trims and body chassis [4,5,6,7,8]. Adhekunle et al. [4] manufactured flax/bio-thermoset (methacrylated soybean oil and methyacrylic anhydride modified soybean oil) composites with different fibre stacking sequences and lay-up angles, leading to a maximum tensile strength of 119 MPa and Young’s modulus of 14 GPa. A flexural strength of 201 MPa and modulus of 24 GPa was also achieved. Flax yarn and flax woven fabric reinforced soy protein concentrated resins (SPC) were prepared by Huang and Netravali [9]. Flax yarn composites showed the highest tensile strength of 298 MPa and a flexural strength of 117 MPa. Table 1 shows some published mechanical properties of synthetic and bio-thermoset composites reinforced by flax fibres.

Table 1.
Examples of mechanical properties of flax-thermoset composites.
| Fibre/Matrix | Processing | Tensile Strength | Tensile Modulus | Flexural Strength | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flax/(MSO)a | Compression | 50–120 MPa | 6–15 GPa | 180 MPa | [4] |
| Flax/(MMSO)b | Compression | 50–120 MPa | 7–15 GPa | 201 MPa | [4] |
| Flax yarn/SPCc | Pultrusion | 298 MPa | 4.3 GPa | 117 MPa | [9] |
| Arctic flax/epoxy | Resin transfer | 280 MPa | 40 GPa | – | [10] |
| Flax/ epoxy | Compression | 280 MPa | 32 GPa | 250 MPa | [5] |
* a—Methacrylated soybean oil; b—methacrylic anhydride-modified soybean oil; c—soy protein concentrated.
The woven flax fabrics are mostly used in thermoset composites to give outstanding mechanical properties; but at an extremely high cost and imposing processing difficulties when compared to non-woven flax mats. Avril et al. [2] have investigated the optimization of pine oil-derived epoxy/flax composites with respect to fibre configurations (non-woven thick mat, unidirectional-UD fabrics and balanced fabrics). The UD flax fabric composites (12 UD layers) showed highest tensile strength of 220 MPa and low impact resistance, while the nonwoven mat composites (two layers) had a tensile strength of about 90 MPa.
Another limitation for the flax composites is that the hydrophilic property of flax, leading to poor interfacial adhesion [11,12]. The flax fibres mainly comprise of polysaccharides including cellulose (64.1%), hemicellulose (16.7%), pectin (1.8%) and lignin (2.0%), with minor components such as bound water, waxes, and other inorganic materials [13]. The hydroxyl groups may be involved in the hydrogen bonding within cellulose molecules, thereby activating these groups or introducing new moieties that form effective interlocks within the system. The interfacial properties can be improved by making appropriate modifications, which give rise to changes in physical and chemical interactions at the interface. Mercerization, acetylation, silane treatment, and other fibre pre-treatments are commonly used for flax modifications to improve the composite performances Table 2 [14,15,16,17,18].

Table 2.
Different treatments of flax-reinforced composites.
| Fiber/Matrix | Treatment | Conditions | Effect on Properties | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flax/PP | Esterification | 10 wt% MA, 25 h, 50 °C | Highest flexural and tensile strength | [14] |
| Flax/phenolic | Esterification | 25 wt% MMA, 30 min, 210 W | More moisture retardant | [15] |
| Flax/epoxy | Alkali treatment | 5 wt% NaOH, 30 min | Tensile strength 21.9%; Flex. Strength 16.1% | [19] |
| Flax/epoxy | Alkali treatment | 4 wt% NaOH, 45 s | Transvers strength, 30% increment | [20] |
| Flax/polyester | Silane treatment | 0.05 wt%, 24 h RT | Hydric fiber/matrix interface | [21] |
| Flax/PP | Esterification | MA-PP coupling agent | Interphase compatibility | [22] |
* MMA—methylmethacrylate; MA—maleic-anhydride.
In addition, for the automobile industry, the environmental durability of materials (temperature, water sensitivity, UV degradation, etc.) plays a very important role in selecting materials for exterior parts (e.g., vehicle body panels and body trims). Lots of studies regarding the environmental resistance were done on flax reinforced composites based on synthetic polymers (PP, epoxy, etc.) [23]. The storage modulus of flax/PP composites was found to increase at rubbery plateau after using zein as a coating on flax fibre due to improved mechanical stability [24]. Assarar and his co-workers [25] reported the influence of water ageing on the flax and glass epoxy composites comprising of 11 unidirectional plies. Flax fibre composites showed a 30% reduction in Young’s modulus after 10 days of water ageing while a similar test done on glass fibre composites resulted in only a 9% decrease until saturation time. A study of moisture absorption and environmental durability of flax (Green and Duralin)/PP composites was conducted by Stamboulis and his co-workers [26]. Green flax/PP composites (18% max. moisture content) were more sensitive to water than Durbin flax/PP composites (12.8%).
Currently, the high cost and difficulties involved in processing of woven fibre fabrics limit the use of flax/bio-epoxy composites in structural applications. To balance the property and economic advantages, a hybrid fibre configuration (nonwoven fibre mat/UD fibre fabrics) was studied to develop new flax reinforced epoxy (FE) composites. In addition, the surface compatibility and environmental resistance of these new composites still remains a challenge and is yet to be solved. Hence, alkali, acetylation, silane treatment and enzymatic treatment were selected for non-woven flax mats to optimize the promising treatments. Competitive mechanical properties (dynamical mechanical properties and tensile) of the composites were obtained through adequate experiments, while the environmental resistance was analyzed through tensile tests after aging conditioning (UV and Xenon conditioning). The effects of fibre pre-treatments on these properties were also presented.
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials and Manufacturing
A bio-sourced resin was chosen: a short pot-life pine oil-derived SuperSap 100/1000 epoxy resin supplied by Entropy. The non-woven flax mats (areal weight 600 g/mm2, thickness 3 mm) were provided by Ecotechnilin Ltd. (Kimbolton, Cambridgeshire, UK). The unidirectional fabrics provided by LINEO (CALDIC Centre, France) have the areal weight 180 g/mm2 and thickness of 0.35 mm. The hybrid composites were made up of two non-woven mats as external layers and five UD layers as laminate core: NW [UD]5 NW.
The composites were manufactured by compression molding at Mahytec, Dole, France (Table 3) at the heating temperature of 90 °C for 2 h under the pressure of 30 bars. The average thickness and fiber mass ratio were respectively 2.9 mm and high content of 57.4%.

Table 3.
The hybrid flax reinforced bio-epoxy composites with treatments.
| Matrix Type | Fibre Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Supersap bio-epoxy | UD fabric | Configuration | Treatment |
| Provided material | |||
| 5 internal layers | Untreated | ||
| Investigating factor | |||
| Non-woven mat | (ttom) | Untreated | |
| 5% NaOH | |||
| Alkali + BTCA | |||
| Alkali + APS | |||
| Laccase-Doga (LD) | |||
* BTCA—Butanetetracarboxylic acid; APS—Amiopropyltriethoxysilane; Laccase-Benzenediol, Doga-dodecyl gallate.
2.2. Fibre Treatments
Non-woven flax fibre mats with different surface treatments were supplied by Valtion Teknillinen Tutkimuskeskus (VTT), Espoo, Finland. Mercerization was performed by immersing the flax mats into 5 wt% NaOH solution for one hour, washing them two times thoroughly with water and drying in 50 °C for 12 h. The NaOH treatment was also done as pre-treatment for butanetetracarboxylic acid (BTCA) and amiopropyltriethoxysilane (APS) treated mats. The BTCA treatment was done by spraying 2.5 wt% BTCA-water solution on both mat surfaces to contain 5% of BTCA, followed by heating at 80 °C for 20 min and drying overnight at 50 °C (to 24 h). APS treatment was done with ethanol (98%): water-solution (80:20) containing 1% APS. Mats were sprayed “full” on both sides with solutions containing 1% of APS. Then the mats were placed in oven at 80 °C for 4 h followed by washing with ethanol-water solution and drying in oven at 50 °C for overnight. The laccase Doga (LD) treatments were carried out as following steps: (a) wetting of the samples with distilled water; (b) activation with laccase; (c) treatment with DOGA; (d) rinsing with water and (d) drying.
2.3. Characterization and Testing
2.3.1. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
Thermal Analysis Instruments Q800 was applied for DMA measurement on neat and modified composites under the operation of single cantilever bending (about 17 mm long). The specimen (13 mm wide) was heated to 200 °C at the rate of 3 °C/min. A frequency of 1 Hz and air cooling was incorporated.
2.3.2. Tensile Testing
The flat coupon tensile test was carried out on the Instron 5/100 kN 5500 R machine according to ASTM D3039 [27] at the cross head speed of 2 mm/min (five specimens per type). For accurate micro-scale strain measurement, a Q-400 system from Dyantec Dynamics (digital image correlation—DIC [11]) was used (Figure 1). The sample surface was sprayed with plain white paint, followed by a random speckled pattern of black dots (Figure 1a). During the tests, the images were sequentially recorded at sub-pixel (micro-strain) resolution and then the patterns were used to identify the two-dimensional displacement through Istra 4 software. The principle strain for the selected area with gauge length of 50 mm was recorded (Figure 1c). The non-contact nature of measurements (DIC method) avoids the influence of attachment skills.
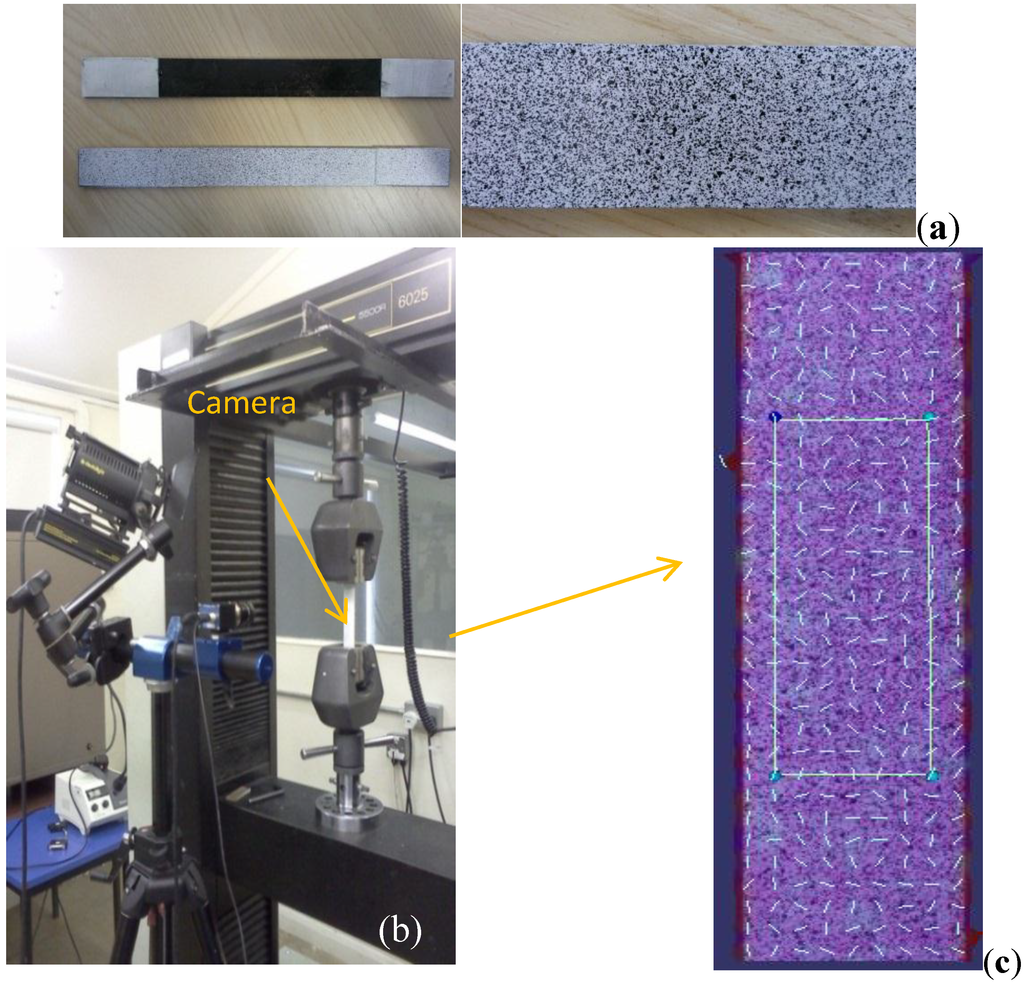
Figure 1.
Digital image correlation (DIC) technique for tension (a) preparation of speckled samples; (b) DIC set-up; (c) evaluated gauge area.
Figure 1.
Digital image correlation (DIC) technique for tension (a) preparation of speckled samples; (b) DIC set-up; (c) evaluated gauge area.
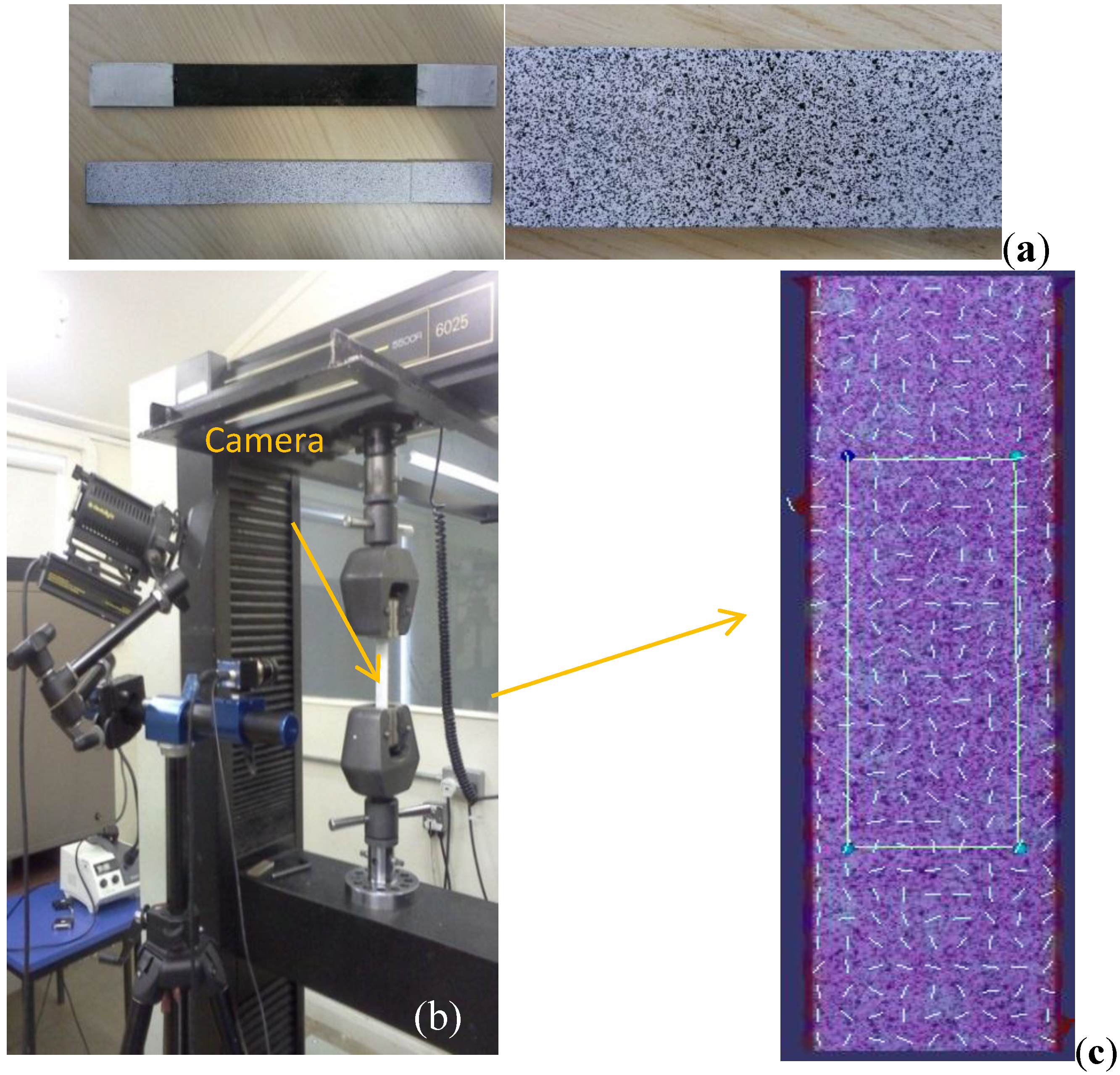
2.3.3. UV and Xenon-arc Light Aging
The tensile properties of the composites before and after light conditioning were determined according to ASTM D3039 [27] as seen in tensile testing. The UV and Xenon Arc light weathering based on BS EN ISO 4892-3 [28] and BS EN ISO 4892-2 [29] was performed at VTT on FE composites. The UV aging conditioning was done by using UVB-313 in the temperature range of −15 to 25 °C cycles for 552 h (23 days) in QUV Accelerated weathering tester and freezer. Similarly, samples were exposed to artificial weathering for 500 h with Xenon Arc light in the apparatus Q-Sun Xe-3-HS and Q-SUN Xenon test Chamber XE-3-H/HSB/HS.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Treatment on Dynamical Mechanical Properties
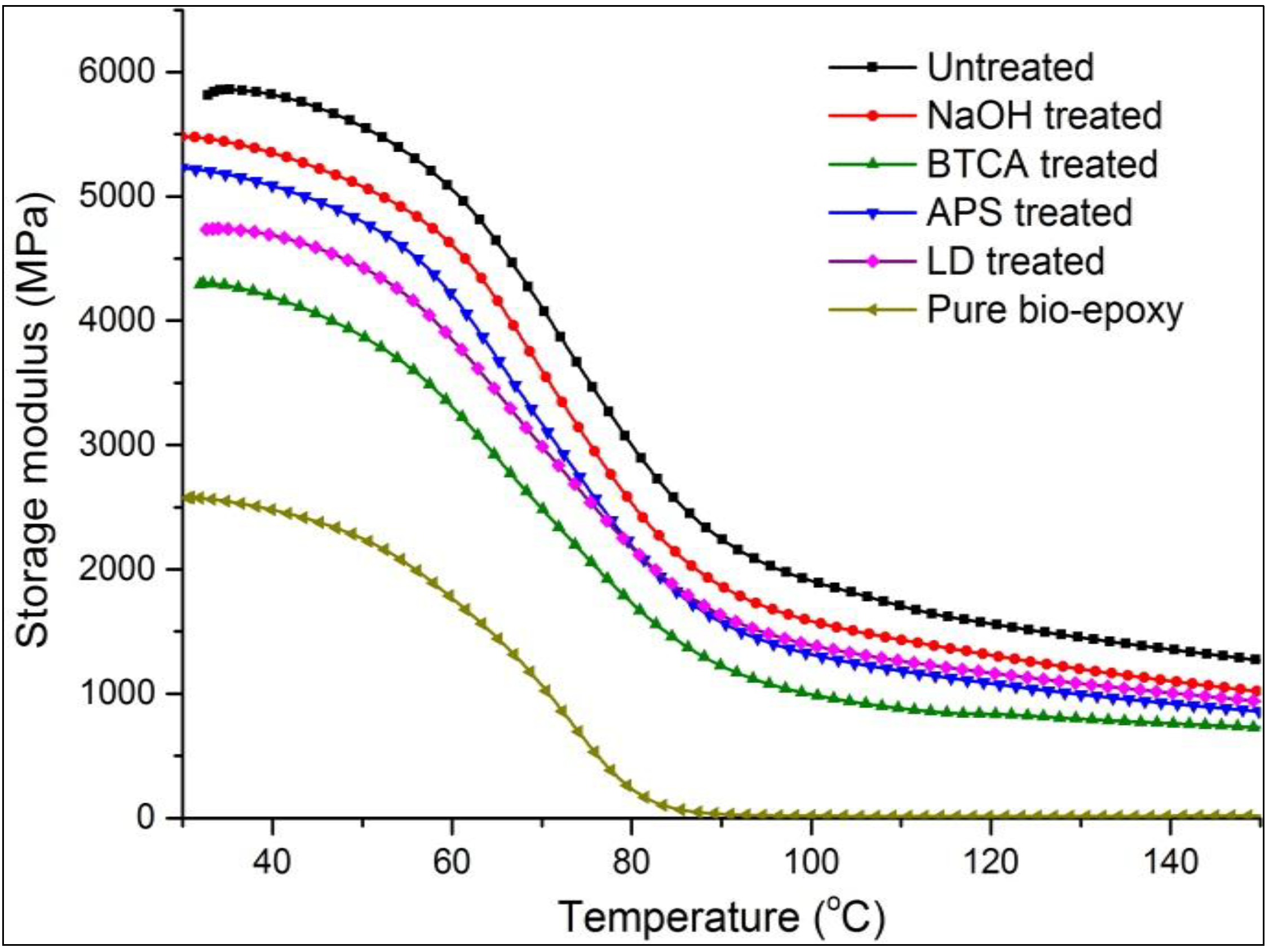
The storage modulus of pure supersap epoxy and composites subjected to the same temperature increase (30 to 150 °C) is shown in Figure 2. Clearly, the addition of flax fibres significantly improved the storage modulus of bio-epoxy resins. The incorporation of chemical treatments leads to a noticeable decrease in modulus of bio-epoxy matrix. The decrease in fibre strength caused by the loss of inter-fibrils matrix (e.g., hemicellulose) during treatments possibly results in fewer constraints on segmental flexibility, hence the reduction in interfacial strength. The highest decrease of stiffness was observed for BTCA composites with nearly 26.9% and 39.9% decrease for storage and flexural modulus, respectively. It is clear from Figure 2 that the storage modulus decreased with a significant fall in the temperature range of approximately 60 to 90 °C due to the glass transition phenomena of bio-epoxy. After the glass transition point, the polymer chain segments are able to move and hence the polymer turns into rubbery state [30]. All the chemical treatments lead to a shift of Tg from 60 °C to slightly lower values (e.g., 53 °C for BTCA treated composites). Surface treatments make the resin adjacent to the fibre/matrix interface stiffer and result in larger gradient of modulus. The transition region is therefore enlarged.
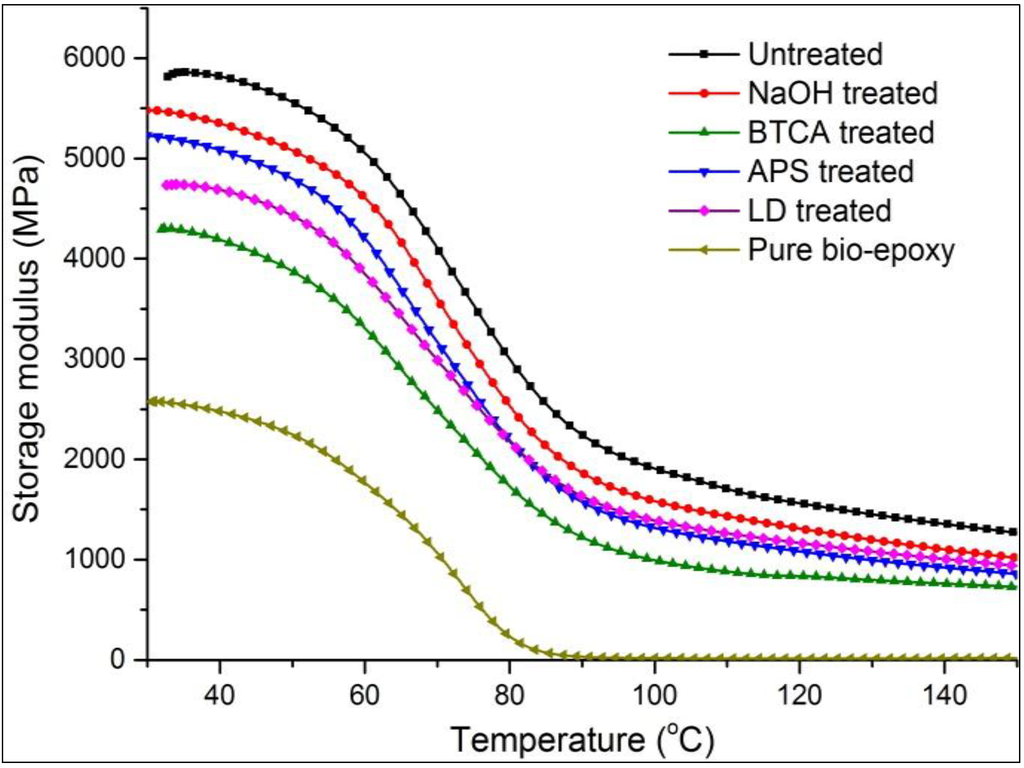
Figure 2.
Variation of storage modulus of resin and flax reinforced epoxy (FE) composites.
Figure 2.
Variation of storage modulus of resin and flax reinforced epoxy (FE) composites.
Loss modulus, which represents the capability of energy dissipation within a material with viscous motions as heat, of FE composites and resin is shown in Figure 3. An α relaxation peak of epoxy resin associated with the glass transition temperature was obtained at 72 °C. Compared to pure epoxy, all the composites showed an increase in Tg (75–77 °C) due to fibre reinforcement effects (Table 4). A β relaxation peak generally may indicate changes in chain segments caused by reorientation in crystalline phase [31]. The non-observation of β transition in flax/supersap composites possibility is the evidence of the absence of crystallinity in flax fibres. The Tg as α relaxation peak shifted slightly to a comparatively lower temperature (75–76 °C), was detected in all treated composites (NaOH, BTCA, APS and LD treated). It has been widely reported that using proper fibre coupling methods, the improvement of interfacial fiber/matrix can cause an increase in glass transition temperature of composites [32]. However, in the present investigation, the treatments had little effect on (increasing) Tg through better interfacial adhesion. This primarily is attributed to the decrease in fibre strength, leading to fewer constraints on segmental flexibility. For the same reason, the highest and lowest loss modulus was found in untreated and BTCA treated composites with the maximum and minimum viscous dissipation, respectively.
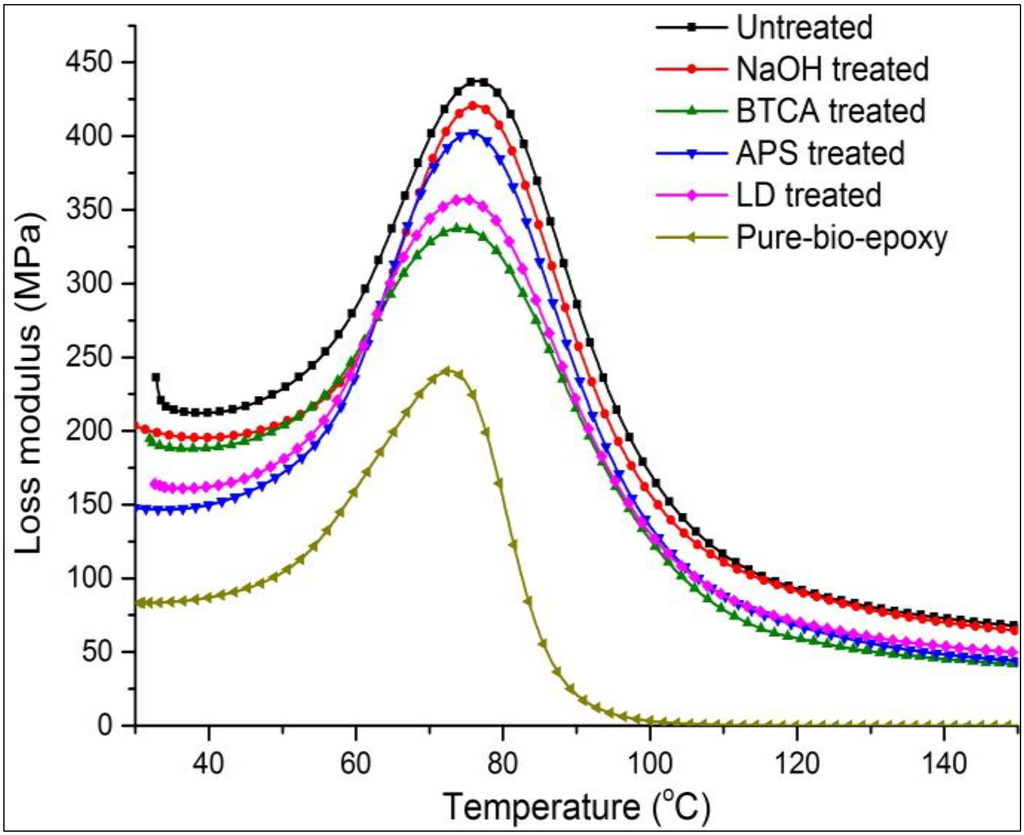
Figure 3.
Effect of treatments on loss modulus of resin and FE composites.
Figure 3.
Effect of treatments on loss modulus of resin and FE composites.
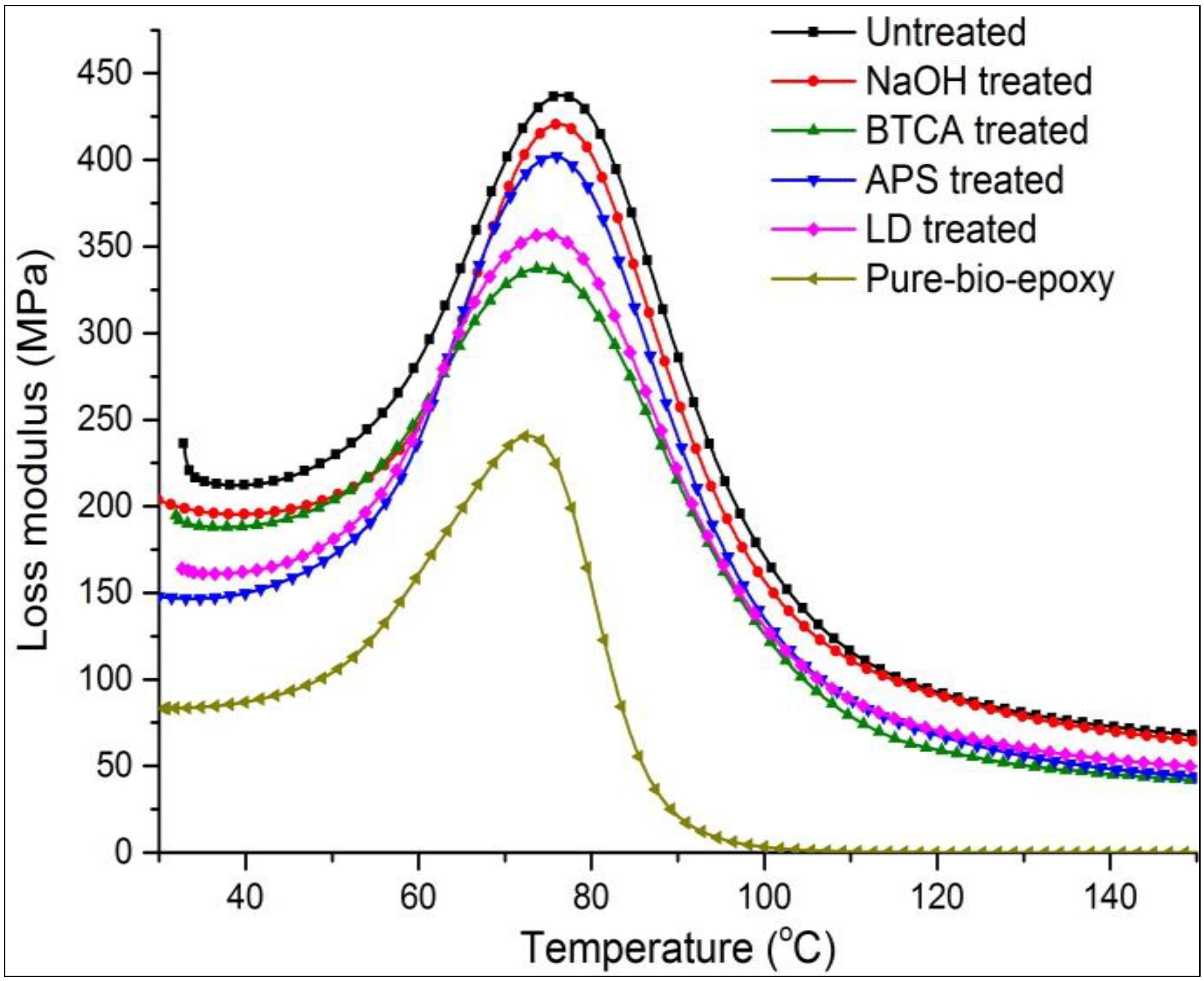

Table 4.
Thermal-mechanical properties of untreated and treated composites.
| Testing material | Tg (Loss) (°C) | Tg (Tanδ) (°C) | Max Eʺ (MPa) | Max Tanδ | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure bio-epoxy | 72.74 | 84.83 | 241 | 0.834 | 0 |
| Untreated | 77.32 | 82.43 | 430 | 0.144 | 1.69 |
| NaOH treated | 75.28 | 81.29 | 400 | 0.176 | 1.61 |
| BTCA treated | 75.49 | 82.00 | 337 | 0.188 | 1.58 |
| APS treated | 76.79 | 81.87 | 356 | 0.155 | 1.66 |
| LD treated | 75.55 | 82.30 | 420 | 0.161 | 1.64 |
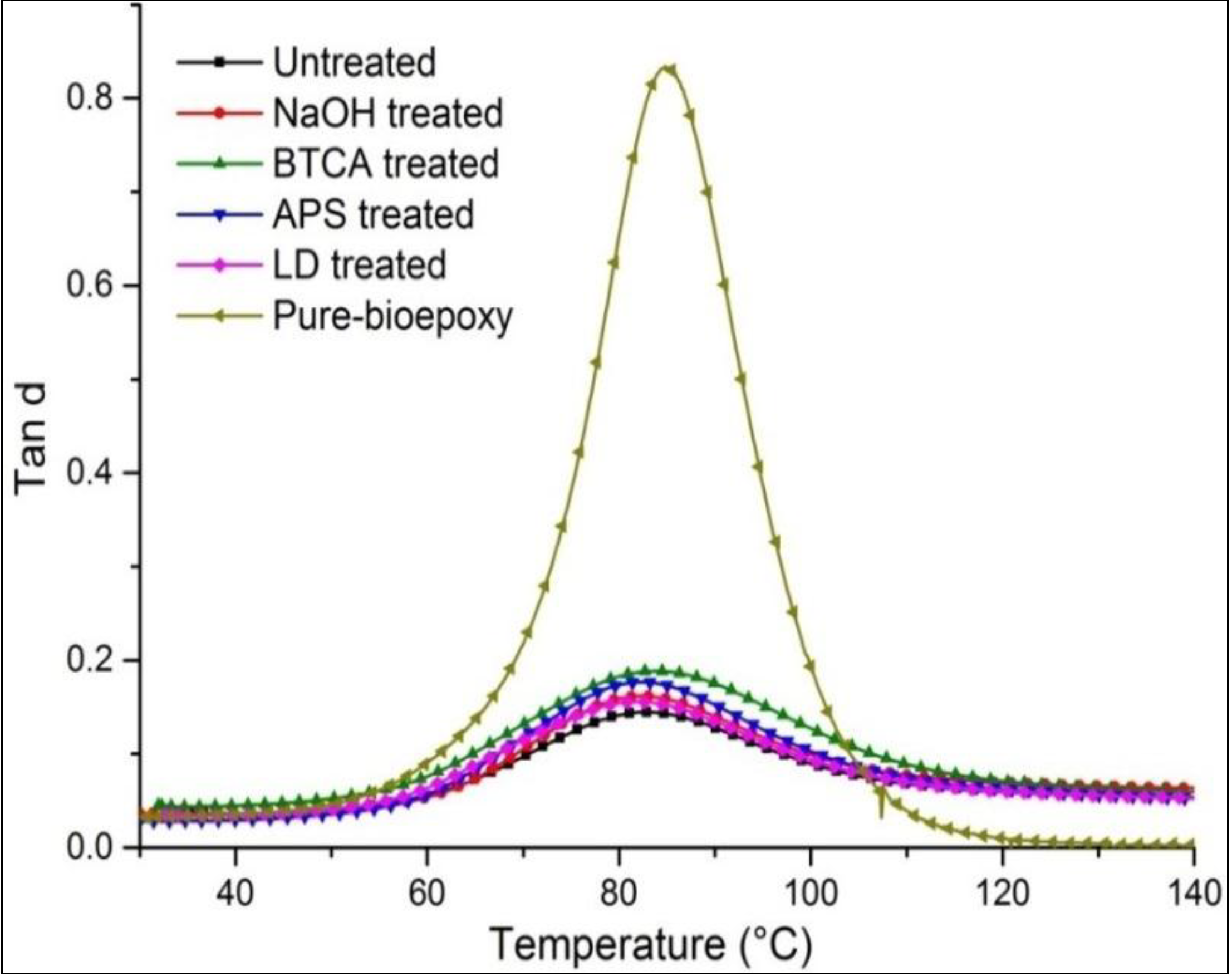
The ratio of storage (elastic) and loss (viscous) modulus is called tanδ (Figure 4). In comparison to the untreated composites, an increase in magnitude of tanδ peak was observed in treated flax/supersap composites. Thus, it will tend to dissipate less energy with lower magnitude of damping peak in comparison to treated composites. The magnitude of tanδ was also reported by Gupta [33] to reflect impact properties of materials. As in the previous study, the untreated composites showed a rebound case subjected to the falling weight impact, while the treated composites broke longitudinally. The untreated FE composites had better damping property, thus dissipating more energy by internal friction.
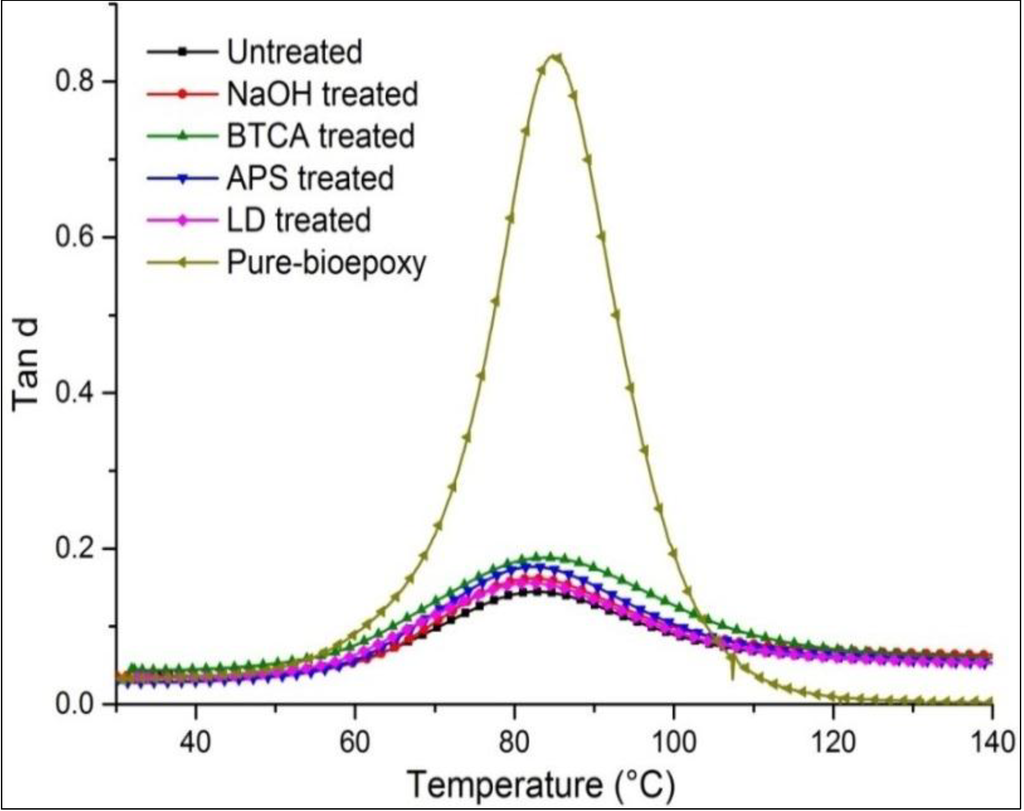
Figure 4.
Representation of tanδ of resin and FE composites with treatments.
Figure 4.
Representation of tanδ of resin and FE composites with treatments.
The bonding properties between flax fibres could also be indicated quantitatively. According to the following equation, the bonding properties for various treated flax composites could be assessed by [24]:
where B is a parameter used to indicate the interfacial bonding strength; for composites; and for pure matrix; is the fibre volume fraction which could be calculated from composite volume , composite weight (Mc), fiber weight ratio (Wf) and resin density (ρm):
The lower value of B parameter indicates lower interfacial strength. From the results summarized in Table 4, B value decreased after all the treatments, possibly owing to the loss of inner matrix of fibre (strength).
3.2. Effect of Treatment on Quasi-Static Tension Properites
The tensile properties of flax/supersap composites were compared through different treatments (non-treated, NaOH, BTCA, APS and Laccase-Doga). Tensile strength and Young’s modulus are shown in Figure 5. The untreated flax/supersap composites exhibited tensile strength and tensile modulus of up to 185 MPa and 14 GPa, respectively. The NaOH treated composites displayed the tensile strength of about 178 MPa, less than 10 MPa reductions in tensile strength. The average tensile strength was observed to be at 175 MPa and 165 MPa for APS and Doga treated composites, respectively. Over 70% reduction of tensile strength was found for the BTCA treated flax/supersap laminates (51 MPa) compared to untreated composites (185 MPa). Clearly, these chemical treatments have no significant effect on improvement in ultimate tensile strength of the composites although they may have positive effect on flax/supersap wettability. The modulus of the elasticity follows the trend: untreated > Doga > APS > NaOH > BTCA. The BTCA treated flax/supersap composites showed the lowest modulus of 5.4 GPa. NaOH treatment was able to maintain the tensile properties at an acceptable level; however the BTCA treatment decreased the tensile properties of the composites. The dissolution of hemicellulose during the treatment increased the fibre/matrix adhesion due to the rough fibre surface; nevertheless the lack of inner matrix (hemicellulose) could possibly give rise to the tensile property reduction of flax fibers themselves. Zhu et al. [34] reported the reduction of tensile properties of non-woven flax mats after alkali, BTCA and APS treatments. A few papers [19,35,36] showed that the chemical treatments only benefit the properties of bio-epoxy composites with high matrix content. As the matrix to fibre ratio decreases below 50 wt%, the fibre properties will contribute more to the composites due to the lack of resin to wet the flax fibres. The selected BTCA treatment may result in the most severe damage of microstructure of flax fibres, hence the insufficient load transfer. The NaOH, APS and Laccase Doga treatments resulted in dissimilar failure mechanisms of fibre/matrix adhesion, but showed similar effects on the tensile properties.
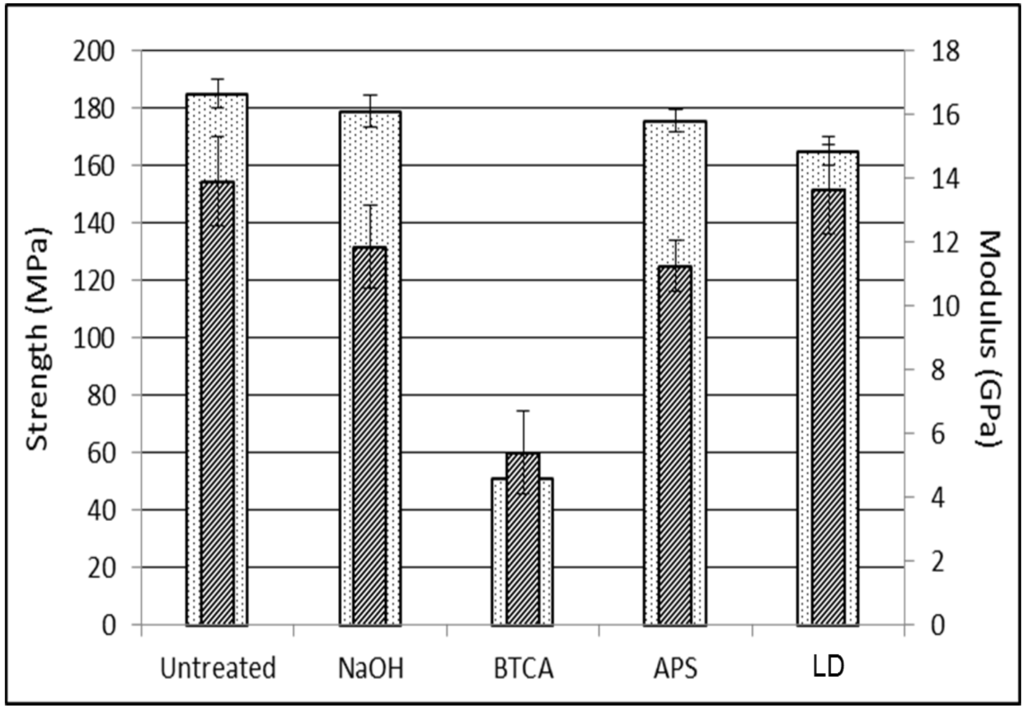
Figure 5.
Tensile strength and modulus of hybrid FE composites.
Figure 5.
Tensile strength and modulus of hybrid FE composites.
Figure 6 shows the representative stress-strain curves obtained from the tension tests of flax/supersap composites with chemical treatments. A quasi-linear behavior was observed for flax/supersap composites, with no clear yield point or transition area. All the curves showed a continuously increasing stress with corresponding increase in strain up to a sudden brittle failure point, after which the force dropped dramatically. The failure progress for non-woven fibre mat reinforced composites in tension has been reported in literature [37,38]. The failure started at the existing cracks or weak sites between the fibres. A substantial reduction of stiffness took place through a series of steps, causing a decrease in the initial slope of the stress/strain curve. Untreated and APS specimens showed the highest elongation of up to 1.7% at the breaking point, while the BTCA composites showed the lowest modulus and breaking elongation at approximately 1.2%. It should however be noted that the NaOH treated composites had a lower decrease in stiffness than untreated specimens. The increase in fibre/matrix adhesion after NaOH treatment may result in relatively difficult fibre re-orientation and crack propagation.
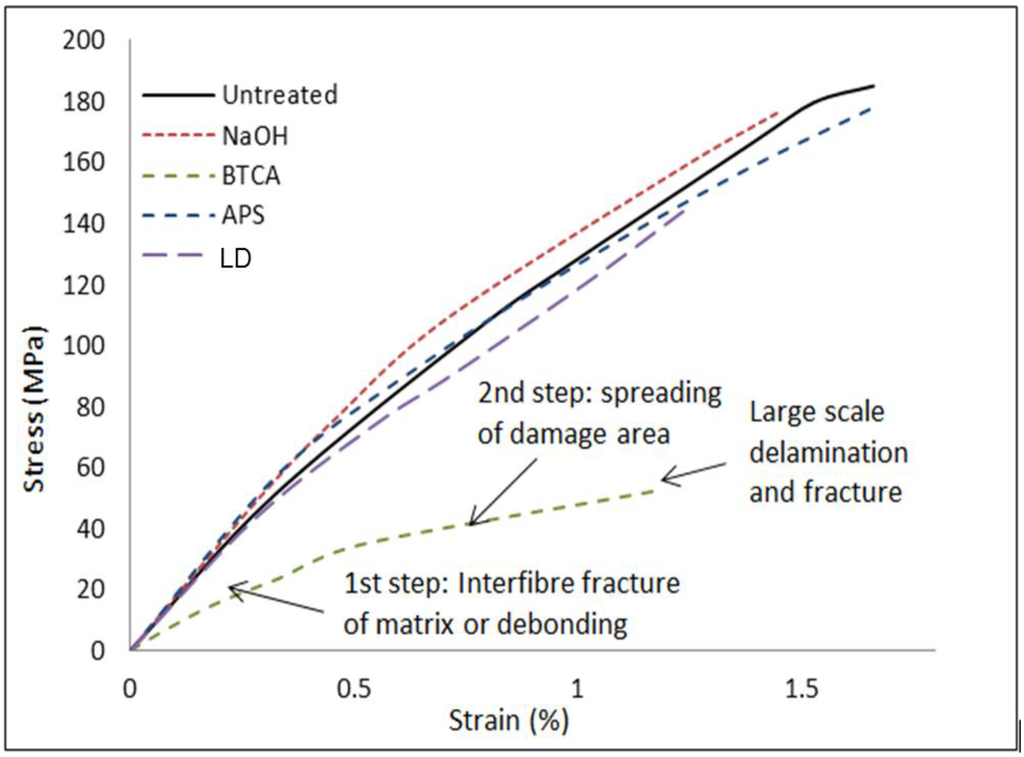
Figure 6.
Stress-strain curves of hybrid FE composites.
Figure 6.
Stress-strain curves of hybrid FE composites.
3.3. Effect of Treatment on UV and Xenon Aging Properties
All the samples not only showed visible changes in colour and colour intensity on the sample surface, but also slight distortion of the samples after the test procedure. Visual changes in the samples can be seen in Figure 7. Large changes were observed after 500 h of Xenon exposure. A small layer of the epoxy resin was degraded off from the surface and also fibres were changed so that there was only white cellulose left on the surface forming a hairy surface. The composites with modified flax mats seem to restrict the changes caused by weathering (visually) a bit better than composite without flax modification. Compared to Xenon exposure, the UV-B used in this test was less effective in degrading the material surface.
The tensile properties of the composites after freeze + UV cycle conditions are shown in the Table 5. It is apparent that the aging condition had only visual effects on the tensile properties of untreated composites as they retained (almost) the same strength (185 MPa) and tensile modulus (14 GPa). The tension strength of NaOH treated composites dropped around 18% from 178 MPa to 147 MPa. LD treated composites showed similar tensile modulus of 13.67 GPa with a slight 8 MPa decrease in tensile strength after aging. For the 500 h Xenon-exposure condition, APS type maintenied its mechanical property. The samples retained tensile strength and modulus at 175 MPa and 11 GPa, respectively. All treated composites had very good mechanical-property resistance to the 500 h exposure condition with up to or less than 10% decrease in the tensile properties. The NaOH treated composites exhibited almost tensile modulus of 11.8 GPa after Xenon conditioning. However, the tension strength and modulus of untreated composites decreased 7% and 36%, respectively.
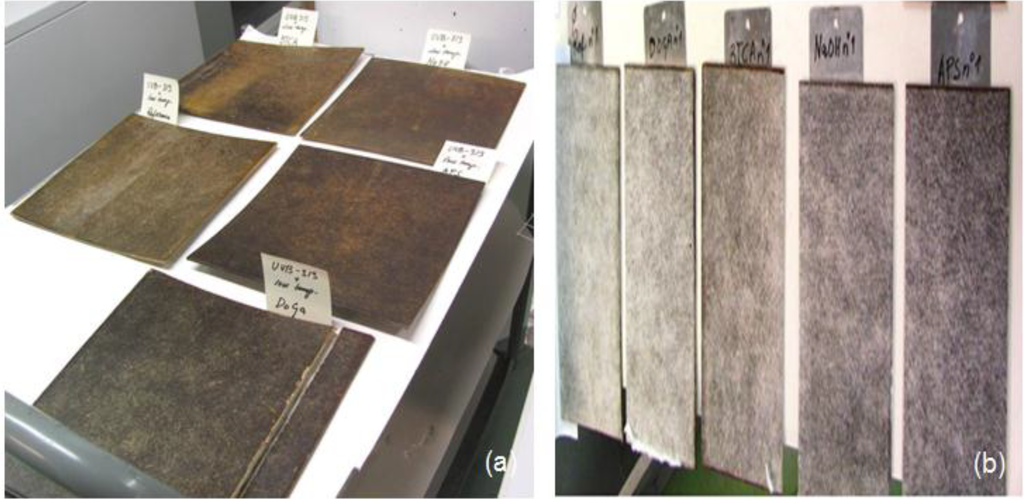

Figure 7.
Flax/supersap bio-epoxy composites samples with and without treatments after aging condition: (a) UV radiation for 552 h; (b) Xenon light for 500 h.
Figure 7.
Flax/supersap bio-epoxy composites samples with and without treatments after aging condition: (a) UV radiation for 552 h; (b) Xenon light for 500 h.
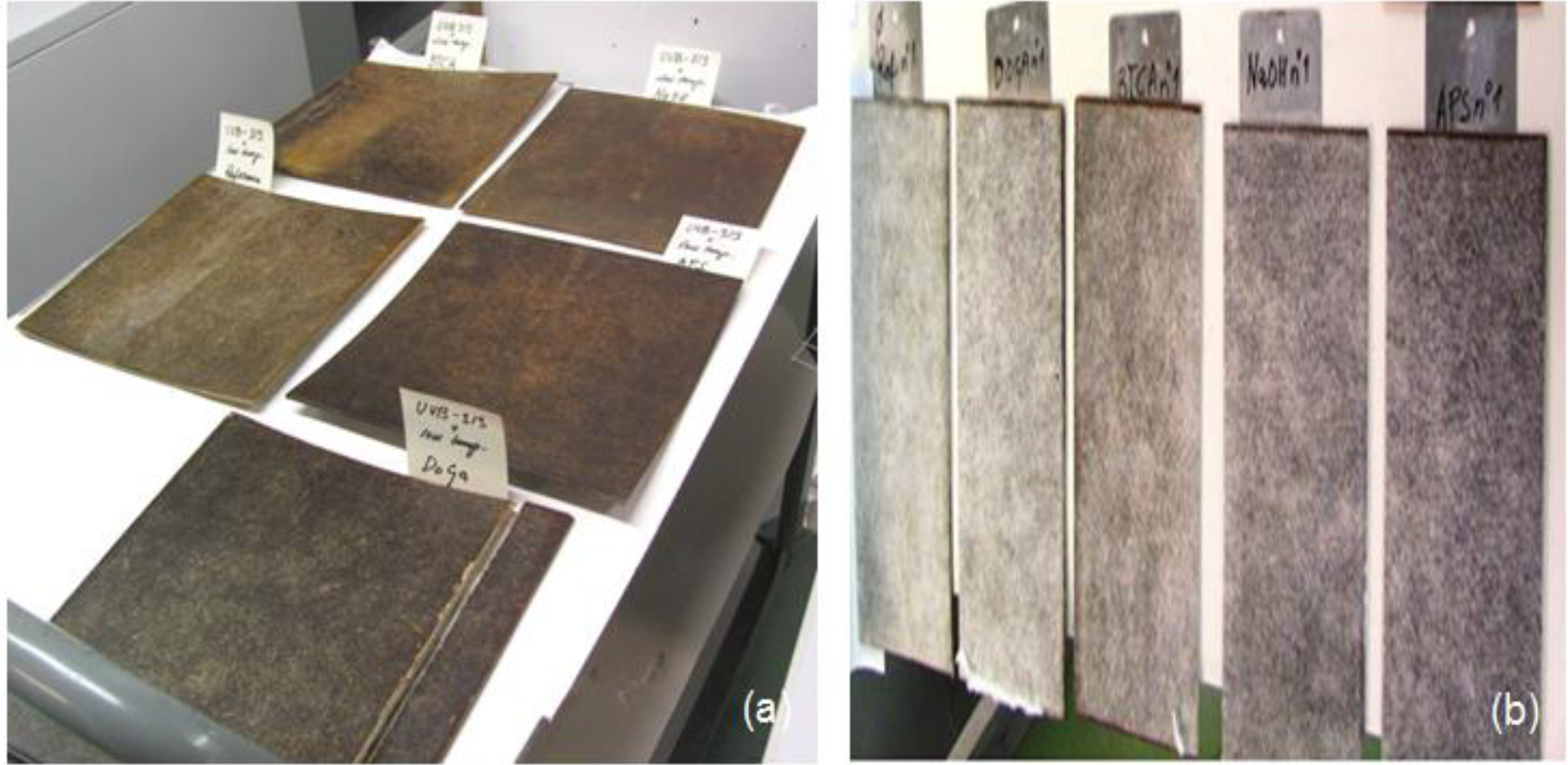


Table 5.
Tension properties of hybrid flax/supersap bio-epoxy composites with different treatments in weathering conditions.
| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | UV | Xenon | Normal | UV | Xenon | |
| Untreated | 185.4 ± 8.5 | 185.4 ± 7.8 | 172.2 ± 8.1 | 13.9 ± 0.4 | 14.0 ± 0.3 | 8.8 ± 0.4 |
| NaOH | 178.5 ± 6.4 | 146.9 ± 6.4 | 169.8 ± 6.5 | 11.9 ± 0.5 | 10.5 ± 0.4 | 11.8 ± 0.5 |
| BTCA | 51.7 ± 6.1 | 40.2 ± 5.8 | 45.9 ± 6.2 | 6.4 ± 0.6 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 6.0 ± 0.2 |
| APS | 175.4 ± 6.2 | 157.3 ± 8.2 | 175.1 ± 6.2 | 11.3 ± 0.4 | 9.8 ± 0.5 | 11.5 ± 0.6 |
| LD | 164.5 ± 5.7 | 157.1 ± 7.0 | 160.3 ± 5.6 | 13.7 ± 0.4 | 13.7 ± 0.2 | 11.9 ± 0.3 |
4. Conclusions
The untreated new flax/epoxy composites (tensile strength of around 185 MPa) show a good potential to be used in automobile applications. Pure NaOH treatment is the most promising one amongst the treatments performed in this study. NaOH composites maintained the tensile strength of around 180 MPa, however, BTCA and other treatments decreased the tensile strength. The improvement in fibre/matrix wettability may not be able to compensate the reduction in fibre strength (due to the removal of interfibrillar matrix by general treatments). The fibre treatments had little effect on glass transition temperature (approximately 75 °C).
This work also suggests that the applied treatments for fibre/supersap bio-epoxy composites (57 wt% fibre ratio) can significantly improve Xenon aging resistance, but have little effect on UV aging. For UV and Xenon aging, the composites with modified flax mats did not show any visual change, which was a bit better than composites without flax modification. With respect to the tensile properties, the untreated composites had the best performance after UV exposure, while for Xenon exposure; the four treated composites (NaOH, BTCA, APS and LD) showed much better resistance.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful for the financial support by the European Commission and the FP7 ECOSHELL Project (Project Reference No. 265838) and would like to acknowledge technical support at Cranfield University and Ecotechnilin for their material support.
Author Contributions
The Jinchun Zhu designed the study, performed the experiments and analysis, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Other authors managed the analyses of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests. The funding sponsors had roles in the design of the study and in the decision to publish results.
References
- Zhu, J.; Abhyankar, H.; Nassiopoulos, E.; Njuguna, J. Tannin-based flax fibre reinforced composites for structural applications in vehicles. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 40, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avril, C.; Bailly, P.A.; Njuguna, J.; Nassiopoulos, E.; Larminat, D.A. Development of Flax-Reinforced Bio-Composites for High-Load Bearing Automotive Parts. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Composite Materials (ECCM), Venice, Italy, 24–28 June 2012.
- Fan, J.; Nassiopoulos, E.; Brighton, J.; de Larminat, A.; Njuguna, J. New Structural Biocomposites for Car Applications. In Proceedings of the Society of Plastics Engineers—EUROTEC 2011 Conference Proceedings, Barcelona, Spain, 3–5 October 2011.
- Adekunle, K.; Cho, S.-W.; Ketzscher, R.; Skrifvars, M. Mechanical properties of natural fiber hybrid composites based on renewable thermoset resins derived from soybean oil, for use in technical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 4530–4541. [Google Scholar]
- Adekunle, K.; Cho, S.-W.; Patzelt, C.; Blomfeldt, T.; Skrifvars, M. Impact and flexural properties of flax fabrics and Lyocell fiber-reinforced bio-based thermoset. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2011, 30, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, J.D.; Shapiro, A.A.; Earthman, J.C.; Saphores, J.-M.; Ogunseitan, O.A. Design and evaluation of bioepoxy-flax composites for printed circuit boards. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2008, 31, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Bledzki, A.K.; Heim, H.-P.; Böttcher, A. Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites Made from Renewable Resources. In Proceedings of the International SAMPE Technical Conference, Forth Worth, TX, USA, 17–21 October 2011.
- Felline, F.; Pappadà, S.; Gennaro, R.; Passaro, A. Resin transfer moulding of composite panels with bio-based resins. SAMPE J. 2013, 49, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Netravali, A. Characterization of flax fiber reinforced soy protein resin based green composites modified with nano-clay particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K. High quality flax fibre composites manufactured by the resin transfer moulding process. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2001, 20, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Njuguna, J.; Abhyankar, H.; Zhu, H.; Perreux, D.; Thiebaud, F.; Chapelle, D.; Pizzi, A.; Sauget, A.; de Larminat, A.; Nicollin, A. Effect of fibre configurations on mechanical properties of flax/tannin composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Abhyankar, H.; Njuguna, J. Effect of Fibre Treatment on Water Absorption and Tensile Properties of Flax/Tannin Composites. In Proceedings of the ICMR 2013, Cranfield, UK, 19–20 September 2013.
- Summerscales, J.; Dissanayake, N.P.J.; Virk, A.S.; Hall, W. A review of bast fibres and their composites. Part 1—Fibres as reinforcements. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, G.; Arbelaiz, A.; Llano-Ponte, R.; Mondragon, I. Effects of fibre treatment on wettability and mechanical behaviour of flax/polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaith, B.S.; Kalia, S. Grafting of flax fiber (Linum usitatissimum) with vinyl monomers for enhancement of properties of flax-phenolic composites. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Carpenter, J.; Hill, C. Deformation and fracture behaviour of flax fibre reinforced thermosetting polymer matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2499–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähn, A.; Schröder, M.W.; Füting, M.; Schenzel, K.; Diepenbrock, W. Characterization of alkali treated flax fibres by means of FT Raman spectroscopy and environmental scanning electron microscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2002, 58, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Njuguna, J.; Abhyankar, H. Recent development of flax fibres and their reinforced composites based on different polymeric matrices. Materials 2013, 6, 5171–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chouw, N.; Yuan, X. Improving the mechanical properties of natural fibre fabric reinforced epoxy composites by alkali treatment. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Weyenberg, I.; Chi Truong, T.; Vangrimde, B.; Verpoest, I. Improving the properties of UD flax fibre reinforced composites by applying an alkaline fibre treatment. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix, S.; Lebrun, L.; Morvan, C.; Marais, S. Study of water behaviour of chemically treated flax fibres-based composites: A way to approach the hydric interface. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.-P.; Specht, K. Unidirectional hemp and flax EP- and PP-composites: Influence of defined fiber treatments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Recent developments in chemical modification and characterization of natural fiber-reinforced composites. Polym. Compos. 2008, 29, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Chemical modification of flax reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assarar, M.; Scida, D.; El Mahi, A.; Poilâne, C.; Ayad, R. Influence of water ageing on mechanical properties and damage events of two reinforced composite materials: Flax-fibres and glass-fibres. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamboulis, A.; Baillie, C.A.; Garkhail, S.K.; Van Melick, H.G.H.; Peijs, T. Environmental durability of flax fibres and their composites based on polypropylene matrix. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2000, 7, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039; Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ISO 4892-3:2013; Plastics. Methods of exposure to laboratory light sources.—Part 3: Fluorescent UV lamps; BSI, International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 4892-2:2013; Plastics. Methods of exposure to laboratory light sources.—Part 2: Xenon-arc lamps; BSI, International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Birley, A.W. Physics of Plastics: Processing, Properties, and Materials Engineering; Hanser Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Short bamboo fiber-reinforced HDPE composites: Influence of fiber content and modification on strength of the composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tabil, L.; Panigrahi, S. Effects of chemical treatments on mechanical and physical properties of flax fiber-reinforced composites. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2008, 15, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Raju Mantena, P.; Al-Ostaz, A. Dynamic mechanical and impact property correlation of nanoclay and graphite platelet reinforced vinyl ester nanocomposites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Brighton, J.; Zhu, H.; Abhyankar, H. Effect of alkali, esterification and silane surface treatments on properites of flax fibres. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chabba, S.; Netravali, A.N. “Green” composites Part 1: Characterization of flax fabric and glutaraldehyde modified soy protein concentrate composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 6263–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Weyenberg, I.; Ivens, J.; De Coster, A.; Kino, B.; Baetens, E.; Verpoest, I. Influence of processing and chemical treatment of flax fibres on their composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-J.; Jang, J. Effect of fibre content on the mechanical properties of glass fibre mat/polypropylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garkhail, S.K.; Heijenrath, R.W.H.; Peijs, T. Mechanical properties of natural-fibre-mat-reinforced thermoplastics based on flax fibres and polypropylene. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2000, 7, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
