Release of Carbon Nanotubes from Polymer Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| ABS | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
|---|---|
| ATR-FTIR | Attenuated total reflectance—fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| AUC | Analytical ultracentrifugation |
| CNF | Carbon nanofiber |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| CRP | Carbon fiber reinforced plastic |
| EVA | Ethylene-vinyl acetate |
| PA6 | Polyamide 6, Nylon 6 |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PEN | Polyethylene naphthalate |
| PMMA | Poly(methyl methacrylate) |
| POM | Polyoxymethylene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| SMPS | Scanning mobility particle sizer |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
2. Results of Release Studies
2.1. Release of Particles Due to Mechanical Impact
| Study | Material | Particle generation method | Nanofiller release? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mazzuckelli et al. [33] | CNF/polymer composite | Composite preparation and wet sawing | Free standing CNFs collected on filter after CNF weighing and wet sawing |
| Bello et al. [34,35,36] | Microfiber (carbon or alumina)/CNT/epoxy composite | Wet and dry drilling, band-sawing under dry conditions, and sawing with a rotary cutting wheel under wet conditions | Submicron and sharp fibers found for all samples, release of CNT agglomerates only for drilling |
| Cena and Peters [37] | CNT/epoxy composite | Sanding | Release of nanosized particles with irregular shapes and protruded CNTs, no free standing CNTs found |
| Wohlleben et al. [25,28] | CNT/POM and CNT/PU composites | Sanding and Taber Abraser | No nanofiller release |
| Methner et al. [38] | CNF/epoxy composite | Wet sawing, surface grinding, and belt sawing | Free standing CNFs found in the process area and at the personal breathing zone |
| Ogura et al. [39] | SWCNT/PP composite | Microgrinder | Particles with protruding SWCNTs, no release of free standing SWCNTs |
| Golanski et al. [40] | CNT/PC and CNT/PA6 composites | Rake and metallic brush | No release for the rake, release of CNTs by metallic brush only when CNTs are poorly distributed in the polymer matrix |
| Schlagenhauf et al. [27] | CNT/epoxy composite | Taber Abraser | Release of CNTs (average length ≈ 304 nm) |
| Hellmann et al. [41] | CNT/epoxy composite | Sanding | Particles with protruding CNTs, no release of free standing CNTs |
| Huang et al. [42] | CNT/epoxy composite | Sanding | No release of CNTs except for a 4 wt% CNT sample |
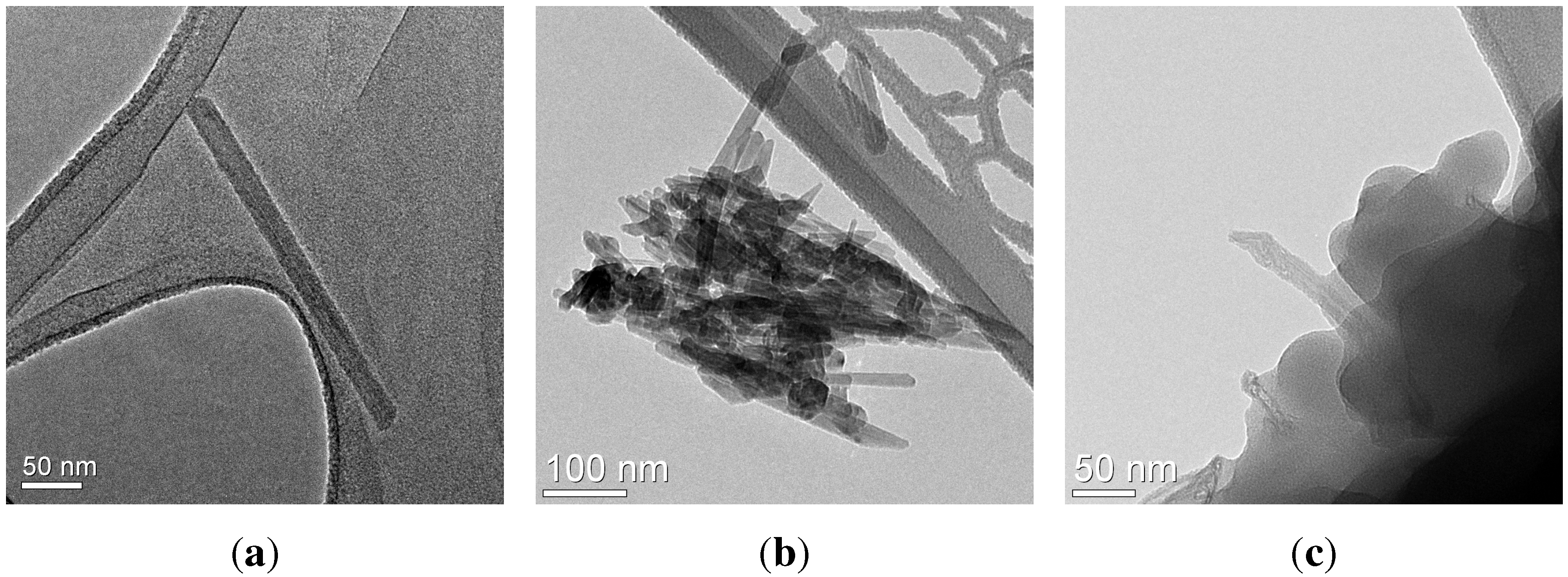
2.2. Release Due to Weathering Processes
| Study | Material | Weathering process | Nanofiller release? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nguyen et al. [53,54] and Petersen et al. [55] | CNT/epoxy composite | UV degradation | Formation of a CNT layer on the surface, no release of CNTs |
| Bocchini et al. [56] | CNT/PP and CNT/PE composites | UV degradation | Not measured |
| Wohlleben et al. [25,28] and Hirth et al. [57] | CNT/POM, CNT/epoxy, and CNT/PU composites | UV degradation with or without moisture | Release of CNTs only when high shear forces are applied on released particles |
| Asmatulu et al. [58] | CNT/epoxy composite | UV degradation only or with salt fog | Not measured |
| Orlov et al. [59] | Different CNT/polymer composites | UV degradation with moisture | Loose CNTs on surface and in cracks are observed by SEM, a release of CNTs was not measured |
| Vilar et al. [60] | CNT/PA6 composite | UV degradation with moisture | Exposed CNTs on the sample surface, weathered and calcinated samples showed a release of CNTs |
| Busquets-Fitè et al. [61] | CNT/PP, CNT/EVA, and CNT/PA6 composites | UV degradation with moisture | No release of CNTs |
| Ging et al. [62] | CNT/epoxy composite with neat and amino functionalized CNTs | UV degradation with high humidity | Formation of a CNT layer on the surface, release not measured |
| Barkoula et al. [48] | CNT/CRP/epoxy composite | Water bath | Not measured |
| Starkova et al. [49] | CNT/epoxy composite | Humidity | Not measured |

2.3. Release Due to Fire
| Study | Material | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Kashiwagi et al. [7,65,66,67] | CNT/PP, CNT/PS, and CNT/PMMA composites | Partially oxidized CNTs found in char with oxidized CNT catalyst |
| Schartel et al. [68] | CNT/PA6 composite | Residuals consisted of a CNT network |
| Verdejo et al. [69] | CNT/silicone foam | Residuals consisted of a CNT network |
| Kim et al. [70] | CNT/PEN composite | Residuals consisted of a CNT network |
| Fu et al. [71] | CNT/wood/PE and CNT-OH/wood/PE composites | Free CNTs on char surface for CNT/wood/PE composite, no CNTs found on char for CNT-OH/wood/PE composite |
| Zammarano et al. [72], Nyden et al. [73], Uddin et al. [74] | CNF/PU foam | No CNFs in smoke, free CNFs found in char, aerosolization of CNFs from the char due to shaking |
| Dittrich et al. [75] | Different carbonaceous nanofillers in PP composites | Formation of residual protection layer, no further investigation of the char |
| Bouillard et al. [76] | CNT/ABS composite | Release of free CNTs and agglomerates of CNTs into air during burning in furnace |

3. Conclusions
| Polymer | Abrasion | Weathering | Fire |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | [76] | ||
| Epoxy | [27,34,35,36,37,38,41,42] | [48,49,53,54,55,57,58,62] | |
| EVA | [61] | ||
| PA6 | [40] | [60,61] | [68] |
| PC | [40] | ||
| PE | [56] | [71] | |
| PEN | [70] | ||
| PMMA | [66,67] | ||
| POM | [25] | [25] | |
| PP | [39] | [56,61] | [7,65,75] |
| PS | [67] | ||
| PU | [28] | [28] | [72,73,74] |
| Silicone | [69] |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coleman, J.N.; Khan, U.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Mechanical reinforcement of polymers using carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Khan, U.; Blau, W.J.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Small but strong: A review of the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube-polymer composites. Carbon 2006, 44, 1624–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Gibson, R.F.; Gordaninejad, F.; Suhr, J. Energy absorption capability of nanocomposites: A review. Composit. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2392–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, L.F.; Brostow, W.; Devaux, E.; Lopez, B.L.; Perez, L.D. Scratch and wear resistance of polyamide 6 reinforced with multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, C.T.H.; Wu, Y.; Fan, S. Aligned carbon nanotube composite films for thermal management. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollertz, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Gutmann, H.; Geiger, T.; Nueesch, F.A.; Chu, B.T.T. Improvement of toughness and electrical properties of epoxy composites with carbon nanotubes prepared by industrially relevant processes. Nanotechnology 2011, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Grulke, E.; Hilding, J.; Harris, R.; Awad, W.; Douglas, J. Thermal degradation and flammability properties of poly(propylene)/carbon nanotube composites. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2002, 23, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, O.; Sundararaj, U. Big returns from small fibers: A review of polymer/carbon nanotube composites. Polym. Composit. 2004, 25, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, C.; Zepp, R.; Andrady, A.; Boverhof, D.; Fehir, R.; Hawkins, D.; Roberts, J.; Sayre, P.; Shelton, B.; Sultan, Y.; Vejins, V.; Wohlleben, W. Release Characteristics of Selected Carbon Nanotube Polymer Composites. Carbon 2014, 68, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.; Riediker, M.; Wick, P.; Mohr, M.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Oxidative stress and inflammation response after nanoparticle exposure: Differences between human lung cell monocultures and an advanced three-dimensional model of the human epithelial airways. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, S27–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Li, N.; Nel, A.E. Potential Health Impact of Nanoparticles. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2009, 30, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helland, A.; Wick, P.; Koehler, A.; Schmid, K.; Som, C. Reviewing the environmental and human health knowledge base of carbon nanotubes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulskamp, K.; Diabate, S.; Krug, H.F. Carbon nanotubes show no sign of acute toxicity but induce intracellular reactive oxygen species in dependence on contaminants. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma-Hock, L.; Treumann, S.; Strauss, V.; Brill, S.; Luizi, F.; Mertler, M.; Wiench, K.; Gamer, A.O.; van Ravenzwaay, B.; Landsiedel, R. Inhalation Toxicity of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes in Rats Exposed for 3 Months. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 112, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomaki, J.; Valimaki, E.; Sund, J.; Vippola, M.; Clausen, P.A.; Jensen, K.A.; Savolainen, K.; Matikainen, S.; Alenius, H. Long, Needle-like Carbon Nanotubes and Asbestos Activate the NLRP3 Inflammasome through a Similar Mechanism. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6861–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurnherr, T.; Brandenberger, C.; Fischer, K.; Diener, L.; Manser, P.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Kaiser, J.P.; Krug, H.F.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Wick, P. A comparison of acute and long-term effects of industrial multiwalled carbon nanotubes on human lung and immune cells in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 200, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, A.R.; Som, C.; Helland, A.; Gottschalk, F. Studying the potential release of carbon nanotubes throughout the application life cycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardak, A.; Gorman, M.E.; Swami, N.; Deshpande, S. Identification of risks in the life cycle of nanotechnology-based products. J. Ind. Ecol. 2008, 12, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, L.C.; Maynard, A.D. Exposure Assessment Approaches for Engineered Nanomaterials. Risk Anal. 2010, 30, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, F.; Nowack, B. The release of engineered nanomaterials to the environment. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.J.; Zhang, L.W.; Mattison, N.T.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Whelton, A.J.; Uddin, N.; Nguyen, T.; Huang, Q.G.; Henry, T.B.; Holbrook, R.D.; et al. Potential Release Pathways, Environmental Fate, And Ecological Risks of Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9837–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowack, B.; Ranville, J.F.; Diamond, S.; Gallego-Urrea, J.A.; Metcalfe, C.; Rose, J.; Horne, N.; Koelmans, A.A.; Klaine, S.J. Potential scenarios for nanomaterial release and subsequent alteration in the environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fissan, H.; Horn, H.G.; Stahlmecke, B.; Wang, J. From nanoobject release of (Bio)nanomaterials to exposure. BioNanoMaterials 2013, 14, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorbau, M.; Hillemann, L.; Stintz, M. Method for the characterization of the abrasion induced nanoparticle release into air from surface coatings. J. Aerosol Sci. 2009, 40, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlleben, W.; Brill, S.; Meier, M.W.; Mertler, M.; Cox, G.; Hirth, S.; von Vacano, B.; Strauss, V.; Treumann, S.; Wiench, K.; et al. On the Lifecycle of Nanocomposites: Comparing Released Fragments and their In-Vivo Hazards from Three Release Mechanisms and Four Nanocomposites. Small 2011, 7, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golanski, L.; Gaborieau, A.; Guiot, A.; Uzu, G.; Chatenet, J.; Tardif, F. Characterization of abrasion-induced nanoparticle release from paints into liquids and air. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2011, 304, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlagenhauf, L.; Chu, B.T.T.; Buha, J.; Nueesch, F.; Wang, J. Release of Carbon Nanotubes from an Epoxy-Based Nanocomposite during an Abrasion Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7366–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlleben, W.; Meier, M.W.; Vogel, S.; Landsiedel, R.; Cox, G.; Hirth, S.; Tomovic, Z. Elastic CNT-polyurethane nanocomposite: synthesis, performance and assessment of fragments released during use. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koponen, I.K.; Jensen, K.A.; Schneider, T. Sanding dust from nanoparticle-containing paints: Physical characterisation. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2009, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, I.K.; Jensen, K.A.; Schneider, T. Comparison of dust released from sanding conventional and nanoparticle-doped wall and wood coatings. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohler, D.; Stintz, M.; Hillemann, L.; Vorbau, M. Characterization of Nanoparticle Release from Surface Coatings by the Simulation of a Sanding Process. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2010, 54, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Asbach, C.; Fissan, H.; Goehler, D.; Stintz, M. Nanoparticle exposure at nanotechnology workplaces: A review. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzuckelli, L.F.; Methner, M.M.; Birch, M.E.; Evans, D.E.; Ku, B.K.; Crouch, K.; Hoover, M.D. Identification and characterization of potential sources of worker exposure to carbon nanofibers during polymer composite laboratory operations. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2007, 4, D125–D130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, D.; Wardle, B.L.; Yamamoto, N.; deVilloria, R.G.; Garcia, E.J.; Hart, A.J.; Ahn, K.; Ellenbecker, M.J.; Hallock, M. Exposure to nanoscale particles and fibers during machining of hybrid advanced composites containing carbon nanotubes. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, D.; Wardle, B.L.; Zhang, J.; Yamamoto, N.; Santeufemio, C.; Hallock, M.; Virji, M.A. Characterization of Exposures to Nanoscale Particles and Fibers During Solid Core Drilling of Hybrid Carbon Nanotube Advanced Composites. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2010, 16, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, D.; Wardle, B.L.; Yamamoto, N.; deVilloria, R.G.; Hallock, M. Exposures to Nanoscale Particles and Fibers During Handling,Processing, and Machining of Nanocomposites and Nanoengineered Composites Reinforced with Aligned Carbon Nanotubes. In Proceedings of the 17th International conference on composite materials (ICCM), Edinburgh, Scotland, July 27–31, 2011.
- Cena, L.G.; Peters, T.M. Characterization and Control of Airborne Particles Emitted During Production of Epoxy/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2011, 8, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methner, M.; Crawford, C.; Geraci, C. Evaluation of the Potential Airborne Release of Carbon Nanofibers During the Preparation, Grinding, and Cutting of Epoxy-Based Nanocomposite Material. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2012, 9, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, I.; Kotake, M.; Shigeta, M.; Uejima, M.; Saito, K.; Hashimoto, N.; Kishimoto, A. Potential release of carbon nanotubes from their composites during grinding. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2013, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golanski, L.; Guiot, A.; Pras, M.; Malarde, M.; Tardif, F. Release-ability of nano fillers from different nanomaterials (toward the acceptability of nanoproduct). J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, A.; Schmidt, K.; Ripperger, S.; Berges, M. Release of ultrafine dusts during the machining of nanocomposites. Gefahrst. Reinhalt. Luft 2012, 72, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Park, J.; Cena, L.; Shelton, B.; Peters, T. Evaluation of airborne particle emissions from commercial products containing carbon nanotubes. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailhot, B.; Morlat-Thérias, S.; Bussière, P.O.; Gardette, J.L. Study of the Degradation of an Epoxy/Amine Resin, 2. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2005, 206, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhot, N.; Morlat-Theias, S.; Ouahioune, M.; Gardette, J.L. Study of the degradation of an epoxy/amine resin, 1 photo- and thermo-chemical mechanisms. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2005, 206, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Maxted, J.; Barber, A.; Lowe, C.; Smith, R. The durability of clear polyurethane coil coatings studied by FTIR peak fitting. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Pellegrin, B.; Bernard, C.; Rabb, S.; Stuztman, P.; Gorham, J.M.; Gu, X.; Yu, L.L.; Chin, J.W. Characterization of Surface Accumulation and Release of Nanosilica During Irradiation of Polymer Nanocomposites by Ultraviolet Light. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 6202–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celina, M.C.; Dayile, A.R.; Quintana, A. A perspective on the inherent oxidation sensitivity of epoxy materials. Polymer 2013, 54, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkoula, N.M.; Paipetis, A.; Matikas, T.; Vavouliotis, A.; Karapappas, P.; Kostopoulos, V. Environmental degradation of carbon nanotube-modified composite laminates: A study of electrical resistivity. Mech. Composit. Mater. 2009, 45, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Buschhorn, S.T.; Mannov, E.; Schulte, K.; Aniskevich, A. Water transport in epoxy/MWCNT composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2138–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popineau, S.; Rondeau-Mouro, C.; Sulpice-Gaillet, C.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Free/bound water absorption in an epoxy adhesive. Polymer 2005, 46, 10733–10740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hoa, S.V.; Pugh, M. Water uptake of epoxy-clay nanocomposites: Model development. Composit. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 3308–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hoa, S.V.; Pugh, M. Water uptake of epoxy-clay nanocomposites: Experiments and model validation. Composit. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Pellegrin, B.; Mermet, L.; Shapiro, A.; Gu, X.; Chin, J. Network aggregation of CNTs at the surface of epoxy/MWCNT composite exposed to UV radiation. In Proceedings of the Nanotechnology 2009: Fabrication, Particles, Characterization, MEMS, Electronics and Photonics—Technical Proceedings of the 2009 NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Expo, NSTI-Nanotech, Houston, TX, May 3-7 2009; Volume 1, pp. 90–93.
- Nguyen, T.; Pellegrin, B.; Bernard, C.; Gu, X.; Gorham, J.M.; Stutzman, P.; Stanley, D.; Shapiro, A.; Byrd, E.; Hettenhouser, R.; Chin, J. Fate of nanoparticles during life cycle of polymer nanocomposites. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2011, 304, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.J.; Lam, T.; Gorham, J.M.; Scott, K.C.; Long, C.J.; Stanley, D.; Sharma, R.; Alexander Liddle, J.; Pellegrin, B.; Nguyen, T. Methods to assess the impact of UV irradiation on the surface chemistry and structure of multiwall carbon nanotube epoxy nanocomposites. Carbon 2014, 69, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, S.; Di Blasio, A.; Frache, A. Influence of MWNT on Polypropylene and Polyethylene Photooxidation. Macromol. Symp. 2011, 301, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirth, S.; Cena, L.; Cox, G.; Tomović, Z.; Peters, T.; Wohlleben, W. Scenarios and methods that induce protruding or released CNTs after degradation of nanocomposite materials Technology Transfer and Commercialization of Nanotechnology. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmatulu, R.; Mahmud, G.A.; Hille, C.; Misak, H.E. Effects of UV degradation on surface hydrophobicity, crack, and thickness of MWCNT-based nanocomposite coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 72, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, A.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Ging, J.; Hubert, A.; Feka, P.; Korach, C.S. Evaluating safety and stability of CNT nanocomposites exposed to environmental conditions. In Proceedings of the Technical Proceedings of the 2012 NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Expo, Santa Clara, CA, June 18-21, 2012; pp. 335–337.
- Vilar, G.; Fernández-Rosas, E.; Puntes, V.; Jamier, V.; Aubouy, L.; Vázquez-Campos, S. Monitoring migration and transformation of nanomaterials in polymeric composites during accelerated aging. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2013, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets-Fité, M.; Fernandez, E.; Janer, G.; Vilar, G.; Vázquez-Campos, S.; Zanasca, R.; Citterio, C.; Mercante, L.; Puntes, V. Exploring release and recovery of nanomaterials from commercial polymeric nanocomposites. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2013, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ging, J.; Tejerina-Anton, R.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Nielsen, M.; Murphy, K.; Gorham, J.M.; Nguyen, T.; Orlov, A. Development of a conceptual framework for evaluation of nanomaterials release from nanocomposites: Environmental and toxicological implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.; Byrd, E.; Embree, N.; Garver, J.; Dickens, B.; Finn, T.; Martin, J. Accelerated UV weathering device based on integrating sphere technology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Auad, M.L.; Williams, R.J.J.; Nutt, S.R. Improving the dispersion and flexural strength of multiwalled carbon nanotubes-stiff epoxy composites through beta-hydroxyester surface functionalization coupled with the anionic homopolymerization of the epoxy matrix. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 2765–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Grulke, E.; Hilding, J.; Groth, K.; Harris, R.; Butler, K.; Shields, J.; Kharchenko, S.; Douglas, J. Thermal and flammability properties of polypropylene/carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Polymer 2004, 45, 4227–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Du, F.M.; Douglas, J.F.; Winey, K.I.; Harris, R.H.; Shields, J.R. Nanoparticle networks reduce the flammability of polymer nanocomposites. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Mu, M.; Winey, K.; Cipriano, B.; Raghavan, S.R.; Pack, S.; Rafailovich, M.; Yang, Y.; Grulke, E.; Shields, J.; Harris, R.; Douglas, J. Relation between the viscoelastic and flammability properties of polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2008, 49, 4358–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartel, B.; Pötschke, P.; Knoll, U.; Abdel-Goad, M. Fire behaviour of polyamide 6/multiwall carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Barroso-Bujans, F.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Saja, J.A.d.; Arroyo, M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Carbon nanotubes provide self-extinguishing grade to silicone-based foams. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3933–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Kim, S.H. Thermal decomposition behavior of carbon-nanotube-reinforced poly(ethylene 2,6-naphthalate) nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Song, P.; Yang, H.; Jin, Y.; Lu, F.; Ye, J.; Wu, Q. Effects of carbon nanotubes and its functionalization on the thermal and flammability properties of polypropylene/wood flour composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammarano, M.; Krämer, R.H.; Harris, R.; Ohlemiller, T.J.; Shields, J.R.; Rahatekar, S.S.; Lacerda, S.; Gilman, J.W. Flammability reduction of flexible polyurethane foams via carbon nanofiber network formation. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyden, M.R.; Harris, R.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Davis, R.D.; Marsh, N.D.; Zammarano, M. Characterizing particle emissions from burning polymer nanocomposites. Tech. Proc. 2010 NSTI Nanotechnol. Conf. Expo 2010, 1, 717–719. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, N.; Nyden, M.R.; Davis, R.D. Characterization of Nanoparticle Release from Polymer Nanocomposites Due to Fire. In Proceedings of the Nanotech 2011 Conference and Expo, Boston, MA, June 13-16, 2011.
- Dittrich, B.; Wartig, K.A.; Hofmann, D.; Mülhaupt, R.; Schartel, B. Carbon black, multiwall carbon nanotubes, expanded graphite and functionalized graphene flame retarded polypropylene nanocomposites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillard, J.; R’Mili, B.; Moranviller, D.; Vignes, A.; Le Bihan, O.; Ustache, A.; Bomfim, J.S.; Frejafon, E.; Fleury, D. Nanosafety by design: risks from nanocomposite/nanowaste combustion. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Cadek, M.; Blake, R.; Nicolosi, V.; Ryan, K.P.; Belton, C.; Fonseca, A.; Nagy, J.B.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Blau, W.J. High Performance Nanotube-Reinforced Plastics: Understanding the Mechanism of Strength Increase. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yan, F.Y.; Xue, Q.J. Investigation of tribological properties of polyimide/carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. a-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2004, 364, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Choudhary, V. Thermal and mechanical properties of poly(trimethyelene terephthalate)/acid-treated multiwalled carbon nanotube composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 7063–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.T.; Tanoglu, M.; Schulte, K. Tensile mechanical behavior and fracture toughness of MWCNT and DWCNT modified vinyl-ester/polyester hybrid nanocomposites produced by 3-roll milling. Mater. Sci. Eng. a-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2009, 523, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Kim, J.D.; Peng, H.Q.; Margrave, J.L.; Khabashesku, V.N.; Barrera, E.V. Improving the dispersion and integration of single-walled carbon nanotubes in epoxy composites through functionalization. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojny, F.H.; Nastalczyk, J.; Roslaniec, Z.; Schulte, K. Surface modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes in CNT/epoxy-composites. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 370, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.C.; Buha, J.; Wang, J.; Ulrich, A.; Nowack, B. Modeling the flows of engineered nanomaterials during waste handling. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Schlagenhauf, L.; Nüesch, F.; Wang, J. Release of Carbon Nanotubes from Polymer Nanocomposites. Fibers 2014, 2, 108-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020108
Schlagenhauf L, Nüesch F, Wang J. Release of Carbon Nanotubes from Polymer Nanocomposites. Fibers. 2014; 2(2):108-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020108
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchlagenhauf, Lukas, Frank Nüesch, and Jing Wang. 2014. "Release of Carbon Nanotubes from Polymer Nanocomposites" Fibers 2, no. 2: 108-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020108
APA StyleSchlagenhauf, L., Nüesch, F., & Wang, J. (2014). Release of Carbon Nanotubes from Polymer Nanocomposites. Fibers, 2(2), 108-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020108




