High Strength and High Modulus Electrospun Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. High Strength and High Modulus Fibers
2.1. Basic Concepts for High Performance Fibers
| Polymer | Theoretical modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | 235 |
| Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) | 250 |
| Polyamide-6 (PA 6) | 157 |
| Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) | 108 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 40 |
| Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) | 35–55 |
| Thermotropic polyester (Vectran) | 126 |
| Poly(p-phenylene terehthalamide) (PPTA) | 156 |
| Poly(phenylene benzobisoxazole) (PBO) | 478 |
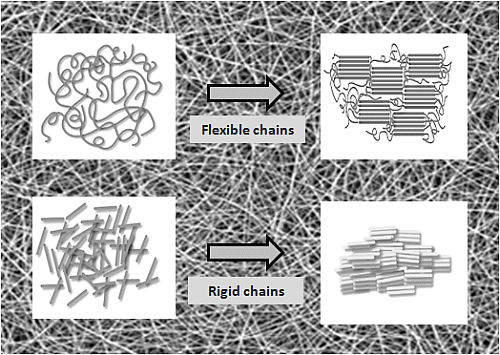
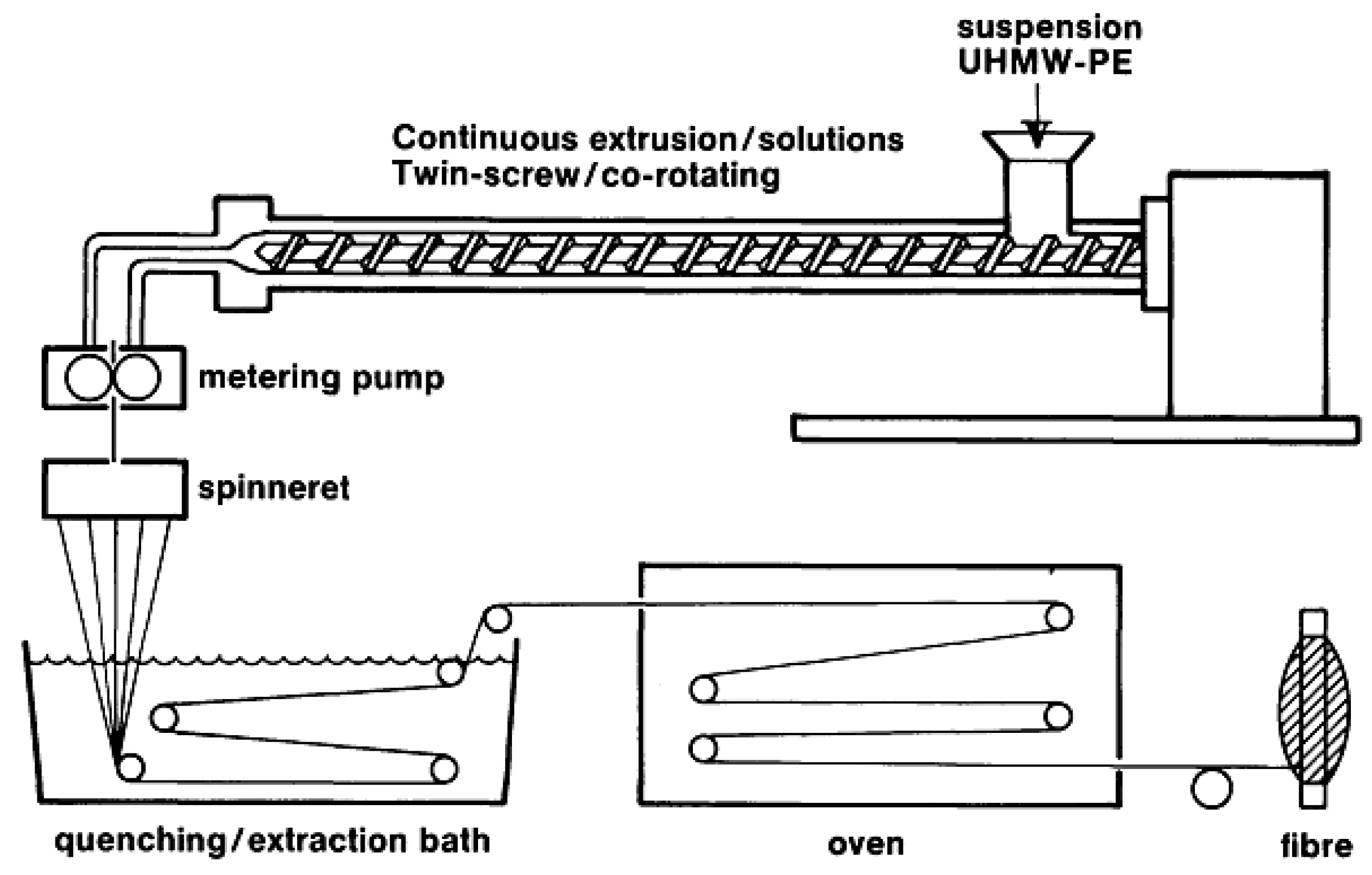
2.2. High Performance Fibers Based on Flexible Polymer Chains
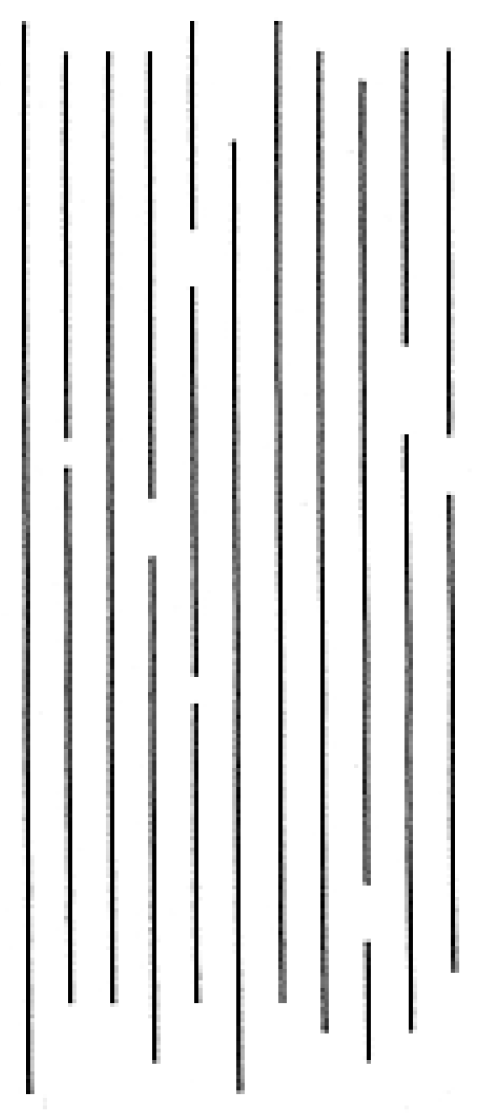
2.3. High Performance Fibers Based on Rigid Polymer Chains

3. Electrospun Nanofibers
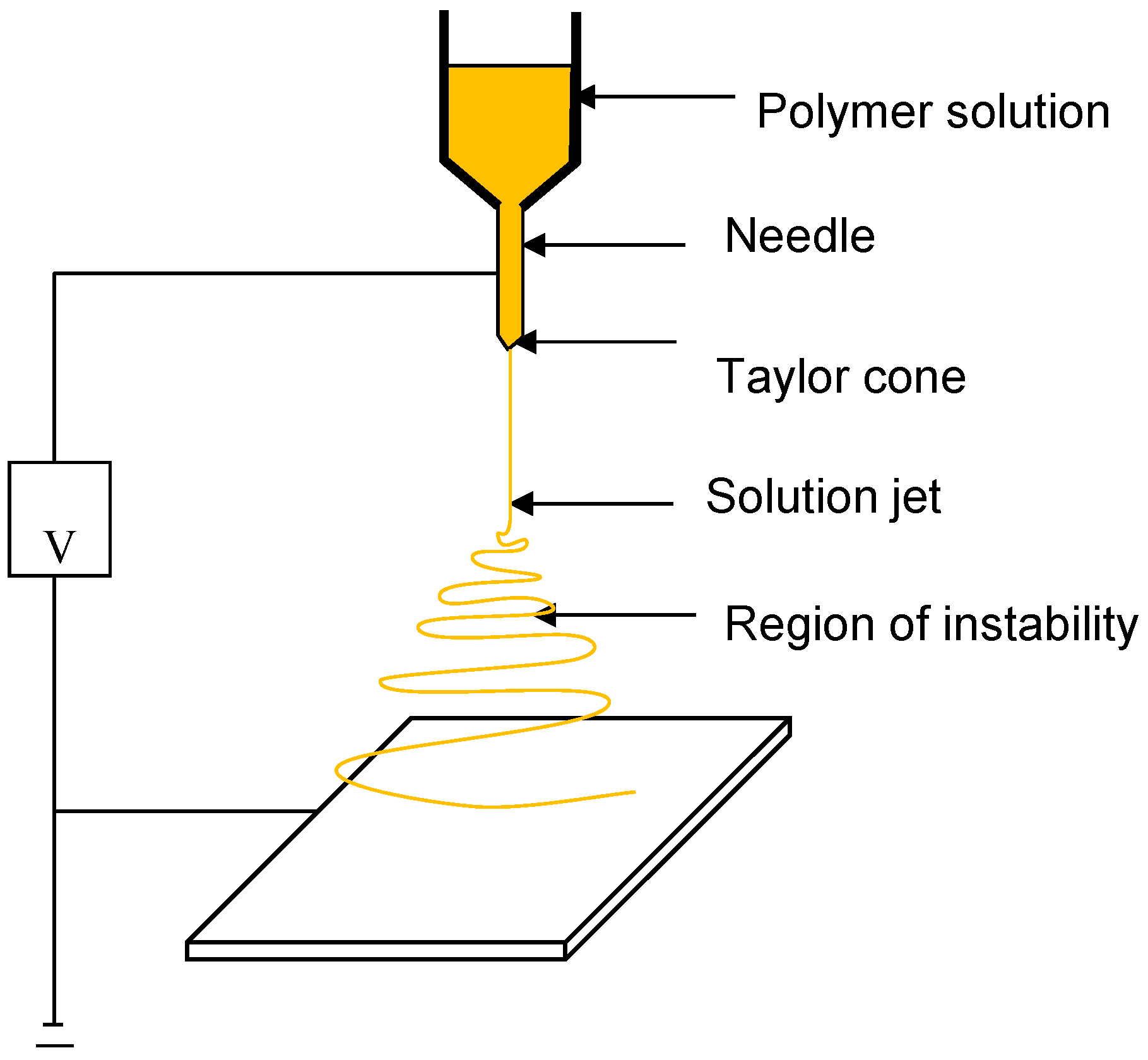
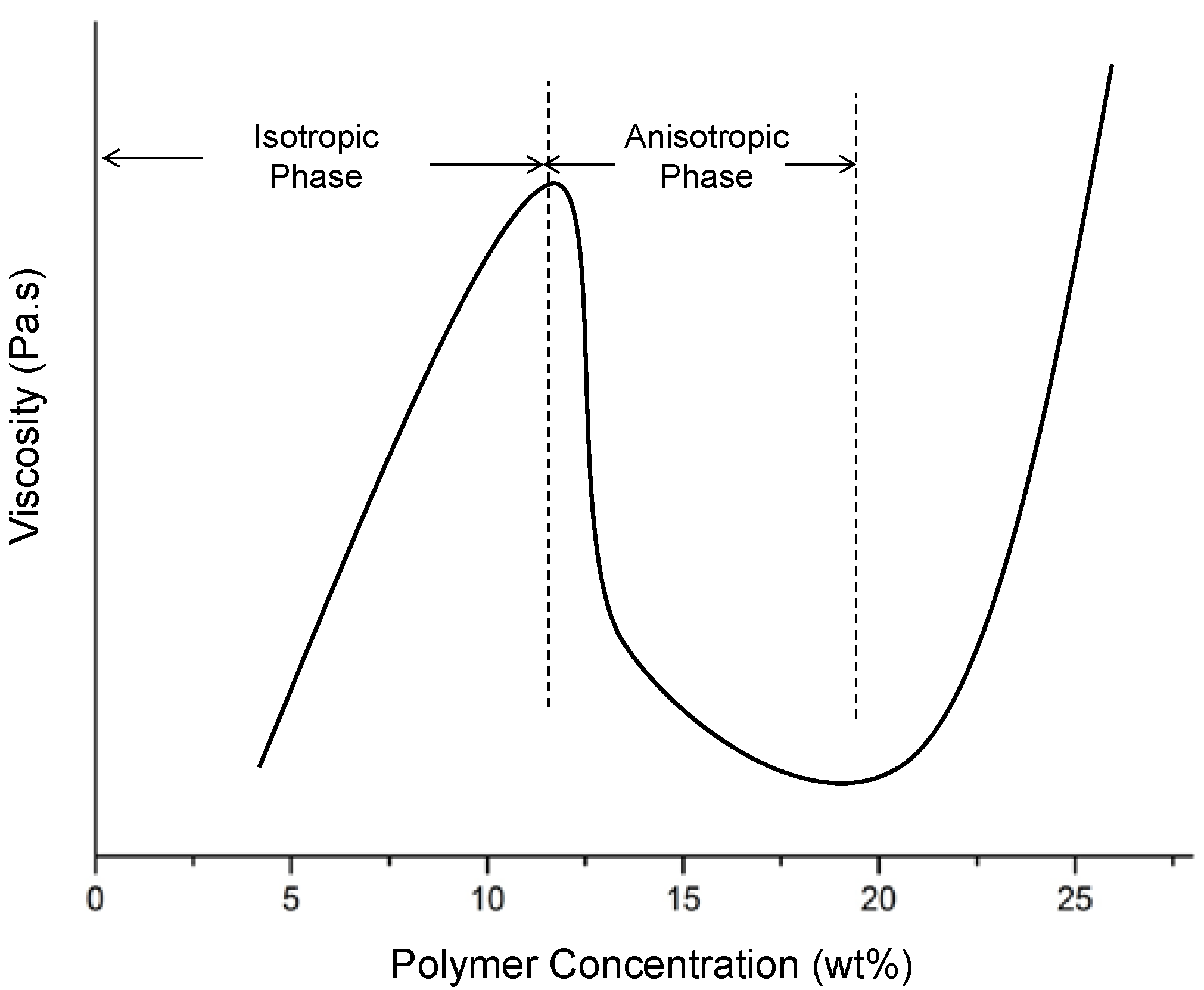
3.1. Basic Concepts of Electrospinning
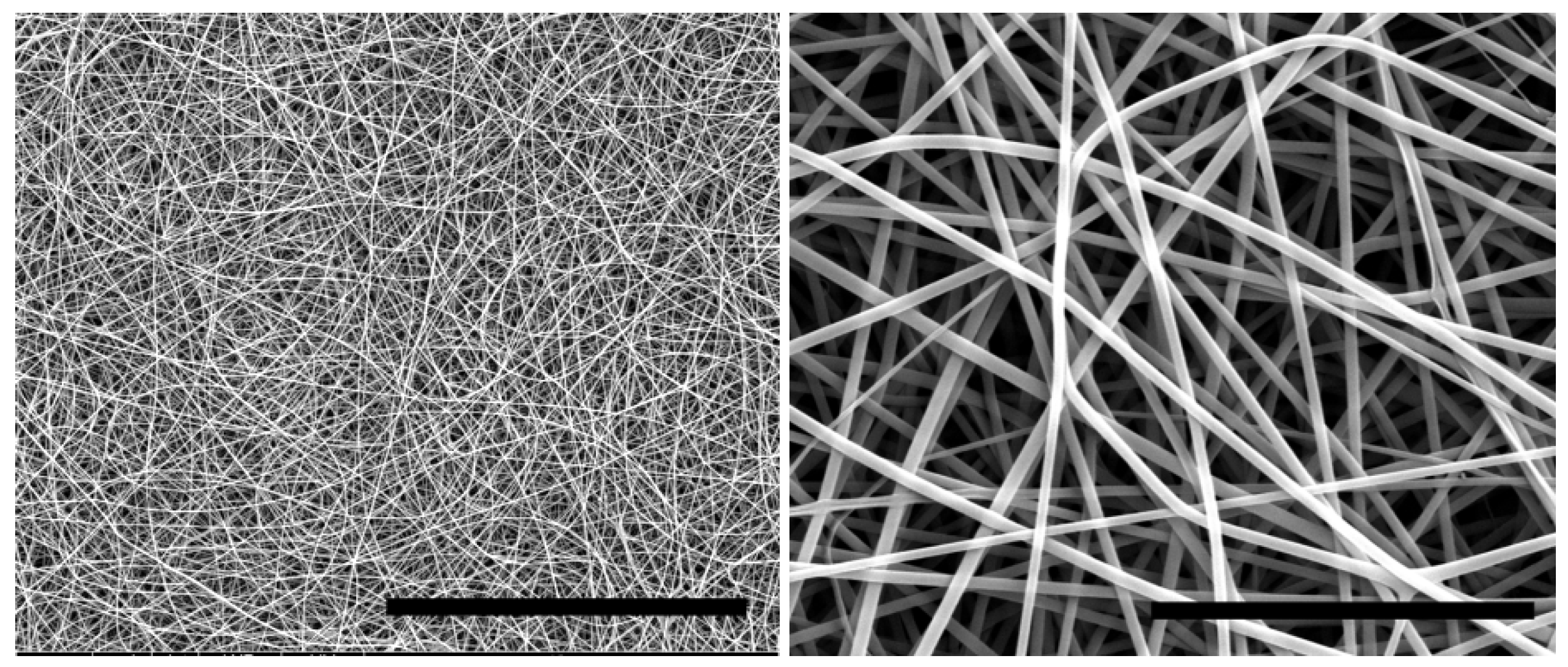
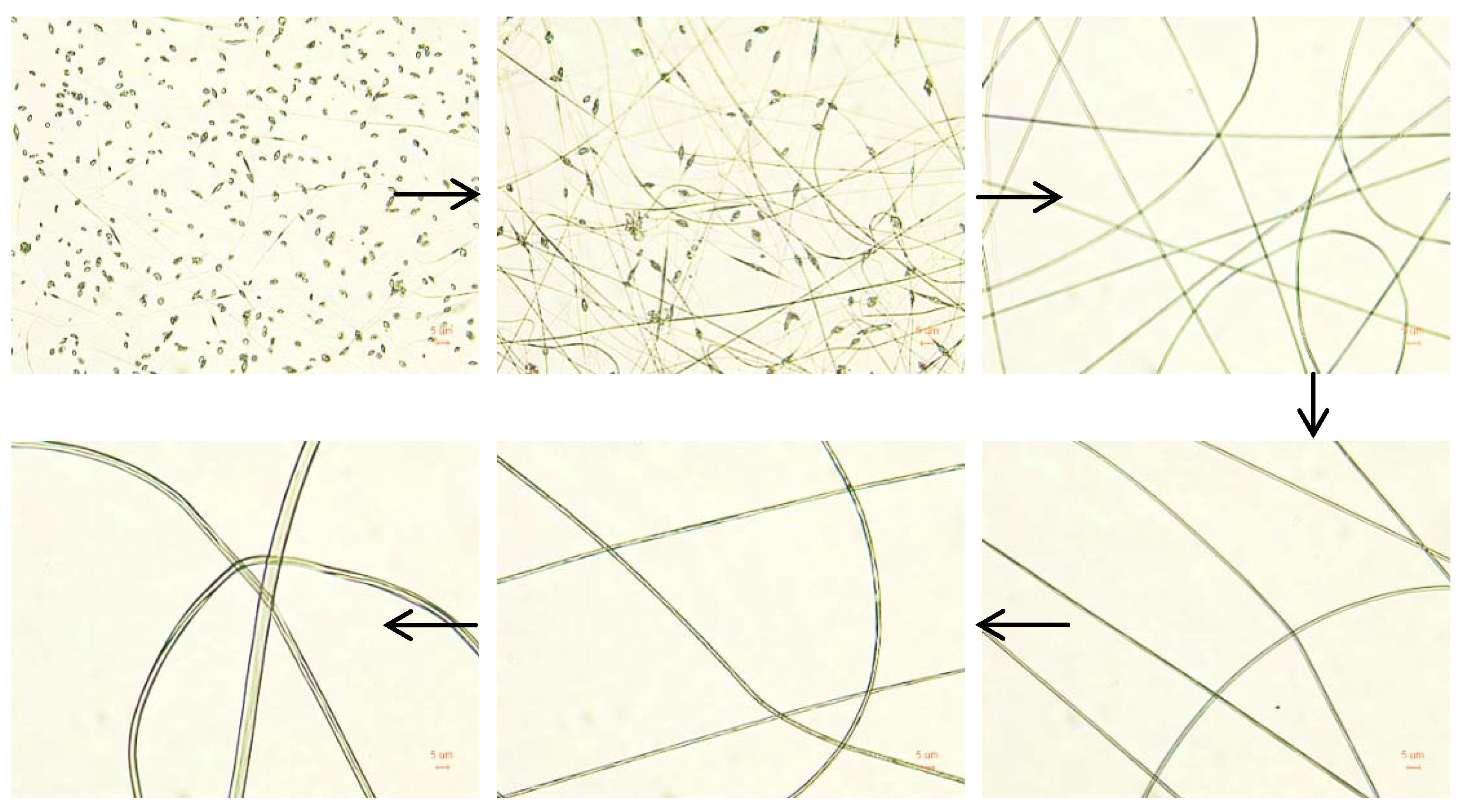
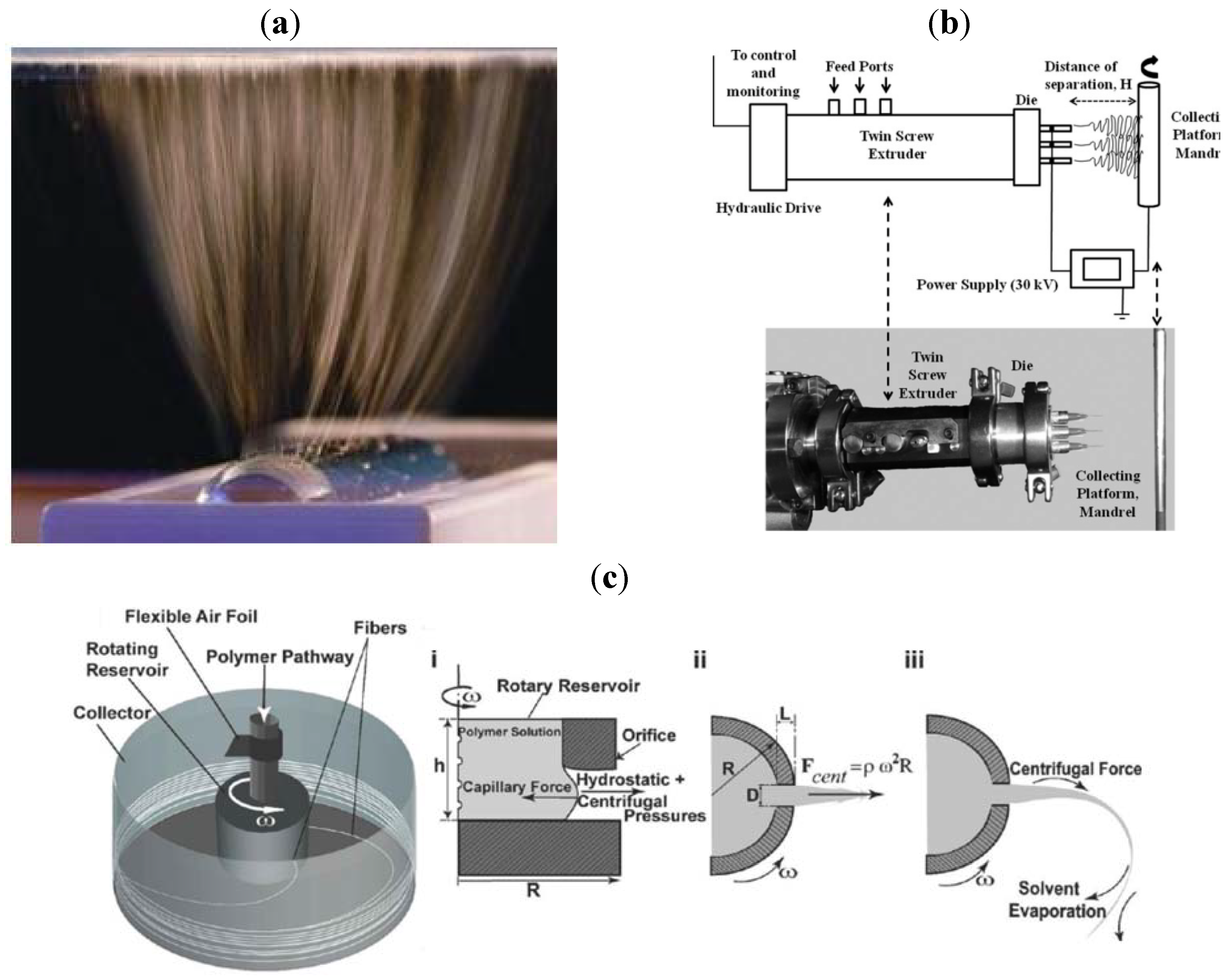
3.2. Electrospun Nanofibers Based on Flexible Chain Polymers
| Polymer | Solvent & concentration | Sample | Modulus (MPa) | Strength (MPa) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA 6 | 6 wt% in 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2- propanol | Nonwoven nanofiber mat | 34 ± 2 | 7.2 ± 0.5 | [65] |
| PA 6,6 | 7.5 wt% in 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2- propanol | Nonwoven nanofiber mat | 21 ± 1 | 6.5 ± 0.8 | |
| PA 6 | 20 wt% in formic acid | Nonwoven nanofiber mat | 19 | 10.5 | [66] |
| Single nanofiber | 902 | 304 | |||
| PA 6,6 | 20 wt% in formic acid | Single nanofiber | 950 ± 390 | 150 ± 49 | [67] |
| PA 6,6 | 10 wt% in formic acid & chloroform (75:25 v/v) | Nanofiber yarn | 1216 | 120 | [68] |
| PA 6 | 12 wt% in formic acid & acetic acid (50:50 w/w) | Single nanofiber | 1320 ± 152 | 78.1 ± 6.0 | [69] |
| PA 6 | 12 wt% in formic acid & acetic acid (50:50 w/w) | Nonwoven nanofiber mat | 418 ± 93 | 57.7 ± 8.9 | [70] |
| PET | 30% (w/v) in TFA & DCM (70:30 v/v) | Nonwoven nanofiber mat | 60 | 3.7 | [71] |
| PA 6/6,6 | Melt | Bulk | 2000–2500 | 50–80 | [23] |
| PET | Melt | Bulk | 2000–3000 | 50–150 | |
| PA 6/6,6 | Melt-spun + drawn | Single fiber | 6000 | 1000 | [40] |
| PET | Melt-spun + drawn | Single fiber | 15000 | 1100 |

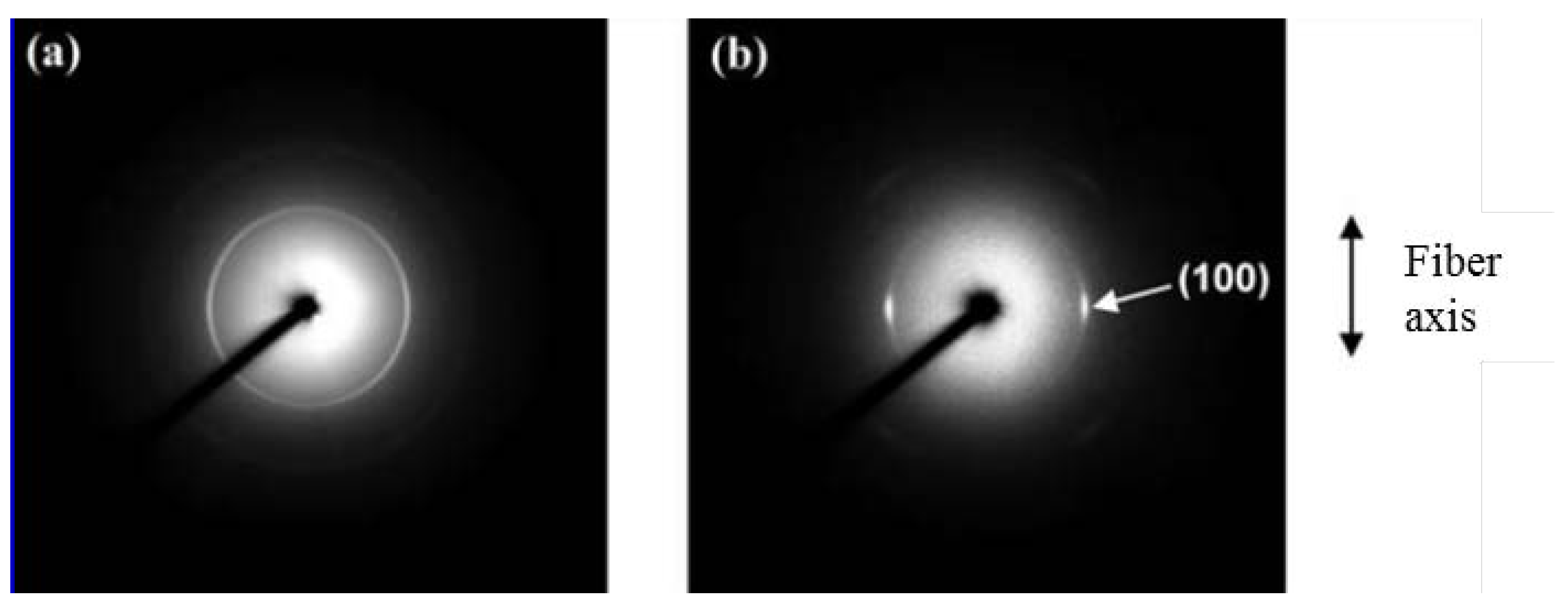
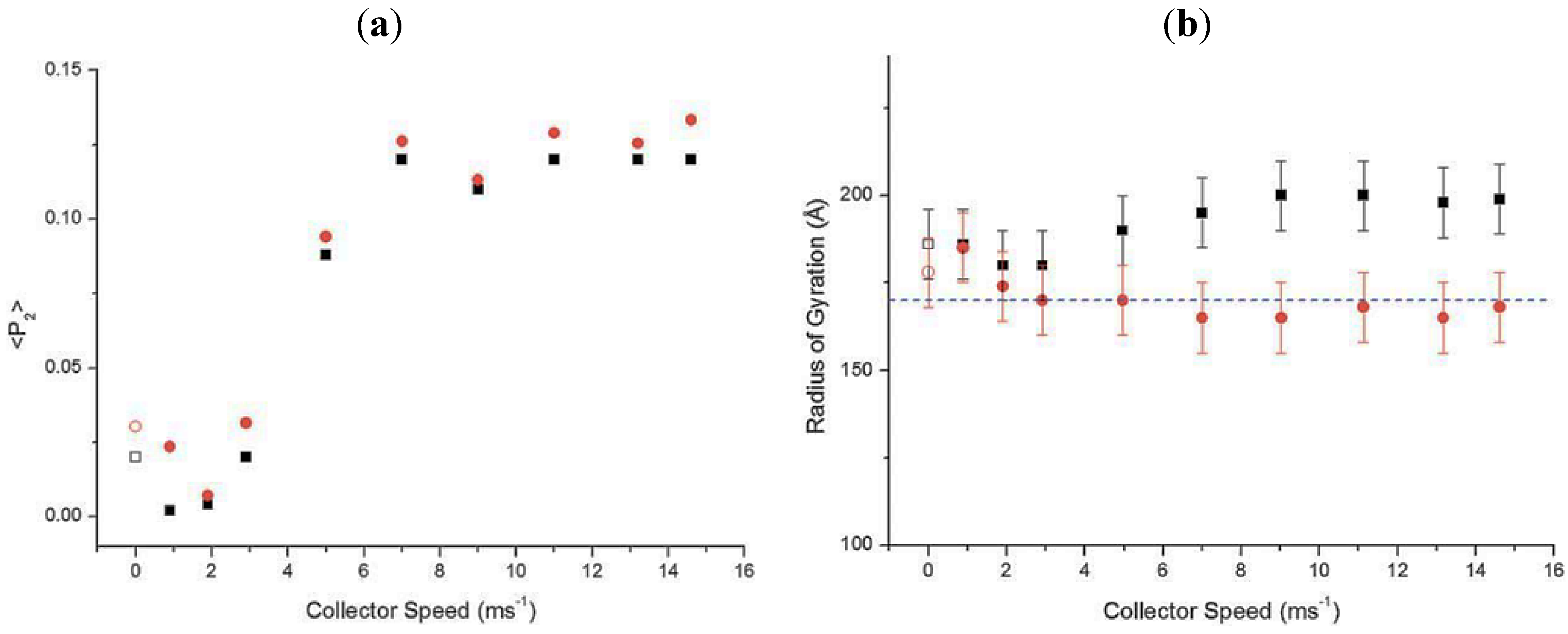
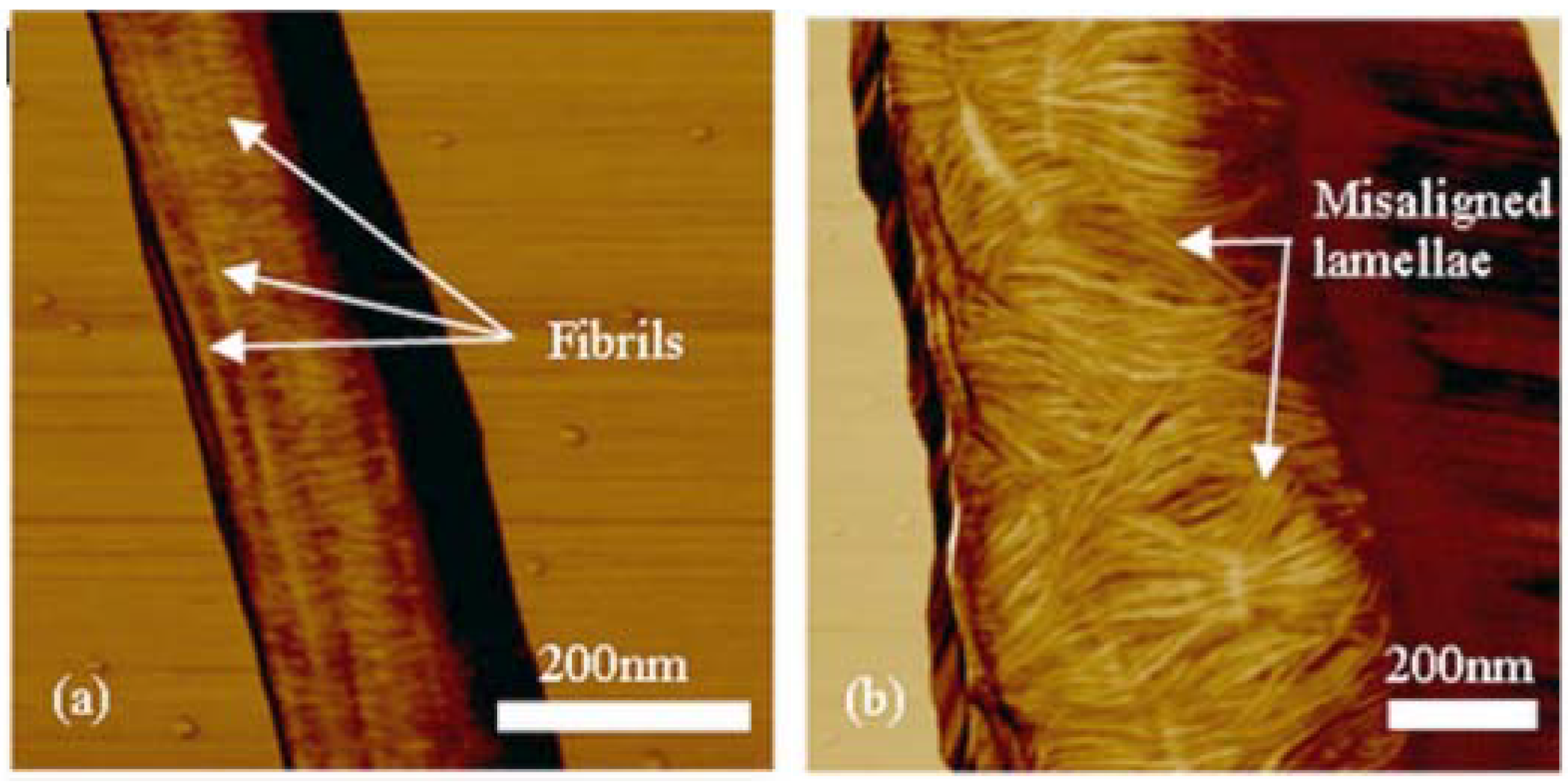
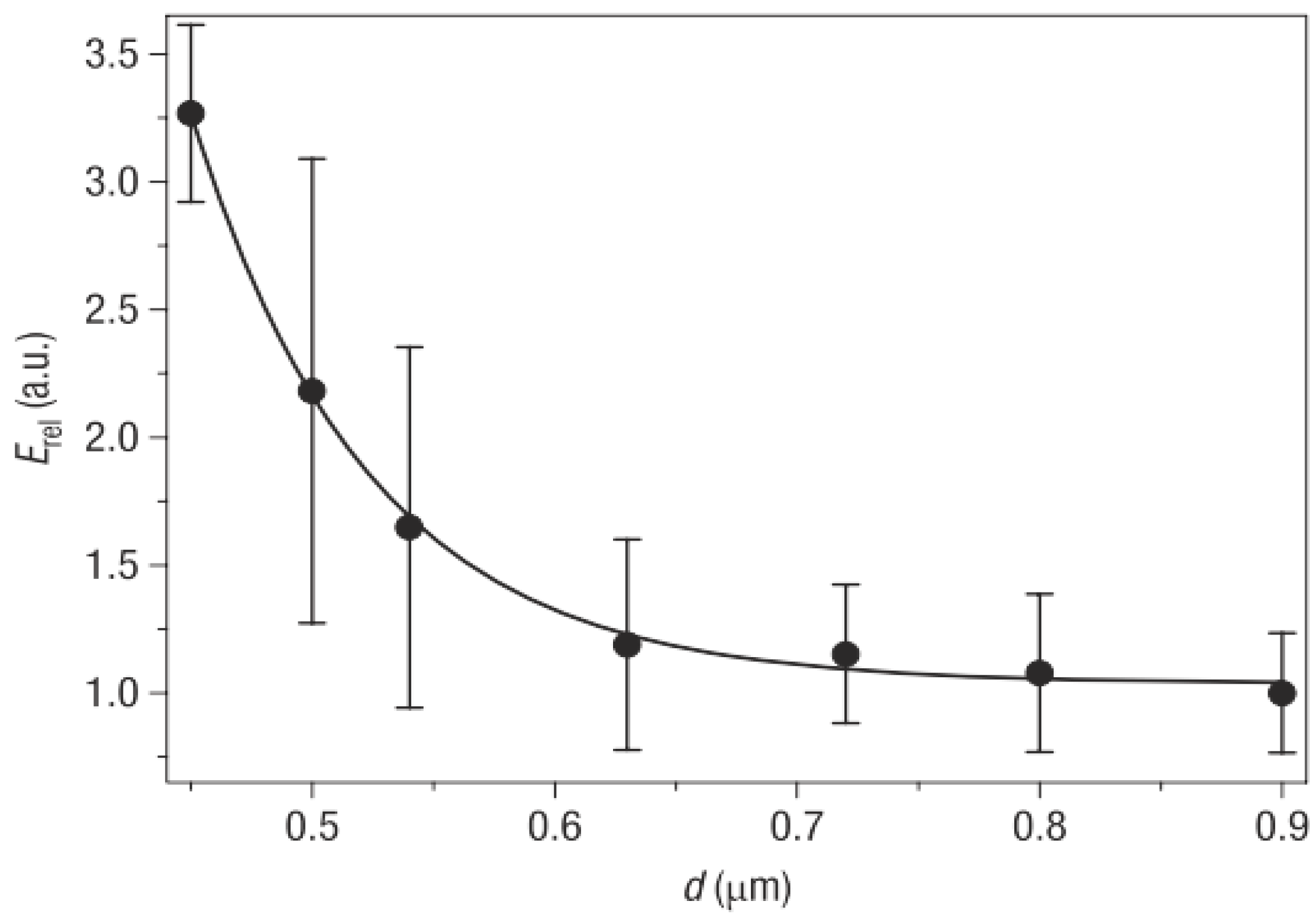
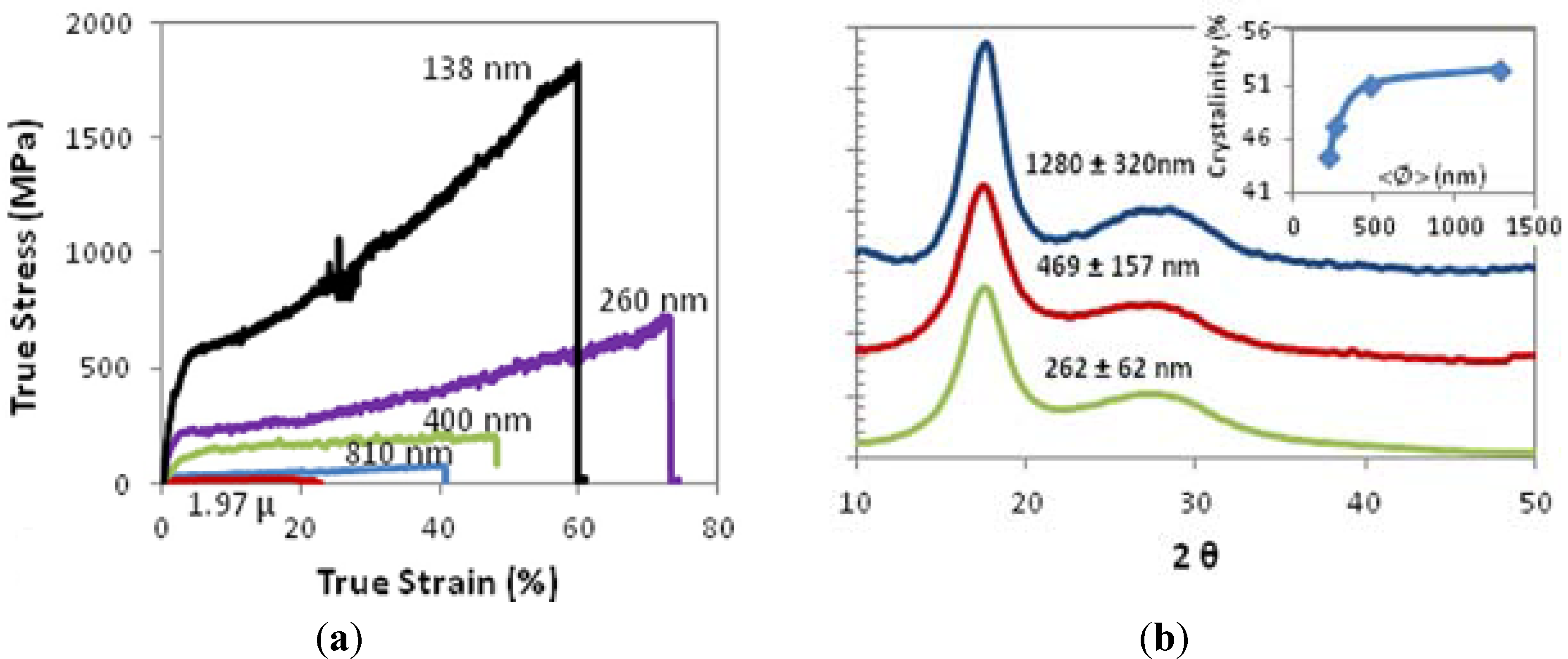
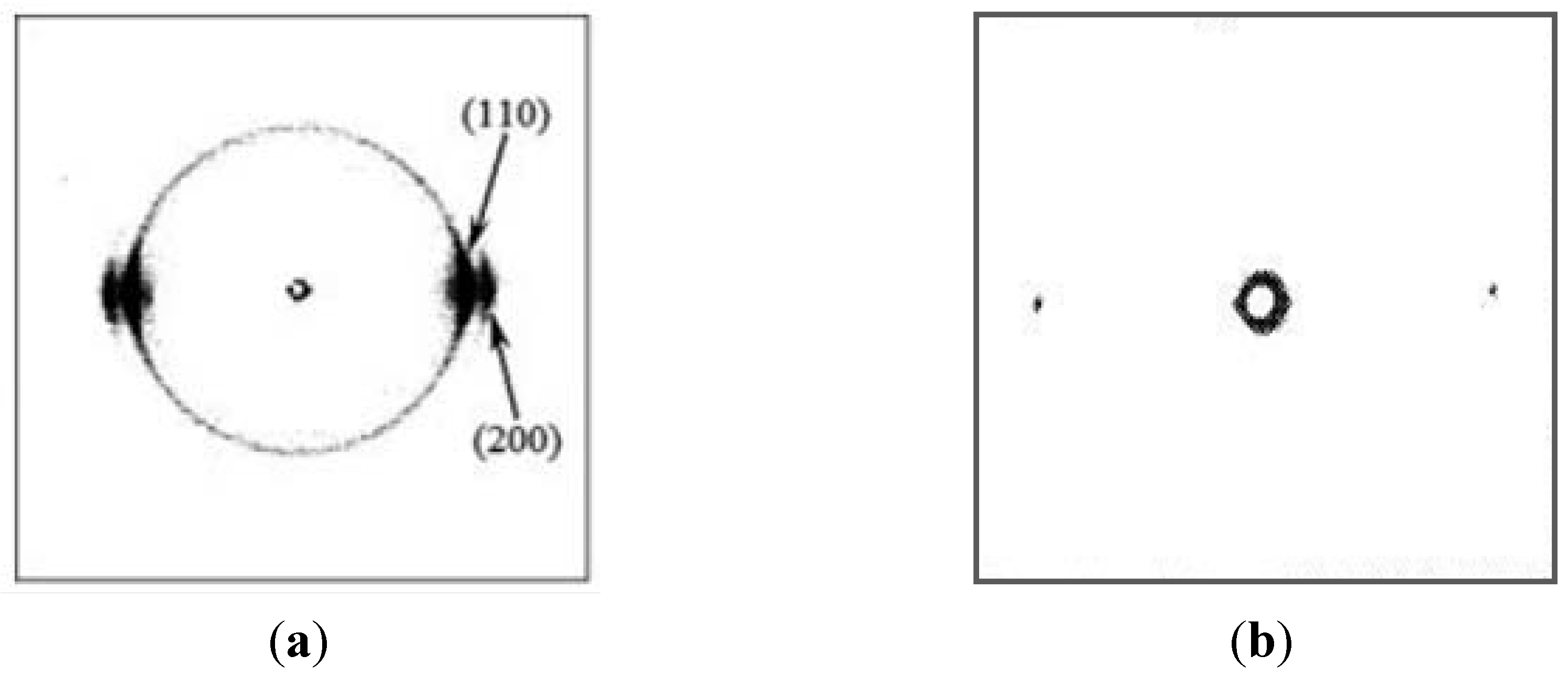
3.3. Electrospun Nanofibers Based on Rigid Chain Polymers
3.3.1. Electrospun PPTA Fibers
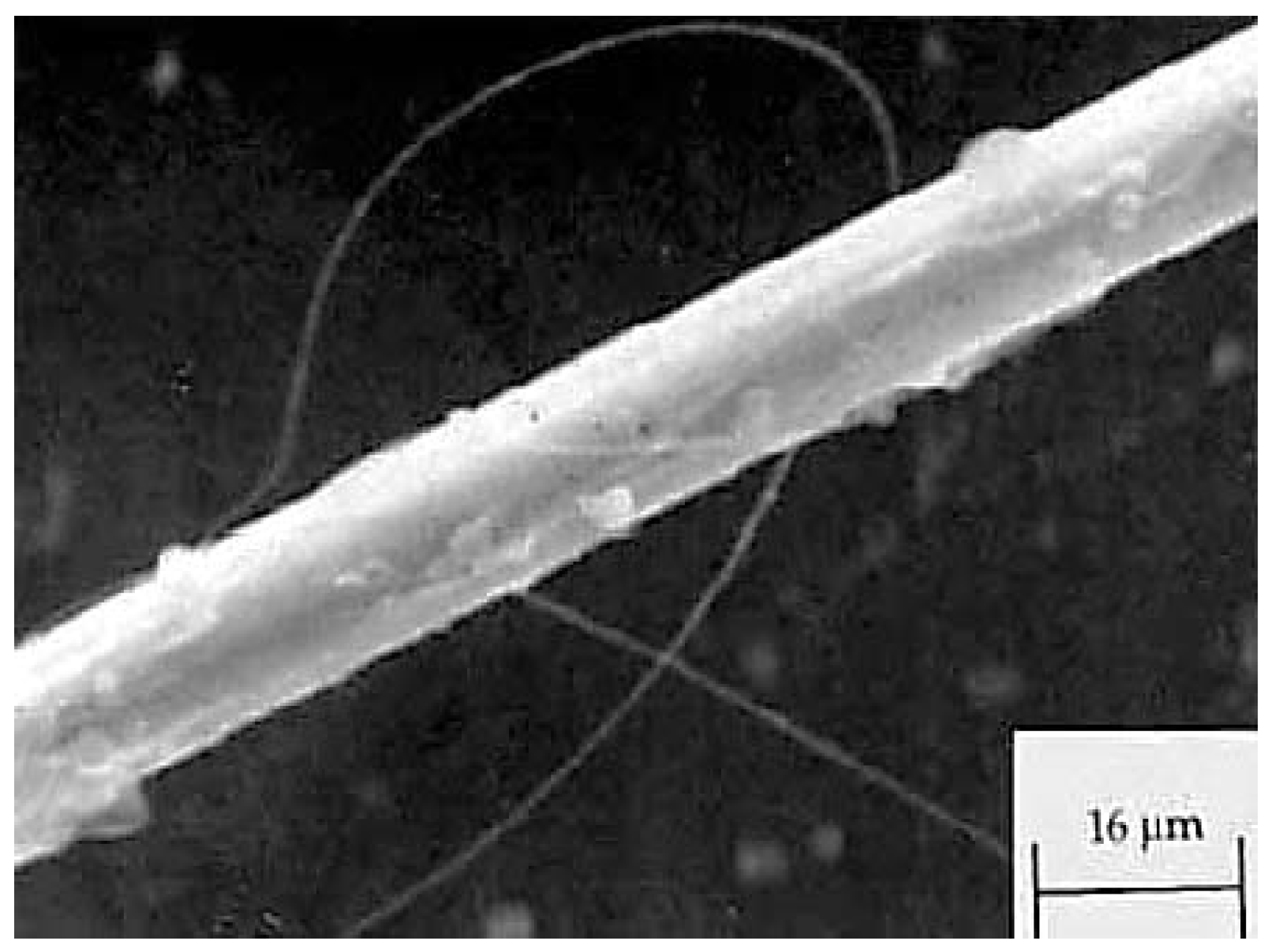
3.3.2. Electrospun Polyimide Nanofiber
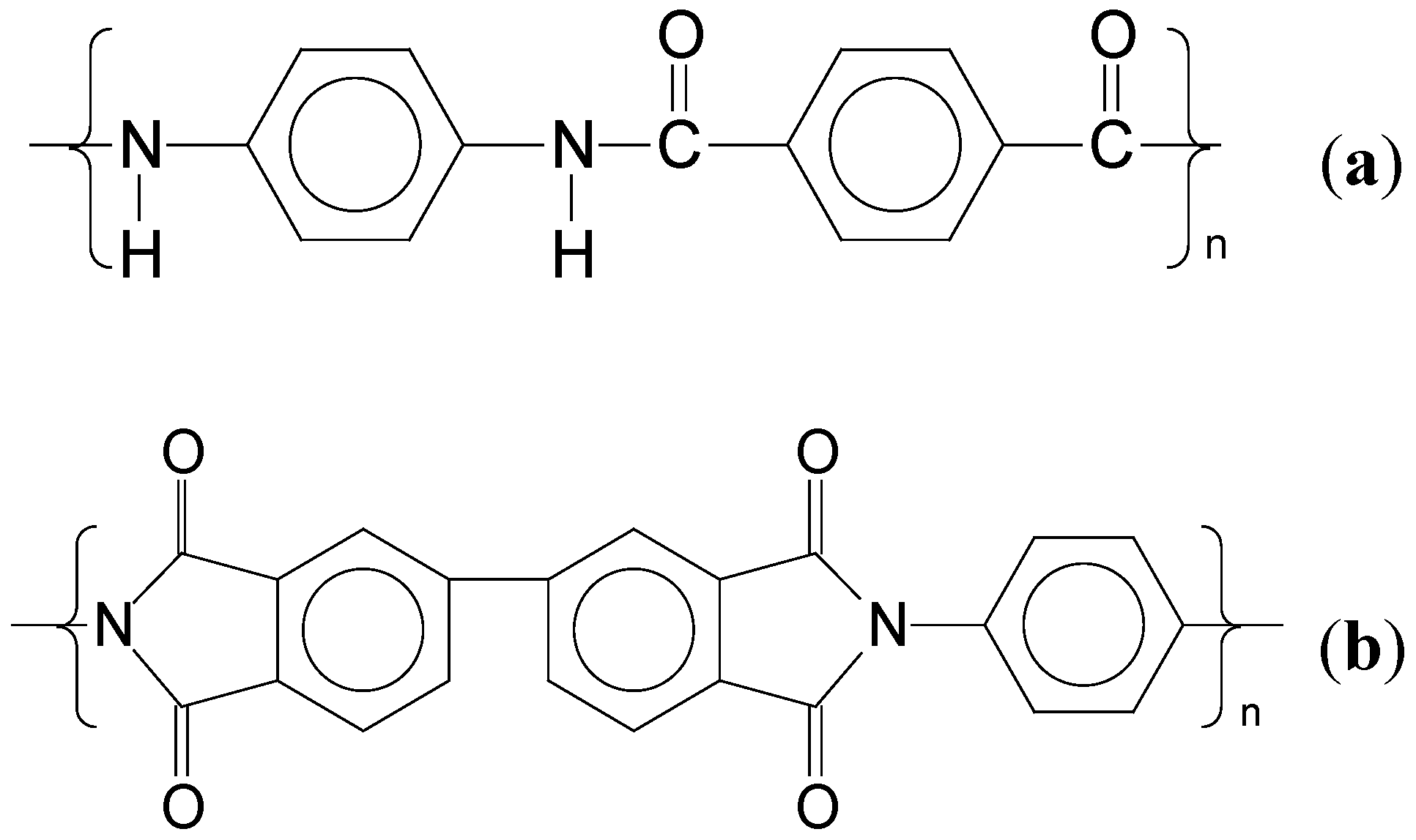
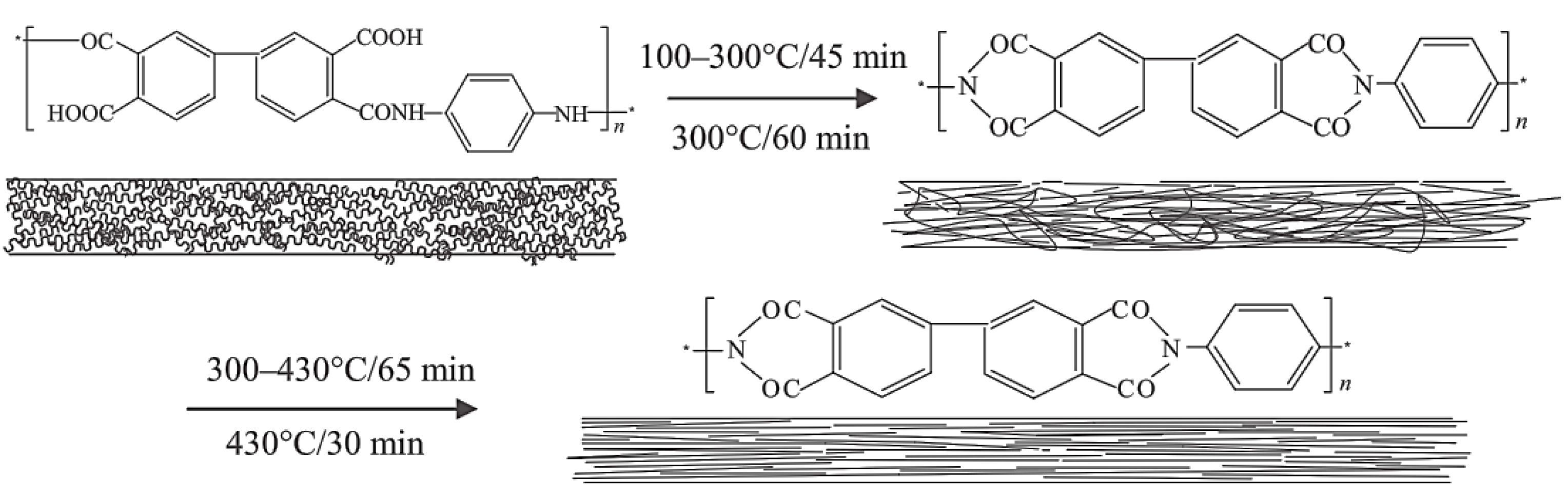
3.4. Other Routes to High Performance Nanofibers
3.4.1. CNT Reinforced Polymer Nanofibers
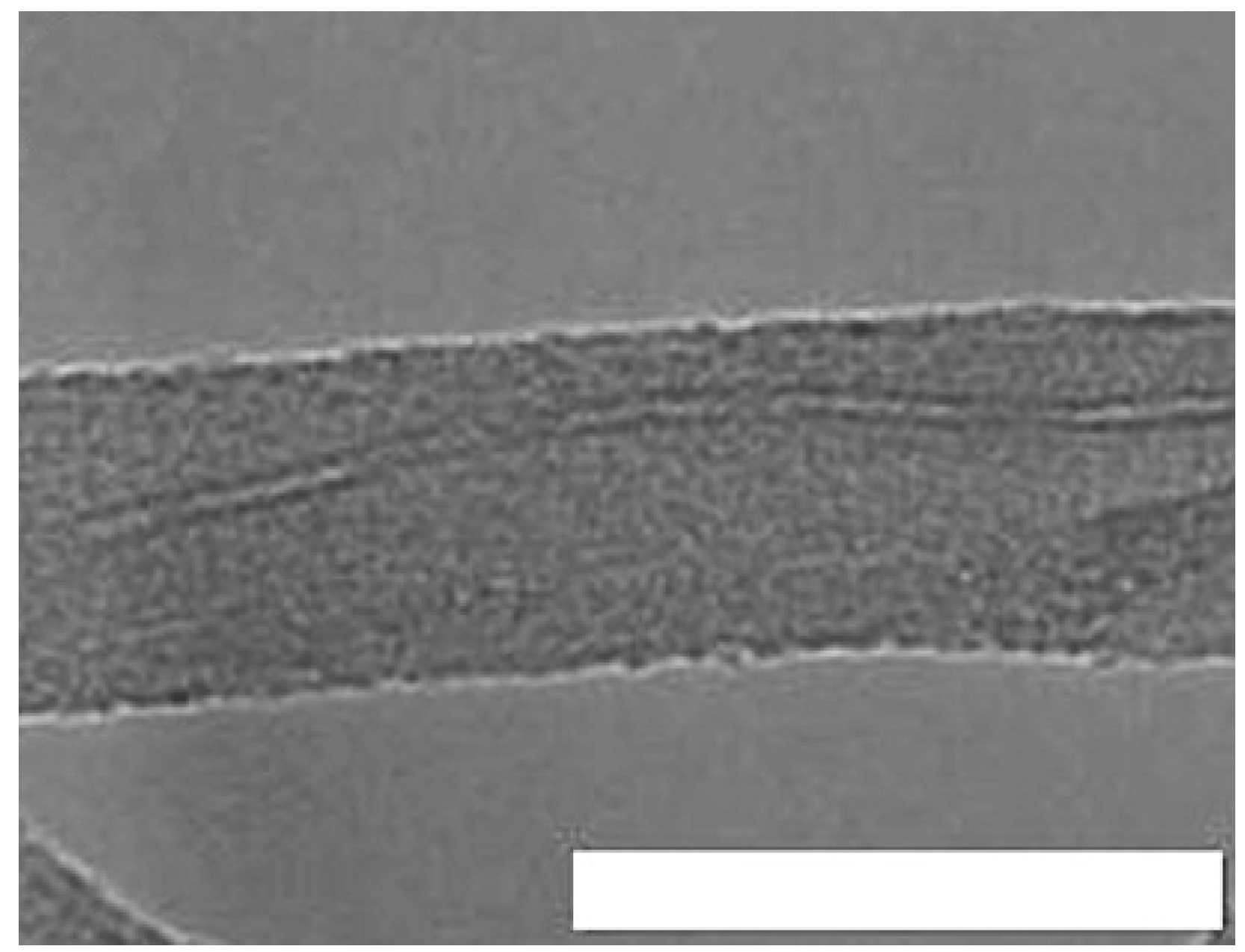
3.4.2. Electrospun Polymer-derived Carbon Nanofibers
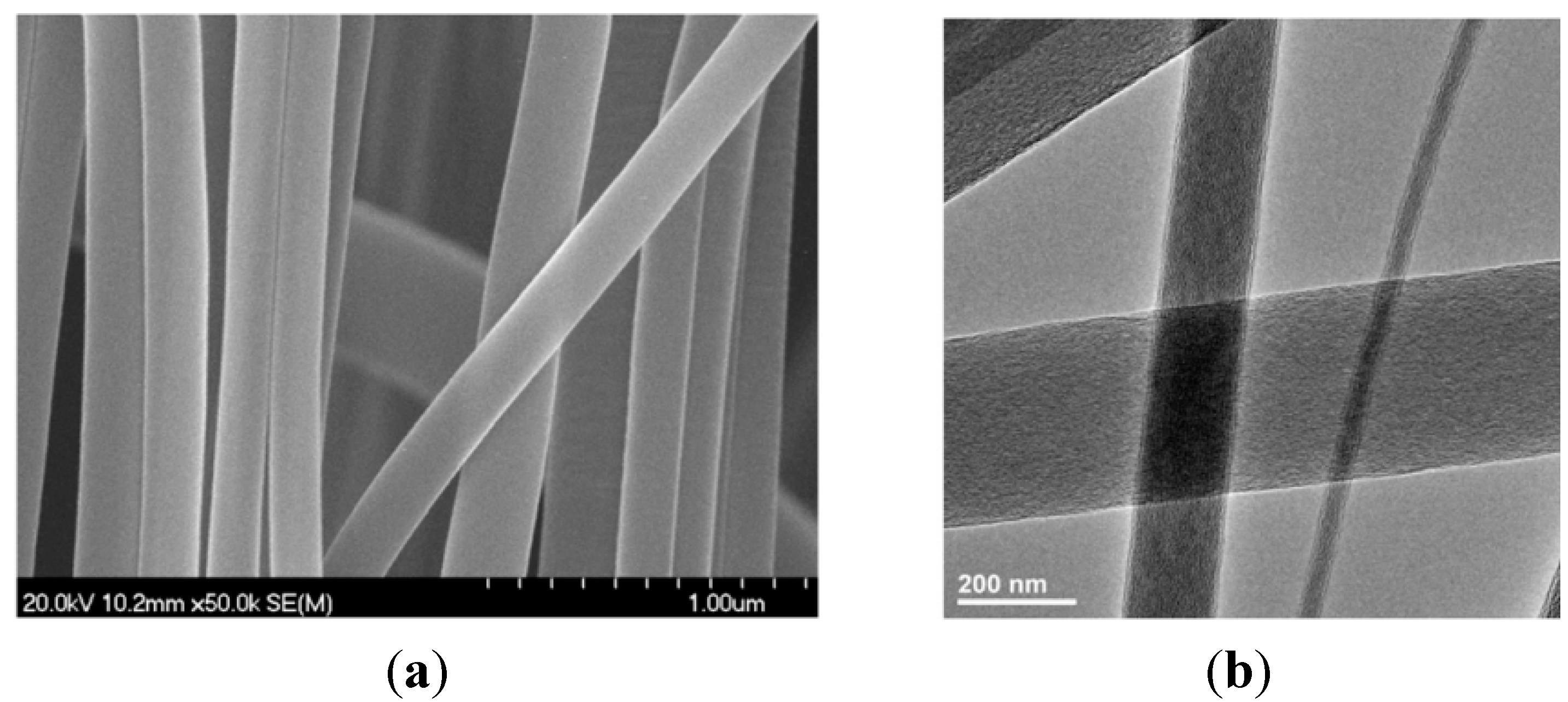
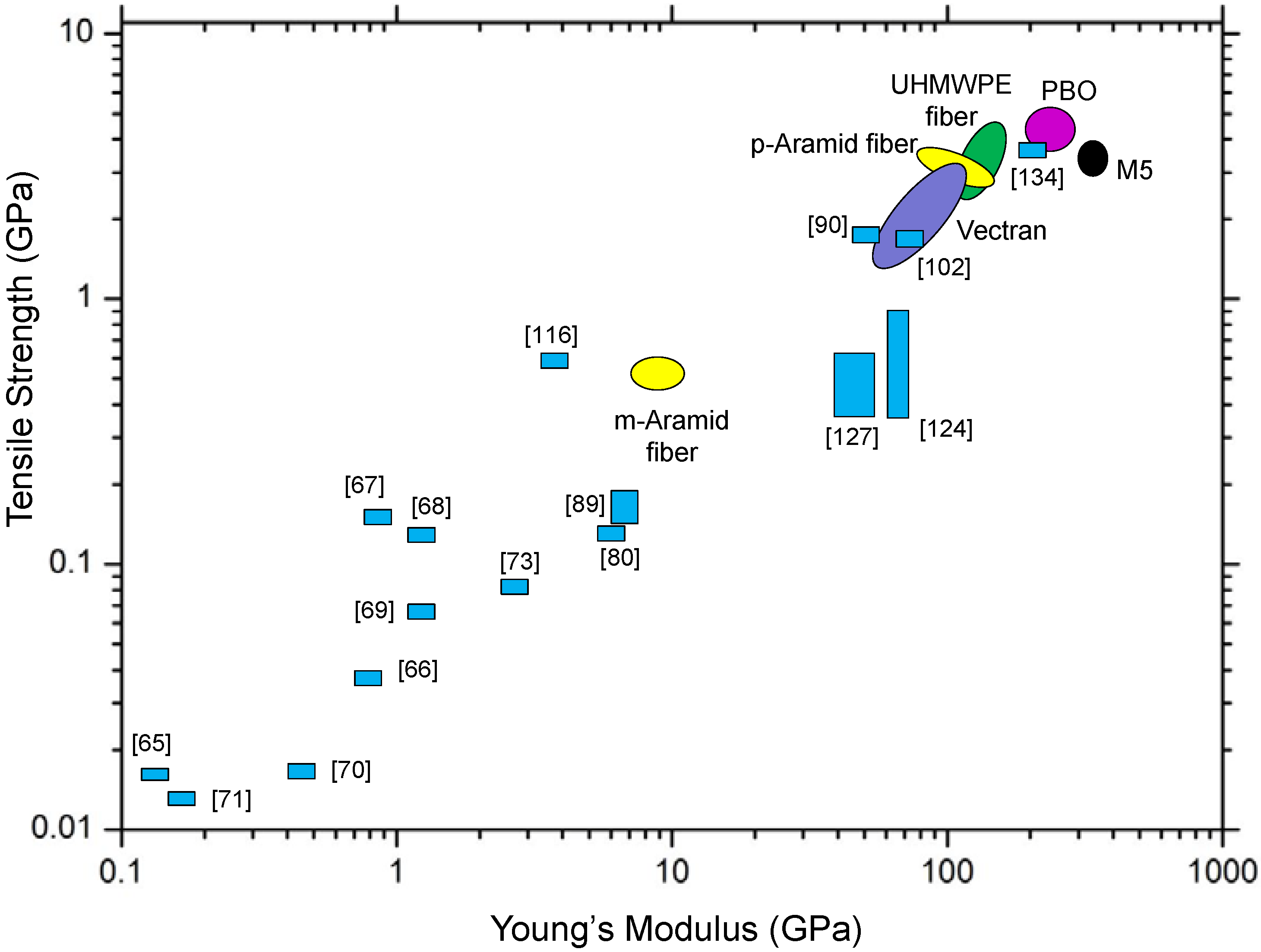
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Reneker, D.H. Mechanical properties of composites using ultrafine electrospun fibers. Polym. Compos. 1999, 20, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, R.; Bergshoef, M.M.; Batlle, C.M.I.; Schönherr, H.; Julius Vancso, G. Electrospinning of Ultra-thin Polymer Fibers, Macromolecular Symposia, 1998; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 141–150.
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured fibers via electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Reneker, D. DNA fibers by electrospinning. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 1997, 36, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Reneker, D.H. Elastomeric nanofibers of styrene-butadiene-styrene triblock copolymer. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 1999, 37, 3488–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd: Singapore, 2005; pp. 90–154. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Aligned biodegradable nanofibrous structure: A potential scaffold for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J. Functional self-assembled nanofibers by electrospinning. In Self-Assembled Nanomaterials I; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 107–171. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kim, S.C.; Pui, D.Y. Investigation of the figure of merit for filters with a single nanofiber layer on a substrate. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2008, 39, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, L.S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Bender, J.D.; Greish, Y.E.; Brown, P.W.; Allcock, H.R.; Laurencin, C.T. Fabrication and optimization of methylphenoxy substituted polyphosphazene nanofibers for biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, H.; Khil, M.; Ra, Y.; Lee, D. Characterization of nano-structured poly (ε-caprolactone) nonwoven mats via electrospinning. Polymer 2003, 44, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Ryu, Y.J.; Kim, K.W.; Choi, S.W. Mechanical behavior of electrospun fiber mats of poly (vinyl chloride)/polyurethane polyblends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C. Electrospinning and mechanical characterization of gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 5361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.M.; Smith, D.J.; Reneker, D.H.; Kataphinan, W. Water absorption and mechanical properties of electrospun structured hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 95, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, H. Über polymerisation. Ber. Deutsch. Chem. Ges. (A and B Series) 1920, 53, 1073–1085. (in German). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeger, A.J. Nobel Lecture: Semiconducting and metallic polymers: The fourth generation of polymeric materials. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2001, 73, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Hammond, W.B.; Goddard, W.A. Crystal structures and properties of nylon polymers from theory. J. Am.Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 12291–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.G. Handbook of Textile Fibres: Man-Made Fibres; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 1984; pp. 192–391. [Google Scholar]
- Staudinger, H. Die Hochmolekularen im festen Zustand. In Die Hochmolekularen Organischen Verbindungen-Kautschuk und Cellulose; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1932; pp. 105–123, (in German). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.H.; Lotmar, W.; Pankow, G. Sur le chlorure de poly-phosphornitrile, caoutchouc inorganique. Helvetica. Chimica. Acta. 1936, 19, 930–948. (in French). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treloar, L.G. Calculations of elastic moduli of polymer crystals: I. Polyethylene and nylon 66. Polymer 1960, 1, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peijs, A.; Jacobs, M.; Lemstra, P. High-performance polyethylene fibers. In Comprehensive Composite Materials. Vol. 1. Fiber Reinforcements and General Theory of Composites; Chou, T.W., Kelly, A., Zweben, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2000; pp. 263–301. [Google Scholar]
- Hageman, J.; Meier, R.J.; Heinemann, M.; De Groot, R. Young modulus of crystalline polyethylene from ab initio molecular dynamics. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 5953–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, B. The ultimate strength and stiffness of polymers. Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1995, 25, 295–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, T.; Martin, C. Elastic modulus of linear polymer crystals. Polymer 1973, 14, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamae, K.; Nishino, T. Crystal moduli of high polymers and their temperature dependence. In Integration of Fundamental Polymer Science and Technology-5; Lemstra, P., Kleintjens, L., Eds.; Springer: Houten, the Netherlands, 1991; pp. 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lemstra, P.; Kirschbaum, R.; Ohta, T.; Yasuda, H. High-strength/high-modulus structures based on flexible macromolecules: Gel-spinning and related processes. In Developments in Oriented Polymers-2; Springer: Houten, the Netherlands, 1987; pp. 39–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lemstra, P.; Van Aerle, N.; Bastiaansen, C. Chain-extended polyethylene. Polym. J. 1987, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemstra, P.; Bastiaansen, C.; Meijer, H. Chain-extended flexible polymers. Die Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1986, 145, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaansen, C.W.; Simmelink, J.A.P.M. Solution of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. US Patent 5,428,079; filed 30 July 1991, and issued 27 June 1995,
- Capaccio, G.; Ward, I. Ultra-high-modulus linear polyethylene through controlled molecular weight and drawing. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1975, 15, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansfield, D.; Capaccio, G.; Ward, I. The preparation of ultra-high modulus polypropylene films and fibres. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1976, 16, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwijnenburg, A.; Pennings, A. Longitudinal growth of polymer crystals from flowing solutions III. Polyethylene crystals in Couette flow. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1976, 254, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwijnenburg, A.; Pennings, A. Longitudinal growth of polymer crystals from flowing solutions. IV. The mechanical properties of fibrillar polyethylene crystals. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Lett. Ed. 1976, 14, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajji, A.; Coates, P.; Dumoulin, M.; Ward, I. Solid Phase Processing of Polymers; Carl Hanser Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2000; pp. 85–210. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.; Lemstra, P.J. Ultrahigh-strength polyethylene filaments by solution spinning/drawing, 2. Influence of solvent on the drawability. Die Makromol. Chem. 1979, 180, 2983–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Lemstra, P.J.; Pijpers, J.P. Tensile strength of highly oriented polyethylene. II. Effect of molecular weight distribution. J. Polym. Sci.: Polym. Phys. Ed. 1982, 20, 2229–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Lemstra, P.; Pijpers, J.; Kiel, A. Ultra-drawing of high molecular weight polyethylene cast from solution. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1981, 259, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Lemstra, P.J. Filaments of high tensile strength and modulus. US Patent 4,430,383; filed 30 September 1982, and issued 7 February 1984,
- Kwolek, S.L. Optically anisotropic aromatic polyamide dopes. US Patent 3,671,542; filed 23 May 1969, and issued 20 June 1972,
- Kwolek, S.; Morgan, P.; Schaefgen, J.; Gulrich, L. Synthesis, anisotropic solutions, and fibers of poly (1, 4-benzamid). Macromolecules 1977, 10, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. Kevlar Aramid Fiber; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, NH, USA, 1993; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bair, T.; Morgan, P.; Killian, F. Poly (1, 4-phenyleneterephthalamides). polymerization and novel liquid-crystalline solutions. Macromolecules 1977, 10, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blades, H. High modulus, high tenacity poly (p-phenylene terephthalamide) fiber. US Patent 3,869,430; filed 30 June 1972, and issued 4 March 1975,
- Dobb, M.; Johnson, D.; Saville, B. Supramolecular structure of a high-modulus polyaromatic fiber (Kevlar 49). J. Polym. Sci.: Polym. Phys. Ed. 1977, 15, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearle, J.W. High-Performance Fibres; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2001; Volume 15, pp. 93–155. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Dang, T.D.; Arnold, F.E.; Bhattacharyya, A.R.; Min, B.G.; Zhang, X.; Vaia, R.A.; Park, C.; Adams, W.W.; Hauge, R.H. Synthesis, Structure, and Properties of PBO/SWNT Composites. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 9039–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, T.; Murase, H.; Yabuki, K. Morphological study on poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole) (PBO) fiber. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1998, 36, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, E.W.; Kim, S.N. Synthesis, spinning, and fiber mechanical properties of poly (p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole). Macromolecules 1981, 14, 920–924. [Google Scholar]
- Sikkema, D.J. Design, synthesis and properties of a novel rigid rod polymer, PIPD or M5: High modulus and tenacity fibres with substantial compressive strength. Polymer 1998, 39, 5981–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichaisit, J.; Young, R. Tensile and compressive deformation of polypyridobisimidazole (PIPD)-based M5 rigid-rod polymer fibres. Polymer 1999, 40, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: a fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrik, S.; Maly, M. Production Nozzle-less Electrospinning Nanofiber Technology, MRS Proceedings, 2009; Materials Research Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009.
- Erisken, C.; Kalyon, D.M.; Wang, H. A hybrid twin screw extrusion/electrospinning method to process nanoparticle-incorporated electrospun nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 165302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senturk-Ozer, S.; Ward, D.; Gevgilili, H.; Kalyon, D.M. Dynamics of electrospinning of poly (caprolactone) via a multi-nozzle spinneret connected to a twin screw extruder and properties of electrospun fibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrossamay, M.R.; McIlwee, H.A.; Goss, J.A.; Parker, K.K. Nanofiber assembly by rotary jet-spinning. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.M.; Shavit-Hadar, L.; Khalfin, R.; Cohen, Y.; Shuster, K.; Zussman, E. Electrospinning of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2007, 45, 766–773. [Google Scholar]
- Peijs, T.; Rijsdijk, H.; De Kok, J.; Lemstra, P. The role of interface and fibre anisotropy in controlling the performance of polyethylene-fibre-reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1994, 52, 449–466. [Google Scholar]
- Carrizales, C.; Pelfrey, S.; Rincon, R.; Eubanks, T.M.; Kuang, A.; McClure, M.J.; Bowlin, G.L.; Macossay, J. Thermal and mechanical properties of electrospun PMMA, PVC, Nylon 6, and Nylon 6, 6. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Stylios, G.K. The tensile properties of electrospun nylon 6 single nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1719–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zussman, E.; Burman, M.; Yarin, A.; Khalfin, R.; Cohen, Y. Tensile deformation of electrospun nylon-6, 6 nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanatgar, R.H.; Borhani, S.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Gharehaghaji, A.A. The influence of solvent type and polymer concentration on the physical properties of solid state polymerized PA66 nanofiber yarn. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, F.; Lu, D.; Bailey, R.J.; Jimenez-Palomar, I.; Stachewicz, U.; Cortes-Ballesteros, B.; Davies, M.; Zech, M.; Bödefeld, C.; Barber, A.H. In situ tensile testing of nanofibers by combining atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 365708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachewicz, U.; Peker, I.; Tu, W.; Barber, A.H. Stress delocalization in crack tolerant electrospun nanofiber networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleirinho, B.; Rei, M.F.; Lopes-DA-Silva, J. Solvent and concentration effects on the properties of electrospun poly (ethylene terephthalate) nanofiber mats. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Ran, S.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Control of structure, morphology and property in electrospun poly (glycolide-co-lactide) non-woven membranes via post-draw treatments. Polymer 2003, 44, 4959–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Z.; Yang, X.P.; Zhang, F.; Hou, X.X. Stretching-induced orientation for improving the mechanical properties of electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber sheet. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 47, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Kongkhlang, T.; Tashiro, K.; Kotaki, M.; Chirachanchai, S. Electrospinning as a new technique to control the crystal morphology and molecular orientation of polyoxymethylene nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15460–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, S.; Reneker, D.H.; Lai, C.; Hou, H. High-Strength Mats from Electrospun Poly (p-Phenylene Biphenyltetracarboximide) Nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.D.; Mitchell, G.R.; Davis, F.J. Chain extension in electrospun polystyrene fibres: A SANS study. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4397–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Lim, C. Physical properties of a single polymeric nanofiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Tan, E.; Ng, S. Effects of crystalline morphology on the tensile properties of electrospun polymer nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 141908–141908–141903. [Google Scholar]
- Bashur, C.A.; Dahlgren, L.A.; Goldstein, A.S. Effect of fiber diameter and orientation on fibroblast morphology and proliferation on electrospun poly (d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) meshes. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5681–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, C.-L.; Boyce, M.C.; Rutledge, G.C. Mechanical properties of individual electrospun PA 6(3)T fibers and their variation with fiber diameter. Polymer 2011, 52, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.Y.; Hufnagel, T.C.; Lim, C.T.; Leong, K.W. Mechanical properties of single electrospun drug-encapsulated nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.K.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, H.; Spinks, G.M. Size-dependent elastic modulus of single electroactive polymer nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 231923–231929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennessey, S.F.; Farris, R.J. Fabrication of aligned and molecularly oriented electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers and the mechanical behavior of their twisted yarns. Polymer 2004, 45, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Reneker, D.H. Polybenzimidazole nanofiber produced by electrospinning. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachewicz, U.; Bailey, R.J.; Wang, W.; Barber, A.H. Size dependent mechanical properties of electrospun polymer fibers from a composite structure. Polymer 2012, 53, 5132–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellekens, R.; Bastiaansen, C. The drawing behavior of polyvinylalcohol fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 2311–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinstein, A.; Zussman, E. Electrospun polymer nanofibers: Mechanical and thermodynamic perspectives. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinstein, A.; Burman, M.; Gendelman, O.; Zussman, E. Effect of supramolecular structure on polymer nanofibre elasticity. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraghi, M.; Arshad, S.; Chasiotis, I. Molecular orientation and mechanical property size effects in electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Polymer 2011, 52, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Papkov, D.; Zou, Y.; Andalib, M.N.; Goponenko, A.; Cheng, S.Z.; Dzenis, Y.A. Simultaneously Strong and Tough Ultrafine Continuous Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Ward, I.; Bashir, Z. An investigation into the possibility of measuring an ‘X-ray modulus’ and new evidence for hexagonal packing in polyacrylonitrile. Polymer 1994, 35, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, D.; Fujii, Y.; Kanamoto, T. Development of oriented morphology and tensile properties upon superdawing of solution-spun fibers of ultra-high molecular weight poly (acrylonitrile). Polymer 2006, 47, 4445–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandrup, J.; Immergut, E.H.; Grulke, E.A.; Abe, A.; Bloch, D.R. Polymer Handbook, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Vol. 5, p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Lewin, M. Handbook of Fiber Chemistry, 3rd Ed. ed; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 812–958. [Google Scholar]
- Bisschops, J. Gelation of concentrated polyacrylonitrile solutions. II. J. Polym. Sci. 1955, 17, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, R.L.; Stockmayer, W.H. An intrinsic viscosity-molecular weight relation for polyacrylonitrile. J. Polym. Sci. 1955, 17, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531. [Google Scholar]
- Theron, S.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A. Experimental investigation of the governing parameters in the electrospinning of polymer solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Lacroix, M.; Pellerin, C. Molecular Orientation in Electrospun Fibers: From Mats to Single Fibers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 9473–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G.; Reneker, D.H. Structure and morphology of small diameter electrospun aramid fibers. Polym. Int. 1995, 36, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Lai, C.; Hou, H. High strength electrospun polymer nanofibers made from BPDA–PDA polyimide. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Peng, X.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Wu, X.-F.; Reneker, D.H.; Hou, H. Mechanical characterization of single high-strength electrospun polyimide nanofibres. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 025308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, T.; Katsura, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Makino, H.; Horio, M. High-strength-high-modulus polyimide fibers I. One-step synthesis of spinnable polyimides. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1986, 32, 3133–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Zakhidov, A.A.; de Heer, W.A. Carbon nanotubes—The route toward applications. Science 2002, 297, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thostenson, E.T.; Ren, Z.; Chou, T.-W. Advances in the science and technology of carbon nanotubes and their composites: a review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1899–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hojjati, M.; Okamoto, M.; Gorga, R.E. Review article: Polymer-matrix nanocomposites, processing, manufacturing, and application: An overview. J. Compos. Mater. 2006, 40, 1511–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-F.; Files, B.S.; Arepalli, S.; Ruoff, R.S. Tensile loading of ropes of single wall carbon nanotubes and their mechanical properties. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderova, O.; Brenner, D.; Ruoff, R.S. Would diamond nanorods be stronger than fullerene nanotubes? Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biercuk, M.; Llaguno, M.C.; Radosavljevic, M.; Hyun, J.; Johnson, A.T.; Fischer, J.E. Carbon nanotube composites for thermal management. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 2767–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-L.; Mai, Y.-W.; Zhou, X.-P. Dispersion and alignment of carbon nanotubes in polymer matrix: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 49, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, N.; Loos, J.; Regev, O.; Koning, C.E. Toolbox for dispersing carbon nanotubes into polymers to get conductive nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salalha, W.; Dror, Y.; Khalfin, R.L.; Cohen, Y.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E. Single-walled carbon nanotubes embedded in oriented polymeric nanofibers by electrospinning. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9852–9855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Q.; He, J.H.; Yu, J.Y. Carbon nanotube-reinforced polyacrylonitrile nanofibers by vibration-electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, P.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Young, R.J. Deformation of isolated single-wall carbon nanotubes in electrospun polymer nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 235707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R.; Zhao, B.; Perea, D.; Itkis, M.E.; Hu, H.; Love, J.; Bekyarova, E.; Haddon, R.C. Preparation of single-walled carbon nanotube reinforced polystyrene and polyurethane nanofibers and membranes by electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.-W.; Wong, S.-C.; Abtahi, M.; Du, X. Mechanical behavior of self-assembled carbon nanotube reinforced nylon 6, 6 fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Ge, J.J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Q.; Reneker, D.H.; Greiner, A.; Cheng, S.Z. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers containing a high concentration of well-aligned multiwall carbon nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 967–973. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, M.V.; Steinert, B.W.; Thomas, V.; Dean, D.R.; Abdalla, M.A.; Price, G.; Janowski, G.M. Morphology and mechanical properties of Nylon 6/MWNT nanofibers. Polymer 2007, 48, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) reinforced cellulose fibers by electrospinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ciselli, P.; Kuznetsov, E.; Peijs, T.; Barber, A. Effective reinforcement in carbon nanotube–polymer composites. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2008, 366, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ciselli, P.; Peijs, T. The extraordinary reinforcing efficiency of single-walled carbon nanotubes in oriented poly (vinyl alcohol) tapes. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 455709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, M.; Yang, Y.; Kang, F. Carbon nanofibers prepared via electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2547–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Yang, K.S.; Kojima, M.; Yoshida, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.A.; Endo, M. Fabrication of Electrospinning-Derived Carbon Nanofiber Webs for the Anode Material of Lithium-Ion Secondary Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 2393–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zussman, E.; Chen, X.; Ding, W.; Calabri, L.; Dikin, D.; Quintana, J.; Ruoff, R. Mechanical and structural characterization of electrospun PAN-derived carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2005, 43, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L.; Bazilevsky, A.V.; Avrahami, R.; Feldman, M. Electrospun Polyaniline/Poly (methyl methacrylate)-Derived Turbostratic Carbon Micro-/Nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Jeong, Y.I.; Ngoc, B.T.N.; Yang, K.S.; Kojima, M.; Kim, Y.A.; Endo, M.; Lee, J.W. Synthesis and characterization of porous carbon nanofibers with hollow cores through the thermal treatment of electrospun copolymeric nanofiber webs. Small 2007, 3, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lai, C.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Y.; Hou, H.; Reneker, D.H.; Fong, H. Development of carbon nanofibers from aligned electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber bundles and characterization of their microstructural, electrical, and mechanical properties. Polymer 2009, 50, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, C.; Choi, Y.O.; Yang, K.S. Preparations of pitch-based CF/ACF webs by electrospinning. Carbon 2003, 41, 2655–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, C.; Yang, K.S. Preparation of carbonized fiber web from electrospinning of isotropic pitch. Synth. Met. 2004, 143, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Gan, L.; Lv, R.; Wang, M.; Huang, Z.-h.; Kang, F.; Shen, W. A film of porous carbon nanofibers that contain Sn/SnOX nanoparticles in the pores and its electrochemical performance as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Carbon 2011, 49, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuyen, N.T.; Ra, E.J.; Geng, H.-Z.; Kim, K.K.; An, K.H.; Lee, Y.H. Enhancement of conductivity by diameter control of polyimide-based electrospun carbon nanofibers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11350–11353. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, C.; Soto, P.; Vilaplana-Ortego, E.; Gomez de Salazar, J.M.; Pico, F.; Rojo, J.M. Carbon nanofibres and activated carbon nanofibres as electrodes in supercapacitors. Carbon 2005, 43, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, W.-J.; Yang, K.-S. Supercapacitors prepared from carbon nanofibers electrospun from polybenzimidazol. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A769–A773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.N.; Naraghi, M.; Chasiotis, I. Strong carbon nanofibers from electrospun polyacrylonitrile. Carbon 2011, 49, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, J.; Bastiaansen, C.W.M.; Peijs, T. High Strength and High Modulus Electrospun Nanofibers. Fibers 2014, 2, 158-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020158
Yao J, Bastiaansen CWM, Peijs T. High Strength and High Modulus Electrospun Nanofibers. Fibers. 2014; 2(2):158-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Jian, Cees W. M. Bastiaansen, and Ton Peijs. 2014. "High Strength and High Modulus Electrospun Nanofibers" Fibers 2, no. 2: 158-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020158
APA StyleYao, J., Bastiaansen, C. W. M., & Peijs, T. (2014). High Strength and High Modulus Electrospun Nanofibers. Fibers, 2(2), 158-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2020158