Mechanical Performance of Cementitious Materials Reinforced with Polyethylene Fibers and Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Program
2.3. Material Characterization Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of the Fresh Mortar
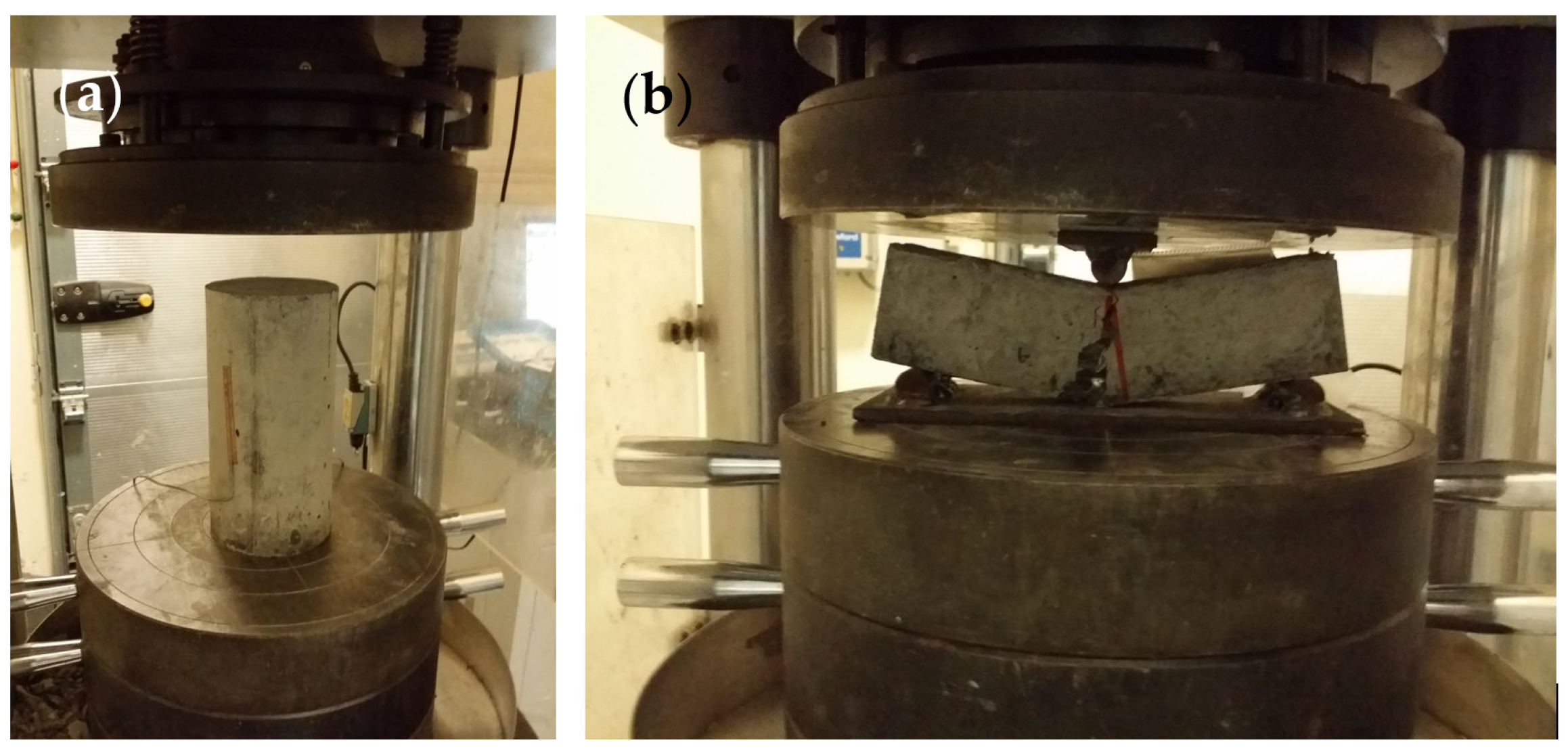
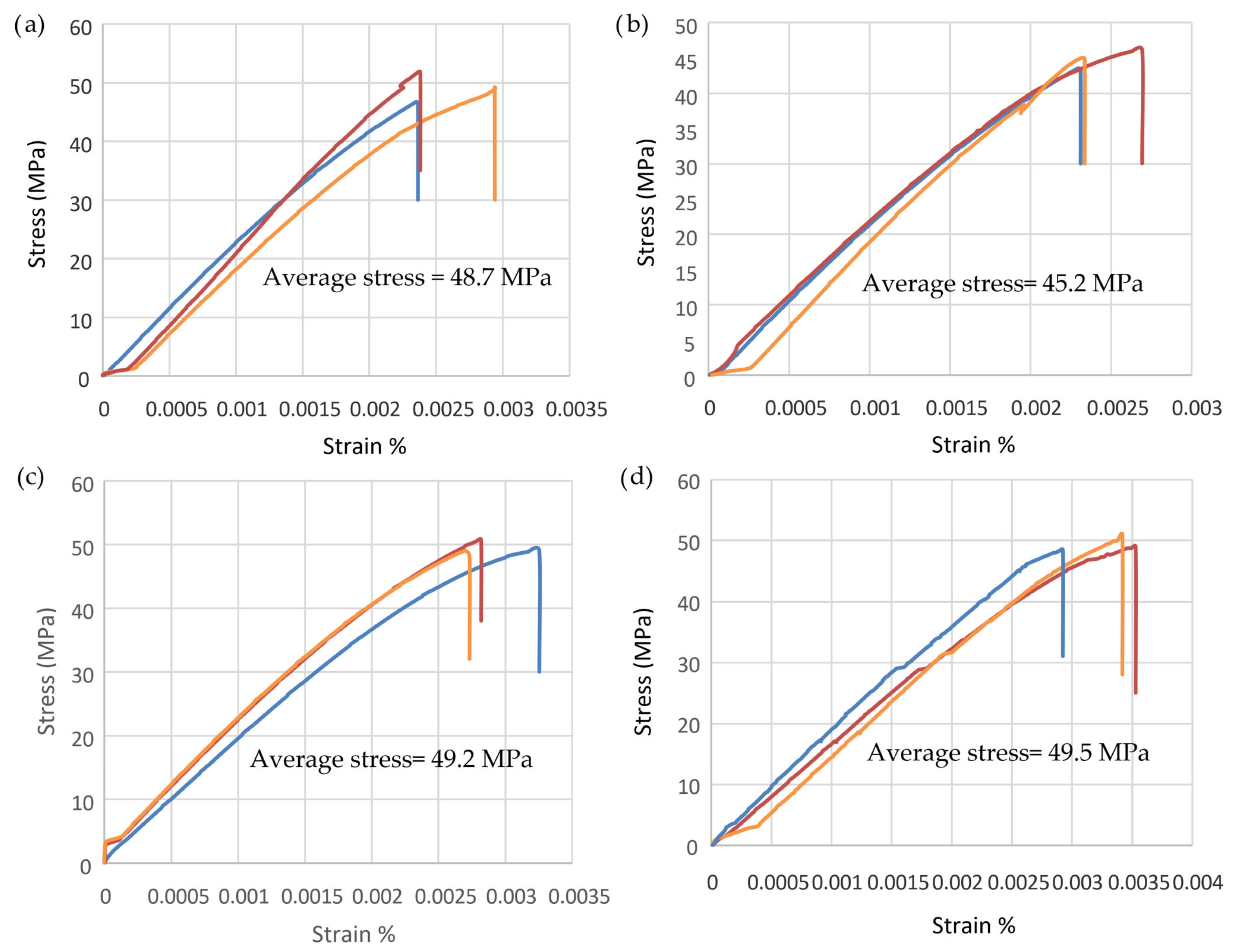
3.2. Compressive Test (Cylinders)
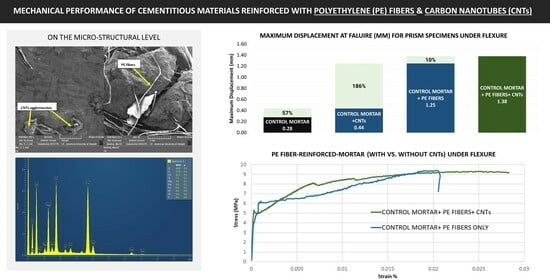
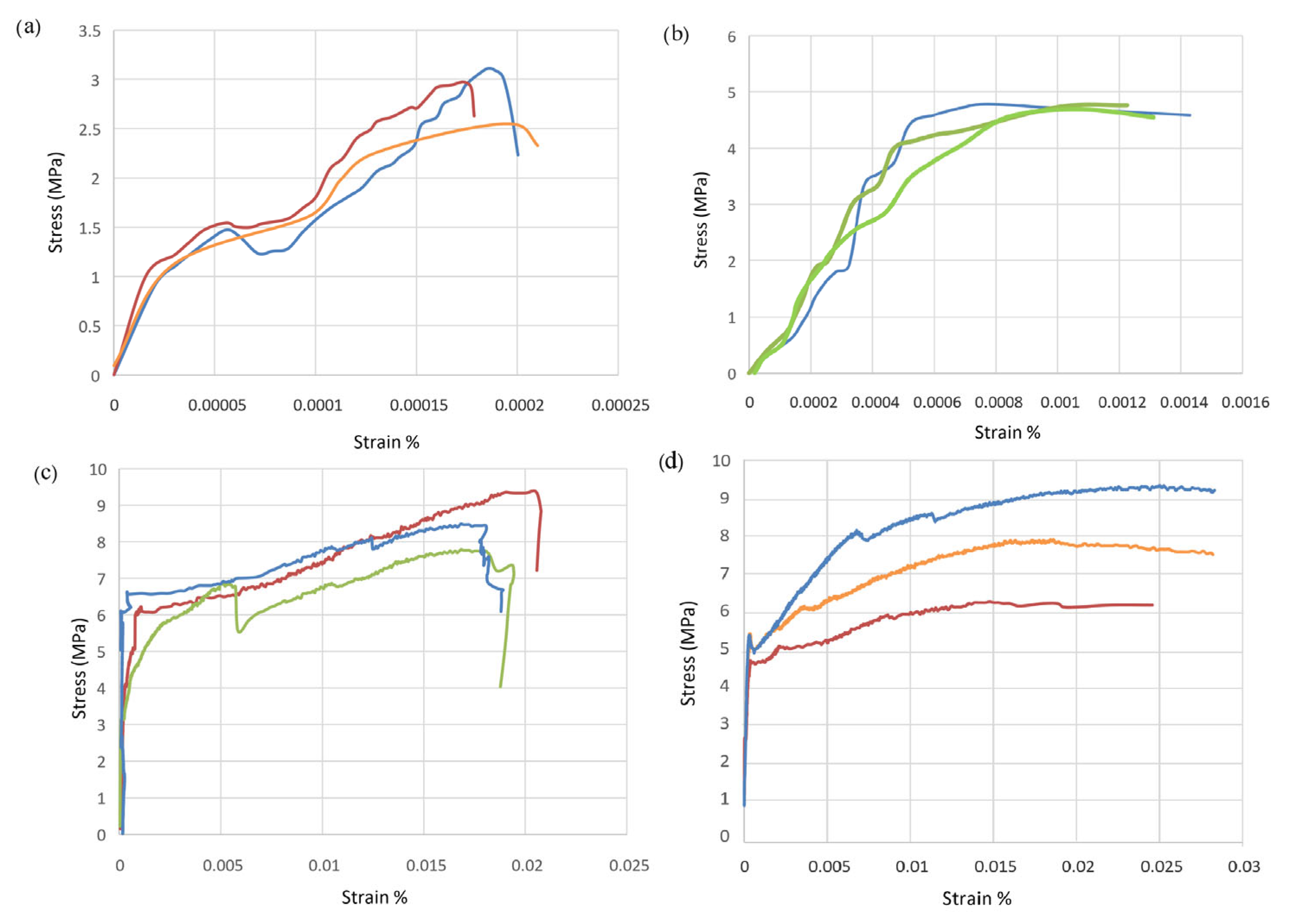
3.3. Flexural Tests (Prisms)
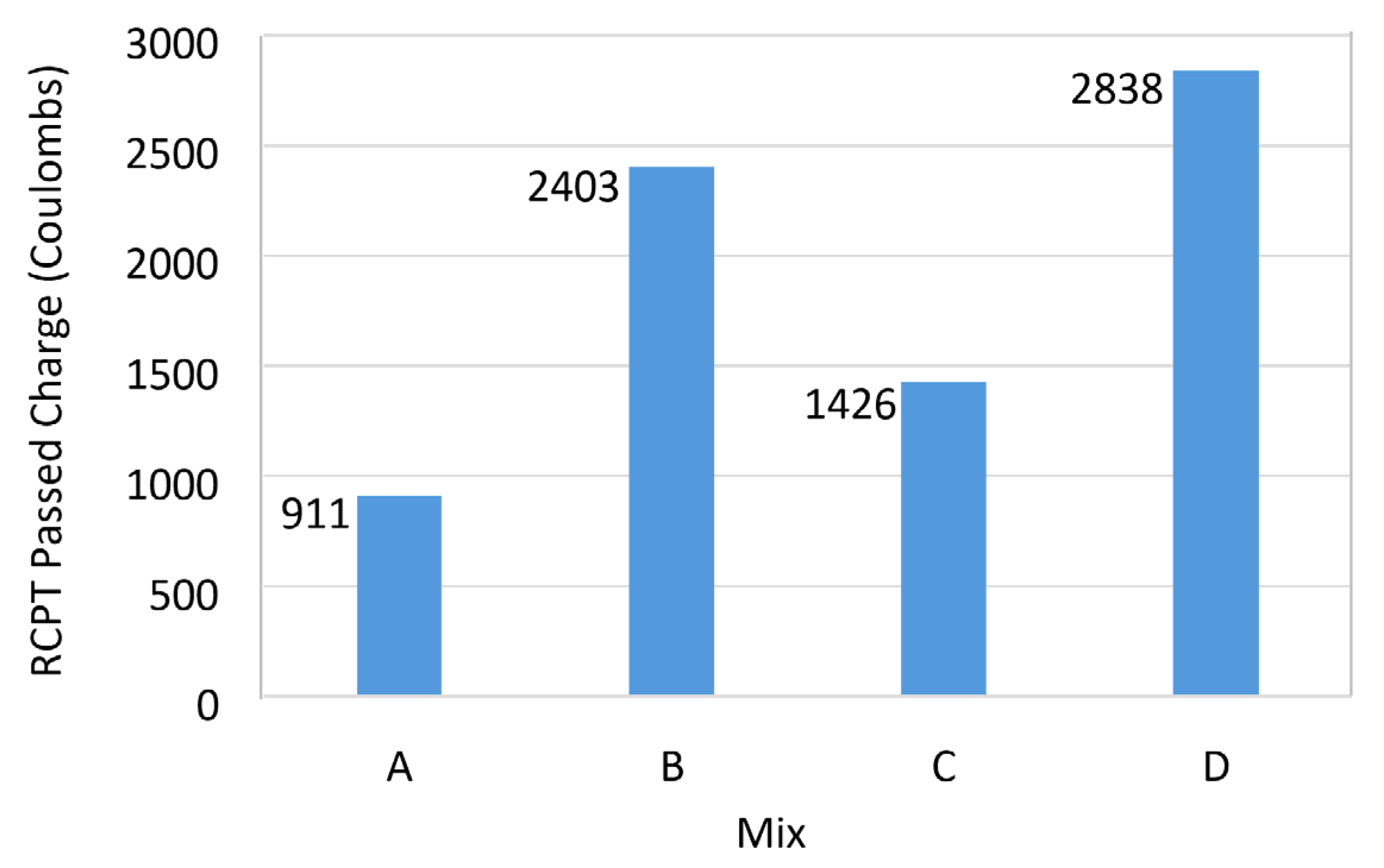
3.4. Rapid Chloride Permeability Test (RCPT)
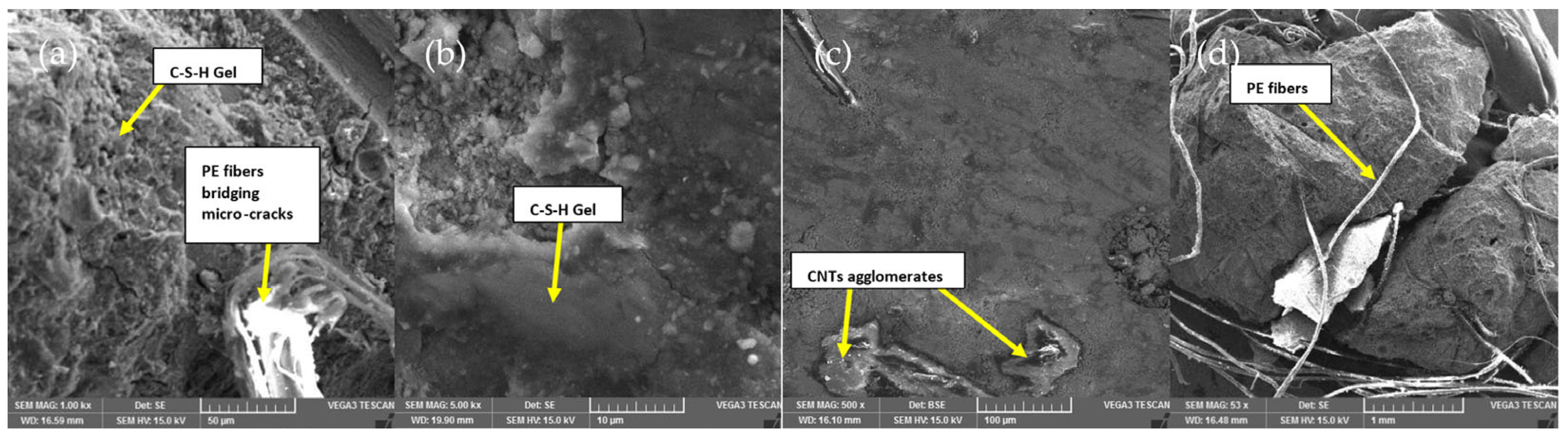
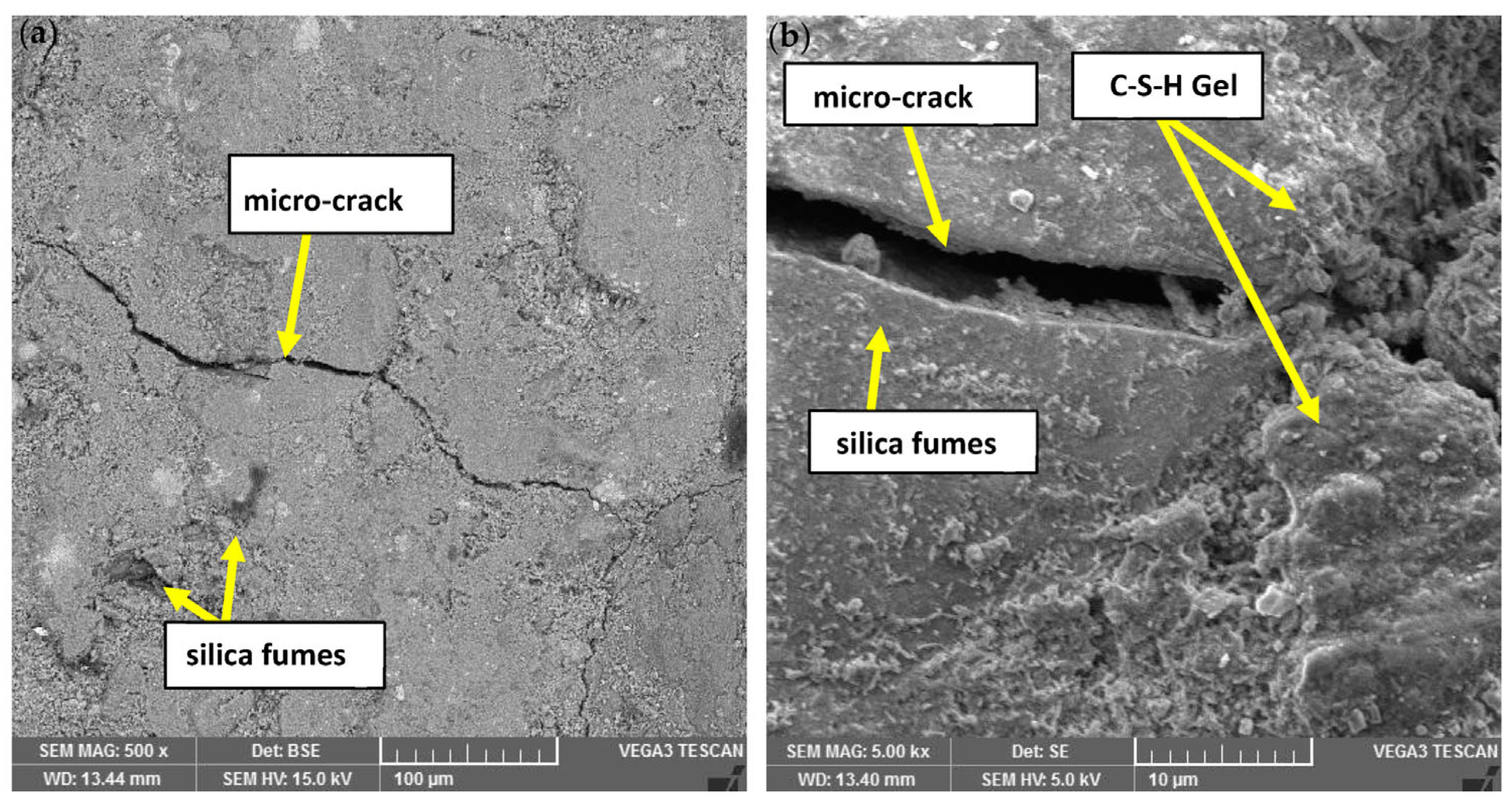
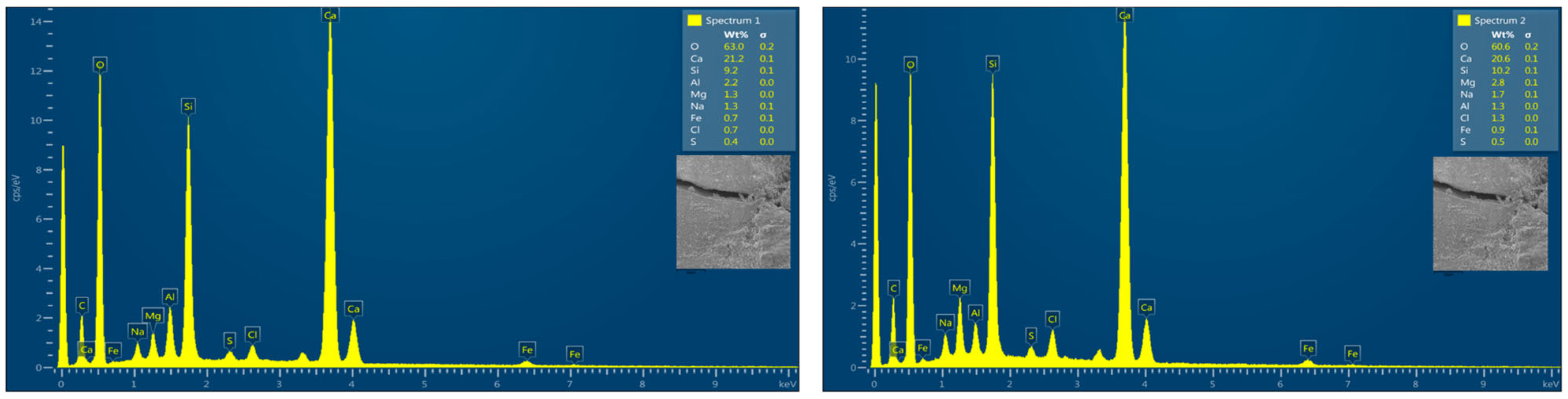
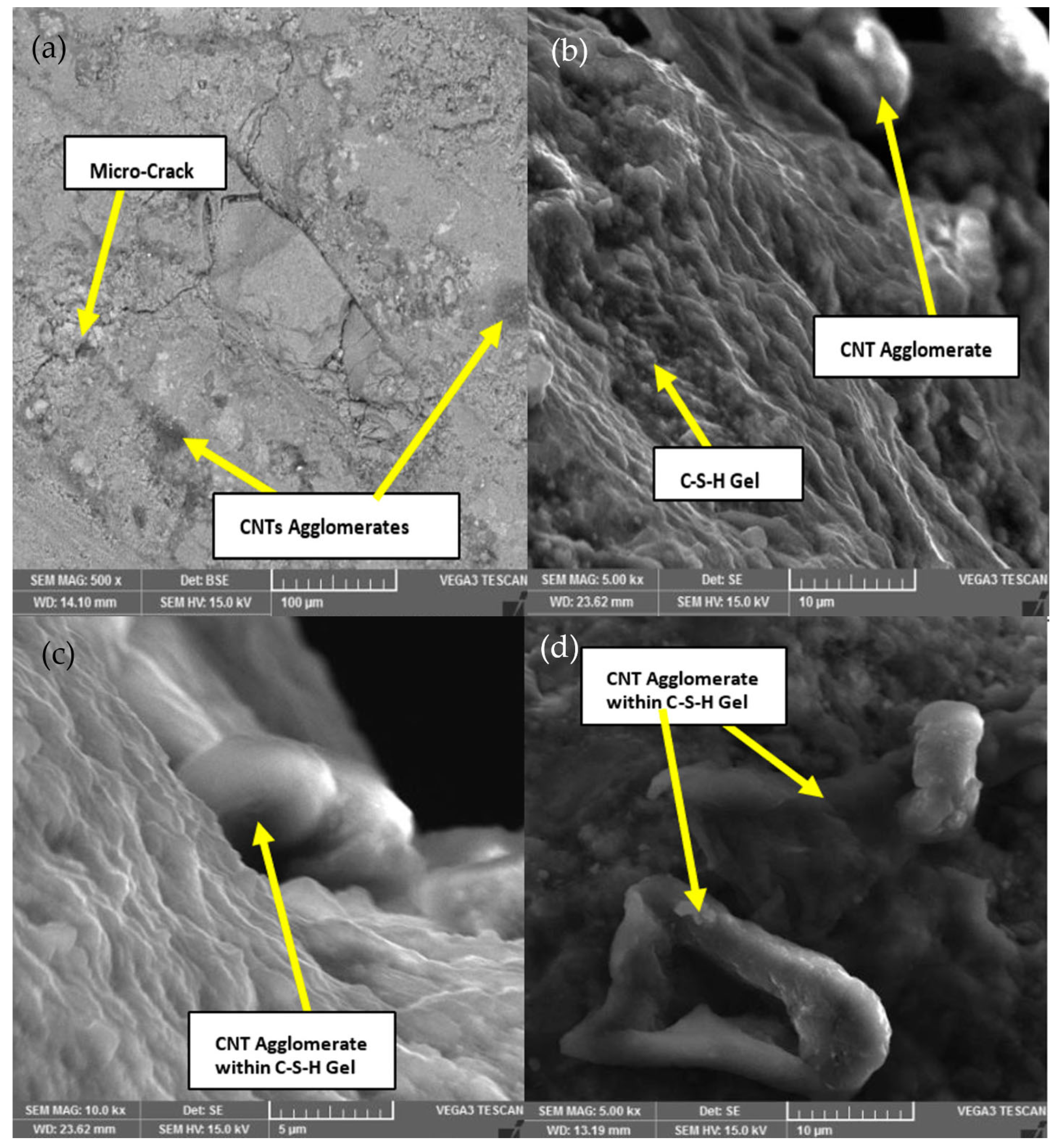
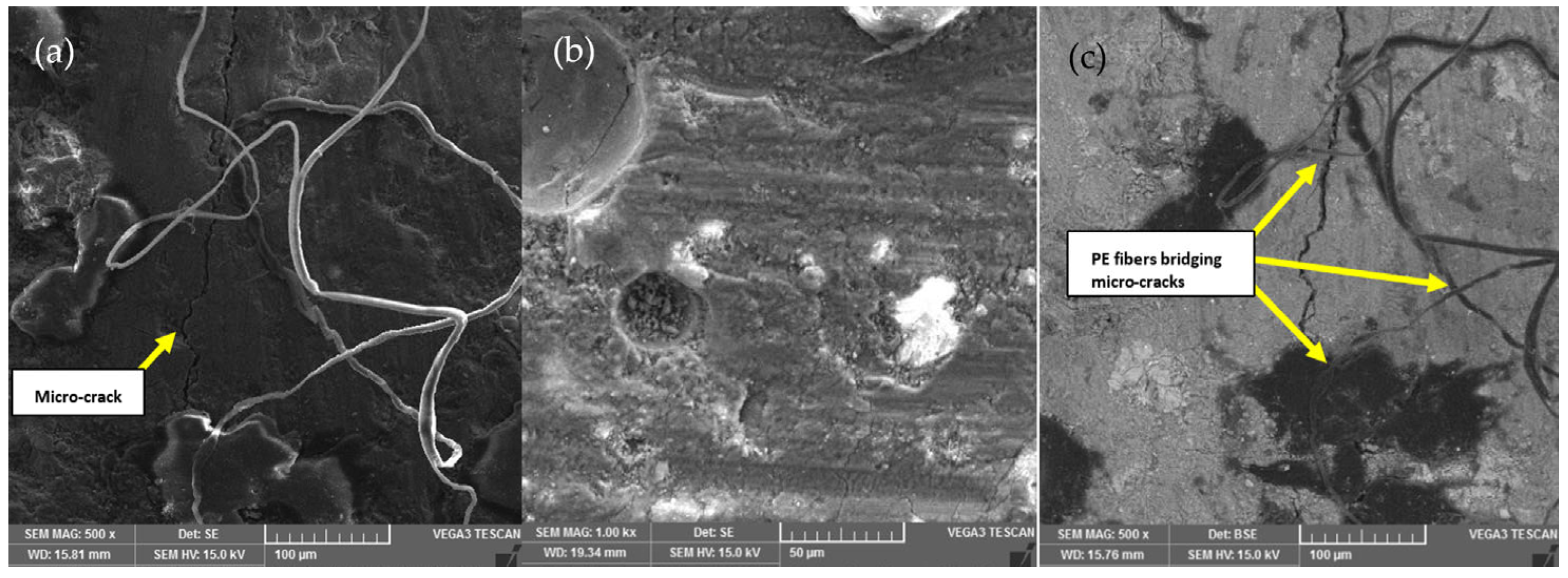
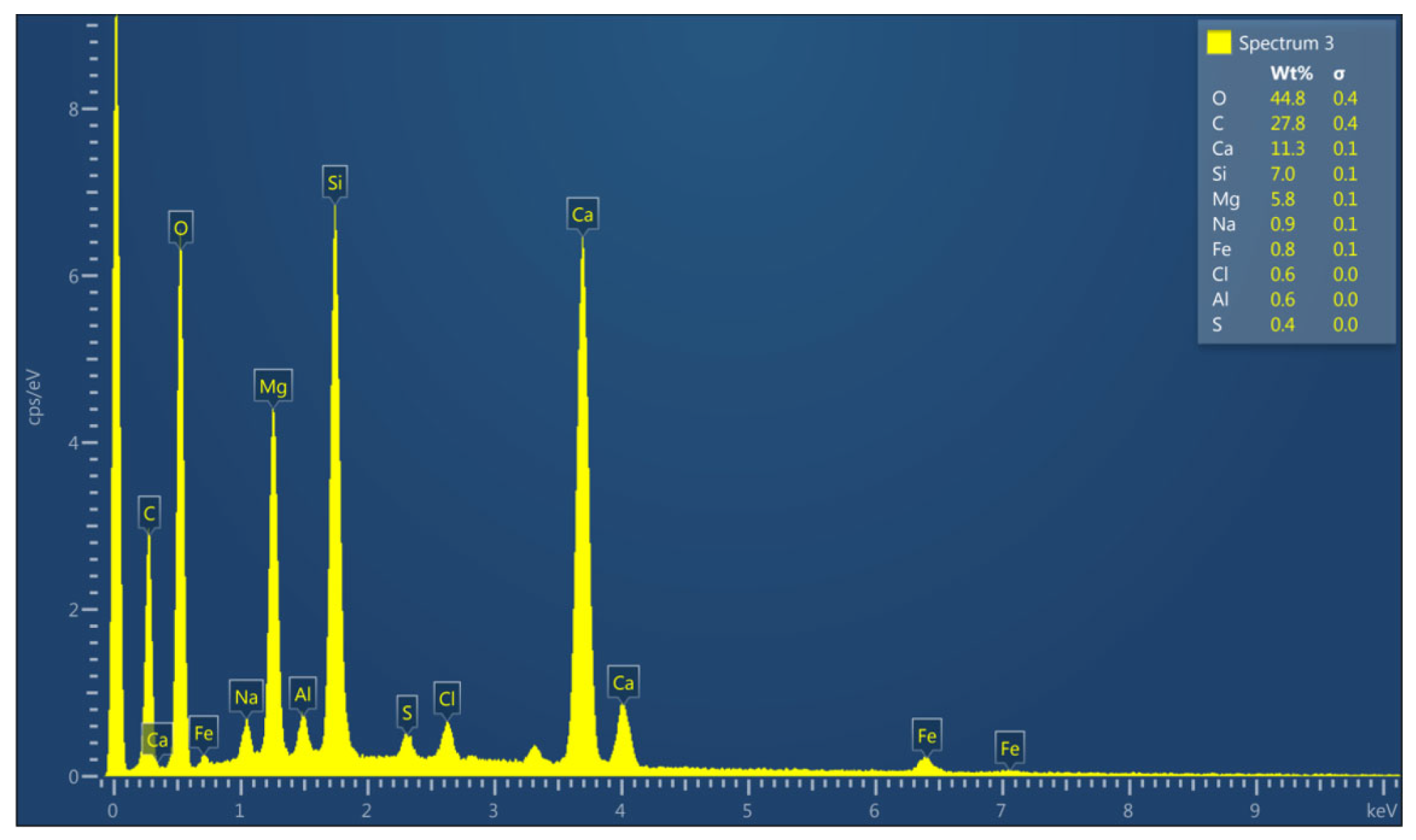
3.5. Morphology Analysis (SEM and EDX Tests)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyson, B.M.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K.; Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Grasley, Z. Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Nanofibers for Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposite Cementitious Materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, G.; Pervushin, G.; Maeva, I.; Keriene, J.; Pudov, I.; Shaybadullina, A.; Buryanov, A.; Korzhenko, A.; Senkov, S. Modification of Construction Materials with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Procedia Eng. 2013, 57, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, G.; Tulliani, J.M.; Musso, S. Carbon nanotubes cement composites. Cassino 2011, 36, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, S.K.; Rudžionis, Ž.; Rajapriya, R. The Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on the Flowability, Mechanical, Microstructural and Durability Properties of Cementitious Composite: An Overview. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, J.; Shi, F.; Shabaz, M. Experimental Analysis of Mechanical Properties and Durability of Cement-Based Composite with Carbon Nanotube. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8777613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunashyal, A.M.; Tippa, S.V.; Quadri, S.S.; Banapurmath, N.R. Experimental Investigation on Effect of Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Fibres on the Behavior of Plain CementMortar Composite Round Bars under Direct Tension. ISRN Nanotechnol. 2011, 20, 856849. [Google Scholar]
- Cerro-Prada, E.; Pacheco-Torres, R.; Varela, F. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on strength and electrical properties of cement mortar. Materials 2021, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Al Ansari, M.S.; Taha, R.; Al Nuaimi, N.; Abu Taqa, A. Carbon Nanotube Effect on the Ductility, Flexural Strength, and Permeability of Concrete. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 6490984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, S.; Cho, S.; Chung, W. Enhanced bonding behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotube cement composites and reinforcing bars. Compos. Struct. 2020, 243, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Sun, Z. Probabilistic model for flexural strength of carbon nanotube reinforced cement-based materials. Compos. Struct. 2020, 253, 112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, S.; Bhuvaneshwari, B.; Iyer, N.R. Can Carbon Nanotubes Make Wonders in Civil/Structural Engineering? Prog. Nanotechnol. Nanomater. 2013, 2, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jeon, J.; Lee, H. Flow, Water Absorption, and Mechanical Characteristics of Normal and High-Strength Mortar Incorporating Fine Bottom Ash Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxa, Z.S.; Boutsioukou, S.; Amenta, M.; Favvas, E.P.; Kourkoulis, S.K.; Alexopoulos, N.D. Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes into White Cement Mortars: The Effect of Concentration and Surfactants. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isfahani, F.; Li, W.; Radaelli, E. Dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and its effects on the properties of cement composites. Cem. Conr. Compos 2016, 74, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomoglou, A.K.; Falara, M.G.; Gkountakou, F.I.; Elenas, A.; Chalioris, C.E. Influence of Different Surfactants on Carbon Fiber Dispersion and the Mechanical Performance of Smart Piezoresistive Cementitious Composites. Fibers 2022, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawreen, A.; Bogas, J. Creep, shrinkage and mechanical properties of concrete reinforced with different types of carbnnanotubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Rana, S.; Fangueiro, R.; Paiva, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced cementitious compositesdeveloped using a novel dispersion technique. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 73, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douba, A.; Emiroglu, M.; Kandil, U.; Taha, M. Very ductile polymer concrete using carbon nanotubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Chen, S.; Korayem, A.; Collins, F.; Wang, C.; Duan, W. Effect of ultrasonication energy on engineering properties of carbon nanotube reinforced cement pastes. Carbon 2015, 85, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.M.; Fattah, K.P.; Tamimi, A.K. Modelling mechanical behavior of cementitious material incorporating CNTs using design of experiments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafa, F.F. Properties and Applications of Fiber Reinforced Concrete. J. King Abdulaziz Univ. Eng. Sci 1990, 2, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Shafei, B. Investigation of Five Synthetic Fibers as Potential Replacements of Steel Fibers in Ultrahigh-Performance Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.H.; Abdul Razak, H. The Effect Of Synthetic Polyethylene Fiber on the Strain Hardening. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, N.; Behfarnia, K. Effect of Nano-Particles on Durability of FiberReinforced Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 934941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S. Mechanical Properties and Nanostructure of Cement-Based Materials Reinforced with Carbon Nanofibers and Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Microfibers. Adv. Mater. Sci. Concr. 2011, 270, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Potapov, V.; Efimenko, Y.; Fediuk, R.; Gorev, D. Impact Resistance of the Cement–Mortar Composite Modified with SiO2 Nanoparticles and Microfiber. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talayero, C.; Aït-Salem, O.; Gallego, P.; Páez-Pavón, A.; Merodio-Perea, R.G.; Lado-Touriño, I. Computational Prediction and Experimental Values of Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Cement. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, V.; Impraimakis, M. Multiscale modeling of carbon nanotube reinforced concrete. Compos. Struct. 2017, 182, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadias, I.E.; Tsongas, K.; Bantilas, K.E.; Falara, M.G.; Thomoglou, A.K.; Gkountakou, F.I.; Elenas, A. Mechanical Characterization of MWCNT-Reinforced Cement Paste: Experimental and Multiscale Computational Investigation. Materials 2023, 16, 5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C1240-20; Standard Specification for Silica Fume Used in Cementitious Mixtures. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Tamimi, A.; Hassan, N.; Fattah, K.; Talachi, A. Performance of cementitious materials produced by incorporating surface treated multiwall carbon nanotubes and silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C128-01; Standard Test Method for Relative Density (Specific Gravity) and Absorption of Fine Aggregate. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- Vairagade, V.S.; Kene, K.S. Experimental Investigation on Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2012, 2, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar]
- E111-04; Standard Test Method for Young’s Modulus, Tangent Modulus, and Chord Modulus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- C1609; Standard Test Method for Flexural Performance of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Duthinh, D.; Starnes, M. Strength and Ductility of Concrete Beams Reinforced with Carbon FRP and Steel; U.S. Department of Commerce-Technology Administration-Building and Fire Research Laboratory: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, A.R. Comparison of Rapid Tests for Evaluation of Chloride Resistance of Concretes with Supplementary Cementitious Materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Sharma, U.; Mishra, G.; Ahalawat, S. Microstructure Improvement of Cementitious Systems using Nanomaterials: A Key for Enhancing the Durability of Concrete. Mech. Phys. Creep Shrinkage Durab. Concr. 2013, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.-M.; Yang, Z.J.; Chang, C.; Song, G. Numerical Assessment of Electric Roadway Deicing System Utilizing Emerging Carbon Nanofiber Paper. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 2012, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Kriven, W.M.; Deventer, J.S. Understanding the Relationship between Geopolymer Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 269, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelisser, F.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Mikowski, A. Effect of the Ca/Si Molar Ratio on the Micro/nanomechanical Properties of Synthetic C-S-H Measured by Nanoindentation. J. Phys. Chem. 2012, 116, 17219–17227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Azizli, K.; Sufian, S.; Man, Z. Effect of Na/Al and Si/Al Ratios on Adhesion Strength of Geopolymers as Coating Material. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 625, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
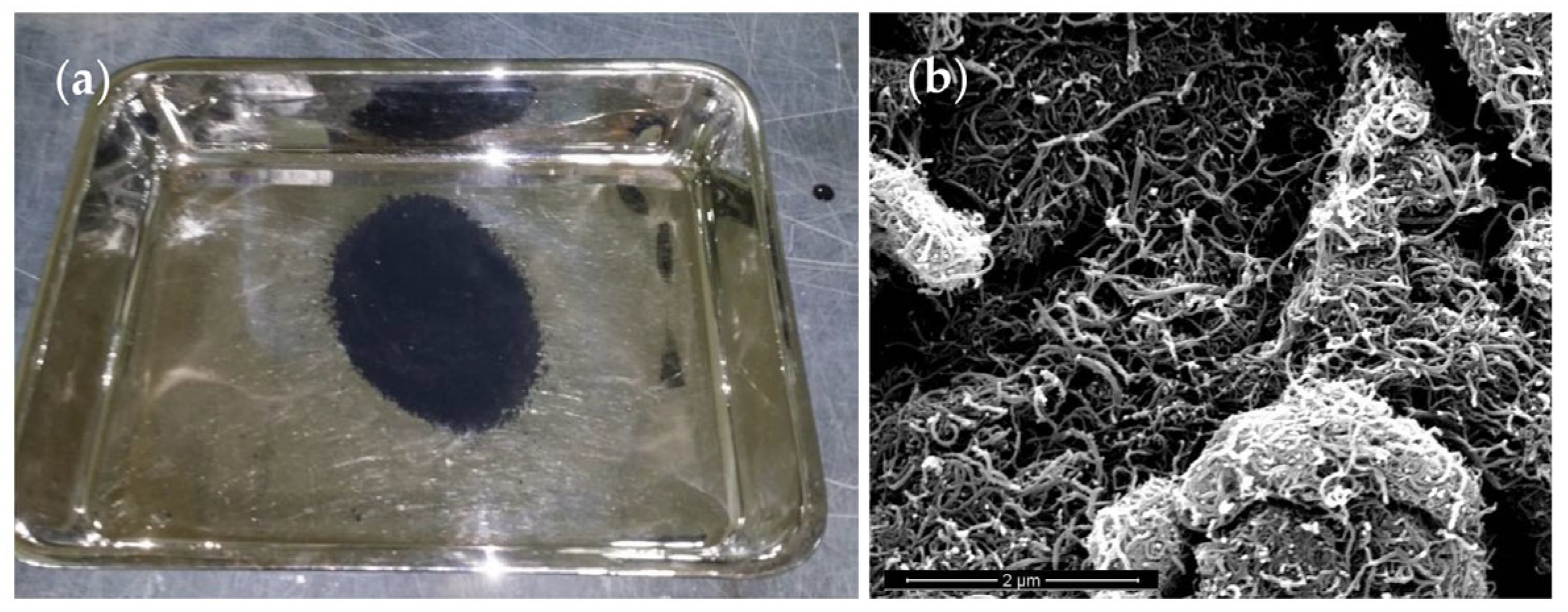






| Type | Diameter | Length | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNT-COOH | 20–40 nm | 10–30 µm | >88% |
| Fiber Type | Tensile Strength | Modulus of Elasticity | Fiber Length | Fiber Diameter | Specific Gravity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra High-Modulus Polyethylene Fibers | 2500 MPa | 70 GPa | 12 mm | 38 µm | 0.96 |
| Mix | Description | Fiber (% of Volume) | CNTs (% wt of Cement) | Cement (kg/m3) | Silica Fumes (kg/m3) | CNTs (g/kg of mix) | Sand (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | Fibers (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Control mortar mix: plain mortar (with 15% silica fumes) | 706 | 125 | 0 | 920 | 380 | |||
| B | Control mortar mix + CNTs | 0.15% | 706 | 125 | 21.405 | 920 | 380 | ||
| C | Control mortar mix + Polyethylene fibers | 2% | 706 | 125 | 920 | 380 | 19.2 | ||
| D | Control mortar mix + CNTs + Polyethylene fibers | 2% | 0.15% | 706 | 125 | 21.405 | 920 | 380 | 19.2 |
| Mix | Slump (cm) | Air Content (%) | Density (kg/m3) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 6 | 2.3 | 2196 | 23.0 |
| B | 6.3 | 2.4 | 2200 | 23.5 |
| C | 3 | 3.2 | 2395 | 23.5 |
| D | 3.6 | 3.5 | 2397 | 23.5 |
| Mix | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Maximum Strain at Failure | Maximum Strain at Yield | Ductility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (control) | 48.7 | 24.82 | 0.0023835 | 0.001506 | 1.583 |
| B (CNTs) | 45.2 | 21.92 | 0.002281 | 0.000957 | 2.383 |
| C (PE fibers) | 49.2 | 20.79 | 0.0027835 | 0.001312 | 2.122 |
| D (CNTs + PE fibers) | 49.5 | 17.22 | 0.0034953 | 0.001836 | 1.903 |
| Mix | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Avg. Peak Displacement at Failure (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| A (control) | 2.87 | 0.2770 |
| B (CNTs) | 4.75 | 0.4359 |
| C (PE fibers) | 8.43 | 1.2486 |
| D (CNTs + PE fibers) | 7.73 | 1.3784 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlAraj, R.R.; Tamimi, A.K.; Hassan, N.M.; Fattah, K.P. Mechanical Performance of Cementitious Materials Reinforced with Polyethylene Fibers and Carbon Nanotubes. Fibers 2024, 12, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12010001
AlAraj RR, Tamimi AK, Hassan NM, Fattah KP. Mechanical Performance of Cementitious Materials Reinforced with Polyethylene Fibers and Carbon Nanotubes. Fibers. 2024; 12(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlAraj, Rashad R., Adil K. Tamimi, Noha M. Hassan, and Kazi Parvez Fattah. 2024. "Mechanical Performance of Cementitious Materials Reinforced with Polyethylene Fibers and Carbon Nanotubes" Fibers 12, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12010001
APA StyleAlAraj, R. R., Tamimi, A. K., Hassan, N. M., & Fattah, K. P. (2024). Mechanical Performance of Cementitious Materials Reinforced with Polyethylene Fibers and Carbon Nanotubes. Fibers, 12(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12010001