Abstract
In the present society, the recycling and reuse of valuable substances are of utmost importance for economic and environmental purposes. At the same time, there is a pressing need to develop new methods to protect the ecosystem from many human activities, including those that have contributed to an ever-increasing presence of pharmaceutical pollutants. In this study, a straightforward approach that applies a magnetic carbon composite for the effective removal of NSAIDs from biological fluids is reported. The composite was produced by recycling wasted handkerchiefs, to provide cellulose to the reactive system and then transformed into carbon via calcination at high temperature. The morphological and structural features of the prepared “Fe3O4@-activated carbon” samples were investigated via thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy. Magnetic solid-state extraction was carried out to reveal the adsorption capabilities of the magnetic carbon composite and then combined with UHPLC–PDA for the determination and quantification of five NSAIDs (furprofen, indoprofen, ketoprofen, flurbiprofen, and indomethacin). The method developed herein proved to be fast and accurate. The adsorbent could be reused for up to 10 cycles, without any decrease in performance; thus, it contributes to an intelligent and sustainable economic strategy projected toward minimal waste generation.
1. Introduction
Currently, for the benefit of society and the environment, it is urgently needed to be able to identify those valuable substances that can be recovered and recycled possibly by using cheap and green procedures in order to reduce the amount of waste that is finally disposed of and that consumes precious land and increases the cost of disposal. An enormous amount of paper waste, around 26% of total waste, originated from wood pulp, and cotton is produced yearly without being recycled or reused implying that the consumption of paper (and pulp) will double by 2060 [1]. Wastepapers mostly contain high percentages of cellulose fibres (90–99%) organised in a 3D interconnected network, which make them fibrous precious materials reusable in many technological domains. The unique properties of cellulose fibres, such as high carbon content, porosity, the presence of carboxylic and hydroxyl functional groups, etc., provide an opportunity for them to be properly exploited, contemporarily making full use of available paper resources. Cellulose-based composites are being explored for their application in numerous fields (biomedical, catalysis, optical, etc.) and as precursors for the synthesis of metal and metal oxides, and directly as carbon source precursors. Some examples have appeared recently that promote the use of filter paper and print paper to form 3D net-like composites containing iron oxide, showing good performance in energy devices [2]. Other possibilities for obtaining functional materials from wastepaper and, when possible, also in the framework of the green chemistry principle, can be found in the environmental remediation, for removal of pollutants by using carbon materials as adsorbents [3]; lately, they are also used in the development of sensitive analytical methods, for extracting potentially toxic substances from food and beverages [4,5].
Establishing effective methods for the determination and removal of contaminants such as pharmaceuticals, additives, and harmful products also deriving from industrial waste, increasingly requires the development of new materials and new strategies. Investigation of contaminants in food, environmental, and biological fluid is currently a need that has to be properly addressed by advancing material chemistry. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are not completely metabolised by humans, so they are excreted into domestic effluents and have, therefore, become a matter of serious concern for public health [6]. Additionally, monitoring NSAIDs in body fluid is essential for toxicological and pharmacokinetics studies. Smart methods that can be adapted for different purposes and matrixes such as removal of NSAIDs from water and analysis of biological fluids might be envisaged, placing the emphasis on higher speed, automation, and reduced consumption of organic solvents, selectivity, environmental friendliness, and cost. Thus far, the techniques mainly used for the extraction of NSAIDs are protein precipitation [7,8], liquid–liquid extraction [9], and solid-phase extraction [10,11]. Protein precipitation (PP) is the fastest and simplest technique for the analysis of NSAIDs. PP consists of denaturing proteins by adding an organic solvent [8]. The subsequent centrifugation allows the separation of the medium in which the analytes are present from the precipitate containing the proteins. Liquid–liquid extraction is widely used in the extraction of analytes from various matrices. This technique allows the extraction of analytes using immiscible solvents. However, considering the acidic character of NSAIDs, the extraction of these analytes in an organic solvent can only be obtained by adjusting the pH of the sample to that corresponding to the protonated form of NSAIDs [12]. Solid-phase extraction has gained increasing popularity over time and is now considered the most reliable sample preparation technique due to the better extraction of the analytes, the elimination of interferents, and the higher recoveries obtained. In the field of chemical analysis, in particular, sample preparation is one of the most significant and critical steps since it greatly affects the quality of the data and the analysis time [13]. Typically, in sample preparation, developing a selective sorbent is the main concern, due to its importance in the extraction of target analytes from complex matrices. Magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) consists of a magnetic material dispersed into a sample solution that can be recovered by applying a magnetic field; the process can be used for various target analyte classes and has proved to be effective and simple [14]. Above all, the main advantage of MSPE, compared with conventional SPE, is the fast isolation of magnetic materials so that the sample pre-treatment time is greatly reduced. In this context, carbon-based materials containing specific metal–organic structures have gained the attention of the scientific community for their easy synthesis, high porosity, and large surface area, which make them ideal absorbents in MSPE. Various magnetic carbon-based materials have been investigated for the separation of organic and inorganic contaminants, such as Fe3O4@MWCNT [15,16,17], NiMn2O4-nanosphere-decorated, cellulose-based carbon fibres [18], magnetic graphene, graphene oxide [19,20], Co@CNTS [21], etc. Currently, their widespread diffusion is limited because of the high cost of production and the cumbersome synthetic procedures, which consume a considerable amount of energy. For this reason, it is highly desirable to obtain carbon-based materials that are easily synthetised, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly [22].
In this study, we propose a new adsorbent based on iron oxide and obtained by using low-cost, abundant wastepaper handkerchiefs through a simple carbothermal reduction method. The wastepaper handkerchiefs were used as a carbon source to generate Fe3O4 in situ, giving a residual porous carbon which has high adsorption capacity. The samples were investigated via SEM–EDX, XRD, thermogravimetric analysis, and Raman spectroscopy to ascertain the effect of the relative proportion of iron and carbon on the stability, structure, and morphology. Finally, the prepared “Fe3O4@-activated carbon” samples were used for the MSPE of some NSAIDs contained in human plasma. The potential of this approach relies on the possible production of a large number of adsorbents, with proven separation capacity starting from waste—wastepaper as in this case—but also scrap iron waste by opportunely modifying the procedure, promoting a complete utilisation of resources for a more sustainable future.
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Standard
Ferric chloride, ammonium acetate, fenbufen, ketoprofen, furprofen, indoprofen, flurbiprofen, and indomethacin were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Ltd. (Milano, Italy). Methanol, acetonitrile, phosphate monobasic, and acetic acid were obtained from CARLO ERBA Reagents (Milano, Italy). Double-distilled water was obtained from a Millipore MilliQ Plus water treatment system (Millipore Bedford Corp., Bedford, MA, USA). The stock solutions of NSAIDs were prepared individually by weighing 20 mg of each powder on an analytical balance and dissolving it in a 10 mL volumetric flask with a mixture of water and methanol (50/50 v/v). The stock solutions were diluted using MilliQ water to prepare the working solutions. Fenbufen was used as the internal standard. All chemicals were of analytical grade and used as received.
2.2. Preparation of “Fe3O4@-Activated Carbon”
Fe2O3 particles were at first prepared through a simple precipitation method. Briefly, 10 mL of 6 M sodium hydroxide was added dropwise to 10 mL of a 2 M solution of ferric chloride under vigorous stirring at 70 °C for 10 min [23]. The yellow-to-brick-red colour change in the solution indicated the formation of Fe(OH)3. Subsequently, the obtained solution was placed in an oven at 100 °C for 3 days. The final product (Fe2O3) was washed with water and methanol before drying at 60 °C for 12 h. The dirty handkerchiefs were cut, washed with water and methanol, and dried at 100 °C. Subsequently, 10 g of handkerchiefs and 10 g of Fe2O3 were dispersed in 200 mL of deionised water and stirred for 12 h at 50 °C to form a colloidal stock solution in which the m:m ratio of C:Fe was 1:1. The precipitate was washed with water and methanol and dried overnight at 80 °C. All samples were made by using this same procedure but changing the amount of Fe2O3, which was progressively reduced to 5, 2.5, and 1.25 g, thus obtaining the 2:1, 4:1, 8:1 (m:m) C:Fe ratio. A sample was made that contained more iron than C, that is, with a 1:2 C:Fe ratio. The samples were labelled in accordance with these ratios. Finally, “Fe3O4@-activated carbon” was selectively obtained via calcination at 600 °C for 1 h, with a ramp of 5 °C/min under a N2 atmosphere [24]. Each sample was ground for about 1 h and 20 min with a 10 min break every 10 min (in order not to overheat the samples), using a ZrO2 jar and spheres in a planetary ball mill PM100 (Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany).
2.3. Characterisation
Morphological analysis was performed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) on gold-sputtered samples using a Phenom XL Desktop (Thermo Fischer Scientific, Monza, Italy) apparatus, obtaining images in backscattering mode with an optical electron magnification of 3000x and 15 KV acceleration voltage. Each sample was then processed using Phenom ProSuite Elemental Mapping Software for the elemental analysis and the atomic distribution.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed using a PerkinElmer STA6000 (PerkinElmer, Italy SpA, Milano, Italy), in a nitrogen atmosphere at 20.0 mL/min in a temperature range of 25–800 °C, with a heating ramp of 5 °C/min. The results were collected and analysed with the Pyris software program.
The Raman spectroscopy analyses were carried out by using a Horiba XploRA ™ PLUS Raman microscope (HORIBA ITALIA Srl, Roma, Italy) with a 100×_VIS objective and 532 nm edge laser. The spectra were collected and processed through Labspec6 spectroscopy suite software.
X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) patterns were collected on a Bruker D2 Phaser benchtop diffractometer (Bruker Italy Srl, Milano, Italy) equipped with a Cukα radiation source operating at 30 kV and 10 mA, a graphite monochromator, and a PSD detector. The patterns were collected in the air with a step size of 0.02° and a counting time of 0.5 s per step in the angular range of 5–70°, using a PMMA sample holder.
2.4. Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction
The blank plasma samples were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Ltd. (Milano, Italy). At the same time, real blood samples were taken from patients at the SS. Annunziata Hospital in Chieti (Italy) as part of routine TDM that did not require extra visits from clinicians.
Blood samples containing EDTA as an anticoagulant were centrifuged at 1500× g for 10 min at 4 °C. From the obtained plasma (2 mL), proteins were eliminated by adding 2 mL of trifluoroacetic acid (25% w/v) and via subsequent centrifugation at 6500× g for 5 min. The supernatant was diluted to 5 mL using 10 mM phosphate buffer pH 3.0.
Then, 15 mg of “Fe3O4@-activated carbon” were added to the obtained plasma sample for the dispersive magnetic solid-phase extraction. The samples were all shaken for 2 min. Subsequently, using a neodymium magnet, the adsorbent material was recovered, and the solution decanted. The analytes were eluted using 500 µL of methanol with 0.5% of triethylamine. The sorbent was recovered using a magnet, while the eluate was analysed via UHPLC.
2.5. UHPLC Apparatus and Operating Conditions
The NSAID analyses were carried out by using an ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography system (ACQUITY H-Class, Waters S.p.A., Milano, Italy). The instrument was equipped with a column heater, a degassing unit coupled with a quaternary pump (Acquity), a UPLC sample manager (Acquity), and a Waters 2996 photodiode array detector.
UHPLC separation of the analytes was achieved using a Kinetex C18 column (100 × 2.1 mm, 2.6 µm particle size), using isocratic elution. Mobile phases were 10 mM phosphate buffer pH 3 (phase A) and acetonitrile (phase B). To improve the peak shape, both phases were added with 0.1% triethylamine. The injection volume was 5 µL. For each analyte, the maximum wavelength was employed for their detection. The Empower 3.0 software (Waters) was utilised for gathering data and running the measurements. The run time was 4.5 min.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Materials Characterisation
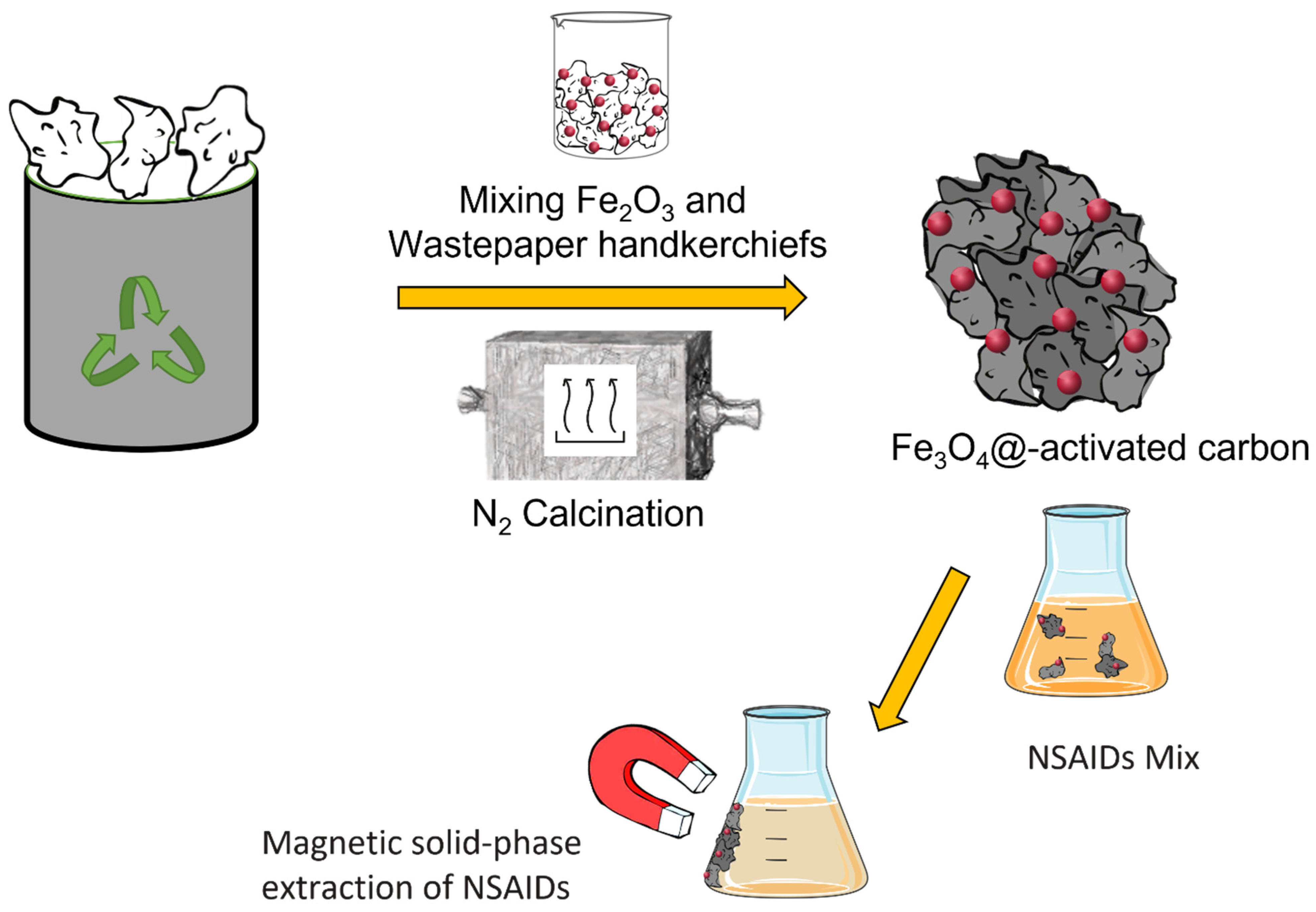
Several protocols can be found in the literature for manufacturing carbon-based structures that comprise graphene, carbon nanotubes, carbon black, etc., and contain iron oxide with paramagnetic properties [22,23,25]. In Figure 1, a step-by-step graphical representation of the overall procedure used in this study is presented. Wasted handkerchiefs recovered from the bins in our laboratory were subjected to washing cycles with water and ethanol and were the source of cellulose in the preparation of a cellulose-based iron composite used as a precursor for the in situ synthesis of Fe3O4. Cellulose ultimately provided carbon for the successive pyrolysis reaction, in which C is the reducing agent.
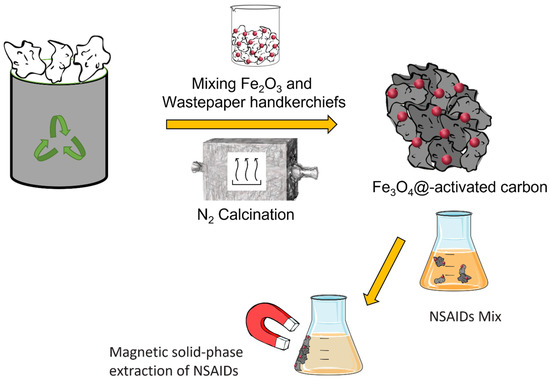
Figure 1.
Graphical representation of the main steps of sample preparation and MSPE of NSAIDs performed in this study.
The wastepaper showed an excellent capacity to absorb the iron oxide by forming a colloidal solution simply due to cellulose which entrapped iron in its fibrous structure.
As shown previously by Liu et al. [24], thermal treatment in pure N2 favours the synthesis of Fe3O4 versus Fe2O3, with the latter requiring enough O2 to be formed. Furthermore, C derived from the cellulose decomposition produced a reducing environment, also beneficial for the synthesis of Fe3O4.
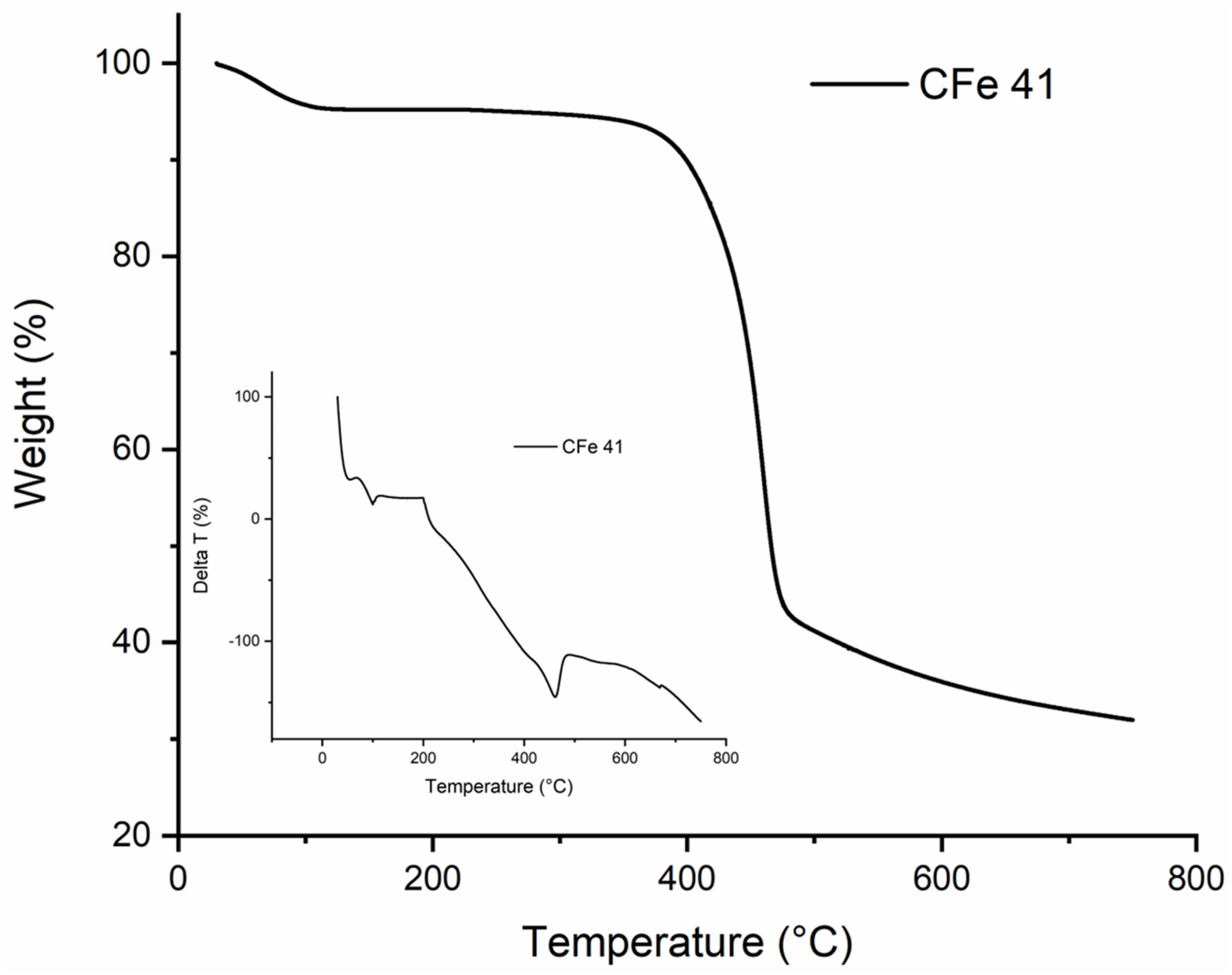
Prior to the thermal treatment, thermal analysis was carried out to optimise the calcination conditions. The thermogram obtained for the CFe41 sample with the respective DTA curve is shown as an example (Figure 2).
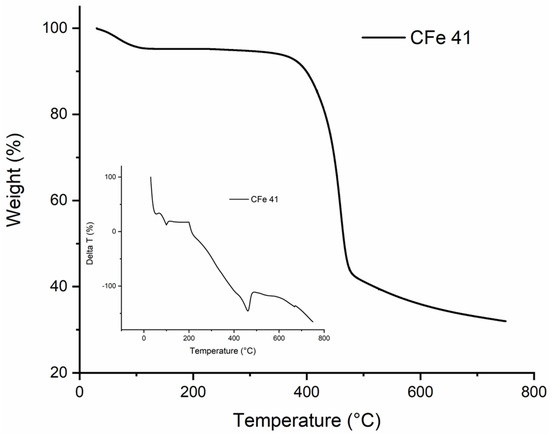
Figure 2.
TG and DTA curves of the CFe 41 sample in N2 atmosphere.
Three stages can be identified for pyrolysis under nitrogen flow. Initially, there was significant weight loss due to dehydration which was also combined with some internal recombination/depolymerisation, starting from room temperature to 200–250 °C. Another important stage was then between 300 °C and 400 °C, caused by a rapid decomposition with the release of some volatiles such as CO, CO2, and the formation of pyrolysis products. In the final stage, up to 600 °C, less weight was lost, and the carbothermal reaction continued more slowly until the completion of calcination, with the final formation of the “Fe3O4@-activated carbon”. Higher temperatures on one side might be needed to release more volatile components and increase the specific surface area and carbon porosity, but on the other side surface functional groups can decompose, and this could worsen the adsorption capacity. In this case, the presence of nitrogen promoted the de-volatilisation of some volatile compounds, while the just in situ produced Fe3O4 acted as a template for the formation of pores in the carbon matrix [3] so that, during the synthesis, the temperature was set to 600 °C. In general, adsorption capacity is attributed to specific surface area and porosity since it has been reported that high SSA and large mesopores enable the adsorbate to more efficiently access the inner active sites, reducing the response time during application [26]. Therefore, it is essential to choose the proper synthesis conditions in order to obtain an optimal structure and maximise the adsorption efficiency.
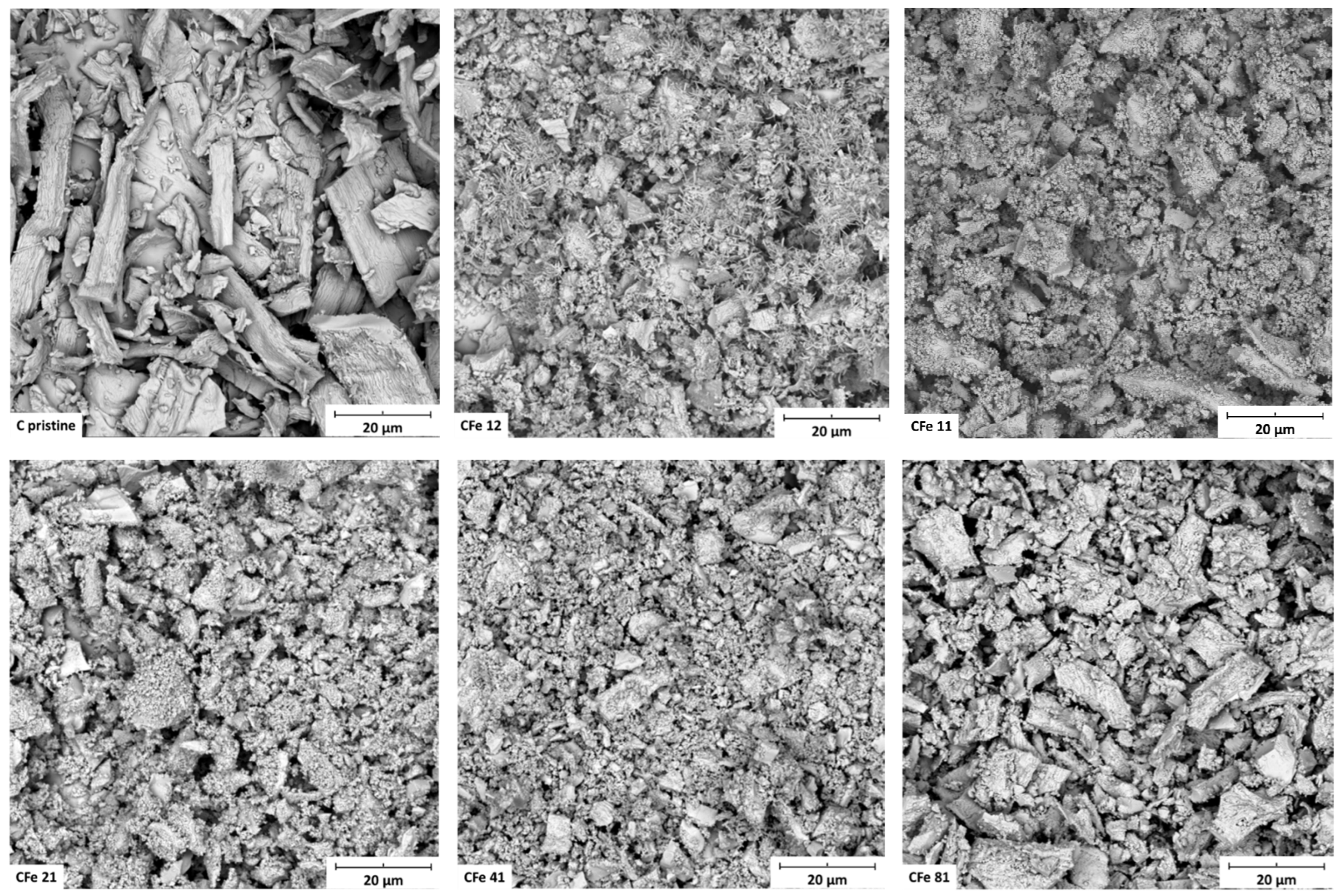
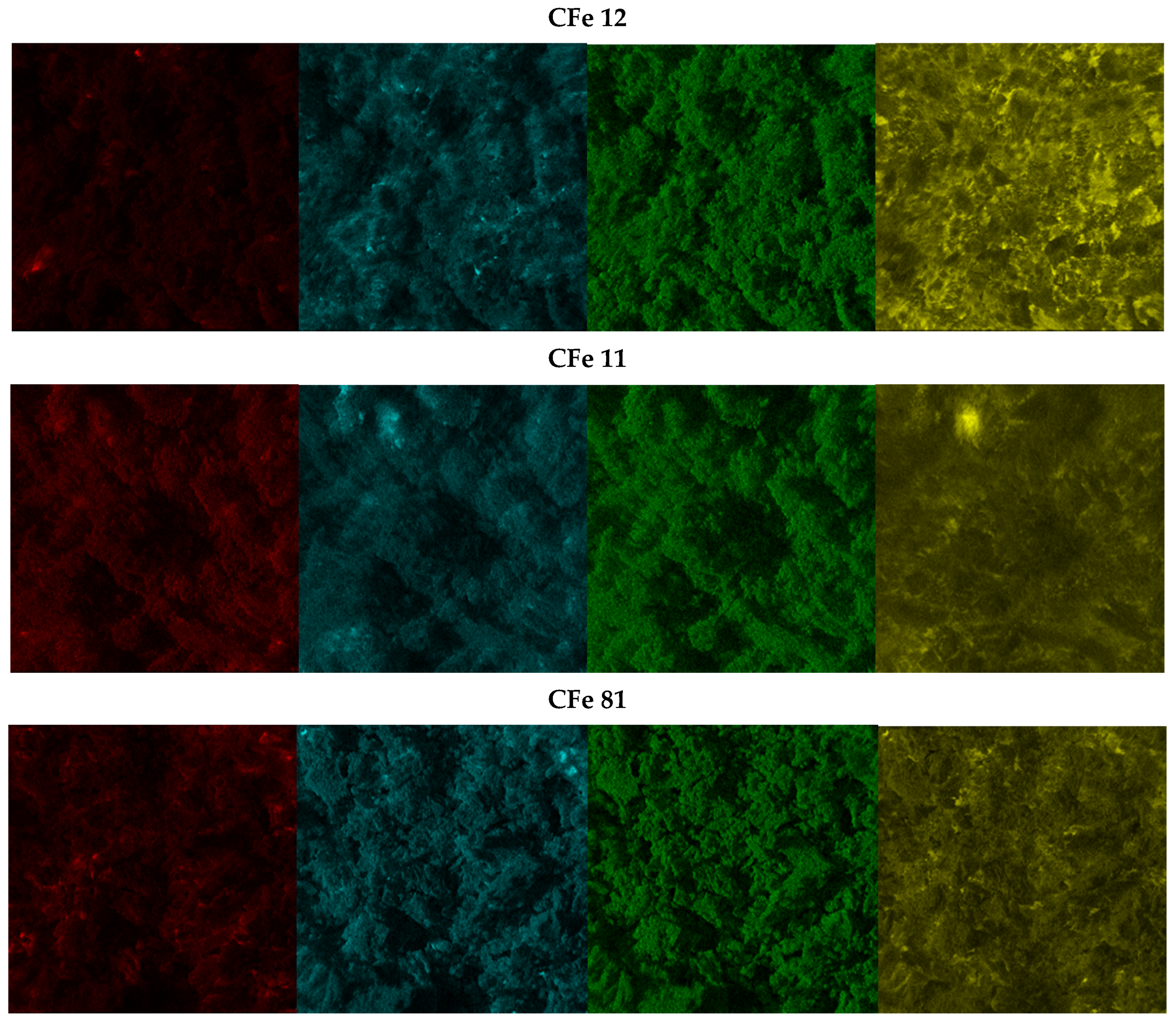
The SEM images (Figure 3) show the morphology of the samples after grinding, all of which appeared very similar, made of large particles (tens of microns) heterogeneously distributed. Additionally, it can be noticed that thinner particles covered the surface of the larger aggregates. The sample with no metal particles (C pristine) included very large fragments likely because it did not undergo the carbothermal reaction. Energy-dispersive X-ray mapping analysis (Figure 4) revealed that iron, carbon, and nitrogen were very homogeneously distributed in the samples. All areas that were investigated showed the same behaviour, and the iron and carbon distributions appeared very similar, suggesting that the iron oxide was very well-embedded in the carbonaceous matrix. The widespread diffusion of oxygen might indicate the presence of oxygen-containing functional groups on the particle surface [5].
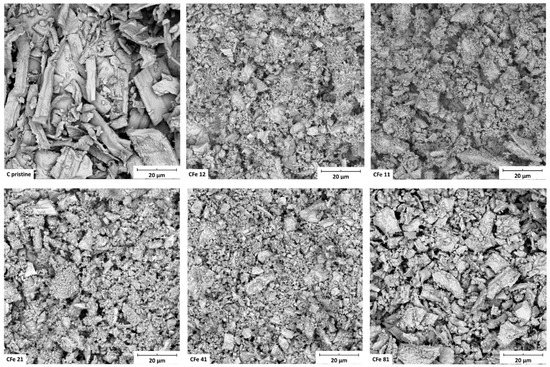
Figure 3.
SEM images of C pristine, CFe12, CFe11, CFe21, CFe41, and CFe81 after grinding in the planetary miller.
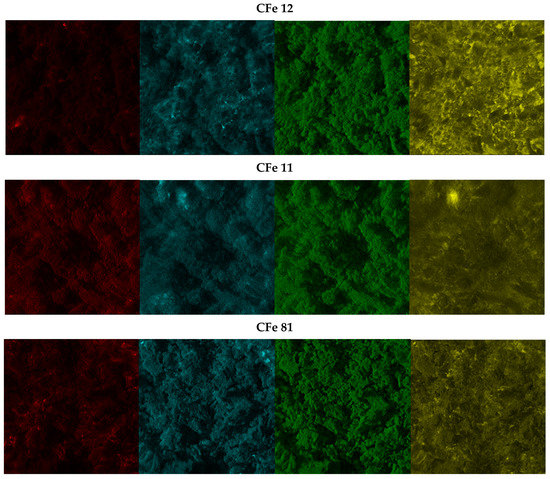
Figure 4.
EDX images of CFe12, CFe11, and CFe81. Colour code: carbon in red, oxygen in blue, nitrogen in green, and iron in yellow.
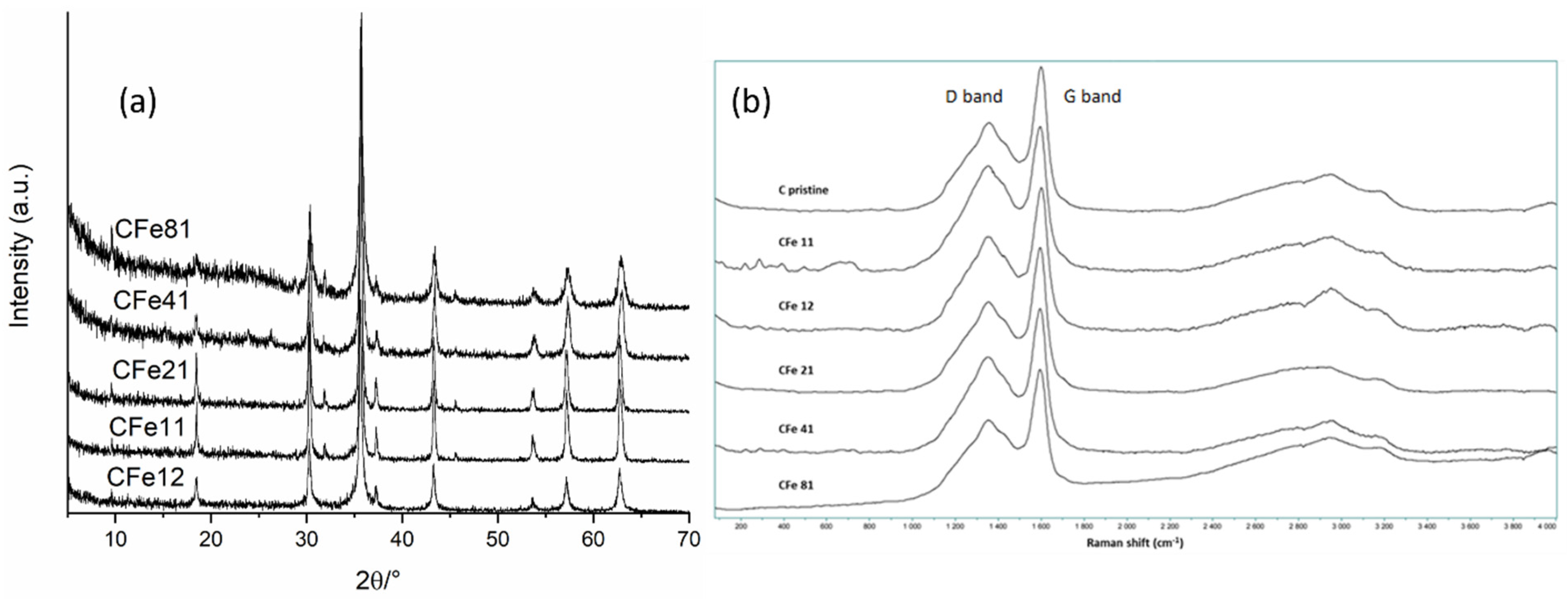
XRD patterns (Figure 5a) were acquired in order to identify the phases in the samples. The diffraction peaks matched very well with the reported data of magnetite (JCPDS No. 19-0629), thus confirming that the synthesis was effective in producing the target phase. When the paper:iron ratio was high, resulting in the presence of more carbon, such as for the CFe41 and CFe81 samples, the XRD patterns showed a lower crystallinity of the Fe3O4 phase, as suggested by the intensities and widths of the peaks. This could be due to the sluggish kinetics of the formation of magnetite, considering that the iron precursor was likely entrapped in the cellulose fibres and less exposed to the nitrogen atmosphere. Additionally, cellulose might have needed more time to decompose and to effectively contribute to the carbothermal reduction at the same calcination temperature, considering its high quantity.
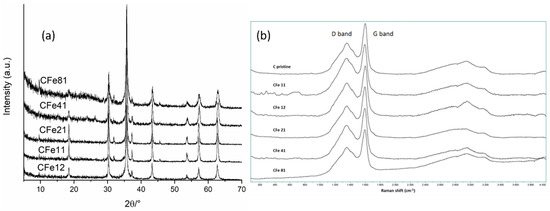
Figure 5.
(a) XRD patterns and (b) Raman spectra of all samples.
Peaks of carbon were not observed in the diffraction patterns because of their low crystallinity and scattering factor. Raman spectroscopy was then used to investigate the graphitisation of carbon (Figure 5b). Low-intensity peaks in the region <500 cm−1 can be assigned to the bands of Fe3O4 [4] but were barely distinguished, only in the sample with the highest starting amount of iron, the CFe11. Two broad bands at about 1330 and 1590 cm−1—the so-called D (sp3 carbon) and G (sp2 carbon) modes—were observed for all the investigated samples which are typical features of carbon materials. It is known that the vibrations responsible for the D mode are frequency-dependent, with resonance effect [27]; also, the intensity of the D band scales inversely with grain dimensions, thus in this case indicating a role surely played by nanometre-sized crystallites [27]. Additionally, G’ bands (2D) were seen in the region >2500 cm−1 which are not ordinary Raman bands, since their shift is dependent on the wavelength of an excitation laser [27]. The presence of G’ bands (2D) that were very broad and of very low intensity, together with a collapsed D band, further suggested that the sample contained a certain amount of amorphous carbon which was expected due to the calcination temperature, and in agreement with XRD results [28]. Very intense 2D-band Raman signals have been reported for samples that were annealed at temperatures higher than 800–850 °C [27,28] that promote a higher degree of carbon graphitisation.
3.2. NSADs Analysis
3.2.1. Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction and Optimisation of Conditions
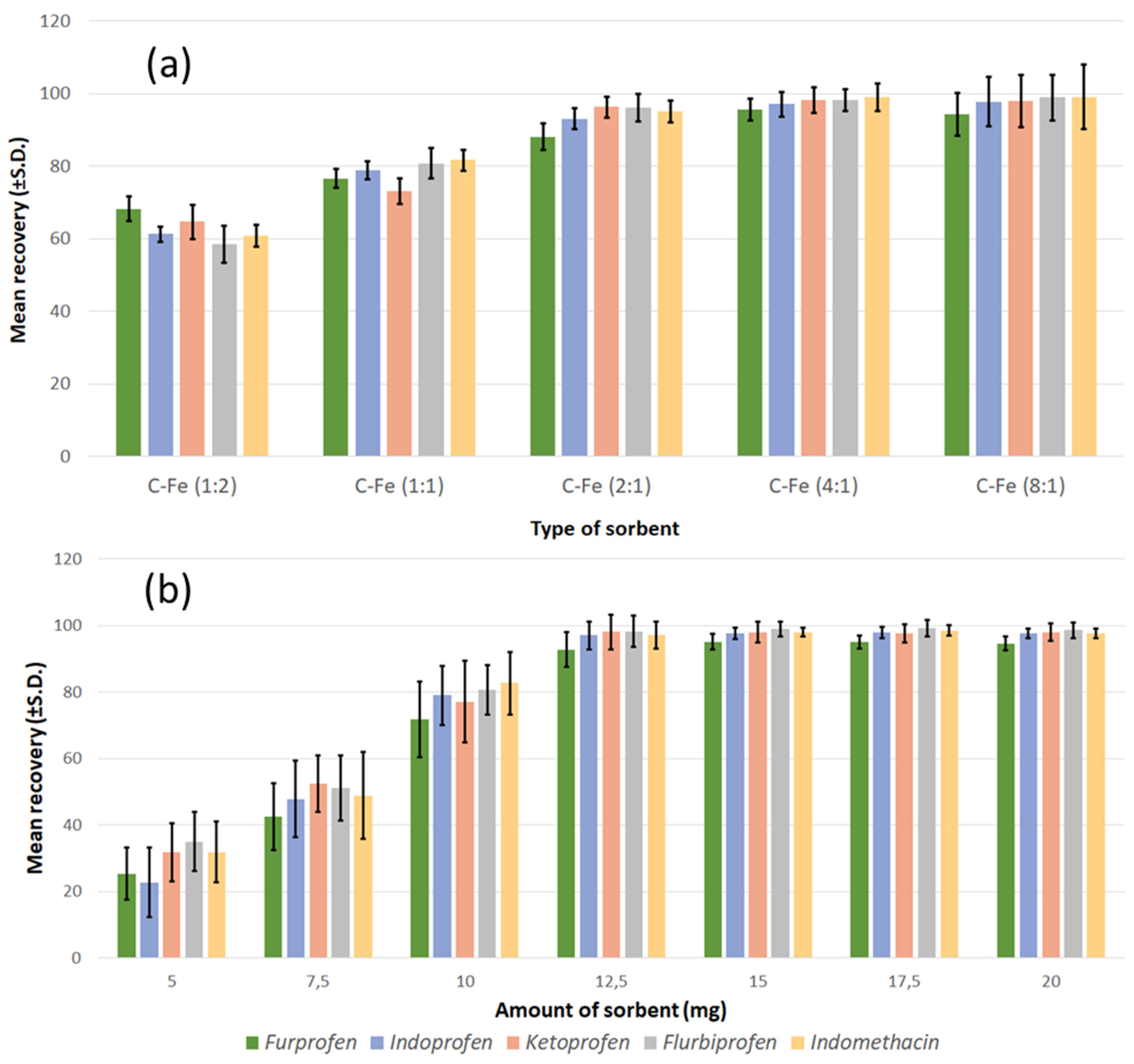
After morphological and structural characterisation, the samples were used as sorbents, and their performance was evaluated in order to determine whether they could be applied for the removal of contaminants and analytical purposes. Standard solutions containing NSAIDs at different concentrations (0.1, 1.0, and 7.5 µg/mL, respectively) were used to investigate the recovery response. The results regarding the type of sorbents (Figure 6a) showed that there was an increase in the adsorption capabilities of the sorbent by increasing the carbon content (from CFe12 to CFe41). However, the sorbent with the highest carbon content (CFe81) had an adsorption capacity slightly lower than that of the CFe41, and also the precision of the method was definitely inferior. This lowering in precision is likely due to the decrease in the separative capacity of the sorbent from the solution containing the analytes when an external magnetic field is applied. According to the results of previous characterisations, the CFe81 sample appeared to possess a lower crystallinity; some preliminary considerations deriving from this observation could suggest that, below a certain crystallinity threshold, there might be some influence of carbon crystallinity on the capability as adsorbent due to a different surface area and porosity.
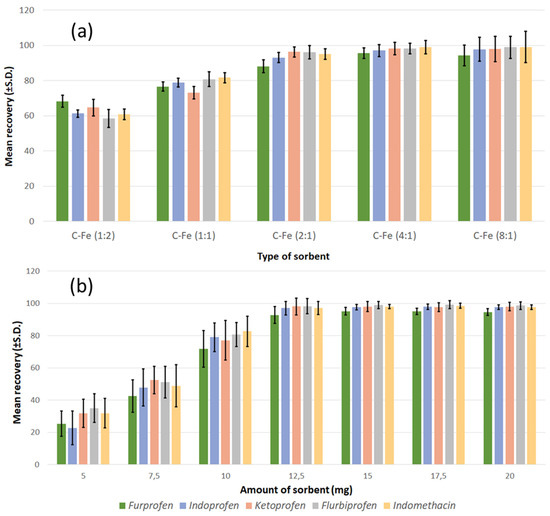
Figure 6.
(a) Effect of sample type and (b) effect of the amount of adsorbent on the extraction efficiency of the analytes in the process of MSPE.
This first set of measurements indicated that the CFe41 sample was the most suitable for further experiments. Therefore, the study of the effect of the quantity of adsorbent on the efficiency of extraction (Figure 6b) was carried out only for this sample, in the range of concentration 5–20 mg, using the NSAID standard solutions, as in the previous experiment. The extraction efficiency raised quickly, while the adsorbent mass increased to the value of 12.5 mg and then remained practically unchanged. A greater surface area became available when the mass of the magnetic carbon composite increased, and this might originate in the observed behaviour. Although 12.5 mg appeared sufficient for the complete adsorption of the analytes, greater repeatability was obtained using a quantity of adsorbent between 15 and 20 mg. Therefore, 15 mg was the quantity of CFe41 selected for further analysis.
The maximum extraction efficiency can be obtained only if the adsorbent is entirely dispersed in the sample; that is, if the mass transfer is completed, and the extraction equilibrium is reached. Therefore, the system has to be given enough time for the effective adsorption of analytes, which is a very important parameter governing the extraction process in MSPE [12,14]. Different standard solutions of NSAIDs were then used to study the recovery at different extraction times (0.5–5 min at 0.5 min intervals). These experiments showed that the extraction efficiency reached the maximum in 2 min, and no further improvement was observed for a longer time. For this reason, in all further experiments, the adsorption time was kept fixed at 2 min.
Additionally, the sample pH greatly influences the MSPE procedure and the extraction efficiency in at least two different ways: (i) the surface properties and structure of the adsorbate can be modified by the pH, and (ii) the molecular form of the target analytes can undergo protonation/deprotonation if pH is lower/higher than pKa, thus hindering adsorption [3,12]. Hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking, and the surface charge density mainly govern the adsorption of NSAIDs on magnetic carbon composites. The pKa values of the investigated targets ranged between 3 and 6, and the extraction recovery was examined in the range of 2–9 pH levels. At a 3.5 pH value, a satisfactory extraction recovery was observed due to the fact that most of the NSAIDs were in a neutral state and could be easily adsorbed onto CFe41.
To assess the influence of the ionic strength on the extraction recovery, sodium chloride was used. The concentration of the tested solutions was in the 0–7 (% w/v) range. It was found that the extraction efficiency lowered as the salt concentration increased. This effect is likely due to the increasing solution viscosity which hinders mass transfer. No salts and a pH of 3.5 were thus selected.
Another important parameter to be considered in the MSPE method is the elution solvent. Various common solvents—namely, acetonitrile, methanol, tetrahydrofuran, isopropanol, and acetone—were tested, purely or added with triethylamine. High recoveries were obtained when 0.5% (v/v) of triethylamine was used as an additive independently of the solvent. Concerning the solvents, methanol with 0.5% (v/v) of triethylamine yielded a superior elution efficacy. In addition, the effect of the eluent volume on desorption efficiency was also studied. Good results were achieved by using 0.5 mL of methanol comprising 0.5% (v/v) of triethylamine.
Finally, reusability was investigated for the CFe41 adsorbent by performing 10 consecutive cycles. The “Fe3O4@-activated carbon” was washed twice with methanol and twice with deionised water. After washing, there was a negligible loss of materials, and the magnetic composite was ready to be used again. Even after 10 consecutive extractions, the recoveries of the investigated NSAIDs did not diminish, which proves the good reusability of the adsorbent.
On the basis of the above discussions, the optimal extraction conditions were as follows: sample solution at pH 3.5, 15 mg of CFe41 as adsorbent material, 2 min of extraction time, and 500 µL of methanol containing 0.5% (v/v) of triethylamine as desorption solution.
3.2.2. Method Validation
The developed MSPE–UHPLC method was validated in terms of some relevant quantitative parameters—namely, selectivity, linearity, limits of detection (LODs), limits of quantification (LOQs), accuracy, precision, recovery, and carry-over.
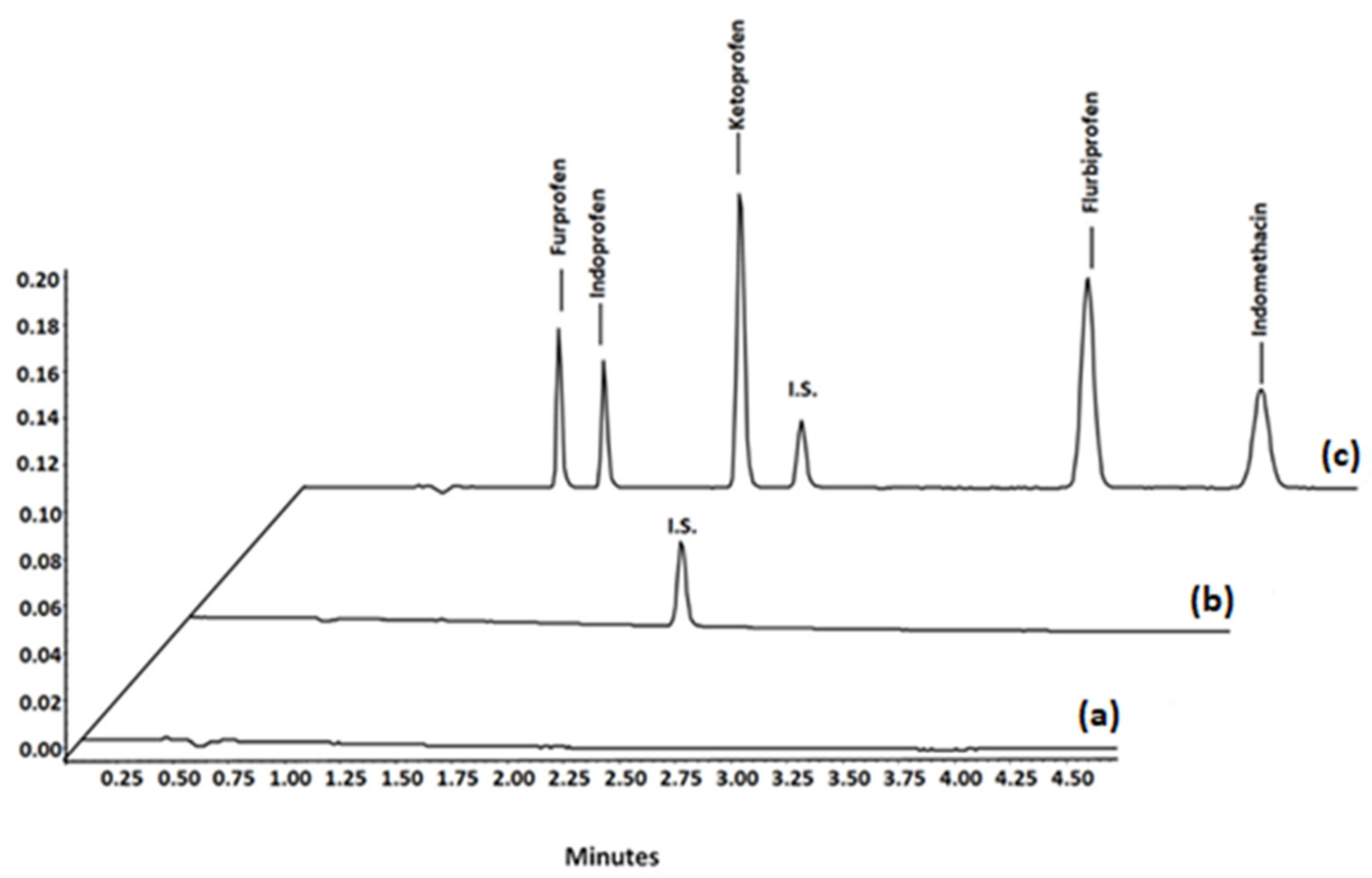
In order to assess the selectivity of the method, six separate batches of blank plasma were analysed to verify the absence of endogenous peaks in the chromatogram at the retention time of the NSAIDs. Subsequently, blank plasma, spiked plasma sample with the I.S., and spiked blank plasma with the NSAIDs (Figure 7) were extracted, tested, and compared.
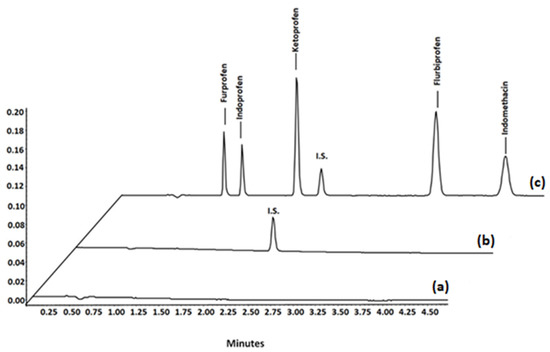
Figure 7.
UHPLC chromatograms of samples subjected to the proposed MSPE method: (a) blank plasma samples; (b) blank plasma samples spiked with internal standard; (c) blank plasma spiked with I.S. and the investigated NSAIDs.
For the evaluation of the intra-day repeatability (RSD%), the analysis of three batches of quality control samples (QC) LLOQ, QCL, QCM, and QCH, prepared independently, was performed in duplicate on the same day and for five consecutive days. Accordingly, the relative standard deviation was calculated. Finally, inter-day precision and accuracy (BIAS%) were evaluated by analysing spiked samples thrice on five different days and calculating the RSD%. The results are reported in Table 1. Seven-point calibration curves were built in the range of 0.005–15 µg/mL by plotting the ratio of the peak area of each NSAID to the peak area of the internal standard, versus their concentrations. The slope, intercept, and coefficient of determination were calculated by least-squares linear regression analysis. The LOQ value of the herein developed method was calculated as a signal-to-noise ratio of 10, while the LOD value was calculated by a signal-to-noise ratio of 3. Then, to investigate the carry-over effect, three blank samples were injected into the UHPLC apparatus, following the injection of two extracted blank plasma spiked with the drugs at the ULOQ concentration. No significant carry-over was detected. The extraction recovery of NSAIDs was calculated by comparing the theoretical and the experimental concentration, after extraction. The peak area ratios of each drug to I.S. were compared with those from drug-free matrix spiked at the QCs concentration. Among the parameters required for the validation of an analytical method according to the US FDA guidelines [29,30], there is also the stability of analytes which has to be assessed after short- and long-term storage, and through several freeze–thaw cycles. The stock solution containing the NSAIDs was monitored at room temperature for 48 h and then for two weeks at 4 °C. No stability issues were found in both cases. A short-term test of 24 h at ambient temperature in plasma solution again revealed good stability of the NSAIDs. The drugs were also stable after monitoring the plasma solution at −20 °C for up to five weeks. Moreover, they were still stable after three freeze–thaw cycles. Finally, the stability of NSAIDs in the extracts was proved after 24 h of storage at 4 °C.

Table 1.
Intra- and inter-day precisions of the proposed MSPE method in human plasma.
3.3. Comparison with Other Methods
In order to further demonstrate the potential applicability of our “Fe3O4@-activated carbon”, the performance of the procedure that we designed for the extraction of NSAIDs was compared with some others found in the literature (Table 2). It was revealed that the proposed MSPE–UHPLC–PDA method has various advantages; for example, LOQs are comparable to those of graphene-based methods, the recovery is higher, and reproducibility is relatively good. The results revealed that this approach for the analysis of NSAIDs in human plasma is simple, reliable, and sensitive. Graphene remains the material which has the largest surface area and that shows very good performances in terms of adsorption of analytes from any matrix which makes it useful in various circumstances. However, the activated carbon presented herein may represent a low-cost alternative in a circular economy context.

Table 2.
Comparison of the proposed method with reported methods for the determination of NSAIDs.
The excellent magnetic properties of the as-prepared “Fe3O4@-activated carbon” enabled very rapid and convenient isolation by using a common magnet, thus showing considerable usefulness as a preconcentration and determination methodology. The MSPE process complies with the principle of green analytical chemistry since it does not need harmful solvents or high temperatures to remove pollutants [14,36]. Moreover, the key interest of this method is related to the convenience, abundance, and non-toxicity of the materials used as precursors. First of all, magnetite (Fe3O4), as well as hematite (α-Fe2O3), are naturally abundant iron oxides, non-toxic to the environment, and relatively cheap, which, apart from being extracted from terrestrial deposits, can also be easily synthesised in the laboratory by using a variety of procedures such as hydrothermal synthesis, sol–gel, co-precipitation, etc. [36]. An interesting possibility to obtain iron precursors is from waste, for instance, from discarded products of the steel industry, construction materials, and vehicles, with an overall 2–4 tons of waste per ton of steel production [37]. Besides the magnetic material that is a relevant part of this composite, carbon, in the way it was produced in this study, also has several advantages in comparison with traditional activated carbons and carbon fibres (also found in the form of felt and clothes), investigated as adsorbents [38]. The cost of materials and synthesis are overall negligible since the handkerchiefs had already been disposed of, and no further treatments were needed to improve their adsorption capacity such as functionalising the surface of carbon, which also retained the necessary porosity from the starting cellulose precursor, as shown by its good performance. In this regard, other recently and intensively studied materials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), despite showing good results, still need more time-consuming, elaborated, and expensive fabrication, with an overall high cost of their final products [39].
4. Conclusions
Fe3O4@-activated carbon was successfully synthesised via pyrolysis with the in situ generation of carbon and magnetic material. The composites used as MDSPE achieved rapid recovery of target analytes; moreover, a good level of determination was proved when the method was coupled with UHPLC analysis of five different NSAIDs in human plasma. The outstanding advantages provided by magnetic carbon adsorbents were revealed herein, including less toxicity, scalability, improved adsorption capacity, target selectivity, and stability in an acidic medium. Thus, the ability of Fe3O4@-activated carbon should not be considered limited to the adsorption of NSAIDs from biological fluids; rather, this approach has also massive potential for the removal of other pharmaceuticals and contaminants from water systems and the environment. The use of abundant and cheap wasted raw materials aims to achieve a sustainable circular economy, giving priority to waste avoidance and waste reduction from the development to the end-of-life stages of a product’s life cycle. Furthermore, the procedure we presented herein agrees with the principle of green chemistry. Overall, this can represent a modest and simple example of “value for money” in which scientific knowledge can push forward technological advances in materials for the benefit of the human economy, health, and the environment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, V.F., P.B. and S.F.; data acquisition and methodology, V.F., P.B., V.C., L.S., F.N. and S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F., V.F. and P.B.; writing—review and editing, all authors; funding, S.F. and G.C.; supervision, S.F, G.C. and F.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
P.B. received funding for his post by MUR (Ministry for Universities and Research) under the act PON “Ricerca e Innovazione” 2014–2020 “Linea di Attività: Azioni IV.6 Green—contratti di ricerca su tematiche ‘Green’—D.M. 1062 del 10/08/2021” grant number ‘CUP D55F21003080005′.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Pietro Di Profio, Francesco Stoppa, and Gianluigi Rosatelli for making part of their equipment available (Raman, SEM–EDX, and XRD, respectively).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Paper Production—and Waste—To Double. Available online: https://www.theworldcounts.com/stories/paper-waste-facts (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Li, M.; Du, H.; Kuai, L.; Huang, K.; Xia, Y.; Geng, B. Scalable Dry Production Process of a Superior 3D Net-Like Carbon-Based Iron Oxide Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12649–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, S.; Chen, P.; Zhu, G.T.; Jiang, X.; Di, S. Eco-friendly and facile one-step synthesis of a three dimensional net-like magnetic mesoporous carbon derived from wastepaper as a renewable adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12419–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L. Green construction of Fe3O4@GC submicrocubes for highly sensitive magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction of five phthalate esters in beverages and plastic bottles. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, S.; Yu, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, S. Net-like mesoporous carbon nanocomposites for magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonamides prior to their quantitation by UPLC-HRMS. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashile, P.P.; Nomngongo, P.N. Magnetic Cellulose-Chitosan Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Removal of Emerging Contaminants: Adsorption Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies. Gels 2021, 7, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streete, P.J. Rapid high-performance liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of overdose concentrations of some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in plasma or serum. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1989, 495, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, R.R. Protein precipitation techniques. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 463, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almeida, H.F.D.; Marrucho, I.M.; Freire, M.G. Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Aqueous Environments with Reusable Ionic-Liquid-based Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, A.R.M.; de Santana, F.J.M.; Bonato, P.S. Stereoselective determination of the major ibuprofen metabolites in human urine by off-line coupling solid-phase microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rehim, M. Recent advances in microextraction by packed sorbent for bioanalysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Archivio, A.A.; Maggi, M.A.; Ruggieri, F.; Carlucci, M.; Ferrone, V.; Carlucci, G. Optimisation by response surface methodology of microextraction by packed sorbent of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography analysis of dialyzed samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawliszyn, J.; Lord, H.L. Handbook of Sample Preparation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; La Barbera, G.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Laganà, A. Recent application of magnetic solid-phase extraction for sample preparation. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1251–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardasani, D.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Purohit, A.K.; Shrivastava, A.R.; Dubey, D.K. Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes assisted dispersive solid phase extraction of nerve agents and their markers from muddy water. Talanta 2011, 86, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaei, M.; Dashtian, K.; Rafiee, Z.; Ghaedi, M. Ultrasonic-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of morphine in urine samples by new imprinted polymer-supported on MWCNT-Fe3O4-NPs: Central composite design optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 33, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, I.; Fernandes, C. Magnetic solid phase extraction for determination of drugs in biological matrices. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T. A magnetic cellulose-based carbon fiber hybrid as a dispersive solid-phase extraction material for the simultaneous detection of six bisphenol analogs from environmental samples. Analyst 2018, 143, 3100–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Jin, R.; Luo, C.; Song, C.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Synthesis of polydopamine-functionalized magnetic graphene and carbon nanotubes hybrid nanocomposites as an adsorbent for the fast determination of 16 priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprapai, P.; Cheewasedtham, W.; Chong, K.F.; Rujiralai, T. Selective magnetic nanographene oxide solid-phase extraction with high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection for the determination of zearalenone in corn samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 4348–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Lin, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S. Facile synthesis of magnetic carbon nanotubes derived from ZIF-67 and application to magnetic solid-phase extraction of profens from human serum. Talanta 2020, 207, 120284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soylak, M.; Ozalp, O.; Uzcan, F. Magnetic nanomaterials for the removal, separation and preconcentration of organic and inorganic pollutants at trace levels and their practical applications: A review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 29, e00109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroni, F.; Bruni, P.; Suzuki, N.; Aihara, Y.; Gabrielli, S.; Carbonari, G.; Agostini, M.; Branchi, M.; Ferrari, S.; Navarra, M.A.; et al. Highly Stable Fe3O4/C Composite: A Candidate Material for All Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 070556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yao, K.; Fu, L.H.; Ma, M.G. Selective synthesis of Fe3O4, g-Fe2O3, and a-Fe2O3 using cellulose-based composites as precursors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroni, F.; Gabrielli, S.; Palmieri, A.; Marcantoni, E.; Croce, F.; Nobili, F. High cycling stability of anodes for lithium-ion batteries based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles and poly(acrylic acid) binder. J. Power Sources 2016, 332, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Q. New insights into the structure–performance relationships of mesoporous materials in analytical science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8766–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuepfer, D.B.; Badaczewski, F.; Guerra-Castro, J.M.; Hofmann, D.M.; Heiliger, C.; Smarsly, M.; Klar, P.J. Assessing the structural properties of graphitic and non-graphitic carbons by Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 2020, 161, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, T.; Yamauchi, S.; Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kurimoto, Y.; Takayama, T.; Yoichi Sakai, Y. Mössbauer and Raman spectroscopic characterization of iron and carbon in iron-loaded Japanese cypress charcoal. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance for Industry-Bioanalytical Method Validation; FDA Food and Drug Administration of the United States, US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research and Center for Veterinary Medicine: Rockville, MD, USA, 2003.
- Guideline on bioanalytical method validation. In 2012 ICH International Conferences on Harmonization (ICH), Q2(R1): Text on Validation of Analytical Procedures, US FDA Federal Register; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2005.
- Locatelli, M.; Ferrone, V.; Cifelli, R.; Barbacane, R.C.; Carlucci, G. Microextraction by packed sorbent and high performance liquid chromatography determination of seven non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in human plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1367, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Mansilla, A.; Munoz De La Pena, A.; Canada-Canada, F.; Gonzalez Gomez, D. Determination of fluoroquinolones and non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in urine by extractive spectrophotometry and photoinduced spectrofluorimetry using multivariate calibration. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 347, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Mao, X.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Development of novel sol–gel coatings by chemically bonded ionic liquids for stir bar sorptive extraction—Application for the determination of NSAIDS in real samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7261–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Neira, C.; Alvarez Lueje, A. Ionic liquids for improving the extraction of NSAIDs in water samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by high performance liquid chromatography-diode array- fluorescence detection. Talanta 2015, 134, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, V.; Carlucci, M.; Ettorre, V.; Cotellese, R.; Palumbo, P.; Fontana, A.; Siani, G.; Carlucci, G. Dispersive magnetic solid phase extraction exploiting magnetic graphene nanocomposite coupled with UHPLC-PDA for simultaneous determination of NSAIDs in human plasma and urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 161, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulfa, M.; Prasetyoko, D.; Bahruji, H.; Nugraha, R.E. Green Synthesis of Hexagonal Hematite (a-Fe2O3) Flakes Using Pluronic F127-Gelatin Template for Adsorption and Photodegradation of Ibuprofen. Materials 2021, 14, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, L.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Islam, S.; Zahan, F.; Biswas, B.; Sharmin, N. A study on the preparation and characterization of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) particles from iron-containing waste materials. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 8, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedidi, H.; Reinert, L.; Soneda, Y.; Bellakhal, N.; Duclaux, L. Adsorption of ibuprofen from aqueous solution on chemically surface-modified activated carbon cloths. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3584–S3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faraji, M.; Shirani, M.; Rashidi-Nodeh, H. The recent advances in magnetic sorbents and their applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 141, 116302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).