Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats—A Review of Production, Physical Properties and Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
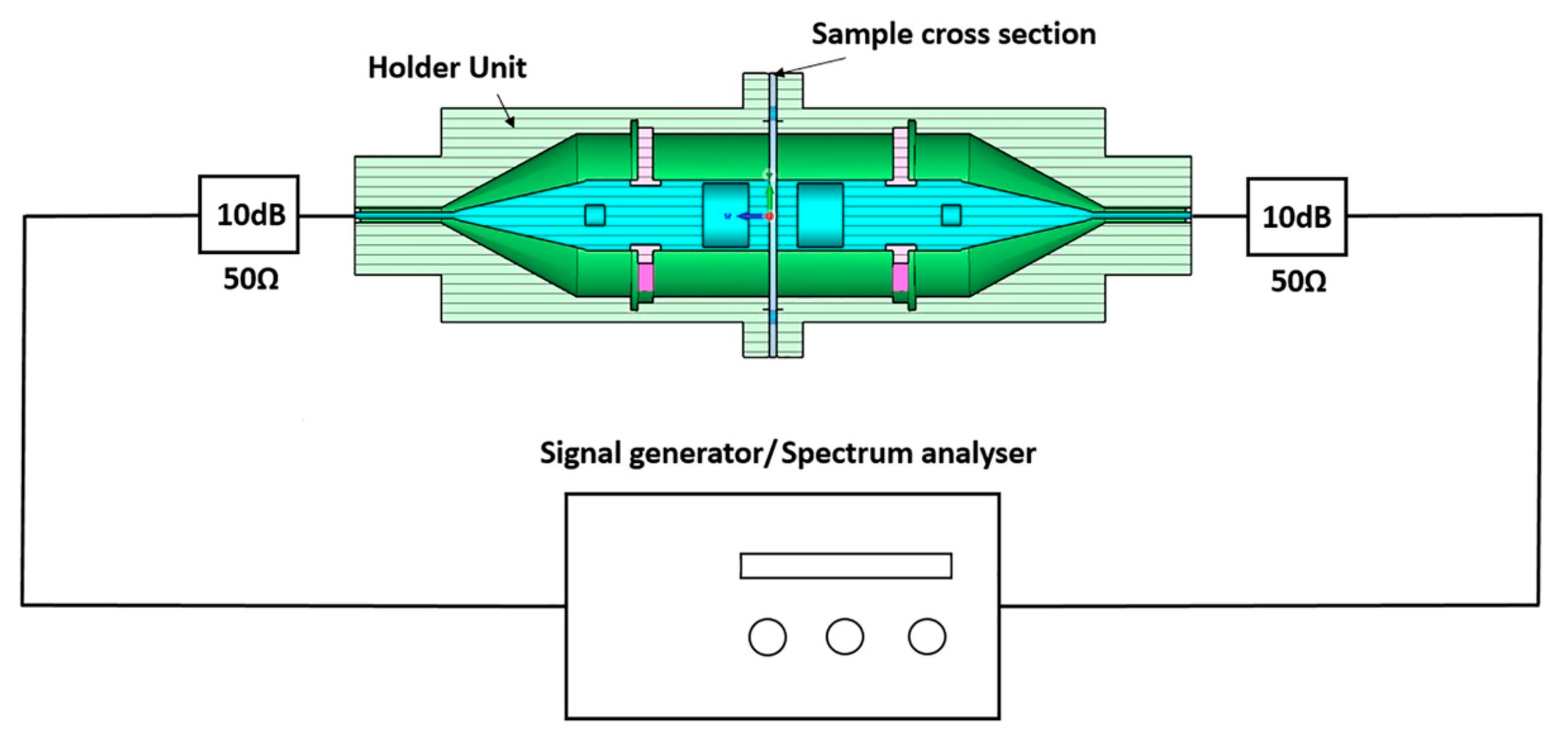
2. Measuring Electromagnetic Shielding and Related Parameters
- -
- Open-field (free-space) method—distance of 30 m between device and receiving antenna; wide variations due to differences in product assembly.
- -
- Shielded-box method—metal box with sample port in one wall, receiving antenna inside, transmitting antenna outside; difficult electrical contact between test specimens and shielded box, limitation of the frequency range to about 500 MHz, poor correlation between tests in different laboratories.
- -
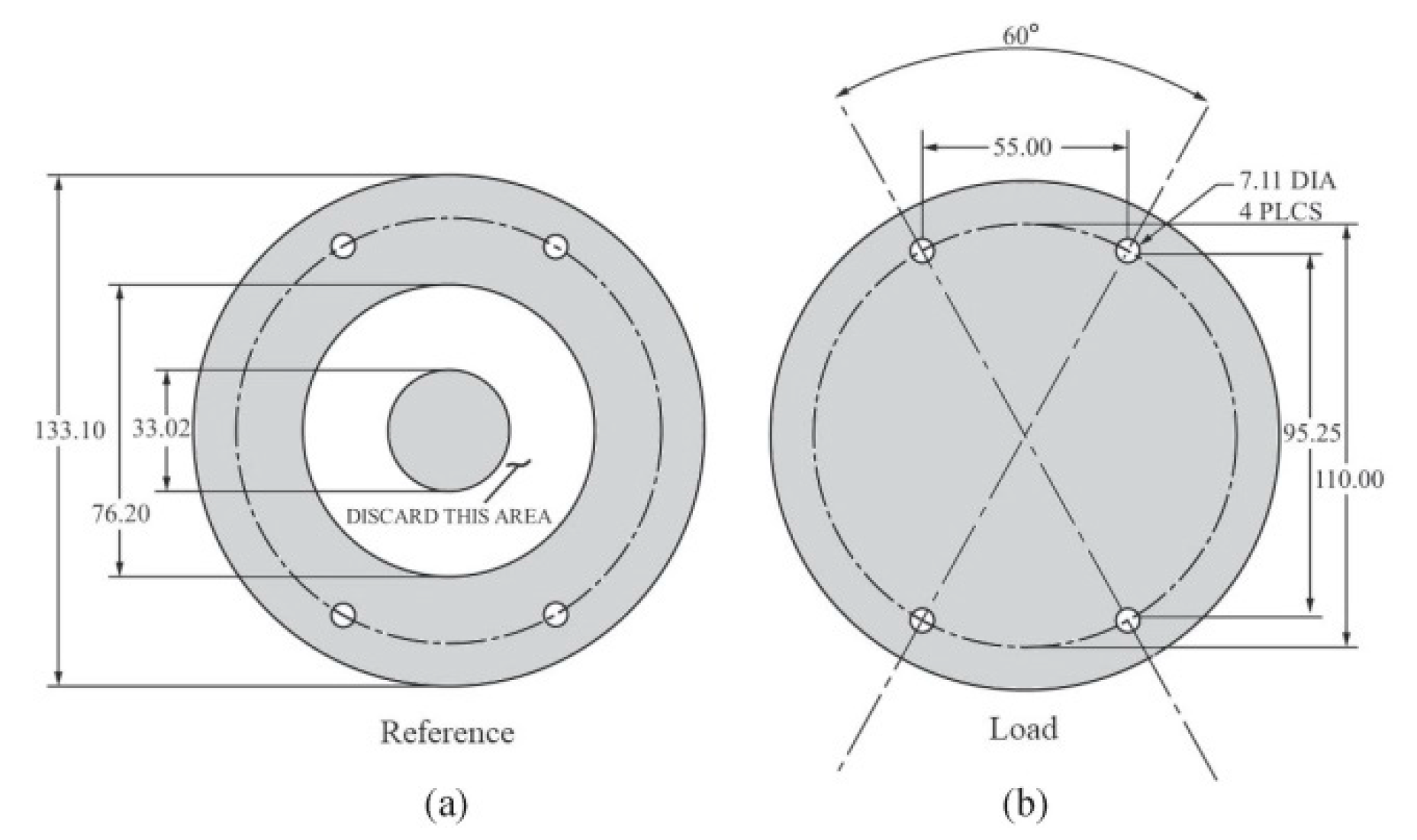
- Coaxial transmission line—e.g., ASTM D4935; standard method for planar specimens, time consuming (several minutes to hours per spectrum, depending on the measurement method), typically in the range from 10 kHz to 1 GHz.
- -
- Shielded-room method—similar to shielded box method, anechoic chamber of typical ground area 2.5 m², large test specimens needed between transmitting and receiving antenna [31].
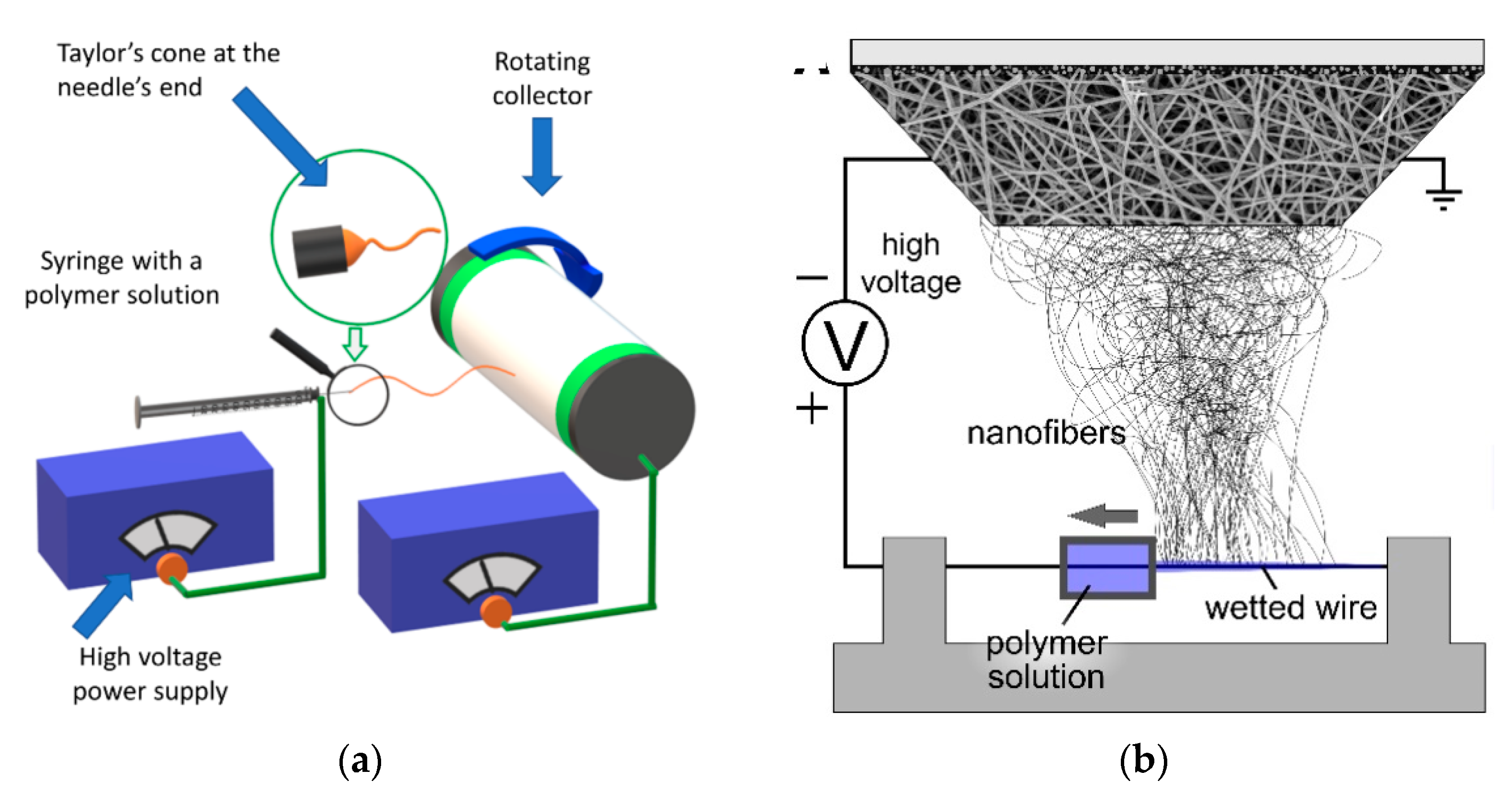
3. Electrospinning Techniques
4. Functionalization of Electrospun Nanofiber Mats for Electromagnetic Shielding
4.1. Conductive Nanofiber Mats
4.2. Magnetic Nanofiber Mats
4.3. Morphology of Nanofiber Mats
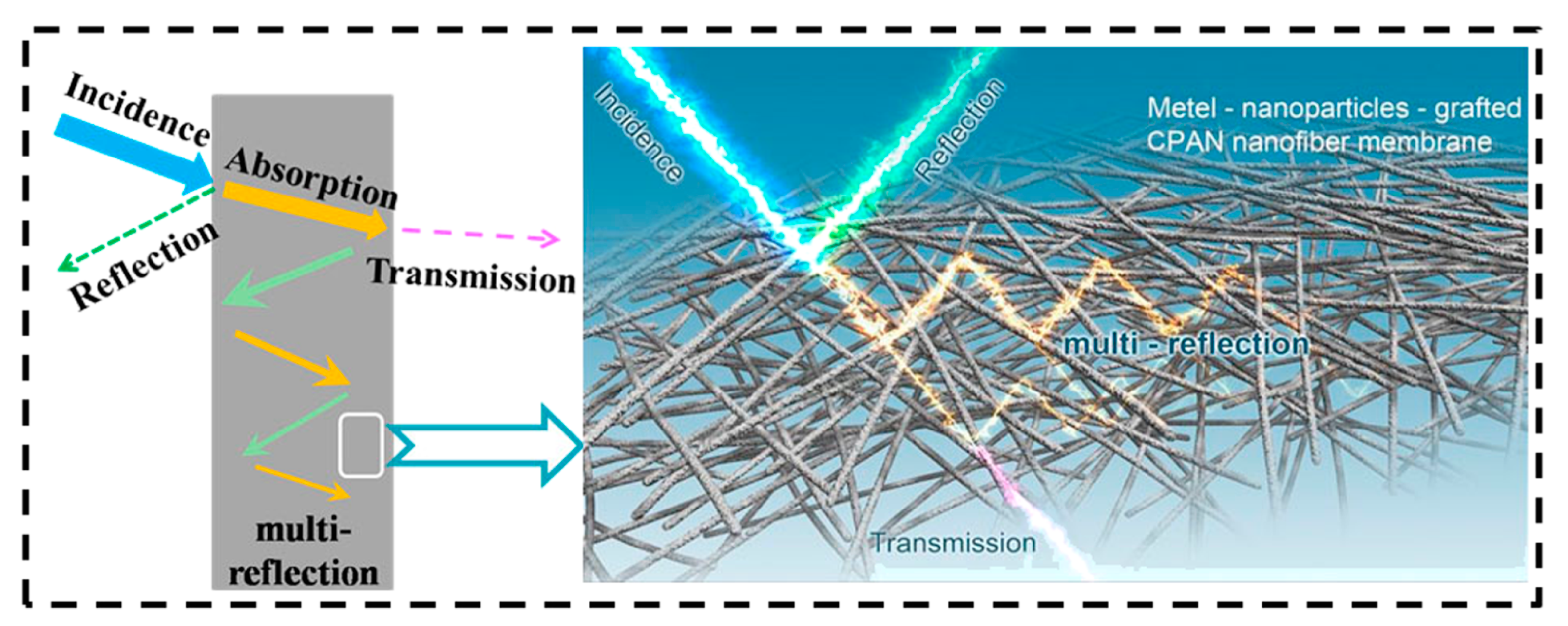
5. Electromagnetic Shielding by Nanofiber Mats in the X-Band and Ku-Band
6. Electromagnetic Shielding by Nanofiber Mats in Other Frequency Bands
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.H.; Chung, D.D.L. Increasing the electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon fiber polymer–matrix composite by using activated carbon fibers. Carbon 2002, 40, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.-S.; Chi, Y.-S.; Kang, T.J. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of multifunctional metal composite fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barudov, E.; Ivanova, M. Study of the parameters of conductive textile fabrics for protection against high-frequency electromagnetic radiation. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th Electrical Engineering Faculty Conference (BulEF), Varna, Bulgaria, 8–11 September 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- EP-European Parliament. Directive 2013/35/EU of the European Parliament and the Council of 26 June 2013 on the minimum health and safety requirements regarding the exposure of workers to the risks arising from physical agents (electromagnetic fields) (20th individual Directive within the meaning of Article 16(1) of Directive 89/391/EEC) and repealing Directive 2004/40/EC. Official Journal of the European Union, 29 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Guo, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. Shielding effectiveness of double-layer magnetic shield of current comparator under radial disturbing magnetic field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 9401907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A.; Malczyk, M.; Stasiak, A.; Osadnik, R.; Paluch, R.; Koruszowic, M.; Pawlyta, J.; Lis, K.; Lehrich, K. Plant growth in microgravity and defined magnetic field. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Communications and Mechatronics Engineering (ICECCME), Mauritius, Mauritius, 7–8 October 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.Y.; Jin, S.H.; Zou, H.M.; Li, L.J.; Ma, X.L.; Lv, G.; Gao, F.; Lv, X.J.; Shu, Q.H. Polymer-based lightweight materials for electromagnetic interference shielding: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 6549–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.O.; Akter, F.; Ehrmann, A. Shielding of static magnetic fields by textiles. Ind. Text. 2013, 64, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, R.R.; Cheng, W.J.; Xiao, H.; Shi, M.W.; Tang, Z.H.; Wang, N. A calculating method for the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of metal fiber blended fabric. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.P.; Liu, S.H.; Guan, H.T. Investigation of electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of polyaniline composite. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, D.D.L. Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon materials. Carbon 2001, 39, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, M.; Shu, J.-C.; Wen, B.; Cao, W.-Q.; Cao, M.-S. Thermally-tailoring dielectric “genes” in graphene-based heterostructure to manipulate electromagnetic response. Carbon 2021, 184, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.S.; Wang, X.X.; Cao, W.Q.; Fang, X.Y.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 2018, 14, 1800987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neruda, M.; Vojtech, L. Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Woven Fabrics with High Electrical Conductivity: Complete Derivation and Verification of Analytical Model. Materials 2018, 11, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, W.; Zhu, H.X.; Yang, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Duan, H.J.; Zhao, G.Z.; Liu, Y.Q. Flexible and robust silver coated non-woven fabric reinforced waterborne polyurethane films for ultra-efficient electromagnetic shielding. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 184, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Tunakova, V.; Militky, J.; Wiener, J. Effect of moisture content on the electromagnetic shielding ability of non-conductive textile structures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusic, T.; Saravanja, B.; Malaric, K. Electromagnetic Shielding Properties of Knitted Fabric Made from Polyamide Threads Coated with Silver. Materials 2021, 14, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Fan, X.; Qin, J.B.; Shi, X.T.; Zhang, G.C. rGO/MXene sandwich-structured film at spunlace non-woven fabric substrate: Application to EMI shielding and electrical heating. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 614, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM Committee on Standards. ASTM D4935-18; Standard Test Method for Measuring the Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Planar Materials. ASTM International: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Wanasinghe, D.; Aslani, F.; Ma, G.W. An experimental and simulation-based study on the effect of carbonyl iron, heavyweight aggregate powders, and carbon fibres on the electromagnetic shielding properties of cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munalli, D.; Dimitrakis, G.; Chronopoulos, D.; Greedy, S.; Long, A. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of carbon fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 173, 106906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.J.; Lee, Y.-s.; Hong, S.-G.; Moon, J.Y. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Dispersion, mechanical properties, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding effectiveness (SE). Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 131, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wu, B.; Song, R.G.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.H.; He, D.P. Electromagnetic shielding and multi-beam radiation with high conductivity multilayer graphene film. Carbon 2019, 155, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Committee on Standards. ASTM E1851-15; Standard Test Method for Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Durable Rigid Wall Relocatable Structures. ASTM International: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standards Association. 299.1-2013; IEEE Standard Method for Measuring the Shielding Effectiveness of Enclosures and Boxes Having all Dimensions between 0.1 m and 2 m. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Piette, M.; Tsigros, C. IEC 61000-4-21 testing: Selective source-mode tuning with two orthogonal antennas scanning system. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on electromagnetic Compatibility–EMC Europe, Hamburg, Germany, 8–12 September 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Marvin, A.C.; Dawson, L.; Flintoft, I.; Dawson, J. A Method for the Measurement of Shielding Effectiveness of Planar Samples Requiring no Sample Edge Preparation or Contact. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2009, 51, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasquez, H.; Espinoza, L.; Lozano, K.; Foltz, H.; Yang, S.Y. Simple Device for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness Measurement. IEEE EMC Soc. Newslett. 2009, 220, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Valente, R.; de Ruijter, C.; Vlasveld, D.; van der Zwaag, S.; Groen, P. Setup for EMI shielding effectiveness tests of electrically conductive polymer composites at frequencies up to 3.0 GHz. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16665–16675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumalraj, R.; Nalankilli, G.; Balasaravanan, T.R.; Roshanraja, K.; Shyamsundar, G. Electromagnetic shielding tester for conductive textile materials. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2010, 35, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Geetha, S.; Kumar, K.K.S.; Rao, C.R.K.; Vijayan, M.; Trivedi, D.C. EMI Shielding: Methods and Materials—A Review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 2073–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittel, D.; Schollmeyer, E. Electrically high-conductive textiles. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzyk, R. Measurement of the volume and surface resistance of textile materials. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2011, 19, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Meding, J.T.; Tuvshinbayar, K.; Döpke, C.; Tamoue, F. Textile electrodes for bioimpedance measuring. Commun. Dev. Assem. Text. Prod. 2021, 2, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.M.; Iskandar, F.; Yun, K.M.; Okuyama, K.; Abdullah, M. Optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 145603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, A.; Lee, J.K.Y.; Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of MWCNT/Cu nanofibers via electrospinning method and analysis of their electrical conductivity by four-probe method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, M.; Yang, H.J.; Shor, L.; Ko, F. Post-spinning modification of electrospun nanofiber nanocomposite from Bombyx mori silk and carbon nanotubes. Polymer 2009, 50, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar]
- Hasiah, S.; Ibrahim, K.; Senin, H.B.; Halim, K.B.K. Electrical Conductivity of Chlorophyll with Polythiophene Thin Film on Indium Tin Oxide as P-N Heterojunction Solar Cell. J. Phys. Sci. 2008, 19, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hedin, N.; Sobolev, V.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhu, Z.T.; Fong, H. Electrical properties of electrospun carbon nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 6453–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.F.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.W.; Hu, M.J.; Xue, H.G.; Li, R.K.Y. Electrically conductive polymer nanofiber composite with an ultralow percolation threshold for chemical vapour sensing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 161, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.F.; Li, B.; Huang, X.W.; Wang, L.; Lin, L.W.; Wang, H.; Xue, H.G. Electrically conductive and fluorine free superhydrophobic strain sensors based on SiO2/graphene-decorated electrospun nanofibers for human motion monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Lin, L.W.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.W.; Xue, H.G.; Gao, J.F. Highly stretchable, anti-corrosive and wearable strain sensors based on the PDMS/CNTs decorated elastomer nanofiber composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A.; Mahltig, B. Magneto-optic measurements on uneven magnetic layers on cardboard. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 045306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regtmeier, A.; Meyer, J.; Mill, N.; Peter, M.; Weddemann, A.; Mattay, J.; Hütten, A. Influence of nanoparticular impurities on the magnetic anisotropy of self-assembled magnetic co-nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 326, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Gai, G.; Zhao, L.; Xu, S.; Xiao, X. One-pot facile electrospinning construct of flexible Janus nanofibers with tunable and enhanced magnetism-photoluminescence bifunctionality. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, V.; Reinholdt, A.; Kreibig, U.; Weirich, T.; Güntherodt, G.; Beschoten, B.; Tillmanns, A.; Krenn, H.; Rumpf, K.; Granitzer, P. Structural and magnetic properties of Ni/NiOxide- and Co/CoOxide core/shell nanoparticles and their possible use for ferrofluids. Z. Phys. Chem. 2006, 220, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Tillmanns, A.; Fraune, M.; Beschoten, B.; Güntherodt, G. Exchange-bias in (110)-oriented CoO/Co bilayers with different magnetocrystalline anisotropies. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 054425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.S.; Chen, S.-S.; Li, C.-W.; Nguyen, N.C.; Nguyen, H.T. A comprehensive review: Electrospinning technique for fabrication and surface modification of membranes for water treatment application. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85495–85514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.D.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Jiang, M.J.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.W. Developments of Advanced Electrospinning Techniques: A Critical Review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, S.; Benko, A. Advances in Fabricating the Electrospun Biopolymer-Based Biomaterials. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, J.L.; Wortmann, M.; Brockhagen, B.; Frese, N.; Diestelhorst, E.; Grothe, T.; Hellert, C.; Ehrmann, A. Comparative Study of Metal Substrates for Improved Carbonization of Electrospun PAN Nanofibers. Polymers 2022, 14, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peranidze, K.; Safronova, T.V.; Kildeeva, N.R. Fibrous Polymer-Based Composites Obtained by Electrospinning for Bone Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClellan, P.; Landis, W.J. Recent Applications of Coaxial and Emulsion Electrospinning Methods in the Field of Tissue Engineering. BioRes. Open Access 2016, 5, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moulefera, I.; Trabelsi, M.; Mamun, A.; Sabantina, L. Electrospun carbon nanofibers from biomass and biomass blends—Current trends. Polymers 2021, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.; Schiffman, J.D. Beyond the single-nozzle: Coaxial electrospinning enables innovative nanofiber chemistries, geometries, and applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, B.; Taylor, R.M.; Reifsnider, K. Mechanical and dielectric properties of aligned electrospun fibers. Fibers 2021, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Conductive electrospun nanofiber mats. Materials 2020, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Park, J.M.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, M.J.; Park, P.G.; Yon, I.-J.; Nah, J.H. Polyvinylidene Fluoride Core–Shell Nanofiber Membranes with Highly Conductive Shells for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 25428–25437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.T.; Wang, F.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Lou, Z.C.; Ji, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, B.; Peng, Y.; Liu, K.; et al. Flexible TaC/C electrospun non–woven fabrics with multiple spatial-scale conductive frameworks for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 151, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Deng, W.T.; Yue, Y.Q.; Meng, F.B. Ultrathin flexible electrospun carbon nanofibers reinforced graphene microgasbags films with three-dimensional conductive network toward synergetic enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 111, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, N.; Jin, C.X.; Lu, X.F.; Wang, C. Lightweight and flexible electrospun polymer nanofiber/metal nanoparticle hybrid membrane for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Park, Y.C.; Kim, M.-H.; Seol, J.H. Electromagnetic Interference Shield of Highly Thermal-Conducting, Light-Weight, and Flexible Electrospun Nylon 66 Nanofiber-Silver Multi-Layer Film. Polymers 2020, 12, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.R.; Li, W.Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.M.; Jiao, H.; Fang, Z.Y.; Lei, Z.L.; Yuan, Y. Scalable fabrication of highly crosslinked conductive nanofibrous films and their applications in energy storage and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, A.; Agrawal, P.R.; Dwivedi, N.; Mondal, D.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Dhakate, S.R. Enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding properties of phenolic resin derived lightweight carbon foam decorated with electrospun zinc oxide nanofibers. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Most recent developments in electrospun magnetic nanofibers: A review. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2020, 15, 1558925019900843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.S.A.; Bakry, A.; Al-Harbi, L.M.; Khowdiary, M.M.; El-Henawy, A.A.; Yoon, J.W. Core/shell PA6 @ Fe3O4 nanofibers: Magnetic and shielding behavior. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.-S.; Park, I.-K. Mechanically Robust Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticle/Polyvinylidene Fluoride Composite Nanofiber and Its Application in a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25660–25665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.; Sabantina, L.; Klöcker, M.; Heide, A.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning Nanofiber Mats with Magnetite Nanoparticles Using Various Needle-Based Techniques. Polymers 2022, 14, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.; Klöcker, M.; Blachowicz, T.; Sabantina, L. Investigation of the Morphological Structure of Needle-Free Electrospun Magnetic Nanofiber Mats. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, M.; Mamun, A.; Klöcker, M.; Moulefera, I.; Pljonkin, A.; Elleuch, K.; Sabantina, L. Magnetic Carbon Nanofiber Mats for Prospective Single Photon Avalanche Diode (SPAD) Sensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadkhani, F.; Montazer, M.; Latifi, M. Microwave absorption and photocatalytic properties of magnetic nickel nanoparticles/recycled PET nanofibers web. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.T.; Zheng, M.H.; Ma, X.F.; Cao, R.; Liu, K.; Yang, W.; Jian, S.; Jiang, S.; Duan, G.G. Electrospun TaC/Fe3C–Fe carbon composite fabrics for high efficiency of electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Commun. 2022, 31, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, K.-H.; Kim, W.-T.; Song, T.-H.; Choi, W.-Y. Magnetic Properties of NiZn Ferrite Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fokin, N.; Grothe, T.; Mamun, A.; Trabelsi, M.; Klöcker, M.; Sabantina, L.; Döpke, C.; Blachowicz, T.; Hütten, A.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetic Properties of Electrospun Magnetic Nanofiber Mats after Stabilization and Carbonization. Materials 2020, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
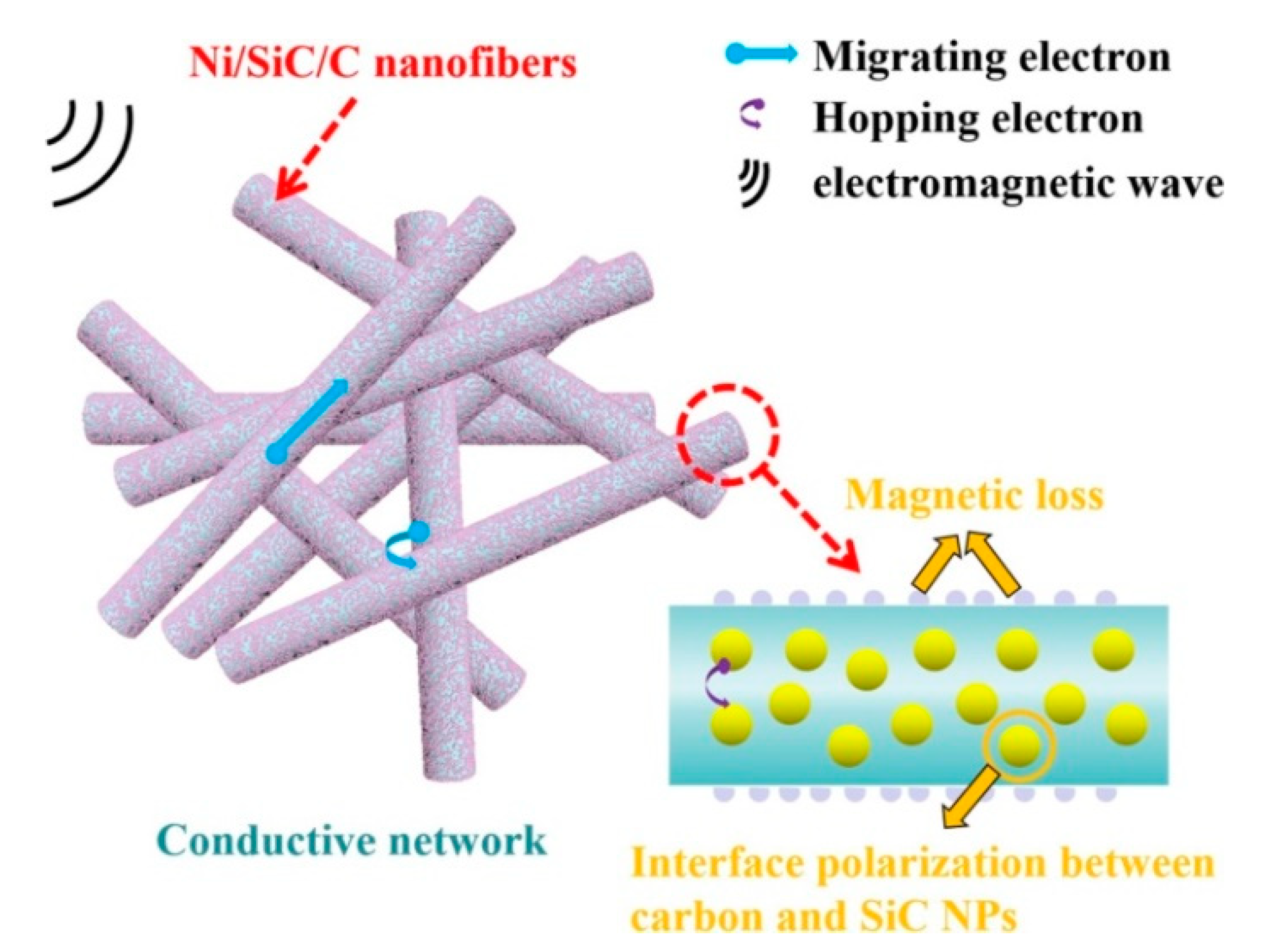
- Huo, Y.S.; Tan, Y.J.; Zhao, K.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhong, L.Y.; Tang, Y.F. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Ni magnetic coating-functionalized SiC/C nanofibers synthesized by electrospinning and magnetron sputtering technology. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 763, 138230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yue, J.L.; Wei, Y.S.; Huang, X.Z.; Tang, X.Z.; Du, Z.J. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of carbon nanofibers functionalized by FeCo coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 483, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, R.; He, D.Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Qiu, J.; Jin, C.X.; Wang, C. Lightweight and flexible Ni-Co alloy nanoparticle-coated electrospun polymer nanofiber hybrid membranes for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Chen, X.H.; Zhou, H.L.; Liu, P.; Fu, S.L.; Yang, J.J.; Gao, Y.H.; Ren, Y.P.; Rong, D. Interfacing MXene Flakes on a Magnetic Fiber Network as a Stretchable, Flexible, Electromagnetic Shielding Fabric. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.N.; Guan, G.G.; Xiang, J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xu, J.H.; Zhang, K.Y. Electrospinning fabrication and enhanced microwave absorption properties of nickel porous nanofibers. J. Alloys Comp. 2022, 891, 161997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, K.-H.; Jang, K.-P.; Kim, S.-W.; Choi, W.-Y. Fabrication of Electrospun Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 Nanofibers Using Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone Precursors and Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance Improvement. Polymers 2021, 13, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Y.; Wang, R.Q.; Huang, W.R.; Kong, L.; Guo, S.W.; Cheng, L.F. Morphology Design of Co-electrospinning MnO-VN/C Nanofibers for Enhancing the Microwave Absorption Performances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13208–13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Yan, M.X.; Jiang, Q.; Peng, H.-K.; Lin, J.-H.; Lou, C.-W. Characterization and Microstructure of Linear Electrode-Electrospun Graphene-Filled Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofiber Films. Materials 2018, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
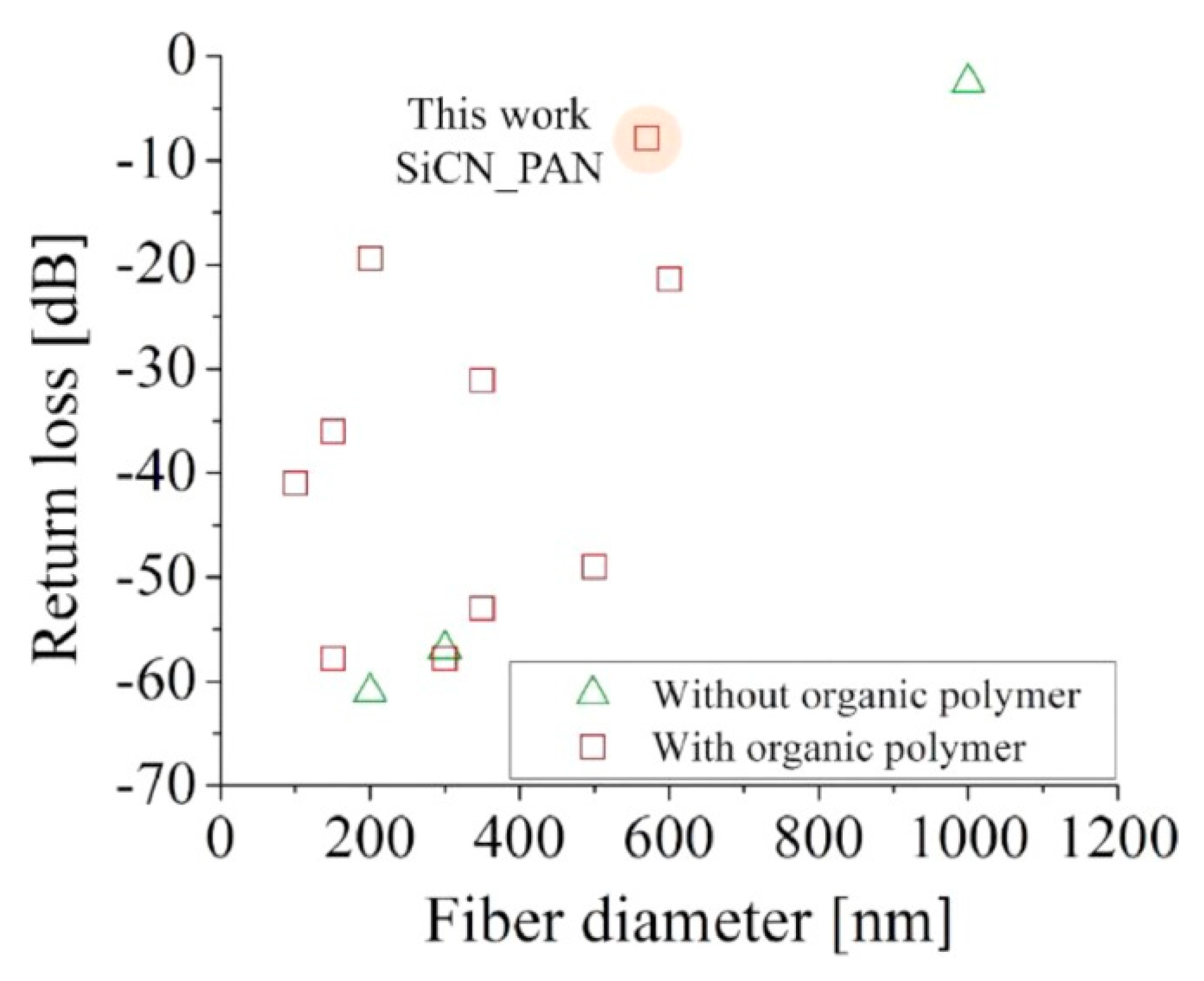
- Ramlow, H.; Marangoni, C.; Motz, G.; Machado, R.A.F. Statistical optimization of polysilazane-derived ceramic: Electrospinning with and without organic polymer as a spinning aid for manufacturing thinner fibers. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
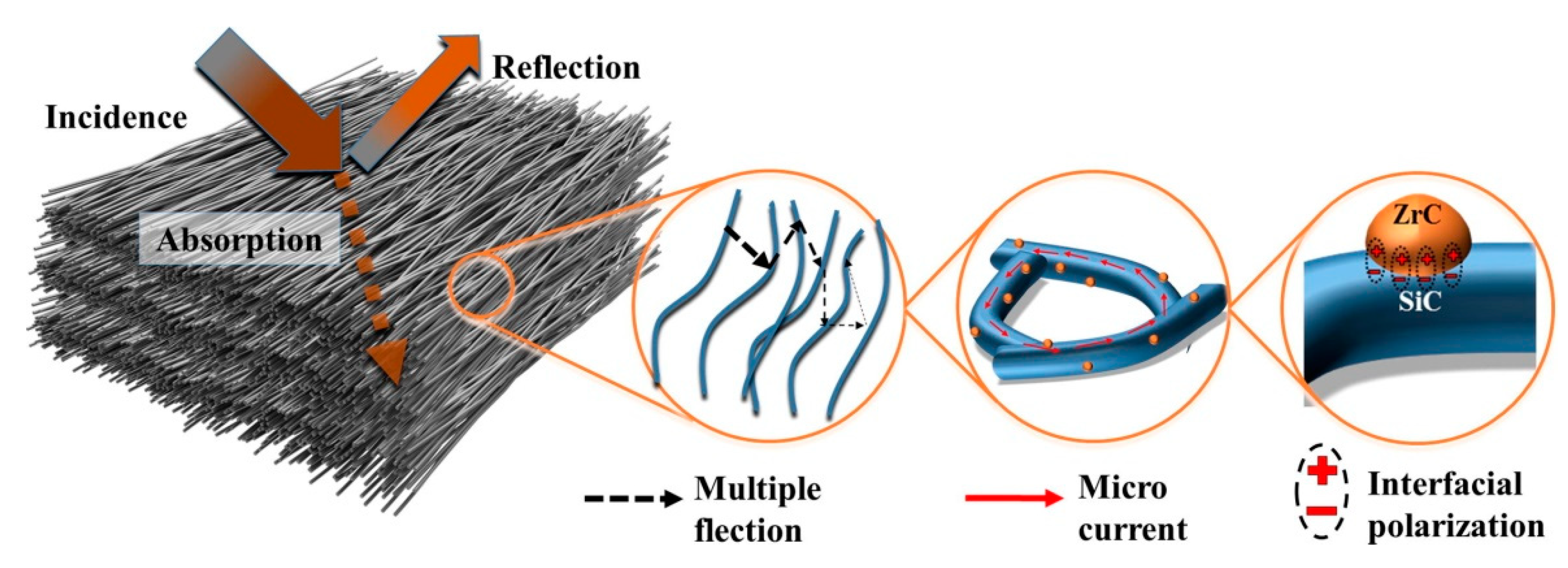
- Hou, Y.; Cheng, L.F.; Zhang, Y.N.; Du, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.J.; Yang, Z.H. High temperature electromagnetic interference shielding of lightweight and flexible ZrC/SiC nanofiber mats. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasouri, K.; Shoushtari, A.M. Fabrication of magnetite nanoparticles/polyvinylpyrrolidone composite nanofibers and their application as electromagnetic interference shielding material. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2017, 31, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Lin, Z.J.; Han, M.S.; Mu, Y.B.; Yu, P.P.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yu, J. Flexible electrospun carbon nanofibers/silicone composite films for electromagnetic interference shielding, electrothermal and photothermal applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Wang, Y.T.; Peng, H.-K.; Zhang, X.F.; Shiu, B.-C.; Lin, J.-H.; Lou, C.-W. Lightweight, flexible and superhydrophobic composite nanofiber films inspired by nacre for highly electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 128, 105685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Song, Y.-N.; Jia, L.-C.; Zhong, G.-J.; Xu, L.; Yan, D.-X.; Lei, J.; Li, Z.-M. Ultrathin, flexible and sandwich-structured PHBV/silver nanowire films for high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 3307–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.H.; Gu, W.H.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, S.L.; Ji, G.B. A breathable and flexible fiber cloth based on cellulose/polyaniline cellular membrane for microwave shielding and absorbing applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.R.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.F.; He, P.; Mi, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Liu, C.T.; Shen, C.Y. Engineering multilayered MXene/electrospun poly(lactic acid) membrane with increscent electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding for integrated Joule heating and energy generating. Compos. Commun. 2021, 26, 100770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Ruan, K.P.; Gu, J.W. Flexible Sandwich-Structured Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Nanocomposite Films with Excellent Thermal Conductivities. Small 2021, 17, 2101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, X.W.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.L.; Yao, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.C.; Gao, J.F. Polyvinylpyrrolidone Assisted Preparation of Highly Conductive, Antioxidation, and Durable Nanofiber Composite with an Extremely High Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21865–21875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Jia, X.T.; He, D.Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, C. Superhydrophobic and Corrosion-Resistant Electrospun Hybrid Membrane for High-Efficiency Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.B.; Kim, S.Y.; Seong, Y.C.; Yang, K.-H.; Choi, H.C. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Buckypaper/Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Composite Membranes for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, Y.N.; Pei, K.; Che, R.C. Temperature induced transformation of Co@C nanoparticle in 3D hierarchical core-shell nanofiber network for enhanced electromagnetic wave adsorption. Carbon 2022, 195, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.S.; Zhang, Z.C.; Chu, H.T.; Liu, Y.J.; Leng, J.S. Research on high electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of a foldable buckypaper/polyacrylonitrile composite film via interface reinforcing. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 113, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, Z.J.; Lv, C.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Lu, G.Y.; Jia, X.T.; Wang, C. Electrospun bifunctional MXene-based electronic skins with high performance electromagnetic shielding and pressure sensing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 221, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, D.Y.; Qiu, J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, C. PAN/W18O49/Ag nanofibrous membrane for high-efficient and multi-band electromagnetic-interference shielding with broad temperature tolerance and good thermal isolating capacity. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 236, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, W.D.; Lu, X.F.; Wang, C. Lightweight and flexible MXene/carboxymethyl cellulose aerogel for electromagnetic shielding, energy harvest and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.H.; Han, Y.K.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, T.H.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, S.-B.; Park, B.J. Absorption-dominant, low reflection EMI shielding materials with integrated metal mesh/TPU/CIP composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Rye, S.H.; Han, Y.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.-B.; Park, B.J. Electromagnetic interference shielding films with enhanced absorption using double percolation of poly (methyl methacrylate) beads and CIP/MWCNT/TPU composite channel. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Min, B.K.; Yi, Y.S.; Choi, C.-G. Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanotubes/waterborne polyurethane based composite ink for electromagnetic interference shielding and sheet heater applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.R.; Guo, K.; Wang, F.Y.; Wu, Z.G.; Zhong, B.; Zuo, S.Y.; Tang, J.; Feng, J.J.; Zhuo, R.F.; Yan, D.; et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties in C band of Ni/C porous nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 800, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, M.; Cao, W.-Q.; Cao, M.-S. Electrospinning and in-situ hierarchical thermal treatment to tailor C–NiCo2O4 nanofibers for tunable microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 171, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Li, B.; Sha, A.M.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.W. Tunable microwave absorption band via rational design of C@TiC nanospheres. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 15576–15581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.D.; Guo, Z.H. Flexible, conductive, porous, fibrillar polymer–gold nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.S.; Kim, J.G.; Bae, T.-S.; Lee, Y.-S. Effect of heat treatment on ZrO2-embedded electrospun carbon fibers used for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2011, 72, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyek, I.; Yazici, M.; Alma, M.H.; Karatas, S. The investigation of the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of multi-layered nanocomposite materials from reduced graphene oxide-doped P(AN-VAc) nanofiber mats/PP spunbond. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 53, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkó, M.; Mattson, M.-O. 5G Wireless Communication and Health Effects—A Pragmatic Review Based on Available Studies Regarding 6 to 100 GHz. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blachowicz, T.; Hütten, A.; Ehrmann, A. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats—A Review of Production, Physical Properties and Performance. Fibers 2022, 10, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10060047
Blachowicz T, Hütten A, Ehrmann A. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats—A Review of Production, Physical Properties and Performance. Fibers. 2022; 10(6):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10060047
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlachowicz, Tomasz, Andreas Hütten, and Andrea Ehrmann. 2022. "Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats—A Review of Production, Physical Properties and Performance" Fibers 10, no. 6: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10060047
APA StyleBlachowicz, T., Hütten, A., & Ehrmann, A. (2022). Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats—A Review of Production, Physical Properties and Performance. Fibers, 10(6), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10060047







