Paint Removal on the 5A06 Aluminum Alloy Using a Continuous Wave Fiber Laser
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
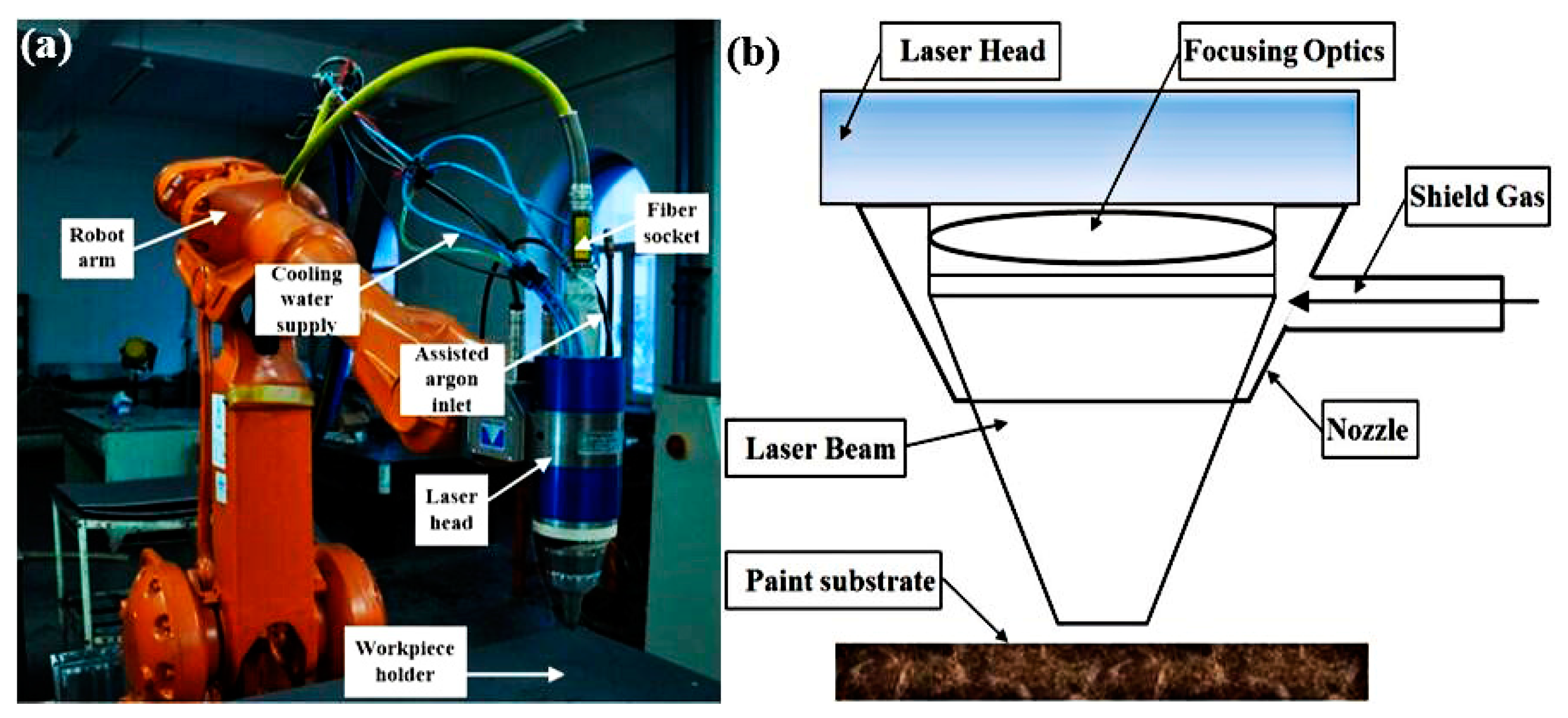
2.1. Experiment Setup
2.2. Theoretical Background
2.2.1. Cleaning Model
2.2.2. Temperature Profiles
2.2.3. Thermal Stress Profiles
2.3. Calculation of the Adhesion and the Cleaning Force
3. Results and Discussion
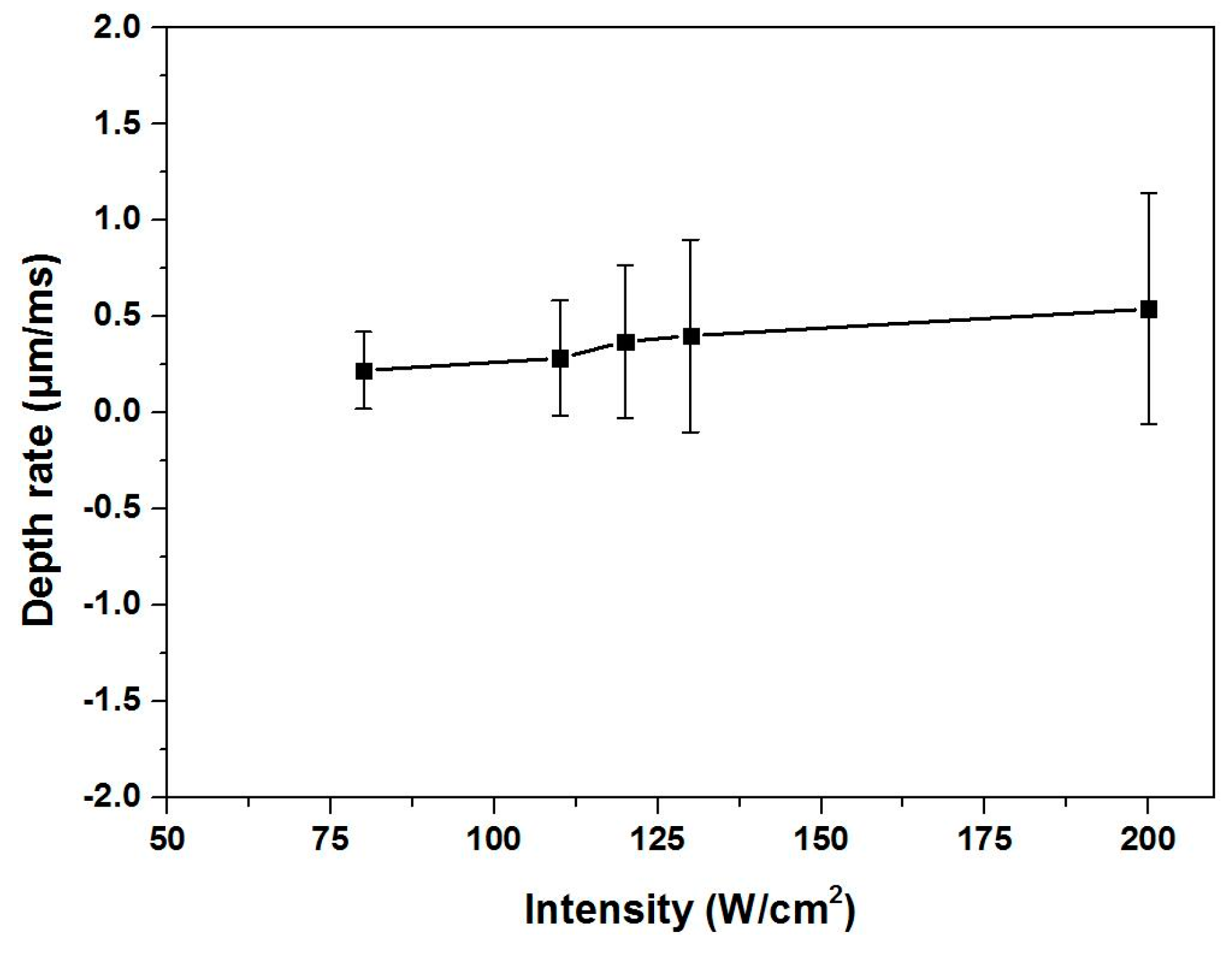
3.1. Removal Depth Rate
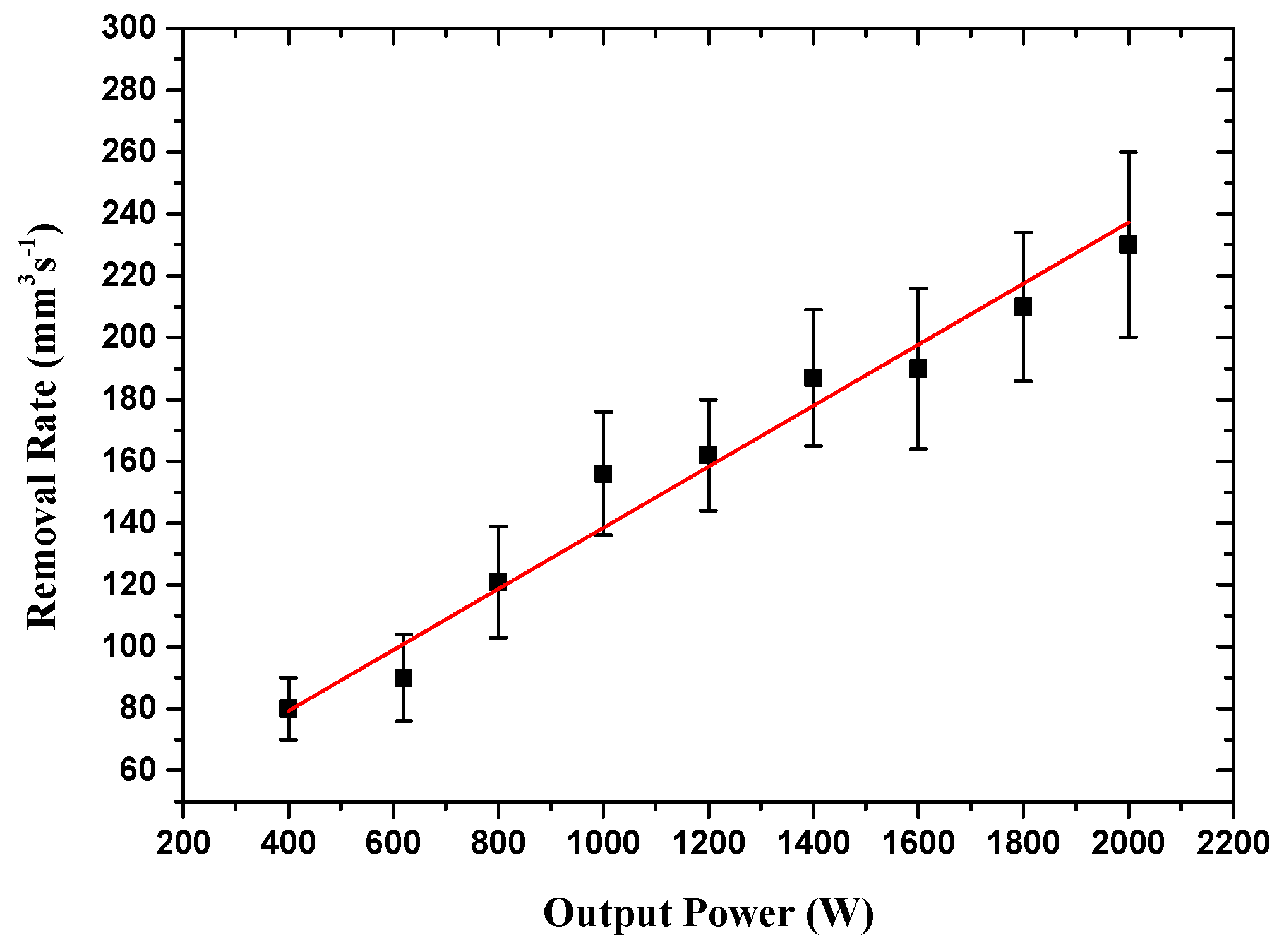
3.2. Removal Rates
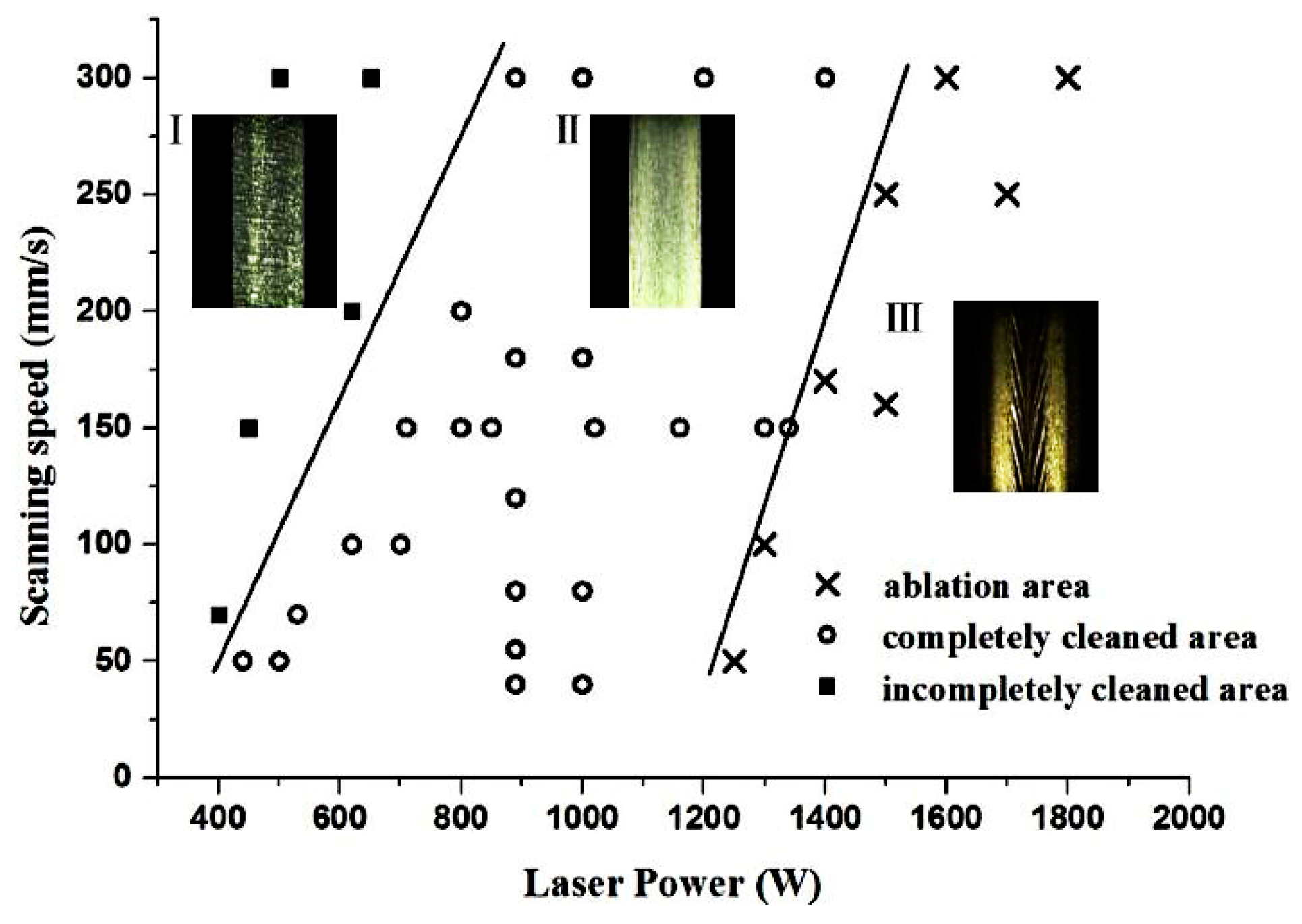
3.3. Optimization of Parameters on Laser Cleaning
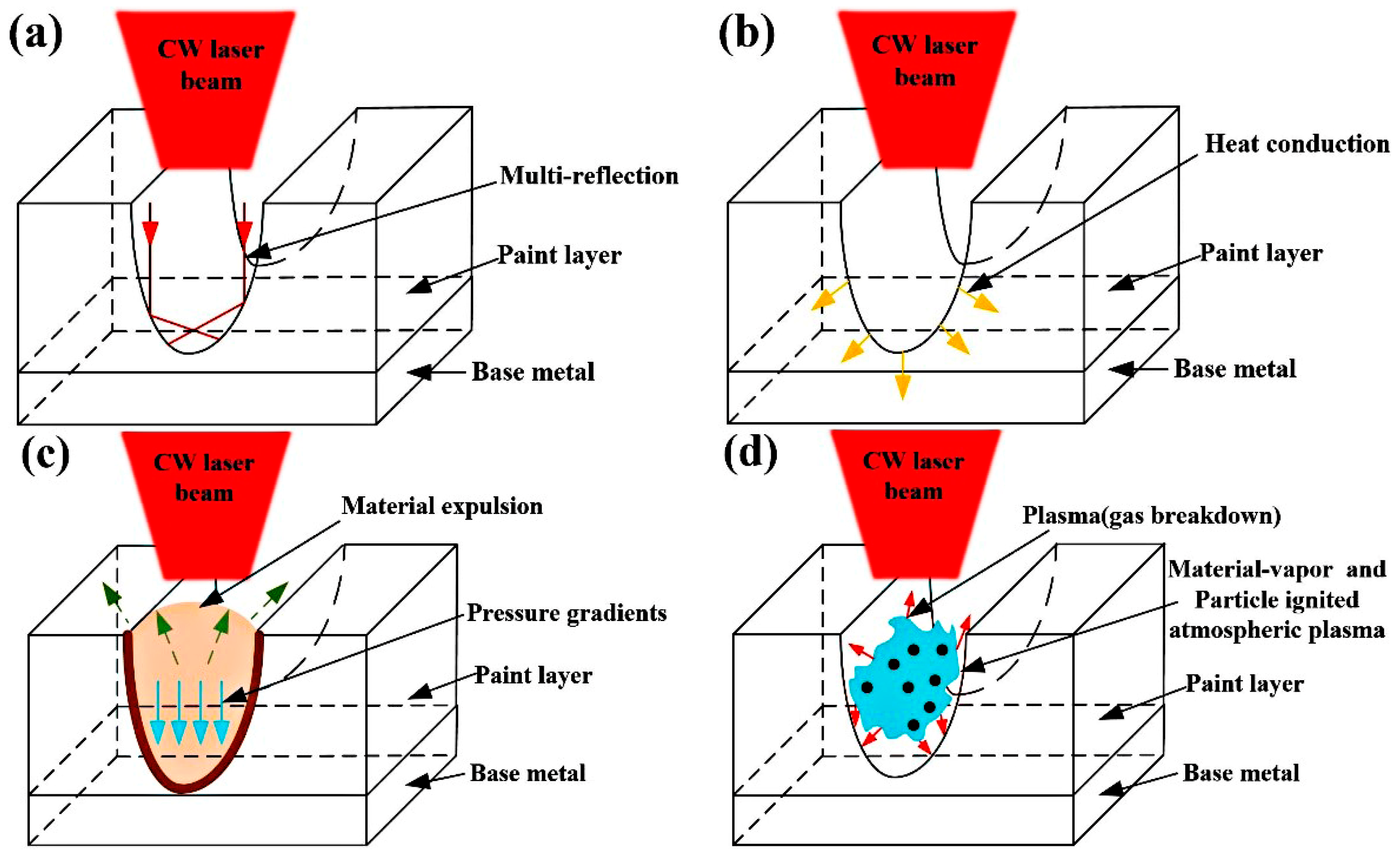
3.4. The Analysis of CW Laser Cleaning Process
3.5. Morphology Analysis of the Cleaned Surfaces
3.6. Performance of the Laser Cleaned Surface
3.6.1. Surface Roughness
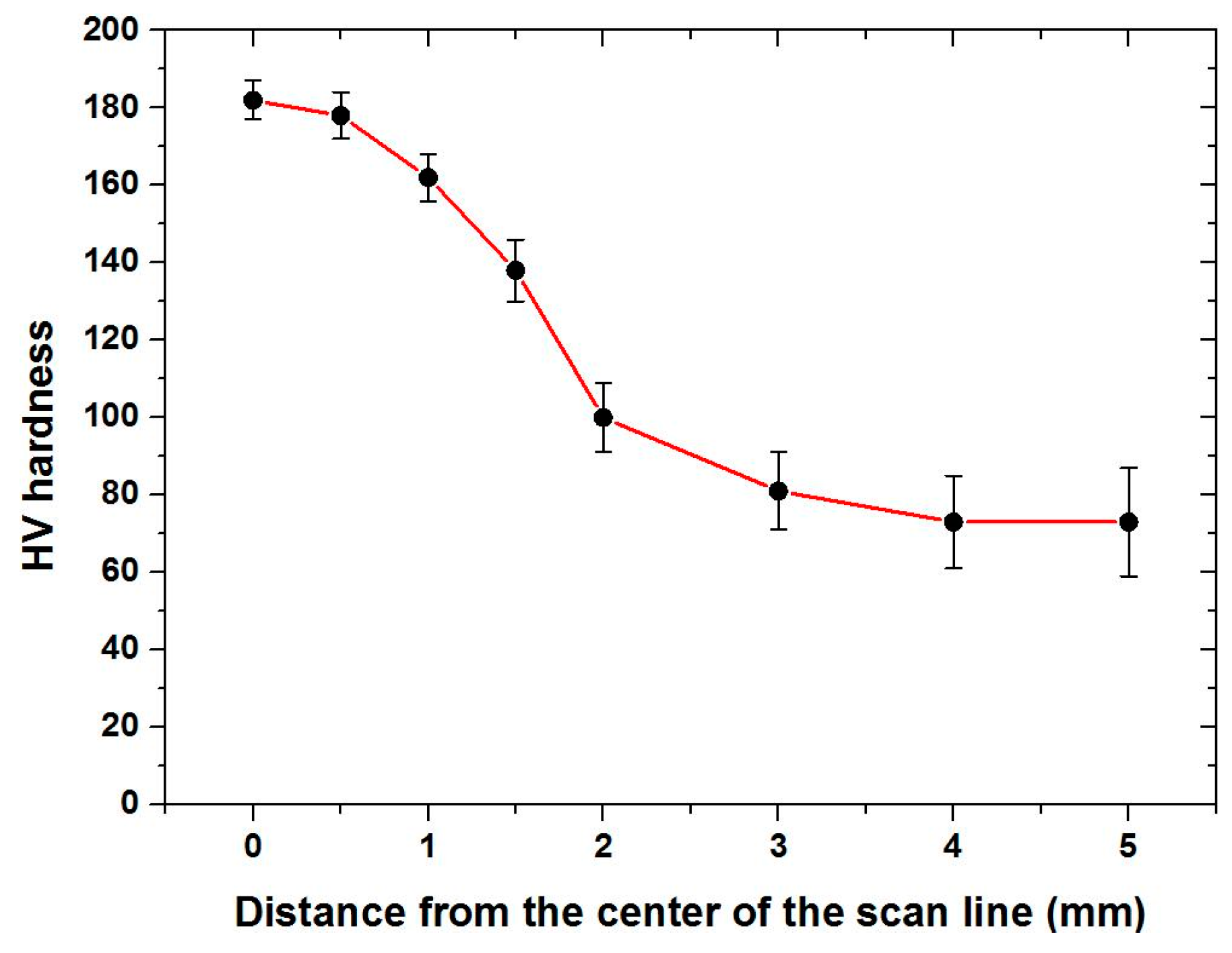
3.6.2. Surface Microhardness
3.6.3. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Department of the Navy Carderock Division; Naval Surface Warfare Center; Peterson Builders Inc. The National Shipbuilding Research Program: Surface Preparation and Coating Handbook; IIT Research Institute: Chicago, IL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.X.; Kwee, T.J.; Tan, K.P.; Choo, Y.S.; Hong, M.H. High-power fibre laser cleaning for green shipbuilding. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2012, 7, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Zhu, H.; Lei, W.; Cheng, Z. Laser cleaning of rust on ship steel using TEA CO2 pulsed laser. In Photonics and Optoelectronics Meetings (POEM) 2009: Industry Lasers and Applications; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7515, p. 75150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.X.; Kwee, T.J.; Tan, K.P.; Choo, Y.S.; Hong, M.H. Laser cleaning of steel for paint removal. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 101, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhukar, Y.K.; Mullick, S.; Shukla, D.K.; Kumar, S.; Nath, A.K. Effect of laser operating mode in paint removal with a fiber laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, G.; Werner, L. Industrial 2 kW TEA CO2 laser for paint stripping of aircraft: Gas flow and chemical lasers. In Proceedings of the SPIE 2502, Gas Flow and Chemical Lasers: Tenth International Symposium, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 5–9 September 1994; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunemi, A.; Hagiwara, K.; Saito, N.; Nagasaka, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Suto, O.; Tashiro, H. Complete removal of paint from metal surface by ablation with a TEA CO2 laser. Appl. Phys. A 1996, 63, 435–439. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, K.; Schuocker, D. Ultrahigh-power lasers and their industrial applications. Laser Phys. 1998, 8, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gobernado Mitre, I.; Prieto, A.C.; Zafiropulos, V.; Spetsidou, Y.; Fotakis, C. On-line monitoring of laser cleaning of limestone by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and laser-induced fluorescence. Appl. Spectrosc. 1997, 51, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauter, C.; Fontaine, J.; Engel, T.; Biernaux, A. Optical and acoustical monitoring of material processing with q-switched Nd:YAG and excimer laser radiation. In Proceedings of the SPIE 2246, Laser Materials Processing and Machining, Frankfurt, Germany, 19–24 June 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.J.J.; Li, L.; Spencer, J.T.; Key, P.H. A comparative study of the effects of laser wavelength on laser removal of chlorinated rubber. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1999, 138, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.J.J.; Li, L.; Spencer, J.T. Removal of chlorinated rubber coatings from concrete surfaces using a 120-W high power diode laser. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 141, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.J.J.; Li, L.; Spencer, J.T. An investigation into the feasibility and characteristics of using a 2.5 kW high power diode laser for paint stripping. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 138, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, M.; Gisario, A.; Tagliaferri, V. Advance in paint stripping from aluminium substrate. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 173, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Willis, D.A. Non-equilibrium phase change in metal induced by nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation. J. Heat Transf. 2002, 124, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.-F.; Xie, Y.-M.; Xiao, X.; Zeng, X.-Z.; Luo, Y. Application of thermal stress model to paint removal by Q-switched Nd: YAG laser. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 074205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.F.; Song, W.D.; Ang, B.W.; Hong, M.H.; Chan, D.S.H.; Low, T.S. A theoretical model for laser removal of particles from solid surfaces. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 1997, 65, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A.C.; Leung, W.P.; Zapka, W.; Ziemlich, W. Laser-cleaning techniques for removal of surface particulates. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 3515–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, J.D.; Hovis, F.E. A thermal detachment mechanism for particle removal from surfaces by pulsed laser irradiation. Microelectron. Eng. 1993, 20, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, K.L. Particles on Surfaces 1; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 77, 129, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.W.; Crouse, P.L.; Li, L.; Smith, A.J.E. Investigation into CO2 laser cleaning of titanium alloys for gas-turbine component manufacture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 4798–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.W.; Crouse, P.L.; Li, L. Comparative interaction mechanisms for different laser systems with selected materials on titanium alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7992–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, K.G. Mechanisms of laser cleaning. In Proceedings of the SPIE 3888, High-Power Lasers in Manufacturing, Osaka, Japan, 1–5 November 1999; pp. 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gathers, G.R. Thermophysical properties of liquid copper and aluminum. Int. J. Thermophys. 1983, 4, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlke, R.D.; Jeyarajan, A.; Wada, H. Summary of Thermal Properties for Casting Alloys and Mold Materials; University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.J.J.; Li, L.; Spencer, J.T. Removal of chlorinated rubber coatings from concrete surfaces using an RF excited CO2 laser. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 114, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, H.A.; Demir, A.G.; Previtali, B.; Taha, Z.A. Process development and monitoring in stripping of a highly transparent polymeric paint with ns-pulsed fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 93, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, W.M.; Mazumder, J. Laser Material Processing; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, K.G. Mechanisms of laser cleaning. In High-Power Lasers in Manufacturing; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 3888, pp. 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Aden, M.; Beyer, E.; Herziger, G. Laser-induced vaporisation of metal as a Riemann problem. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1990, 23, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, C.J. Theoretical modeling of rapid surface vaporization with back pressure. Aiaa J. 1979, 1, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.L.; Mazumder, J. One-imensional steady-state model for damage by vaporisation and liquid expulsion due to laser-material interaction. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 62, 4579–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, W.R.; Cheung, N.; Peixoto, L.C.; Garcia, A. Corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of an Al 9 wt% Si alloy treated by laser surface remelting. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2009, 4, 820–831. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, K.; McMahon, M.; Steen, W. Microstructure and corrosion properties of laser surface processed aluminium alloys: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 231, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ferreira, M.; Almeida, A.; Vilar, R.; Watkins, K.; McMahon, M.; Steen, W. Localized corrosion of laser surface melted 2024-T351 aluminium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 81, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasa, E.; Deckers, J.; Kruth, J.-P.; Kruth, J. The investigation of the influence of laser re-melting on density, surface quality and microstructure of selective laser melting parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2011, 17, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Huang, W.; Song, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G. The improvement of localized corrosion resistance in sensitized stainless steel by laser surface remelting. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 102, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajie, L.; Fengming, Q.; Cuirong, L.; Zhisheng, W. Flow law, microstructure and corrosion behavior of friction stir welded 5A06 alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 2353–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cullen, D.A.; Kar, S.; Free, M.L.; Allard, L.F. Evaluation of Al3Mg2 precipitates and Mn-rich phase in aluminum-magnesium alloy based on scanning transmission electron microscopy imaging. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4933–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Huang, W. Parameters and surface performance of laser removal of rust layer on A3 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 166, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, M.; Jung, I.-H. The evolution of the growth morphology in Mg–Al alloys depending on the cooling rate during solidification. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4848–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, W.; Yang, Y. Laser surface remelting of plasma sprayed nanostructured Al2O3–13 wt% TiO2 coatings on titanium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8603–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Shen, J.; Hu, S. Microstructure and performance of the laser melted aluminum bronze layers with and without using activator. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 066513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haixiang, C.; Dejun, K. Effect of laser remelting on amorphous formation and electrochemical corrosion of laser thermal sprayed Al–Ti–Ni coating. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 086545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, F.E.; Perpetuo Briguente, F.; Reis, A.G.D.; Vasconcelos, G.D.; Pereira Reis, D.A. Investigation on the microstructure and creep behavior of laser remelted thermal barrier coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 369, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, E.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Ma, W.; Lu, H.; Wu, S. Optimized microstructure and properties of Cr3C2-NiCr cermet coating by HVOF/laser hybrid processing. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2019, 28, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, T.; Ono, T.; Narazaki, Y.; Naka, Y.; Kawakami, M. Improvement of corrosion resistance of magnesium metal by rare earth elements. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Pehkonen, S.; Liang, B.; Ting, Y.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.-T. Superhydrophobic fluoropolymer-modified copper surface via surface graft polymerisation for corrosion protection. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, S.; Wang, Z. One-step fabrication of superhydrophobic surface on beryllium copper alloys and corrosion protection application. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 556, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X.; Fu, Y.Q.; Guo, B.; Tan, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P.; Fu, Y.Q.R. Roll-to-roll manufacturing of robust superhydrophobic coating on metallic engineering materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2174–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, M.L.; Bello, J.M. Laser surface treatment and corrosion behaviour of martensitic stainless AISI 420 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1992, 158, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ingelgem, Y.; Vandendael, I.; Van den Broek, D.; Hubin, A.; Vereecken, J. Influence of laser surface hardening on the corrosion resistance of martensitic stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7796–7801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Al | Si | Cu | Zn | Mg | Mn | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ballance | ≤0.4 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.2 | 5.8~6.8 | 0.5~0.8 | 0.02~0.1 |
| Properties | 5A06 Aluminum Alloy | Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 238 | 0.3 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 2700 | 1300 |
| Specific Heat Capacity (J/kg·K) | 1000 | 2510 |
| Thermal Diffusivity (m2/s) | 8.8 × 10−8 | 9.19 × 10−8 |
| Linear Expansion Coefficient (K−1) | 30 × 10−6 [25] | 1.00 × 10−6 |
| Absorption Rate | 0.642 | 0.614 |
| Reflectivity | 0.358 [16] | 0.193 |
| Transmittance | – | 0.193 |
| Absorption Coefficient (m−1) | 10000 × 104 | 2.27 × 104 |
| Elasticity Modulus (N·m−2) | 7 × 1010 [24] | 1.0 × 1010 |
| Sample No. | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (W/cm2) | 3.3 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 11.9 | 13.6 | 15.3 | 19.1 |
| Ra (μm) | 1.247 | 1.373 | 1.291 | 0.967 | 1.308 | 1.461 | 2.394 |
| Sample No. | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vs (mm/s) | 50 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 |
| Ra (μm) | 3.251 | 2.533 | 3.254 | 3.525 | 4.061 | 4.335 | 5.042 |
| Sample | Ecorr (V) | icorr (A·cm−2) | ηIE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polished 5A06 block | −9.03 × 10−1 | 3.538 × 10−4 | – |
| Partially damaged paint layer | −8.61 × 10−1 | 7.42 × 10−5 | 79.02% |
| Laser cleaning at 11.9 W/cm2 | −6.39 × 10−1 | 5.145 × 10−5 | 85.46% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, B.; Tian, Z. Paint Removal on the 5A06 Aluminum Alloy Using a Continuous Wave Fiber Laser. Coatings 2019, 9, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080488
Lu Y, Yang L, Wang Y, Chen H, Guo B, Tian Z. Paint Removal on the 5A06 Aluminum Alloy Using a Continuous Wave Fiber Laser. Coatings. 2019; 9(8):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080488
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yao, LiJun Yang, Yang Wang, Hao Chen, Bin Guo, and Ze Tian. 2019. "Paint Removal on the 5A06 Aluminum Alloy Using a Continuous Wave Fiber Laser" Coatings 9, no. 8: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080488
APA StyleLu, Y., Yang, L., Wang, Y., Chen, H., Guo, B., & Tian, Z. (2019). Paint Removal on the 5A06 Aluminum Alloy Using a Continuous Wave Fiber Laser. Coatings, 9(8), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080488




