Surface Activation of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) with Atmospheric Pressure Ar + H2O Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
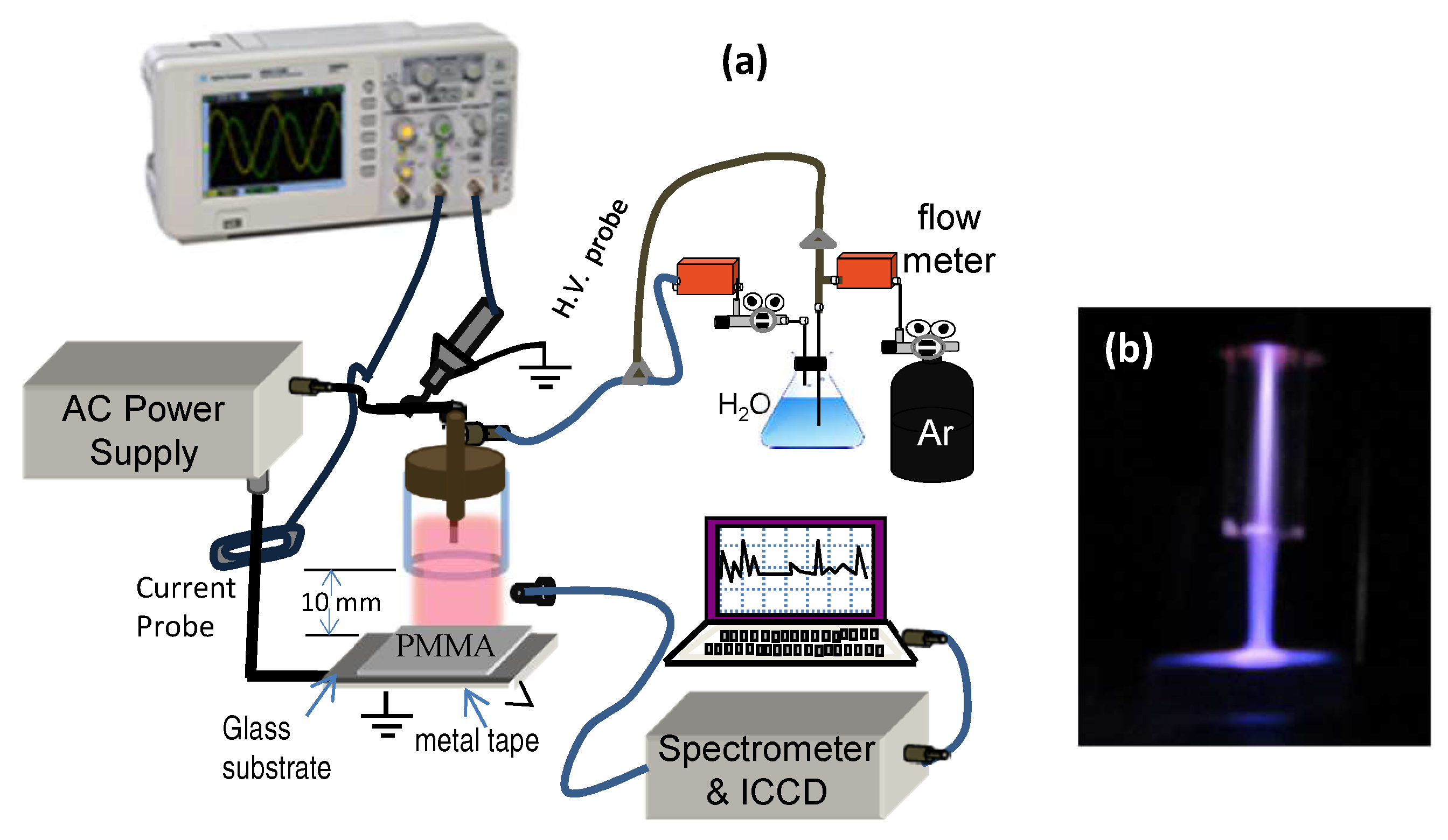
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
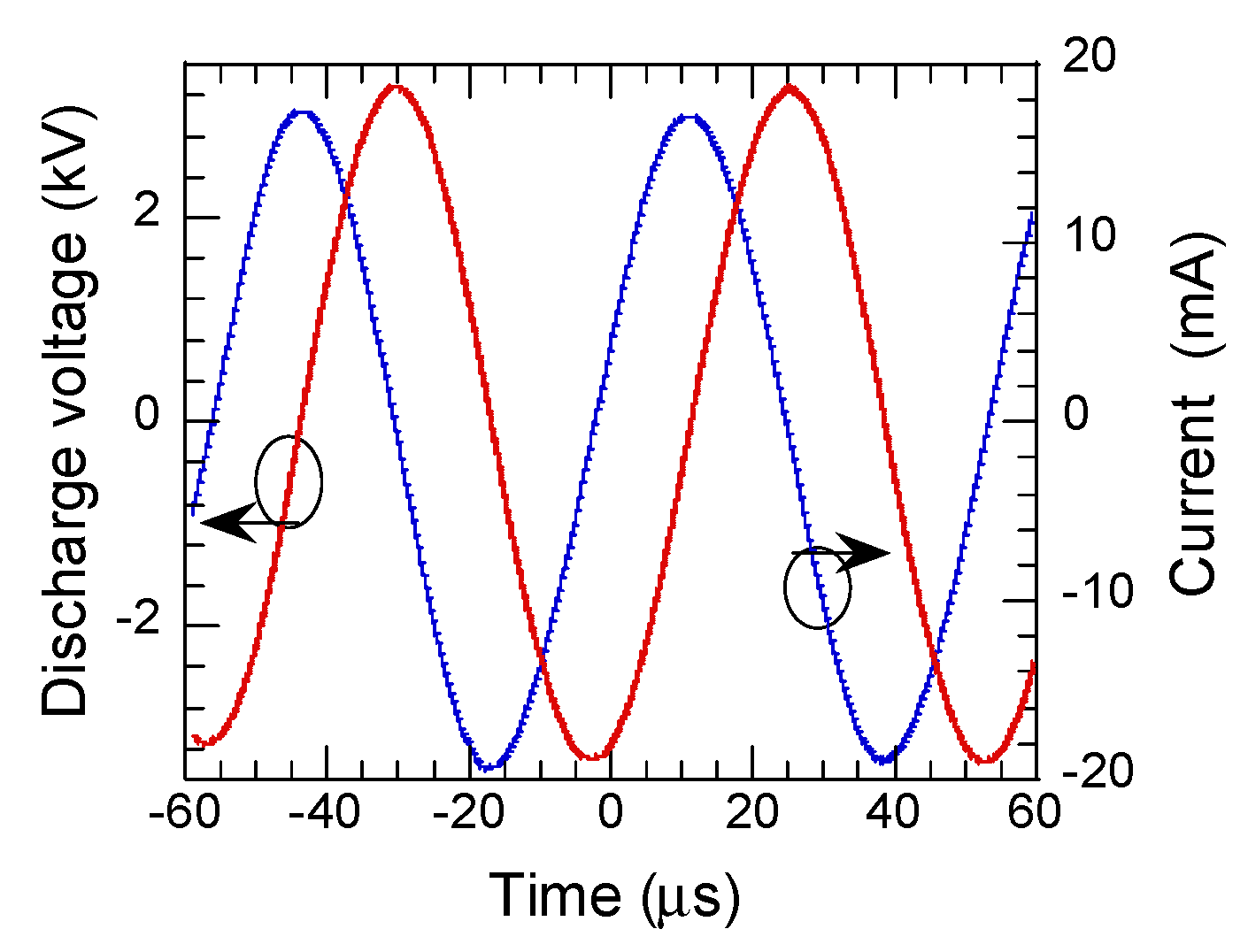
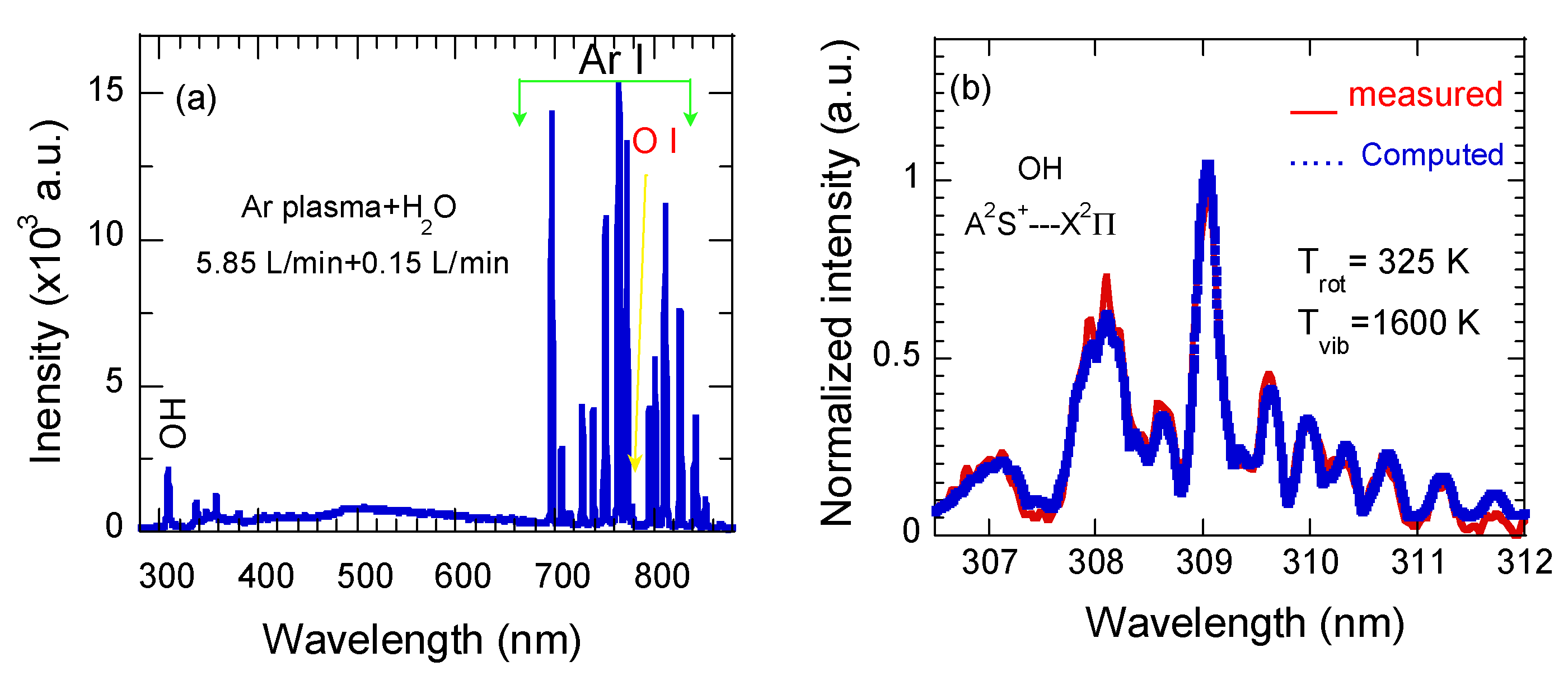
3.1. Electrical and Optical Characteristics Ar + H2O Plasma Jet
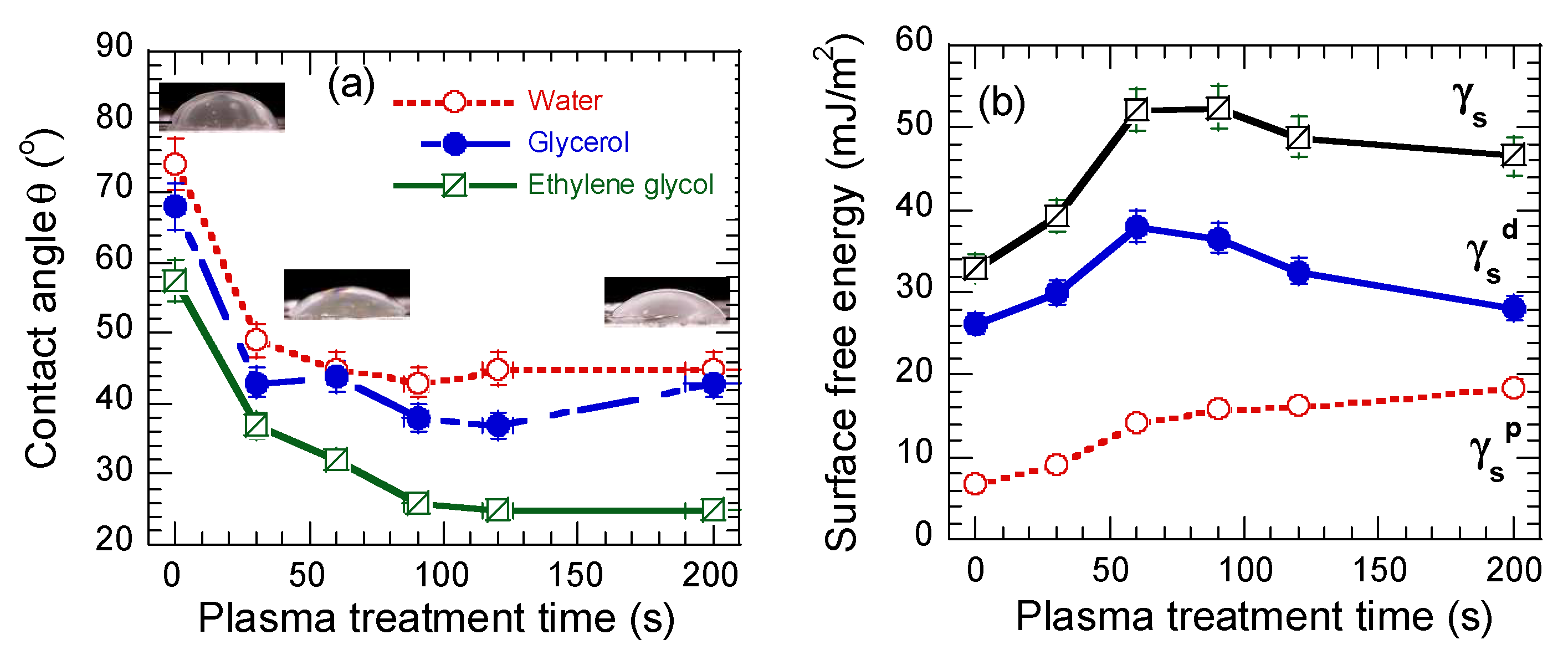
3.2. Contact Angles and Surface Free Energy Measurements
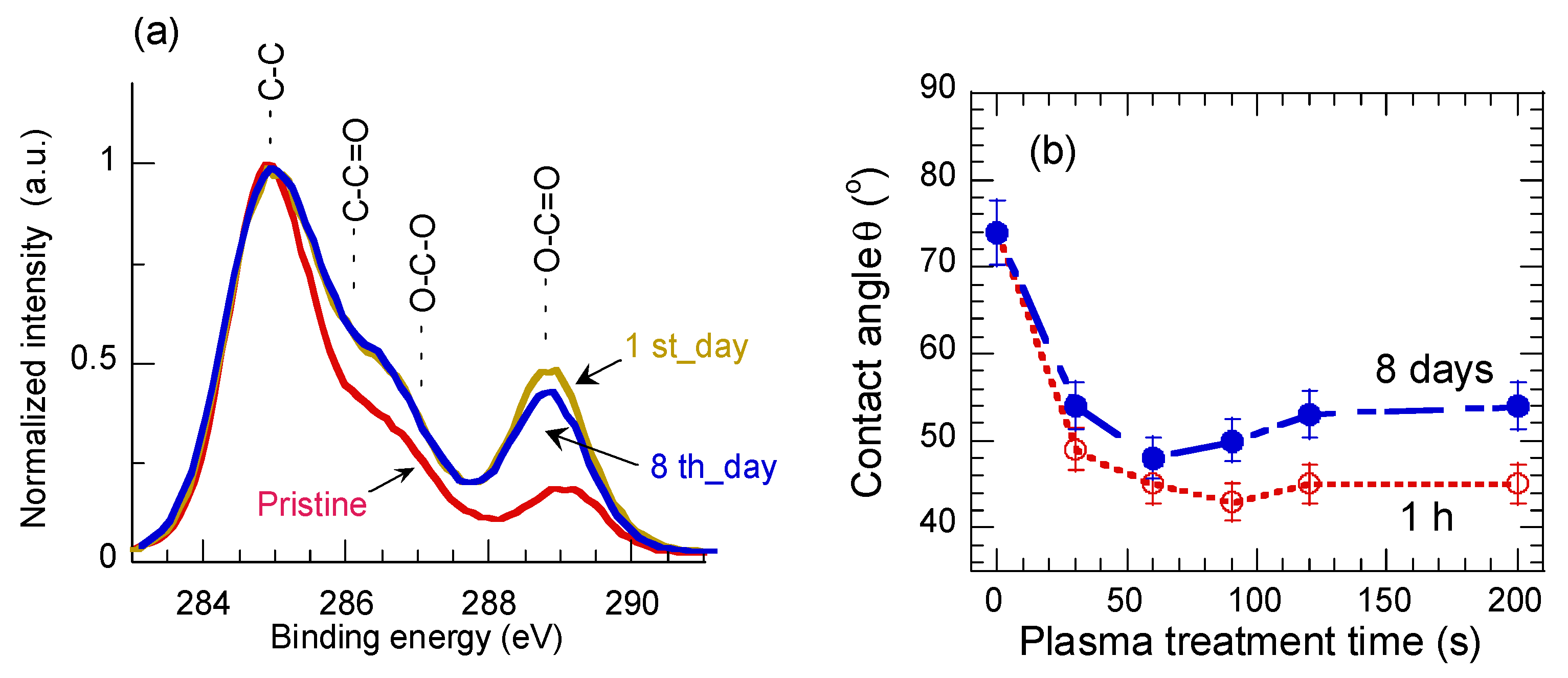
3.3. XPS
3.4. AFM Surface Morphology
3.5. Optical Properties
3.6. Ageing Effect
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, U.; Karim, K.J.B.A.; Buang, N.A. A review of the properties and applications of poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA). Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, A.M.S. The influence of humidity on the deformation and fracture behavior of PMMA. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 124, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanne, A.; Movva, H.C.P.; Kang, S.; McClellan, C.; Corbet, C.M.; Banerjee, S.K. Poly(methyl methacrylate) as a self-assembled gate dielectric for graphene field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 083106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickler, M.; Rhein, T. Polymethacrylates. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 5th ed.; Elvers, B., Hawkins, S., Schulz, G., Eds.; Wiley-VHS: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 473. [Google Scholar]
- Garrett, T.R.; Bhakoo, M.; Zhang, Z. Bacterial adhesion and biofilms on surfaces. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2008, 18, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riau, A.K.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Dohlman, C.H.; Mehta, J.S. Surface modifications of the PMMA optic of a keratoprosthesis to improve biointegration. Cornea 2017, 36, S15–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Gao, O.; Sun, Y.; Huang, C. Surface modification of hydrophobic PMMA intraocular lens by the immobilization of hydroxyethyl methacrylate for improving application in ophthalmology. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2011, 31, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Kim, D.H.; Kovacik, P.; Sojoudi, H.; Wang, M.; Gleason, K.K. Polymer thin films and surface modification by chemical vapor deposition: Recent progress. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2016, 7, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, R.; Chen, J.L.; Stuckey, D.C.; Steele, T.W. Poly(methyl methacrylate) surface modification for surfactant-free real-time toxicity assay on droplet microfluidic platform. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13801–13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evea, S.; Mohr, J. Study of the surface modification of the PMMA by UV-radiation. Procedia Eng. 2009, 1, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.; Liu, X.; Chikthimmah, N.; Lee, Y.S. Polymer surface modification using UV treatment for attachment of natamycin and the potential applications for conventional food clingwrap (LDPE). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 386, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, E.; Ogawa, D.; Nakamura, K. Oxygen functionalization of MWCNTs in RF-dielectric barrier discharge Ar/O2 plasma. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 265301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, P.; Knes, R.; Fredrich, J. Surface cleaning by plasma-enhanced desorption of contaminants (PEDC). Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 112, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabesawa, H.; Hiruma, T.; Hitobo, T.; Wakabayashi, S.; Asaji, T.; Abe, T.; Seki, M. Low-pressure plasma-etching of bulk polymer materials using gas mixture of CF4 and O2. AIP Adv. 2013, 3, 112105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkov, O.V.; Khadem, M.; Lim, W.S.; Kim, D.E. A review of recent applications of atmospheric pressure plasma jets for materials processing. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2015, 12, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelschatz, U. Dielectric-barrier discharges: Their history, discharge physics, and industrial applications. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2003, 23, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, E.; Yehia, A.; Bazavan, M.; Ishijima, T. Optical emission and surface characterization of stainless steel treated by pulsed microwave-atmospheric helium plasma jet. Eur. Phys. J. D 2017, 71, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlbeck, J.; Schnabel, U.; Polak, M.; Winter, J.; Von Woedtke, T.; Brandenburg, R.; von dem Hagen, T.; Weltmann, K.D. Low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma sources for microbial decontamination. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 44, 013002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, U.; Munzert, P.; Kaiser, N. Surface modification of PMMA by DC glow discharge and microwave plasma treatment for the improvement of coating adhesion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 142–144, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesel, A.; Mozetic, M. Surface modification and ageing of PMMA polymer by oxygen plasma treatment. Vacuum 2012, 86, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiper, A.; Borcia, G. Argon versus helium dielectric barrier discharge for surface modification of polypropylene and poly(methyl methacrylate) films. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2013, 33, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Shao, T.; Zhang, C. Surface modifications of polymethylmetacrylate films using atmospheric pressure air dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Vacuum 2012, 86, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawde, S.M.; Deshmukh, K. Surface characterization of air plasma treated poly vinylidene fluoride and poly methyl methacrylate films. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laux, C.O. Radiation and nonequilibrium collisional-radiative models, in van karman Institute Lecture Series 2002-07. In Physico-Chemical Modeling of High Enthalpy and Plasma Flows; Fletcher, D., Magin, T., Charbonnier, J.M., Sarma, G., Eds.; Von Karman Institute: Rhode-Saint-Genese, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surface Tension Components and Molecular Weight of Selected Liquids. Available online: https://www.accudynetest.com/surface_tension_table.html (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- Abdel-Fattah, E.; Bazavan, M.; Shindo, H. Temperature measurements in microwave argon plasma source by using overlapped molecular emission spectra. Phys. Plasma 2015, 22, 093509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chang, Y.C.; Wu, S.Y. Contact angle analysis of low temperature cyclonic atmospheric pressure plasma modified polyethylene terephthalate. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 3575–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheimer, M.R.; Fozza, A.C.; Holländer, A. Industerial processing of polymers by low pressure plasmas: The role of UV radiation. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. Sect. B 1999, 151, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamson, G.; Briggs, D. High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers: The Scienta ESCA300 Database; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kostova, K.G.; Nishime, T.M.C.; Castro, A.H.R.; Toth, A.; Hein, L.R.D.O. Surface modification of polymeric materials by cold atmospheric plasma jet. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siow, K.S.; Britcher, L.; Kumar, S.; Griesser, H.J. Plasma methods for the generation of chemically reactive surfaces for biomolecule immobilization and cell colonization. Plasma Process. Polym. 2006, 3, 392–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
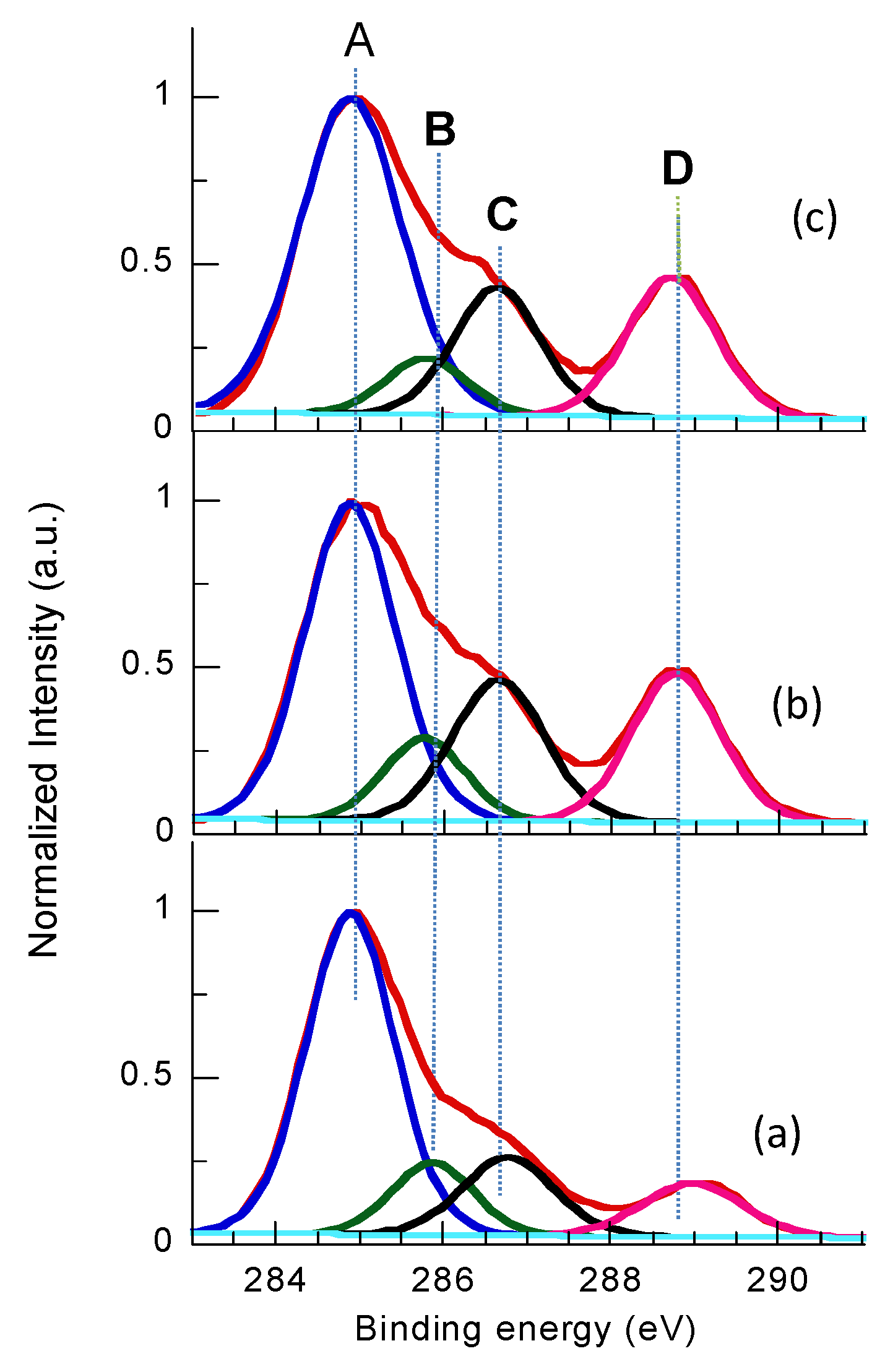
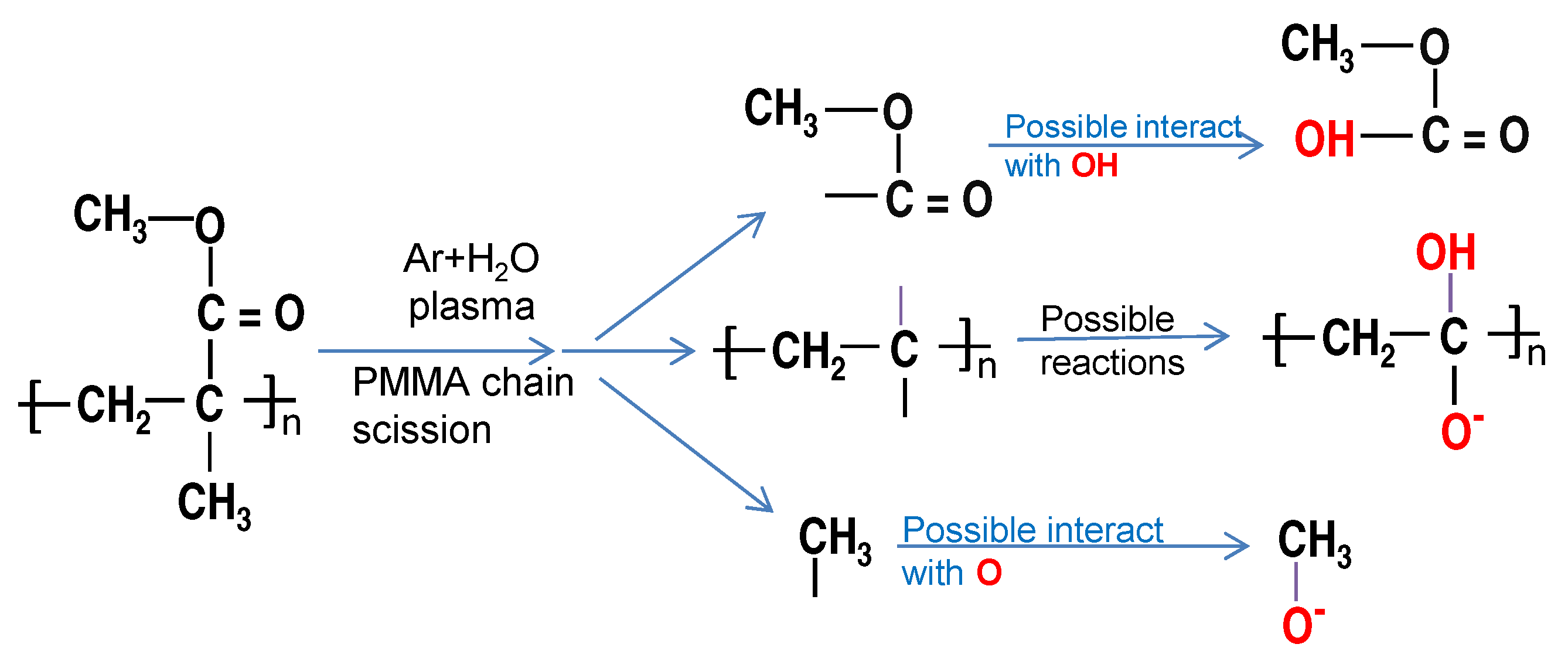
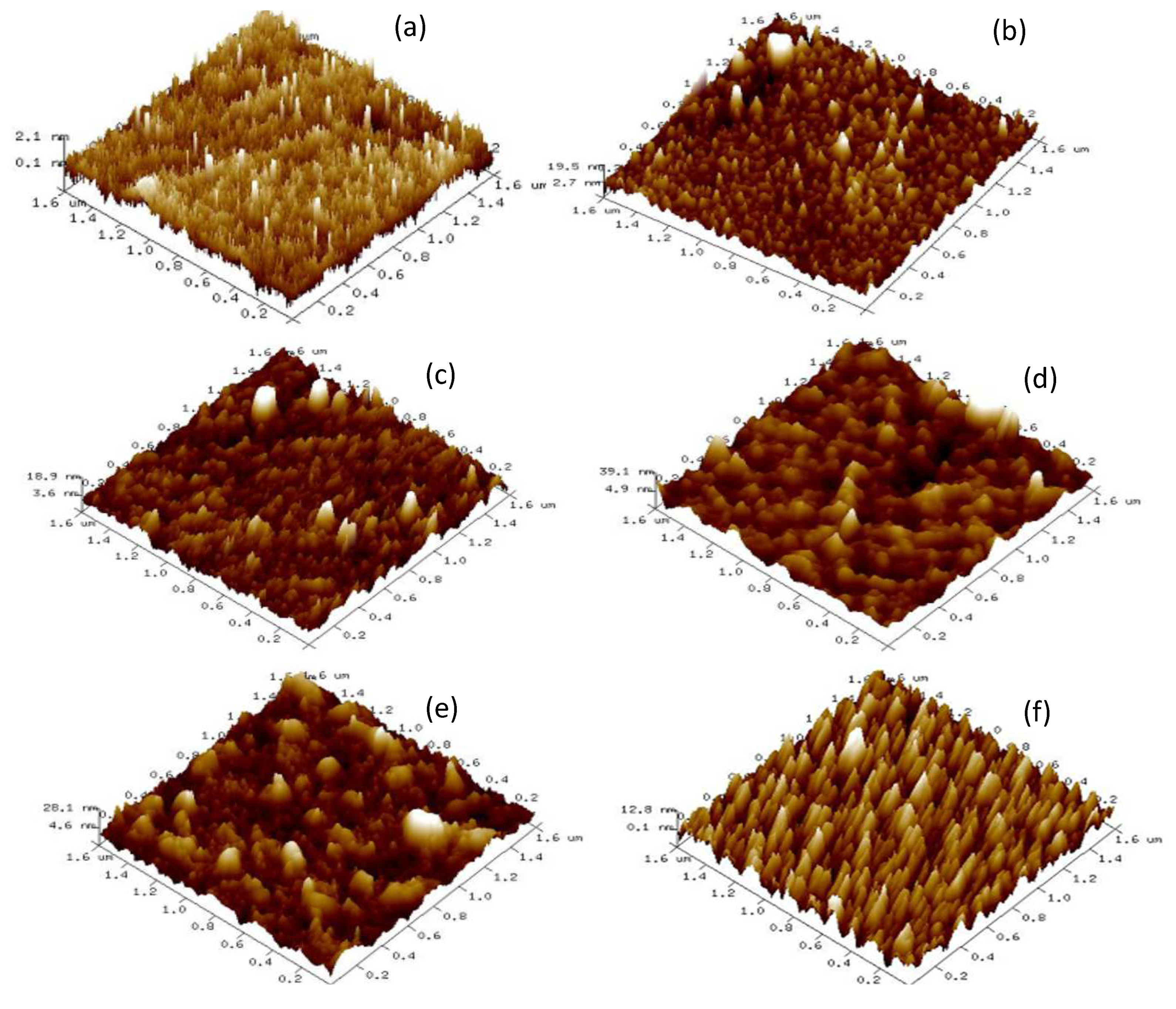
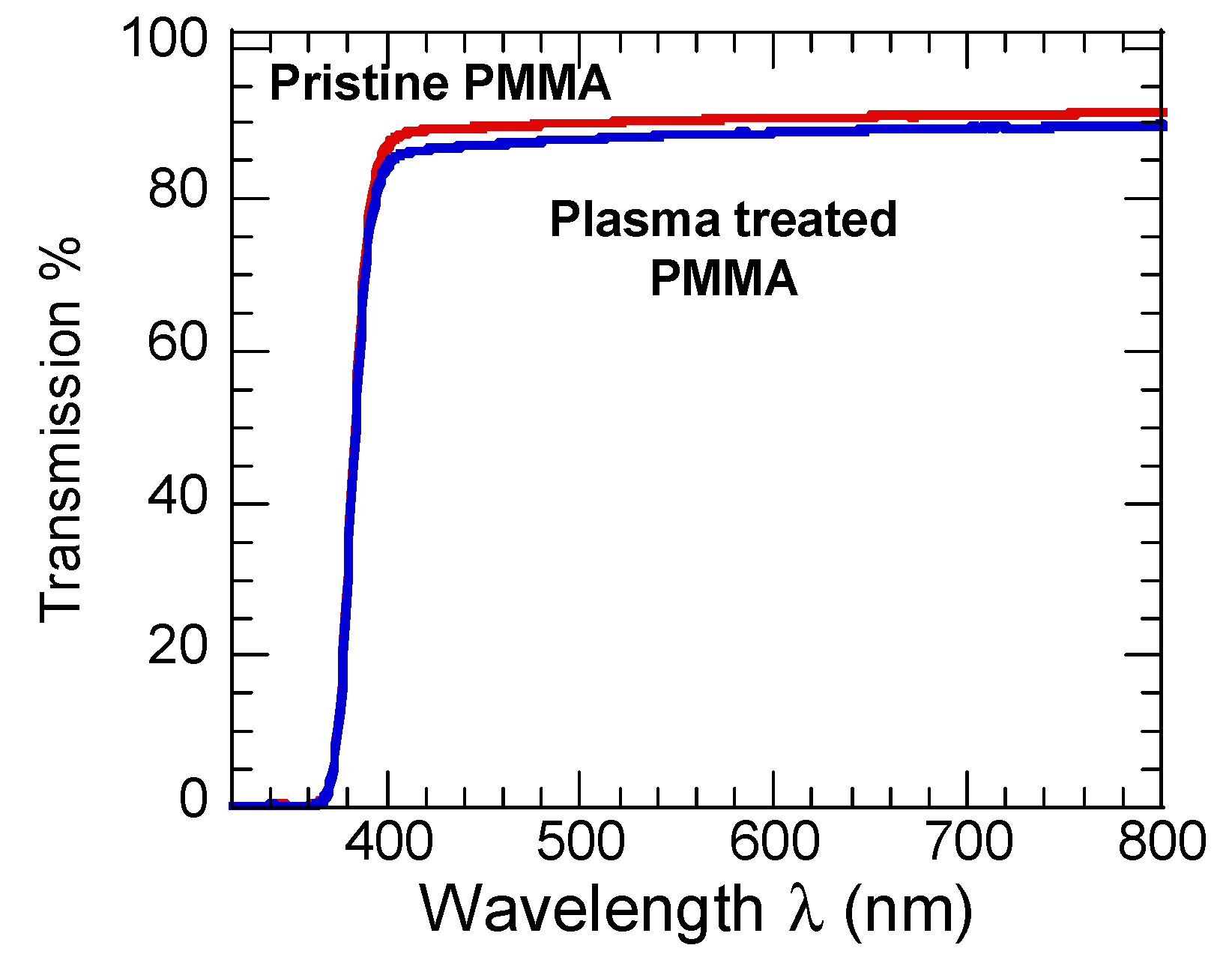
| Time (s) | Chemical Composition [%] | Atomic Ratio [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1s | O1s | N1s | O/C | |
| 0 | 76.33 | 20.65 | 2.96 | 27 |
| 30 | 66.38 | 32.05 | 1.57 | 48.3 |
| 60 | 66.01 | 32.75 | 1.24 | 49.6 |
| 90 | 65.58 | 33.36 | 1.06 | 50.5 |
| 120 | 65.79 | 33.40 | 0.81 | 50.8 |
| 200 | 66.28 | 32.50 | 1.22 | 49 |
| Time (s) | C–C % | C–C=O % | C–O % | O–C=O % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 49.40 | 2.35 | 16.62 | 8.73 |
| 30 | 35.20 | 3.10 | 13.83 | 15.39 |
| 60 | 34.77 | 3.05 | 12.69 | 15.25 |
| 90 | 34.34 | 4.29 | 12.59 | 14.94 |
| 120 | 34.57 | 6.02 | 10.41 | 14.57 |
| 200 | 34.87 | 6.39 | 10.19 | 14.25 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel–Fattah, E. Surface Activation of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) with Atmospheric Pressure Ar + H2O Plasma. Coatings 2019, 9, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040228
Abdel–Fattah E. Surface Activation of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) with Atmospheric Pressure Ar + H2O Plasma. Coatings. 2019; 9(4):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040228
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel–Fattah, Essam. 2019. "Surface Activation of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) with Atmospheric Pressure Ar + H2O Plasma" Coatings 9, no. 4: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040228
APA StyleAbdel–Fattah, E. (2019). Surface Activation of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) with Atmospheric Pressure Ar + H2O Plasma. Coatings, 9(4), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040228





