Piezoresistive Characteristics of Nylon Thread Resistive Memories for Wearable Strain Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
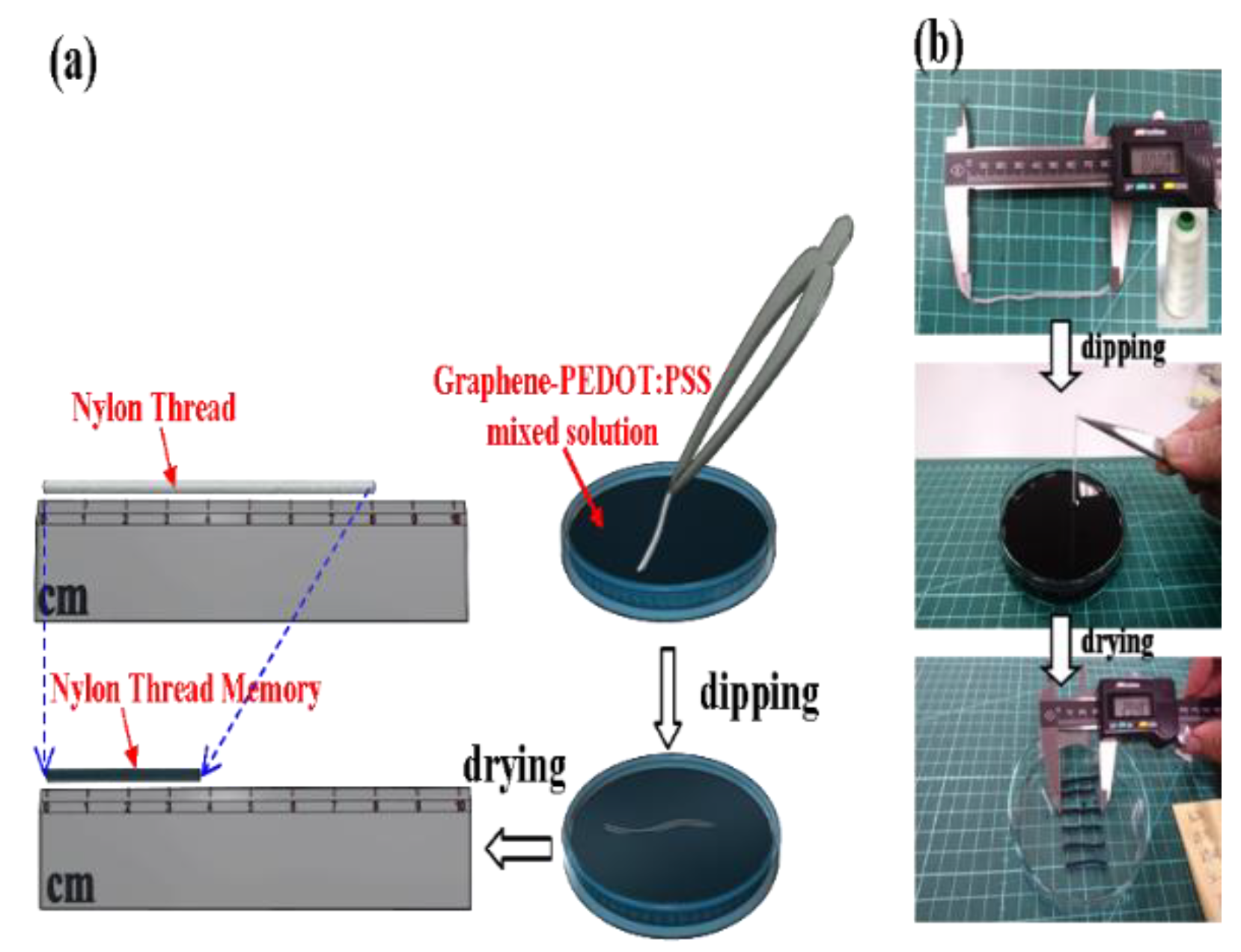
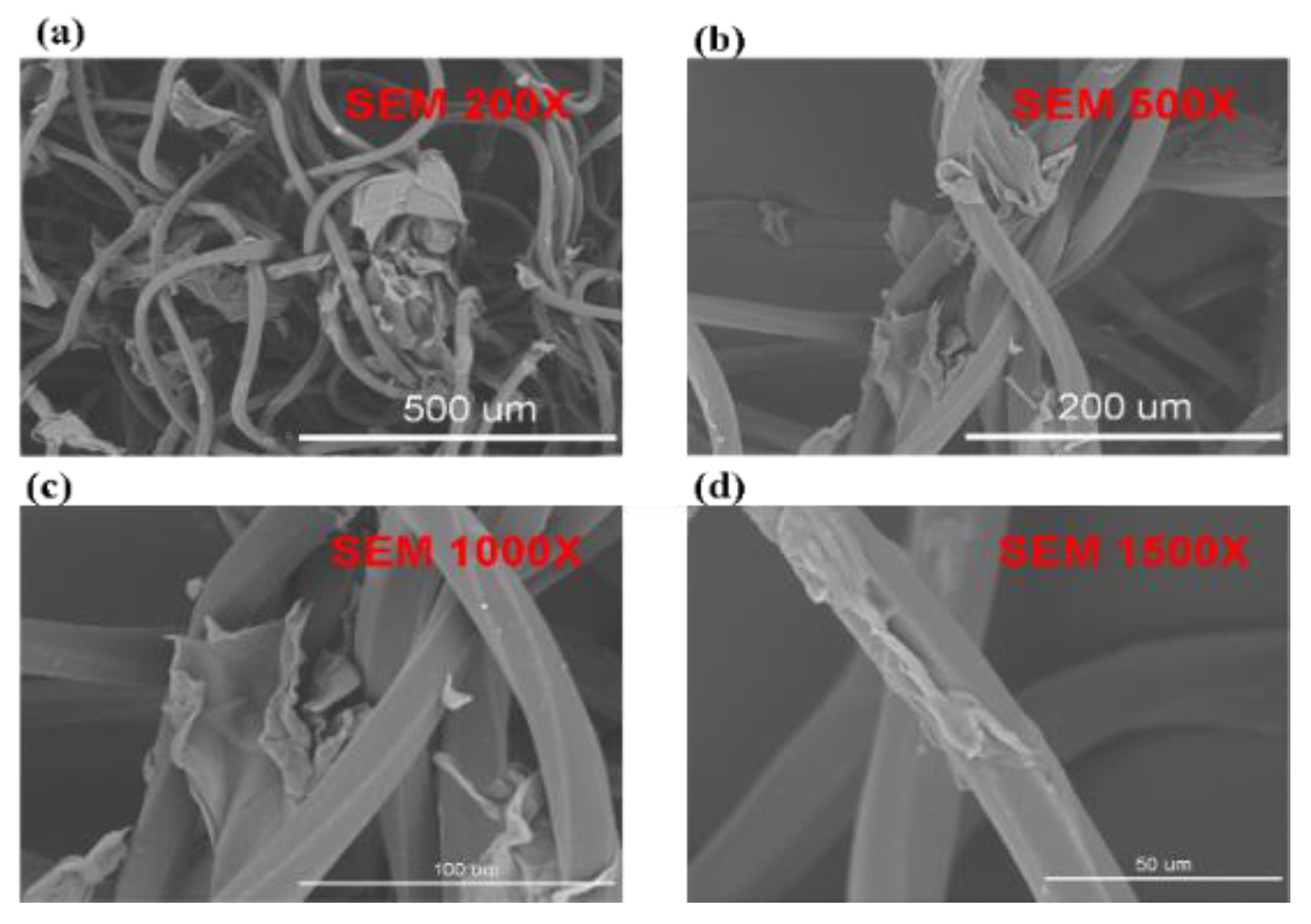
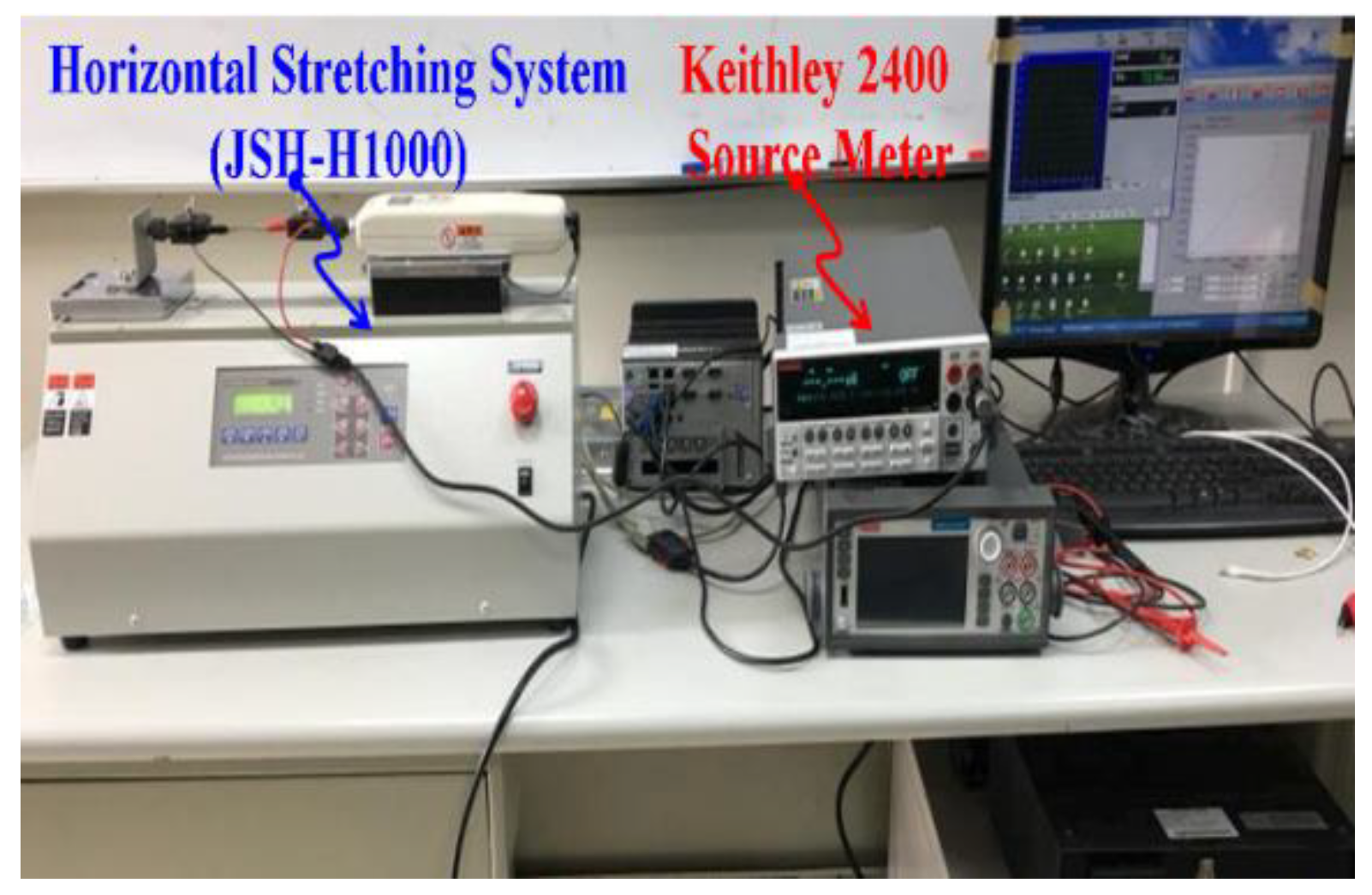
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
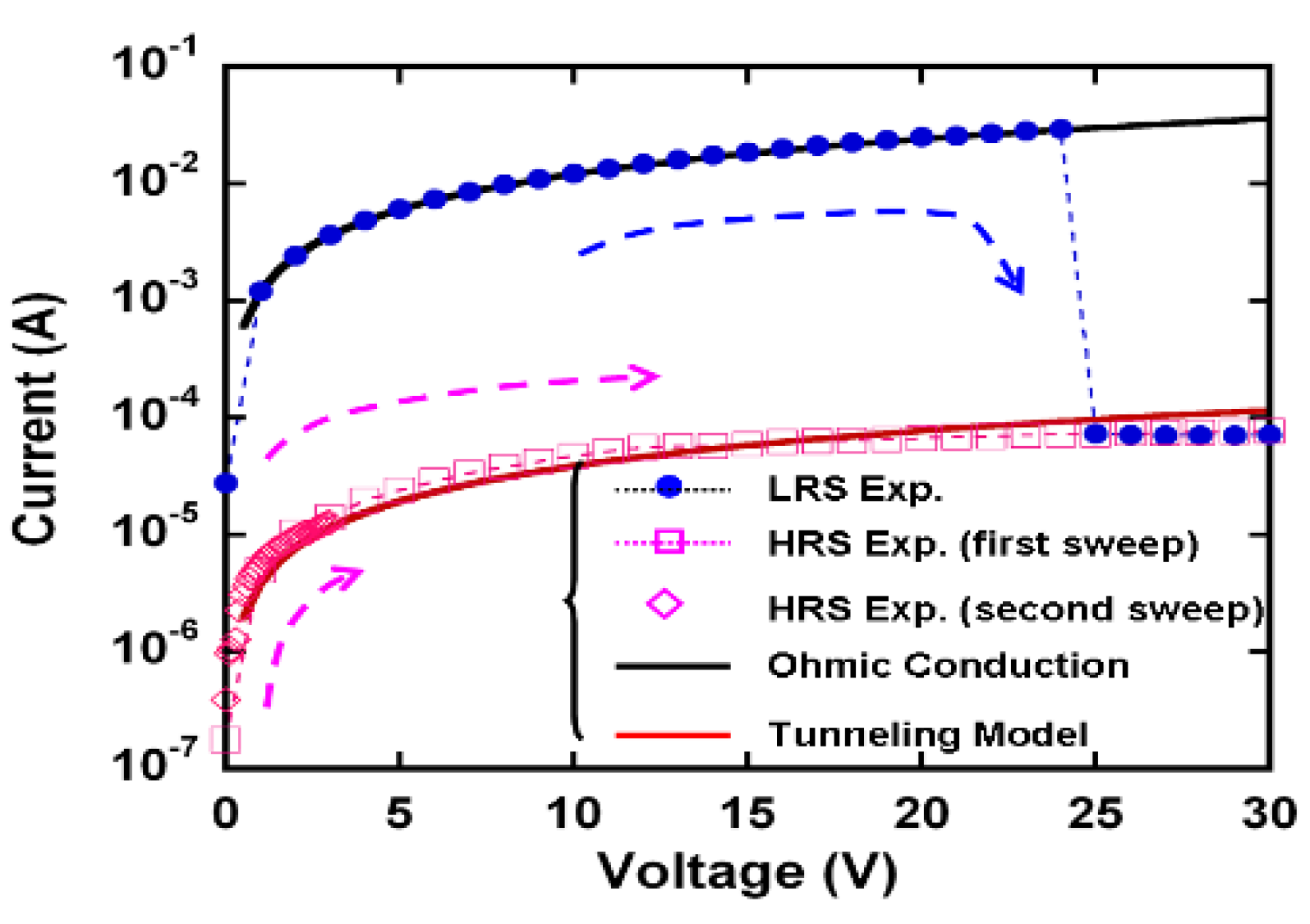
3.1. WORM Characteristics
3.2. Piezoresistive Characteristics of the NT Resistive Memory
3.3. A Highly Sensitive and Durable Strain Sensor
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Service, R.F. Electronic textiles charge ahead. Science 2003, 301, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, C.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.N.; Ahn, S.H.; Suh, K.Y. A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibres. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccioni, M.; Orgiu, E.; Cosseddu, P.; Locci, S.; Bonfiglio, A. Towards the textile transistor: Assembly and characterization of an organic field effect transistor with a cylindrical geometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 143515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.K. Highly stretchable non-volatile nylon thread memory. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Invernale, M.A.; Sotzing, G.A. Conductivity trends of PEDOT-PSS impregnated fabric and the effect of conductivity on electrochromic textile. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.M. Fiber-based wearable electronics: A review of materials, fabrication, devices, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeon, C.; Kim, G.; Lim, J.W.; Yun, S.J. Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS treated by sodium dodecyl sulphate for stretchable fabric heaters. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5888–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, S.; Razal, J.M.; Innis, P.C.; Jeiranikhameneh, A.; Beirne, S.; Wallace, G.G. Knitted strain sensor textiles of highly conductive all-polymeric fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21150–21158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Balasubramaniam, K.; Ramaprabhu, S. One-pot synthesis of conducting graphene-polymer composites and their strain sensing application. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Swetha, P.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-enabled wearable sensors for healthcare. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1700889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Pasta, M.; Mantia, F.L.; Cui, L.F.; Jeong, S.; Deshazer, H.D.; Choi, J.W.; Han, S.M.; Cui, Y. Stretchable, porous, and conductive energy textiles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Fan, J.A.; Xu, S.; Song, Y.M.; Choi, K.J.; Yeo, W.H.; Lee, W.; Nazaar, S.N.; et al. Experimental and theoretical studies of serpentine microstructures bonded to prestrained elastomers for stretchable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotya, M.; Hernandez, Y.; King, P.J.; Smith, R.J.; Nicolosi, V.; Karisson, L.S.; Blighe, F.M.; De, S.; Wang, Z.; McGovern, I.T.; et al. Liquid phase production of graphene by exfoliation of graphite in surfactant/water solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.K. Tunable piezoresistive sensors based on pencil-on-paper. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 073117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
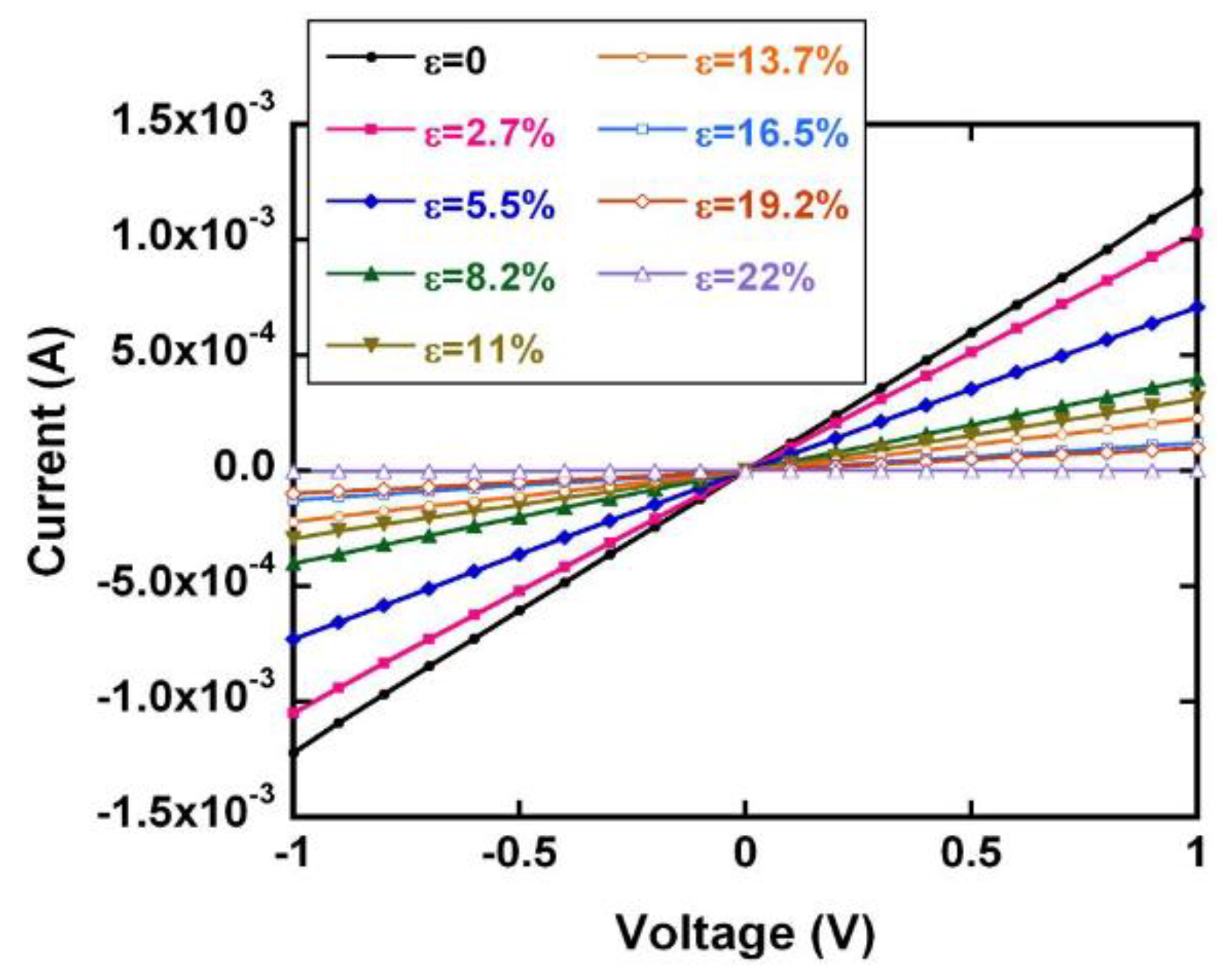
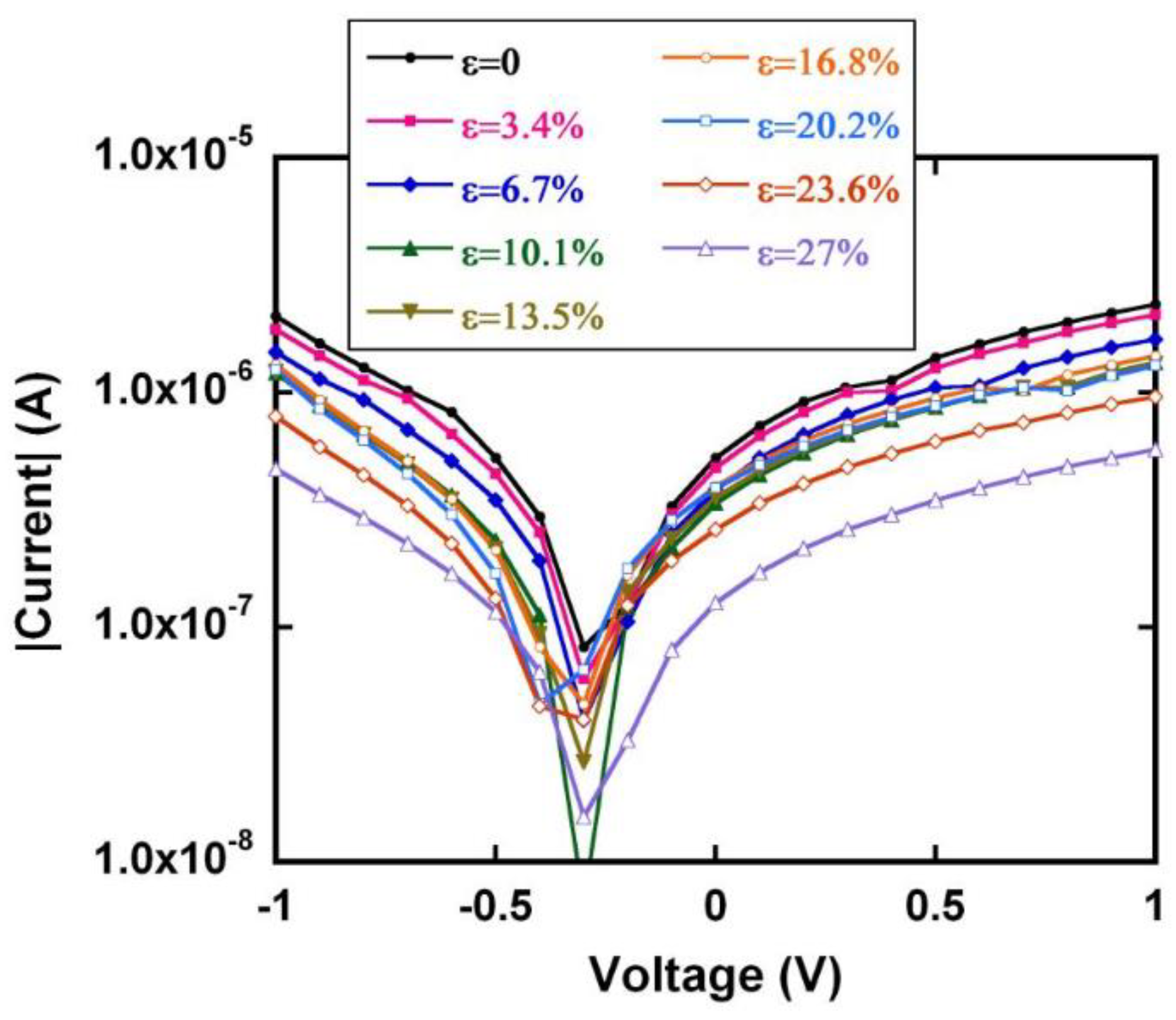

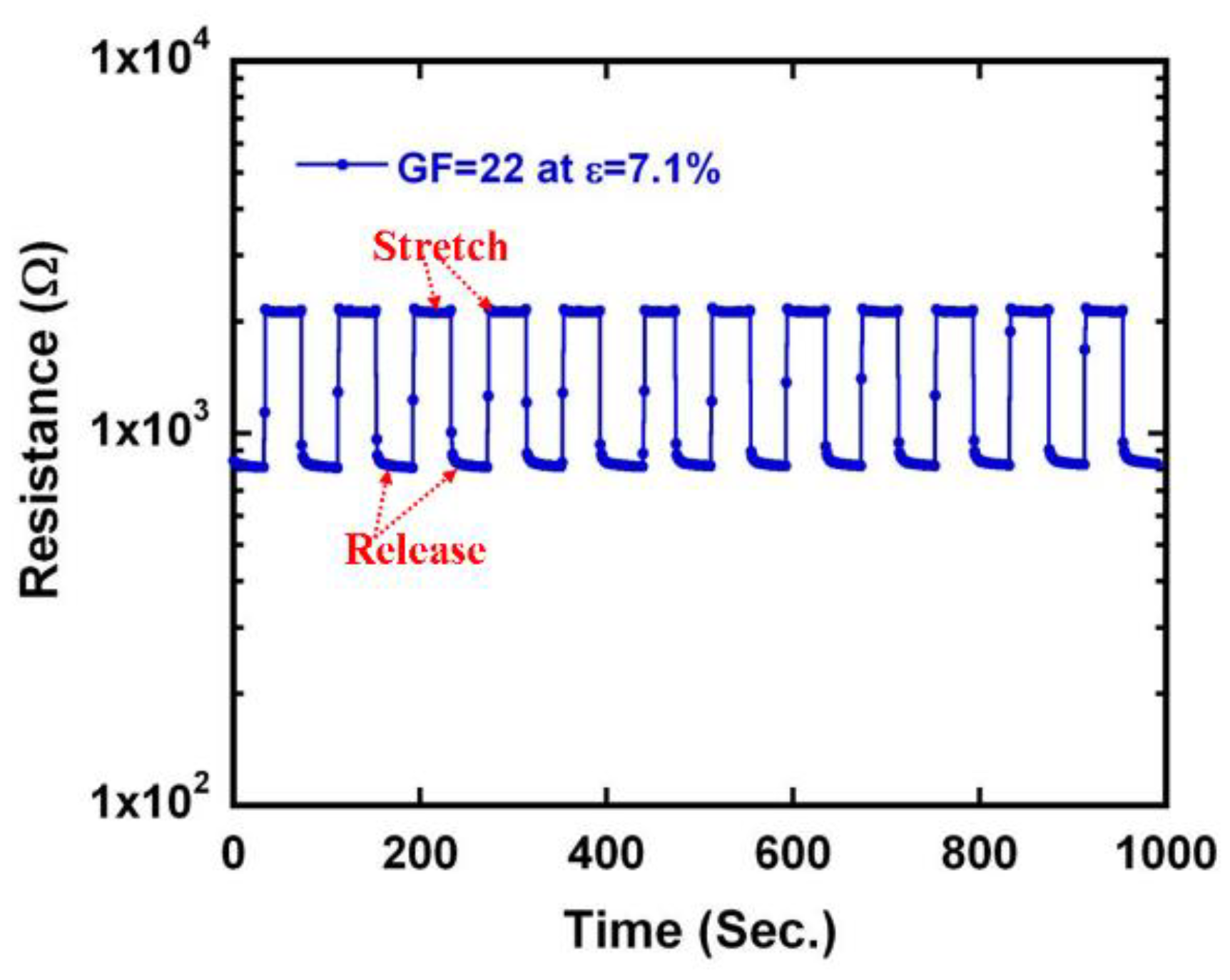
| ε | ΔR/R0 | GF |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.027 | 0.16 | 5.97 |
| 0.055 | 0.68 | 12.35 |
| 0.082 | 2.02 | 24.48 |
| 0.110 | 3.01 | 27.39 |
| 0.137 | 4.41 | 32.13 |
| 0.165 | 8.71 | 52.85 |
| 0.192 | 11.18 | 58.14 |
| 0.220 | 609.93 | 2775.16 |
| ε | ΔR/R0 | GF |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.034 | 0.11 | 3.15 |
| 0.067 | 0.40 | 5.94 |
| 0.101 | 0.77 | 7.63 |
| 0.135 | 0.79 | 5.86 |
| 0.168 | 0.66 | 3.91 |
| 0.202 | 0.83 | 4.10 |
| 0.236 | 1.47 | 6.25 |
| 0.269 | 3.14 | 11.66 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, T.-K. Piezoresistive Characteristics of Nylon Thread Resistive Memories for Wearable Strain Sensors. Coatings 2019, 9, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9100623
Kang T-K. Piezoresistive Characteristics of Nylon Thread Resistive Memories for Wearable Strain Sensors. Coatings. 2019; 9(10):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9100623
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Ting-Kuo. 2019. "Piezoresistive Characteristics of Nylon Thread Resistive Memories for Wearable Strain Sensors" Coatings 9, no. 10: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9100623
APA StyleKang, T.-K. (2019). Piezoresistive Characteristics of Nylon Thread Resistive Memories for Wearable Strain Sensors. Coatings, 9(10), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9100623




