Halogen-Free Phosphonate Ionic Liquids as Precursors of Abrasion Resistant Surface Layers on AZ31B Magnesium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
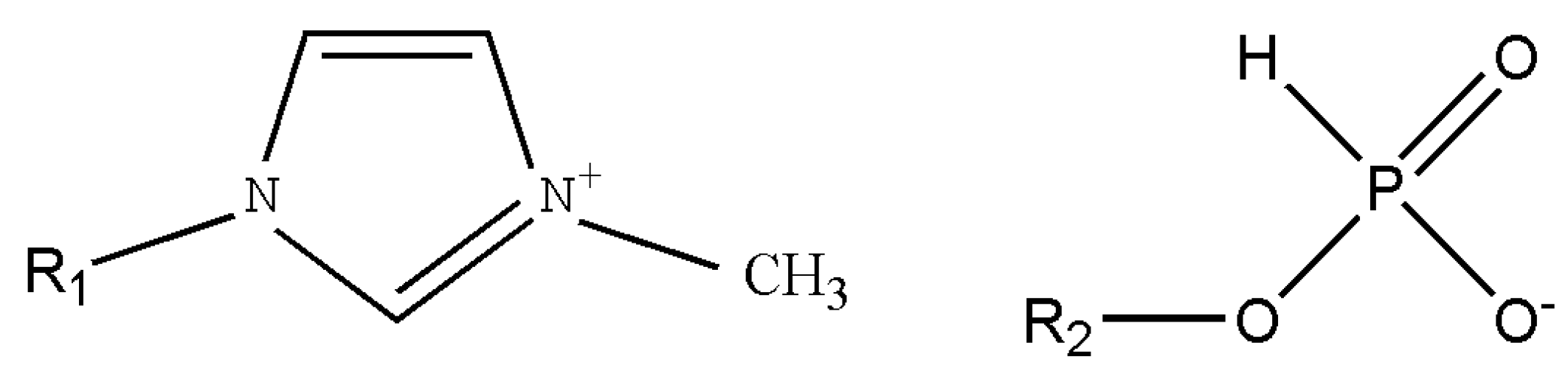

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Growth of Coatings on Mg AZ31B.
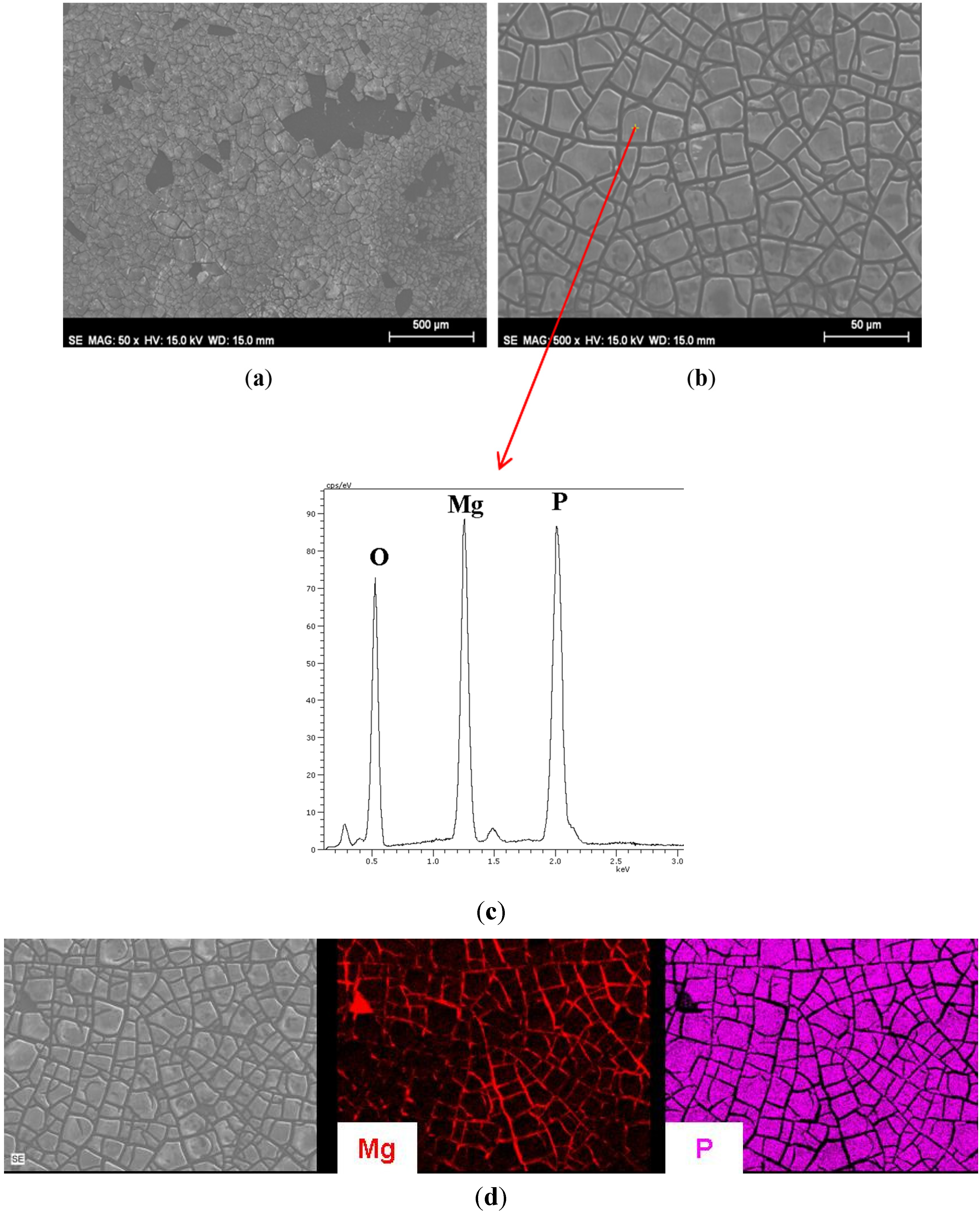
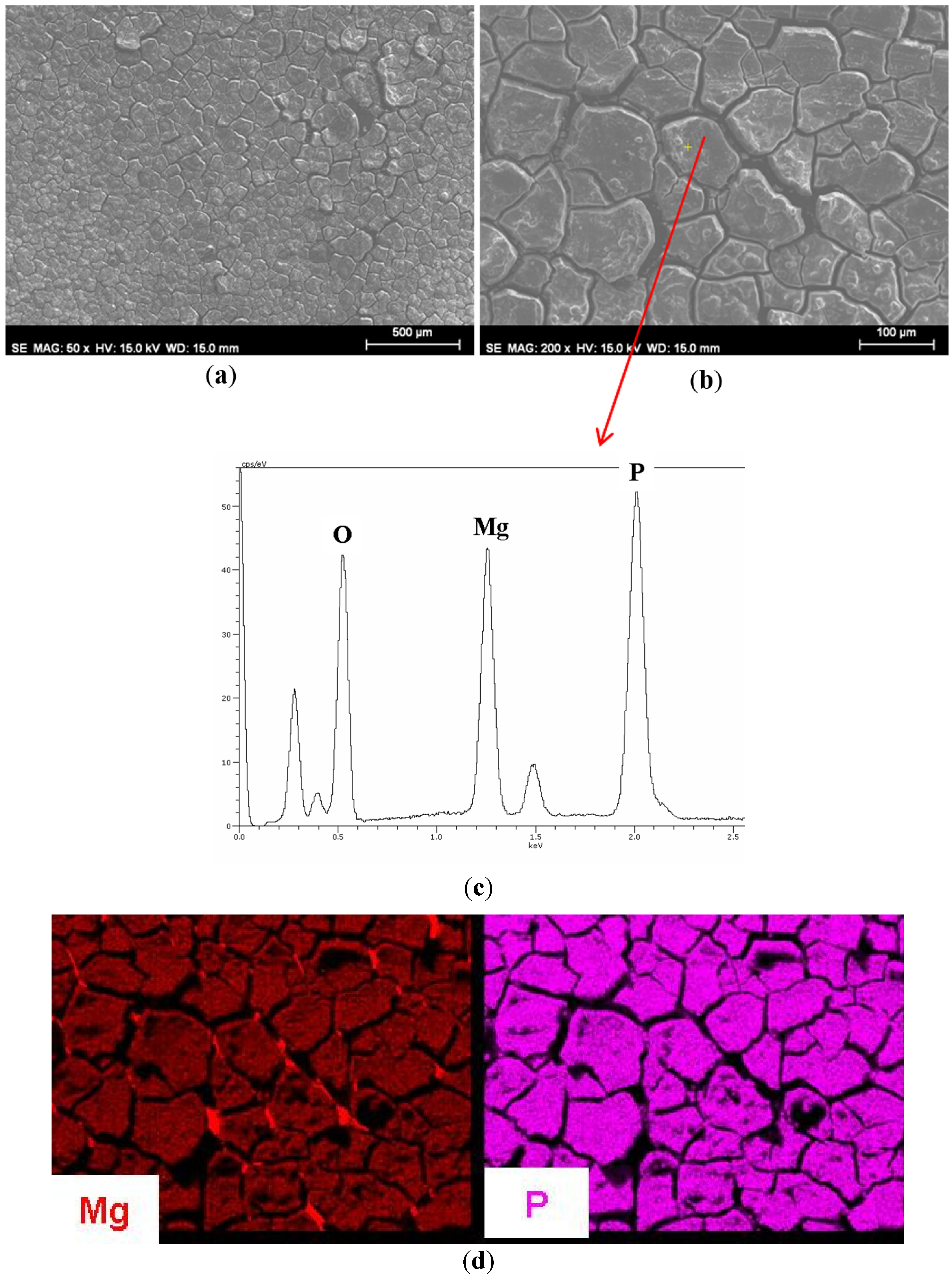
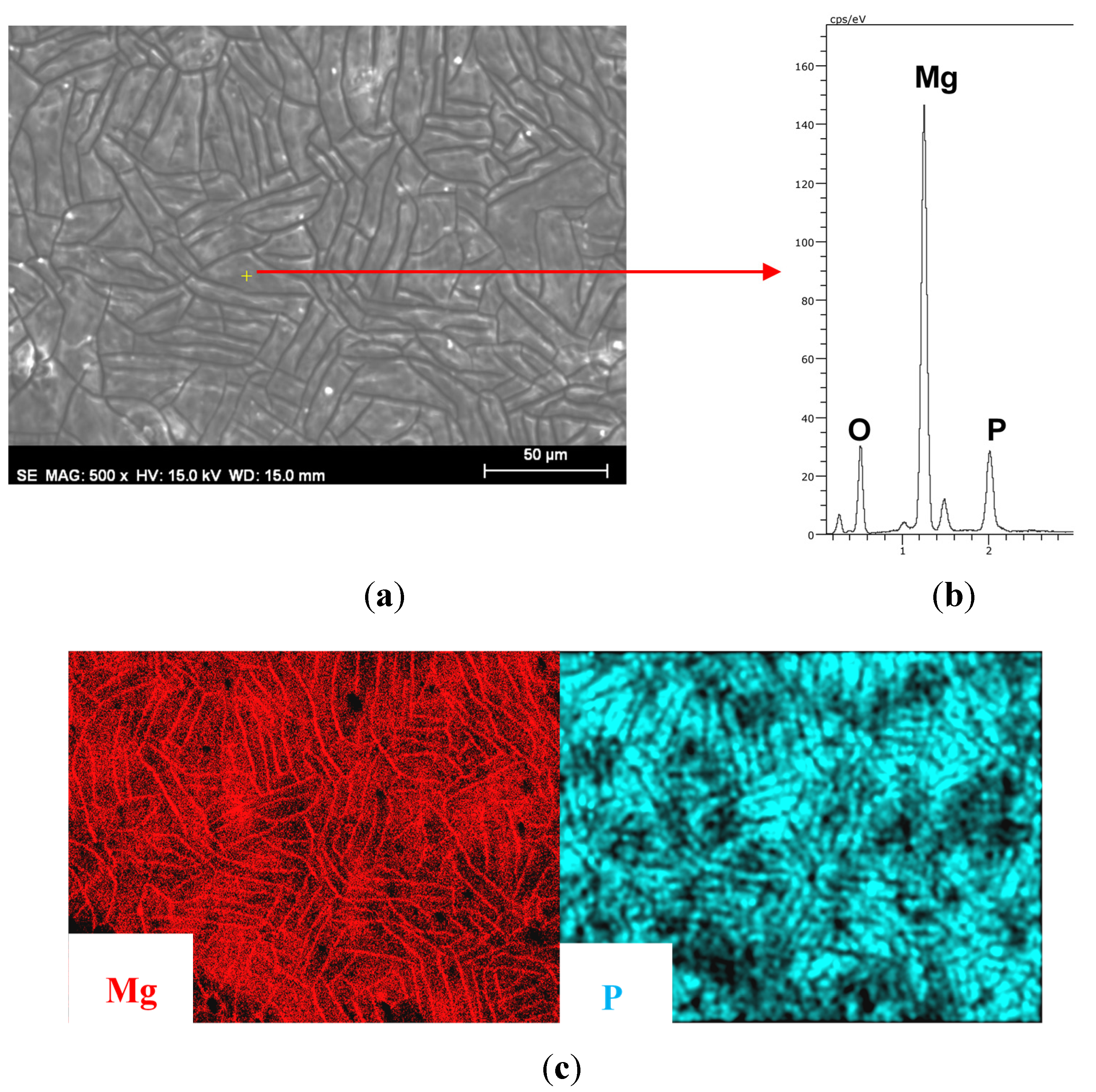
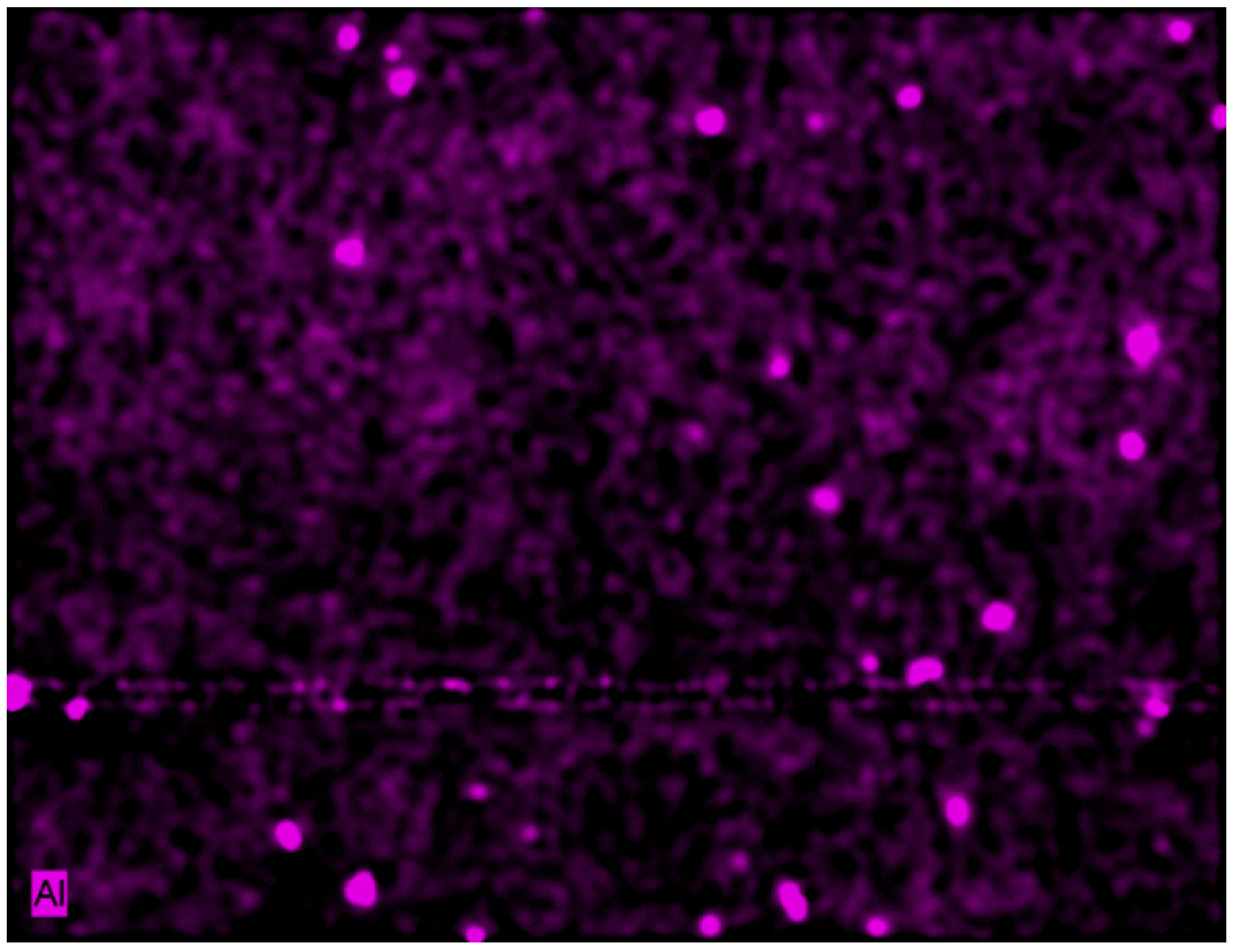
| Material | Ra (μm) (standard deviation) |
|---|---|
| AZ31B | 0.22 (0.03) |
| AZ31B + LEP102 | 0.34 (0.03) |
| AZ31B + LMP101 | 0.68 (0.08) |
| AZ31B + LMP102 | 2.10 (0.31) |
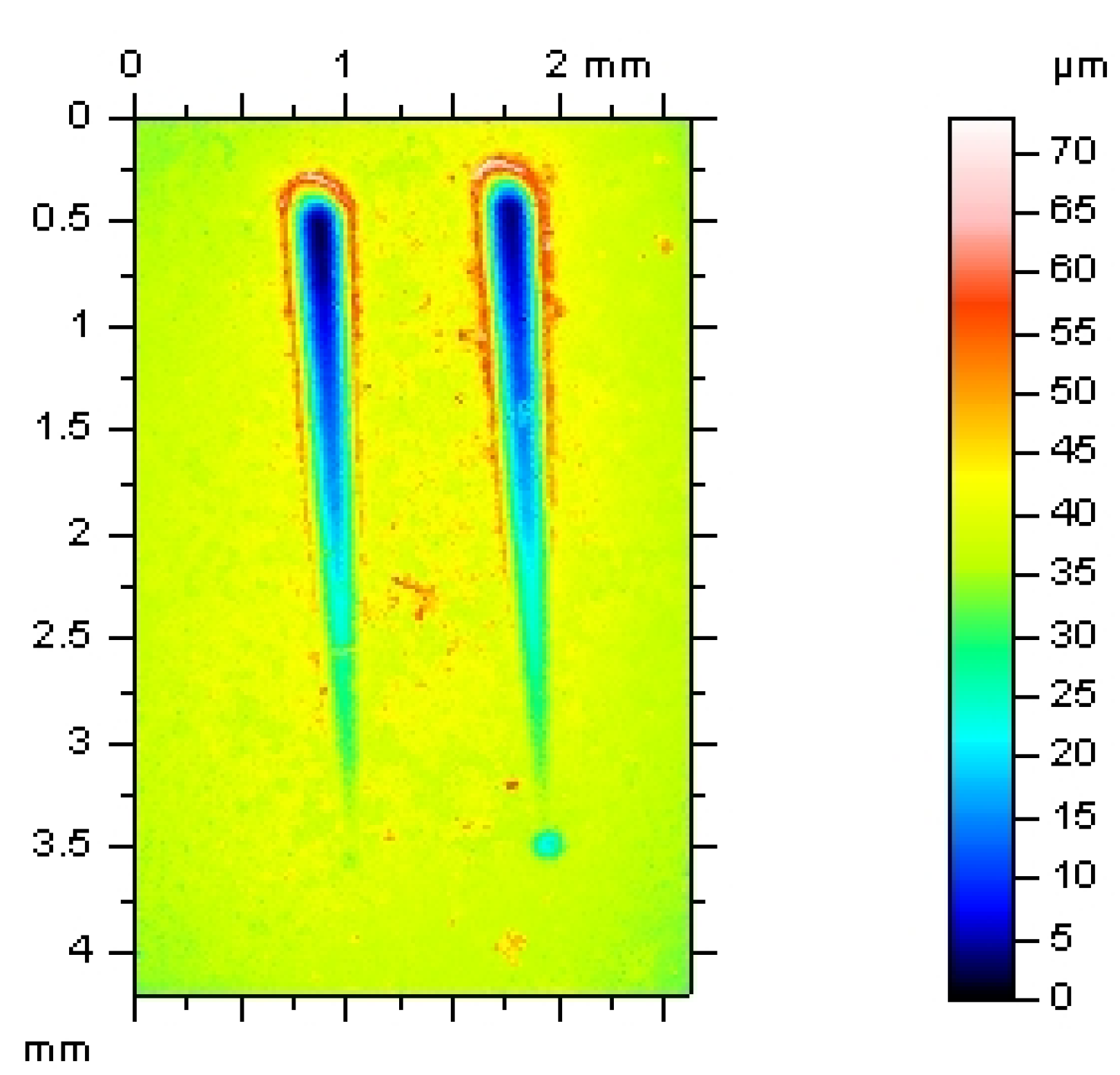
3.2. Abrasion Resistance of the New Coatings
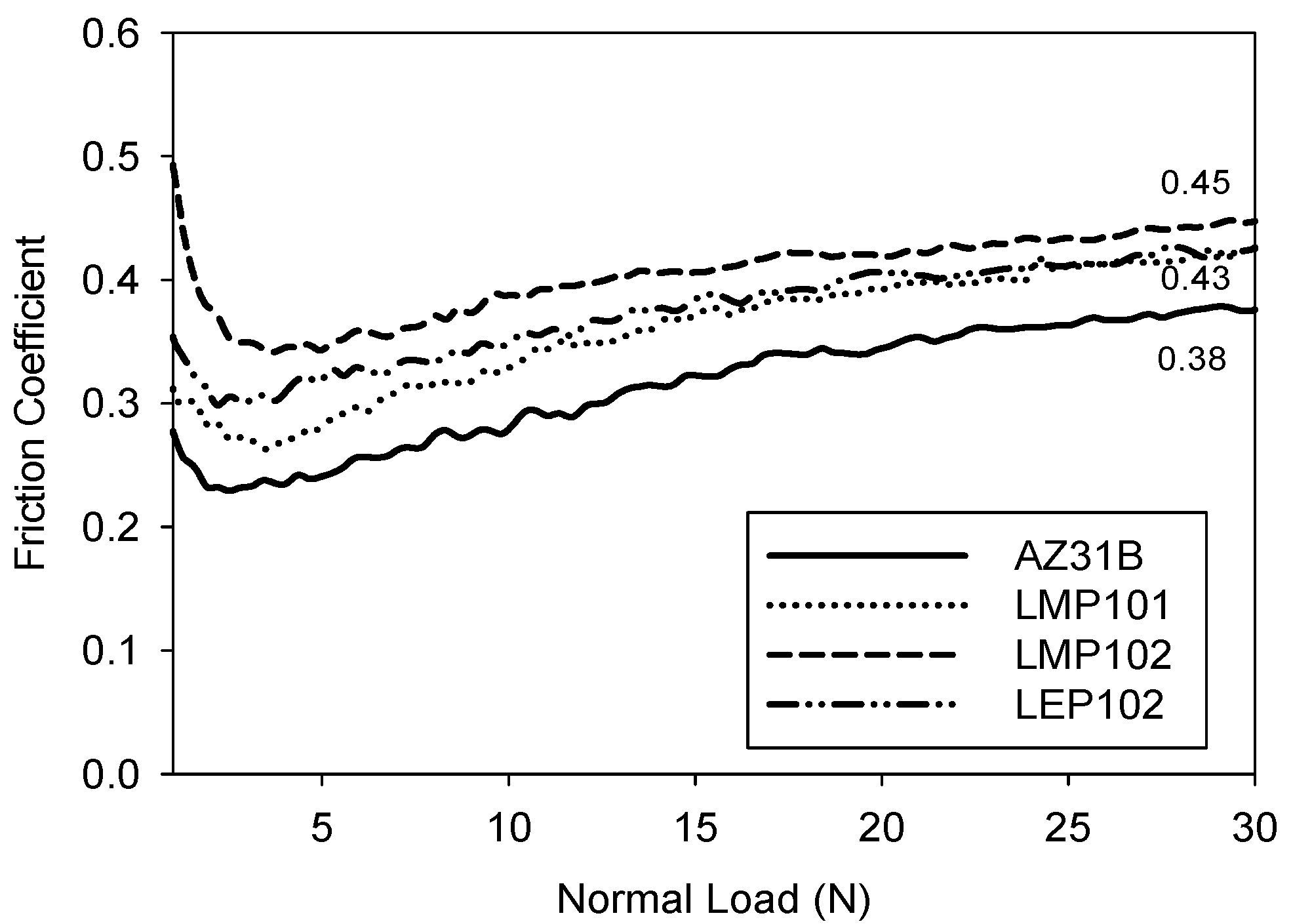
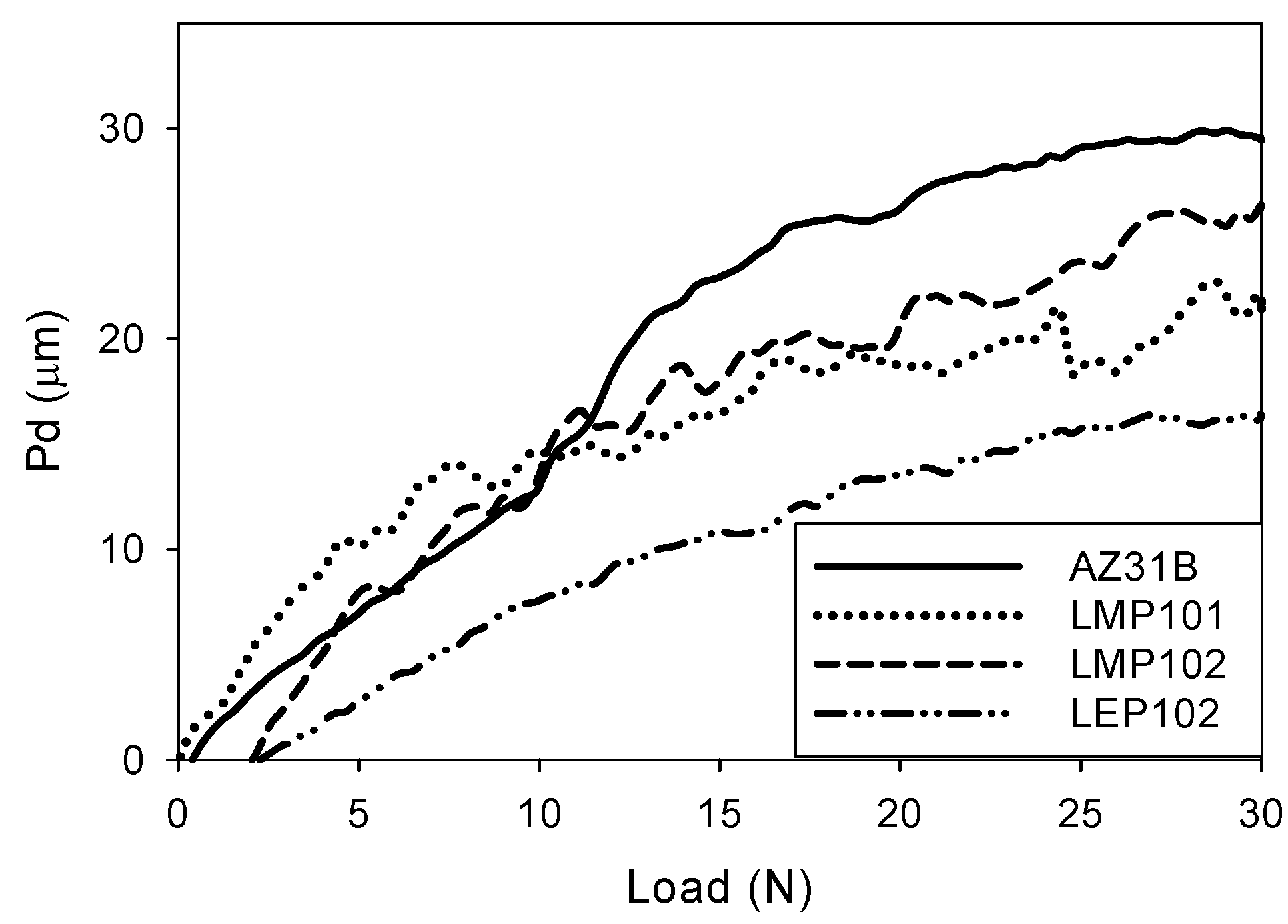
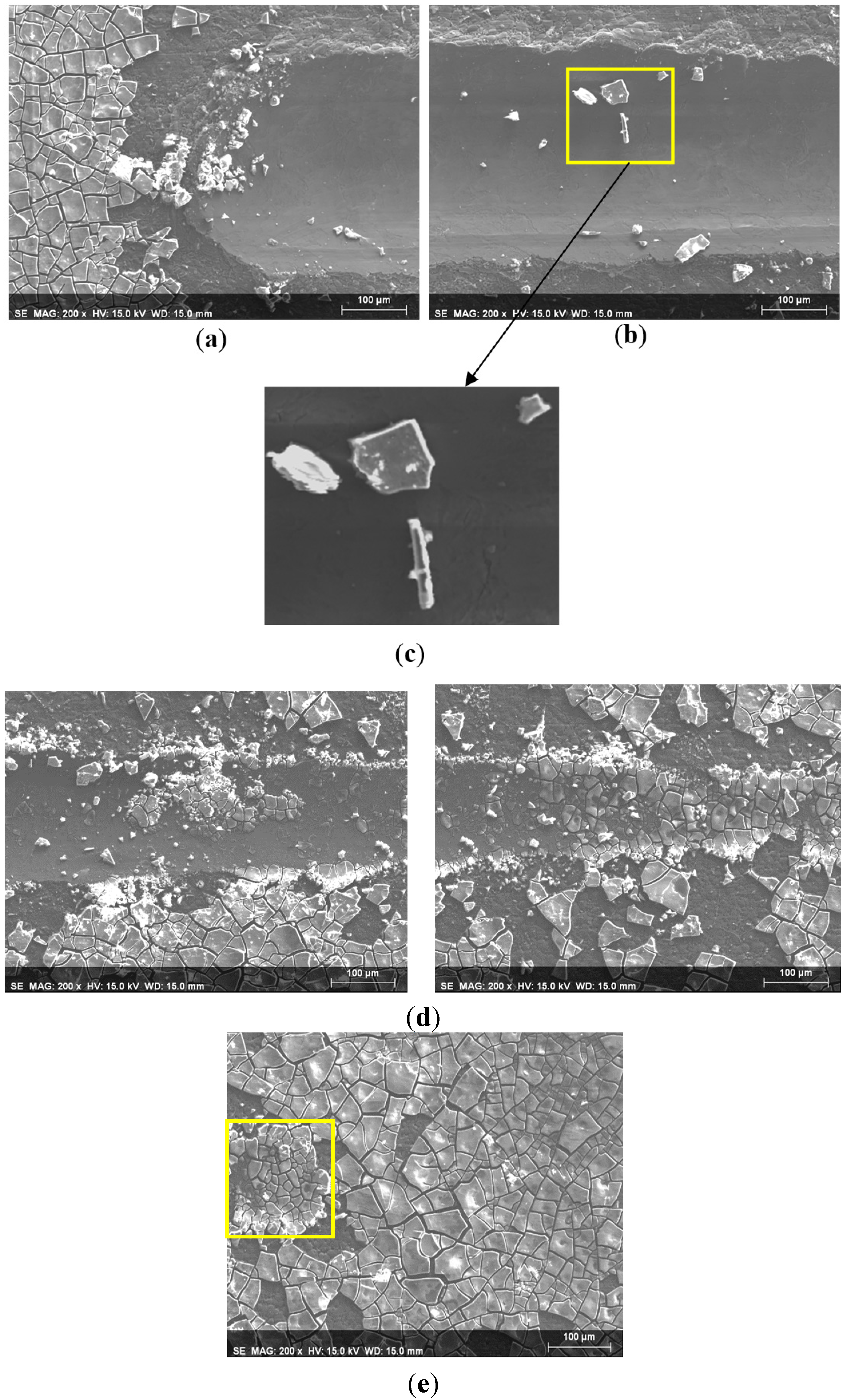
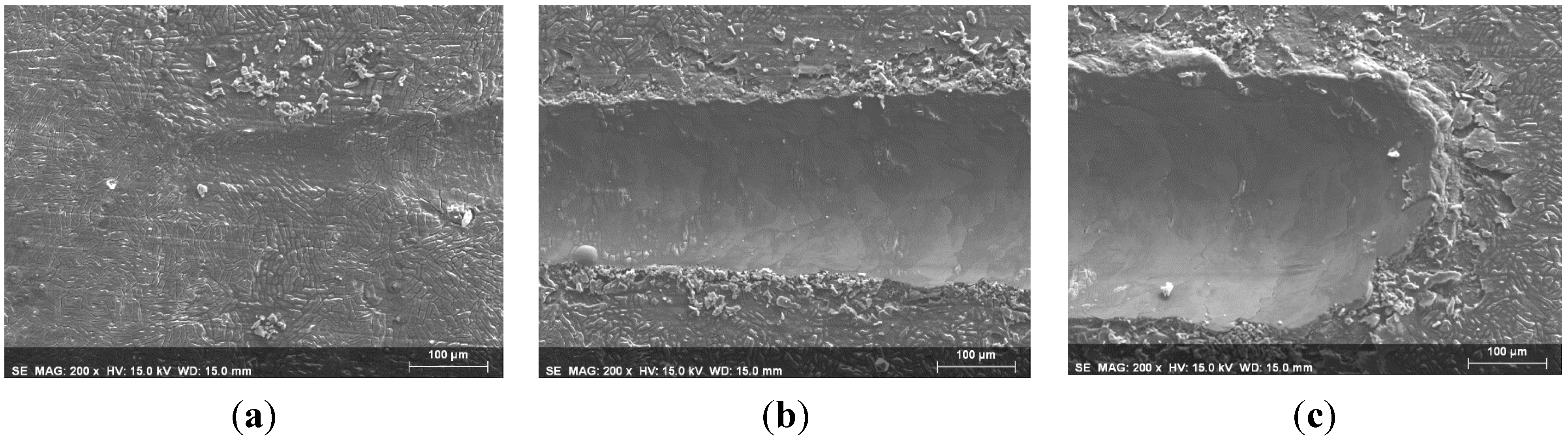
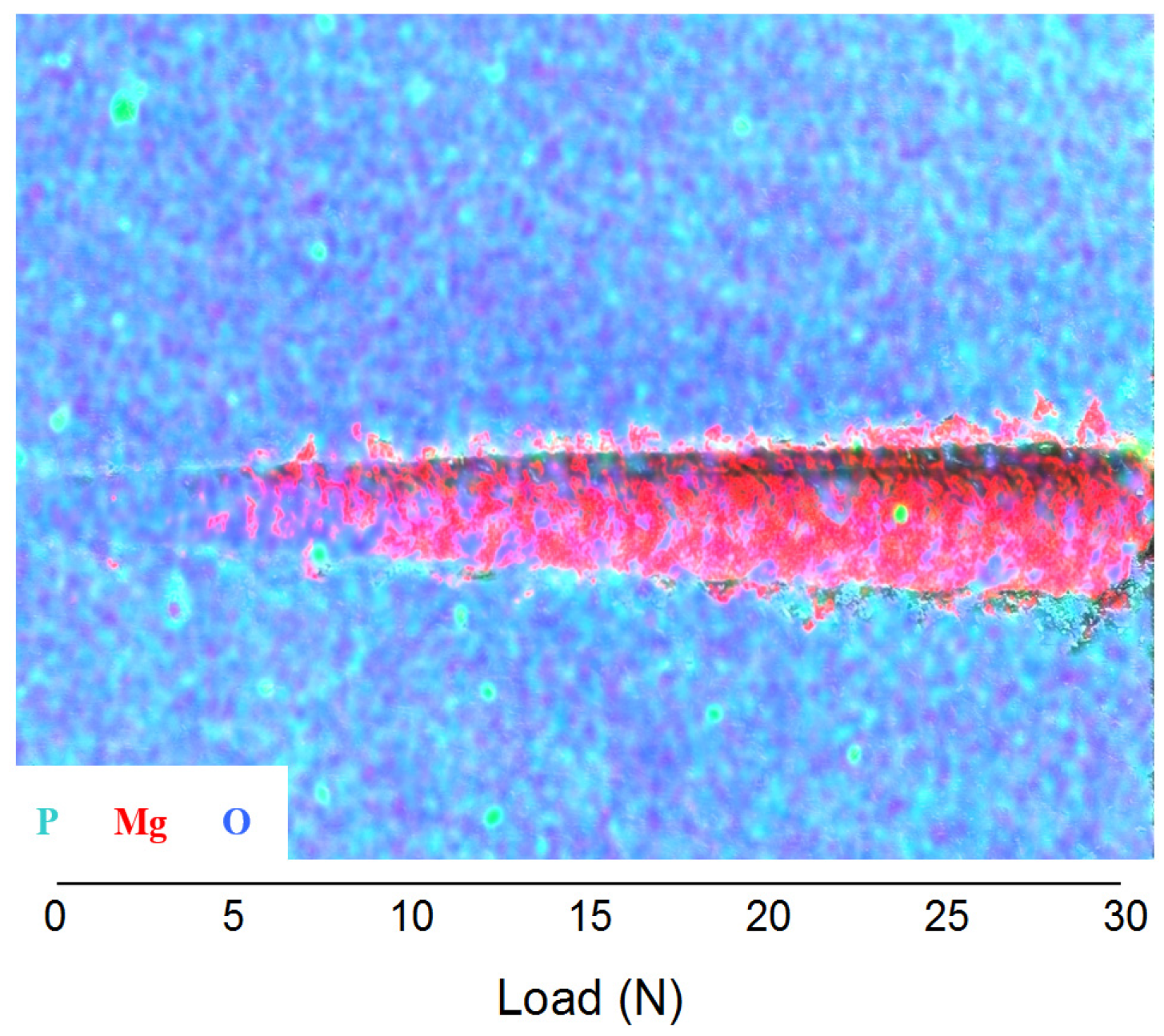
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khramov, A.N.; Balbyshev, V.N.; Kasten, L.S.; Mantz, R.A. Sol-gel coatings with phosphonate functionalities for surface modification of magnesium alloys. Thin Solid Films 2006, 514, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taltavull, C.; Lopez, A.J.; Torres, B.; Rams, J. Dry sliding wear behaviour of laser surface melting treated AM60B magnesium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 236, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I. Ionic liquids in tribology. Molecules 2009, 14, 2286–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Ionic liquid lubricants: Designed chemistry for engineering applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez, M.D.; Jiménez, A.E.; Sanes, J.; Carrion, F.J. Ionic liquids as advanced lubricant fluids. Molecules 2009, 14, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torimoto, T.; Tsuda, T.; Okazaki, K.; Kuwabata, S. New frontiers in materials science opened by ionic liquids. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1196–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacio, M.; Bhushan, B. A review of ionic liquids for green molecular lubrication in nanotechnology. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluecker, E.; Wasserscheid, P. Ionic liquids in mechanical engineering. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2011, 83, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, A.; Howlett, P.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. A review of ionic liquid lubricants. Lubricants 2013, 1, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Angell, C.A.; Ansari, Y.; Zhao, Z.F. Ionic liquids: Past, present and future. Faraday Discuss 2012, 154, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez, M.D. Introduction to the ionic liquids special issue. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, F. Alkyl imidazolium ionic liquids as friction reduction and anti-wear additive in polyurea grease for steel/steel contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Inada, T.; Sasaki, R.; Nanao, H. Tribo-chemistry of phosphonium-derived ionic liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium–steel contact. Part 3. Ti6Al4V lubricated with imidazolium ionic liquids with different alkyl chain lengths. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Hernández-Battez, A.; Blanco, D.; Viesca, J.L.; Fernández-González, A. Lubrication of TiN, CrN and DLC PVD coatings with 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium tris(pentafluoroethyl)trifluorophosphate. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Howlett, P.C.; Sun, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Transition in wear performance for ionic liquid lubricants under increasing load. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, N. Special issue on ionic liquids as lubricants. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Inada, T.; Okada, Y. Tribological properties of halogen-free ionic liquids. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia Pisarova, L.; Steudte, S.; Dörr, N.; Pittenauer, E.; Allmaier, G.; Stepnowski, P.; Stolte, S. Ionic liquid long-term stability assessment and its contribution to toxicity and biodegradation study of untreated and altered ionic liquids. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 903–922. [Google Scholar]
- Pejaković, V.; Kronberger, M.; Mahrova, M.; Vilas, M.; Tojo, E.; Kalin, M. Pyrrolidinium sulfate and ammonium sulfate ionic liquids as lubricant additives for steel/steel contact lubrication. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronberger, M.; Pejaković, V.; Gabler, C.; Kalin, M. How anion and cation species influence the tribology of a green lubricant based on ionic liquids. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, F.; Gabler, C.; Zare, P.; Mahrova, M.; Dörr, N.; Bayon, R.; Fernandez, X.; Binder, W.H.; Hernaiz, M.; Tojo, E.; et al. Dicationic ionic liquids as lubricants. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, A.C.F.; Dörr, N.; Pádua, A.A.H. Predicting thermophysical properties of ionic liquids as a function of temperature and pressure. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.D.; Jiménez, A.E. Surface interactions in lubrication of titanium, aluminium, and titanium–aluminium alloys with the ionic liquid [C2mim]Tf2N under increasing temperature. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Yagi, S.; Koyama, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Lubricity and corrosiveness of ionic liquids for steel-on-steel sliding contacts. Proc. Ins. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predel, T.; Pohrer, B.; Schluecker, E. Ionic liquids as alternative lubricants for special applications. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2010, 33, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa, T.; Jiménez, M.; Sanes, J.; Jimenez, A.E.; Iglesias, M.; Bermudez, M.D. Ultralow friction with a protic ionic liquid boundary film at the water-lubricated sapphire-stainless steel interface. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, A.E.; Bermudez, M.D. Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contact. Part 2: Friction, wear and surface interactions at high temperature. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 37, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, A.E.; Bermudez, M.D. Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contact. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 33, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Khemchandani, B.; Howlett, P.C.; Sun, J.Z.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Ionic liquids as antiwear additives in base oils: Influence of structure on miscibility and antiwear performance for steel on aluminium. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 11544–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Biddulph, S.M.; Howlett, P.C.; Sun, J.Z.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. A comparison of phosphorus and fluorine containing IL lubricants for steel on aluminum. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 8224–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, D.; Wang, H.Z.; Feng, D.P. Tribological performance of phosphate ionic liquids as lubricants for steel-on-aluminum contacts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2013, 227, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Hu, L.T.; Feng, D.P. Tribological behaviours of novel crown-type phosphate ionic liquids as lubricants for steel/aluminium contacts. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2013, 65, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Wang, H.; Feng, D. Tribological performance and mechanism of phosphate ionic liquids as additives in three base oils for steel-on-aluminum contact. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 55, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, C.; Carrión, F.J.; Bermúdez, M.D. Scratch resistance of new polystyrene nanocomposites with ionic liquid-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 52, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurín, N.; Sanes, J.; Bermudez, M.D. Effect of graphene and ionic liquid additives on the tribological performance of epoxy resin. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 56, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.C.; Xin, J.Y.; Miao, Q.Q.; Wang, J.J. Ionic liquid-based green processes for energy production. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7838–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashassi-Sorkhabi, H.; Es’haghi, M. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic media by [BMIm]Br ionic liquid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Hua, Y.X. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel by alkylimidazolium ionic liquids in hydrochloric acid. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Murulana, L.C.; Ebenso, E.E. Inhibitive effect of imidazolium based aprotic ionic liquids on mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid medium. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 4286–4295. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.A.M.; Messali, M.; Moussa, Z.; Alzahrani, A.Y.; Alamry, B.; Hammouti, S.N. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel by imidazolium and pyridinium cations ionic liquids in acidic environment. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 29, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, A.; Messali, M.; Zarrok, H.; Salghi, R.; Ali, A.A.; Hammouti, B.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Bentiss, F. Synthesis, characterization and comparative study of new functionalized imidazolium-based ionic liquids derivatives towards corrosion of C38 steel in molar hydrochloric acid. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 6998–7015. [Google Scholar]
- Likhanova, N.V.; Domínguez-Aguilar, M.A.; Olivares-Xometl, O.; Nava-Entzana, N.; Arce, E.; Dorantes, H. The effect of ionic liquids with imidazolium and pyridinium cations on the corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic environment. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Lucero, D.; Olivares-Xometl, O.; Martínez-Palou, R.; Likhanova, N.V.; Domínguez-Aguilar, M.A.; Garibay-Febles, V. Synthesis of selected vinylimidazolium ionic liquids and their effectiveness as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in aqueous sulfuric acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 7129–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhanova, N.V.; Olivares-Xometl, O.; Guzmán-Lucero, D.; Domínguez-Aguilar, M.A.; Nava, N.; Corrales-Luna, M.; Mendoza, M.C. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in acidic environment by imidazolium ionic liquids containing vinyl-hexafluorophosphate as anion. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 4514–4536. [Google Scholar]
- Tüken, T.; Demir, F.; Kicir, N.; Sigircik, G.; Erbil, M. Inhibition effect of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide against steel corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2012, 59, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barham, H.A.; Brahim, S.A.; Rozita, Y.; Mohamed, K.A. Carbon steel corrosion behaviour in aqueous carbonated solution of MEA/bmim DCA. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, F. [BMIM]BF4 ionic liquids as effective inhibitor for carbon steel in alkaline chloride solution. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 4268–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M.; Uznanska, J. The effect of ionic liquids on the corrosion inhibition of copper in acidic chloride solutions. Int. J. Corros. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; McKenzie, K.J. Application of ionic liquids to the electrodeposition of metals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 4265–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Abbott, A. Electrodeposition from Ionic Liquids; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Ryder, K.S. Electroplating using ionic liquids. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 2013, 43, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubac, Z.; Metikos-Hukovic, M.; Roncevic, I.S.; Petravic, M.; Peter, R. Functionalization of biodegradable magnesium alloy implants with alkylphosphonate self-assembled films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 2152–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, E.; De Rose, J.A.; Hoffmann, P.; Mathieu, H.J.; Bhushan, B.; Cichomski, M. Phosphonate self-assembled monolayers on aluminium surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, M.; Howlett, P.C.; Tan, S.K.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Birbilis, N. An ionic liquid surface treatment for corrosion protection of magnesium alloy AZ31. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, B52–B55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbilis, N.; Howlett, P.C.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Exploring corrosion protection of Mg via ionic liquid pretreatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4496–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, P.C.; Zhang, S.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. An investigation of a phosphinate-based ionic liquid for corrosion protection of magnesium alloy AZ31. Aus. J. Chem. 2007, 60, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, P.C.; Efthimiadis, J.; Hale, P.; van Riessen, G.A.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Characterization of the magnesium alloy AZ31 surface in the ionic liquid trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, C392–C398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, P.C.; Khoo, T.; Mooketsi, G.; Efthimiadis, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. The effect of potential bias on the formation of ionic liquid generated surface films on Mg alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Howlett, P.C.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Lin, J.; Forsyth, M. Synthesis and physical property characterisation of phosphonium ionic liquids based on P(O)2(OR)2- and P(O)2(R)2-anions with potential application for corrosion mitigation of magnesium alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiadis, J.; Neil, W.C.; Bunter, A.; Howlett, P.C.; Hinton, B.R.W.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Potentiostatic control of ionic liquid surface film formation on ZE41 magnesium alloy. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2010, 2, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, M.; Neil, W.C.; Howlett, P.C.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Hinton, B.R.W.; Rocher, N.; Kemp, T.F.; Smith, M.E. New insights into the fundamental chemical nature of ionic liquid film formation on magnesium alloy surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2009, 1, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.P.; Latham, J.A.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Howlett, P.C.; Forsyth, M. A review of ionic liquid surface film formation on Mg and its alloys for improved corrosion performance. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 110, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsentriecy, H.H.; Luo, H.M.; Meyer, H.M.; Grado, L.L.; Qu, J. Effects of pre-treatment and process temperature of a conversion coating produced by an aprotic ammonium-phosphate ionic liquid on magnesium corrosion protection. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 123, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Sanes, J.; Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Surface interactions, corrosion processes and lubricating performance of protic and aprotic ionic liquids with OFHC copper. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Jiménez, A.E.; Martínez-Nicolás, G.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M.D. Abrasion resistance of magnesium alloys with surface films generated from phosphonate imidazolium ionic liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinosa, T.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M.-D. Halogen-Free Phosphonate Ionic Liquids as Precursors of Abrasion Resistant Surface Layers on AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. Coatings 2015, 5, 39-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings5010039
Espinosa T, Sanes J, Bermúdez M-D. Halogen-Free Phosphonate Ionic Liquids as Precursors of Abrasion Resistant Surface Layers on AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. Coatings. 2015; 5(1):39-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings5010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinosa, Tulia, José Sanes, and María-Dolores Bermúdez. 2015. "Halogen-Free Phosphonate Ionic Liquids as Precursors of Abrasion Resistant Surface Layers on AZ31B Magnesium Alloy" Coatings 5, no. 1: 39-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings5010039
APA StyleEspinosa, T., Sanes, J., & Bermúdez, M.-D. (2015). Halogen-Free Phosphonate Ionic Liquids as Precursors of Abrasion Resistant Surface Layers on AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. Coatings, 5(1), 39-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings5010039






