Effect of Plasma Cloud Shielding on Heat and Mass Transfer Mechanism During Laser Cladding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Equations and Parameter Settings During Laser Cladding
2.1. The Control Equations of Temperature Field
2.1.1. Without Considering the Shielding Effect of the Plasma Cloud
2.1.2. Considering the Shielding Effect of the Plasma Cloud
2.2. Flow Field Equations
2.3. Heat and Mass Transfer Equations
2.4. Boundary Conditions and Source Terms
3. Numerical Modeling and Material Selection
4. Analysis of Numerical Simulation Results
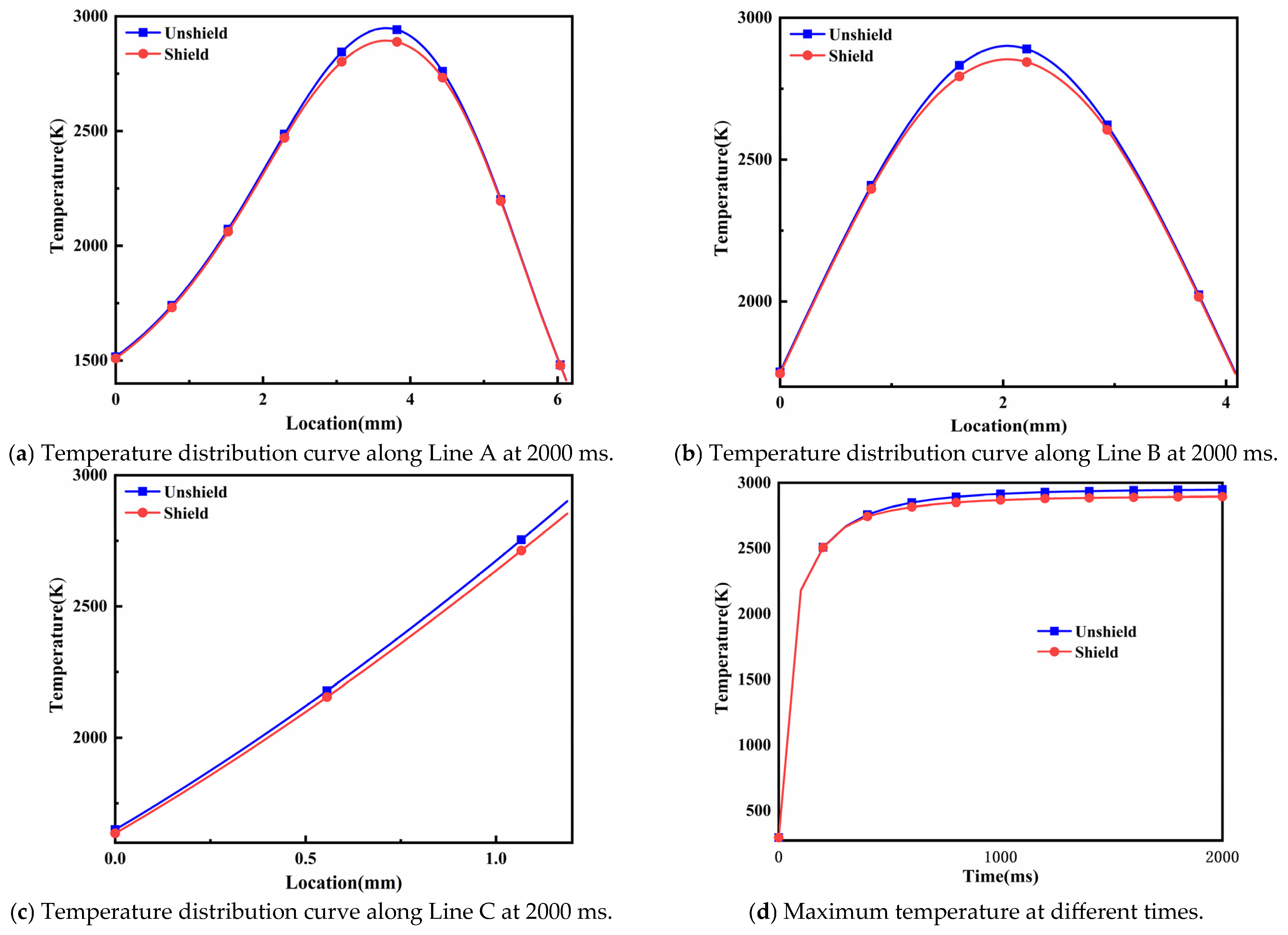
4.1. Temperature Field Results
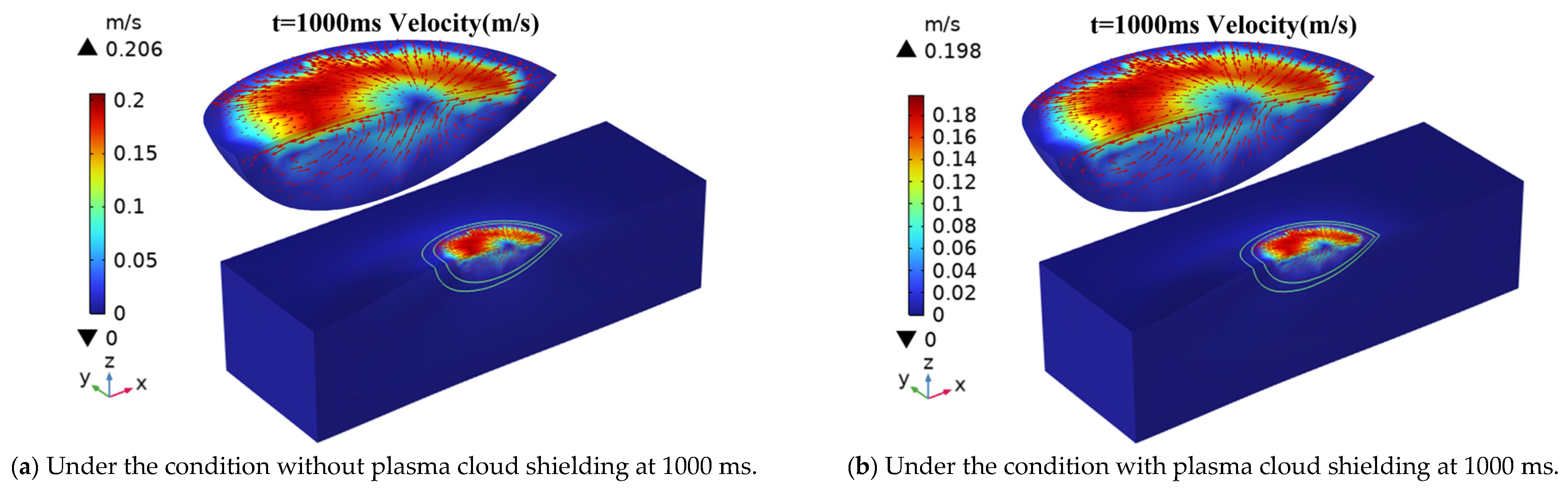
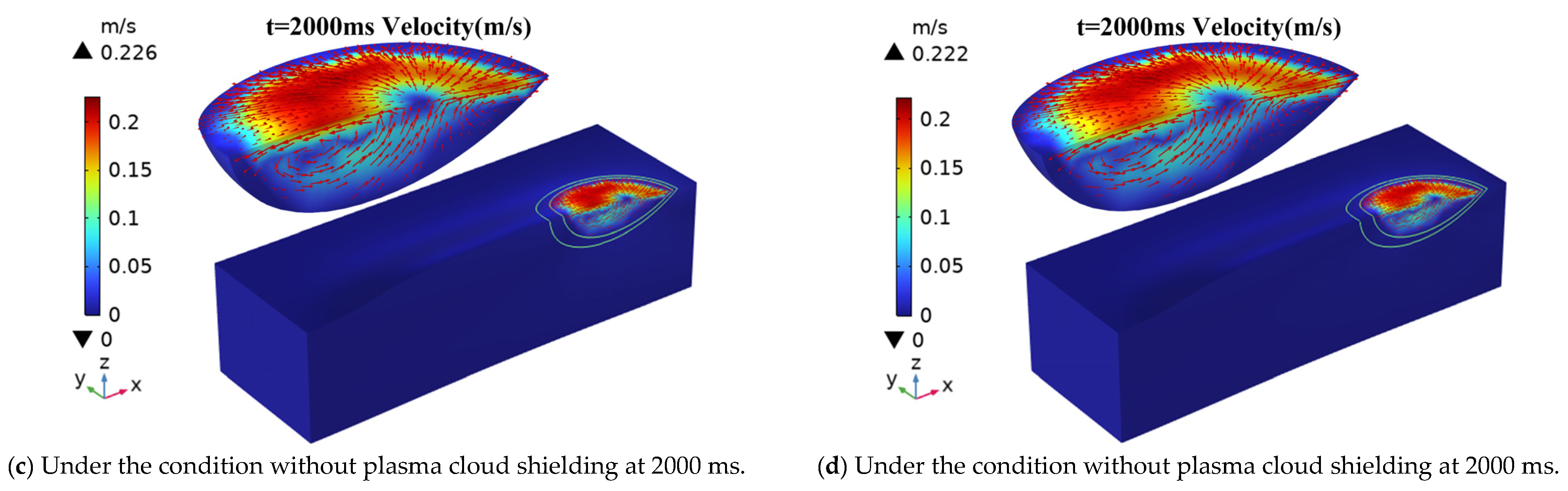
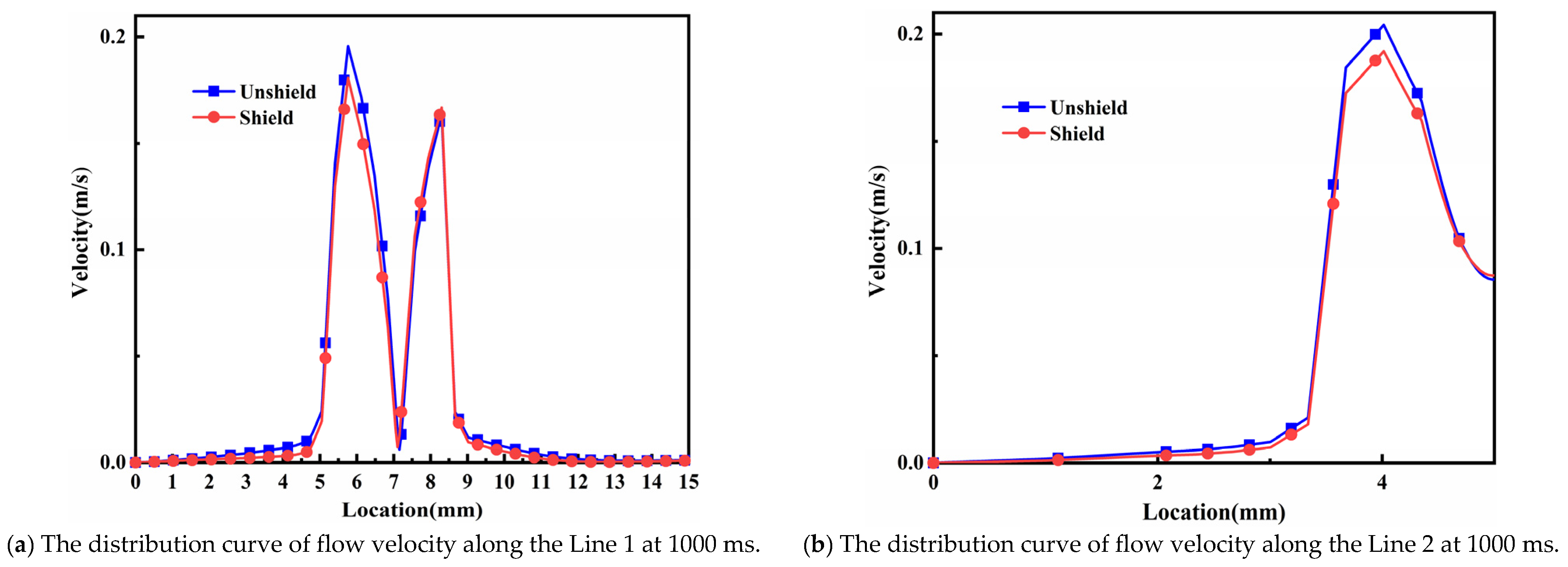
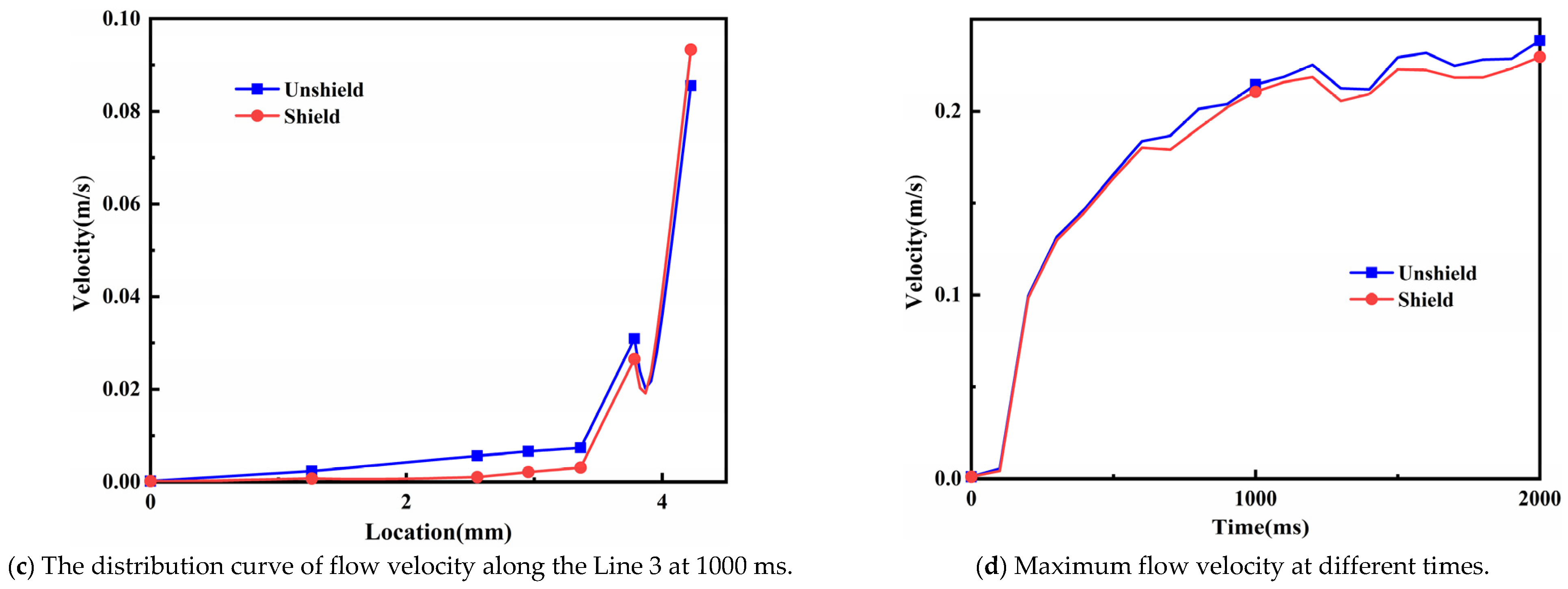
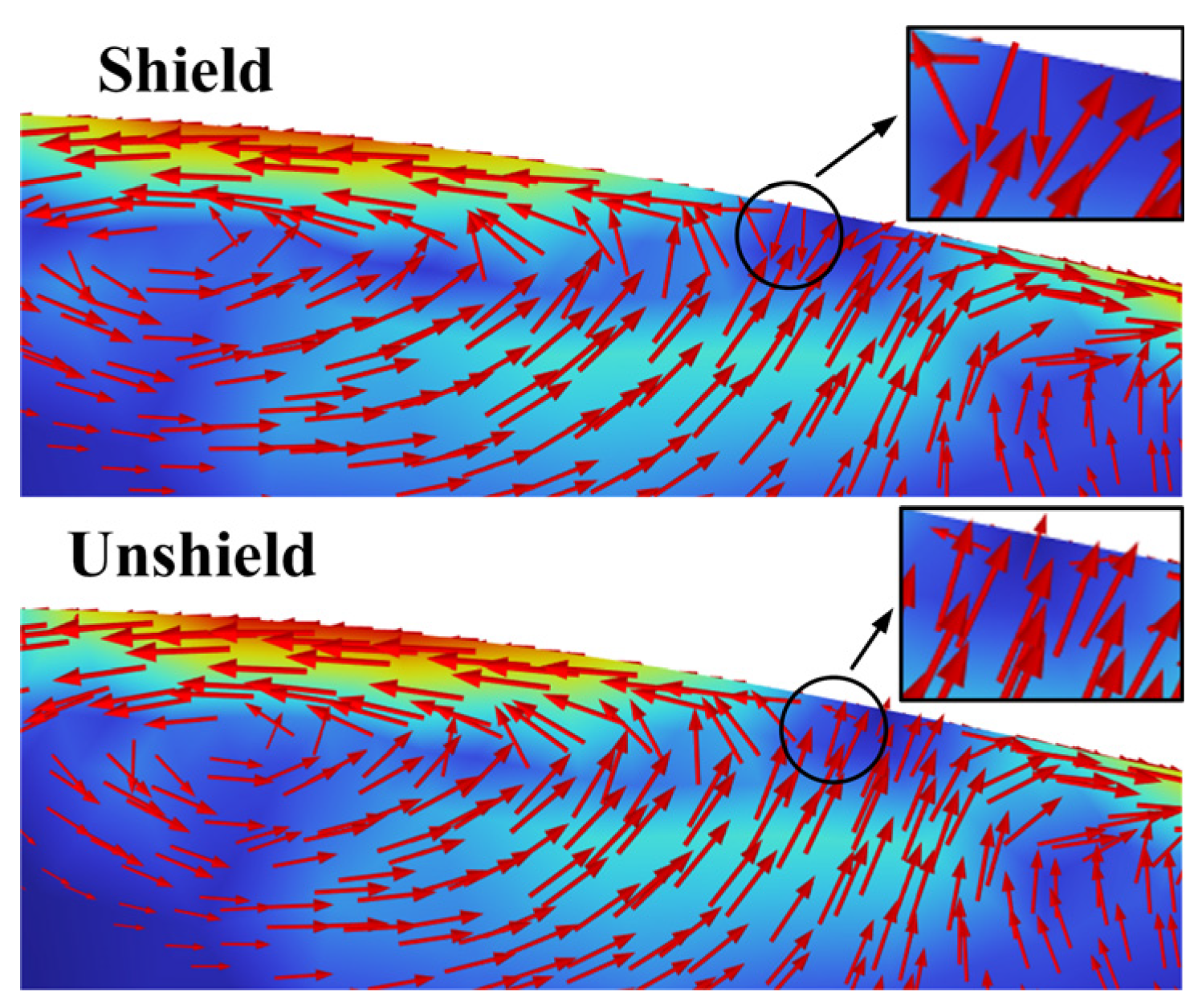
4.2. Analysis of Flow Field Results
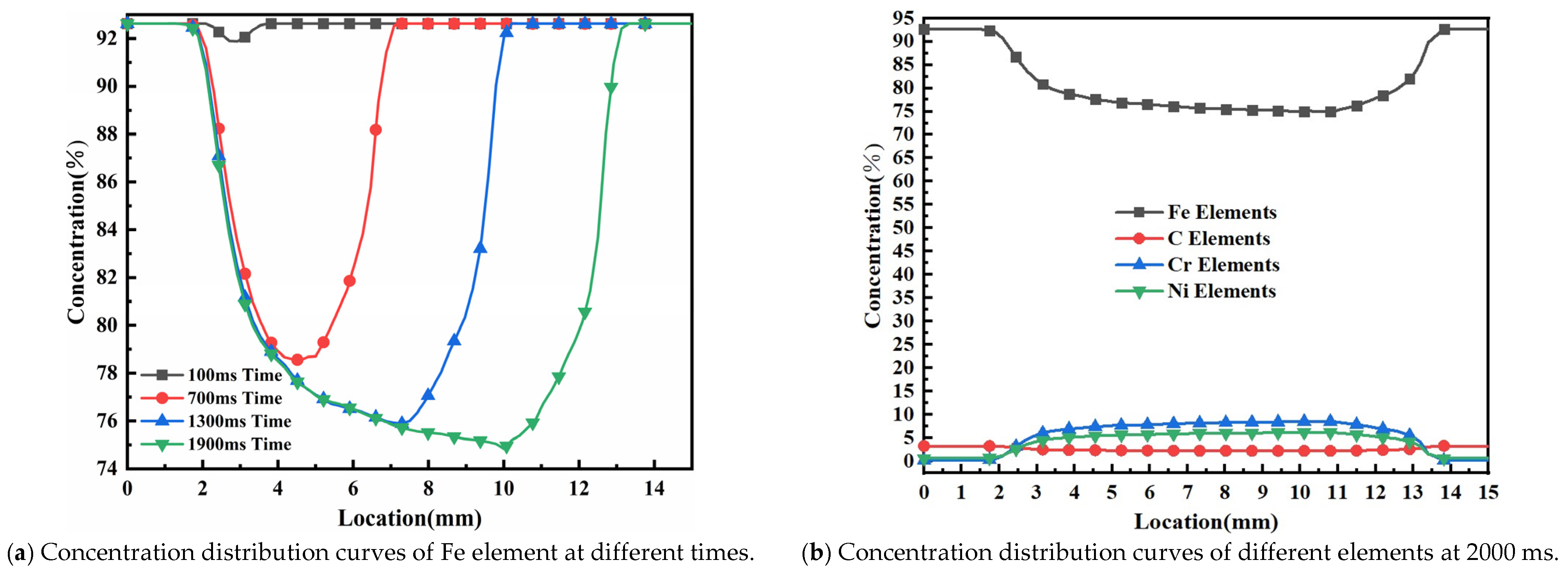
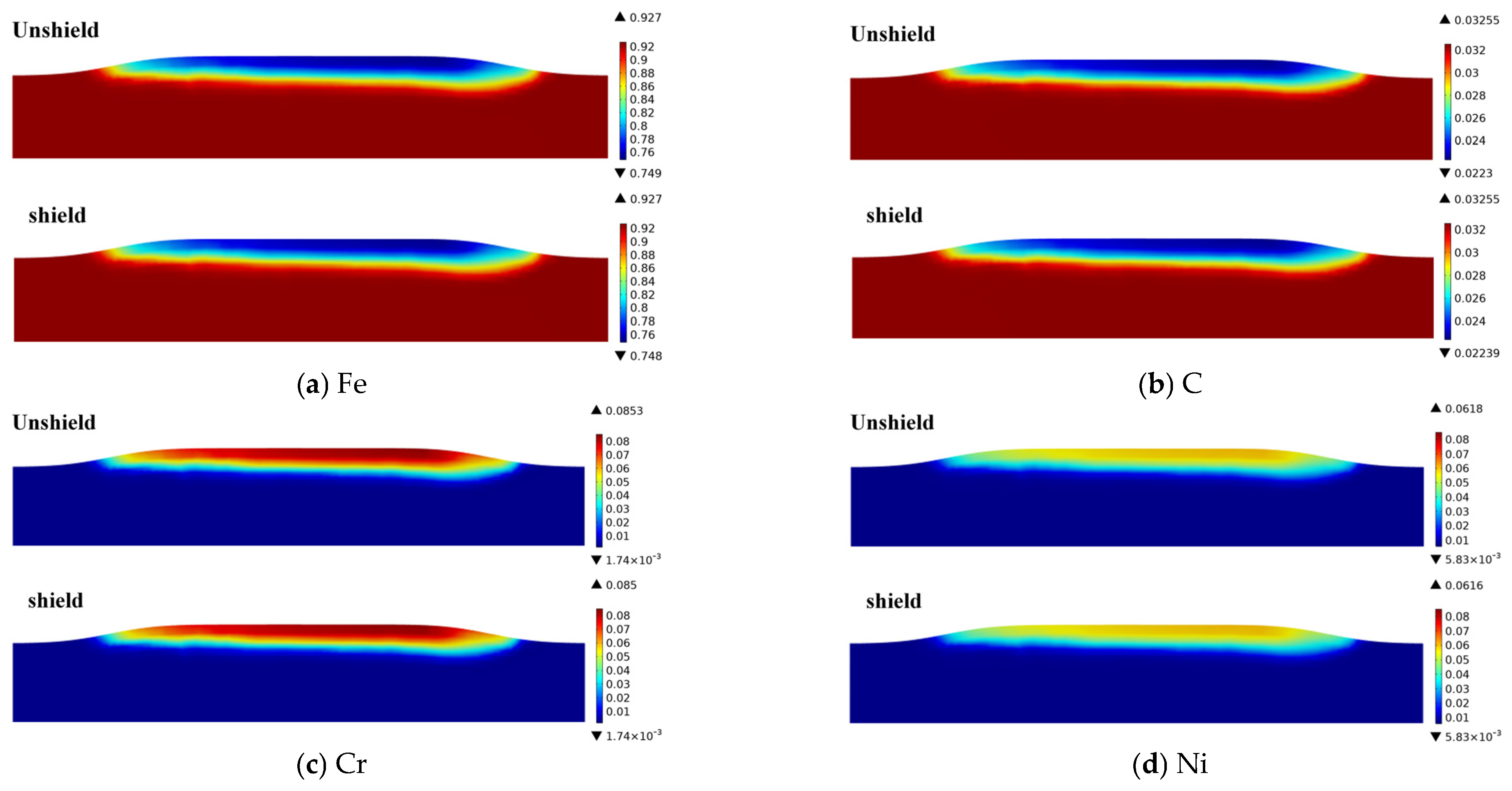
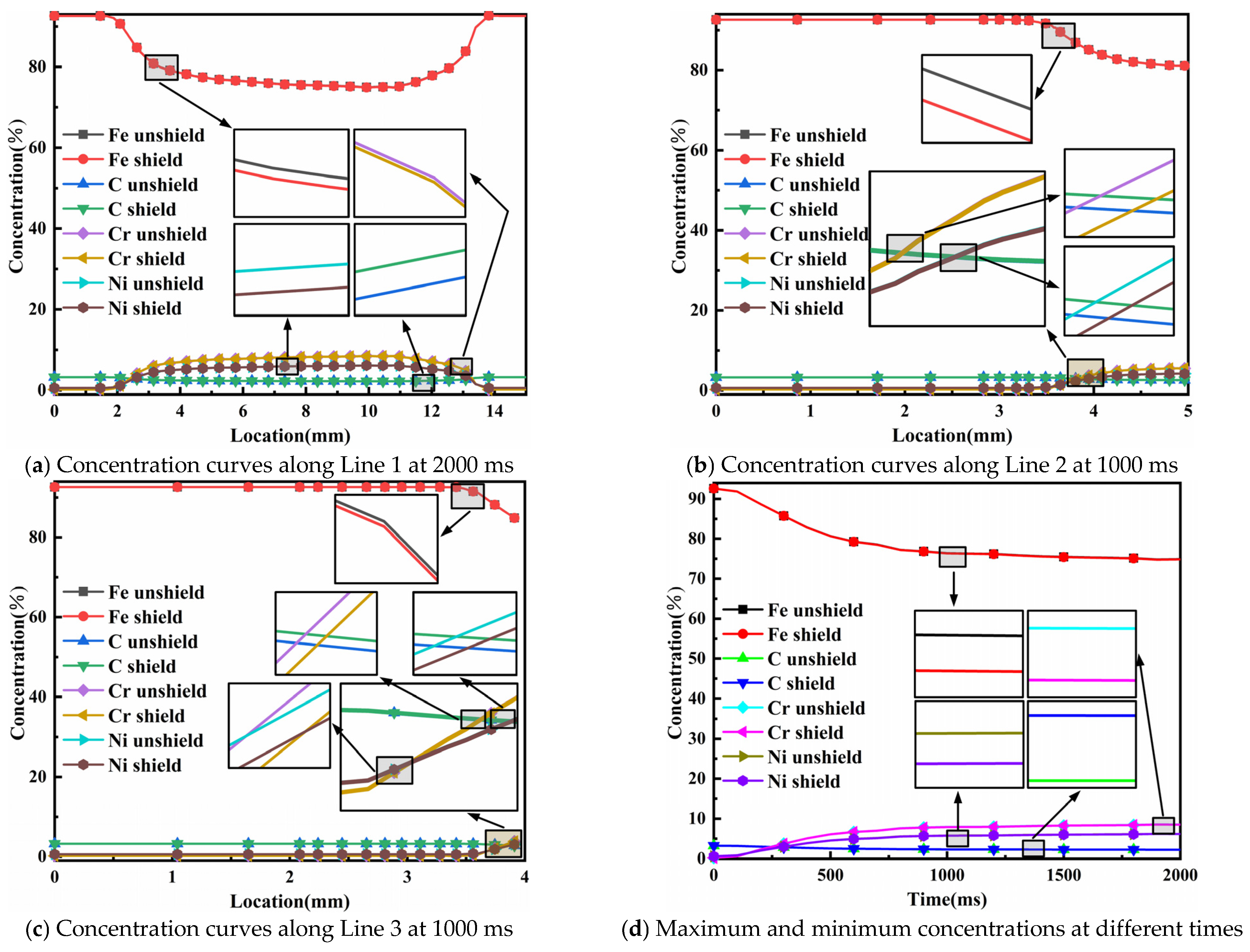
4.3. Analysis of Concentration Field Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Yu, Z.; Du, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhang, T.; Bai, Y.; Chen, S. Laser Cladding of High-Temperature Alloy: Research Status and Development. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 27, 2402956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Feng, M.; Chen, C.; Lian, G. Microstructure evolution, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of CoCrCu0.5FeNiSix high-entropy alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 5539–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.; Cao, L.; Zhao, D.; Long, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhong, J.; Bi, G. Study on the microstructure and wear resistance of laser clad martensitic stainless steel 420 with different content of TiC. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 46, 112615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Liu, Y.; Ni, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Effects of laser energy density on microstructure, texture and tribological property of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 61, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamidullin, B.; Tsivilskiy, I.; Gorunov, A.; Gilmutdinov, A. Modeling of the effect of powder parameters on laser cladding using coaxial nozzle. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 364, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Feng, A.; Zhao, P.; Pan, X.; Feng, H. Effect of Energy Density on the Microstructure and Wear Resistance of NickelBased WC Coatings by Laser Cladding of Preset Zr702 Alloy Plates. Coatings 2023, 13, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Wu, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X. Femtosecond Laser Ablation of Metal Models Based on Biphasic Delay Model. Chin. J. Phys. 2019, 68, 57901. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, M.; Han, X. Study on the influence of shielding effect for plasma cloud on multi-field coupling mechanism during laser cladding. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2025, 239, 1953–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Feng, G.Y.; Jing, S.; Han, J.H.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, K. Damage characteristics of laser plasma shock wave on rear surface of fused silica glass. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 085202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Li, X.; Rui, M.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H. Research on the Impact of Plasma Shock Wave Effect of Femtosecond Laser Abrasion on Surface Gear. Appl. Laser 2022, 42, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, X.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, G.; Rui, M. Research on the Effect of Plasma Shock Wave on the Morphology of Femtosecond Laser Abraded Gear. Appl. Laser 2023, 43, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S. Simulation and Process Parameter Optimization Research on Laser Cleaning of 2219 Aluminum Alloy Coatings. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China, 2022; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Han, X. Influencing mechanism of the active elements on the surface tension of the laser cladding molten pool and the determination of the critical concentration. J. Laser Appl. 2025, 37, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Han, X. Study on the macro-mesoscopic cross-scale influencing mechanism of the active element S on the solidification behavior during laser cladding. Appl. Phys. A 2025, 131, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marla, D.; Bhandarkar, U.V.; Joshi, S.S. A model of laser ablation with temperature-dependent material properties, vaporization, phase explosion and plasma shielding. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 116, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Narayan, J. Pulsed-laser evaporation technique for deposition of thin films: Physics and theoretical model. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F. Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Garrelie, F.; Aubreton, J.; Catherinot, A. Monte Carlo simulation of the laser-induced plasma plume expansion under vacuum: Comparison with experiments. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 5075–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Han, X. Optimization of pulse laser cladding process parameters and analysis of heat and mass transfer and phase transformation based on GA-BP neural network. Appl. Phys. A 2025, 131, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, C.; Hao, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, L. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation on three-dimensional modelling of single-track geometry and temperature evolution by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 129, 106287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennon, W.D.; Incropera, F.P. A continuum model for momentum, heat and species transport in binary solid-liquid phase change systems—I. Model formulation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1987, 30, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Yu, G.; He, X.; Li, S. Numerical simulation of thermal behavior and multicomponent mass transfer in direct laser deposition of Co-base alloy on steel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 104, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, M.; Han, X.; Li, S.; Feng, L. Study on the mechanism of heat and mass transfer behavior during multiple passes and multiple layers pulsed Laser cladding regarding the overlap ratio. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2024, 14644207251346735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Han, X. Quantitative evaluation method for the impact parameters during the process of pulsed laser cladding of Fe60. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Liu, D.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, W. Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding Fe60 Alloy Layer on Stainless Steel. Heat Treat. 2017, 32, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Toyserkani, E.; Khajepour, A.; Corbin, S. 3-D finite element modeling of laser cladding by powder injection: Effects of laser pulse shaping on the process. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2004, 41, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z. Research on Thermal and Mass Transport in Laser Additive Manufacturing of High-Temperature Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chemin, A.; Fawaz, M.W.; Amans, D. Investigation of the blast pressure following laser ablation at a solid–fluid interface using shock waves dynamics in air and in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 574, 151592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, Y.; Feng, C. Experimental Study on the Degree of Metal Material Damage Based on Acoustic Emission Signals. Equip. Manag. Maint. 2021, 25, 133–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. Research on the Electron Beam Evaporation Characteristics of Metals and Alloys. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Nonferrous Metals Research Institute, Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 12–42. [Google Scholar]
- Alder, B.J.; Wainwright, T.E. Phase transition for a hard sphere system. J. Chem. Phys. 1957, 27, 1208–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

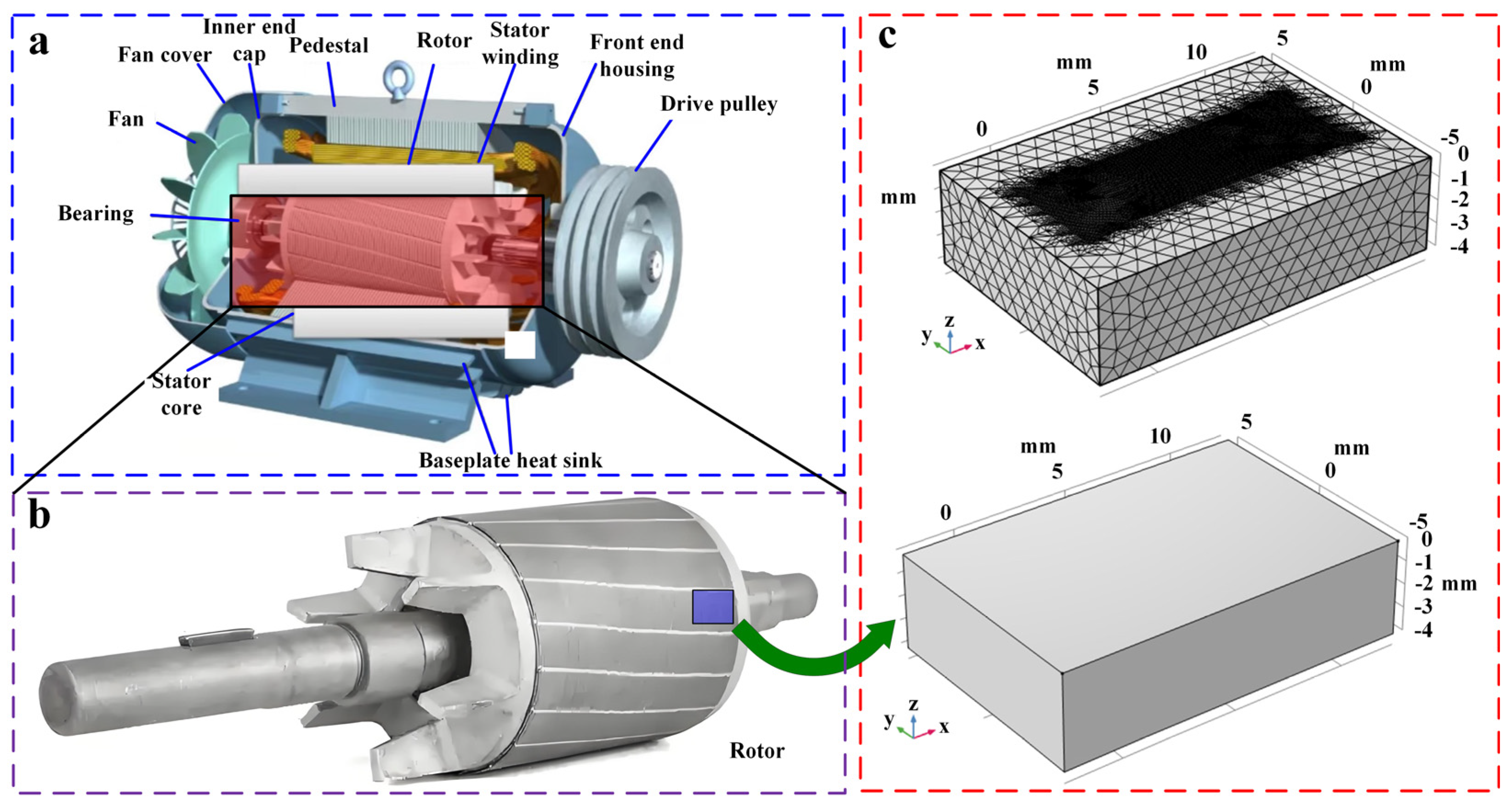
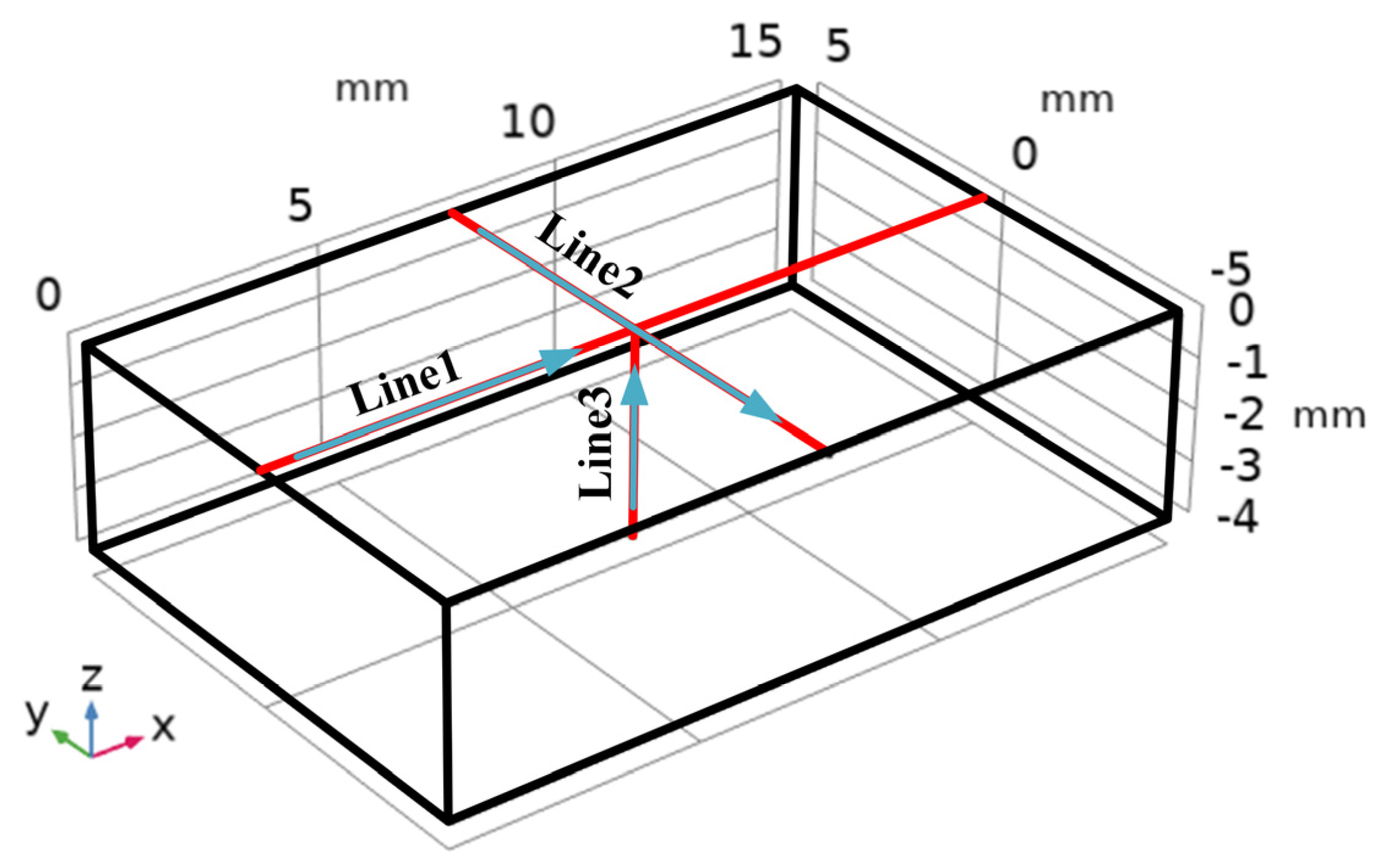
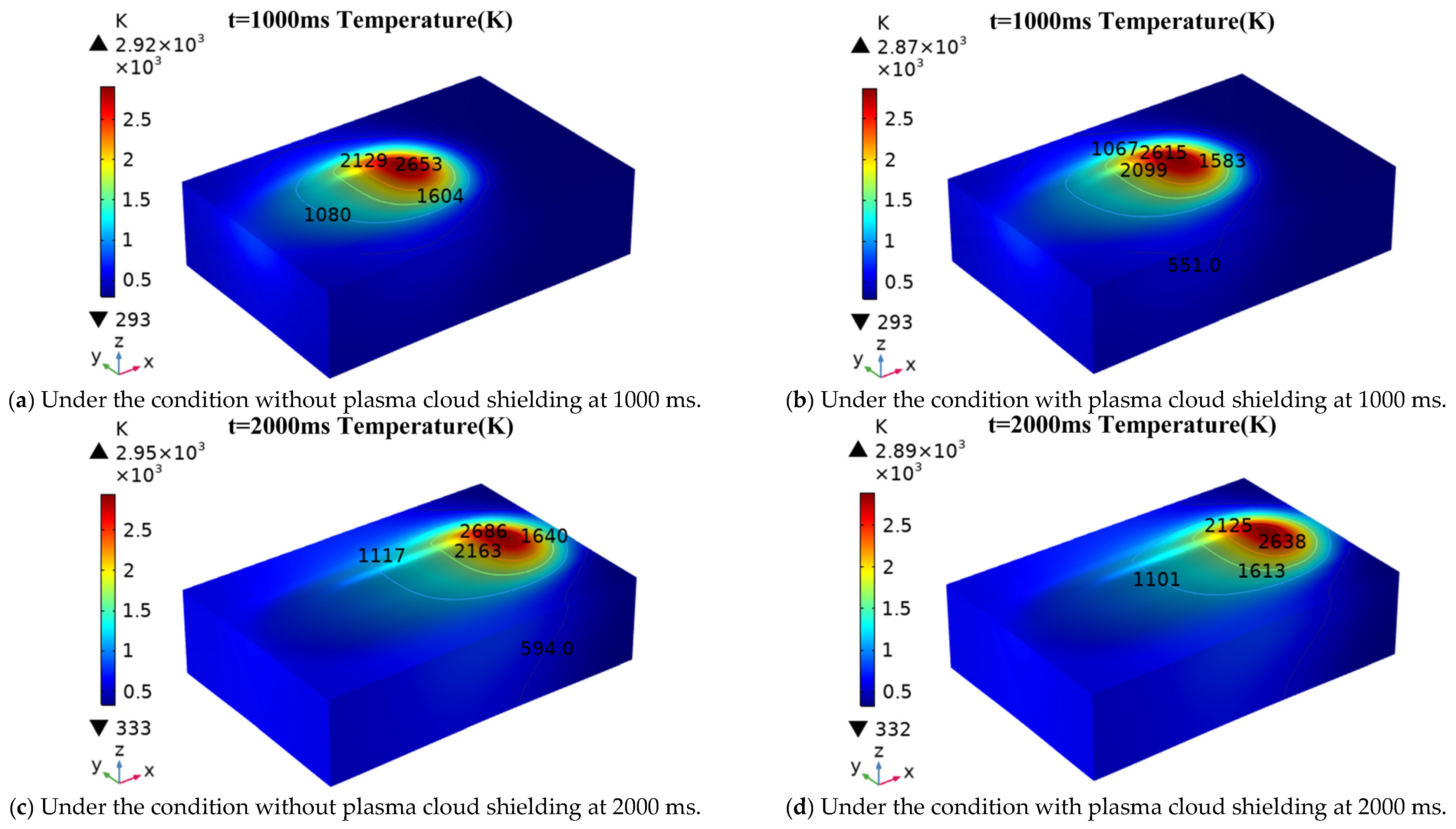
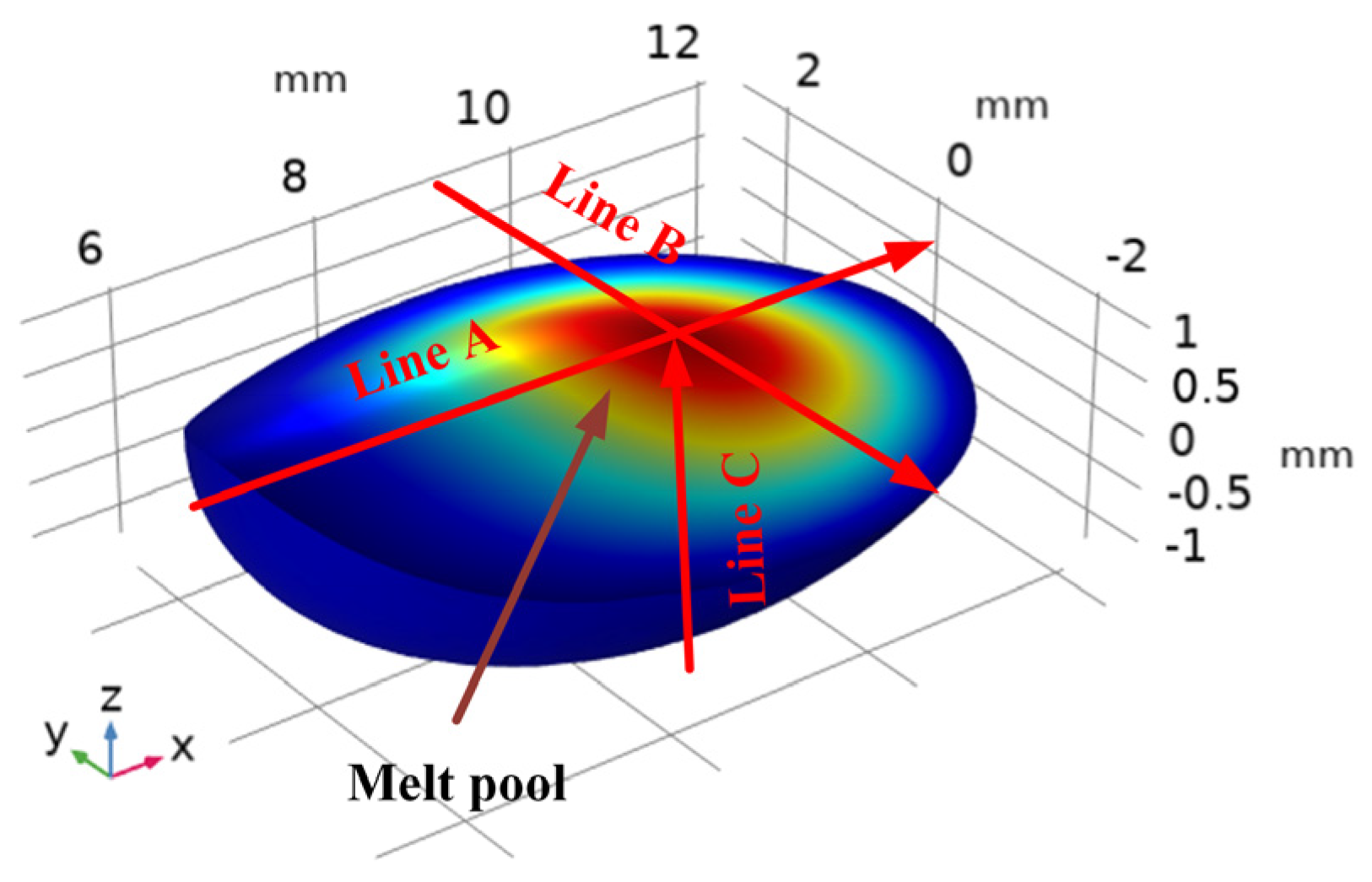
| Element | Ni | Mo | Cr | Mn | Si | C | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.35 | 2.73 | 3.25 | 0.05 | Bal. |
| Element | Cr | Ni | Si | B | C | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 18 | 12 | 2 | 4.2 | 1.2 | Bal. |
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 6.347 | −19,574 | 0 | 0 |
| Cr | 5.849 | −16,415 | 0 | 0 |
| Ni | 6.666 | −20,765 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, L.; Sun, M.; Ding, J.; Li, N. Effect of Plasma Cloud Shielding on Heat and Mass Transfer Mechanism During Laser Cladding. Coatings 2025, 15, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090991
Shang H, Sun Y, Wang X, Feng L, Sun M, Ding J, Li N. Effect of Plasma Cloud Shielding on Heat and Mass Transfer Mechanism During Laser Cladding. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090991
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Hang, Yichang Sun, Xuejun Wang, Lei Feng, Meng Sun, Jinhua Ding, and Ning Li. 2025. "Effect of Plasma Cloud Shielding on Heat and Mass Transfer Mechanism During Laser Cladding" Coatings 15, no. 9: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090991
APA StyleShang, H., Sun, Y., Wang, X., Feng, L., Sun, M., Ding, J., & Li, N. (2025). Effect of Plasma Cloud Shielding on Heat and Mass Transfer Mechanism During Laser Cladding. Coatings, 15(9), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090991






