Significantly Improved Protection Performance of Lotus-Leaf-Extract-Modified Mortar Against Chloride Corrosion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Raw Materials and Preparation Process for LLE-Modified Mortar
2.2. Mechanical Property Testing of LLE-Modified Mortar
2.3. Microstructural Characterization of LLE Modifier and LLE-Modified Mortar
2.4. Corrosion Protection Performance Evaluation of LLE-Modified Mortar
2.4.1. Electrochemical Corrosion Testing
2.4.2. X-CT Tomography for Corrosion Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Compositional Analysis of LLE
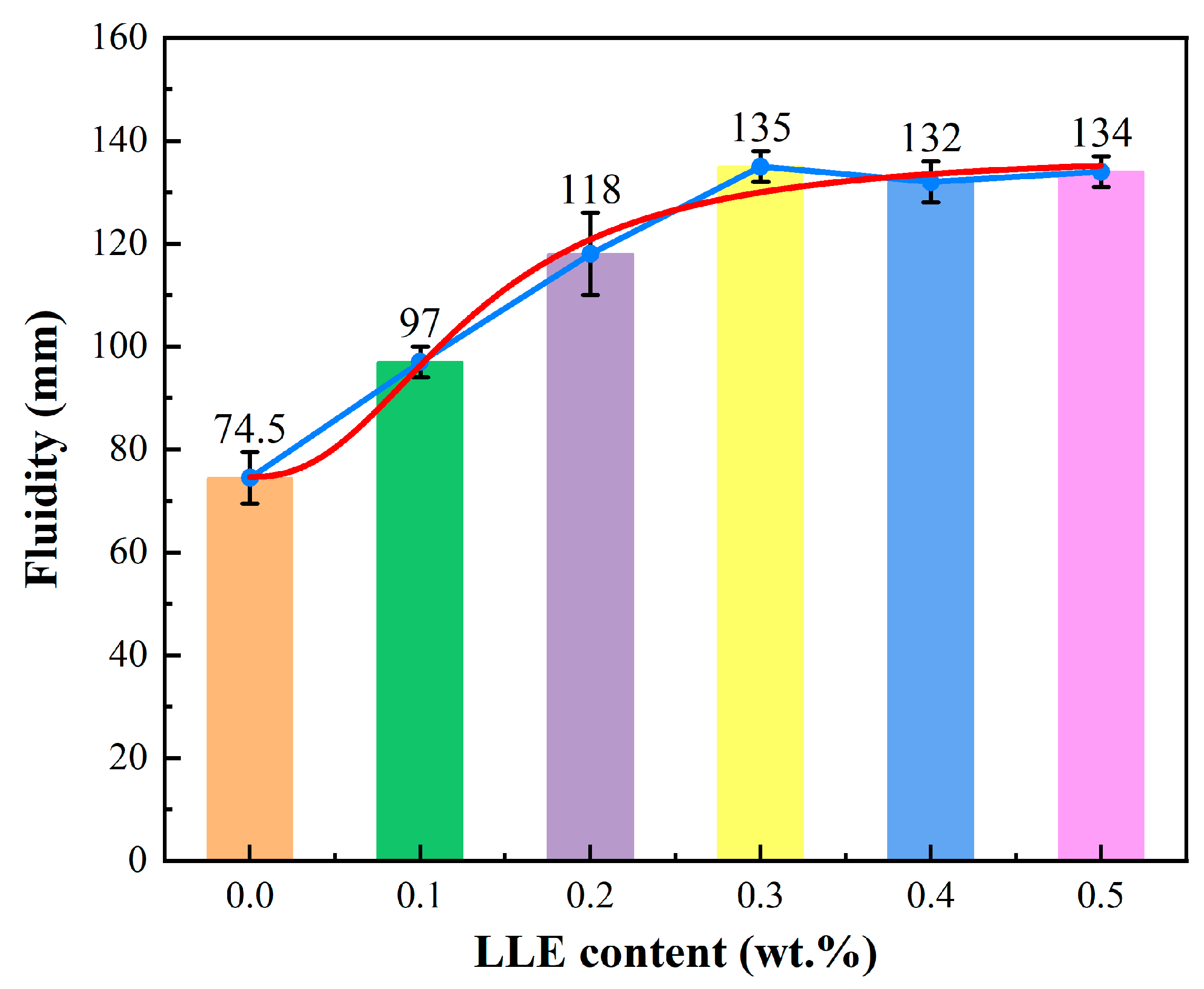
3.2. Effect of LLE Modifier on Cement Paste Fluidity
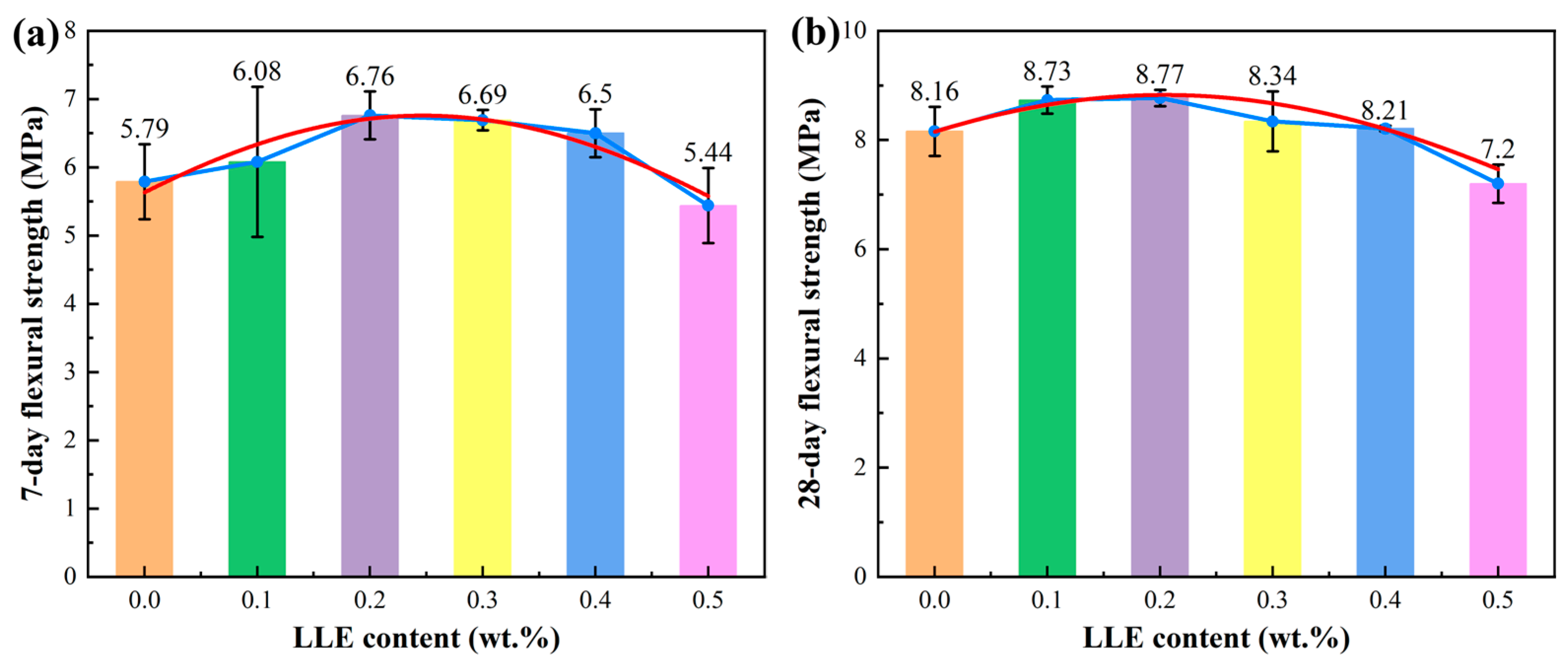
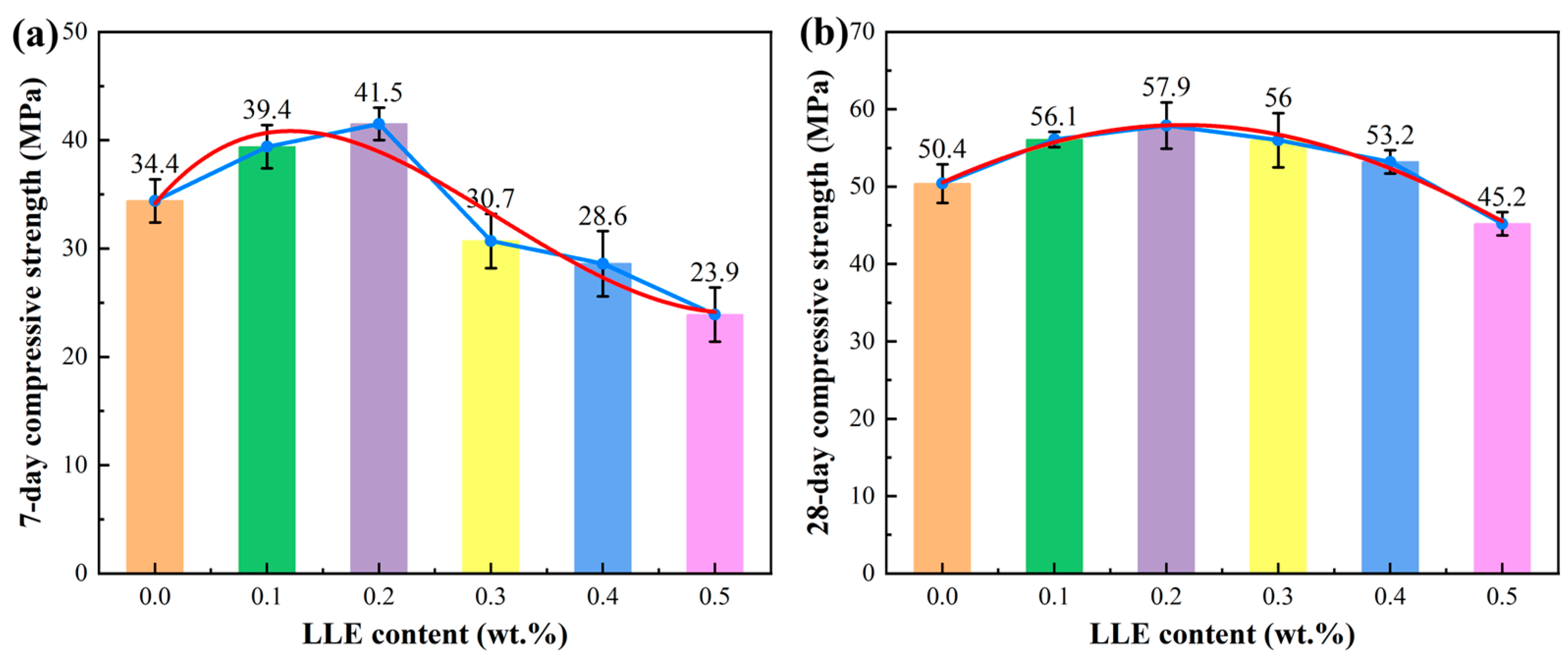
3.3. Effect of LLE Modifier on Mortar Mechanical Properties
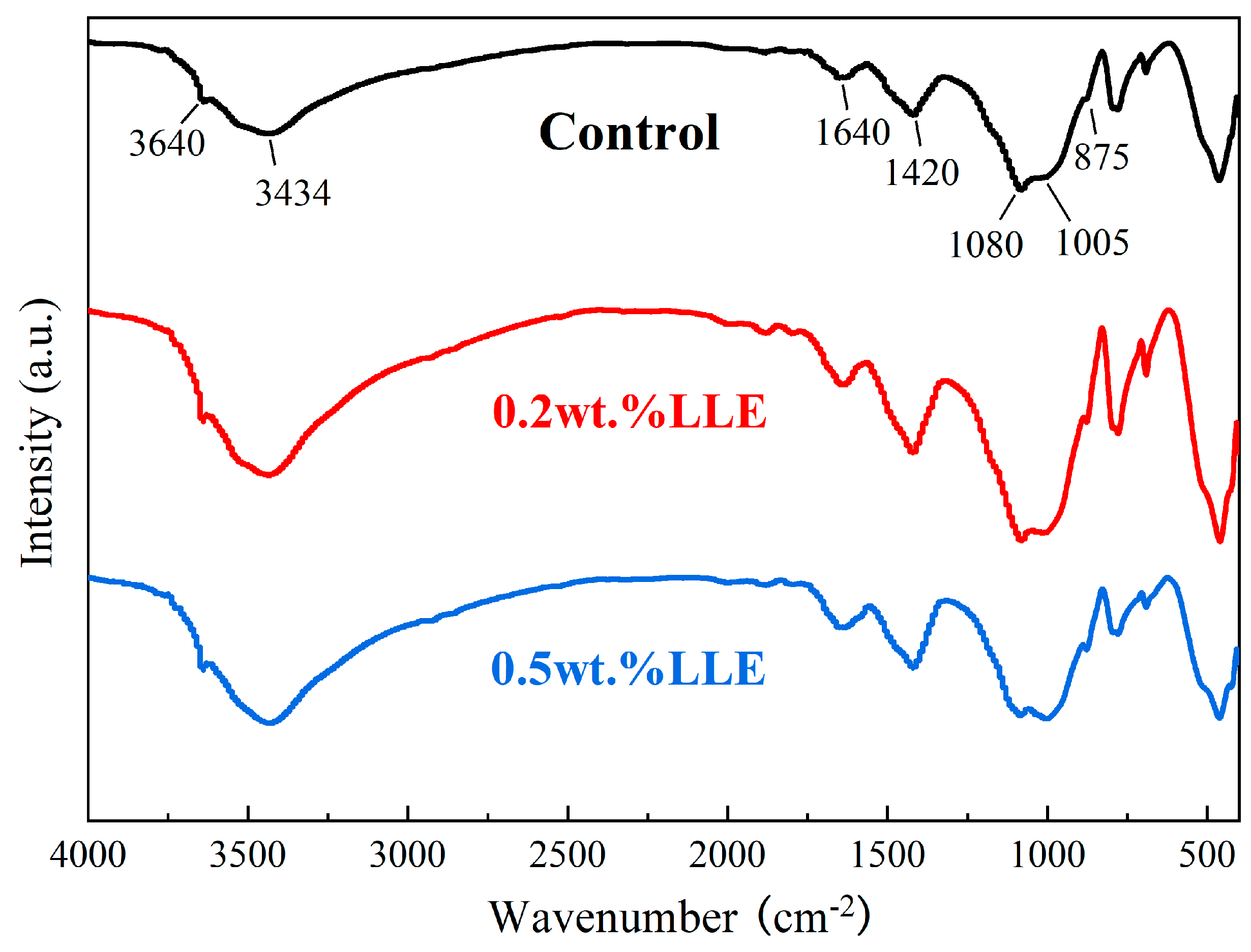
3.4. Influence of LLE Modifier on Cement Hydration Reactions
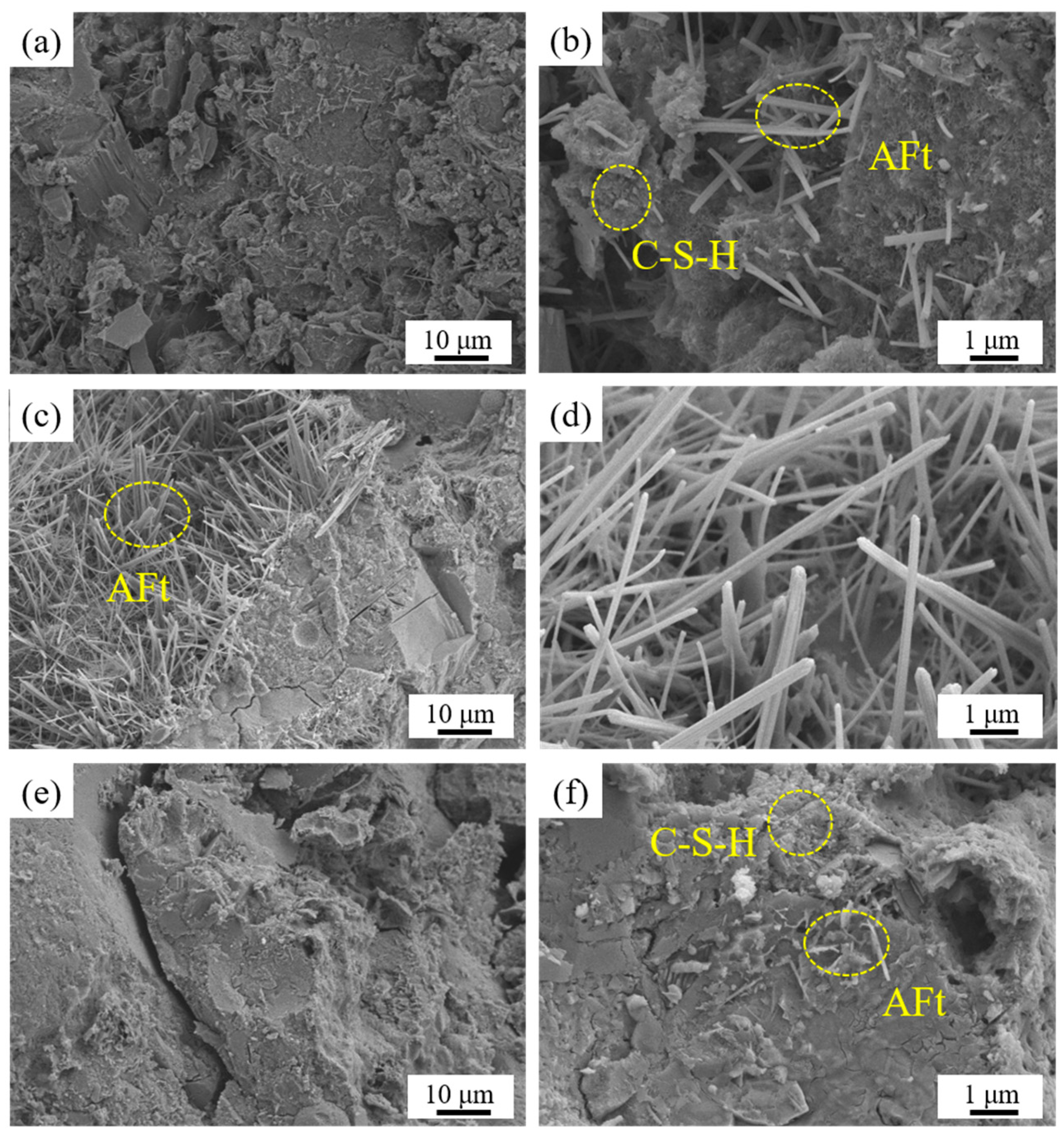
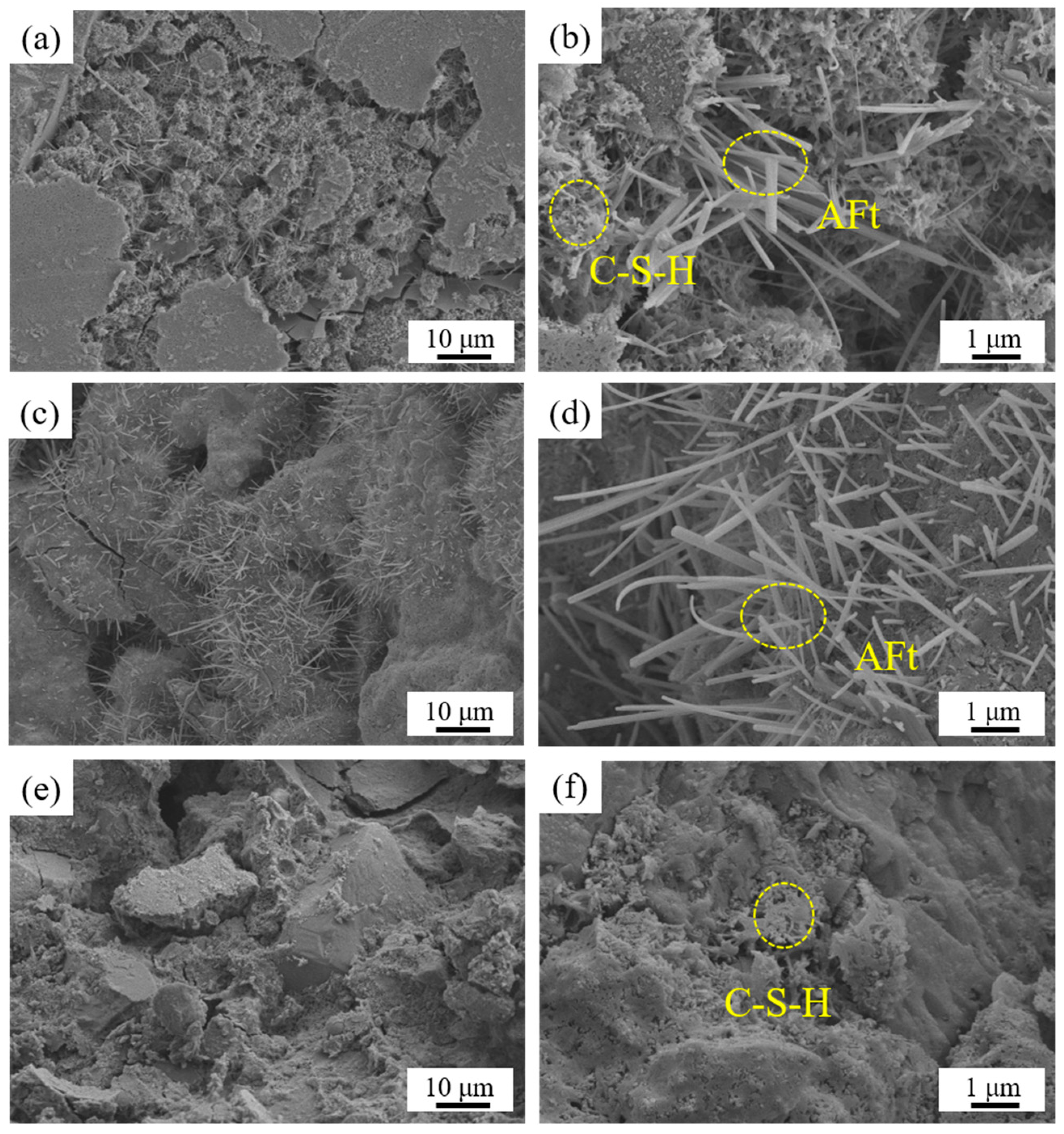
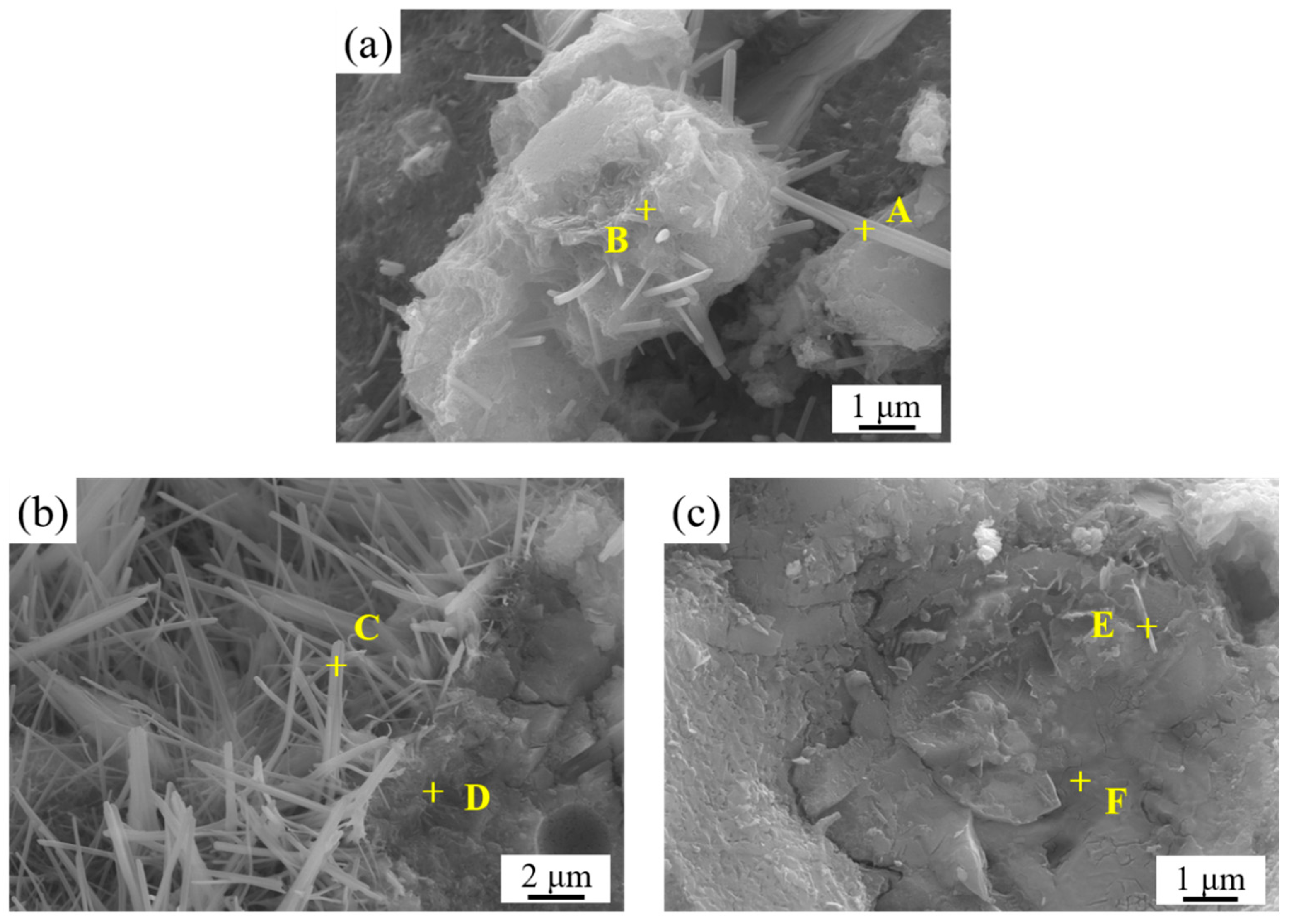
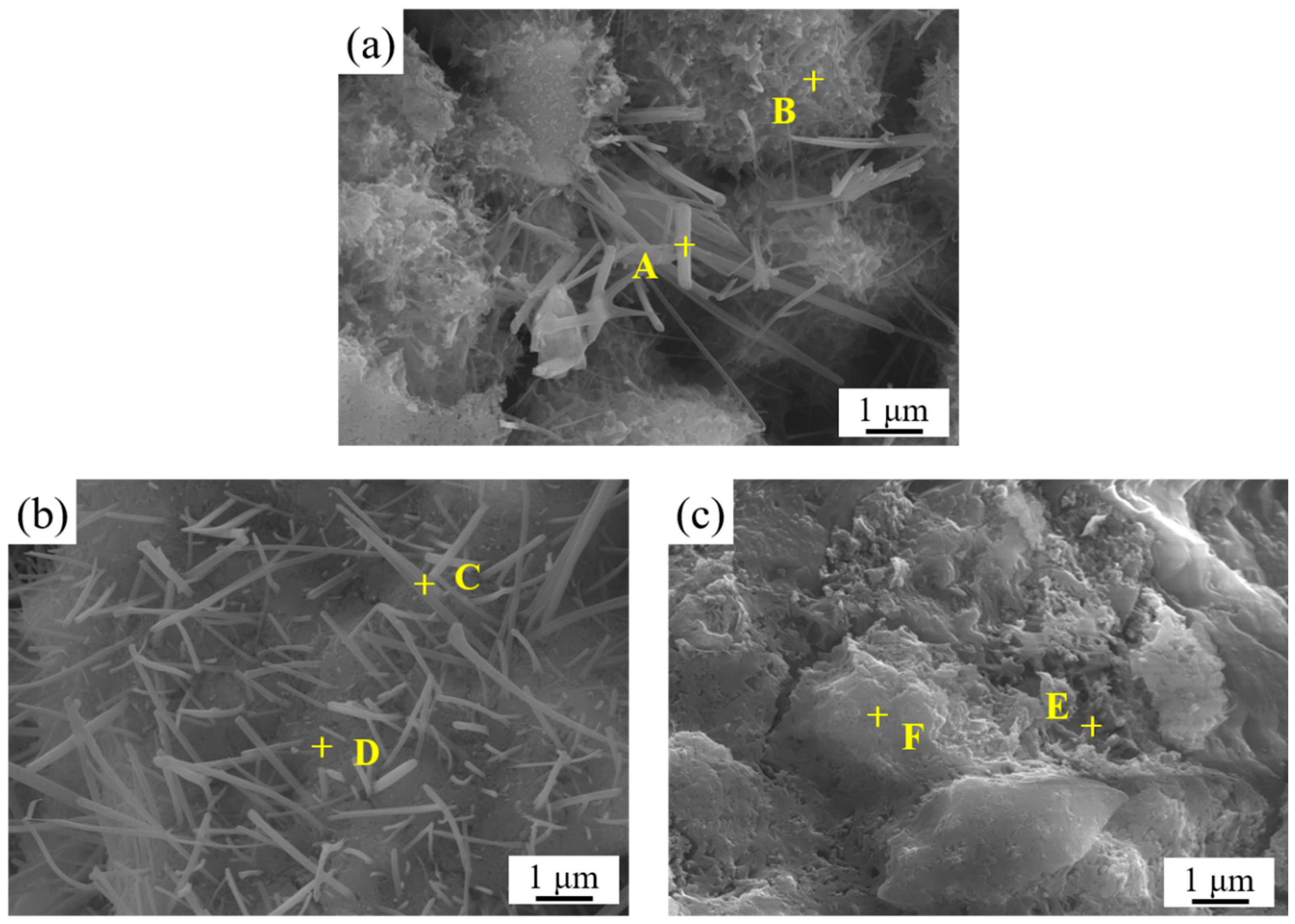
3.5. SEM Surface Morphology Analysis of LLE-Modified Mortar
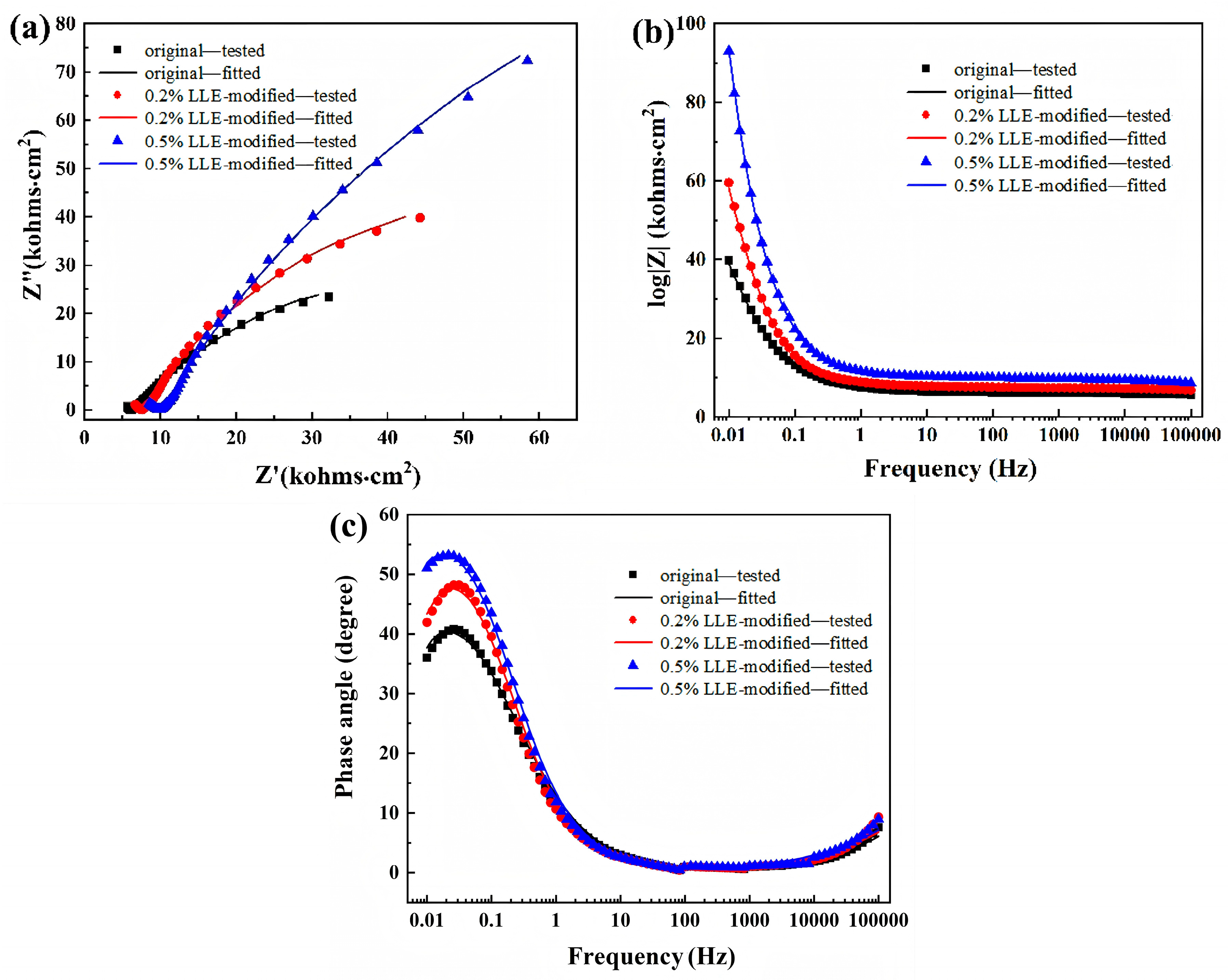
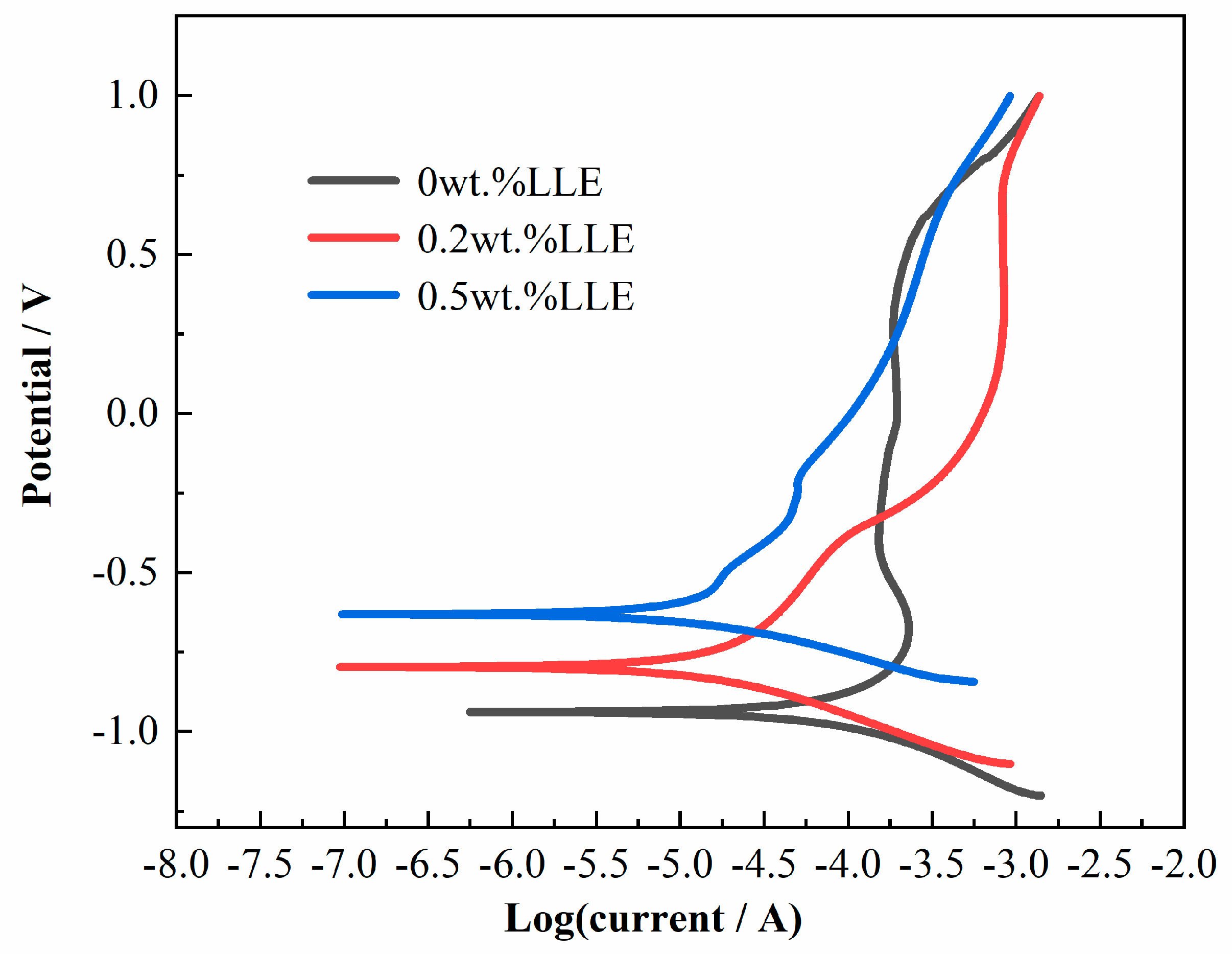
3.6. Chloride Corrosion Protection Performance via Electrochemical Analysis
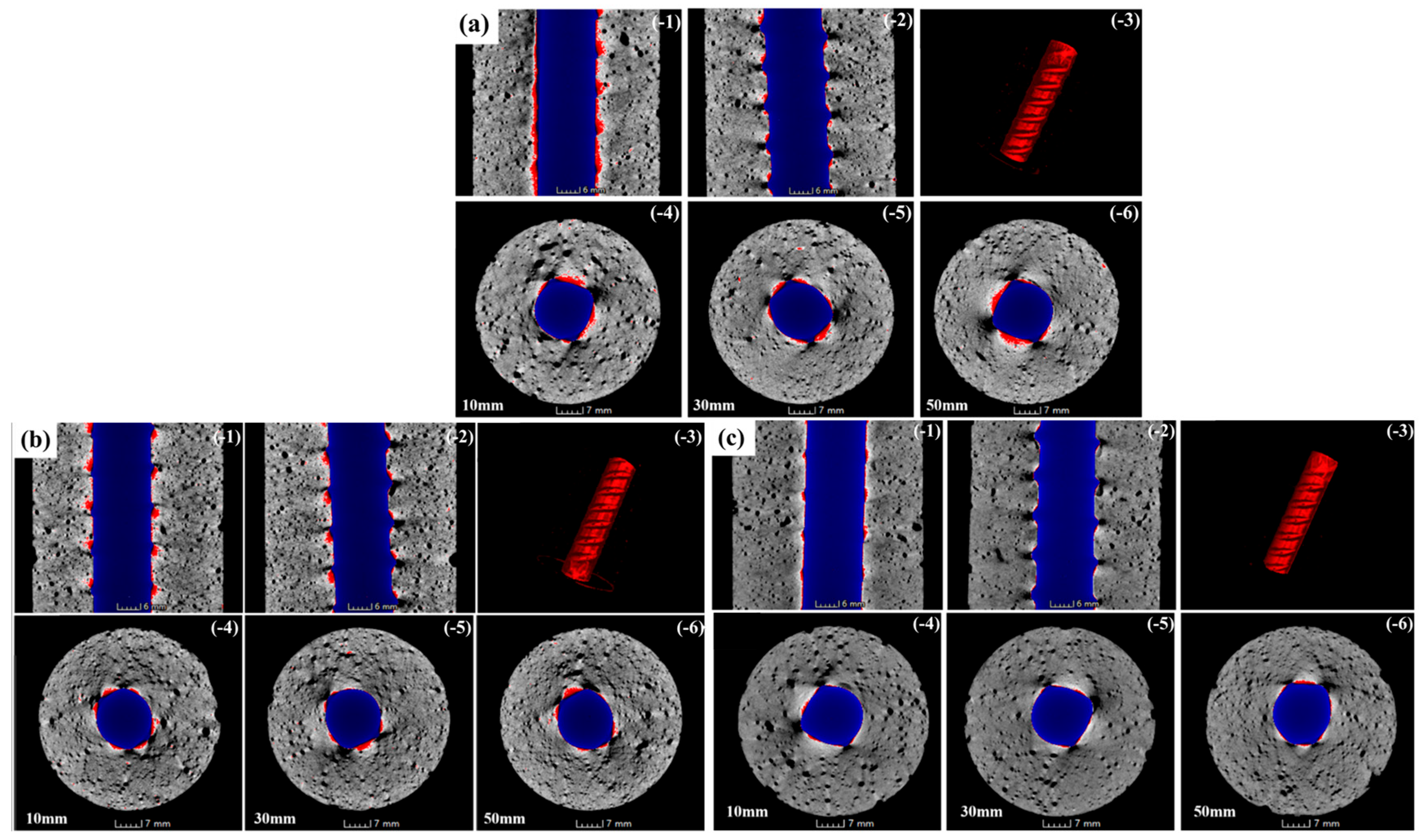
3.7. Corrosion Products and Distribution Characteristics of LLE-Modified Mortar–Rebar Specimens Based on X-CT Analysis
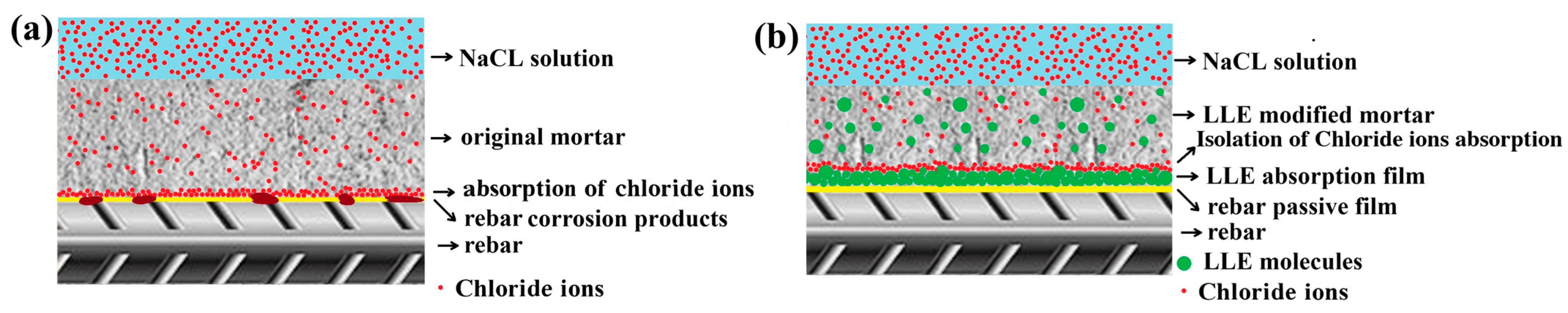
3.8. Corrosion Protection Mechanism of LLE-Modified Mortar Against Chloride Corrosion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, S.K.; Chye, L.K.; Northwood, D.O. Chloride ingress in concrete as measured by field exposure tests in the atmospheric, tidal and submerged zones of a tropical marine environment. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.H.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, J.D.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.R. Randomness of critical chloride concentration of reinforcement corrosion in reinforced concrete flexural members in a tidal environment. Ocean Eng. 2019, 172, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.M. Challenges and opportunities in corrosion of steel in concrete. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mahadevan, S. Chloride-induced reinforcement corrosion and concrete cracking simulation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, C.A.; Papadakis, V.G. Consequences of steel corrosion on the ductility properties of reinforcement bar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 2316–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.K.; Nakamura, H.; Kunieda, M.; Ueda, N. Three Dimensional Behaviour of Concrete Cracking Due to Rebar Corrosion. Procedia Eng. 2011, 14, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Bazarchi, E.; Chiniforush, A.A.; Aghdam, P.P.; Ghodoosi, F. Rebar corrosion detection, protection, and rehabilitation of reinforced concrete structures in coastal environments: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 126, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. Reinforcement corrosion in concrete structures, its monitoring and service life prediction—A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Chen, E.; Li, W.G. A review on corrosion detection and protection of existing reinforced concrete (RC) structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.H.; Nguyen, C.V.; Bui, Q.H. Mechanical model for shear strength prediction of corrosion-damaged reinforced concrete beams under various corrosion schemes. Eng. Struct. 2025, 335, 120357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.L.; Si, Z.; Huang, L.Z.; He, Y.L.; Liu, X.R.; Zhang, Y.L. A review of the repair measures for reinforced concrete affected by chloride ion corrosion. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 102, 112028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielen, H.; Demet, L.; Audenaert, A.; Craeye, B. Behaviour of commercial cementitious repair mortars under various environmental conditions: A resistivity-based approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhu, Z.Y.; She, W. A superhydrophobic mortar with ultra-robustness for self-cleaning, anti-icing, and anti-corrosion. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Castel, A. Long-term durability of underground reinforced concrete pipes in natural chloride and carbonation environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.X.; Tong, L.Y.; Meftah, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.F. Improved predictions of permeability properties in cement-based materials: A comparative study of pore size distribution-based models. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 133927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maaddawy, T.; Soudki, K. Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Repair to Extend Service Life of Corroded Reinforced Concrete Beams. J. Compos. Constr. 2005, 9, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, C.A.; Assaad, J.J. Stability and bond properties of polymer-modified self-consolidating concrete for repair applications. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarde, B.; Patil, Y.D. Recent Research Status on Polymer Composite Used in Concrete-An Overview. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 3780–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, J.; Mirza, M.S.; Lapointe, R. Laboratory and field performance of polymer-modified cement-based repair mortars in cold climates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2002, 16, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobbekaduwa, D.; Nanayakkara, O.; Krevaikas, T.; Sarno, L.D. Effect of organic corrosion inhibitors on the behaviour of repair mortars and reinforcement corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 451, 138787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, S.Z.; Yusoff, A.H.; Zakaria, S.K.; Taib, M.A.A.; Teo, P.T. Plant Extracts as Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Ferrous Metal Alloys: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 304, 127030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berke, N.S.; Hicks, M.C. Predicting long-term durability of steel reinforced concrete with calcium nitrite corrosion inhibitor. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 26, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, M.; Ming, J. In-depth insight into the role of molybdate in corrosion resistance of reinforcing steel in chloride-contaminated mortars. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 132, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, R.; Bautista, A.; Velasco, F.; Soleimani, M.; Pourfath. Green corrosion inhibition for carbon steel reinforcement in chloride-polluted simulated concrete pore solution using Urtica Dioica extract. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Song, Z.; Han, H.; Saddick, D.; Jiang, L.; Wang, W.; Chu, H. A novel green reinforcement corrosion inhibitor extracted from waste Platanus acerifolia leaves. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, R.; Chitra, S.; Hemapriya, V.; Chung, I.; Kim, S.; Prabakaran, M. Implications of eco-addition inhibitor to mitigate corrosion in reinforced steel embedded in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kwon, Y.J.; Lee, K.Y. Analysis of Chemical Composition, Vitamin, Mineral and Antioxidative Effect of the Lotus Leaf. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 37, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwada, Y.; Aoshima, A.; Ikeshiro, Y.; Chen, Y.; Furukawa, H.; Itoigawa, M.; Fujioka, T.; Mihashi, K.; Cosentino, L.M.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; et al. Anti-HIV benzylisoquinoline alkaloids and flavonoids from the leaves of Nelumbo nucifera, and structure–activity correlations with related alkaloids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Luo, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Li, H. Preparation and Corrosion Inhibition of Super Hydrophobic Adsorption Film of Lotus Leaf Extract on Mild Steel. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2022, 42, 903–912. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Cao, J.N.; Xiang, Q.; Bai, X.Y. Theory Study about Inhibition of Alkaloids in Lotus Leaf Extraction. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 2011, 39, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar Jha, V.; Ji, G. Lotus leaves coating on copper substrates and their corrosion performances in sodium chloride solutions. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.K.; Jana, S.; Pal, S.; Ji, G.; Prakash, R. Thin-Film Coating of the Hydrophobic Lotus Leaf on Copper by the Floating Film Transfer Method and Investigation on the Corrosion Behavior of Coated Copper in Saline Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Wang, J.; Guan, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance of Carbon Steel Rebar in Chloride-Containing Water Solutions: The Role of Lotus Extract in Corrosion Inhibition. Metals 2025, 15, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, N.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Qin, K. Ultrasound-assisted enzyme extraction of total flavonoids from lotus leaf (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) and its antioxidant activity. LWT 2025, 215, 117224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Carrasco, L.; Torrens-Martín, D.; Morales, L.M.; Martínez-Ramírez, S. Infrared spectroscopy in the analysis of building and construction materials. In Infrared Spectroscopy–Materials Science, Engineering and Technology; BoD—Books on Demand: Hamburg, Germany, 2012; p. 510. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Carrasco, L.; Claramunt, J.; Ardanuy, M. Autoclaved cellulose fibre reinforced cement: Effects of silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.D.; Pan, G.H.; Sun, W. In Situ Observation Microstructure Character Changes in the Carbonation Process of Hardened Cement Paste Using ESEM/EDS. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 194, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, B. Coconut coir dust extract as a novel green corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in the chloride-contaminated concrete pore solution. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallaiya, K.; Subramaniam, R.; Srikandan, S.S.; Gowri, S.; Rajasekaran, N.; Selvaraj, A. Electrochemical characterization of the protective film formed by the unsymmetrical Schiff’s base on the mild steel surface in acid media. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 3857–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
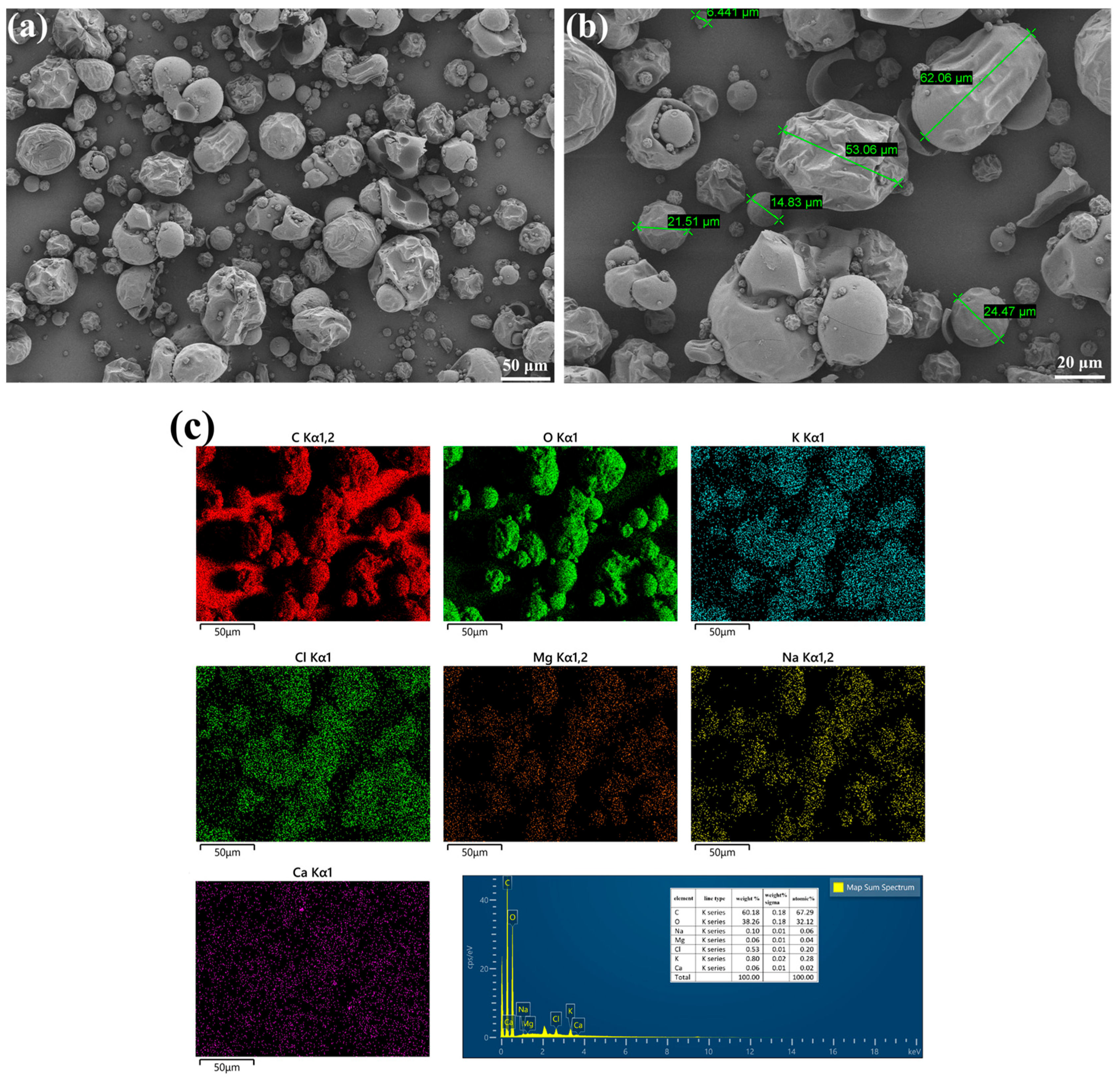
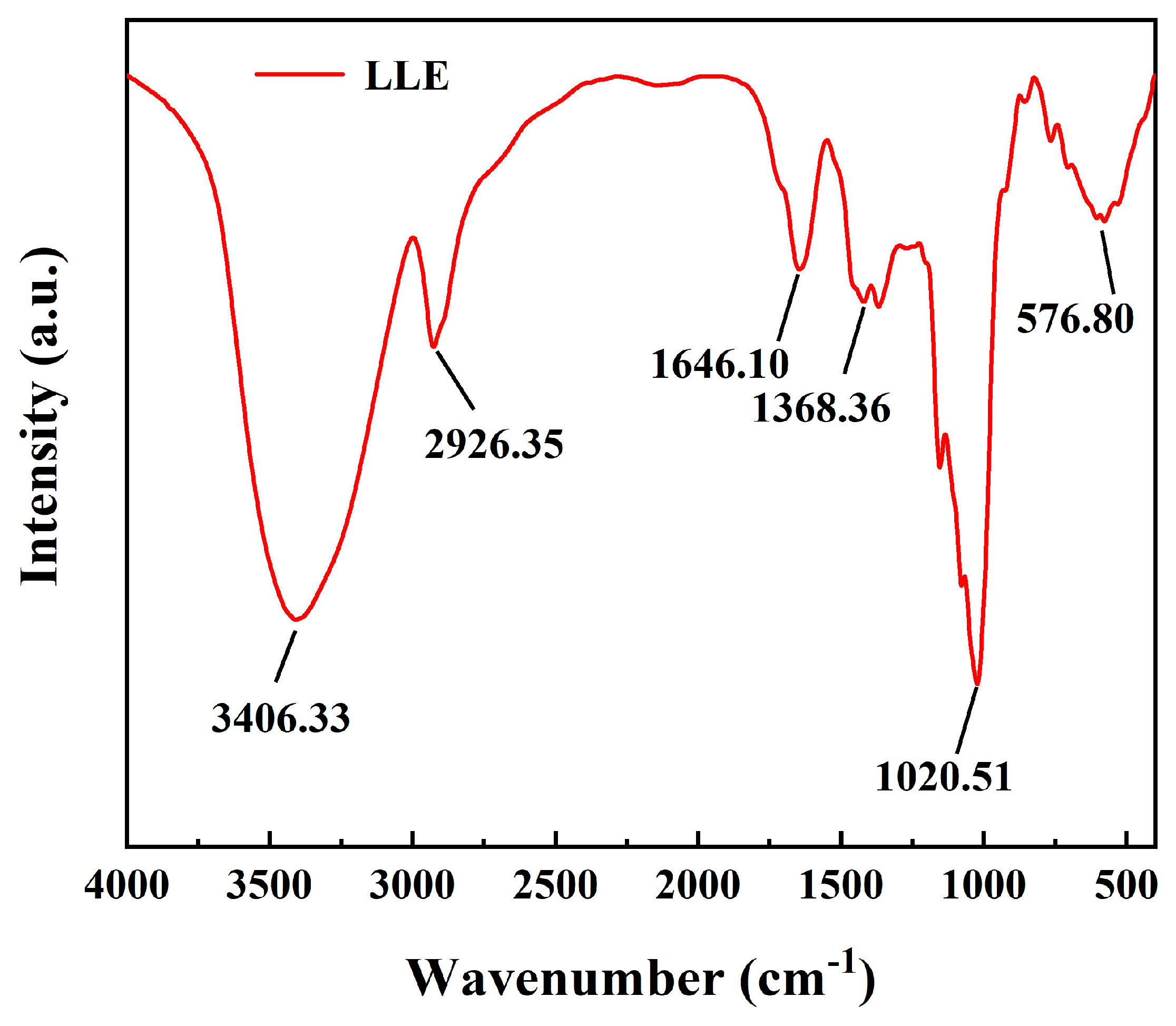


| Oxide | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | Na2O | K2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt%) | 62.66 | 21.72 | 5.30 | 3.39 | 1.09 | 2.08 | 0.41 | 0.79 | 1.87 |
| Rebar | Fe | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Carbon Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRB400 | Balance | 0.25 | 0.80 | 1.60 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.54 |
| Position | Elements (at.%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | Ca | Si | Al | S | |
| A | 71.68 | 7.48 | 17.76 | 2.12 | 0.96 |
| B | 71.09 | 15.73 | 8.31 | 3.55 | 1.31 |
| C | 74.77 | 14.92 | 4.24 | 3.25 | 2.82 |
| D | 58.36 | 26.39 | 12.18 | 1.96 | 1.12 |
| E | 72.91 | 16.66 | 5.12 | 4.31 | 1.01 |
| F | 61.12 | 23.92 | 2.13 | 12.54 | 0.29 |
| Position | Elements (at.%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | Ca | Si | Al | S | |
| A | 67.72 | 20.93 | 5.87 | 3.04 | 2.45 |
| B | 60.76 | 33.69 | 4.19 | 0.76 | 0.60 |
| C | 68.95 | 18.05 | 9.29 | 2.17 | 1.54 |
| D | 64.23 | 22.16 | 11.62 | 1.24 | 0.75 |
| E | 65.21 | 4.93 | 28.14 | 0.90 | 0.82 |
| F | 72.69 | 12.31 | 12.25 | 1.60 | 1.14 |
| LLE (wt%) | Rs (Ω·cm2) | Yf × 10−5 (Ω−1·sn·cm−2) | n1 | Rf (kΩ·cm2) | Ydl × 10−5 (Ω−1·sn·cm−2) | n2 | Rct (kΩ·cm2) | η (%) | RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6.54 | 3.69 | 0.49 | 6.27 | 0.15 | 0.67 | 116.11 | - | - |
| 0.20 | 7.58 | 7.11 | 0.47 | 7.75 | 0.12 | 0.76 | 157.80 | 26.41 | 1.5 |
| 0.50 | 7.24 | 7.14 | 0.43 | 10.14 | 0.08 | 0.77 | 402.3 | 71.13 | 1.8 |
| LLE Content | βa (mV/Dec) | βc (mV/Dec) | Ecorr (V) | icorr × 10−6 (A/cm2) | η (%) | RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 wt% | 5.89 | 3.87 | −0.94 | 2.69 | -- | - |
| 0.2 wt% | 6.09 | 3.13 | −0.80 | 0.56 | 79.22 | 2.1 |
| 0.5 wt% | 7.54 | 1.68 | −0.63 | 0.53 | 80.48 | 2.4 |
| Plant Extract Source | Corrosive Medium | η | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urtica dioica leaf | Alkaline sodium chloride solution | 77.00% | [24] |
| Damask Rose leaf | Alkaline sodium chloride solution | 81.90% | [26] |
| Lotus leaf | Alkaline sodium chloride solution | 96.96% | Our previous work [33] |
| Lotus leaf | Mortar in sodium chloride solution | 80.48% | This paper |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Hua, Q.; Guan, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Song, D. Significantly Improved Protection Performance of Lotus-Leaf-Extract-Modified Mortar Against Chloride Corrosion. Coatings 2025, 15, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090983
Wu C, Zhu Y, Hua Q, Guan H, Wang H, Wang G, Zhang S, Song D. Significantly Improved Protection Performance of Lotus-Leaf-Extract-Modified Mortar Against Chloride Corrosion. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090983
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Changyun, Yangshun Zhu, Quan Hua, Hao Guan, Haoyu Wang, Guowei Wang, Shuguang Zhang, and Dan Song. 2025. "Significantly Improved Protection Performance of Lotus-Leaf-Extract-Modified Mortar Against Chloride Corrosion" Coatings 15, no. 9: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090983
APA StyleWu, C., Zhu, Y., Hua, Q., Guan, H., Wang, H., Wang, G., Zhang, S., & Song, D. (2025). Significantly Improved Protection Performance of Lotus-Leaf-Extract-Modified Mortar Against Chloride Corrosion. Coatings, 15(9), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15090983




