Upcycling Coffee Silverskin Waste into Functional Textile Coatings: Evaluation on Cotton, Lyocell, Wool, and Silk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coffee Silverskin (CS) Sample
2.2. Residue Pre-Treatments
2.3. Coating Paste Formulation
2.4. Textile Substrates and Coating Process
2.5. Determination of the Coatings’ Performance on Different Substrates
3. Results
3.1. Cellulose-Based Textile Substrates
3.2. Protein-Based Textile Substrates
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carus, M.; Dammer, L. The circular bioeconomy—Concepts, opportunities, and limitations. Ind. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuța, P.; Sonia, A. Oil press cakes and meals valorization through circular economy approaches: A review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Singh, A.; Sharma, R.; Malaviya, P. Conversion of Food Waste into Energy and Value-Added Products: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 1759–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Difonzo, G.; Grassi, S.; Paciulli, M. Upcycling of agro food chain by-products to obtain high value added foods. Foods 2022, 11, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavahian, M.; Mathad, G.N.; Pandiselvam, R.; Lin, J.; Sun, D.W. Emerging technologies to obtain pectin from food processing by-products: A strategy for enhancing resource efficiency. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán Aranguren, D.D.; Robledo, S.; Gomez Restrepo, E.; Arboleda Valencia, J.W.; Tarazona, N.A. Scientometric overview of coffee by-products and their applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İşmal, Ö.E. Greener natural dyeing pathway using a by-product of olive oil; prina and biomordants. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xue, J.; Yang, X.; Ke, Y.; Ou, R.; Wang, Y.; Madbouly, S.A.; Wang, Q. From plant phenols to novel bio-based polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 125, 101473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Vilaça, H.; Antunes, J.; Rocha, A.; Silva, C. Textile bio-based and bioactive coatings using vegetal waste and by-products. Base Diseño Innovación 2022, 7, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Dietrich, S.; Schulz, H.; Mondschein, A. Comparison of the technical performance of leather, artificial leather, and trendy alternatives. Coatings 2021, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, A.; Esposito, F.; Cirillo, T.; Silva, A.; Silva, C. Coffee Silverskin: Unveiling a Versatile Agri-Food By-Product for Ethical Textile Coatings. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Research in Technologies, Information, Innovation and Sustainability, Madrid, Spain, 18 October 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Schwarz, S.; Rieke-Zapp, J.; Cantergiani, E.; Rawel, H.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Martuscelli, M.; Gottstein, V.; Angeloni, S. Coffee by-products as sustainable novel foods: Report of the 2nd international electronic conference on foods—“Future foods and food technologies for a sustainable world. Foods 2021, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Sinha, S.K.; Ghosh, S. Moisture management behaviour of modified polyester wool fabrics. Fashion Text. 2015, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X. Fabric permeability testing. In Fabric Testing; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 189–227. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatraman, P. Evaluating the performance of fabrics for sportswear. In Materials and Technology for Sportswear and Performance Apparel; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 272–299. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.G. Cotton Fibre Quality: Science and Technology; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Gao, A.; Zhang, Y. Flame retardant finishing of cotton fabric based on synergistic compounds containing boron and nitrogen. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.-W.; Zhang, G.-X.; Zhang, F.-X. Enhancement of flame retardancy of cotton fabrics by grafting a novel organic phosphorous-based flame retardant. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, W. A review on raw materials, commercial production and properties of lyocell fiber. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, H. Permeability and wicking properties of modal and lyocell woven fabrics used for clothing. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2017, 12, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. A review of the sustainable methods in imparting shrink resistance to wool fabrics. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 18, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.M.; Leighs, S.J. Effect of surface treatments on physicomechanical, stain-resist, and UV protection properties of wool fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.M.; Rippon, J.A. The Colouration of Wool and Other Keratin Fibres; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, M.; Matsudaira, M. Comparison of woollen eco-friendly anti-felting treatment with classic anti-felting procedures. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchi, I.; Boschi, A.; Arosio, C.; Bertini, F.; Freddi, G.; Catellani, M. Bio-based conductive composites: Preparation and properties of polypyrrole (PPy)-coated silk fabrics. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, G.; Mossotti, R.; Innocenti, R. Degumming of silk fabric with several proteases. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 106, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lin, J.; Pei, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, D.; Huang, Z. Recent advances in environmentally friendly and green degumming processes of silk for textile and non-textile applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Subasinghe, A.; Kim, N.K. Natural fibers: Their composites and flammability characterizations. Multifunct. Polym. Compos. 2015, 1, 102–143. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, F.; Liu, D.; Wu, Y. Silk-based conductive materials for smart biointerfaces. Smart Med. 2023, 2, e20230004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, J.K.; Hasturk, O.; Falcucci, T.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk chemistry and biomedical material designs. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.U.D.; Zargar, M.I.; Masoodi, M.H.; Alshehri, S.; Alam, P.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshlowi, A.; Shivakumar, H.G.; Ali, M.; Shakeel, F. Silk fibroin as an efficient biomaterial for drug delivery, gene therapy, and wound healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mio, H.; Kano, J.; Saito, F.; Kaneko, K. Effects of rotational direction and rotation-to-revolution speed ratio in planetary ball milling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 332, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Dong, H.; Wu, Q.; Ye, X. Influence of ball size distribution on grinding effect in horizontal planetary ball mill. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A.; Barczewski, M.; Kosmela, P.; Mysiukiewicz, O.; Kuzmin, A. Coffee silverskin as a multifunctional waste filler for high-density polyethylene green composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, R.; Avolio, R.; Castaldo, R.; Cocca, M.; Gentile, G.; Cirillo, T.; Nolasco, A.; Errico, M.E. Upcycling coffee silverskin into biobased functional coatings. Coatings 2024, 469, 143063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, A.; Squillante, J.; Velotto, S.; D’Auria, G.; Ferranti, P.; Mamone, G.; Esposito, F. Valorization of coffee industry wastes: Comprehensive physicochemical characterization of coffee silverskin and multipurpose recycling applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sahi, A.; Gundu, S.; Kumari, P.; Klepka, T.; Sionkowska, A. Silk-Based Biomaterials for Designing Bioinspired Microarchitecture for Various Biomedical Applications. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ferri, L.; Lorenzi, A.; Carcano, E.; Draghi, L. Silk fabrics modification by sol–gel method. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.X.; He, J.H.; Kong, H.Y. Waterproof and dustproof of wild silk: A theoretical explanation. J. Nano Res. 2013, 22, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, K.; Ifuku, N.; Isogai, A. Silk composite with a fluoropolymer as a water-resistant protein-based material. Polymers 2018, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, G.; Gogoi, S.; Karak, N. Dimer acid based waterborne hyperbranched poly(ester amide) thermoset as a sustainable coating material. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 112, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, D.; Wéry, M.; Uyttendaele, W.; Vanneste, M. Bio-based waterborne PU for durable textile coatings. Polymers 2021, 13, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, H.E.; Luzzi, S.; D’Arrigo, P.; Griffini, G. Life Cycle Environmental Impact Considerations in the Design of Novel Biobased Polyurethane Coatings. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 8065–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samyn, P.; Cosemans, P.; Vandenhaute, T. Ab Initio Life-Cycle Analysis Assisting the Selection of Eco-Friendly Additives in Bio-Based Coatings. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 76. [Google Scholar]




| Characterisation Results | (Specific Conditions) | Cellulose-Based | Protein-Based | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Lyocell | Wool | Silk | ||
| Martindale Abrasion Resistance * (ISO 5470-2:2003) | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Determination of Resistance to Damage by Flexing * (ISO 7854:1995) | 1 | 0 | 1.5 | 2 | |
| Determination of Permeability to Air (ISO 9237:1995) | lm−2 s−1 | 0.05 ± 0.1 | 1.79 ± 1.0 | 2.36 ± 0.6 | 0.06 ± 0.1 |
| Colour Fastness to Rubbing ** (ISO 105-X12:2016) | dry conditions | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4–5 |
| wet conditions | 2–3 | 2 | 2 | 2–3 | |
| Colour Fastness to Water ** (ISO 105-E01:2013) | 4 | 3–4 | 3–4 | 3–4 | |
| Characterisation Tests | Raw Fabrics | CS-Coated Fabrics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Angle | Absorption Time | Contact Angle | Absorption Time | ||
| Cellulose-based | Cotton | 31.79° ± 1.04° | 2.55 ± 0.50 s | 111.48° ± 1.63° | hydro-repellent |
| Lyocell | 130.27° ± 7.88° | 48.03 ± 6.01 s | 116.15° ± 2.49° | hydro-repellent | |
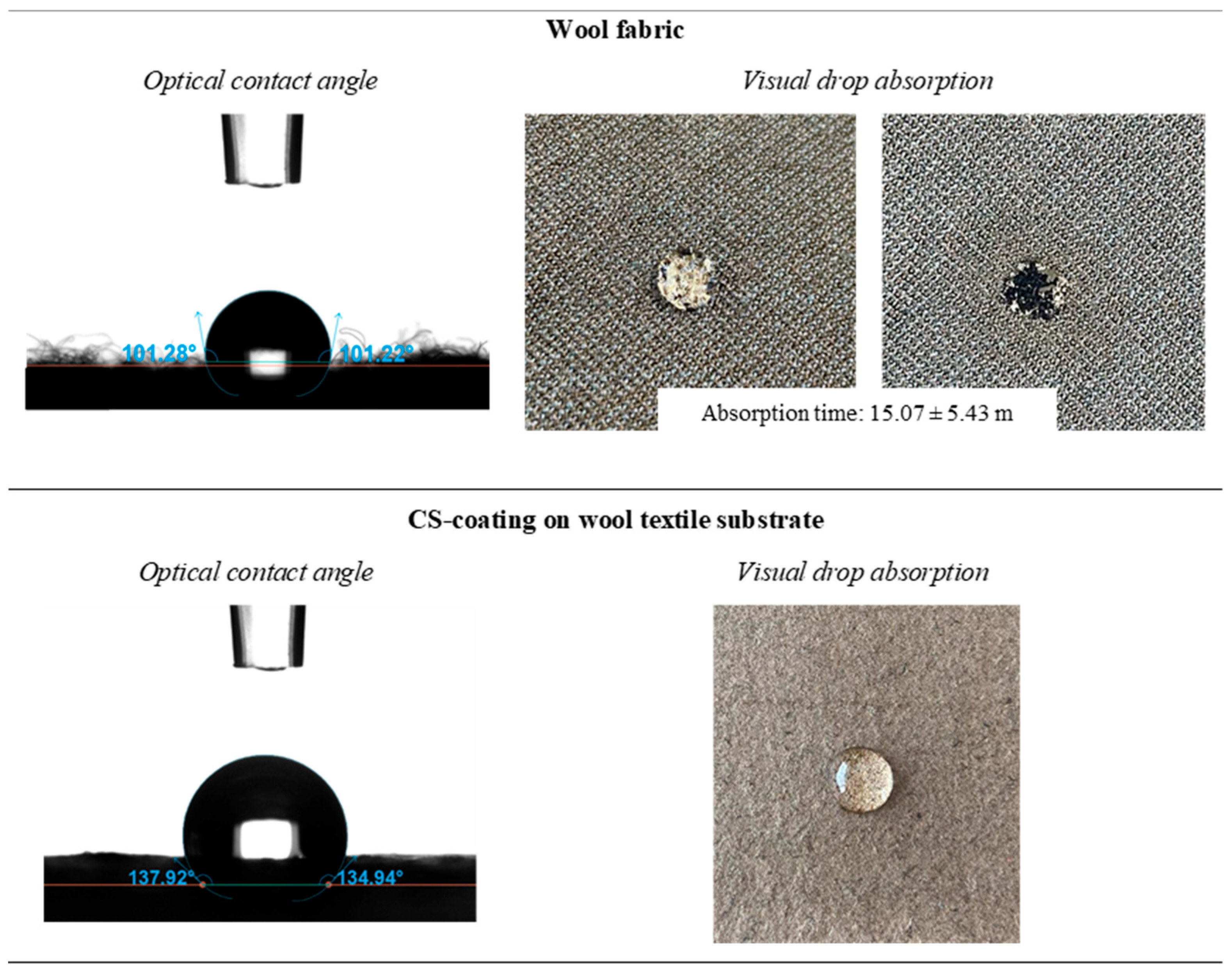
| Protein-based | Wool | 101.27° ± 3.18° | 15.07 ± 5.43 m | 134.90° ± 1.70° | hydro-repellent |
| Silk | 26.71° ± 5.48° | 1.50 ± 0.34 s | 121.03° ± 1.26° | hydro-repellent | |
| AATCC 195-2010 | Cellulose-Based | Protein-Based | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Lyocell | Wool | Silk | ||
| Liquid Moisture Management test | no pre-treatment | fast absorption and slow drying fabric | water-penetration fabric | water repellent fabric | water repellent fabric |
| with pre-treatment | fast absorption and slow drying fabric | water-penetration fabric | waterproof fabric | waterproof fabric | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nolasco, A.; Esposito, F.; Cirillo, T.; Silva, A.; Silva, C.J. Upcycling Coffee Silverskin Waste into Functional Textile Coatings: Evaluation on Cotton, Lyocell, Wool, and Silk. Coatings 2025, 15, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091033
Nolasco A, Esposito F, Cirillo T, Silva A, Silva CJ. Upcycling Coffee Silverskin Waste into Functional Textile Coatings: Evaluation on Cotton, Lyocell, Wool, and Silk. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091033
Chicago/Turabian StyleNolasco, Agata, Francesco Esposito, Teresa Cirillo, Augusta Silva, and Carla Joana Silva. 2025. "Upcycling Coffee Silverskin Waste into Functional Textile Coatings: Evaluation on Cotton, Lyocell, Wool, and Silk" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091033
APA StyleNolasco, A., Esposito, F., Cirillo, T., Silva, A., & Silva, C. J. (2025). Upcycling Coffee Silverskin Waste into Functional Textile Coatings: Evaluation on Cotton, Lyocell, Wool, and Silk. Coatings, 15(9), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091033








