Study on the Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism of HEDP and Mechanical Performance Degradation of HSGPSW Under Tensile Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
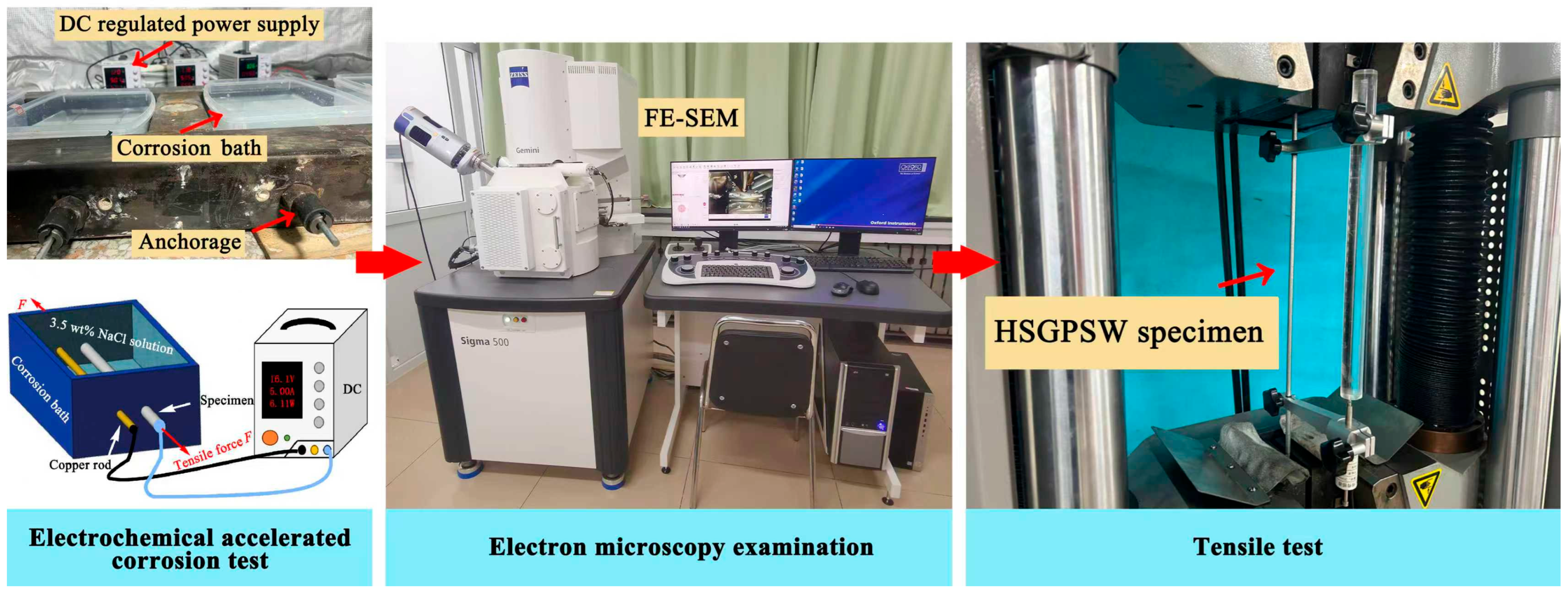
2.1. Electrochemical Corrosion Test
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.3. Tensile Test
3. Analysis of Experimental Results
3.1. Experimental Observations
3.2. Experimental Results
3.2.1. Corrosion Test Results
3.2.2. Analysis Results of Corrosion Product Characteristics
3.2.3. Surface Morphology of the Specimens
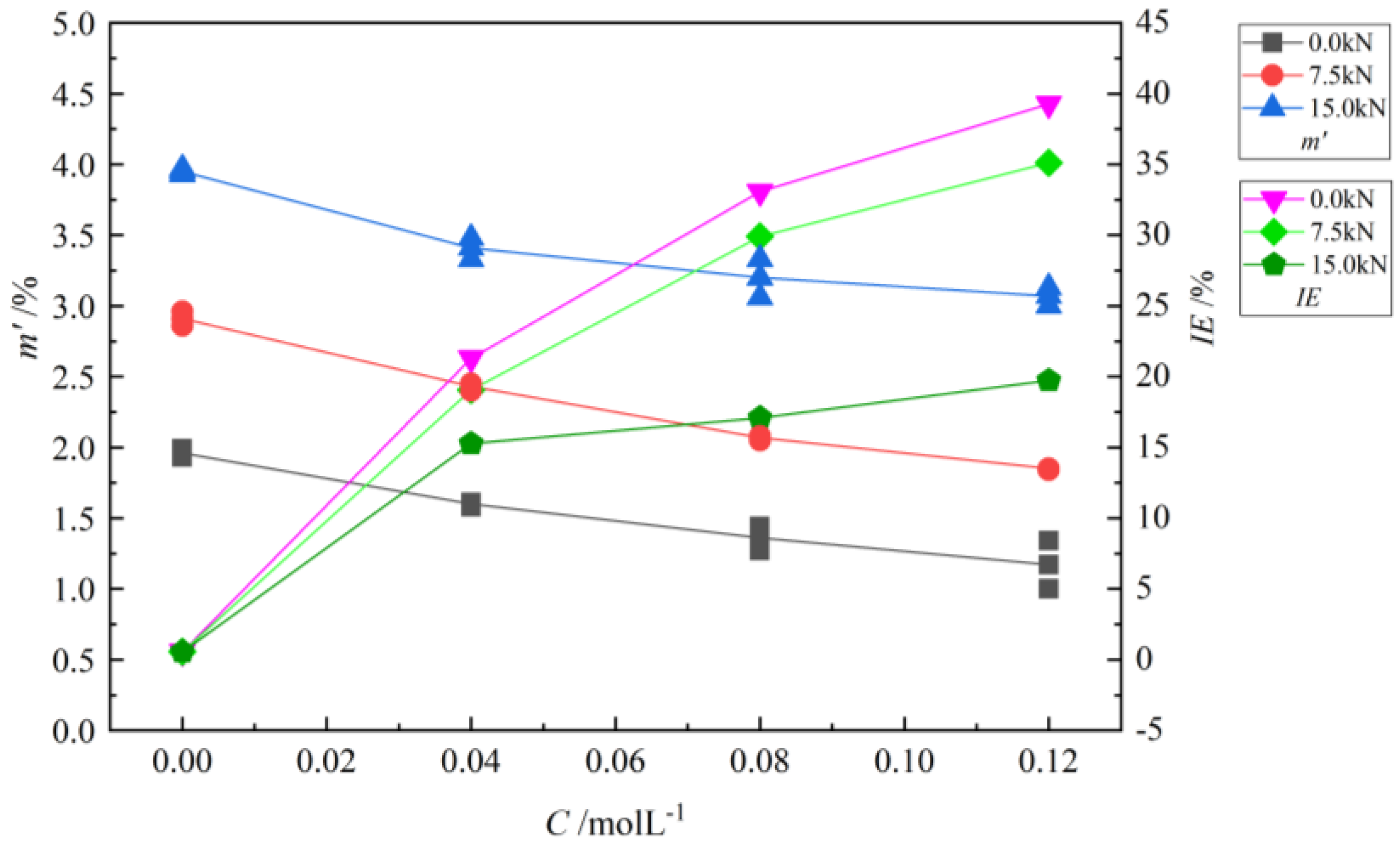
3.2.4. Tensile Test Results
4. Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism and Engineering Recommendations
4.1. Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism
4.2. Engineering Application Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, P.M.; Xin, G.F.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Long, G.X.; Yuan, Y.G.; Liu, X.G. Experimental Study on Corrosion Process Differences of Bridge Cable Cross Section. China J. Highw. Transp. 2022, 35, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.P.; Chen, Y.G. An Analysis on Fretting Wear of Stay Cable with Parallel Steel Wire Bundle. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2023, 40, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, H.L.; Wang, B.; Wang, D.G.; Ye, J.H.; Li, C.C.; Sun, Y.W.; Shen, X.M.; Zhang, D.K. Tribo-Corrosion-Fatigue Behaviors of the Parallel Wires of Main Cable in the Suspension Bridge. Wear 2024, 548–549, 205363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JT/T 775-2010; Stay Cable of Parallel Steel Wires for Large-Span Cable-Stayed Bridge. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB 50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Ma, Y.F.; Wu, X.F.; Peng, A.Y.; Lu, B.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.R. Stress Distribution Characteristic of Corrosion-Damaged Parallel Steel Wire Suspender. China Sci. Pap. 2023, 18, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, F.; Qi, S.K.; Zou, Y.Q.; Lin, C.K.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H.J. Experimental Study on Degradation of Mechanical Properties of Corroded High Strength Steel Wire. Eng. Mech. 2020, 37, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.X.; Liu, F.R.; Zhu, S.C.; Huang, F.W. Experimental Study of Fatigue Performance Optimization for Steel Strand Cables. World Bridge 2020, 48, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Miao, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, X.L. Corrosion Characteristics and Damage Constitutive Model of Galvanized Steel Wires for Bridge Cables. Structures 2021, 34, 3414–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Bai, N.N.; Lan, C.M.; Li, H.; Spencer, B.F. Predictive Model for Fatigue Life in Parallel-Wire Stay Cables Considering Corrosion Variability. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2023, 19, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Cai, Z. Ultrasonic Surface Rolling Process Enhances Fretting Fatigue Resistance of Martensitic Steel via Nanolamellar Structure Design. Tribol. Int. 2025, 211, 110912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X. Achieving Ultrahigh Strength and Uniform Elongation in a Low Carbon Low Alloyed Dual-Phase Steel via Architecting Heterogeneous Structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 941, 148614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaoui, E.H.; Mansour, A.A.; Allah, A.E.A.; Nadia, A.; Messali, M.; Bazzi, L.; Ramli, Y.; Salghi, R. Electrochemical and DFTB Investigations of Pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Trione Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for N80 Carbon Steel in 3.5% NaCl. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1346, 143194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, F.A.E.; Valencia, M.H.; López, B.V.; López, J.B.; Martinez, L.L.L. Electrochemical and Computational Study of the Epicatechin-3-Gallate Isolated from Green Tea Leaves as a Corrosion Inhibitor for 1018 Carbon Steel in Sulfuric Acid. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2025, 20, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, R.; Khayati, R.G.; Darezereshki, E. Electrochemical-Surface and Theoretical Investigations of the Interactions of Salvia Officinalis Extract as a Green and Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitor and Zinc Cations for Corrosion Protection of Carbon Steel in Sodium Chloride Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 433, 127962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.T.; Wei, J.; Dong, J.H.; Ke, W.; Wang, T.G.; Fan, Q.X. Corrosion Inhibition Behavior of 1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid on 20SiMn Steel in Simulated Concrete Pore Solution Containing Cl−. Acta Metall. Sin. 2020, 56, 898–908. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Gao, X.; He, W.; Chen, T.; Ma, H.Y. 1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid (HEDP)-Zn Complex Thin Films for the Corrosion Protection of Cold-Rolled Steel (CRS). Corros. Sci. 2019, 157, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Li, M.D.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhang, H. Application of 1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid in Boiler Water for Industrial Boilers. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A.; Turgoose, S. Inhibition by Zinc–1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid Mixtures of Galvanic Corrosion of Mild Steel Coupled to Copper in Dilute Chloride Solution and Effect of Benzotriazole. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.T.; Xu, H.W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tan, X.J. Cerium chloride and L-arginine as effective hybrid corrosion inhibitor for 5052 aluminum alloy in 3.5% NaCl solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 221226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, S. Reusing an expired drug as a sustainable corrosion inhibitor for bronze in 3.5% NaCl and simulated acid rain solutions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Badaoui, H.; Ait Mansour, A.; Nchioua, I.; Arrousse, N.; Messali, M.; Bazzi, L.; Salghi, R.; Ramli, Y.; Hammouti, B. A comprehensive study on the corrosion inhibition of N80 carbon steel by acetamide derivatives in a 3.5% NaCl corrosive medium utilizing electrochemical methods and the DFTB approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Elements | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.88% | 1.03% | 0.40% | 0.012% | 0.007% | 0.23% |
| Specimen ID | C (molL−1) | σ (kN) | V′ (gcm−2h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-01 | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.93 |
| N-02 | 1.01 | ||
| T-01 | 0.04 | 0.0 | 0.65 |
| T-02 | 0.70 | ||
| T-03 | 0.08 | 0.0 | 0.58 |
| T-04 | 0.61 | ||
| T-05 | 0.12 | 0.0 | 0.57 |
| T-06 | 0.59 | ||
| N-03 | 0.00 | 7.5 | 1.61 |
| N-04 | 1.59 | ||
| T-07 | 0.04 | 7.5 | 1.22 |
| T-08 | 1.25 | ||
| T-09 | 0.08 | 7.5 | 1.05 |
| T-10 | 1.09 | ||
| T-11 | 0.12 | 7.5 | 1.00 |
| T-12 | 1.01 | ||
| N-05 | 0.00 | 15.0 | 2.33 |
| N-06 | 2.31 | ||
| T-13 | 0.04 | 15.0 | 2.01 |
| T-14 | 1.93 | ||
| T-15 | 0.08 | 15.0 | 1.80 |
| T-16 | 1.81 | ||
| T-17 | 0.12 | 15.0 | 1.76 |
| T-18 | 1.79 |
| Specimen ID | C (molL−1) | σ (kN) | V′ (gcm−2 h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-07 | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.90 |
| N-08 | 0.92 | ||
| T-19 | 0.04 | 0.0 | 0.73 |
| T-20 | 0.75 | ||
| T-21 | 0.08 | 0.0 | 0.69 |
| T-22 | 0.60 | ||
| T-23 | 0.12 | 0.0 | 0.51 |
| T-24 | 0.68 | ||
| N-09 | 0.00 | 7.5 | 1.46 |
| N-10 | 1.41 | ||
| T-25 | 0.04 | 7.5 | 1.22 |
| T-26 | 1.18 | ||
| T-27 | 0.08 | 7.5 | 1.06 |
| T-28 | 1.05 | ||
| T-29 | 0.12 | 7.5 | 1.00 |
| T-30 | 0.99 | ||
| N-11 | 0.00 | 15.0 | 2.05 |
| N-12 | 2.10 | ||
| T-31 | 0.04 | 15.0 | 1.76 |
| T-32 | 1.84 | ||
| T-33 | 0.08 | 15.0 | 1.83 |
| T-34 | 1.70 | ||
| T-35 | 0.12 | 15.0 | 1.68 |
| T-36 | 1.75 |
| Specimen ID | Inhibition Stage | Major Elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Fe | O | C | P | Na | Cl | ||
| T-09 | 1 | 52.3 | 3.8 | 28.7 | 9.6 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| N-04 | 35.4 | 21.6 | 25.9 | 9.2 | 0.0 | 3.4 | 4.5 | |
| T-27 | 2 | 22.8 | 26.7 | 29.4 | 10.2 | 1.3 | 4.4 | 5.5 |
| N-09 | 6.9 | 45.2 | 28.1 | 8.4 | 0.00 | 5.7 | 8.8 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, B.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, G. Study on the Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism of HEDP and Mechanical Performance Degradation of HSGPSW Under Tensile Stress. Coatings 2025, 15, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091020
Lin B, Yang M, Liu X, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Xu G. Study on the Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism of HEDP and Mechanical Performance Degradation of HSGPSW Under Tensile Stress. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091020
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Baoyao, Mingchun Yang, Xinyu Liu, Zian Zhang, Hao Zhang, Zengli Liu, Yanlei Zhou, and Gangnian Xu. 2025. "Study on the Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism of HEDP and Mechanical Performance Degradation of HSGPSW Under Tensile Stress" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091020
APA StyleLin, B., Yang, M., Liu, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, Z., Zhou, Y., & Xu, G. (2025). Study on the Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism of HEDP and Mechanical Performance Degradation of HSGPSW Under Tensile Stress. Coatings, 15(9), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091020






