Pulsed Current Electrodeposition of Gold–Copper Alloys Using a Low-Cyanide Electrolyte
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrochemical Setup
2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements
2.3. Preparation of Electrolytes
2.4. Electrodeposition Procedure
2.5. Coating Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
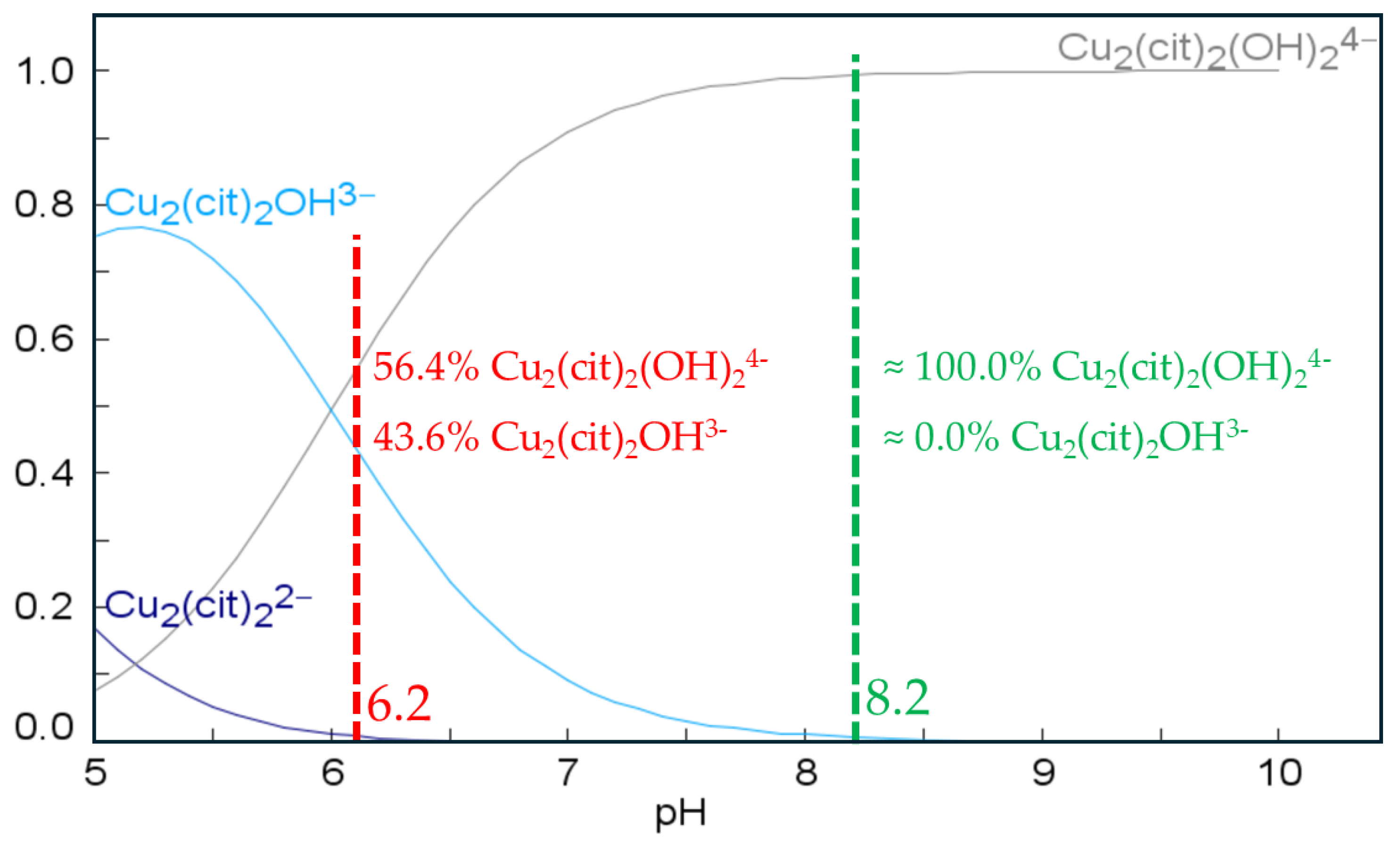
3.1. Electrolyte Composition
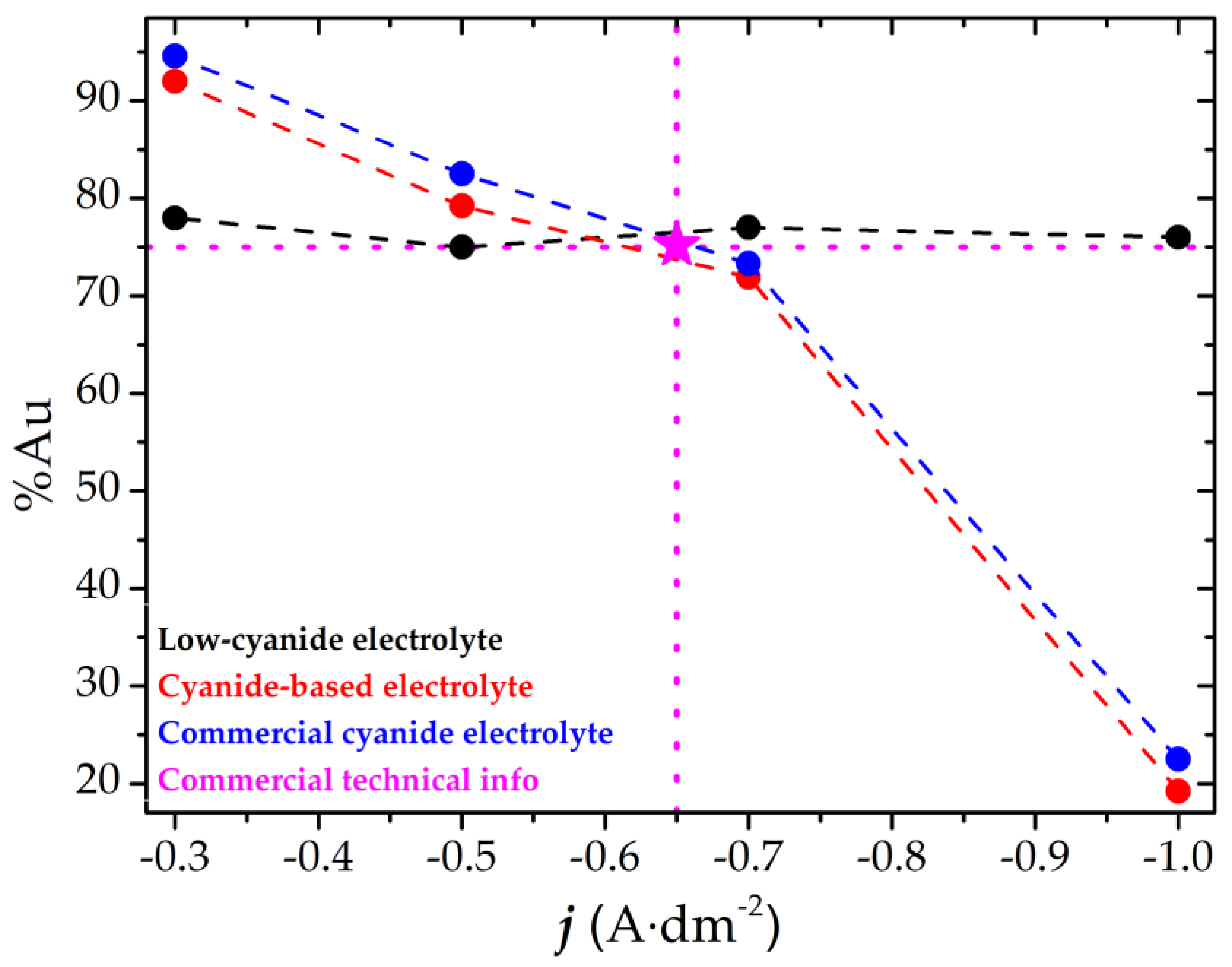
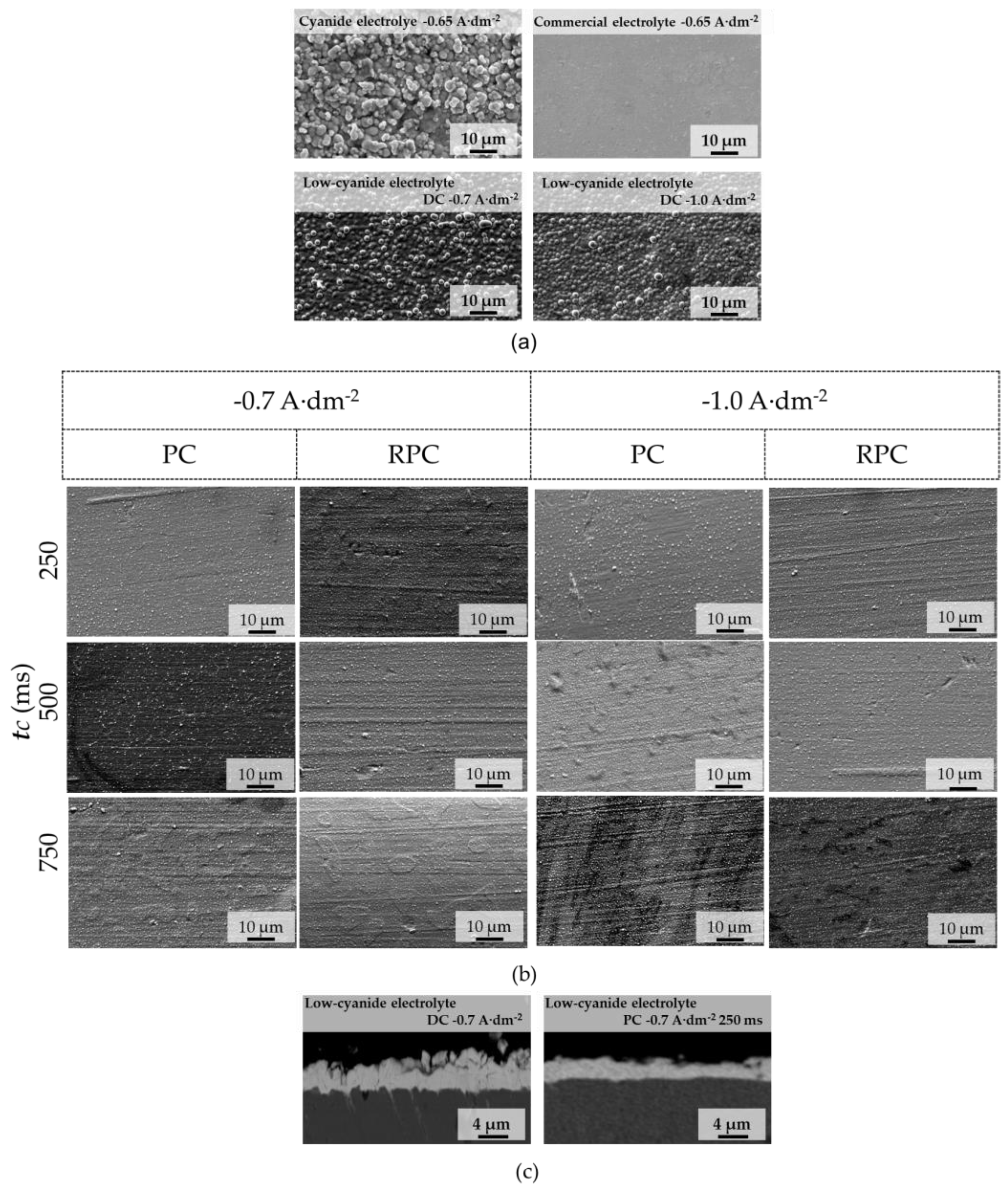
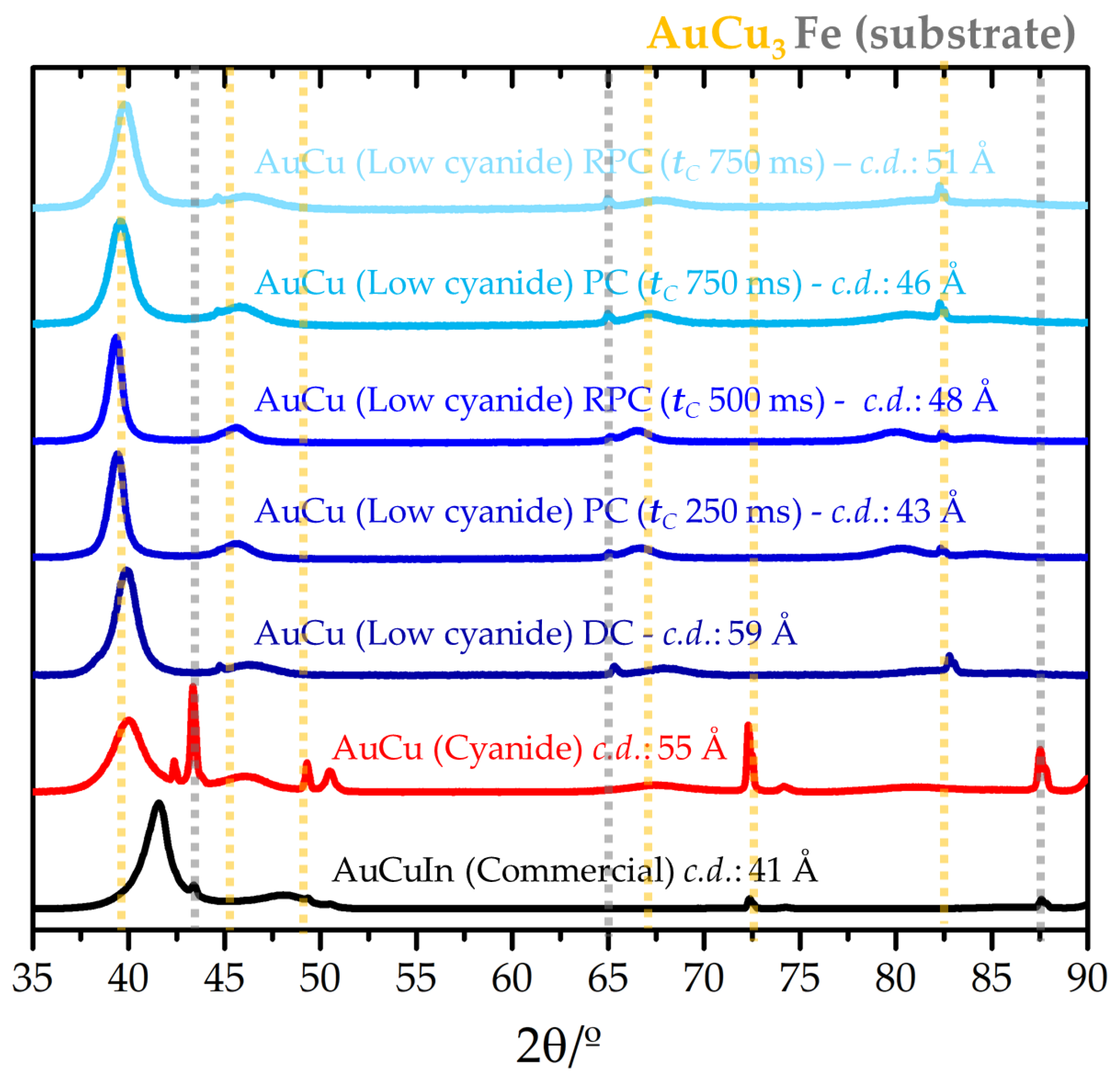
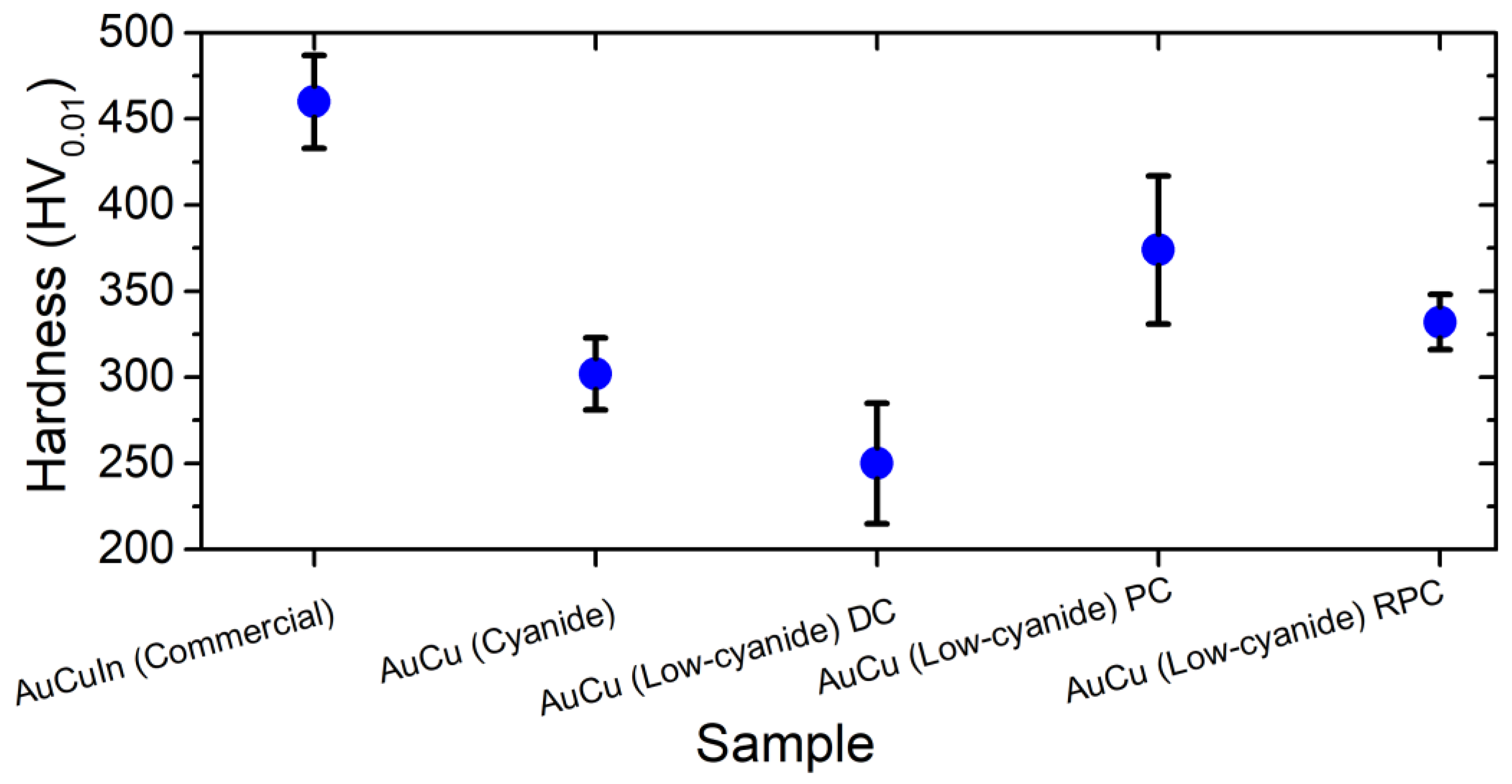
3.2. Coating Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| c.d. | Crystal Domain |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| DC | Direct Current |
| EDX | Energy-Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| FESEM | Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| Kt | Karat |
| OCV | Open Circuit Voltage |
| PC | Pulsed Current |
| RP | Polarization Resistance |
| RPC | Reverse Pulsed Current |
| SCE | Standard Calomel Electrode |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
Appendix A



References
- Giurlani, W.; Zangari, G.; Gambinossi, F.; Passaponti, M.; Salvietti, E.; Di Benedetto, F.; Caporali, S.; Innocenti, M. Electroplating for Decorative Applications: Recent Trends in Research and Development. Coatings 2018, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ren, P.; Meng, H. Electrodeposition of Nanocrystalline Au-Cu Alloy Coatings with High Hardness and Corrosion Resistance for Electronic Contact Application. Mater. Lett. 2023, 330, 133320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhong, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. The Effect of Complexing Agents on the Oriented Growth of Electrodeposited Microcrystalline Cuprous Oxide Film. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 2561–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, A. Gold plating in the electronics industry. Gold Bull. 1981, 14, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.; Kohl, P.A. Electrochemical Study of the Gold Thiosulfate Reduction. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Jeong, E.-S.; Lee, K.-T.; Jin, S.; Lee, W.Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, M.H. On the Role of Complexing Agents in Co-Electrodeposition of SnAg Alloy with Uniform Composition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 166, 107751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatherley, P.G.; Watkins, K.G.; McMahon, M. The Properties of Copper Cyanide Electrolytes: A Comparison of Sodium and Potassium Formulations. Trans. IMF 1992, 70, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, P.A. Electrodeposition of Gold. In Modern Electroplating, 5th ed.; Schlesinger, M., Paunovic, M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Stratmann, M. (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Electrochemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, J. OMEGAL 180 CDF. Available online: https://macdermidenthone.com/solutions/precious-metals/gold/omegal-180-cdf-cadmium-free-gold-copper-indium-process (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Dimitrijević, S.B.; Rajčić-Vujasinović, M.M.; Jančić-Hajneman, R.M.; Bajat, J.B.; Trujić, V.K.; Trifunović, D.D. Temperature effect on decorative gold coatings obtained from electrolyte based on mercaptotriazole—Comparison with cyanide. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 105, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M.A. Deep eutectic solvents and applications in electrochemical sensing. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosu, O.; Bârsan, M.M.; Cristea, C.; Săndulescu, R.; Brett, C.M.A. Nanostructured electropolymerized poly(methylene blue) films from deep eutectic solvents. Optimization and characterization. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosu, O.; Barsan, M.M.; Cristea, C.; Săndulescu, R.; Brett, C.M. Nanocomposites based on carbon nanotubes and redox-active polymers synthesized in a deep eutectic solvent as a new electrochemical sensing platform. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3919–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.A.; Liew, M.-J.; Roy, S. Electrodeposition of gold from a thiosulfate-sulfite bath for microelectronic applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, C104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okinaka, Y.; Hoshino, M. Some recent topics in gold plating for electronics applications. Gold Bull. 1998, 31, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.A. Gold electrodeposition for microelectronic, optoelectronic and microsystem applications. Gold Bull. 2007, 40, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, H.; Hagiwara, K. Fabrication of gold bumps using gold sulfite plating. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, T.; Kato, M.; Sato, J.; Yoshizawa, K.; Homma, T.; Okinaka, Y.; Yoshioka, O. Mechanism of sulfur inclusion in soft gold electrodeposited from the thiosulfate-sulfite bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, C659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-Q.; Yu, H.-H.; Jin, L.; Yang, F.-Z.; Wu, D.-Y.; Zhan, D.-P.; Tian, Z.-Q. Insights into the effects of chloride ions on cyanide-free gold electrodeposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 102514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, H.; Kagaya, Y. Gold plating using the disulfiteaurate complex. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, L135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, T.; Okinaka, Y.; Sasano, J.; Kato, M. Development of new electrolytic and electroless gold plating processes for electronics applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2006, 7, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Okinaka, Y. Some recent developments in non-cyanide gold plating for electronics applications. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijević, S.; Trujić, V.K.; Rajčić-Vujasinović, M.M. Development of new noncyanide technology in gold plating. In Proceedings of the 14th International Research/Expert Conference—TMT 2010, Mediterranean Cruise, 1–18 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrijević, S.; Mirić, M.; Vl, K.; Madić, B.; Dimitrijević, S. Recovery of precious (Au, Ag, Pd, Pt) and other metals by e-scrap processing. Izv. Khim. Bulg. Akad. Nauk. 2014, 46, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnova, O.; Brovin, A.; Pilipenko, A.; Zhelavska, Y. Studying the kinetics of electrode reactions on copper, silver and gold in acid thiourea-citrate electrolytes. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 6, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapson, W.S.; Groenewald, T. Gold Usage; Academic Press: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Satpathy, B.; Kumari, A.; Das, K.; Das, S. Controlled modulation of coating morphology, mechanical properties and anti-tarnishing response of nanocrystalline Au-Cu alloy coatings electrodeposited from a thiourea (TU)-based non-toxic cyanide-free bath: Effect of current density variation. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O.; Nikonov, A.; Pylypenko, O.; Brovin, A. Thiocarbamide-citrate electrolytes as an alternative to cyanide electrolytes in solving the problems of environmental protection and prevention of emergency situations. Mater. Sci. Forum 2021, 1038, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolati, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Ahmadi, M.R. An electrochemical study of Au–Ni alloy electrodeposition from cyanide–citrate electrolytes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 577, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.A.; Russell, A.E.; Roy, S. The development of a stable citrate electrolyte for the electrodeposition of copper–nickel alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.Q.; Han, K.Q.; Yu, M.H.; Zhang, C.Y. Effect of sodium citrate on electrochemical behaviour of copper in acid bath. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 913, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigos, A.; Wołowicz, M.; Janusz-Skuza, M.; Starowicz, Z.; Szczerba, M.J.; Bogucki, R.; Beltowska-Lehman, E. Citrate-based baths for electrodeposition of nanocrystalline nickel coatings with enhanced hardness. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 850, 156857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Hara, A.; Bigos, A.; Ozga, P. Electrodeposition of Zn-Mn-Mo layers from citrate-based aqueous electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 202, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapontseva, Y.S.; Kublanovsky, V.S.; Vyshnevskyi, O.A. Electrodeposition of CoMoRe alloys from a citrate electrolyte. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 766, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umicore. AURUNA® 559 Fine Gold Electrolyte. Available online: https://mds.umicore.com/en/electroplating/products/product-finder/auruna-559-fine-gold-electrolyte (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Chandrasekar, M.S.; Pushpavanam, M. Pulse and pulse reverse plating—Conceptual, advantages and applications. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, F.; Oldham, K.B. A modification of the Stern—Geary linear polarization equation. Corros. Sci. 1971, 11, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojo, M.; Stanković, V. Electrochemical deposition of gold in citrate solution containing thallium. Acta Chim. Slov. 2008, 55, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Park, C.; Kim, C.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, J.-H. Cyclic voltammetry studies of copper, tin and zinc electrodeposition in a citrate complex system for CZTS solar cell application. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigdomenech, “SPANA”, Chimera: 3. June 2006. Available online: https://www.amphos21.com/producto/chimera-4-2/ (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Miller, B.; Menezes Affonso, S. Conductivity and other transport parameters in ammonium citrate gold baths. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1976, 123, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisner, P.; Fredenberg, M.; Belov, I. Pulse and pulse reverse plating of copper from acid sulphate solutions. Trans. IMF 2010, 88, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Honma, H. Advanced copper electroplating for application of electronics. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 169–170, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, J.P.G. Electroplating, electrode kinetics and electrocrystallisation. Trans. IMF 2010, 88, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, E.; Durut, F.; Botrel, R.; Theobald, M.; Legaie, O.; Popa, I.; Vignal, V. Influence of the electrochemical parameters on the properties of electroplated Au-Cu alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, D223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yoshiba, M.; Nagoshi, T.; Chang, T.-F.M.; Yamane, D.; Machida, K.; Masu, K.; Sone, M. High-strength electroplated Au–Cu alloys as micro-components in MEMS devices. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, D244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, A.; Kiss, L.F.; Demirel, A.L.; Varga, L.K.; Mikó, A. Tuning grain size, morphology, hardness and magnetic property of electrodeposited nickel with a single multifunctional additive. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 267, 124681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Kalscheuer, C.; Hassanzadegan Aghdam, P. Impact resistance and properties of (Cr,Al,Si)N coatings deposited by gas flow sputtering with pulsed DC supply. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshandeh, R.; Akhbarizadeh, A.; Araghi, A. Investigating the tribochemical behavior of the hard chromium coating deposited via the electroplating method with direct and pulse current on copper substrate. Metall. Res. Technol. 2015, 112, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.; Zaroog, O.S. Copper Alloys: Corrosion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-803581-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Shiraishi, T.; Takuma, Y.; Hisatsune, K. Corrosion resistance evaluation of Pd-free Ag–Au–Pt–Cu dental alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Species Au(I) | log β | E0 (V) vs. NHE | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au(CN)2− | 38.7 | −0.595 | [12] |
| Au(S2O3)(SO3)25− | 30.8 | — | [13] |
| Au(S2O3)(SO3)23− | 27.1 | — | [14] |
| Au(SO3)23− | 26.8 | 0.111 | [15] |
| Au(S2O3)23− | 26.1 | 0.153 | [12] |
| Au(SCN)2− | 17.5 | 0.662 | [12] |
| AuCl2− | 9.2 | 1.154 | [12] |
| Technique | j (A·dm−2) | jC (A·dm−2) | tC (ms) | jA (A·dm−2) | tA (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 0.7 | 2.8 | 250 | 0 | 750 |
| 1.4 | 500 | 500 | |||
| 0.9 | 750 | 250 | |||
| 1.0 | 4.0 | 250 | 750 | ||
| 2.0 | 500 | 500 | |||
| 1.3 | 750 | 250 | |||
| RPC | 0.7 | 2.8 | 250 | 0.56 | 421 |
| 1.4 | 500 | 0.28 | 362 | ||
| 0.9 | 750 | 0.18 | 239 | ||
| 1.0 | 4.0 | 250 | 0.80 | 412 | |
| 2.0 | 500 | 0.40 | 341 | ||
| 1.3 | 750 | 0.26 | 221 |
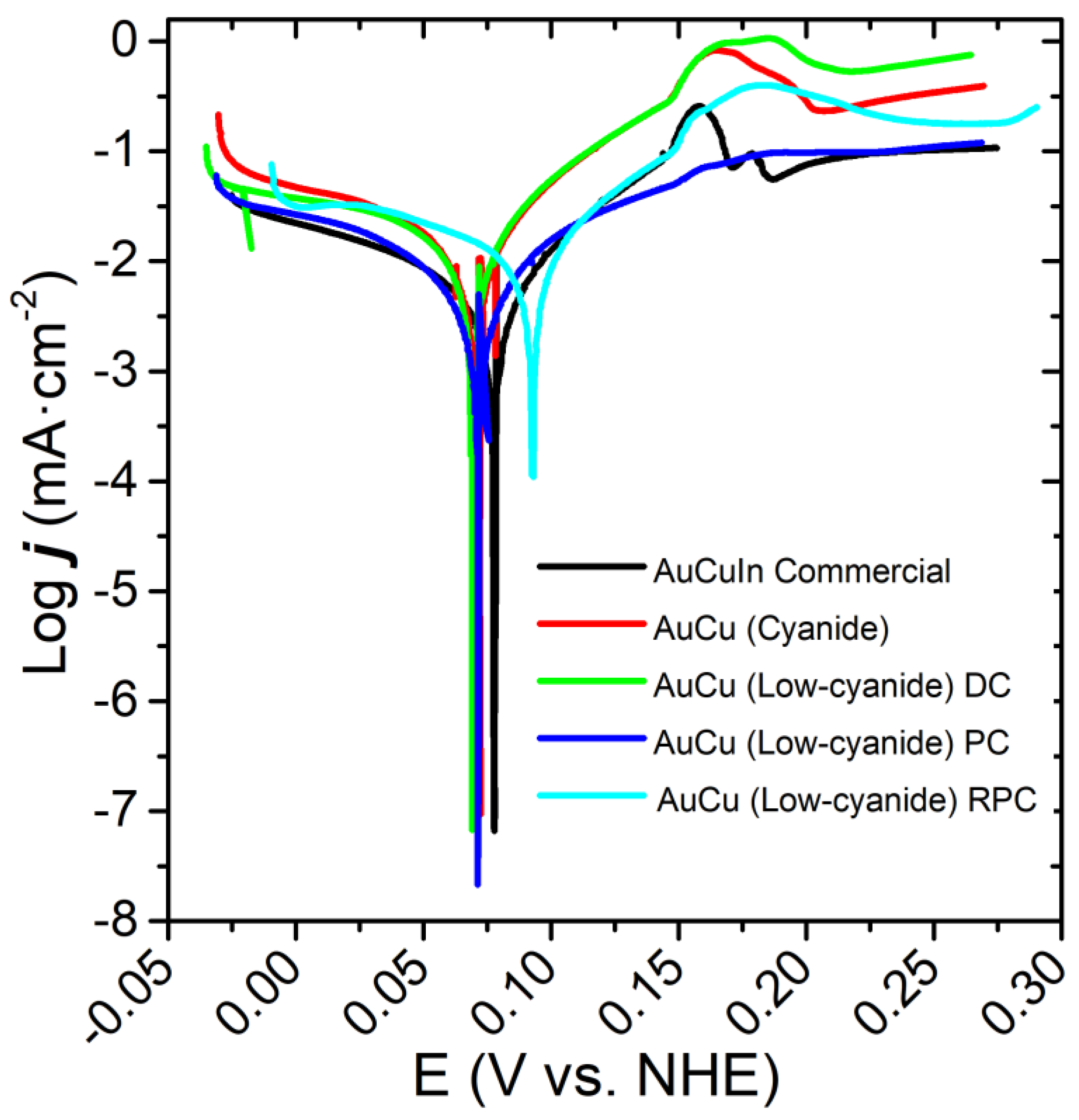
| Sample | ECORR (mV vs. NHE) | jCORR (µA·cm−2) | RP (Ω·cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial AuCuIn | 74.0 ± 20.5 | 4.8 ± 2.6 | 4349 ± 130 |
| AuCu (Cyanide) | 74.7 ± 5.0 | 16.1 ± 1.8 | 732 ± 102 |
| AuCu (Low-cyanide) DC | 70.5 ± 0.8 | 26.8 ± 2.8 | 624 ± 36 |
| AuCu (Low-cyanide) PC | 78.5 ± 5.1 | 4.1 ± 0.0 | 4061 ± 114 |
| AuCu (Low-cyanide) RPC | 83.9 ± 14.4 | 7.8 ± 1.7 | 1854 ± 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amazian, M.; Andreu, T.; Sarret, M. Pulsed Current Electrodeposition of Gold–Copper Alloys Using a Low-Cyanide Electrolyte. Coatings 2025, 15, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070778
Amazian M, Andreu T, Sarret M. Pulsed Current Electrodeposition of Gold–Copper Alloys Using a Low-Cyanide Electrolyte. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070778
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmazian, Mohamed, Teresa Andreu, and Maria Sarret. 2025. "Pulsed Current Electrodeposition of Gold–Copper Alloys Using a Low-Cyanide Electrolyte" Coatings 15, no. 7: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070778
APA StyleAmazian, M., Andreu, T., & Sarret, M. (2025). Pulsed Current Electrodeposition of Gold–Copper Alloys Using a Low-Cyanide Electrolyte. Coatings, 15(7), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070778







