Influence of Alkaline Activator Properties on Corrosion Mechanisms and Durability of Steel Reinforcement in Geopolymer Binders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
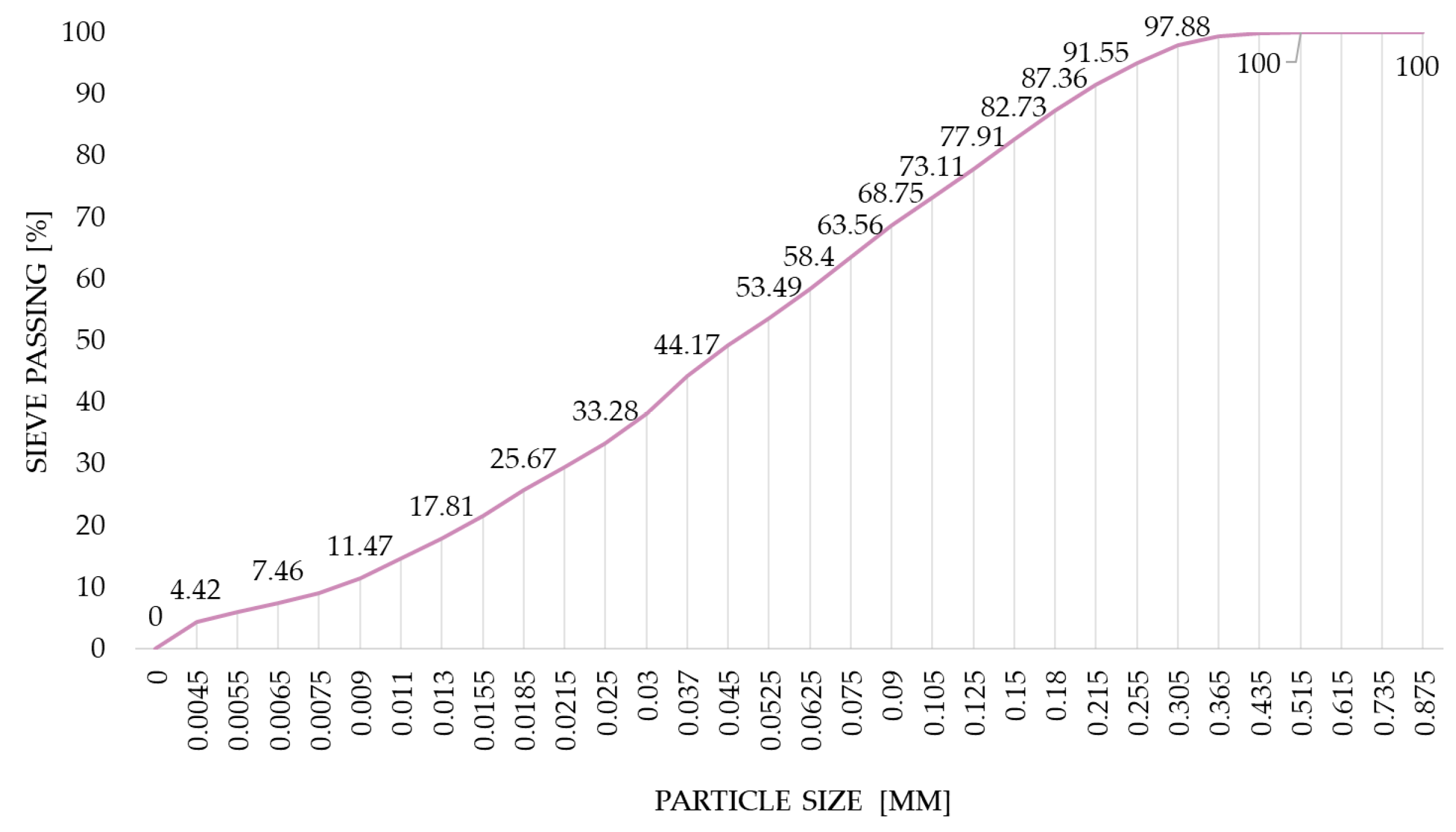
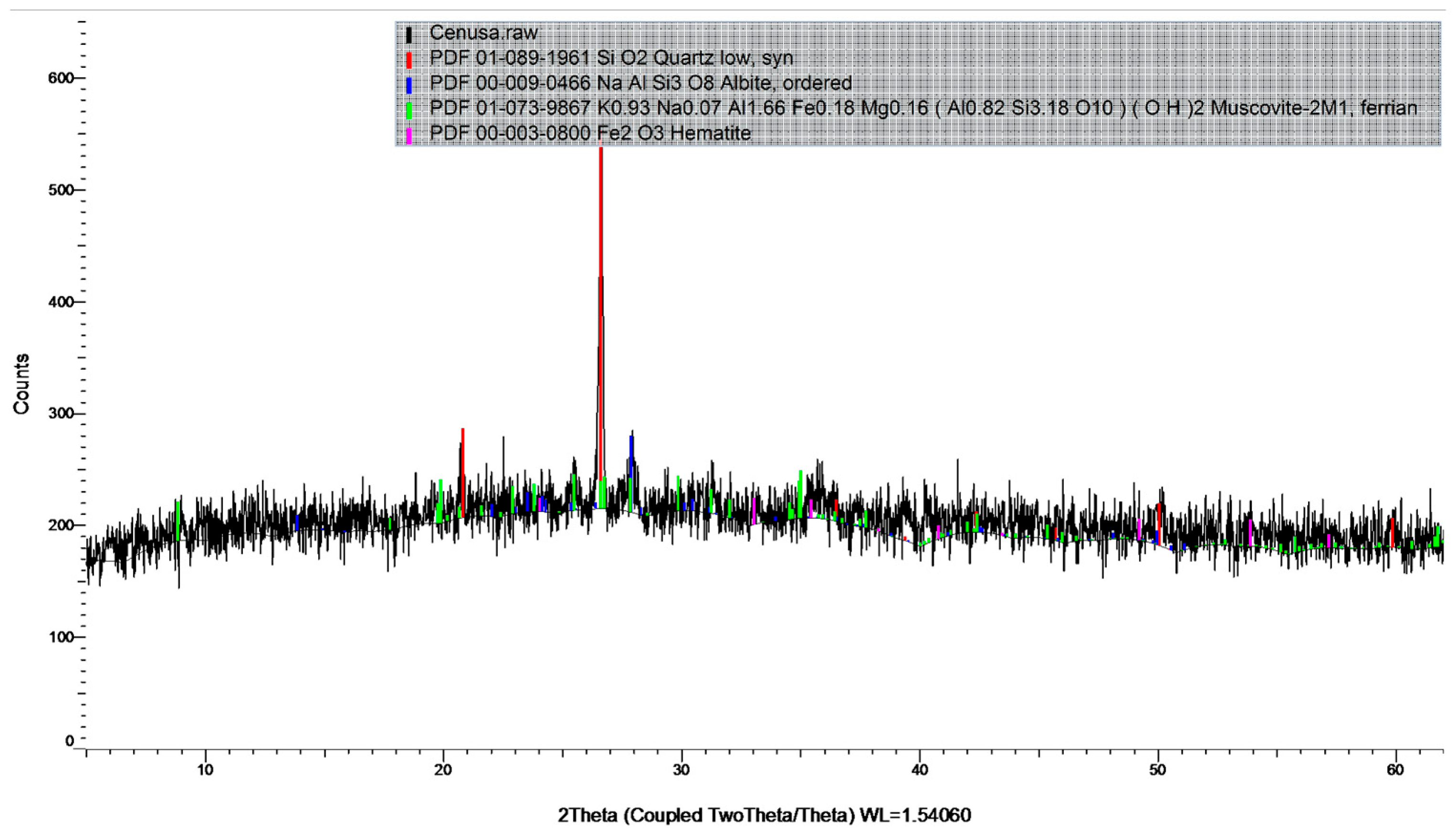
2.1. Materials
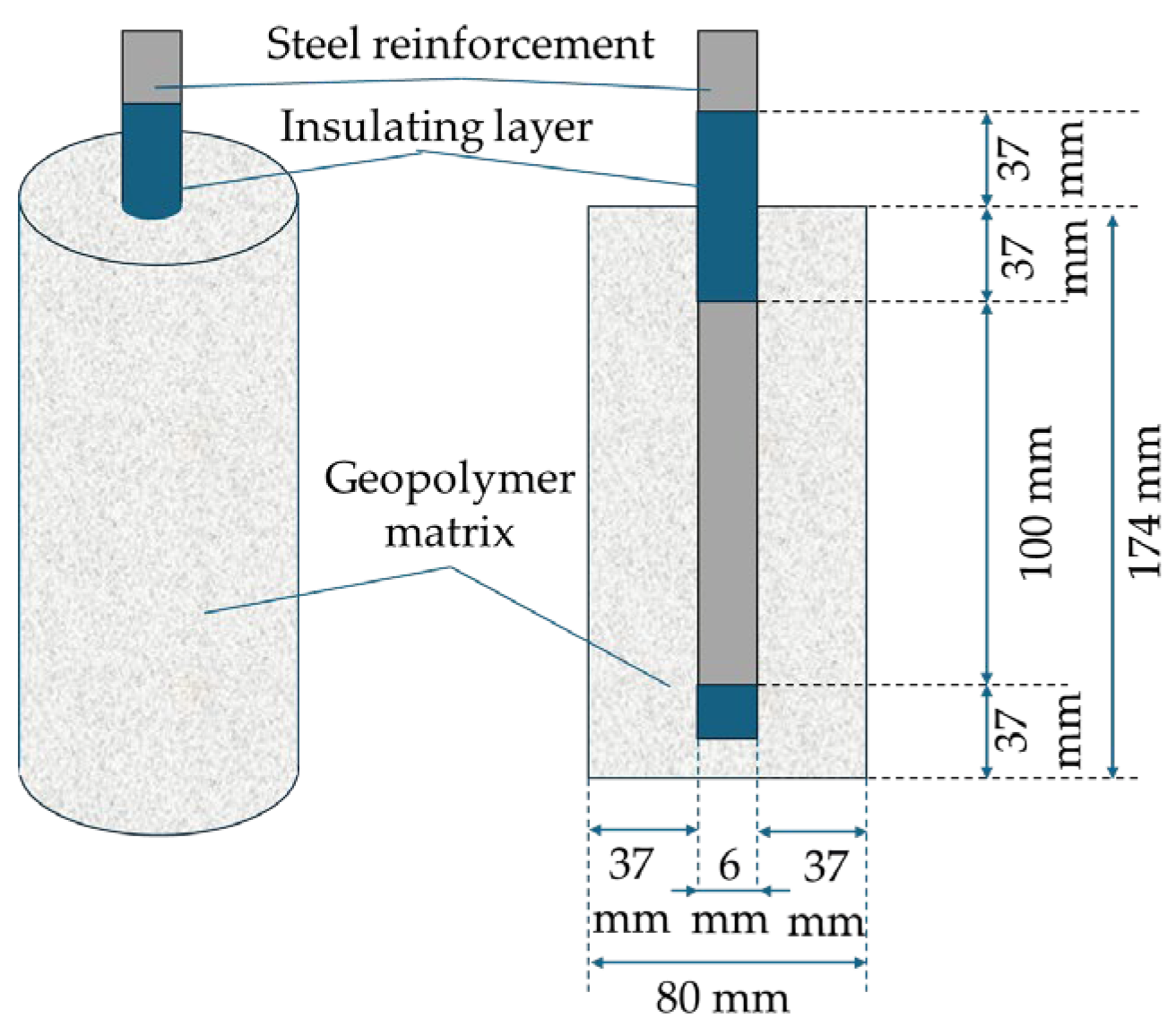
2.2. Production of the Alkali-Activated Geopolymer Binder and Sampling
2.3. Physico-Mechanical Characterization of Geopolymer Binder
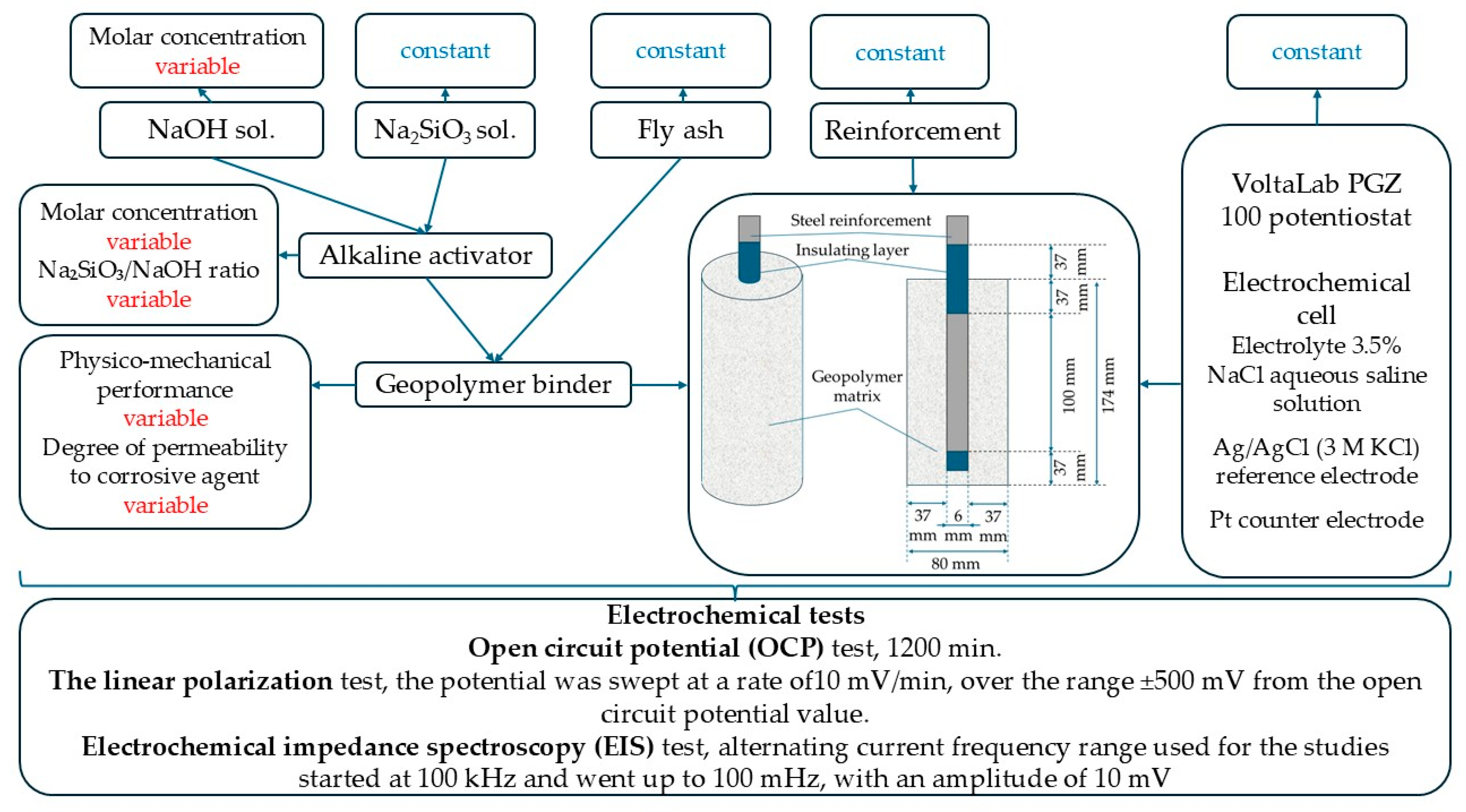
2.4. Electrochemical Analysis
- -
- Identify localized corrosion areas on the metal surface;
- -
- Detect signs of corrosion product migration into the binder adjacent to the reinforcement;
- -
- Environmental conditions and correlation with binder properties.
3. Results and Discussions
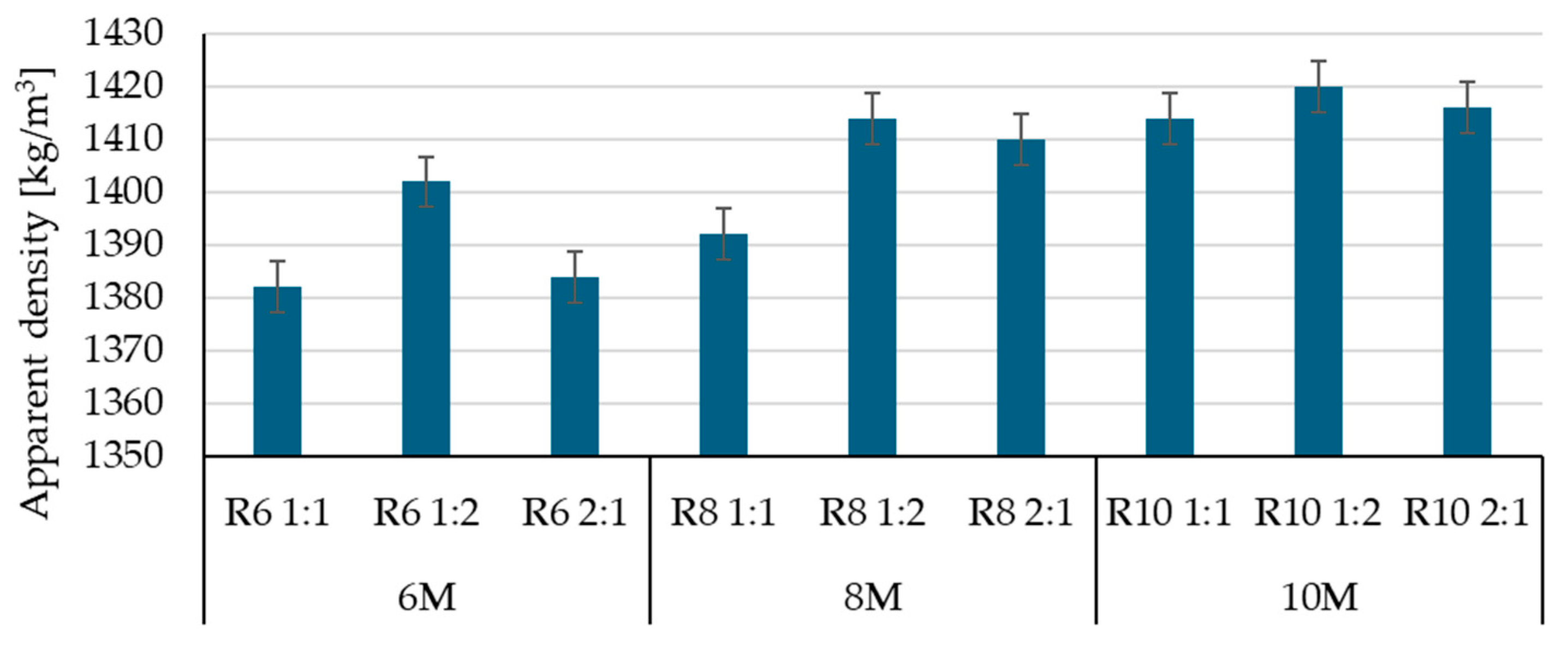
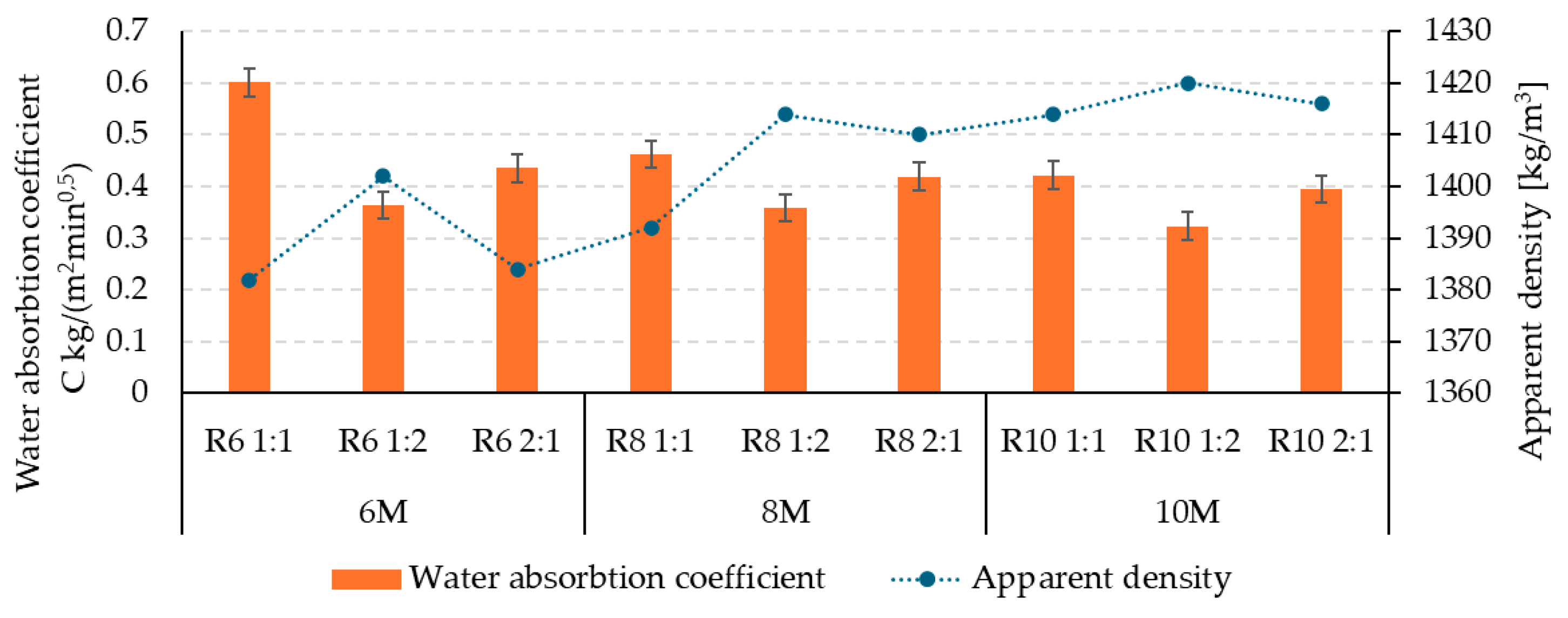
3.1. Influence of Alkaline Activator on the Physico-Mechanical Characteristics of Geopolymer Binder
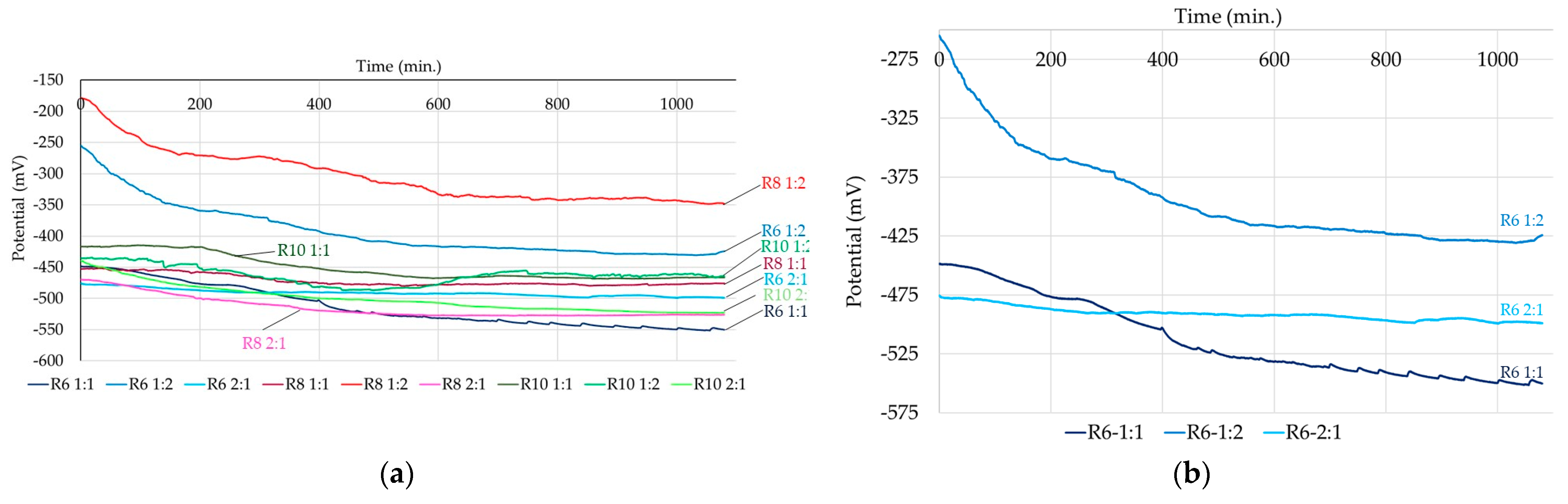
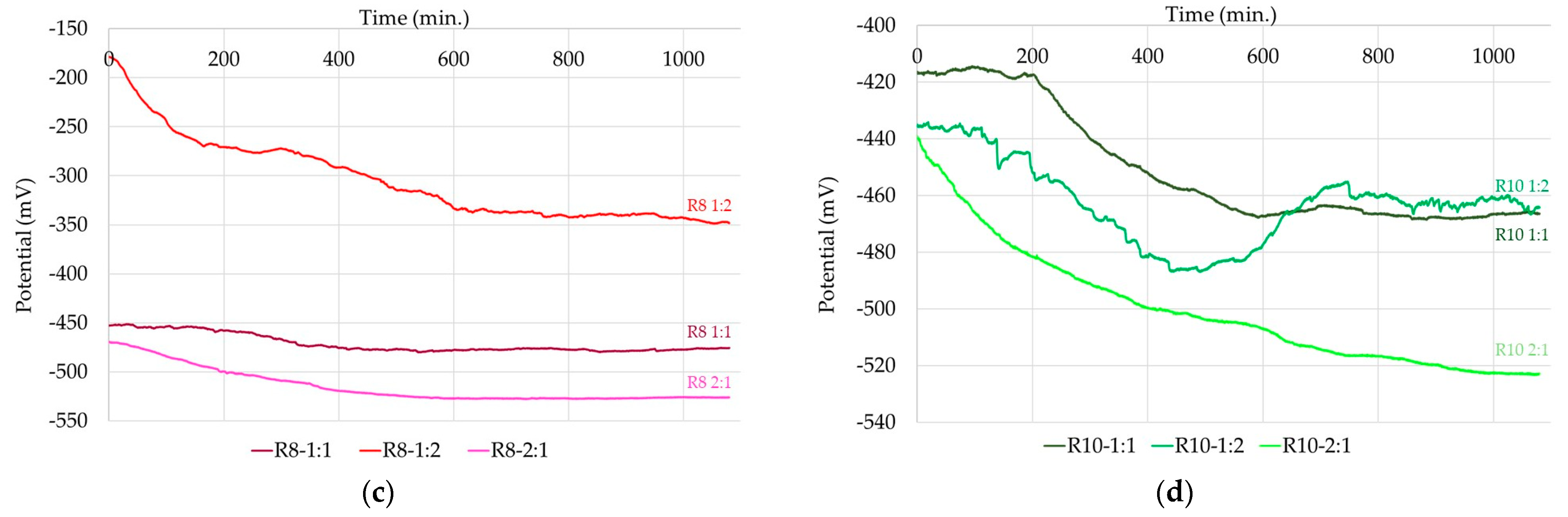
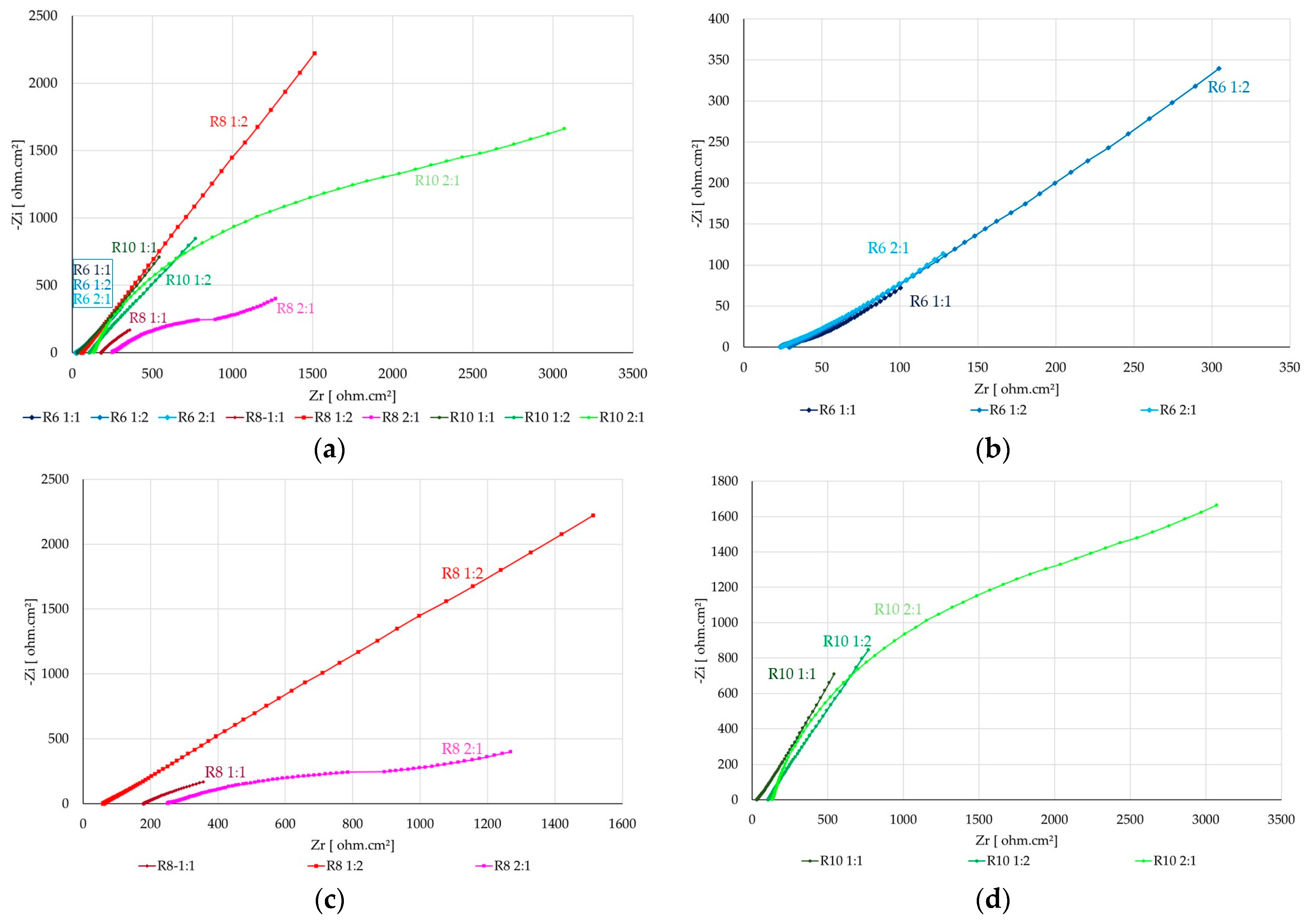
3.2. Corrosion Kinetics of Steel Reinforcement Embedded in Geopolymer Binder
- a)
- The anodic iron oxidation reaction,
- b)
- Cathodic reduction reaction of oxidizing species in the environment,
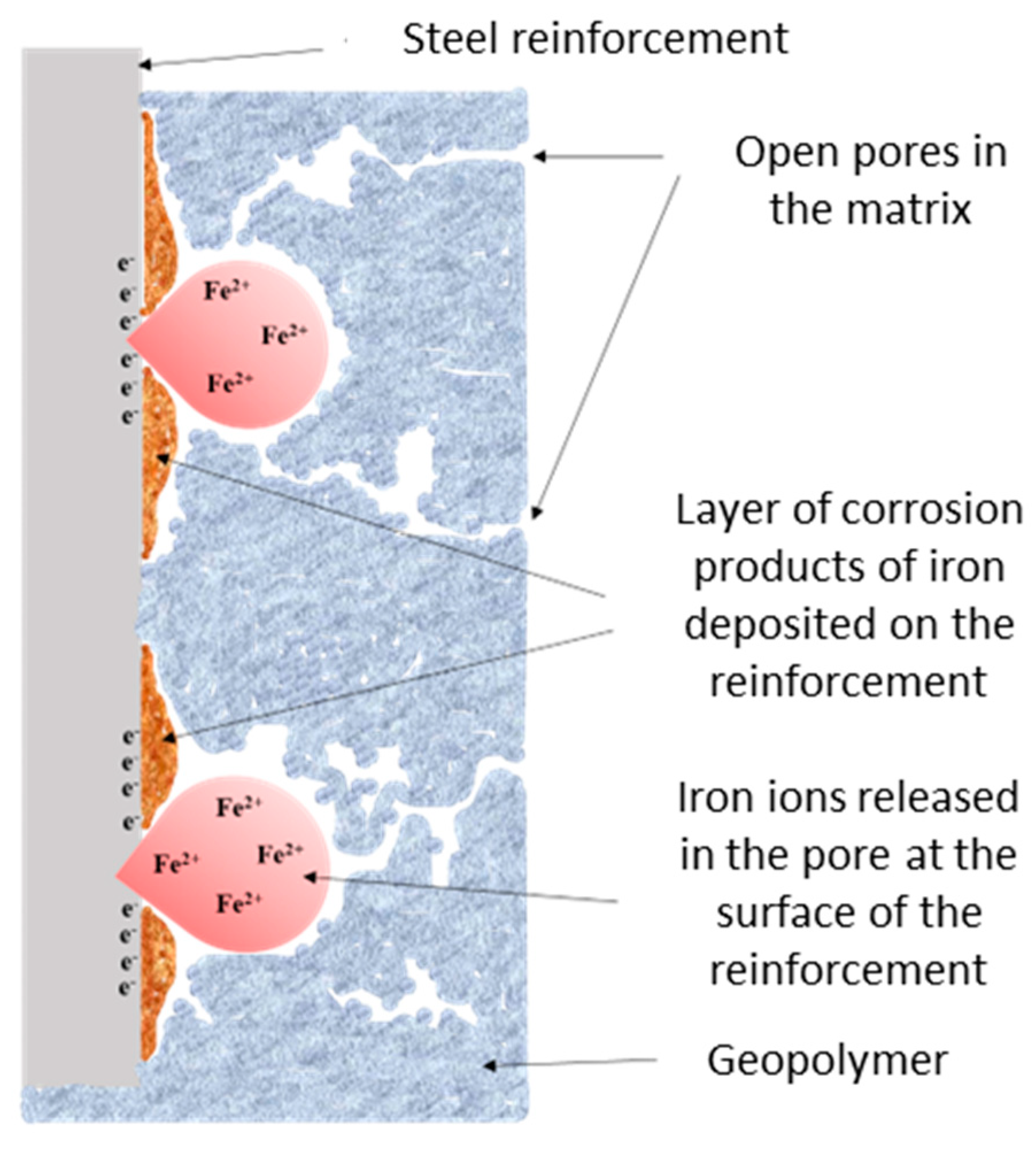
3.3. The Corrosion Mechanism of Steel Reinforcement Embedded in Geopolymer Binder
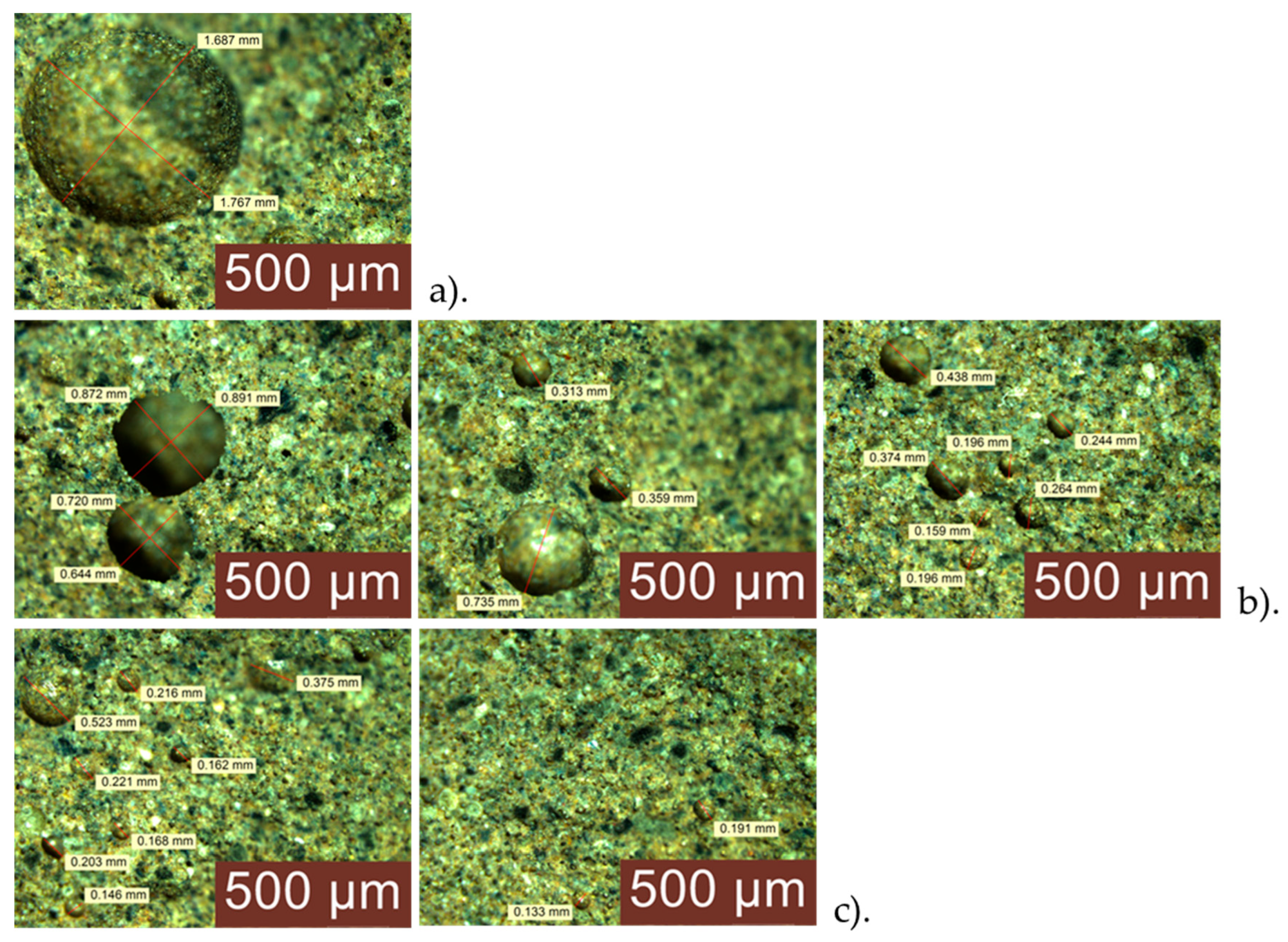
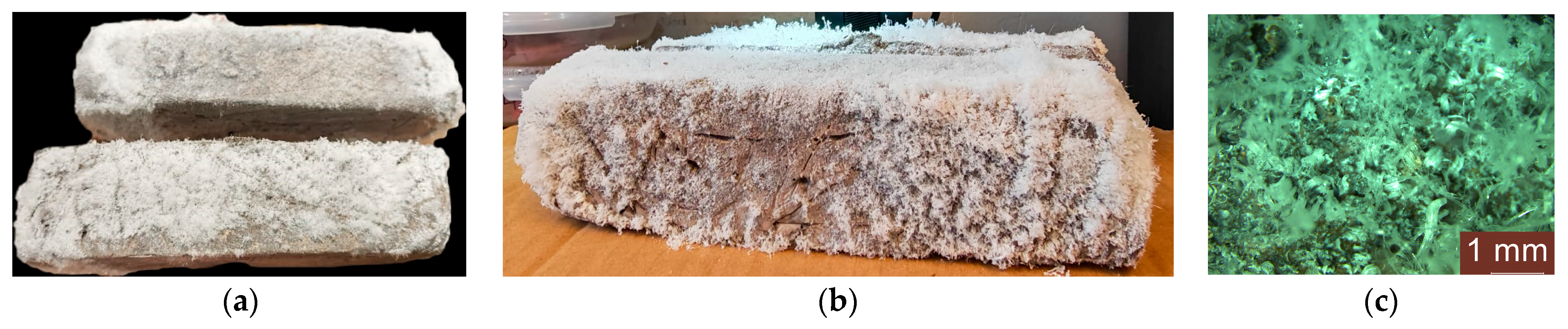
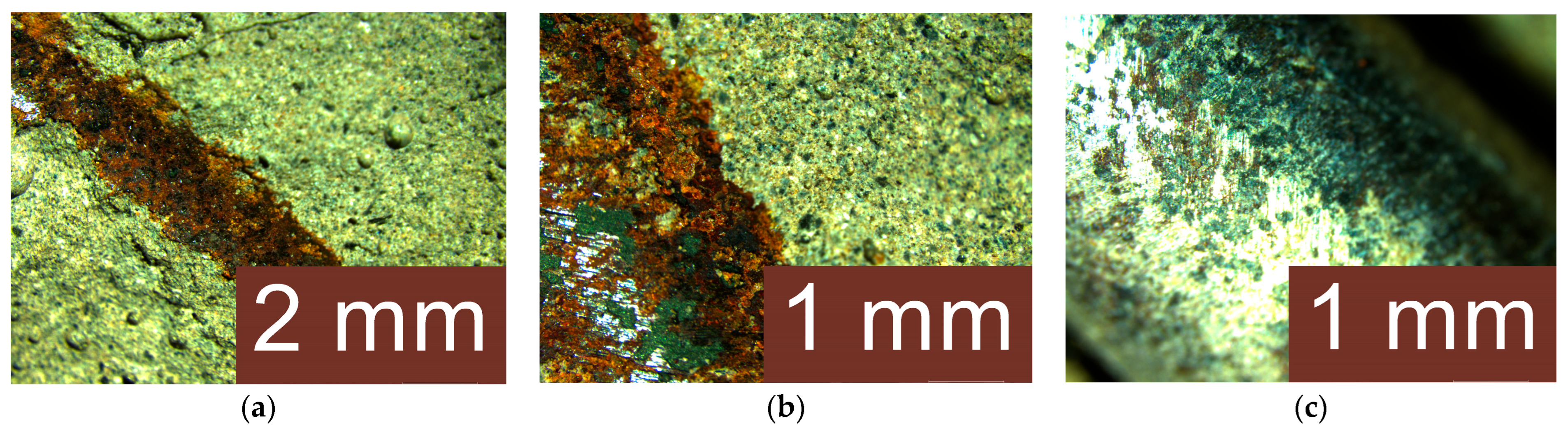
3.4. Analysis of the Geopolymer Reinforcement Interface After Experimental Testing Under Chloride-Induced Corrosive Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.; Bhuiyan, S.; Setunge, S.; Ward, L. Chloride Induced Corrosion in Different Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, E. Industrially Interesting Approaches to Low-CO2 Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C. The Greening of the Concrete Industry. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Habert, G.; Bouzidi, Y.; Jullien, A. Environmental Impact of Cement Production: Detail of the Different Processes and Cement Plant Variability Evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, L.; Dong, H.; Tan, H. Modeling of Carbon Dioxide Measurement on Cement Plants. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 610–613, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Pang, Y. CO2 Emissions Due to Cement Manufacture. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 685, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntzinger, D.N.; Eatmon, T.D. A Life-Cycle Assessment of Portland Cement Manufacturing: Comparing the Traditional Process with Alternative Technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahasenan, N.; Smith, S.; Humphreys, K. The Cement Industry and Global Climate Change: Current and Potential Future Cement Industry CO2 Emissions. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, Kyoto, Japan, 1–4 October 2002; pp. 995–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Aïtcin, P.C. Cements of Yesterday and Today: Concrete of Tomorrow. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, A.V. Obtaining and Characterization of New Materials. Materials 2021, 14, 6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, I.; Luhar, S.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Razak, R.A.; Vizureanu, P.; Sandu, A.V.; Matasaru, P.D. A State-of-the-Art Review on Innovative Geopolymer Composites Designed for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burduhos Nergis, D.D.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P. XRD and TG-DTA Study of New Alkali Activated Materials Based on Fly Ash with Sand and Glass Powder. Materials 2020, 13, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaludin, L.; Razak, R.A.; Abdullah, M.M.; Vizureanu, P.; Bras, A.; Imjai, T.; Sandu, A.V.; Abd Rahim, S.Z.; Yong, H.C. The Suitability of Photocatalyst Precursor Materials in Geopolymer Coating Applications: A Review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; d’Espinose de Lacaillerie, J.B.; Roussel, N. An Environmental Evaluation of Geopolymer Based Concrete Production: Reviewing Current Research Trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.K.; Collins, F.G. Carbon Dioxide Equivalent (CO2-e) Emissions: A Comparison between Geopolymer and OPC Cement Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.T.; Kayali, O.; Khennane, A.; Black, J. A Mix Design Procedure for Low Calcium Alkali Activated Fly Ash-Based Concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 79, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warid Wazien, A.Z.; Mustafa, M.; Abdullah, A.B.; Razak, R.A.; Rozainy, M.M.A.Z.R.; Faheem, M.; Tahir, M.; Faris, M.A. Review on Potential of Geopolymer for Concrete Repair and Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Green Design and Manufacture 2016 (IConGDM 2016), Phuket, Thailand, 7 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.K.; Maitra, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, S. Microstructural and Morphological Evolution of Fly Ash based Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, M.; Dombrowski, K.; Buchwald, A. Life-Cycle Analysis of Geopolymers. In Geopolymers: Structures, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Provis, J.L., Van Deventer, J.S.J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 194–210. [Google Scholar]
- Figiela, B.; Šimonová, H.; Korniejenko, K. State of the Art, Challenges, and Emerging Trends: Geopolymer Composite Reinforced by Dispersed Steel Fibers. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2022, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, C.; Natali, M.E.; Balbo, A.; Chiavari, C.; Zanotto, F.; Manzi, S.; Bignozzi, M.C. Corrosion Behavior of Steel in Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Mortars in the Light of Their Microstructural, Mechanical and Chemical Characterization. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 80, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Thomas, M. Service Life Prediction and Performance Testing—Current Developments and Practical Applications. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, G.K.; Buenfeld, N.R. The Presentation of the Chloride Threshold Level for Corrosion of Steel in Concrete. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, M.S.; Kupwade-Patil, K.; Elchalakani, M.; Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.G. Corrosion of Steel Bars Induced by Accelerated Carbonation in Low and High Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer Concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 61, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.W.; Setunge, S. Long Term Permeation Properties of Different Fly Ash Geopolymer Concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupwade-Patil, K.; Allouche, E.N. Examination of Chloride-Induced Corrosion in Reinforced Geopolymer Concretes. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 25, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, N.; Abraham, R.; Raj, S.D. Durability Characteristics of Steel Fibre Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ou, Z. Durability of Alkali-Activated Materials in Aggressive Environments: A Review on Recent Studies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Le, T.A.; Lee, K. Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of Sea Sand-Based Geopolymer Concrete and the Corrosion of Embedded Steel Bar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaee, M.; Castel, A. Chloride-Induced Corrosion of Reinforcement in Low-Calcium Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, W.A.; Ruiz, J.H.B.; Gómez, R.J.T. Corrosion of Reinforcing Bars Embedded in Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete Subjected to Chloride Attack. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noushini, A.; Castel, A. A Resistivity-Based Approach to Indicate Chloride Permeability of Geopolymer Concrete. In Proceedings of the Concrete Institute of Australia Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 2 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Olivia, M.; Nikraz, H. Durability of Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete in a Seawater Environment. In Proceedings of the Concrete 2011 Conference, Perth, Australia, 12 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; García-Lodeiro, I.; Palomo, A. Durability of Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Cementitious Materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupathy, K.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Law, D.W.; Setunge, S.; Keerthiprasad, H.K.; Gunasekara, C. Durability of Low-Calcium Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete Culvert in a Saline Environment. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntingh, Y. Durability and Diffusive Behaviour Evaluation of Geopolymeric Material. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, R.R.; Provis, J.L.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Pore Solution Composition and Alkali Diffusion in Inorganic Polymer Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, G.; Duan, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Improving Stabilization/Solidification of Mswi Fly Ash with Coal Gangue Based Geopolymer via Increasing Active Calcium Content. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusty, J.K.; Pradhan, B. Evaluation of Durability and Microstructure Evolution of Chloride Added Fly Ash and Fly Ash-Ggbs Based Geopolymer Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 401, 132925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradani, L.S.R.; Pradhan, B. Evaluation of Electrochemical Behavior of Steel in Pore Solution of Geopolymer Concrete and Microstructural Characteristics Under Aggressive Environment, and Correlating with Geopolymerization Process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 480, 141540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; Alarcón, M.; De Gutiérrez, R.; Delvasto, S. Corrosion Resistance in Activated Fly Ash Mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osio-Norgaard, J.; Gevaudan, J.P.; Srubar, W.V. A Review of Chloride Transport in Alkali-Activated Cement Paste, Mortar, and Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, D.M.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A.; González, J.A. A Study on the Passive State Stability of Steel Embedded in Activated Fly Ash Mortars. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.U.A. Effects of Alkali Solutions on Corrosion Durability of Geopolymer Concrete. Adv. Concr. Constr. 2014, 2, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, J.B. Chloride and Carbonation Induced Corrosion of Steel in Fly Ash Geopolymer Pore Solution. Master’s Thesis, The University of Akron, Akron, OH, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Monticelli, C.; Criado, M.; Fajardo, S.; Bastidas, J.M.; Abbottoni, M.; Balbo, A. Corrosion Behavior of a Low Ni Austenitic Stainless Steel in Carbonated Chloride-Polluted Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 55, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Monticelli, C.; Fajardo, S.; Gelli, D.; Grassi, V.; Bastidas, J.M. Organic Corrosion Inhibitor Mixtures for Reinforcing Steel Embedded in Carbonated Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittarelli, F.; Mobili, A.; Giosuè, C.; Belli, A.; Bellezze, T. Corrosion Behaviour of Bare and Galvanized Steel in Geopolymer and Ordinary Portland Cement Based Mortars with the Same Strength Class Exposed to Chlorides. Corros. Sci. 2018, 134, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundra, S.; Criado, M.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L. Chloride-Induced Corrosion of Steel Rebars in Simulated Pore Solutions of Alkali-Activated Concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundra, S.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L. Chloride-Induced Corrosion of Steel in Alkali-Activated Cements: A Review. In Proceedings of the 71st RILEM Annual Week & ICACMS 2017, Chennai, India, 3–8 September 2017; pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Cui, Y.; Jin, Z.; Gao, L. Chloride Transport and Related Influencing Factors of Alkali-Activated Materials: A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuaklong, P.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Influence of Recycled Aggregate on Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete Properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2300–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuaklong, P.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Properties of Metakaolin–High Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete Containing Recycled Aggregate from Crushed Concrete Specimens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnefeld, F.; Leemann, A.; Lucuk, M.; Svoboda, P.; Neuroth, M. Assessment of Phase Formation in Alkali Activated Low and High Calcium Fly Ashes in Building Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, S. Mechanical, Microstructural, and Durability Characterization of Fly Ash/Slag-Based Geopolymer with Limited OPC and Different Alkaline Activator Ratios. Ph.D. Thesis, The Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Chalee, W. Effect of Sodium Hydroxide Concentration on Chloride Penetration and Steel Corrosion of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete under Marine Site. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 63, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Lam, E.S.S.; Li, B.; Wu, B. Effect of Alkali Contents, Moduli and Curing Time on Engineering Properties of Alkali Activated Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najimi, M.; Ghafoori, N.; Sharbaf, M. Alkali-Activated Natural Pozzolan/Slag Mortars: A Parametric Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennakoon, C.; Shayan, A.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Xu, A. Chloride Ingress and Steel Corrosion in Geopolymer Concrete Based on Long Term Tests. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.K.; Kumar, S. Role of Particle Fineness on Engineering Properties and Microstructure of Fly Ash Derived Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Brown, T.; Song, S. Effects of Aluminates on the Formation of Geopolymers. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2005, 117, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Castel, A.; François, R. Influence of Steel–Concrete Interface Defects Owing to the Top-Bar Effect on the Chloride-Induced Corrosion of Reinforcement. Mag. Concr. Res. 2011, 63, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, Q.; Yao, Q.; Guan, X.; Hu, P. Chloride Resistance of Class C/Class F Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortars with Different Strength Grades. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Zeedan, S.R. The Effect of Activator Concentration on the Residual Strength of Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Pastes Subjected to Thermal Load. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A. Effect of the Activator Dose on the Compressive Strength and Accelerated Carbonation Resistance of Alkali Silicate-Activated Slag/Metakaolin Blended Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; San Nicolas, R.; Brice, D.G.; Kilcullen, A.R.; Hamdan, S.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Influence of Fly Ash on the Water and Chloride Permeability of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars and Concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hu, J.; Ma, Y.; Guo, W.; Huang, H.; Wei, J.; Yin, S.; Yu, Q. Characterization of the passive film formed on the reinforcement surface in alkali activated fly ash: Surface analysis and electrochemical evaluation. Corros. Sci. 2020, 165, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakoute, H.K.; Elimbi, A.; Yanne, E.; Djangang, C.N. Utilization of Volcanic Ashes for the Production of Geopolymers Cured at Ambient Temperature. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 38, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; De la Torre, A.G.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Palomo, A. An XRD Study of the Effect of the SiO2/Na2O Ratio on the Alkali Activation of Fly Ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Fajardo, S.; Gómez, P.P.; Bastidas, J.M. Corrosion Rate and Corrosion Product Characterisation Using Raman Spectroscopy for Steel Embedded in Chloride Polluted Fly Ash Mortar. Mater. Corros. 2013, 64, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Kriven, W.M.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Understanding the Relationship between Geopolymer Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 269, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Miranda, J.M.; González, J.A.; Palomo, A. Steel Passive State Stability in Activated Fly Ash Mortars. Mater. Constr. 2010, 60, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.; Alcocel, E.G.; Sánchez, I.; Garcés, P.; Zornoza, E. Corrosion Resistance of Steel Reinforcements Embedded in Alkali Activated Ground Granulated SiMn Slag Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L. Durability of Alkali-Activated Materials: Progress and Perspectives. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Long, K.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Long, W.J. Carbonation and Chloride Ions’ Penetration of Alkali-Activated Materials: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Sobrados, I.; Bastidas, J.M.; Sanz, J. Corrosion Behaviour of Coated Steel Rebars in Carbonated and Chloride-Contaminated Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Mortar. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 99, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Gong, Z.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; et al. Insight into Anti-Corrosion Mechanism of Copper in 0.5 M Sulfuric Acid Solution Via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots as Novel Inhibitors. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2025, 43, e01305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Ren, H.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Al-Sadoon, M.K. Nepeta cataria L. Leaf Extracts as Eco-Conscious Corrosion Inhibitor for Copper in H2so4 Medium. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 711, 136399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Ren, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, R.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Guo, L.; Al-Sadoon, M.K. A Novel Corrosion Inhibitor for Copper in Sulfuric Acid Media: Complexation of Iodide Ions with Benincasa Hispida Leaf Extract. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 705, 135710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Ren, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Cao, X.; Dai, Q.; Guo, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Insight into the Anti-Corrosion Performance of Crop Waste as a Degradable Corrosion Inhibitor for Copper in Sulfuric Acid Medium. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaharudin, F.S.; Zainal, F.F.; Hayazi, N.F.; Parimin, N.; Nadzri, N.I.M.; Hastuty, S.; Kusbiantoro, A. Investigation of Corrosion Behaviour of Mild Steel Embedded in Geopolymer Paste with Curing and Non-Curing Process. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2023, 68, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, F.F.; Amli, S.F.M.; Hussin, K.; Rahmat, A.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B. Corrosion Studies of Fly Ash and Fly Ash-Slag Based Geopolymer. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 209, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C876-09; Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Hardjito, D.; Rangan, B.V. Development and Properties of Low-Calcium Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete; Research Report GC 1; Curtin University of Technology: Perth, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lăzărescu, A.-V.; Hegyi, A.; Csapai, A.; Popa, F. The Influence of Different Aggregates on the Physico-Mechanical Performance of Alkali-Activated Geopolymer Composites Produced Using Romanian Fly Ash. Materials 2024, 17, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, R.M.; Man, Z.; Azizli, K.A. Concentration of NaOH and the Effect on the Properties of Fly Ash Based Geopolymer. Proc. Eng. 2016, 148, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovnaník, P. Effect of Curing Temperature on the Development of Hard Structure of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; Williams, R. Effect of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash on the Properties of Geopolymer Cured at Ambient Temperature. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5276–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Collins, F. Effect of Sodium Silicate on Efflorescence Formation and Strength of Geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 57, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Birnin-Yauri, U.A.; Garba, S. The Effect and Mechanism of Chloride Ion Attack on Portland Cement Concrete and the Structural Steel Reinforcement. Ife J. Sci. 2006, 8, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, D.D.N.; Yadav, S.; Saha, J.K. Role of Climatic Conditions on Corrosion Characteristics of Structural Steels. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J. Application of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy to Evaluate the Corrosion Behavior of 2304 Duplex Stainless Steel Reinforced Rebar in Concrete Exposed in Chloride-Rich Environment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 8039–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitián, B.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Puga, B. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy as a Tool for Materials Selection: Water for haemodialysis. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7772–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, M.; Li, X.; Ooi, A.; Tada, E.; Nishikata, A. Passivation Mechanism of Galvanized Steel Rebar in Fresh Concrete. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Tokieda, H.; Shitanda, I.; Itagaki, M. Evaluation of Chloride Ion Concentration and Ph on Depassivation of Steel Rebar in Concrete Investigated by Electrochemical Impedance Measurement of Probe Electrodes. Mater. Trans. 2021, 62, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocijan, A.; Merl, D.K.; Jenko, M. The Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic and Duplex Stainless Steels in Artificial Saliva with the Addition of Fluoride. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Dong, C.F.; Xiao, K.; Li, X.G. Characterization of Passive Film on 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel in Sodium Thiosulphate Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, H.S.; Seikh, A.H.; Mohammed, J.A.; Luqman, M.; Ragab, S.A.; Almotairy, S.M. Influence of Chloride Ions on Elec-Trochemical Corrosion Behavior of Dual-Phase Steel over Conventional Rebar in Pore Solution. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cu/CuSO4 | Ag/AgCl | SHE | SCE | Corrosion Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| >−200 mV | >−100 mV | +120 mV | >−80 mV | Low (10% risk of corrosion) |
| −200 to −350 mV | −100 to −250 mV | +1200 to −30 mV | −80 to −230 mV | Intermediate corrosion risk |
| <−350 mV | <−250 mV | <−30 mV | <−230 mV | High (>90% risk of corrosion |
| <−500 mV | <−400 mV | <−180 mV | <−380 mV | Severe corrosion |
| Corrosion Current [µA/cm2] | Corrosion Rate [µm/year] | Corrosion Stage of the Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| <0.1 | <1.17 | Passive |
| 0.1–0.5 | 1.17–5.85 | Low |
| 0.5–1.0 | 5.85–11.7 | Moderate |
| >1.0 | >11.7 | High |
| Oxide Composition (%) | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 |
| 46.94 | 23.83 | 10.08 | 10.72 | 2.63 | 0.45 | 0.62 | 1.65 | 0.25 | |
| TiO2 | Cr2O3 | Mn2O3 | ZnO | SrO | CO2 | L.O.I. | SiO2+Al2O3 | ||
| 0.92 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.03 | - | 2.11 | 70.77 | ||
| R0.045 | 31.40 | ||||||||
| Geopolymer Mixture Code | R6 1:1 | R6 1:2 | R6 2:1 | R8 1:1 | R8 1:2 | R8 2:1 | R10 1:1 | R10 1:2 | R10 2:1 |
| NaOH solution molar concentration (M) | 6 | 8 | 10 | ||||||
| Na2SiO3/NaOH ratio | 1:1 | 1:2 | 2:1 | 1:1 | 1:2 | 2:1 | 1:1 | 1:2 | 2:1 |
| Alkaline activator to fly ash ratio (mass) | 0.95 | ||||||||
| Sample | E (i = 0) (mV) | Rp (Ωcm2) | icor (μA/cm2) | βa (mV) | βc (mV) | vcorr (μm/Y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R6–1:1 | −928.3 | 236.62 | 101.2 | 298.5 | −88.3 | 1184 |
| R6–1:2 | −823.1 | 467.73 | 39.4 | 259.9 | −67.0 | 461.3 |
| R6–2:1 | −874.3 | 220.97 | 102.7 | 267.5 | −87.0 | 1201 |
| R8–1:1 | −484.8 | 28700 | 0.72 | 110.9 | −117.9 | 8.43 |
| R8–1:2 | −726.6 | 5160 | 4.2 | 563.5 | −69.2 | 46.6 |
| R8–2:1 | −565.1 | 15070 | 2.2 | 143.5 | −151.7 | 26.1 |
| R10–1:1 | −880.0 | 348.21 | 41.7 | 175.8 | −55.4 | 487.5 |
| R10–1:2 | −871.9 | 804.71 | 23.5 | 310.7 | −65.7 | 275.3 |
| R10–2:1 | −613.1 | 21260 | 1.1 | 159.3 | −193.9 | 12.9 |
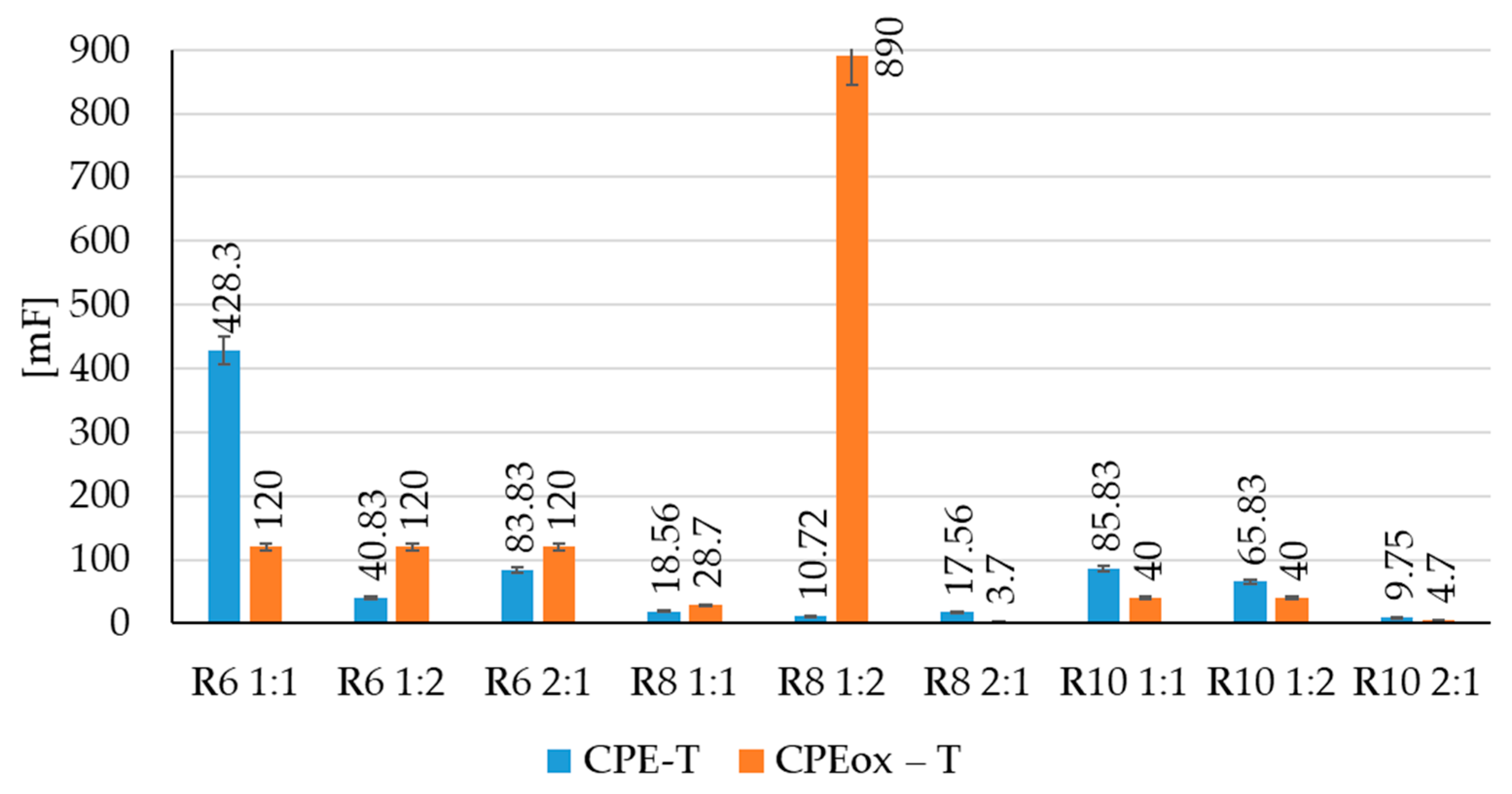
| Sample | Rs (Ω) | CPE-T (mF) | CPE-P | Rp (Ω) | Rox (Ω) | CPEox-T (mF) | CPEox-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R6–1:1 | 22 | 428.3 | 0.6599 | 5500 | 2000 | 120 | 0.2939 |
| R6–1:2 | 29 | 40.83 | 0.5599 | 9500 | 2000 | 120 | 0.2939 |
| R6–2:1 | 23 | 83.83 | 0.4599 | 9500 | 2000 | 120 | 0.2939 |
| R8–1:1 | 64 | 18.56 | 0.5899 | 8500 | 200 | 28.7 | 0.5839 |
| R8–1:2 | 53 | 10.72 | 0.6899 | 12500 | 1000 | 890 | 0.7839 |
| R8–2:1 | 251 | 17.56 | 0.5899 | 2500 | 600 | 3.7 | 0.6839 |
| R10–1:1 | 25 | 85.83 | 0.7599 | 8800 | 1800 | 40 | 0.5939 |
| R10–1:2 | 105 | 65.83 | 0.7859 | 8800 | 1800 | 40 | 0.5939 |
| R10–2:1 | 134 | 9.75 | 0.7899 | 5500 | 1400 | 4.7 | 0.5839 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chira, M.; Lăzărescu, A.-V.; Hegyi, A.; Vermesan, H.; Csapai, A.; Ionescu, B.A.; Toader, T.P.; Florean, C. Influence of Alkaline Activator Properties on Corrosion Mechanisms and Durability of Steel Reinforcement in Geopolymer Binders. Coatings 2025, 15, 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060734
Chira M, Lăzărescu A-V, Hegyi A, Vermesan H, Csapai A, Ionescu BA, Toader TP, Florean C. Influence of Alkaline Activator Properties on Corrosion Mechanisms and Durability of Steel Reinforcement in Geopolymer Binders. Coatings. 2025; 15(6):734. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060734
Chicago/Turabian StyleChira, Mihail, Adrian-Victor Lăzărescu, Andreea Hegyi, Horatiu Vermesan, Alexandra Csapai, Bradut Alexandru Ionescu, Tudor Panfil Toader, and Carmen Florean. 2025. "Influence of Alkaline Activator Properties on Corrosion Mechanisms and Durability of Steel Reinforcement in Geopolymer Binders" Coatings 15, no. 6: 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060734
APA StyleChira, M., Lăzărescu, A.-V., Hegyi, A., Vermesan, H., Csapai, A., Ionescu, B. A., Toader, T. P., & Florean, C. (2025). Influence of Alkaline Activator Properties on Corrosion Mechanisms and Durability of Steel Reinforcement in Geopolymer Binders. Coatings, 15(6), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060734








