Abstract
This study investigates the hydrothermal synthesis of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) from photovoltaic (PV) waste glass and carbide sludge as a strategy for resource recovery and sustainable chromium removal from wastewater. Waste-derived precursors were co-ground, blended at controlled Ca/Si molar ratios (0.8, 1.0, 1.2), and hydrothermally treated at 180 °C for 96 h to yield C-S-H with tunable morphology and crystallinity. Comprehensive characterization using XRD, FT-IR, SEM-EDX, and UV-Vis spectroscopy revealed that a Ca/Si ratio of 1.0 produced a well-ordered tobermorite/xonotlite structure with a high surface area and fibrous network, which is optimal for adsorption. Batch adsorption experiments showed that this material achieved rapid and efficient Cr(III) removal, exceeding 90% uptake within 9 h through a combination of surface complexation, ion exchange (Ca2+/Na+ ↔ Cr3+), and precipitation of CaCrO4 phases. Morphological and structural evolution during adsorption was confirmed by SEM, FT-IR, and XRD, while EDX mapping established the progressive incorporation of Cr into the C-S-H matrix. These findings highlight the viability of upcycling industrial waste into advanced C-S-H sorbents for heavy metal remediation. Further work is recommended to address sorbent regeneration, long-term stability, and application to other contaminants, providing a foundation for circular approaches in advanced wastewater treatment.
1. Introduction
The rapid expansion of photovoltaic (PV) deployment is projected to generate over eight million tonnes of end-of-life module glass annually by 2030, presenting an urgent resource-recovery challenge for the circular economy [1]. Today, acetylene-production carbide sludge accumulates worldwide as a highly alkaline waste which is rich in reactive CaO but remains under-utilized in high-value applications [2]. Converting these streams into functional materials would divert them from landfill, conserve primary raw minerals, and align with global circular-economy policies [3].
Chromium contamination persists as a priority water quality issue because trivalent Cr(III) and, especially, hexavalent Cr(VI) can trigger cytotoxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic effects when discharged from electroplating, tanning, or pigment industries [4,5]. Conventional treatments—alkaline precipitation, membrane filtration, or ion exchange—often incur high chemical demand, produce secondary sludge, or lose efficiency at low metal concentrations, motivating exploration of alternative sorbents with greater sustainability and selectivity [6].
Calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H), the principal binding phase in hydrated cement, has emerged as a promising low-cost adsorbent because its layered tobermorite/xonotlite nanostructure hosts abundant Ca-OH and silanol edge sites capable of surface complexation and cation exchange with heavy-metal ions [7,8]. Recent studies report that C-S-H prepared from coal gangue or fly ash effectively immobilizes Cr(III/VI) through coupled adsorption–precipitation mechanisms, yet performance depends critically on Ca/Si ratio and microstructure [9,10].
Hydrothermal synthesis offers a controllable route to well-crystallized 11 Å tobermorite at relatively low temperatures (~180 °C). It has been applied to diverse silica–calcium waste combinations, including container glass with cement dust [11], solar-panel glass with limestone [12], and silicate slag and silica fume [13]. However, the concurrent valorization of PV glass as a Si source and carbide sludge as a Ca source for tailored C-S-H adsorbents remains largely unexplored, particularly with respect to Cr(III) remediation. Moreover, the influence of Ca/Si stoichiometry on phase assemblage, textural properties, and resultant adsorption kinetics under realistic wastewater conditions has not been systematically evaluated.
Against this backdrop, the present work aims to (i) synthesize C-S-H exclusively from PV waste glass and carbide sludge via hydrothermal processing at selected Ca/Si ratios; (ii) elucidate the relationship between precursor chemistry, crystallinity, and surface morphology; and (iii) assess the kinetics and mechanisms of Cr(III) sequestration through a suite of spectroscopic (FT-IR), diffraction (XRD), and microscopic (SEM-EDX) techniques. By integrating waste valorization with advanced materials engineering, this study seeks to advance circular-economy strategies while delivering an efficient sorbent platform for heavy-metal-laden effluents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Wasted PV glass (WPVG) was supplied by the PV panel manufacturing factory Trung Viet Glass, Vietnam.
Wasted carbide sludge (WCS) was supplied by Sovigaz Welding Rod Industry Steam Joint Stock Company, Vietnam. Both PVG and WCC were analyzed for chemical crystallinity and composition by XRD (Bruker D8 Advance, Berlin, Germany) and XRF (ARL Advant, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) respectively.
2.2. Preparation of C-S-H Materials
The synthesis of C-S-H from PV waste glass and carbide sludge proceeds in four main stages: pre-treatment, mixing and pelletizing, hydrothermal reaction, and post-treatment/characterization. First, equal masses of WPVG and WCS are co-ground in a ball mill (Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany) until the resulting powder passes completely through a 0.45 mm sieve; material that fails to meet this criterion is returned to the mill. Once the desired particle size is attained, its chemical and phase composition are verified by XRD and XRF. The sieved powder is then slurried with deionized water at targeted Ca/Si molar ratios of 0.8; 1.0 and 1.2, and the homogeneous mixture is pressed into pellets using a standardized mold. These pellets are transferred to a hydrothermal autoclave (Zhengzhou Keda Machinery and Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd., Zhengzhou, China) and treated at 180°C for 96 h under autogenous steam pressure. Following the hydrothermal reaction, the pellets are dried at 90°C for 24 h to yield the C-S-H product. Finally, the synthesized C-S-H is characterized by XRD, FT-IR(Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan), and SEM (Hitachi S-4800, Tokyo, Japan), as well as by functional groups, morphology, and elemental distribution. A flowchart for the process of synthesizing CSH is shown in Figure 1a. The hydrothermal autoclave used in the experiment is illustrated in Figure 1b.
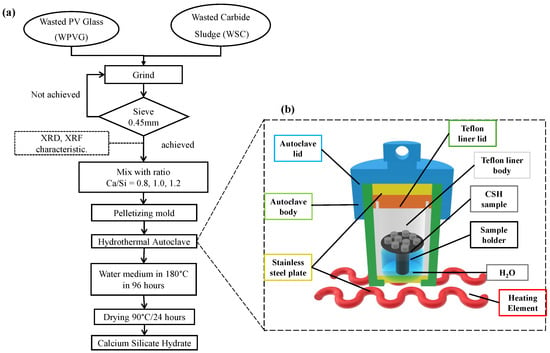
Figure 1.
(a) Flowchart of preparation of CSH by hydrothermal method using WPVG and WCS. The WPVG and WSC were mixed with Ca/Si molar ratios of 0.8, 1.0, and 1.2 following hydrothermal treatment at 180 °C for 96 h. (b) Hydrothermal autoclave used in experiment.
2.3. Evaluation of Cr(III) Removal Using Obtained CSH
Cr(III) adsorption by the synthesized C-S-H was evaluated using simulated wastewater spiked with Cr(III) at a concentration of 8 g/L and a pH of 7.5. In each test, a fixed mass of dried C-S-H powder was dispersed in Cr(III)-containing solution at a predetermined solid-to-liquid ratio, and the pH was adjusted as required. The suspension was agitated on an orbital shaker at 150 rpm to ensure thorough contact between adsorbent and metal ions. After equilibrium was reached, the solid and liquid phases were separated by vacuum filtration. The filtrate was analyzed by UV-Vis (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) spectrophotometry (300–800 nm), and Cr(III) concentration was quantified via a calibration curve to determine the amount of ion removed. Adsorption capacity was calculated from the difference between initial and equilibrium concentrations. The recovered C-S-H was then oven-dried at 90 °C for 12 h and subjected to SEM, EDX, FT-IR, and XRD analyses to reveal morphological, elemental, and structural changes associated with Cr(III) uptake. The process of Cr(III) removal is shown in Figure 2.
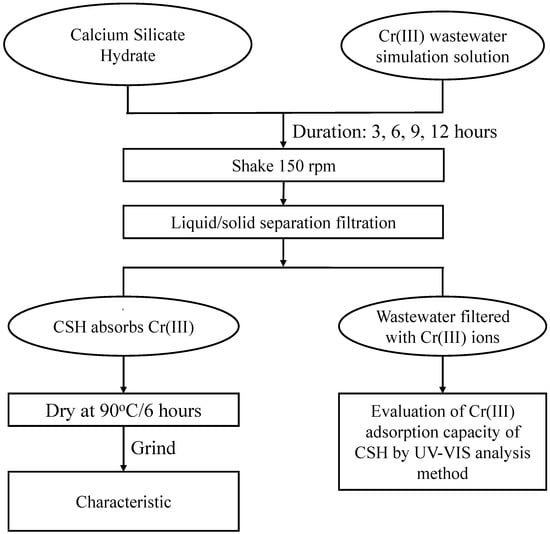
Figure 2.
Flowchart of evaluation of Cr(III) removal using obtained CSH.
2.4. Characterization of Materials
For chemical composition analysis using X-ray fluorescing (XRF) method. The sample was characterized by X-ray at 40 kV (ARL Advant, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
For phase analysis using film XRD, the sample was put into an XRD machine (Bruker D8 Advance, Berlin, Germany) with 2theta scanning from 5 to 60° and operation at 40 kV and 40 mA.
For morphology analysis using SEM, the sample was glued to copper substrate with carbon tape, and SEM analysis was carried out (Hitachi S-4800) at 10 kV.
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) (Thermo Scientific Nicolet 6700 FTIR, USA) was used to analyze the chemical bonds in CSH materials scanning wavenumbers in a range of 400–4000 cm−1.
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-VIS) (Shimadzu, 2600i mJ) spectrophotometry was applied to determine the concentration of Cr(III) ions remaining in solution after adsorption. In this procedure, samples were filtered and analyzed in the 300–800 nm wavelength range, with absorbance values correlated with concentration via a standard calibration curve constructed from Cr(III) standards.
3. Results
As shown in Table 1, the chemical composition of raw materials analyzed by XRF confirms that the PV waste glass is a classical soda-lime-silicate material, with SiO2 dominating at 73.14 wt% [14]. The network-formers for SiO2 are balanced by substantial fluxing oxides, CaO at 10.98 wt% and Na2O at 9.78 wt%, which together lower the glass melting temperature and promote network depolymerization under hydrothermal conditions [13].

Table 1.
Chemical composition of PV waste glass and carbide waste sludge.
It can also be seen that, whereas carbide sludge exhibits a highly calcium-rich profile, with CaO comprising 70.48 wt%, SiO2 is present at only 5.33 wt%. The negligible Na2O content (0.05 wt%) remains at trace levels. This chemical distribution makes the sludge an excellent Ca-source complement to the silica-rich glass for CSH synthesis. When blended at selected Ca/Si feed ratios (0.8; 1.0, and 1.2), the two waste streams deliver the stoichiometry required for C-S-H nucleation and growth.
An SEM micrograph of the raw precursor blend (Figure 3a) reveals irregular, angular fragments and heterogeneous agglomerates characteristic of mixed PV waste glass and carbide sludge, reflecting incomplete particle comminution and uneven surface textures prior to hydrothermal treatment [15].
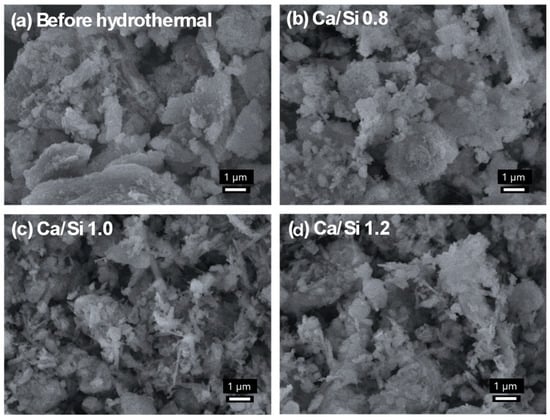

Figure 3.
SEM images at 10,000× magnification: (a) pre-synthesis; (b–d) after hydrothermal treatment with WPVG and WCS at 180 °C/96 h and different molar ratios of Ca/Si: (b) 0.8; (c)1.0; and (d) 1.2.
At a Ca/Si ratio of 0.8 (Figure 3b), plate-like and foil-shaped C-S-H particles predominate, forming loosely stacked platelets with relatively smooth surfaces, indicative of low silicate polymerization and predominantly amorphous C-S-H gel formation under milder calcium-rich conditions [16,17]. When the Ca/Si ratio is elevated to 1.0 (Figure 3c), the morphology transitions to a web of interwoven fibrous and rod-like nanostructures, reflecting enhanced silicate chain condensation and the nucleation of xonotlite-type domains under hydrothermal conditions [16,17].
Further raising the Ca/Si ratio to 1.2 (Figure 3d) yields denser, crumpled aggregates with reduced interstitial voids, as higher calcium concentration drives directional growth and partial crystallization into more compact C-S-H clusters [16,18]. These compact morphologies coincide with a decrease in plate-like tobermorite or xonotlite content and stronger interparticle bonding, resulting in lower porosity and potentially greater structural stability during adsorption cycles.
Overall, SEM analysis confirms that hydrothermal treatment transforms the raw precursor into C-S-H whose morphology-and thus adsorption performance - is strongly governed by Ca/Si ratio. The optimal fibrous network at Ca/Si = 1.0 maximizes surface area and active sites, whereas lower or higher ratios yield less favorable platelet or nodular structures.
The FT-IR spectra of C-S-H samples (Figure 4a, 4000–400 cm−1) display a characteristic broad O-H stretching band centered at ~3400 cm−1, arising from interlayer and adsorbed water molecules [19]. Its full width at half-maximum decreases slightly as Ca/Si increases from 0.8 to 1.2, indicating a gradual loss of structurally bound water with rising calcium content. In the 1800–400 cm−1 region (Figure 4b), several diagnostic vibrations are resolved.
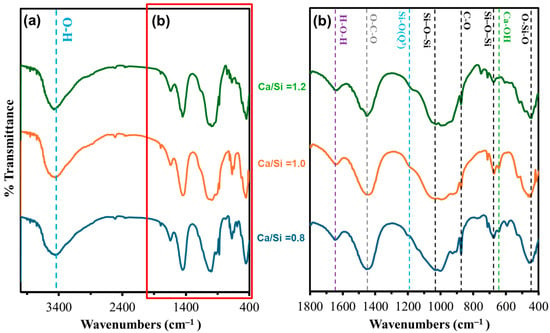
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectra for wavenumber ranges (a) 4000–400 cm−1 and (b) 1800–400 cm−1 for CSH with Ca/Si molar ratios of 0.8, 1.0, and 1.2.
A weak, broad feature at ~1635 cm−1 corresponds to molecular-water H-O-H bending. Its intensity diminishes as Ca/Si increases, consistent with reduced water retention in denser C-S-H structures [19]. Also apparent are two carbonate modes: the out-of-plane bend at ~875–880 cm−1 and the asymmetrical stretch at ~1400–1500 cm−1 [19]. Both intensify modestly with higher Ca/Si, evidencing superficial carbonation of excess Ca2+ during sample handling [19].
The pronounced band at 1050–1080 cm−1 is assigned to symmetric Si-O-Si bridge stretching within silicate chains [19]. Its peak position shifts from ~1075 cm−1 (Ca/Si = 0.8) toward ~1050 cm−1 (Ca/Si = 1.2), indicating gradual depolymerization of silicate chains as more calcium is incorporated [19]. The Si-O-Si asymmetric stretch at ~960 cm−1 remains strong at Ca/Si = 1.0, reflecting optimal chain connectivity in tobermorite-like C-S-H [19]. A smaller band at 650–670 cm−1, due to Si-O-Si bridging-oxygen bending, intensifies at intermediate Ca/Si, supporting enhanced polymerization [19]. The O-Si-O tetrahedral bending band at 440–500 cm−1 sharpens most at Ca/Si = 1.0, indicating the formation of well-ordered silicate layers [19].
The Ca-OH deformation mode at 631–633 cm−1 appears as a distinct shoulder, growing with Ca/Si ratio, confirming residual portlandite-like species embedded in the C-S-H matrix [20].
In general, the FT-IR data corroborate the XRD and SEM findings. At low Ca/Si (0.8), C-S-H is a less-ordered, water-rich gel; at Ca/Si = 1.0, silicate chains achieve optimal connectivity (tobermorite-like); and at Ca/Si = 1.2, excess calcium leads to partial depolymerization, enhanced carbonation, and decreased bound-water content.
The XRD results shown in Figure 5 reveal that the diffraction pattern of the raw carbide sludge (a) is dominated by six sharp reflections at 2θ ≈ 18°, 28°, 34°, 47°, 50° and 54°, which match the portlandite (Ca(OH)2; PDF# 100-8781) reference data. This confirms that calcium hydroxide is the principal crystalline phase present in the sludge prior to any hydrothermal reaction, with negligible contributions from silicate or carbonate phases. In contrast, the PV waste glass (b) exhibits a broad, featureless hump centered around 2θ ≈ 22° with virtually no discrete peaks. This amorphous halo is characteristic of quenched silicate glass and indicates the absence of long-range order, confirming that the glass fraction predominantly contributes a reactive, non-crystalline silica source for C-S-H formation.
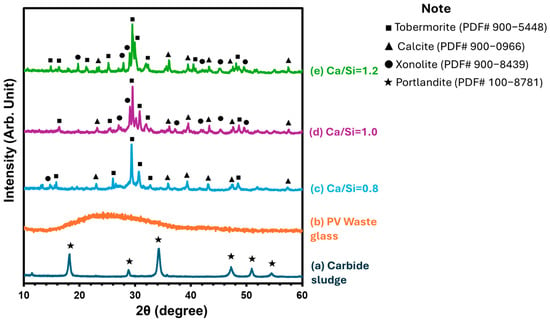
Figure 5.
XRD results of following samples: (a) carbide sludge; (b) PV waste glass; (c) Ca/Si = 0.8; (d) Ca/Si = 1.0; (e) hydrothermal product at Ca/Si = 1.2.
After hydrothermal treatment at Ca/Si = 0.8 (Figure 5c), sharp new peaks emerge at 2θ ≈ 16°, 26°, 30°, 31°, 32° and 48°, corresponding to the reflections of tobermorite (PDF# 900-5448). A minor feature at ~13° indicates trace xonotlite (PDF# 900-8439). Concurrently, weaker peaks at ~23°, 36°, 39°, 43°, 47° and 57° reveal the presence of calcite (PDF# 900-0966), formed by partial carbonation of dissolved Ca2+. The relatively low intensity and broader width of the tobermorite reflections suggest a mainly amorphous gel with nascent crystalline domains.
Increasing the Ca/Si ratio to 1.0 (Figure 5d), sharpens and intensifies the tobermorite reflections, signaling enhanced crystal growth and larger coherent domains. Xonotlite peaks at 2θ ≈ 27°, 29°, 37°, 41°, 45°, and 49° also become more pronounced, reflecting increased silicate chain polymerization under more balanced Ca/Si stoichiometry. The calcite peaks are still present but are slightly less intense relative to the tobermorite reflections, indicating that more calcium is incorporated into the silicate hydrate framework rather than precipitating as carbonate.
At Ca/Si = 1.2 (Figure 5e), tobermorite reflections not only grow sharper but also display additional low-angle peaks at ~14° and ~21°, characteristic of varied interlayer spacings in tobermorite polytypes. Xonotlite reflections persist but decrease in relative intensity, suggesting that excess calcium favors the ordering of tobermorite over high-temperature polymorphs. Calcite reflections remain detectable yet weak, confirming that although minor carbonation occurs, the formation of well-crystallized C-S-H phases predominates at higher Ca/Si ratios.
In conclusion, the XRD data demonstrate a clear evolution from predominantly portlandite and amorphous glass precursors to increasingly well-ordered C-S-H phases—first as mixed tobermorite/xonotlite at Ca/Si = 0.8, then to highly crystalline tobermorite at higher Ca/Si ratios—while the residual calcite content decreases as more Ca2+ is sequestered into the hydrate structure.
Based on structural and morphological analyses, the C-S-H sample with Ca/Si = 1.0 exhibited the most favorable combination of well-defined xonotlite-type crystallinity, interconnected fibrous networks, and high specific surface area. In contrast, the Ca/Si = 0.8 gel remained largely amorphous with fewer accessible adsorption sites, while the Ca/Si = 1.2 material formed dense aggregates with reduced porosity. Consequently, the Ca/Si = 1.0 composition was selected for detailed batch-mode adsorption experiments to quantify Cr(III) uptake, determine kinetic parameters, and elucidate equilibrium isotherms under controlled conditions.
Adsorption tests using the Ca/Si = 1.0 C-S-H sorbent revealed a rapid initial uptake of Cr(III), followed by a slower approach to equilibrium. It can be seen from Table 2 and Figure 6a that within the first 3 h, solution concentration falls from 7.96 g L−1 to 5.21 g L−1, corresponding to 34.6% removal. This stage reflects adsorption onto readily accessible surface sites and is driven by the steep concentration gradient between solution and sorbent [21]. Between 3 and 6 h, removal accelerates to 73.3% as more active sites become available and intraparticle diffusion contributes to uptake. By 9 h, Cr(III) concentration reaches 0.65 g L−1 (91.8% removal), indicating that equilibrium is essentially attained; further contact yields diminishing gains. The accompanying decolorization of the test solutions in Figure 6b, from deep green at 3 h to nearly colorless at 9 h, visually corroborates the UV-Vis data and confirms efficient Cr(III) sequestration Consequently, we may say that a 9 h contact time is sufficient to achieve >90% removal in practical applications, balancing treatment efficiency against operational time.

Table 2.
Results of UV-VIs analysis of Cr(III) concentration and adsorption efficiency of CSH.
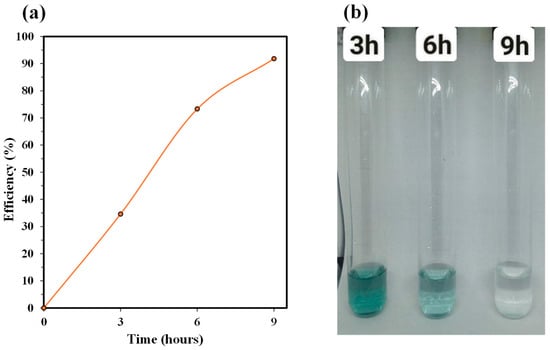
Figure 6.
(a) Graph of Cr(III) adsorption efficiency of CSH mineral. (b) Simulated Cr(III) wastewater solutions at different adsorption times.
The results of FT-IR spectrum analysis of H2O-CSH before and after Cr(III) adsorption are shown in Figure 7a,b. The H2O-CSH after adsorbing Cr(III) still retains the characteristic bonds of CSH (Si-O-Si, O-C-O, O-H,…) in the wavenumber range of 400–1800 cm−1. In addition, new characteristic peaks appear in the FT-IR spectra of H2O-CSH materials after Cr(III) adsorption at 3, 6, and 9 h, including peaks characteristic of the symmetric elastic vibration of Cr-O-Cr at a wavenumber of ~750 cm−1 and the elastic vibration of Cr-O at wavenumbers in the range 480–620 cm−1 [22,23]. These new characteristic bonds also prove that Cr(III) after adsorption has formed bonds on the surface of CSH material.
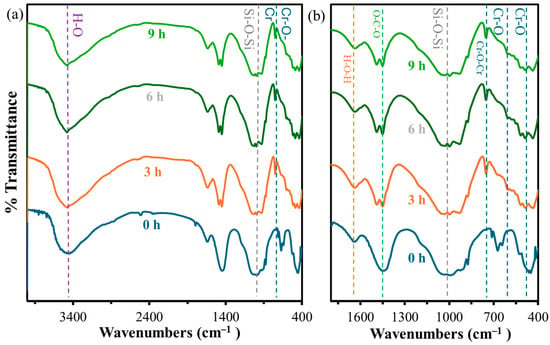
Figure 7.
FT-IR results for CSH at wavenumber ranges of (a) 400–4000 cm–1 and (b) 400–1800 cm−1.
SEM images at 10,000× magnification revealed distinct changes in C-S-H surface morphology as Cr(III) adsorption proceeded, as can be seen in Figure 8. At 0 h (Figure 8a), the microscopic surface image shows a highly porous network of interwoven, plate-like and fibrous C-S-H crystallites with abundant exposed silicate surfaces and interparticle voids, characteristic of hydrothermally synthesized C-S-H at Ca/Si ≈ 1.0. Such open morphologies provide a high density of silanol and Ca-OH sites ideal for initial ion exchange and surface complexation on C-S-H materials. After 3 h of contact (Figure 8b), thin, irregular platelets and small nodular clusters begin to coat the original C-S-H fibers and plates, indicating early adsorption and possible surface complexation of Cr(III) as Cr-O-Si or Cr-OH species, as mentioned in the FT-IR analysis.
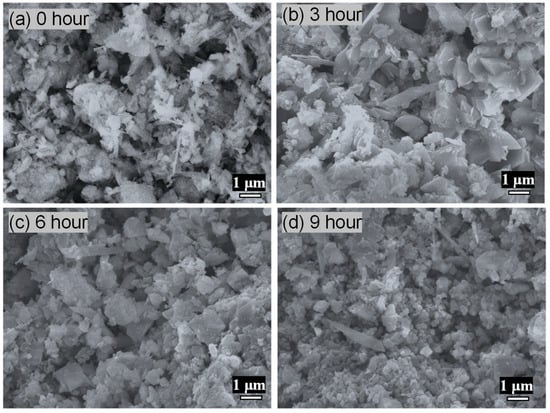
Figure 8.
SEM images of CSH at 10,000 times magnification at different adsorption times: (a) 0 h; (b) 3 h; (c) 6 h; and (d) 9 h.
The SEM micrograph at 6 h (Figure 8c) reveals that the surface deposits have grown into discrete, nearly spherical nanoparticles (tens to hundreds of nanometers), which partially mask the underlying C-S-H morphology. These nodular aggregates are consistent with heterogeneous nucleation of Cr(OH)3 or mixed Cr-Si hydroxide phases on C-S-H surfaces, reflecting studies in which similar spherical Cr(III) precipitates have been reported [24].
At 9 h (Figure 8d), the SEM image shows a nearly continuous, compact layer of fine nanospheres fully covering the C-S-H network, indicating that most high- and medium-affinity sites are occupied and that further removal proceeds via surface precipitation [25].
The progressive morphological transformation—from exposed fibrous networks to fully coated surfaces—correlates directly with the kinetic profile of Cr(III) uptake. Early-stage adsorption occurs via site-specific complexation on silicate surfaces, while later stages are marked by surface precipitation of Cr(OH)3, ultimately leading to near-saturation of the C-S-H sorbent by 9 h. This SEM evidence substantiates a two-mechanism uptake model combining ion exchange/surface complexation and subsequent precipitation.
The wide-angle XRD patterns (Figure 9a, 2θ = 5–80°) of the Ca/Si = 1.0 C-S-H sample, before (0 h) and after Cr(III) adsorption (3, 6, and 9 h), consistently display the diagnostic reflections of tobermorite (PDF #900-5448) and xonotlite (PDF #900-8439). The major tobermorite peaks near 2θ ≈ 16°, 26°, 30° and 48°, and the xonotlite peak at ≈ 13°, remain visible at all contact times, confirming that the underlying C-S-H crystal framework is preserved throughout adsorption.
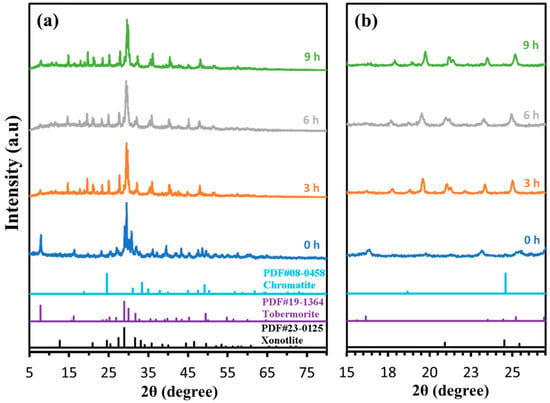
Figure 9.
XRD results with (a) 2θ = 5°–80°, (b) 2θ = 15°–28° for H2O-CSH adsorbing Cr(III) at different adsorption times: 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 9 h.
A closer view between 15° and 28° (Figure 9b) reveals the incremental appearance of low-intensity reflections at 2θ ≈ 19°, 25° and 35° after 3 h of contact, which coincide with chromatite reference diffraction data (CaCrO4; PDF #101-0940). These emergent peaks grow slightly more pronounced by 6 h and 9 h, indicating the formation of a Ca-Cr-O phase on the C-S-H surface during Cr(III) uptake. Although the chromatite reflections are modest in intensity—likely due to limited precipitate loading—their presence unambiguously demonstrates that chromium is not merely adsorbed as an ion complex but also partially precipitates as a calcium chromate phase bound to C-S-H [26,27].
Overall, the XRD data support a dual-mechanism uptake involving (i) retention of tobermorite/xonotlite structure, and (ii) in situ generation of a CaCrO4-type phase as Cr(III) is sequestered. This finding aligns with reports in the literature of heavy-metal adsorption on C-S-H, where surface complexation is often coupled with secondary phase precipitation under alkaline conditions.
This research needs to be considered in the context of experimental conditions. First, our research group succeeded in obtaining CSH using WPVG and WCS with a Ca/Si molar ratio of 1.0 by hydrothermal treatment at 180 °C for 96 h in water medium. The obtained CSH could promote the removal of Cr(III) by up to 90% after 9 h of immersion. In comparison with other studies using fly ash [28], wasted glass powder [29], and steel slag [30], our synthesis route is more simple and more readily available in Vietnam than those described in previous reports. WPVG and WCS are widely abundant in Vietnam on a mass scale, and our research may be seen as a novel use of wasted calcium and silicate resources in Vietnam. In addition, the Cr(III) removal rate of obtained C-S-H (91.8% yield) is higher than that of macadamia-activated carbon (MAC) (yield varies from 56–72.2%) [31].
After 6 h of contact time between CSH110/24 and Cr(III)-containing solution, the Cr(III) solution was reduced by up to 95% and Cr(III) content was briefly 0.65 g/L, thereby meeting the requirements of Vietnam standard number 5945:2005 (issued in 2005), which states that chrome (III) concentration in chrome-containing wasted water must be below 2mg/L. In summary, hydrothermal synthesis of PV waste glass and carbide sludge delivers C-S-H phases whose structural and textural properties are strongly governed by Ca/Si ratio, with Ca/Si = 1.0 yielding a well-crystallized tobermorite/xonotlite network, high surface area, and optimal pore structure. This composition achieved rapid and efficient Cr(III) removal—over 90% within 9 h—through a synergistic mechanism of surface complexation, ion exchange (Ca2+/Na+ ↔ Cr3+), and heterogeneous precipitation of CaCrO4, as confirmed by UV–Vis kinetics, FT-IR Cr-O vibrational bands, SEM morphology evolution, XRD detection of chromatite reflections, and EDX elemental mapping. These findings demonstrate the viability of waste-derived C-S-H as a low-cost, sustainable sorbent for chromium remediation. Nevertheless, assessments of sorbent regeneration, long-term stability under fluctuating pH and ionic strength, and performance with multi-contaminant effluents remain necessary. Future studies should also extend this approach to other priority heavy metals and explore pilot-scale synthesis to validate operational feasibility.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the successful hydrothermal synthesis of C-S-H using photovoltaic waste glass and carbide sludge as sustainable, low-cost precursors. By precisely controlling the Ca/Si molar ratio, it was possible to tailor the phase composition and microstructure of C-S-H, with a ratio of 1.0 yielding well-crystallized tobermorite/xonotlite structures and an interconnected fibrous morphology that optimized adsorption performance. Adsorption experiments confirmed that this material achieved rapid and efficient removal of Cr(III) from aqueous solutions, reaching over 90% removal within 9 h through a synergistic mechanism involving surface complexation, ion exchange (Ca2+/Na+ ↔ Cr3+), and the heterogeneous precipitation of CaCrO4 on the C–S–H surface. A combination of advanced characterization techniques (XRD, FT-IR, SEM-EDX, UV-Vis) provided comprehensive insight into the adsorption mechanism and the evolution of material properties during metal uptake. These results not only validate the valorization of industrial waste for environmental remediation but also highlight the significant potential of hydrothermally engineered C-S-H as an effective sorbent for toxic metals. However, further research is warranted to evaluate long-term stability, regeneration ability, and performance under multi-component conditions, as well as to extend this approach to other priority contaminants and pilot-scale application. This work provides a foundation for the development of circular, resource-efficient solutions for advanced wastewater treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.T.K. and L.P.H.C.; investigation, P.T.K. and T.N.Q.; resources, P.T.K. and T.N.Q.; writing—review and editing, P.T.K., T.N.Q. and L.P.H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) under grant number B2023-20-19.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology (HCMUT), VNU-HCM for sup-porting this study. This research is funded by Vietnam National University HoChiMinh City (VNU-HCM).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Husain, A.A.; Hasan, W.Z.W.; Shafie, S.; Hamidon, M.N.; Pandey, S.S. A review of transparent solar photovoltaic technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Tan, J.; Yang, M.; Yi, Y. Using freshwater sludge and carbide sludge to produce expansive agents for civil engineering applications: A feasibility study. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 67, 106131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, N.; Giduthuri, A.T.; Khan, M.U.; Garrison, R.; Ahring, B.K. Improved valorization of sewage sludge in the circular economy by anaerobic digestion: Impact of an innovative pretreatment technology. Waste Manag. 2022, 154, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgaki, M.-N.; Charalambous, M. Toxic chromium in water and the effects on the human body: A systematic review. J. Water Health 2022, 21, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukadida, K.; Cachot, J.; Morin, B.; Clerandeau, C.; Banni, M. Moderate temperature elevation increases susceptibility of early-life stage of the Mediterranean mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, to metal-induced genotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Jin, X.-T.; Zou, Y.-C.; Li, D.-N.; Feng, P.; Luo, Y.-H. Removal of total chromium in wastewater via simultaneous photocatalysis and adsorption using calcium silicate hydrate-based composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 24038–24046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casar, Z.; Mohamed, A.K.; Bowen, P.; Scrivener, K. Atomic-Level and Surface Structure of Calcium Silicate Hydrate Nanofoils. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 18652–18661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L. Recycling heavy metal ions by ultrathin nanosheet-assembled calcium silicate hydrate for the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater via Fenton-like reactions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 682, 132871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Cao, P.; Jiang, H.; Luo, J.; Jiang, T. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites-calcium silicate hydrate composite from coal fly ash with co-activation of Ca(OH)2-NaOH for aqueous heavy metals removal. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z.; Guijian, L.; Shuchuan, P.; Chuncai, Z.; Arif, M. Immobilization of hexavalent chromium in soil-plant environment using calcium silicate hydrate synthesized from coal gangue. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, N.; Trice, C.; Nicholson, J. 11 Å tobermorite from cement bypass dust and waste container glass: A feasibility study. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 93, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Nguyen, V.P.; Pham, T.K. SYNTHESES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF CALCIUM-BASED GEOPOLYMER FROM SOLAR-CELL PANEL-GLASS WASTE BY HYDROTHERMAL METHOD. Mater. Tehnol. 2024, 58, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fang, C.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Kang, D.; Wang, K. Study on Crystal Growth of Tobermorite Synthesized by Calcium Silicate Slag and Silica Fume. Materials 2023, 16, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, K.T.; Vázquez, A.I.S.; Valdés, J.J.R.; Rodríguez, J.I.; Figueroa, M.G.P.; García, S.P.; Castelló, J.B.C.; Méndez, A.Á. Photovoltaic Glass Waste Recycling in the Development of Glass Substrates for Photovoltaic Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borek, K.; Czapik, P. Utilization of Waste Glass in Autoclaved Silica–Lime Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Khakhutov, M.; Buhl, J.-C. Hydrothermal synthesis of CSH-phases (tobermorite) under influence of Ca-formate. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 51, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Ai, H. A Study on the Hydrothermal Synthesis of Calcium Silicate Products by Calcination of Full-Component Waste Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lu, L.; Struble, L.J.; Hu, S. Effect of C/S ratio on morphology and structure of hydrothermally synthesized calcium silicate hydrate. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2011, 26, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Poe, B.; McMillan, P.F.; Cong, X. Structure of Calcium Silicate Hydrate (C-S-H): Near-, Mid-, and Far-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Garcia, M.; Gaitero, J.J.; Santos, J.I.; Dolado, J.S.; Aymonier, C. Supercritical hydrothermal flow synthesis of xonotlite nanofibers. J. Flow Chem 2018, 8, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, H.S.; Mohammad, M.R. Study the Structure, Morphology and Vibration Modes for K2CrO4 and K2Cr2O7. J. Al-Nahrain Univ. 2017, 20, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, C.; Tabbal, M.; Christidis, T.; Isber, S.; Nsouli, B.; Zahraman, K. Microstructural characterization of chromium oxide thin films grown by remote plasma assisted pulsed laser deposition. J. Phys. Conderence Ser. 2007, 59, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, T.M.; Hameed N., A. Synthesis and structural characterization of Cr2O3 nanoparticles prepared by using Cr(NO3) 3. 9H2O and triethanolamine under microwave irradiation. Adv. Phys. Theor. Appl. 2015, 44, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Omotoso, O.; Ivey, D.; Mikula, R. Containment mechanism of trivalent chromium in tricalcium silicate. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 60, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, F.; Qu, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Q. Synthesis, Characterization and Hexavalent Chromium Adsorption Characteristics of Aluminum- and Sucrose-Incorporated Tobermorite. Materials 2017, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Castro, J.D.; Sanabria-González, N.R.; Giraldo-Gómez, G.I. Experimental data of adsorption of Cr(III) from aqueous solution using a bentonite: Optimization by response surface methodology. Data Brief 2020, 28, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Luo, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Rao, M.; Li, G. Using solid waste to treat wastewater: Preparation of flowerlike calcium silicate hydrate from coal fly ash for cadmium removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 348, 127690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Fang, C.; Liu, T.; Zheng, S.; Lei, G.; Jiang, G. Waste glass powder as a high temperature stabilizer in blended oil well cement pastes: Hydration, microstructure and mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 439, 137359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Upadhyay, S.; Dubey, S.; Singh, K.K. Waste to wealth: Recovery of value-added products from steel slag. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesaoana, M.; Pakade, V.E.; Chimuka, L. Crosslinker-less surface-imprinted Macadamia derived activated carbons for trace Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 14, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).