Effects of Al/Ti Additions on the Corrosion Behavior of Laser-Cladded Hastelloy C276 Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials’ Preparation
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Material Characterization
3. Results
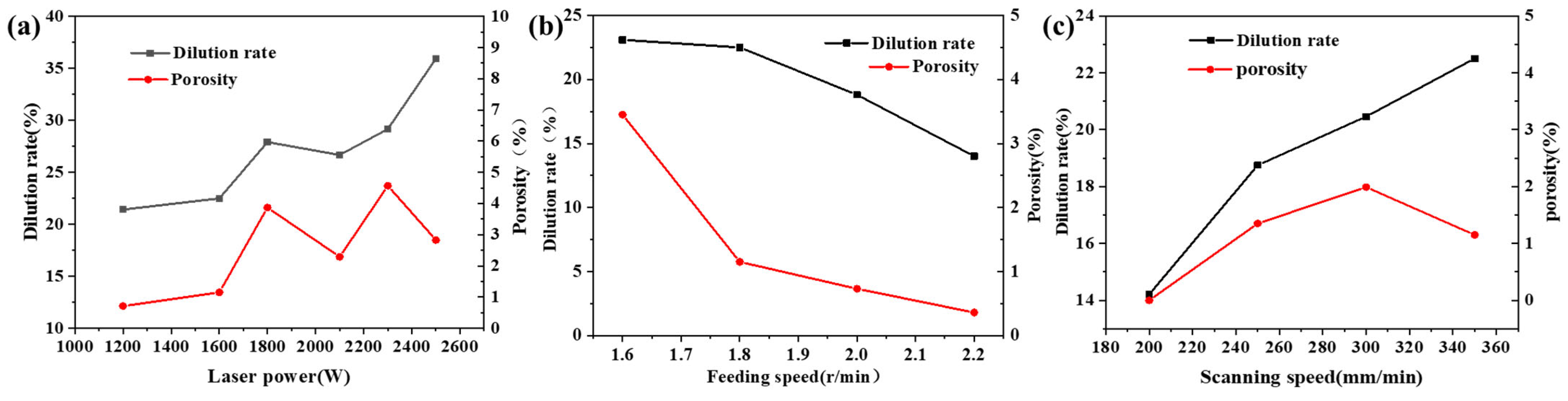
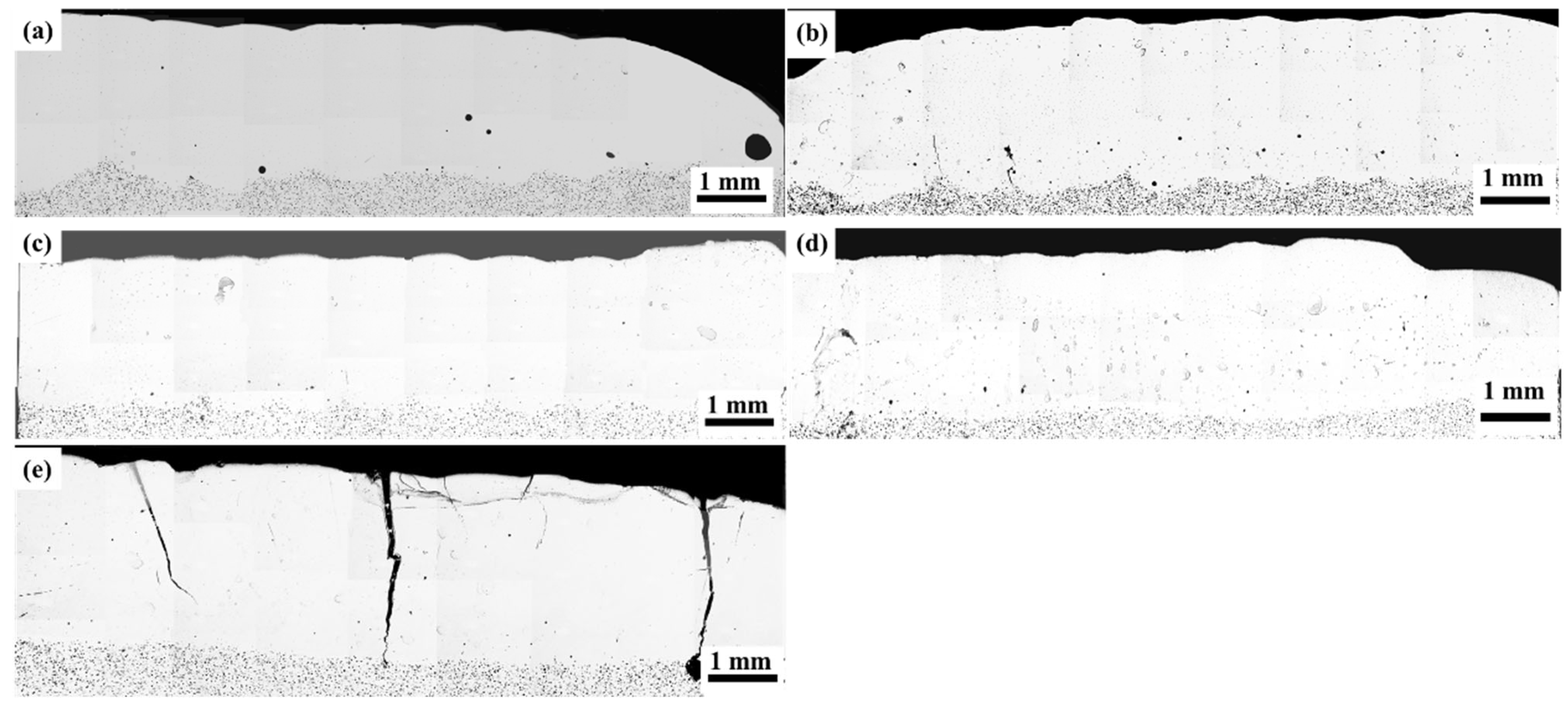
3.1. Porosity
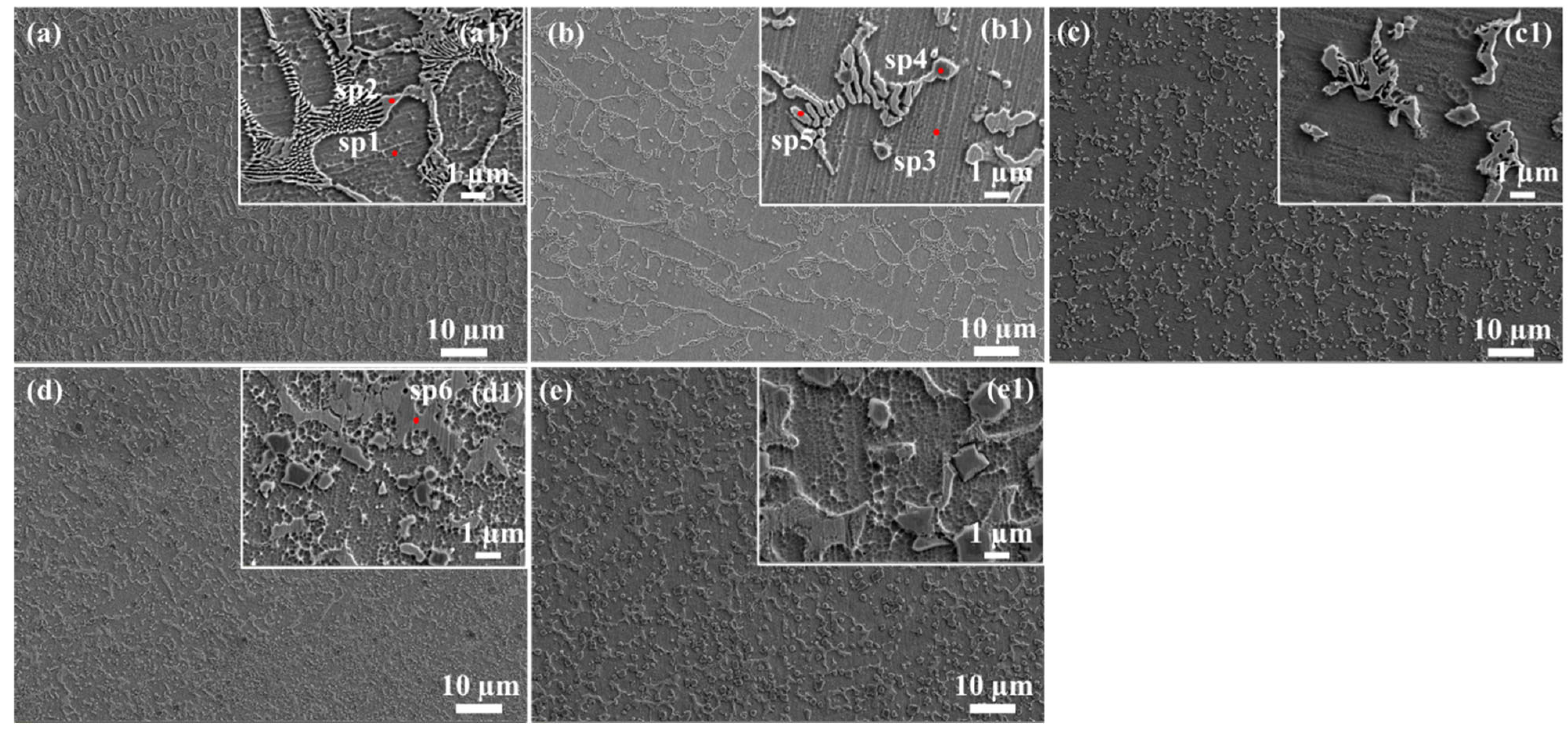
3.2. Microstructure
3.3. Corrosion Resistance
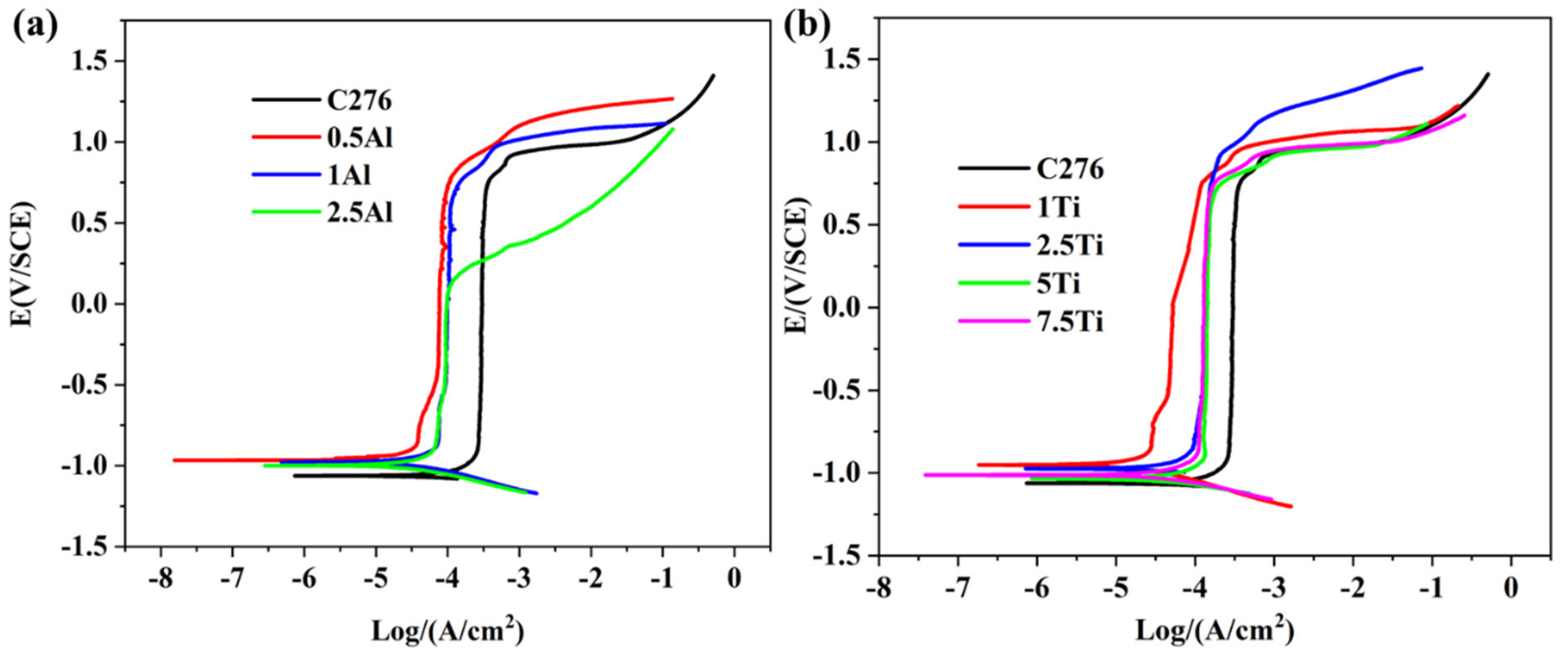
3.3.1. Polarization Curve
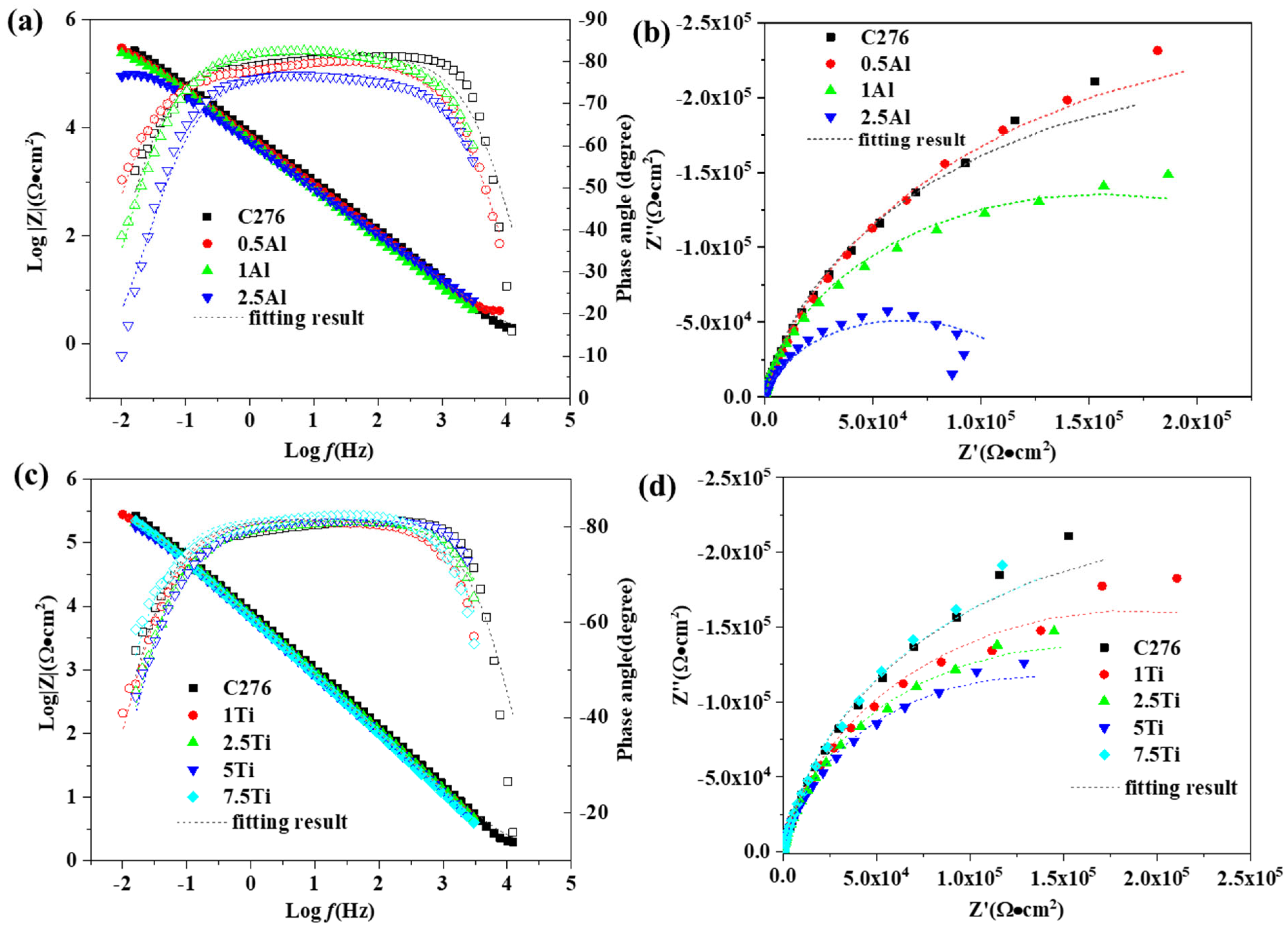
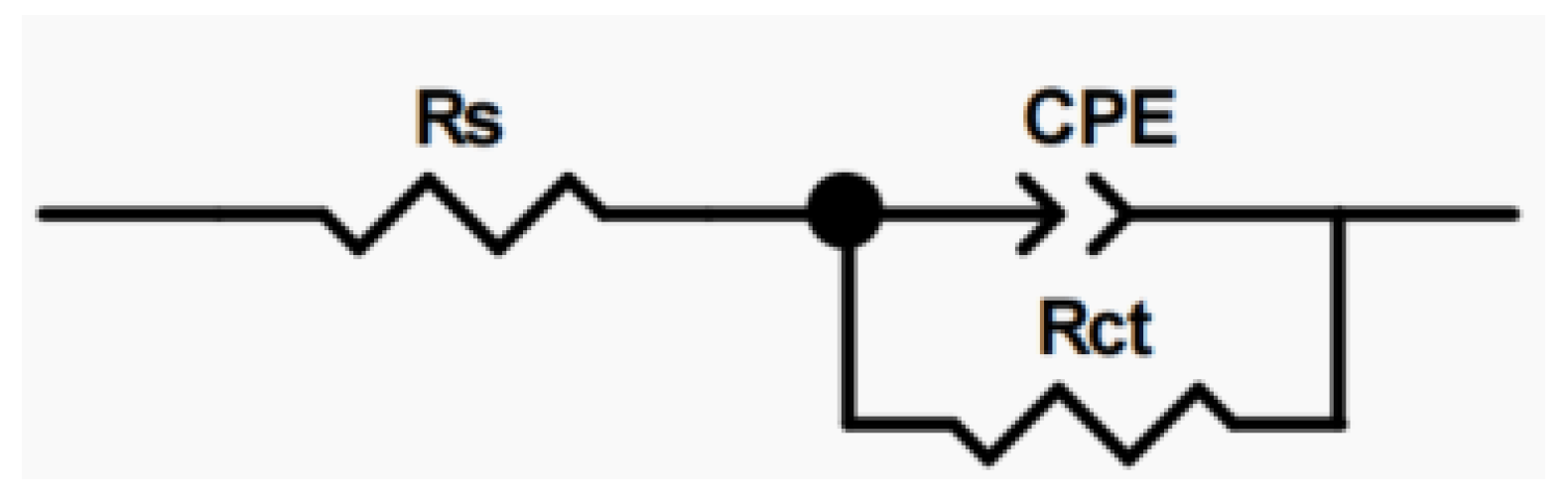
3.3.2. EIS Measurement
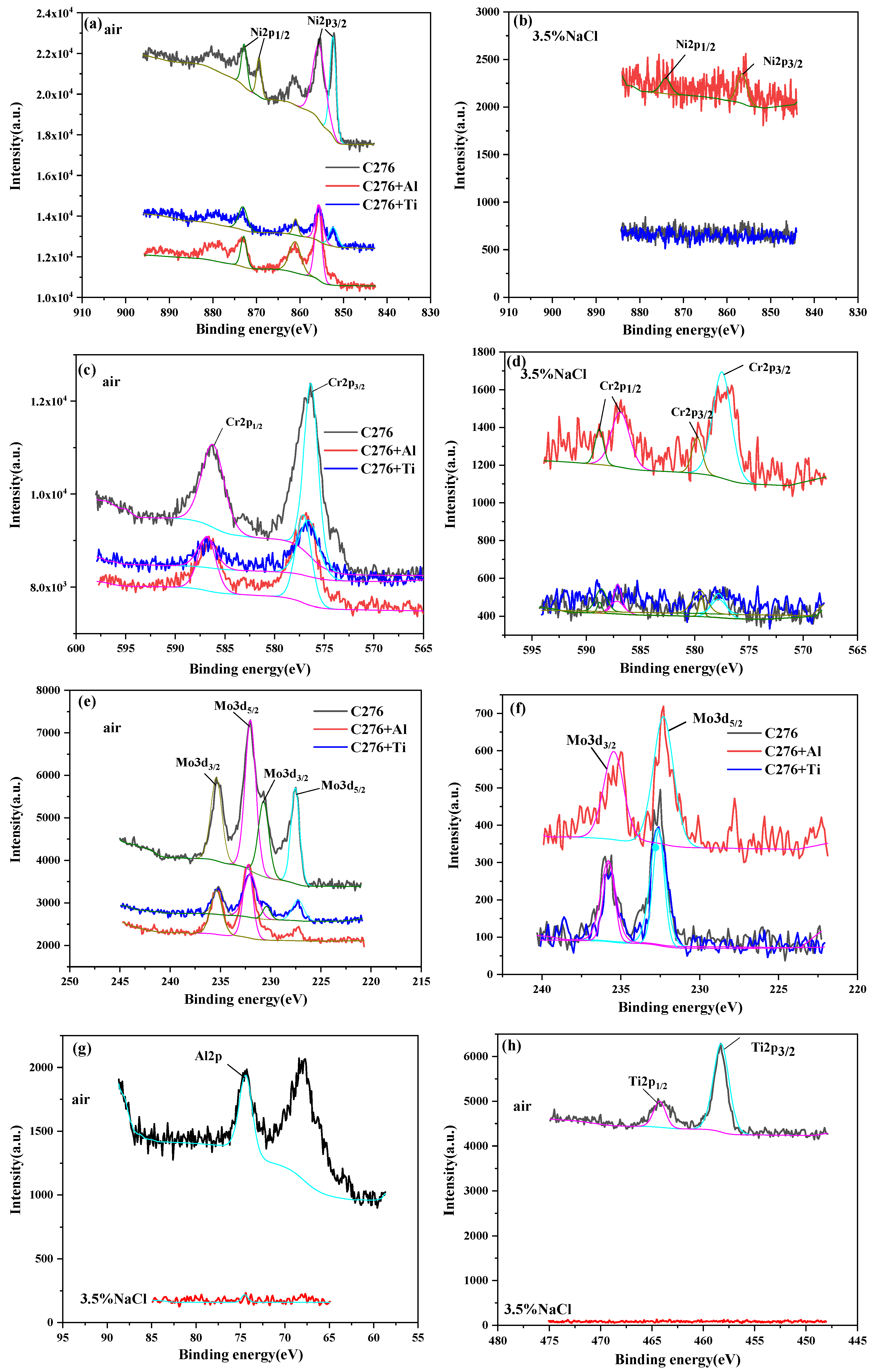
3.3.3. XPS Measurement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
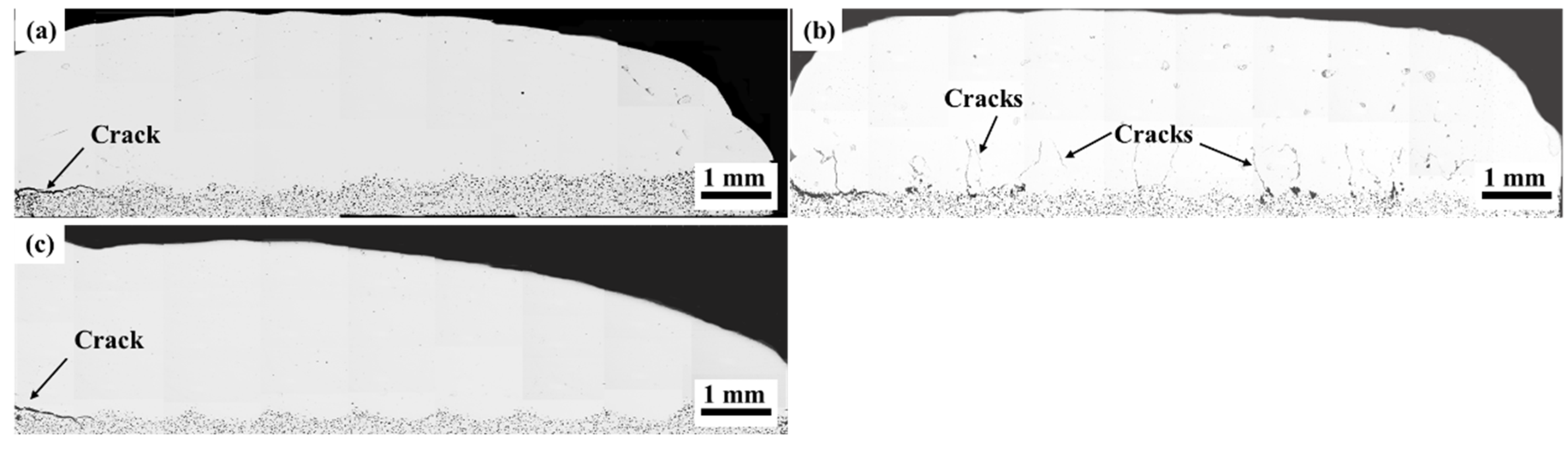
- Ti additions (1–7.5 wt.%) significantly reduced the porosity in Hastelloy C276 coatings, with 7.5 wt.% Ti creating defect-free layers by suppressing CO2/CO gas formation via preferential oxidation. However, excessive Ti (10 wt.%) induced longitudinal cracking due to thermal stress and brittle phase formation. Al additions (0.5–2.5 wt.%) eliminated porosity but caused interfacial cracking, attributed to mismatched thermal expansion coefficients.
- (2)
- Ti additions promoted TiC and NiTi precipitation, coarsening eutectic structures and increasing crack susceptibility at higher Ti contents. Al additions fragmented the networked eutectic structure into isolated phases, altering the stress distribution. Both elements modified the γ-Ni matrix’s elemental segregation behavior, particularly Mo and Cr redistributions.
- (3)
- Al/Ti-modified coatings exhibited higher initial corrosion potentials but narrower passivation ranges compared to unmodified C276. Al-enriched coatings formed less-stable Al2O3/Al(OH)3 films prone to localized corrosion, while Ti-modified layers developed TiO2/TiC phases that marginally improved passivation at 7.5 wt.% Ti. Crack formation in high-Ti/Al coatings further degraded the corrosion resistance by exposing fresh surfaces to electrolytes.
- (4)
- XPS analysis confirmed that oxide films (Cr2O3, NiO, and MoO2) dominated passivation in unmodified coatings, while Al/Ti additions introduced Al2O3 and TiO2, respectively. The inferior stability of these oxides, coupled with crack-induced defects, accelerated corrosion in aggressive environments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, S.; Yan, S.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Ren, W. Microstructure and mechanical property of NiCuFeBSi alloy with laser cladding on substrate of gray cast irons. Chin. J. Lasers 2012, 39, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Nadal, R.L.; Roca, A.S.; Fals, H.D.C.; Zoqui, E.J. Mechanical properties of thixoformed hypoeutectic gray cast iron. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 226, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Geng, S.; Sun, L.; Skuratov, V. A review on cracking mechanism and suppression strategy of nickel-based superalloys during laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1001, 175164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, M.; Hamzekolaei, H.G.; Mohammadi, N.; Yazdanshenas, M.; Hamounpeyma, M.; Afshari, H. Investigating the effect of laser cladding parameters on the microstructure, geometry and temperature changes of Inconel 718 superalloy using the numerical and experimental procedures. Mater. Commun. 2023, 35, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Weng, F.; Dai, J. Research and development status of laser cladding on magnesium alloys: A review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 93, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lian, Y.; Qian, P.; Chen, R.; Zhang, J. Optimized composition design of nickel-based corrosion-resistant alloy for enhanced mechanical properties by integrating experimental design and high-throughput screening. Mater. Commun. 2025, 46, 112574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Luo, H.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X. Effect of Cr on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of nickel-based alloys in hydrochloric acid. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 2867–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, S.; Bai, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, J. Corrosion characteristics and mechanisms of typical iron/nickel-based alloys in reductive supercritical water environments containing sulfides. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 187, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Weng, F.; Bi, G.; Chew, Y.; Liu, S.; Ma, G.; Moon, S.K. Characterization of wear properties of the functionally graded material deposited on cast iron by laser-aided additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 4097–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, C. Process optimization, microstructure and microhardness of coaxial laser cladding TiC reinforced Ni-based composite coatings. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.X.; Jin, H.; Li, J.D.; Zhang, J.W.; Ban, C.Y. Microstructure and properties of Ni-WC gradient composite coating prepared by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 7905–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ren, X.; Qiang, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B. Microstructure and properties of Inconel 718 matrix composite coatings reinforced with submicron TiC particles prepared by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 637, 157920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Yu, T.; Sun, J.; Guan, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–C–TiN-reinforced Ni204-based laser-cladding composite coating. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 5918–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Guan, C.; Sun, J. Microstructure and wear resistance behavior of Ti–C–B4C-reinforced composite coating. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 25136–25148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, F.; Yu, T.; Ma, Z.; Qu, S.; Sun, Z. Effect of TiC content on themicrostructure and wear performance of in situ synthesized Ni-based composite coatings by laser direct energy deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 444, 128678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, D.; Tang, H. Diode laser cladding of Fe-based alloy on ductile cast iron and related interfacial behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 286, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Tian, W.; Liao, W.H.; Hua, L. Microstructure and porosity evaluation in laser-cladding deposited Ni-based coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 294, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.N.; Essa, K.; Attallah, M.M. Optimisation of selective laser melting for a high temperature Ni-superalloy. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Chao, C. Influence of energy density on energy demand and porosity of 316L stainless steel fabricated by selective laser melting. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2018, 5, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, G.L.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, S.S.; Ying, W.L. Microstructure evolution and properties of in-situ ceramic particles reinforced Fe-based composite coating produced by ultrasonic vibration assisted laser cladding processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 403, 126445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Hari, P.R.; Vishnu, G.; Arivarasu, M.; Ramkumar, K.D.; Arivazhagan, N.; Rao, M.N.; Reddy, G.M. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of super alloy C-276 by continuous Nd: YAG laser welding. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, D.; Ma, G.; Zhou, S.; Jin, Z.; Wu, D. Cavitation erosion behavior of Hastelloy™ C276 weld by laser welding. Wear 2019, 420-421, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Miao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Wu, B. Orientation, dendrites and precipitates in Hastelloy C276 alloy fabricated by laser and arc hybrid additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 3129–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansana, B.; Mahapatra, T.R.; Sahu, P.; Sahu, S.K. Tribological and electrochemical corrosion performance analysis of Hastelloy C276 under different loading conditions. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 24, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Niu, F.; Wu, D.; Qu, Y. Electrochemistry corrosion properties of pulsed laser welding Hastelloy C-276. Phys. Procedia 2013, 41, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Q. Influence of CeO2 addition on forming quality and microstructure of TiCx-reinforced CrTi4-based laser cladding composite coating. Mater. Charact. 2021, 171, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F.; Dai, X.Q. Laser induction hybrid rapid cladding of WC particles reinforced NiCrBSi composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4708–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadolkar, P.B.; Watkins, T.R.; De Hosson, J.T.M.; Kooi, B.J.; Dahotre, N.B. State of residual stress in laser-deposited ceramic composite coatings on aluminum alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, C.; Da Sun, S.; Easton, M.; Orchowski, N.; Matthews, N.; Brandt, M. Influence of macrosegregation on solidification cracking in laser clad ultra-high strength steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 340, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Lippold, J.C. The effect of multiple post-weld heat treatment cycles on the weldability of Waspaloy. Weld. J. 2002, 81, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.J.; Peng, J.Q. Four hot corrosion resistant materials for IGT blades. Procedia Eng. 2015, 130, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Bai, S.L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, Z.D. Effect of mechanical polishing on corrosion behavior of Hastelloy C22 coating prepared by high power diode laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 303, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, B.P.; Biesinger, M.C.; Mclntyre, N.S. Use of oxygen/nickel ratios in the XPS characterization of oxide phases on nickel metal and nickel alloy surfaces. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2012, 185, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ke, W.; Sun, W.H.; Hou, W.L.; Chang, X.C.; Wang, J.Q. Slurryerosion-corrosion behaviour of high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) sprayedFe-based amorphous metallic coatings for marine pump in sand-containingNaCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3177–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bai, S.L. The anti-corrosion behavior under multi-factor impingement of Hastelloy C22 coating prepared by multilayer laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 437, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



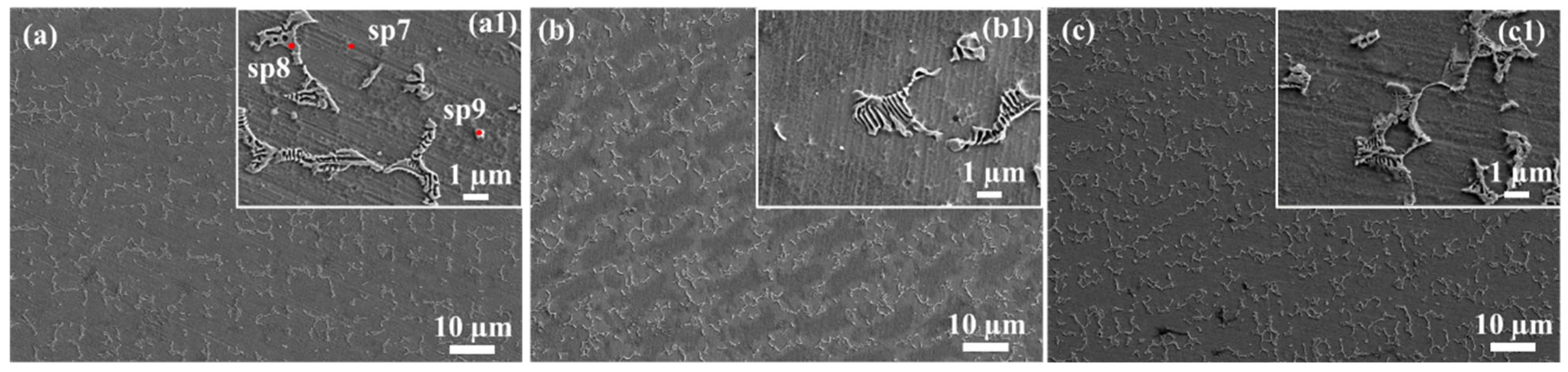

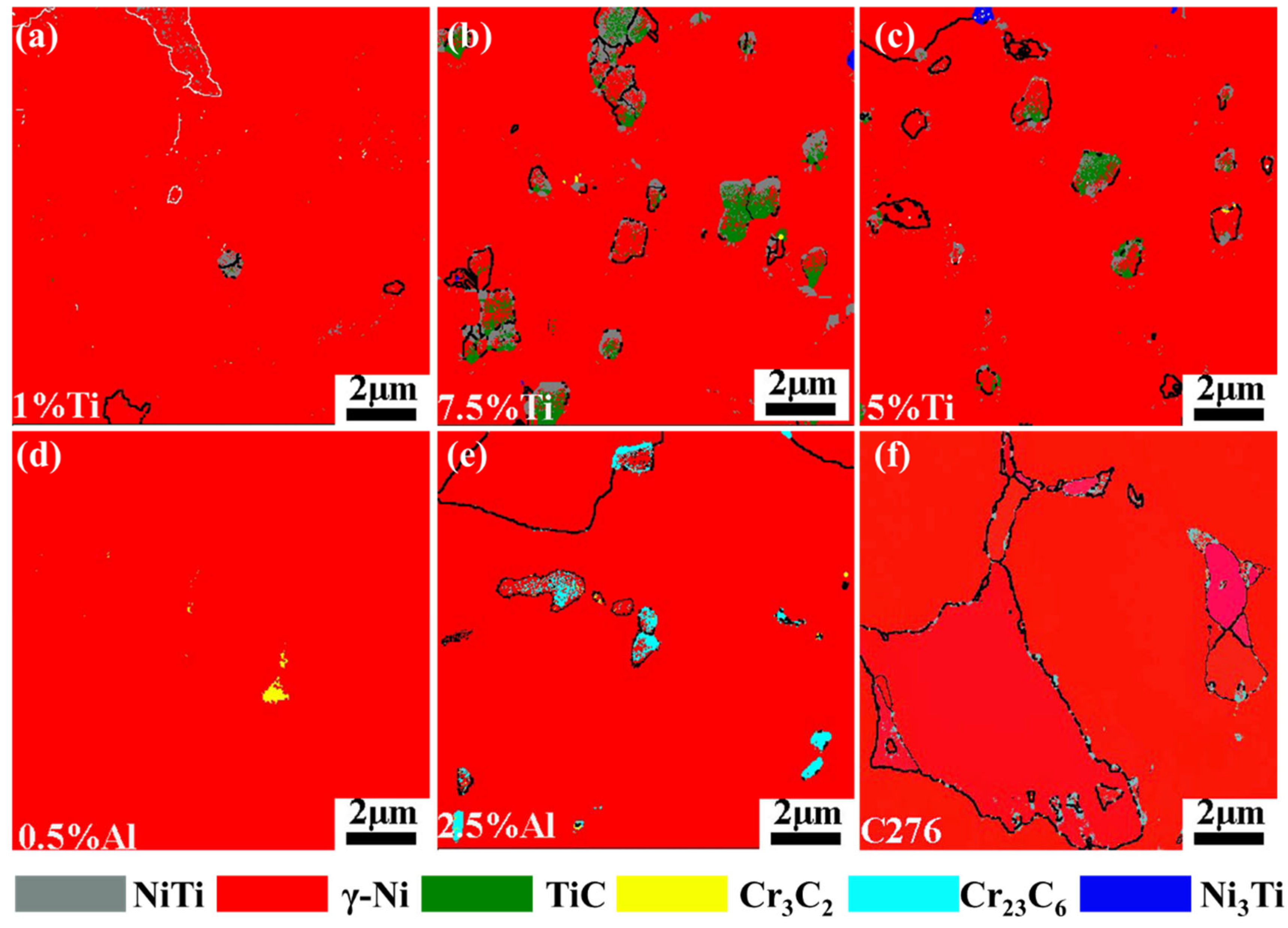


| C | P | Mo | W | Fe | Mn | Cr | Si | O | V | Ni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hastelloy C276 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 16.0 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.3 | 15.7 | 0.7 | 0.04 | 0.6 | Bal. |
| C | P | Si | S | Mn | Fe | ||||||
| QT500-7 | 3.5–3.9 | ≤0.08 | 2.5–3.0 | ≤0.03 | 0.3–0.8 | Bal. |
| Laser Power (W) | Scanning Speed (mm/min) | Power Flow Rate (r/min) | Step-over Width (mm) | Shielding Gas Flow (L/min) | Laser Spot Size (mm) | Carrier Gas Flow (L/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1200–2500 | 200–350 | 1.6–2.2 | 1.85 | 40 | 4.0 | 5 |
| Position | C | Fe | Ni | Mo | Cr | O | W | Si | V | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp1 | 27.6 | 23.9 | 16.7 | 11 | 9.2 | 6.9 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Sp2 | 25.8 | 26.2 | 16.5 | 11.2 | 10.7 | 6.1 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 0.5 | |
| Sp3 | 25.8 | 26.1 | 17.4 | 11 | 10 | 6.3 | 2.2 | 1.1 | ||
| Sp4 | 23 | 32.7 | 15.7 | 6.9 | 14.7 | 5.7 | 1.3 |
| C | Ti | Cr | Fe | Ni | W | Mo | Si | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp1 | 18.98 | 19.16 | 16.04 | 40.32 | 0.77 | 3.13 | |||
| Sp2 | 45.53 | 5.23 | 5.79 | 16.09 | 1.36 | 16.8 | 4.22 | ||
| Sp3 | 20.55 | 3.79 | 20.46 | 10.61 | 42.97 | 1.62 | |||
| Sp4 | 5.73 | 76.09 | 16.72 | 0.77 | 0.69 | ||||
| Sp5 | 21.50 | 2.69 | 4.73 | 0.92 | 1.16 | ||||
| Sp6 | 29.84 | 8.28 | 17.79 | 8.98 | 20.84 | 1.80 | |||
| Sp7 | 22.60 | 16.15 | 48.03 | 1.09 | 8.53 | 2.58 | 0.96 | ||
| Sp8 | 31.49 | 8.00 | 0.51 | 7.15 | 3.17 | 29.24 | 1.23 | ||
| Sp9 | 24.10 | 19.14 | 7.46 | 0.03 | 1.32 | 0.58 |
| Samples | C276 | 1%Ti | 2.5%Ti | 5%Ti | 7.5%Ti | 0.5%Al | 1%Al | 2.5%Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Icorr(A/cm2) | 1.16 × 10−4 | 3.77 × 10−5 | 5.57 × 10−5 | 8.24 × 10−5 | 8.65 × 10−5 | 1.83 × 10−5 | 7.02 × 10−5 | 7.53 × 10−5 |
| Ecorr/V | −1.062 | −0.95 | −0.975 | −1.03 | −1.01 | −0.965 | −0.978 | −0.998 |
| Corrosion rate (mm/A) | 0.384 | 0.125 | 0.185 | 0.273 | 0.286 | 0.061 | 0.233 | 0.25 |
| Width of the passivation zone/V | 1.57 | 1.53 | 1.45 | 1.49 | 1.54 | 1.57 | 1.54 | 0.95 |
| Samples | C276 | 1%Ti | 2.5%Ti | 5%Ti | 7.5%Ti | 0.5%Al | 1%Al | 2.5%Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 1.541 | 1.694 | 1.161 | 0.662 | 1.637 | 2.367 | 1.7 | 2.421 |
| Rct (Ω·cm2) | 4.696 × 105 | 3.74 × 105 | 3.183 × 105 | 2.7 × 105 | 4.614 × 105 | 5.599 × 105 | 3.108 × 105 | 1.272 × 105 |
| CPE-T/μF | 2.36 × 10−5 | 2.822 × 10−5 | 2.668 × 10−5 | 2.976 × 10−5 | 2.886 × 10−5 | 3.016 × 10−5 | 3.188 × 10−5 | 3.687 × 10−5 |
| CPE-P/μF | 0.909 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.908 | 0.916 | 0.885 | 0.913 | 0.863 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Rong, P.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, S.; Chen, R.; Wen, T.; Cheng, S.; et al. Effects of Al/Ti Additions on the Corrosion Behavior of Laser-Cladded Hastelloy C276 Coatings. Coatings 2025, 15, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060678
Chen Y, Rong P, Fang X, Liu Y, Wu Y, Zhang Z, Cao S, Chen R, Wen T, Cheng S, et al. Effects of Al/Ti Additions on the Corrosion Behavior of Laser-Cladded Hastelloy C276 Coatings. Coatings. 2025; 15(6):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060678
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yong, Peng Rong, Xin Fang, Yan Liu, Ying Wu, Zhenlin Zhang, Shaoting Cao, Ruiwen Chen, Ting Wen, Shixiang Cheng, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Al/Ti Additions on the Corrosion Behavior of Laser-Cladded Hastelloy C276 Coatings" Coatings 15, no. 6: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060678
APA StyleChen, Y., Rong, P., Fang, X., Liu, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, Z., Cao, S., Chen, R., Wen, T., Cheng, S., Yang, X., & Chen, Y. (2025). Effects of Al/Ti Additions on the Corrosion Behavior of Laser-Cladded Hastelloy C276 Coatings. Coatings, 15(6), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060678







