Effect of Sc/Y Co-Doping on Initial Alumina Growth of Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposited FeCoNiCrAl High-Entropy Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
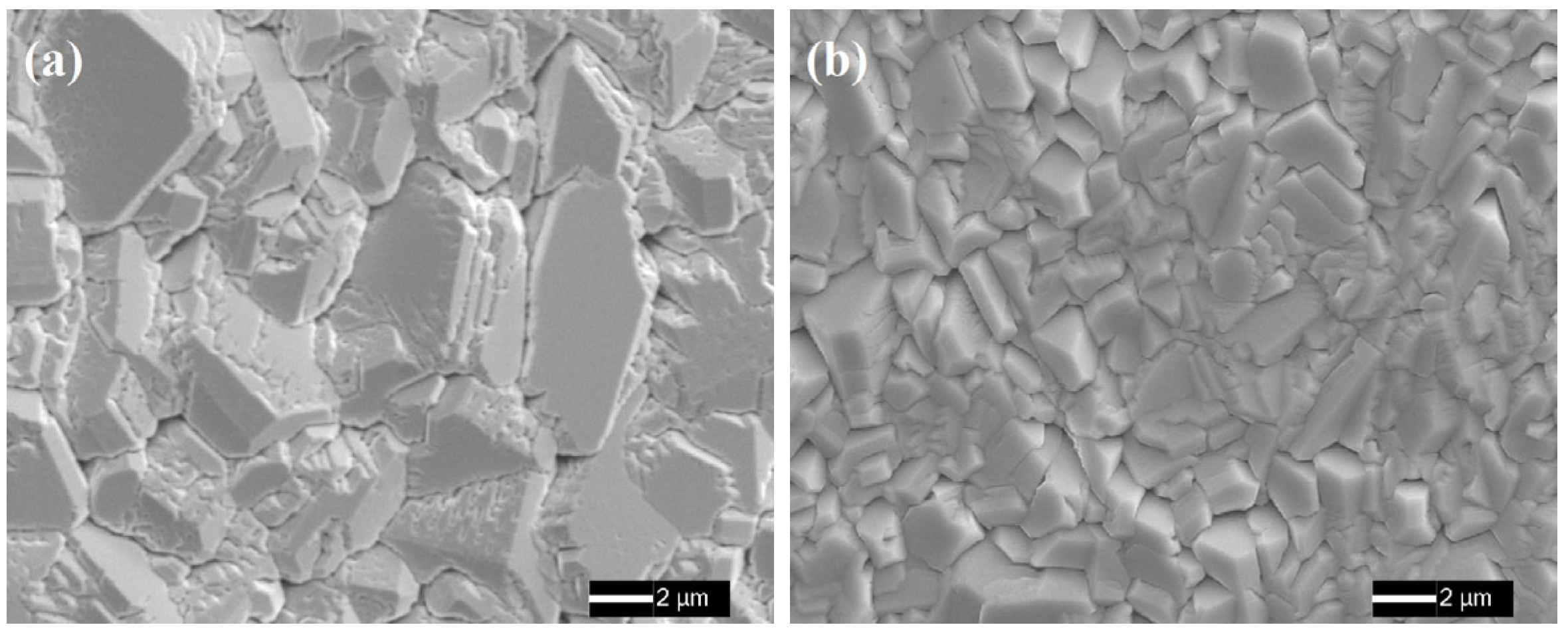
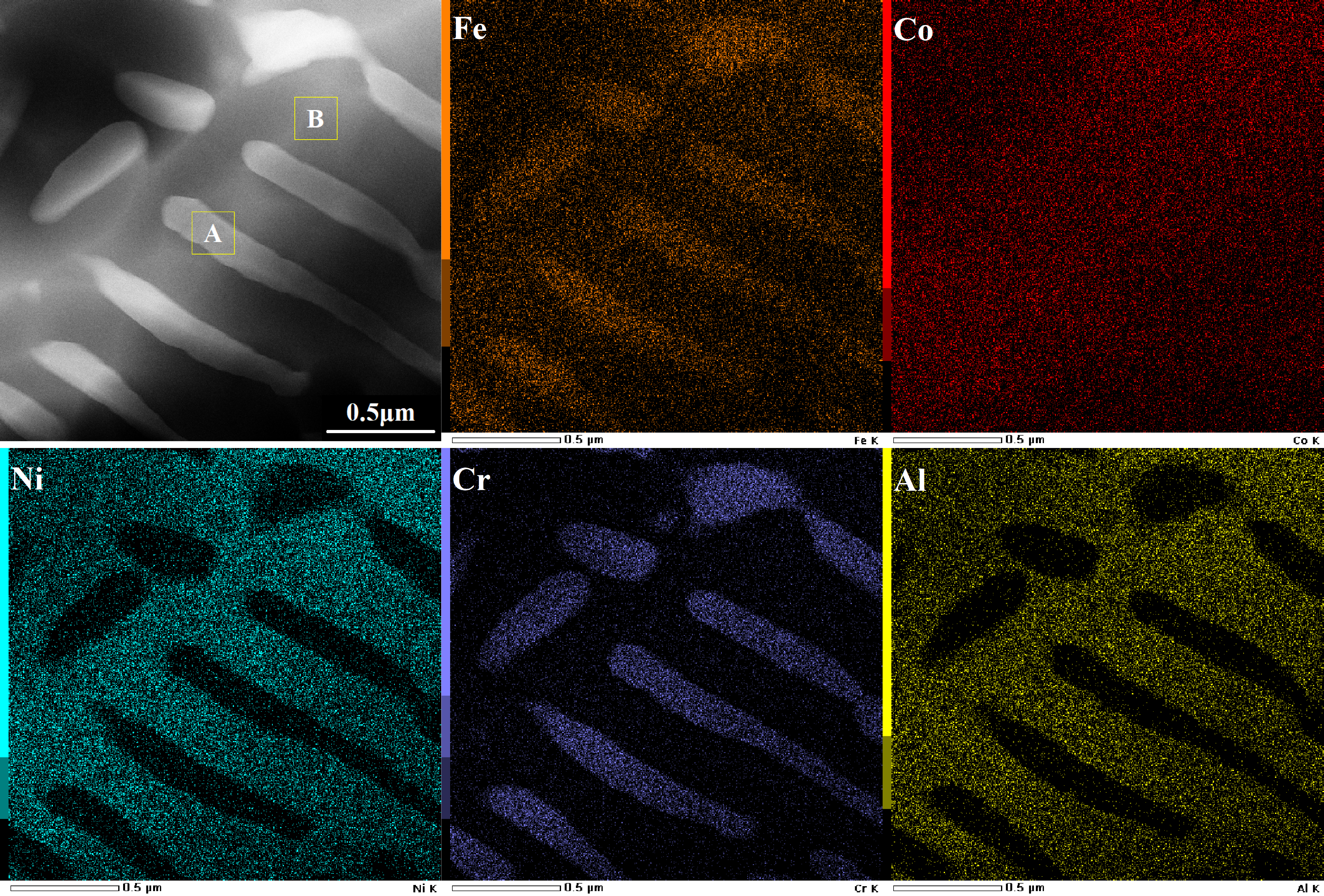
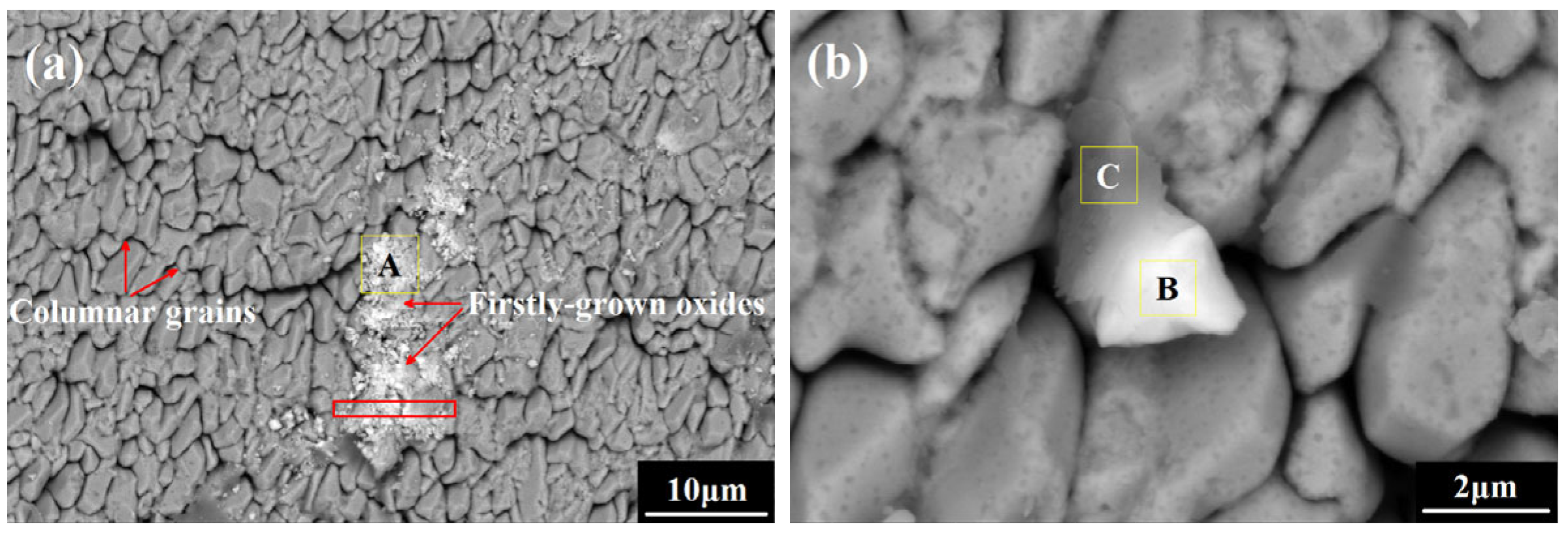
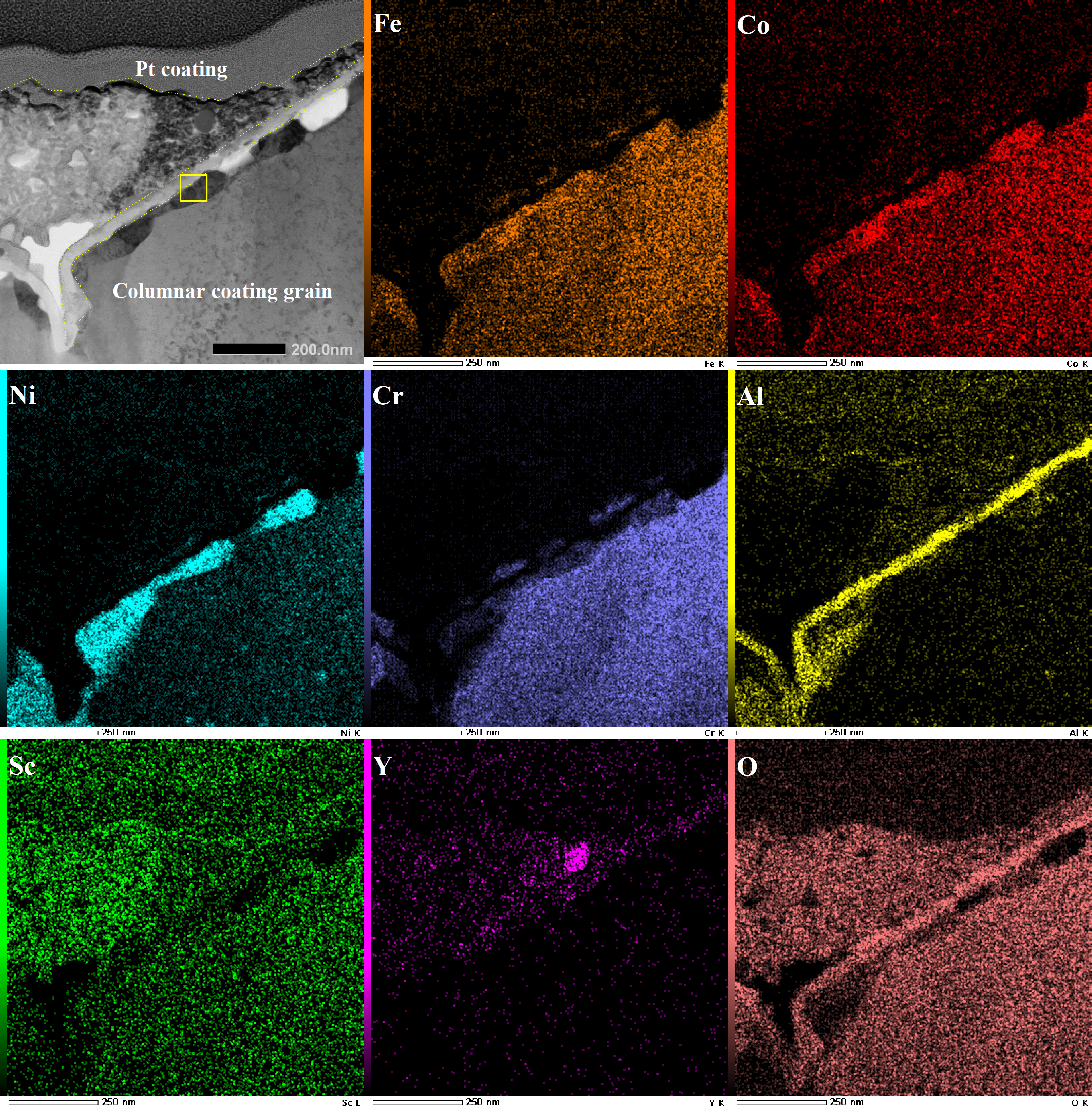
3.1. Coating Microstructure Characterization
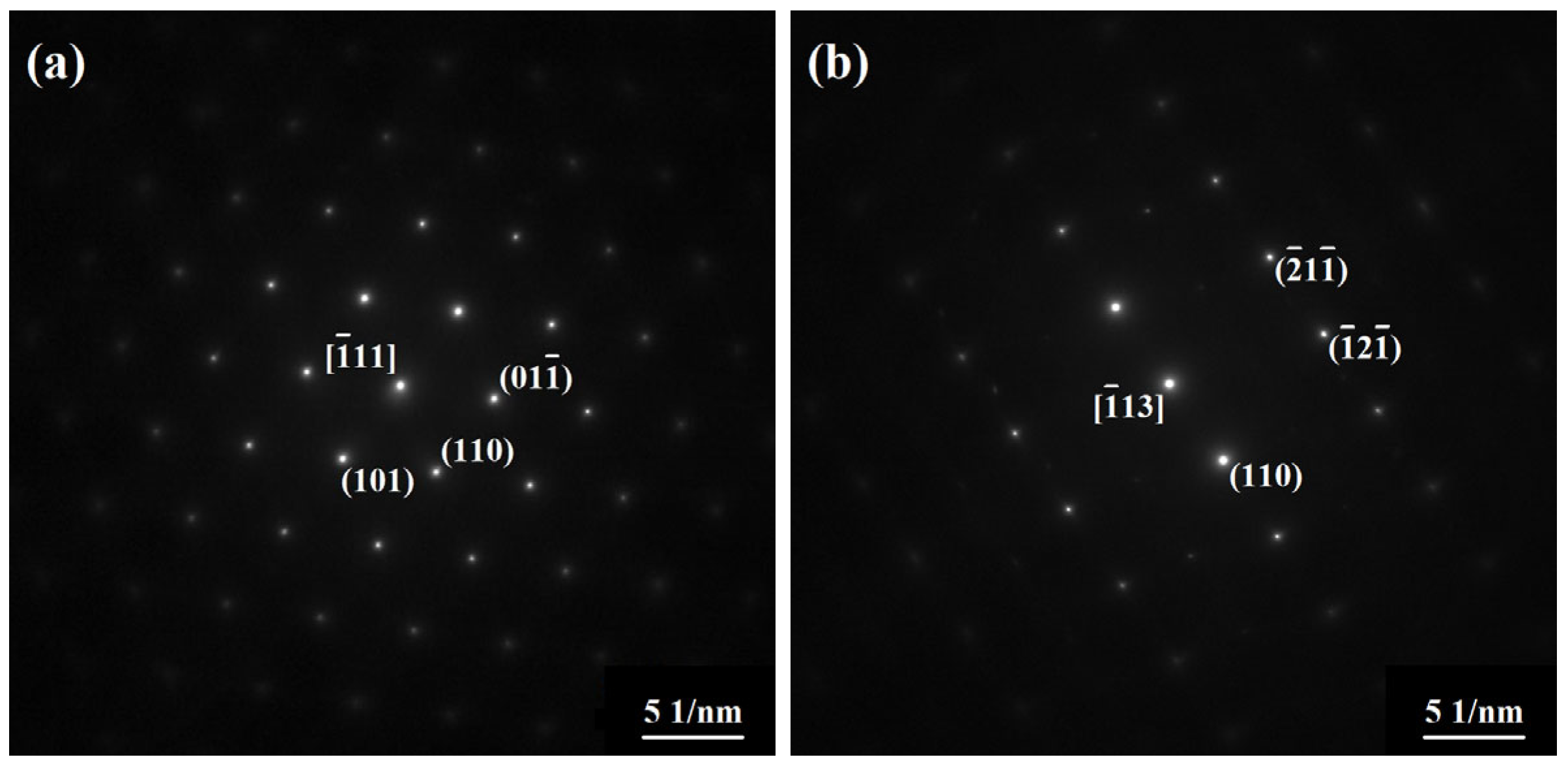
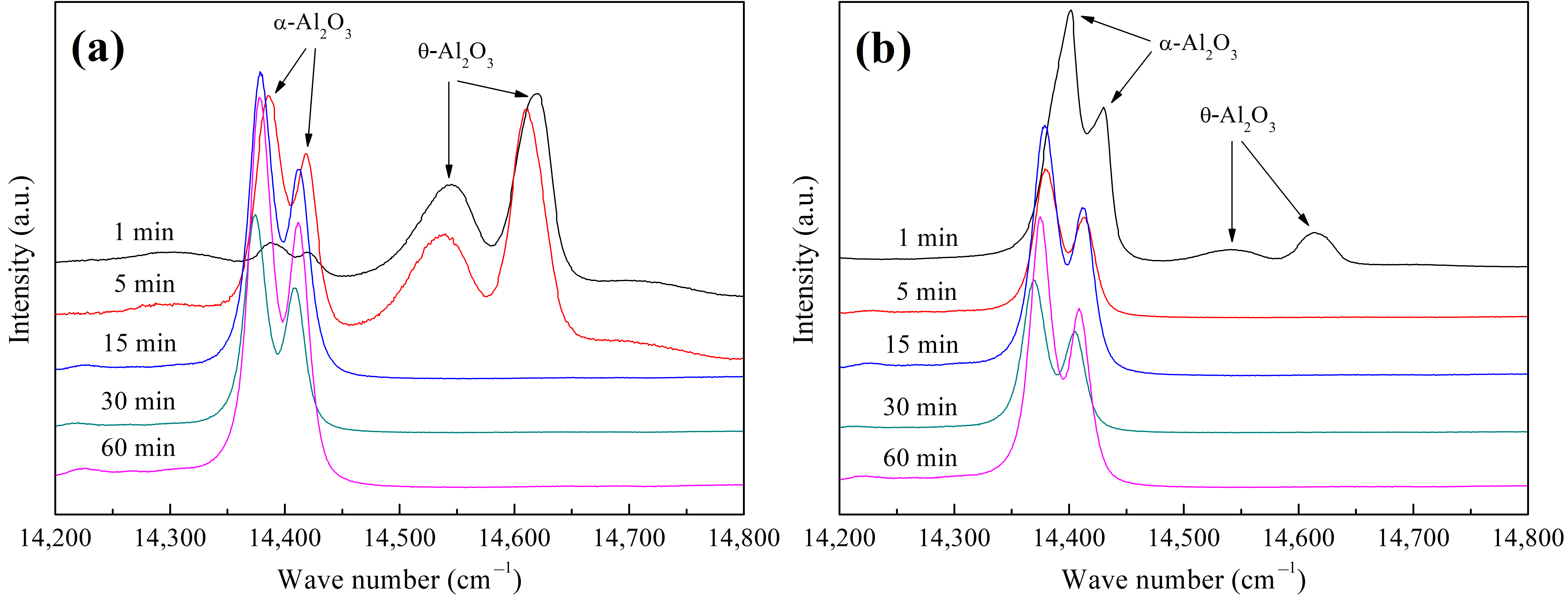
3.2. Oxide Phase Identification
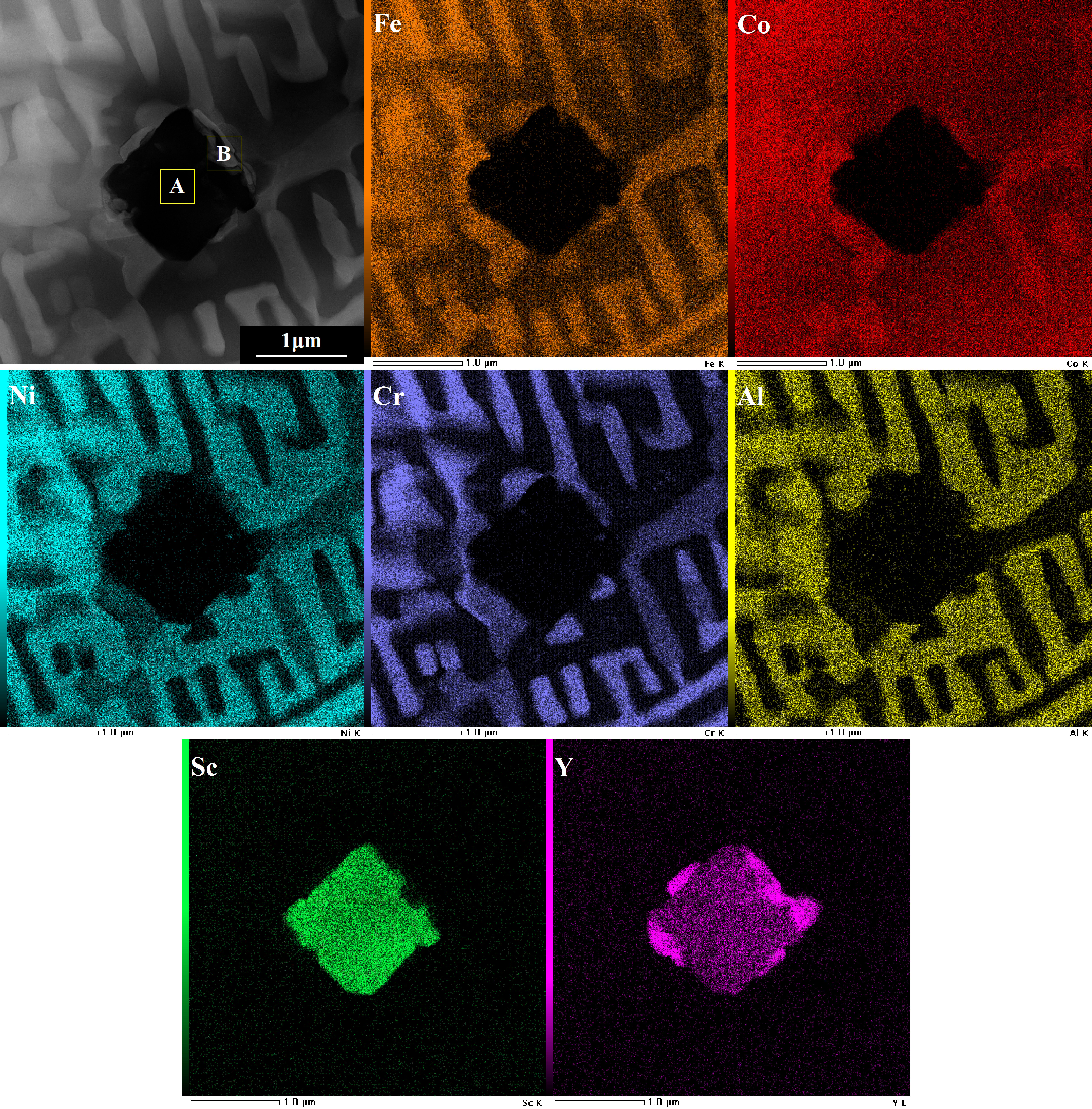
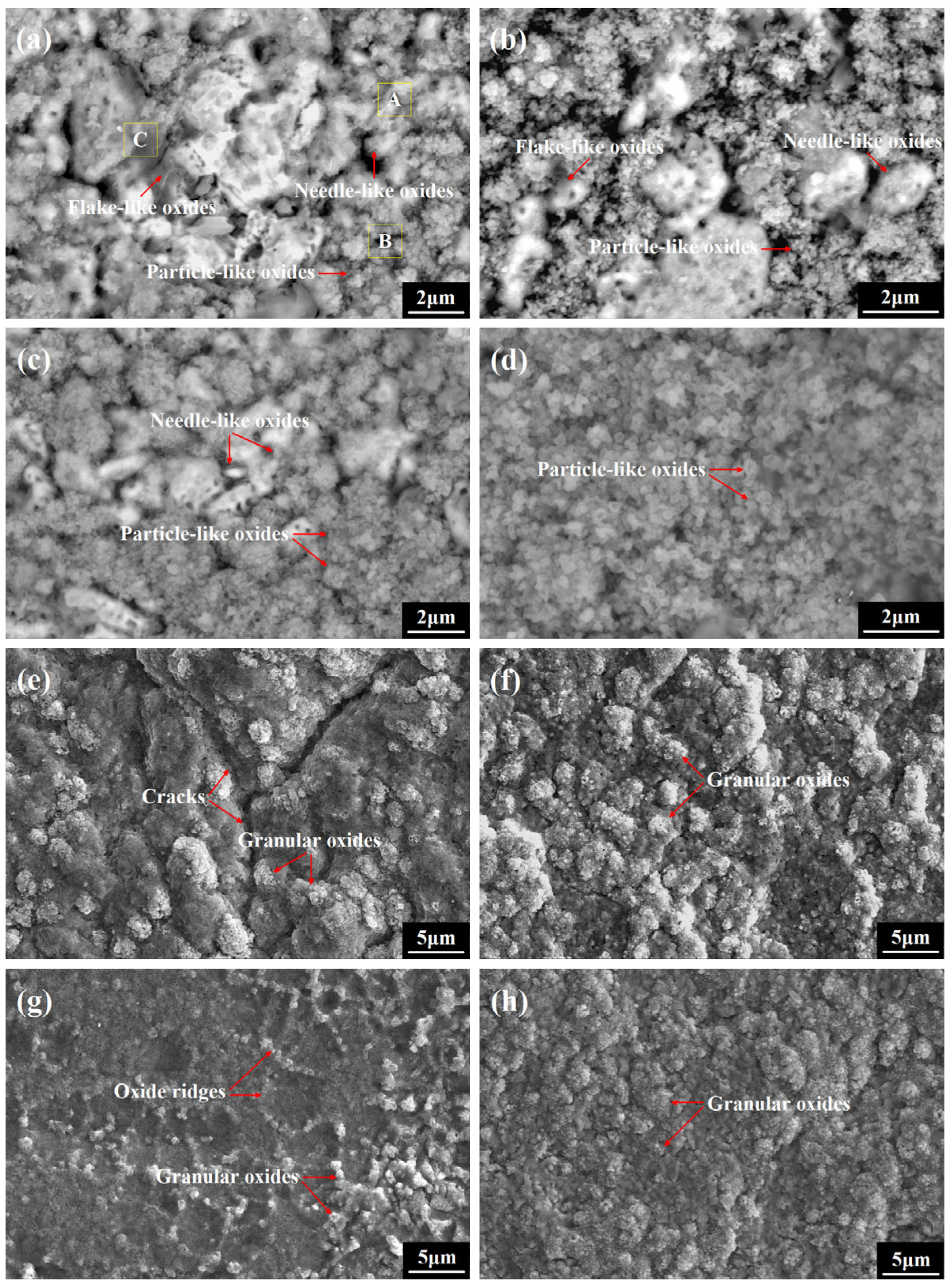
3.3. Oxide Morphology Observation
3.4. Intrinsic Factor Affecting the “Accelerating Effect”
4. Conclusions
- During coating preparation, Sc and Y refined the coating grains and stabilized the coating phases owing to the obstruction of grain growth and element diffusion to the superalloy substrate, and they eventually formed co-precipitated phases, as Sc and Y are congeners and have the same outermost electron arrangement and steady-state valence, which allowed them to combine with each other.
- In the initial oxidation stage, the θ- to α-Al2O3 phase transformation was rapidly achieved on the undoped coating, while the evolution process was further accelerated on the co-doped coating with no crack initiation or ridge formation. The preferential formation of Sc/Y-rich oxides provided rapid diffusion channels for oxygen inward penetration, and the refined coating grains provided more grain boundaries for Al outward migration, thus promoting the nucleation of α-Al2O3 beneath the Sc/Y-rich oxides and visually expediting the θ-α phase transformation, as the evolution process was directly skipped.
- The direct formation of α-Al2O3 on the co-doped coating surface stimulated by the preferentially grown Sc/Y-rich oxides decreased the growth fraction of θ-Al2O3 and eliminated the initial formation of cracks originating from the θ-α phase transformation, hence reducing the contribution of θ-Al2O3 growth to the rapid oxidation of the coating and maintaining the integrity of the alumina film, which could improve the oxidation resistance of the FeCoNiCrAl high-entropy coating during the early oxidation process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pi, Y.H.; Park, J.S. Effect of the thermal barrier coating set up and modeling in numerical analysis for prediction gas turbine blade temperature and film cooling effectiveness. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 164, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Choi, M.; Choi, G. Thermodynamic performance study of large-scale industrial gas turbine with methane/ammonia/hydrogen blended fuels. Energy 2023, 282, 128731. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Qin, Z.; Luo, J.; Bai, M.; Liu, J.; Yu, D. Research on active modulation of gas turbine cooling air flow. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 230 Pt B, 120874. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Peng, X.; Lü, W.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, J. Ultra-high temperature oxidation resistant refractory high entropy alloys fabricated by laser melting deposition: Al concentration regulation and oxidation mechanism. Corros. Sci. 2023, 224, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Yang, S.; Zhang, C. Micro-nano dual-scale coatings prepared by suspension precursor plasma spraying for resisting molten silicate deposit. Coatings 2024, 14, 1123. [Google Scholar]
- Gudivada, G.; Pandey, A.K. Recent developments in nickel-based superalloys for gas turbine applications: Review. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 963, 171128. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhu, W.; Peng, X.M. Reliability assessment and lifetime prediction of TBCs on gas turbine blades considering thermal mismatch and interfacial oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 423, 127572. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yang, G. Understanding of degradation-resistant behavior of nanostructured thermal barrier coatings with bimodal structure. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Wei, X.; Cao, J.; Ma, Y.; Su, H.; Zhao, T.; You, J.; Lv, Y. Thermal corrosion properties of composite ceramic coating prepared by multi-arc ion plating. Coatings 2024, 14, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; He, L.M.; Guo, Y.; Shan, X.; Li, J.H.; Guo, F.W.; Zhao, X.F.; Ni, N.; Xiao, P. Effects of reactive element oxides on the isothermal oxidation of β-NiAl coatings fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 357, 322–331. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.H.; Li, S.S.; Wang, Y.N.; Gui, P.P.; Zhang, M.Y.; Guo, K.Y.; Liu, M.J.; Yang, G.J. Unraveling β-NiAldegradation in aluminide coatings: A comparative study of isothermal oxidation and vacuum heat treatment. Corros. Sci. 2025, 251, 112946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Z.; He, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B.Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, H.B. Theformation mechanisms of HfO2 located in different positions of oxide scales on Ni-Al alloys. Corros. Sci. 2020, 167, 108481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Gong, J.; Sun, C. The effect of Re and Hf interaction on the oxidation performance in ReHf co-doped NiAl coating. Corros. Sci. 2024, 240, 112447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Wei, L.; Guo, H. The interaction between Dy, Pt and Mo during the short-time oxidation of (γ’ plus β) two-phase Ni-Al coating on single crystal superalloy with high Mo content. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 430, 127999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Weaver, M. Microstructural investigation of the thermally grown oxide on grain-refined overdoped NiAl-Zr. Oxid. Met. 2019, 92, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Q.; Guo, H.B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Gong, S.K.; Xu, H.B. Cyclic oxidation ofβ-NiAl with various reactive element dopants at 1200 °C. Corros. Sci. 2013, 66, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, M.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Niu, Y.S.; Bao, Z.B.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, F.H. Co-doping effect of Hf and Y on improving cyclic oxidation behavior of (Ni,Pt)Al coating at 1150 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 178, 109093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adharapurapu, R.R.; Zhu, J.; Dheeradhada, V.S.; Lipkin, D.M.; Pollock, T.M. Effective Hf-Pd Co-doped β-NiAl(Cr) coatings for single-crystal superalloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 76, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Q.; Zhou, L.X.; Zhu, K.J.; Gu, J.; Zheng, S.H. Isothermal oxidation behavior of scandium and yttrium co-doped B2-type iron-aluminum intermetallics at elevated temperature. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.R.; Crespo, V.; Nin, J.; Clavé, G.; Dosta, S. Adhesion of thermal barrier coatings: Influence of the bond coat application technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 503, 132031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Feng, W.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y. Performance and failure modes of thermal barrier coatings deposited by EB-PVD on blades under real service conditions in gas turbine. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1008, 176889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiong, K.; Li, D.; Hou, C.; Fan, X. A thermal mechanical coupled damage accumulation model for rare earth-doped EB-PVD TBCs under isothermal oxidation, cyclic oxidation and creep conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 505, 132088. [Google Scholar]
- Ozgurluk, Y.; Doleker, K.M.; Karaoglanli, A.C. Hot corrosion behavior of YSZ, Gd2Zr2O7 and YSZ/Gd2Zr2O7 thermal barrier coatings exposed to molten sulfate and vanadate salt. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 438, 96–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.S.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, M.H.; Yang, L.L.; Wang, J.L.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, F.H. Oxidation behavior of Al/Y co-modified nanocrystalline coatings with different Al content on a nickel-based single-crystal superalloy. Corros. Sci. 2020, 170, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Q.; Guo, H.B.; Peng, H.; Gong, S.K.; Xu, H.B. Improved alumina scale adhesion of electron beamphysical vapor deposited Dy/Hf-doped β-NiAl coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, R.; Li, Y. Recent advances in the performance and mechanisms of high-entropy alloys under low- and high-temperature conditions. Coatings 2025, 15, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Ritchie, R.O.; Meyers, M.A. Mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys with emphasis on face-centered cubic alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 102, 296–345. [Google Scholar]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Weaver, M.L. Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNimulti-component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Huang, A.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Zhao, X. Y-Hf co-doped Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi high-entropy alloy with excellent oxidation resistance and nanostructure stability at 1200 °C. Scr. Mater. 2021, 203, 114105. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, D.; Fietzek, H.; Galetz, M.; Heilmaier, M. The effect of micro-alloying with Zr and Nb on the oxidation behavior of Fe3Al and FeAl alloys. Intermetallics 2013, 41, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ullah, I.; Shah, S.S.A.; Aziz, T.; Zhang, S.H.; Song, G.S. Effect of Cr nanoparticle dispersions with various contents on the oxidation and phase transformation of alumina scale formation on Ni2Al3 coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 438, 128397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, L.; Xi, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Si, J.; Zhu, K. Phase transformation behavior of alumina grown on FeAl alloys with reactive element dopants at 1273 K. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, T.L.; Marquis, E.A. Effects of minor alloying elements on alumina transformation during the transient oxidation of β-NiAl. Oxid. Met. 2021, 95, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.; Kupka, M. High-temperature oxidation behaviour of B2 FeAl based alloy with Cr, Zr and B additions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pint, B.A.; Hobbs, L.W. Limitations on the use of ion implantation for the study of the reactive element effect in β-NiAl. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, X.W. Modeling of θ→α alumina lateral phase transformation with applications to oxidation kinetics of NiAl-based alloys. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybichi, G.C.; Smialek, J.L. Effect of the θ-α-Al2O3 transformation on the oxidation behavior of β-NiAl+Zr. Oxid. Met. 1989, 31, 275–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Li, T.; Pan, W. Oxidation of a La2O3-modified aluminide coating. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandee, P.; Gourlay, C.; Belyakov, S.; Patakham, U.; Zeng, G.; Limmaneevichitr, C. AlSi2Sc2 intermetallic formation in Al-7Si-0.3Mg-xSc alloys and their effects on as-cast properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 731, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pint, B.A. Progress in understanding the reactive element effect since the Whittle and Stringer literature review. In John Stringer Symposium on High Temperature Corrosion; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2003; pp. 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Xiao, P. Y-Hf co-doped AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating with superior oxidation and spallation resistance at 1100 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtin, P.; Brunelle, J.; Pijolat, M.; Soustelle, M. Influence of surface area and additives on the thermal stability of transition alumina catalyst supports. II: Kinetic model and interpretation. Appl. Catal. 1987, 34, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buban, J.P.; Matsunaga, K.; Chen, J.; Shibata, N.; Ching, W.Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Ikuhara, Y. Grain boundary strengthening in alumina by rare earth impurities. Science 2006, 311, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.T.; Xu, C.M. Effect of NiAl microcrystalline coating on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of NiAl-28Cr-5Mo-1Hf. Oxid. Met. 2002, 58, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Priimak, K. Interfacial segregation, pore formation, and scale adhesion on NiAl alloys. Oxid. Met. 2005, 63, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pint, B.A.; Treska, M.; Hobbs, L.W. The effect of various oxide dispersions on the phase composition and morphology of Al2O3 scales grown on β-NiAl. Oxid. Met. 1997, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pint, B.A. Experimental observations in support of the dynamic-segregation theory to explain the reactive-element effect. Oxid. Met. 1996, 45, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Microstructure evolution and oxidation resistance properties of oxide dispersion strengthened FeCrAl alloys at 1100 °C. Vacuum 2024, 227, 113371. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Bojarczuk, N.A.; Guha, S.; Ramanathan, S. Transmission electron microscopy studies on structure and defects in crystalline yttria and lanthanum oxide thin films grown on single crystal sapphire by molecular beam synthesis. Philos. Mag. 2010, 90, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, P.; Huber, G.; Kurfiss, M.; Schilling, M. Crystalline growth of cubic (Eu, Nd):Y2O3 thin films on α-Al2O3 by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. A 2005, 80, 627–630. [Google Scholar]
- Heffelfinger, J.R.; Carter, C.B. The effect of surface structure on the growth of ceramic thin films. Philos. Mag. Lett. 1997, 76, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pint, B.A. Optimization of reactive-element additions to improve oxidation performance of alumina-forming alloys. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, D.P.; Stringer, J. Improvements in high temperature oxidation resistance by additions of reactive elements or oxide dispersions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1980, 295, 309–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Chen, D.; Gao, X.; Liu, T.; Qin, G.; Chen, R.; Wu, S.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. Contribution of Sc doping to the growth and adhesion of alumina scale on AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 2024, 252, 116272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, F. The reactive element effect of ceria particle dispersion on alumina growth: A model based on microstructural observations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
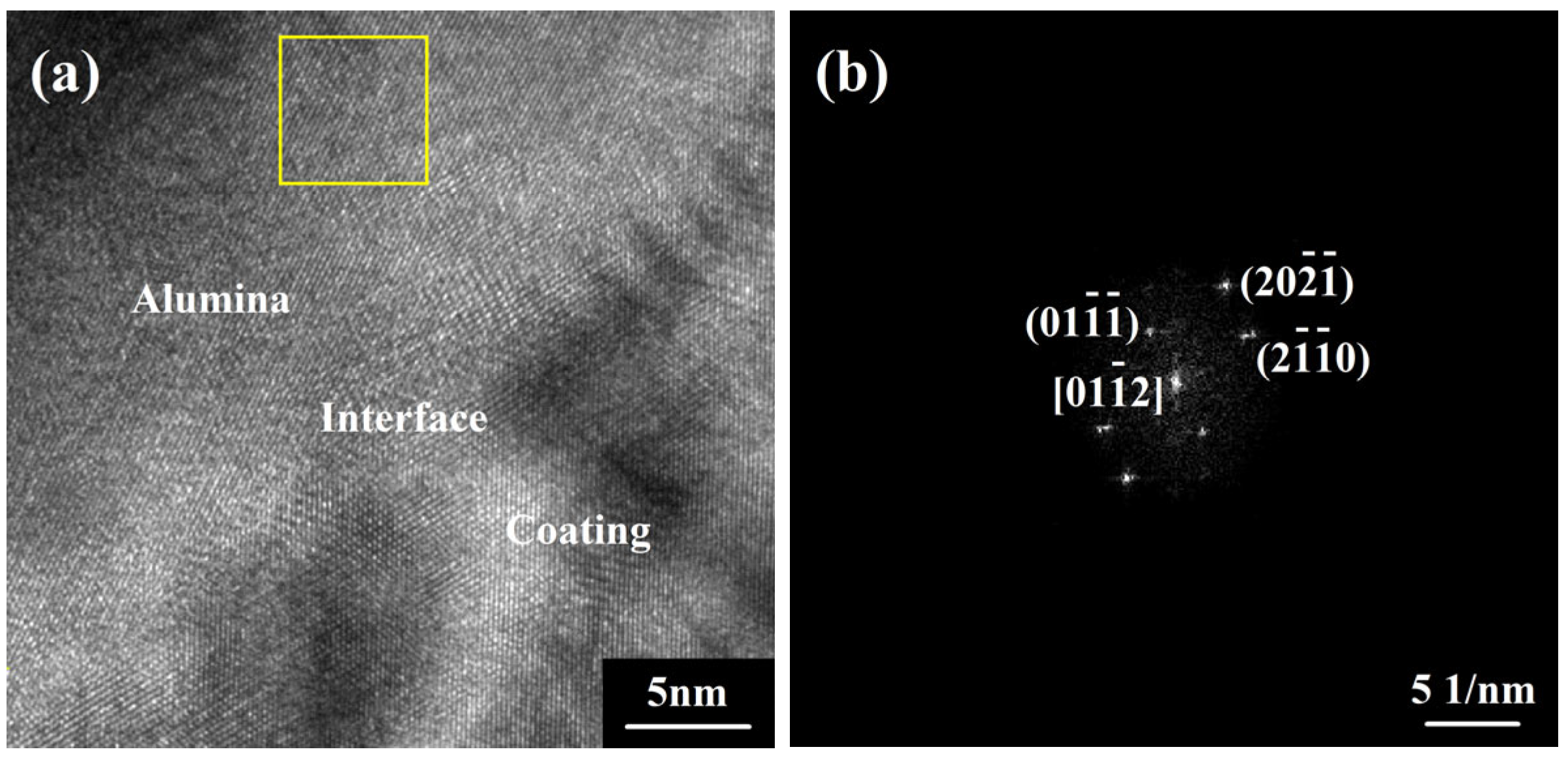


| Target Compositions | Fe | Co | Ni | Cr | Al | Sc | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-20Co-20Ni-20Cr-20Al | Bal. | 21.74 | 20.60 | 18.42 | 19.98 | - | - |
| Fe-20Co-20Ni-20Cr-19.9Al-0.05Sc-0.05Y | Bal. | 20.80 | 21.88 | 19.64 | 19.79 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Fe | Co | Ni | Cr | Al | W | Mo | Ta | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone A (LW zone) | 23.83 (±0.27) | 12.61 (±0.14) | 16.26 (±0.16) | 30.27 (±0.24) | 15.24 (±0.09) | 0.85 (±0.11) | 0.61 (±0.07) | 0.33 (±0.21) |
| Zone B (LG zone) | 29.47 (±0.31) | 11.3 (±0.10) | 10.32 (±0.14) | 38.94 (±0.27) | 8.95 (±0.07) | 0.53 (±0.13) | 0.34 (±0.09) | 0.15 (±0.17) |
| Zone C (DG zone) | 10.64 (±0.20) | 14.36 (±0.11) | 33.17 (±0.29) | 12.92 (±0.21) | 28.61 (±0.14) | - | 0.21 (±0.07) | 0.09 (±0.12) |
| Fe | Co | Ni | Cr | Al | Sc | Y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone A | 6.86 (±0.10) | 4.02 (±0.14) | 5.51 (±0.17) | 5.23 (±0.12) | 1.24 (±0.07) | 52.78 (±0.38) | 24.35 (±0.32) |
| Zone B | 13.91 (±0.12) | 13.40 (±0.11) | 8.30 (±0.12) | 11.81 (±0.09) | 3.14 (±0.09) | 9.21 (±0.17) | 40.24 (±0.41) |
| 1 min | 5 min | 15 min | 30 min | 60 min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-20Co-20Ni-20Cr-20Al | 92.93 | 54.67 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Fe-20Co-20Ni-20Cr-19.9Al-0.05Sc-0.05Y | 12.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Fe | Co | Ni | Cr | Al | O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone A | 4.42 (±0.11) | 2.65 (±0.06) | 5.93 (±0.11) | 8.73 (±0.17) | 27.51 (±0.28) | 50.76 (±0.44) |
| Zone B | 3.90 (±0.11) | 5.21 (±0.11) | 4.23 (±0.08) | 7.47 (±0.14) | 29.65 (±0.24) | 49.54 (±0.32) |
| Zone C | 11.62 (±0.14) | 6.83 (±0.09) | 10.73 (±0.16) | 8.97 (±0.19) | 17.98 (±0.21) | 43.87 (±0.37) |
| Fe | Co | Ni | Cr | Al | Sc | Y | O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone A | 7.78 (±0.09) | 4.85 (±0.11) | 12.65 (±0.16) | 9.21 (±0.21) | 7.14 (±0.07) | 1.83 (±0.17) | 9.11 (±0.20) | 47.43 (±0.44) |
| Zone B | 3.36 (±0.11) | 0.53 (±0.07) | 1.65 (±0.08) | 3.83 (±0.18) | 5.99 (±0.10) | 5.04 (±0.24) | 21.15 (±0.39) | 58.45 (±0.47) |
| Zone C | 5.91 (±0.14) | 2.60 (±0.10) | 6.79 (±0.11) | 9.88 (±0.16) | 20.35 (±0.22) | - | - | 54.47 (±0.41) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Zheng, S.; Gu, J.; Si, J. Effect of Sc/Y Co-Doping on Initial Alumina Growth of Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposited FeCoNiCrAl High-Entropy Coating. Coatings 2025, 15, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121436
Li D, Zheng S, Gu J, Si J. Effect of Sc/Y Co-Doping on Initial Alumina Growth of Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposited FeCoNiCrAl High-Entropy Coating. Coatings. 2025; 15(12):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121436
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongqing, Shuhui Zheng, Jian Gu, and Jiajun Si. 2025. "Effect of Sc/Y Co-Doping on Initial Alumina Growth of Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposited FeCoNiCrAl High-Entropy Coating" Coatings 15, no. 12: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121436
APA StyleLi, D., Zheng, S., Gu, J., & Si, J. (2025). Effect of Sc/Y Co-Doping on Initial Alumina Growth of Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposited FeCoNiCrAl High-Entropy Coating. Coatings, 15(12), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121436






