Study on Acoustic and Mechanical Properties of AlSi7Mg/TPU Porous Interpenetrating Phase Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
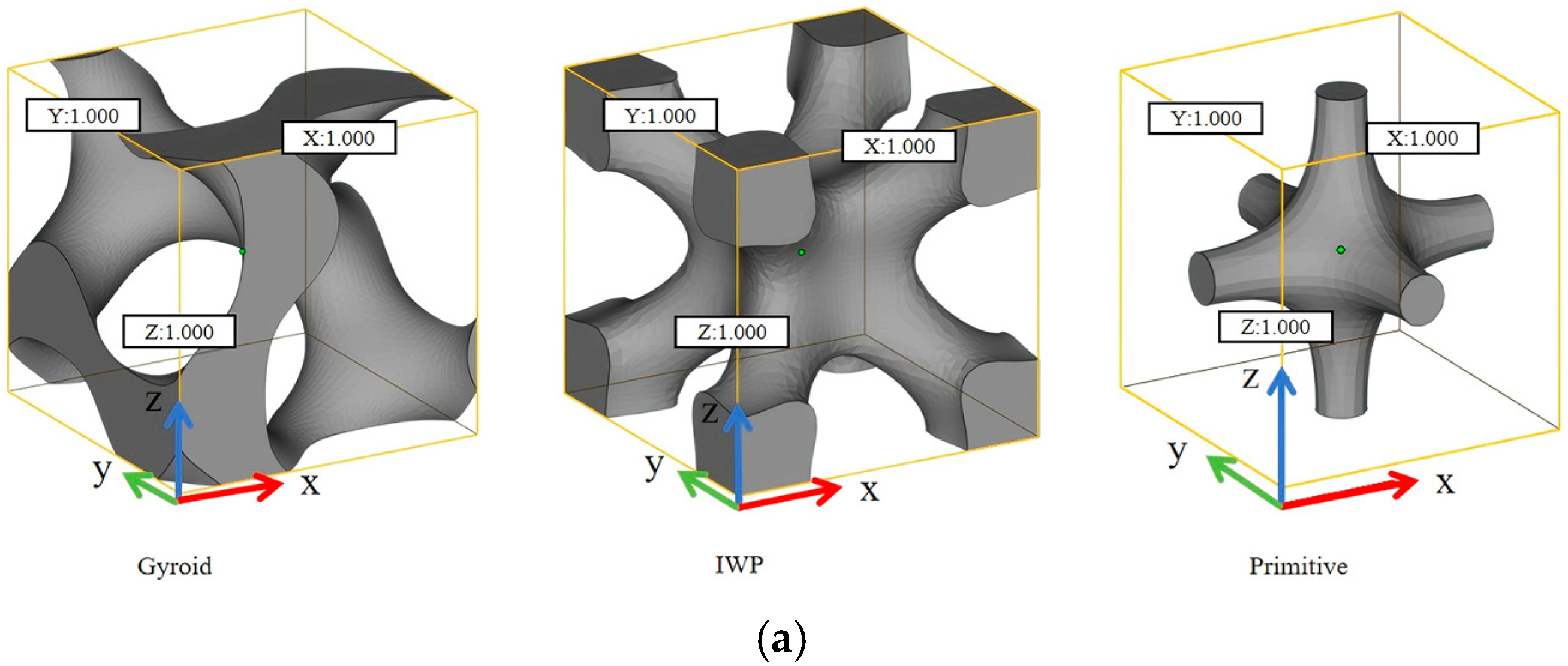
2.1. Design of TPMS
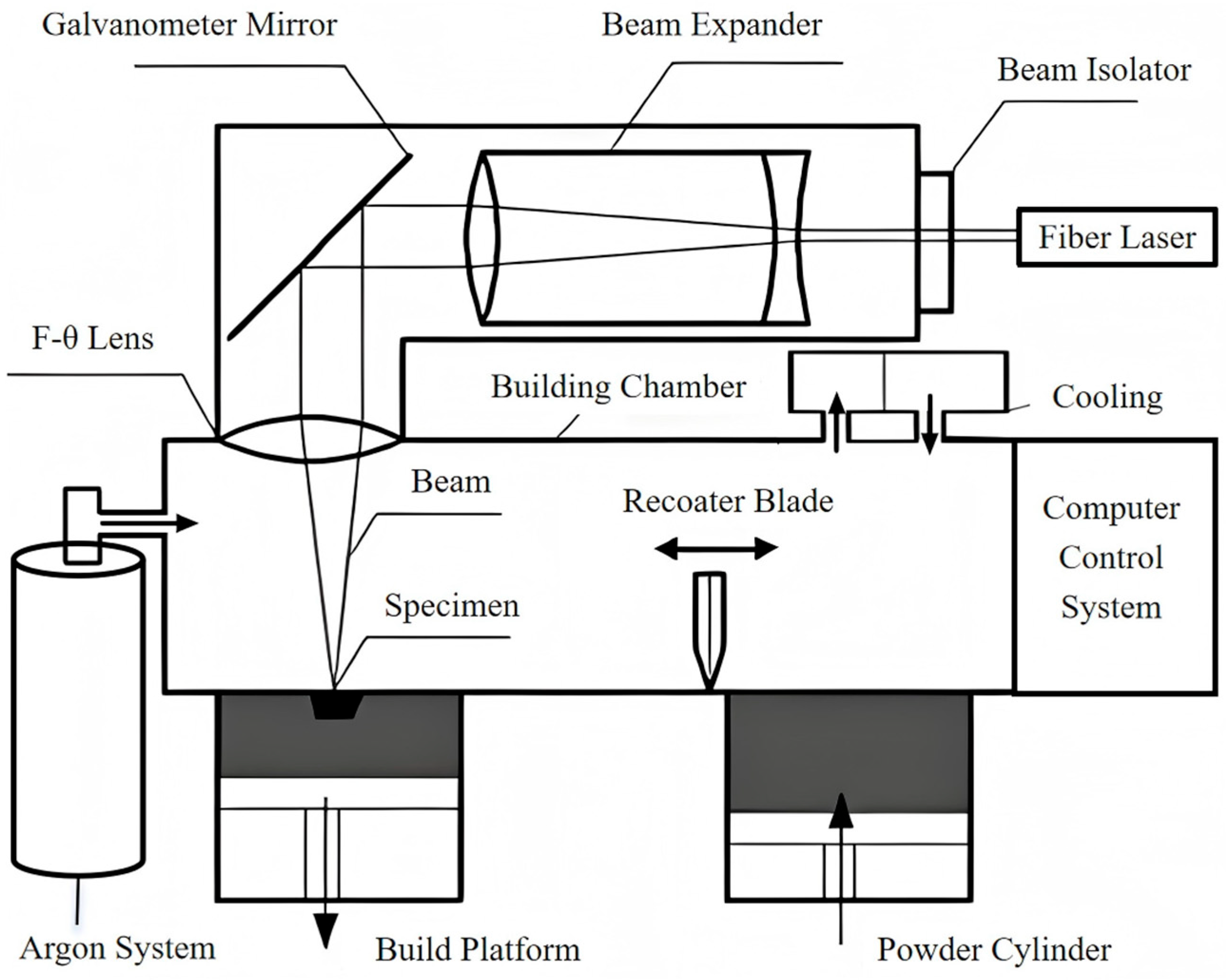
2.2. Additive Manufacturing of TPMS
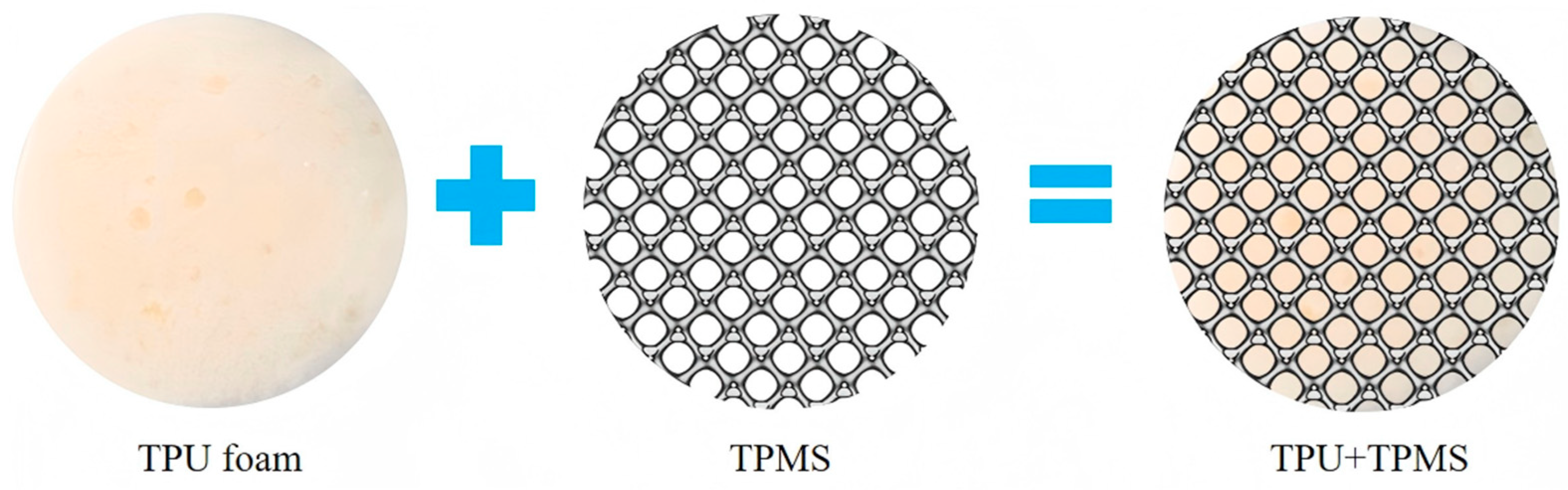
2.3. Fabrication of IPCs
2.4. Specimen Test
2.4.1. Acoustic Test
2.4.2. Compression Test
3. Results and Discussion
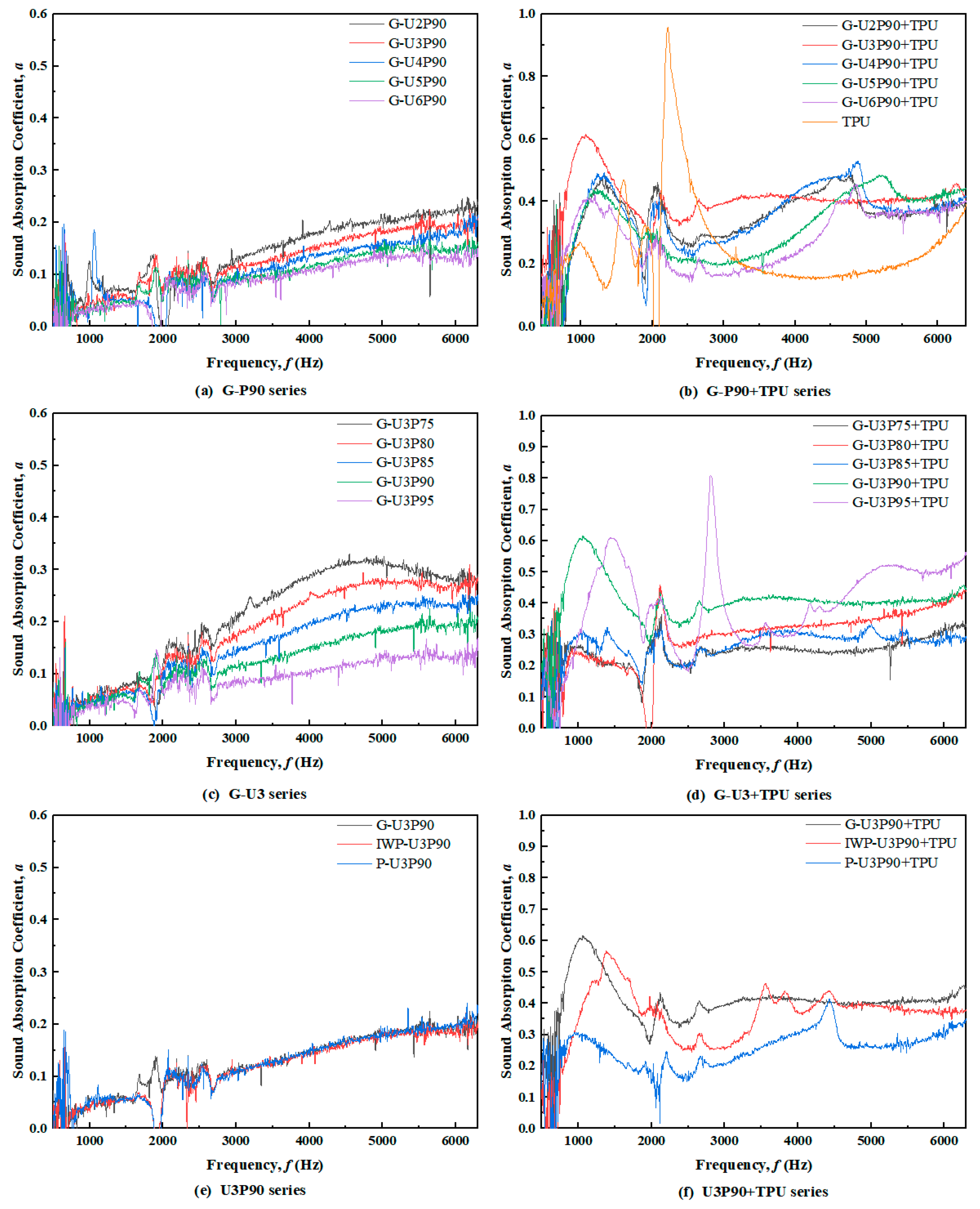
3.1. Sound Absorption Performance Analysis
3.1.1. Unit Cell Size
3.1.2. Porosity
3.1.3. Structural Topology
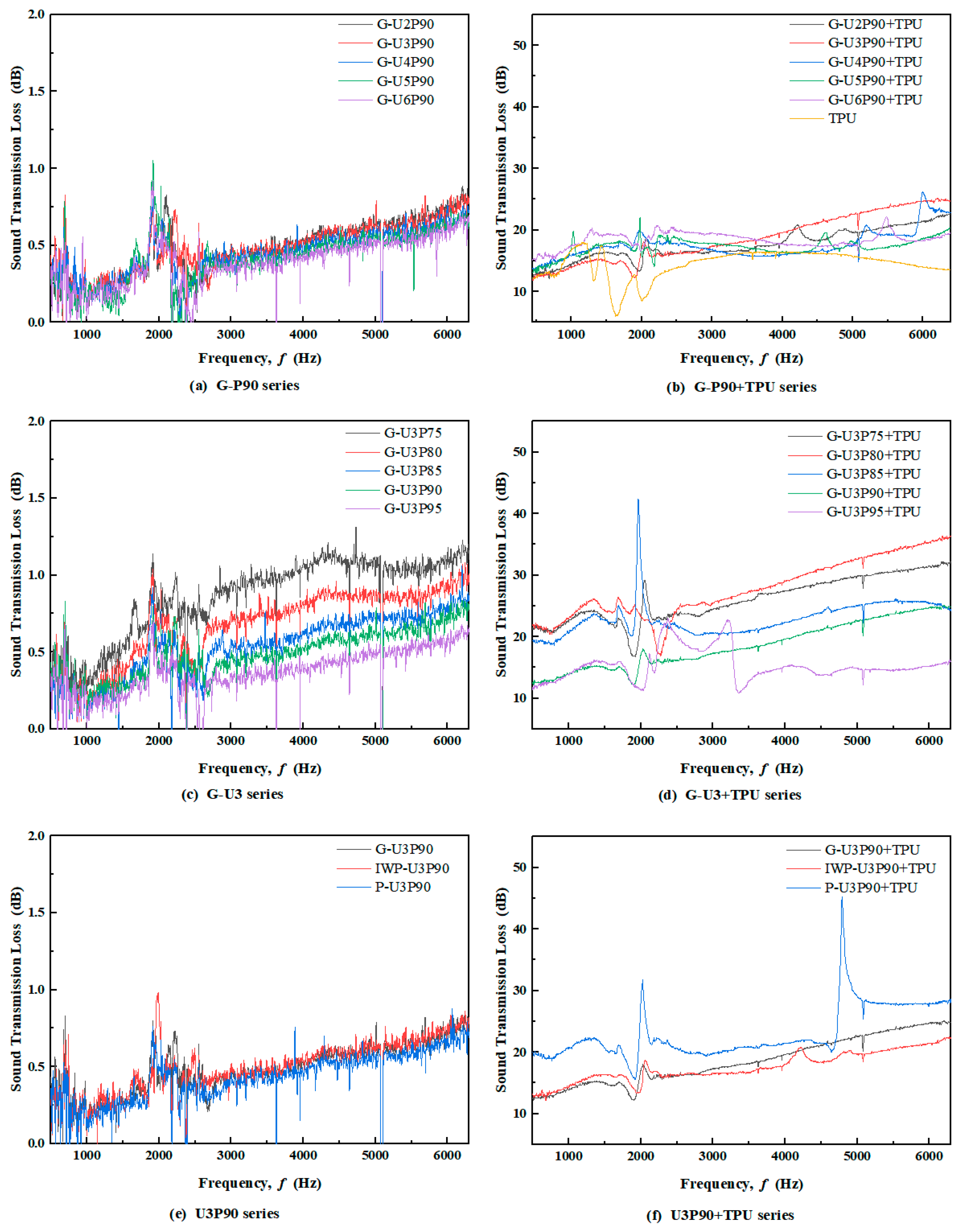
3.2. Transmission Loss Analysis
3.2.1. Unit Cell Size
3.2.2. Porosity
3.2.3. Structural Topology
3.3. Compressive Performance Analysis
3.3.1. Elastic Modulus Analysis
3.3.2. Failure Behavior Analysis
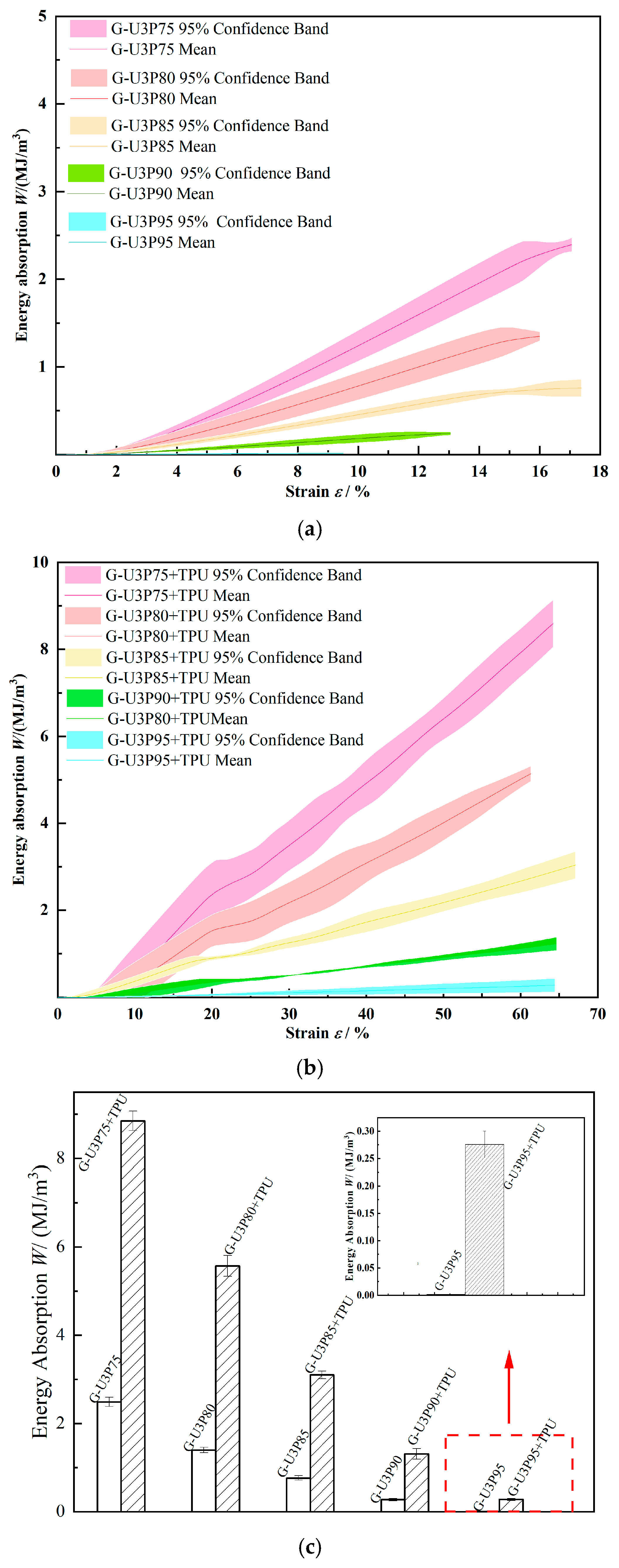
3.3.3. Energy Absorption Analysis
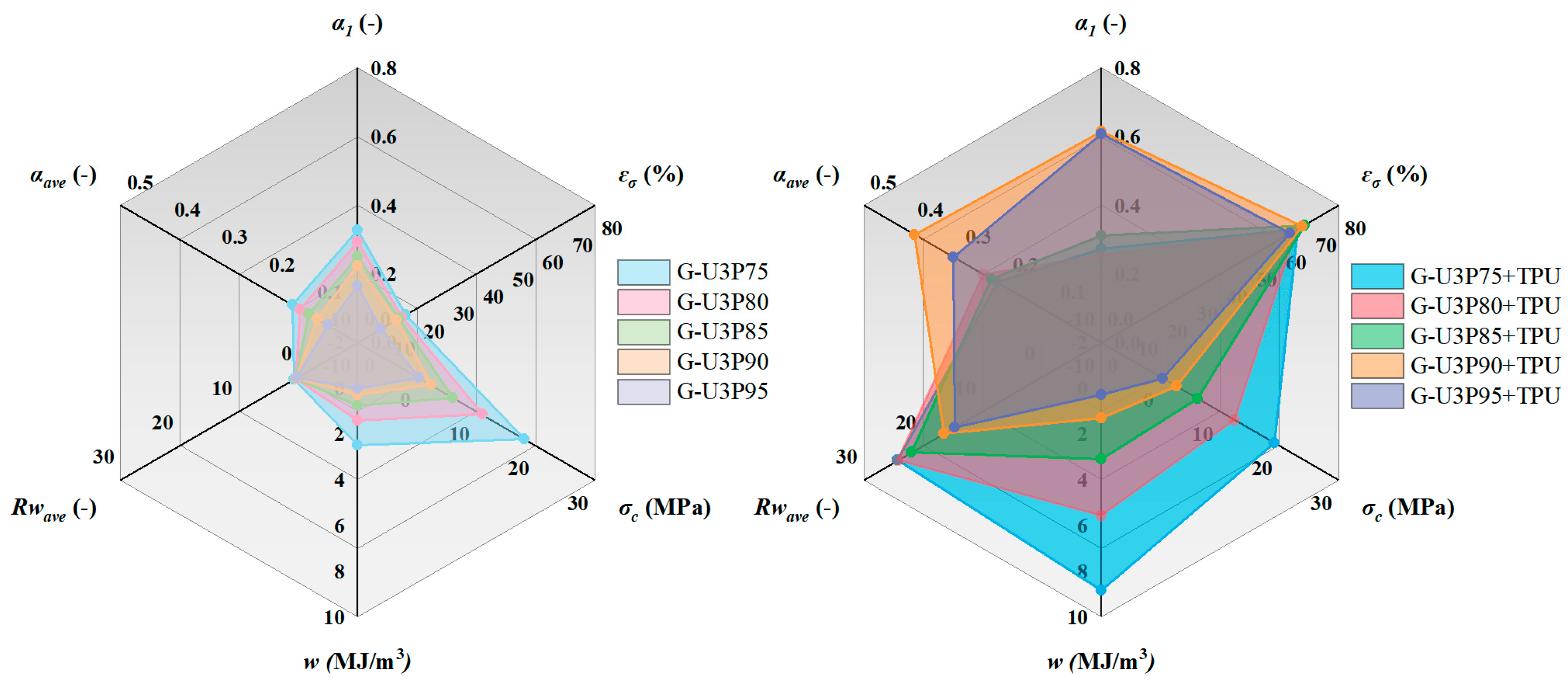
3.4. Comprehensive Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1).
- IPC configurations acoustically outperform unfilled aluminum alloy TPMS structures. The first peak of the acoustic absorption coefficient shifts to lower frequencies, and the average absorption coefficient within the 500–6300 Hz range increases by a factor of 1.59. Furthermore, the composites demonstrate a substantial improvement in sound insulation, with the average normal incidence transmission loss (TL) enhanced by a factor of 35.58.
- (2).
- It has been demonstrated that unfilled aluminum alloy gyroid structures exhibit abbreviated yield plateaus. Within the 75%–85% porosity range, compressive failure occurs at approximately 15% strain. This failure is primarily due to 45° shear-band brittle fracture. When porosity exceeds 85%, the failure mechanism transitions to localized brittle collapse. Specifically, at porosities greater than 90%, the compressive failure strain is reduced to approximately 8%, and the shear-band angles deviate to 60° ± 5°, a consequence of stress field distortion. Following TPU infiltration, the IPC structures develop ductile plateaus exceeding 60% strain under quasi-static compression, accompanied by substantial enhancement in energy absorption performance. G-U3P75+TPU demonstrated the best energy absorption characteristics, based on experimental data presented as mean ± 95% CI (n = 3).
- (3).
- The AlSi7Mg/TPU interpenetrating-phase configuration has been demonstrated to enhance acoustic absorption, sound insulation, and compressive performance in porous structures. The synergy of these properties makes the proposed IPCs highly suitable for advanced applications, including aerospace interiors, vibration–isolation platforms, transportation components, and specialized acoustic structures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.Q.; Gong, H.; Gao, J.Z. Enhancement in the fatigue resistances of triply periodic surfaces-based scaffolds. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 245, 108119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.X.; Shen, L.M.; Zhao, Y.M.; Wei, K.; Wang, Z.G. Elastic wave manipulation via functional incorporation of air-solid phases in hybrid TPMS. Compos. Commun. 2023, 44, 101745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Van, V.; Choudhry, N.K.; Panda, B.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Tran, P. Performance of concrete beam reinforced with 3D printed Bioinspired primitive scaffold subjected to three-point bending. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, M.L.; Jiang, C.L.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.D.; Fu, J.H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Analysis on the convective heat transfer process and performance evaluation of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface (TPMS) based on Diamond, Gyroid and Iwp. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 201, 123642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, R.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, H.N.; Bao, R.Q.; Zhang, N.J. Heat transfer characterization of waste heat recovery heat exchanger based on flexible hybrid triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 157, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baobaid, N.; Ali, M.I.; Khan, K.A.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K. Fluid flow and heat transfer of porous TPMS architected heat sinks in free convection environment. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 33, 101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Chang, L.; Mahmoud, H.A. Enhancing the efficiency and energy capacity of the improved airplane body under external maneuvering loads. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 109255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.P.; Li, H.Q.; Han, J.J.; Ma, Y.C.; Zhou, H.R.; Cheng, J.C.; Shi, J.; Miao, Z.Q.; Yu, B.; Lin, F. Mechanical and damping performances of TPMS lattice metamaterials fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. China Foundry 2024, 21, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.L.; Xu, R.N.; Jiang, P.X. Morphology, flow and heat transfer in triply periodic minimal surface based porous structures. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 170, 120902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.J.; Hu, J.Q.; Liu, L.W.; Zhao, W.; Xin, X.Z.; Song, X.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Leng, J.S. Mechanical properties of diamond-type triply periodic minimal surface structures fabricated by photo-curing 3D printing. Compos. Struct. 2025, 352, 118695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Cai, X.M.; Pan, C.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, P.; Fan, Z.Q.; Gao, Y.B.; Li, Z.H.; et al. Mechanical response and response mechanism of AlSi10Mg porous structures manufactured by laser powder bed fusion: Experimental, theoretical and numerical studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2022, 849, 143381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Feih, S.; Daynes, S.; Chang, S.; Wang, M.Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, W.F. Energy absorption characteristics of metallic triply periodic minimal surface sheet structures under compressive loading. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 23, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Matos, C.; Duarte, I.; Olhero, S.; Miranda, G. Effect of TPMS reinforcement on the mechanical properties of aluminium–alumina interpenetrating phase composites. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 6, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mo, H.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Xia, S.; Jia, X.; Zhou, L.; Lu, Y. Compressive properties and fracture behaviours of Ti/Al interpenetrating phase composites with additive-manufactured triply periodic minimal surface porous structures. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 31, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Karathanasopoulos, N. Static and dynamic damping mechanical performance of architected metal-epoxy interpenetrating phase composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 182, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhao, M.; Sun, G.H.; Pei, S.C.; Kong, X.N.; Bai, P.K. Sound absorption performance of micro-perforated plate sandwich structure based on triply periodic minimal surface. J. Mater. Res. Technol. -JMRT 2023, 27, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.G.; Wen, G.L.; Yin, H.F.; Wang, Z.P.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.M. Revealing the sound insulation capacities of TPMS sandwich panels. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 540, 117303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.J.; Kong, X.N.; Zhang, P.F.; Pei, S.C.; Ge, L.P.; Nie, Y.F.; Liu, B. Sound absorption performance of a micro-perforated plate sandwich structure based on selective laser melting. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2024, 19, 2321607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.Q.; Fan, X.L. Mechanical behavior of interpenetrating phase composite structures based on triply periodic minimal surface lattices. Compos. Struct. 2024, 337, 118044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Q.; Zhang, B.B.; Liu, Y.B.; Suo, T.; Xu, P.; Zhang, J.J. Interpenetrating phase composite foam based on porous aluminum skeleton for high energy absorption. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, A.; Xuan, P. Mechanical behavior of aluminum foam/polyurethane interpenetrating phase composites under monotonic and cyclic compression. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 116, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, G.; Esperto, V.; Rubino, F. A Finite Element Analysis Framework for Assessing the Structural Integrity of Aero-Engine Ceramic Matrix Composite Component Coatings. Metals 2025, 15, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, A.H. Infinite Periodic Minimal Surfaces Without Self-Intersections; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1970; Volume 5541. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.K.; Li, J.W.; Liu, C.; Deng, M.J.; Liao, X.; Wang, D. Study on the Anisotropy of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Porous Structures. Coatings 2023, 13, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB 9.11 (R2021b); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2021.
- Zhang, M.K.; Liu, C.; Deng, M.J.; Li, Y.H.; Li, J.W.; Wang, D.; Ancona, A. Graded Minimal Surface Structures with High Specific Strength for Broadband Sound Absorption Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Coatings 2023, 13, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Deng, M.; Wang, G.; Yin, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. Multicavity structures with triply periodic minimal surface for broadband and perfect sound absorption manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Sci. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 4, 5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qi, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, B.; Hu, L.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Sound transmission loss and bending properties of sandwich structures based on triply periodic minimal surfaces. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 204, 112324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.K.; Yang, Y.Q.; Xu, M.Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Mechanical properties of multi-materials porous structures based on triply periodic minimal surface fabricated by additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2021, 27, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Zhan, J.; Song, C.H.; Yan, Z.W.; Deng, Z.T.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.Q. Design and performance of a novel neutron shielding composite materials based on AlSi10Mg porous structure fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Hiremath, S.S. Additively manufactured mechanical metamaterials based on triply periodic minimal surfaces: Performance, challenges, and application. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 5077–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, W.; Godakawela, J.; Gatti, C.; Keshavanarayana, S.; Sharma, B. Fibro-porous materials: 3D-printed hybrid porous materials for multifunctional applications. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 94, 104470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Peng, J.F.; Sun, X.; Xie, H.; Ding, Y.; He, W. Distribution of microstructure, elastic modulus and residual stress near the interface in laser repaired GH4169 superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 966, 171625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.; Pande, S.S.; Lee, D.; Turner, K.T. The interplay of polymer bridging and entanglement in toughening polymer-infiltrated nanoparticle films. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6372–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiu, J.; Tang, B.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S. Novel semi-interpenetrating network structural phase change composites with high phase change enthalpy. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Q.; Liu, J.A.; Wang, Y.H.; Song, D.; Cao, R.Z.; Yang, X.Z. Enhanced sound absorption characteristic of aluminum-polyurethane interpenetrating phase composite foams. Mater. Lett. 2022, 323, 132595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
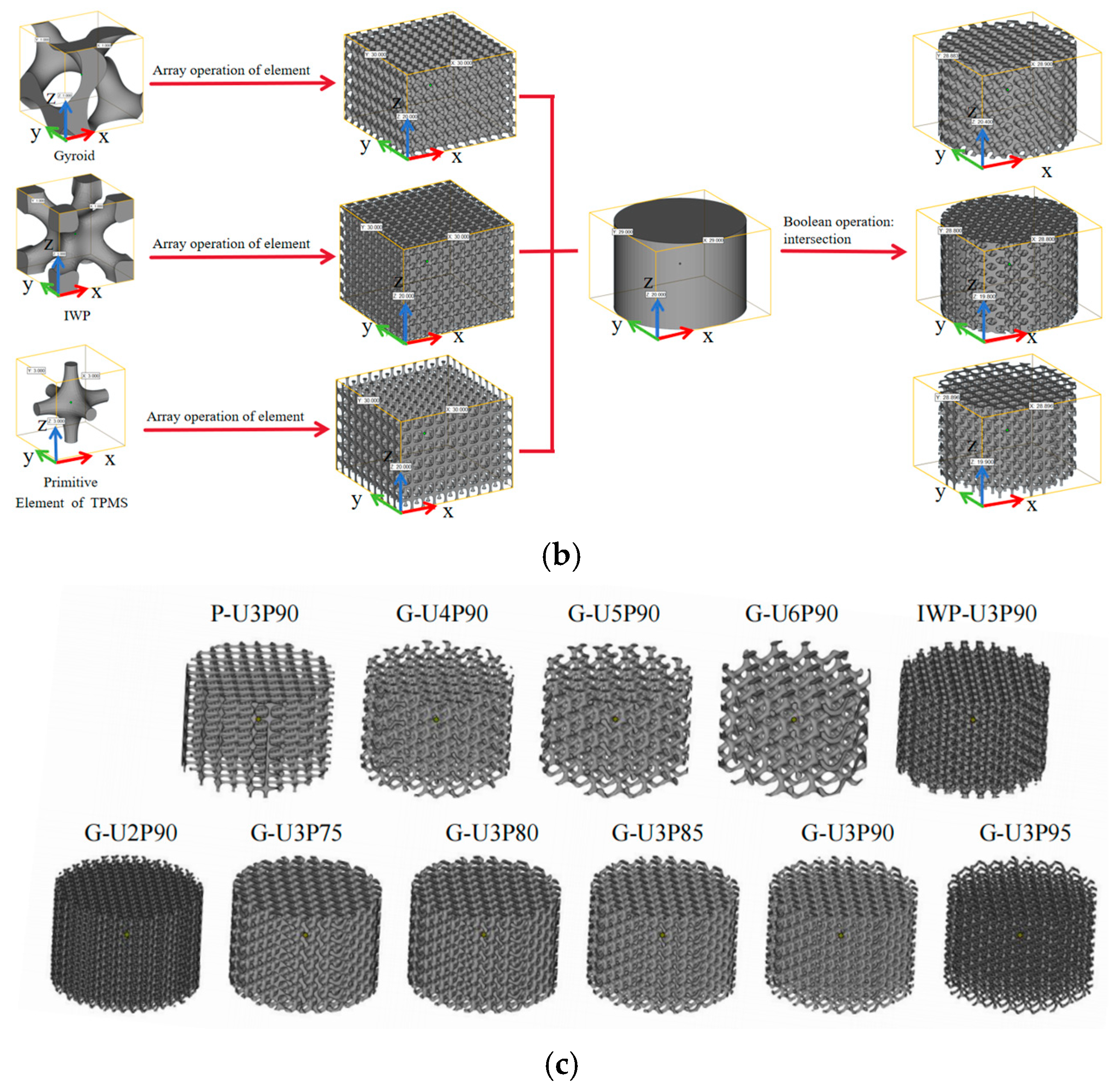
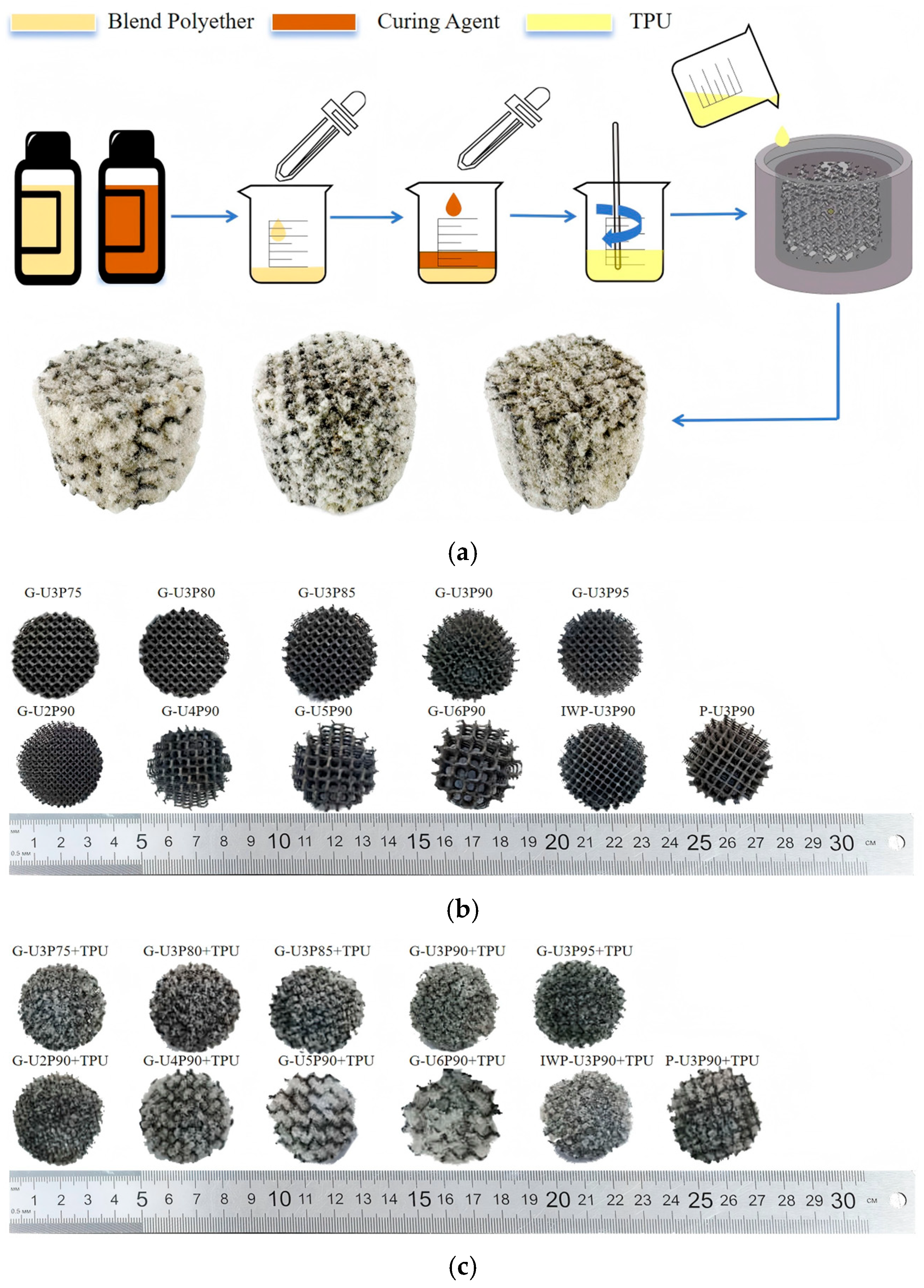

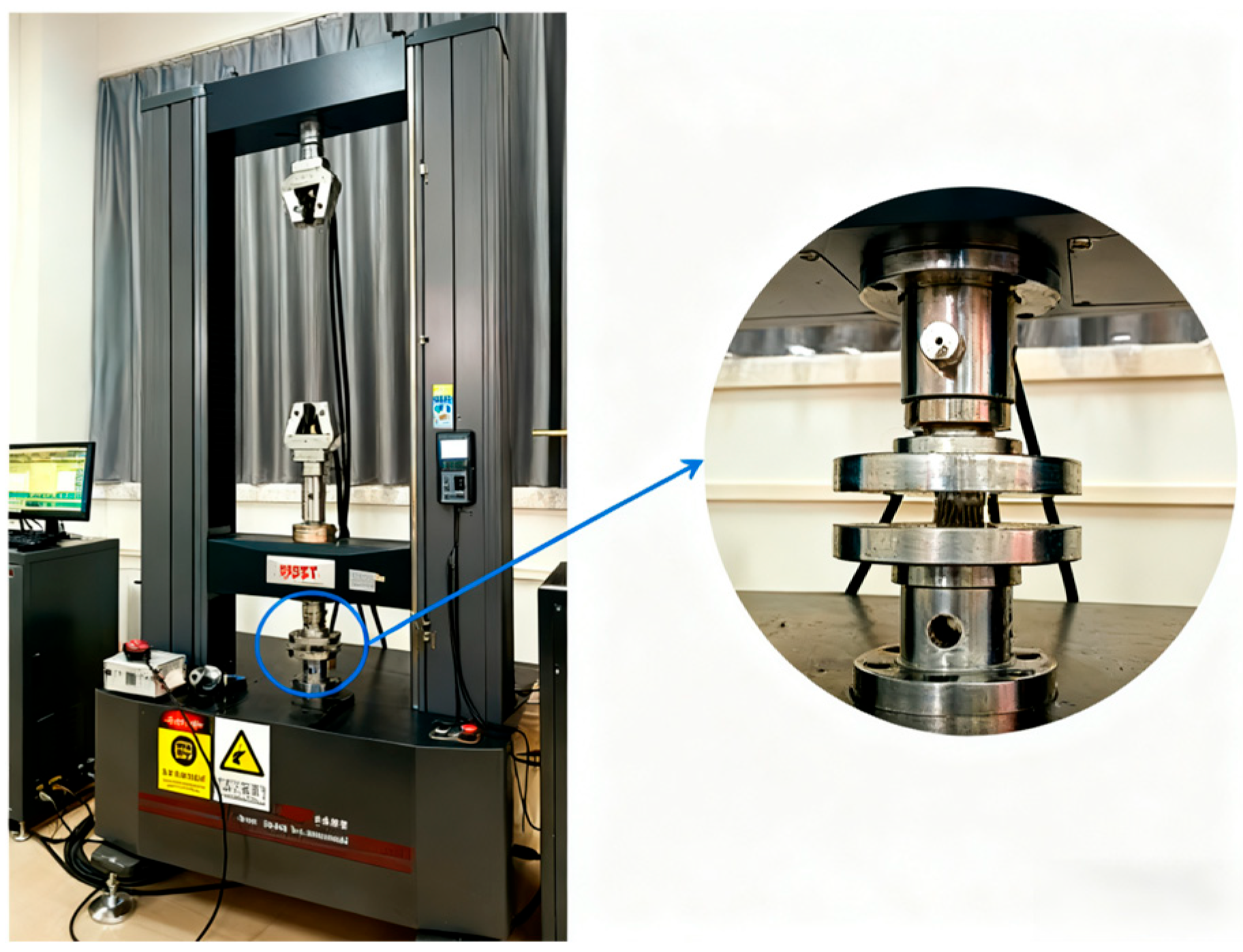


| Specimens | Unit Cell Size/mm | Specimen Height/mm | Specimen Diameter/mm | Porosity /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-U2P90 | 2 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| G-U3P90 | 3 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| G-U4P90 | 4 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| G-U5P90 | 5 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| G-U6P90 | 6 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| G-U3P75 | 3 | 20 | 29 | 75 |
| G-U3P80 | 3 | 20 | 29 | 80 |
| G-U3P85 | 3 | 20 | 29 | 80 |
| G-U3P90 | 3 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| P-U3P90 | 3 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| IWP-U3P90 | 3 | 20 | 29 | 90 |
| Specimen No. | Porosity (%) | Weight (g) | First-Peak Frequency f1 (Hz) | First-Peak Absorption Coefficient α1 | Average Absorption Coefficient αave |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-U2P90 | 90 | 2.238 | 6160 | 0.249 | 0.106 |
| G-U3P75 | 75 | 7.082 | 4546 | 0.330 | 0.138 |
| G-U3P80 | 80 | 5.623 | 6188 | 0.309 | 0.122 |
| G-U3P85 | 85 | 3.981 | 6298 | 0.252 | 0.103 |
| G-U3P90 | 90 | 2.479 | 6194 | 0.225 | 0.086 |
| G-U3P95 | 95 | 1.033 | 6296 | 0.168 | 0.063 |
| G-U4P90 | 90 | 2.670 | 6246 | 0.217 | 0.082 |
| G-U5P90 | 90 | 2.819 | 6222 | 0.178 | 0.071 |
| G-U6P90 | 90 | 2.908 | 6380 | 0.161 | 0.055 |
| IWP-U3P90 | 90 | 2.508 | 6128 | 0.221 | 0.083 |
| P-U3P90 | 90 | 2.702 | 6158 | 0.240 | 0.090 |
| Specimen No. | TPU Mass Fraction(%) | Weight (g) | First-Peak Frequency f1 (Hz) | First-Peak Absorption Coefficient α1 | Average Absorption Coefficient αave |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-U2P90+TPU | 24.9 | 2.982 | 4860 | 0.485 | 0.299 |
| G-U3P75+TPU | 13.0 | 8.141 | 2140 | 0.364 | 0.219 |
| G-U3P80+TPU | 14.7 | 6.592 | 2124 | 0.457 | 0.231 |
| G-U3P85+TPU | 17.7 | 4.840 | 1042 | 0.383 | 0.249 |
| G-U3P90+TPU | 20.0 | 3.100 | 1060 | 0.616 | 0.393 |
| G-U3P95+TPU | 44.5 | 1.860 | 3234 | 0.782 | 0.311 |
| G-U4P90+TPU | 21.3 | 3.394 | 4870 | 0.529 | 0.278 |
| G-U5P90+TPU | 19.5 | 3.496 | 5174 | 0.485 | 0.258 |
| G-U6P90+TPU | 18.8 | 3.583 | 4850 | 0.456 | 0.254 |
| IWP-U3P90+TPU | 18.9 | 3.092 | 1384 | 0.567 | 0.315 |
| P-U3P90+TPU | 24.9 | 3.573 | 4426 | 0.423 | 0.230 |
| Specimen No. | Porosity (%) | Weight (g) | Peak Transmission-Loss Frequency, fmax (Hz) | Maximum Normal Incidence Transmission Loss, TLmax (dB) | Average Normal Incidence Transmission Loss, TLave (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-U2P90 | 90 | 2.238 | 6208 | 0.8837 | 0.378 |
| G-U3P75 | 75 | 7.082 | 4734 | 1.312 | 0.683 |
| G-U3P80 | 80 | 5.623 | 6242 | 1.079 | 0.524 |
| G-U3P85 | 85 | 3.981 | 6204 | 1.063 | 0.424 |
| G-U3P90 | 90 | 2.479 | 6206 | 0.834 | 0.403 |
| G-U3P95 | 95 | 1.033 | 1908 | 0.708 | 0.308 |
| G-U4P90 | 90 | 2.670 | 1912 | 0.824 | 0.373 |
| G-U5P90 | 90 | 2.819 | 1912 | 1.054 | 0.339 |
| G-U6P90 | 90 | 2.908 | 1912 | 0.914 | 0.327 |
| IWP-U3P90 | 90 | 2.508 | 1990 | 0.981 | 0.402 |
| P-U3P90 | 90 | 2.702 | 6058 | 0.877 | 0.347 |
| Specimen No. | Weight (g) | TPU Mass Fraction(%) | Peak Transmission-Loss Frequency, fmax (Hz) | Maximum Normal Incidence Transmission Loss, TLmax (dB) | Average Normal Incidence Transmission Loss, TLave (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-U2P90+TPU | 2.982 | 24.9 | 6278 | 22.457 | 16.156 |
| G-U3P75+TPU | 8.141 | 13.0 | 6192 | 32.142 | 24.298 |
| G-U3P80+TPU | 6.592 | 14.7 | 6180 | 34.437 | 25.544 |
| G-U3P85+TPU | 4.840 | 17.7 | 1964 | 42.425 | 21.987 |
| G-U3P90+TPU | 3.100 | 20.0 | 6206 | 25.121 | 16.454 |
| G-U3P95+TPU | 1.860 | 44.5 | 2732 | 22.989 | 14.712 |
| G-U4P90+TPU | 3.394 | 21.3 | 6002 | 26.156 | 16.805 |
| G-U5P90+TPU | 3.496 | 19.5 | 1976 | 21.987 | 16.604 |
| G-U6P90+TPU | 3.583 | 18.8 | 5789 | 22.121 | 17.915 |
| IWP-U3P90+TPU | 3.092 | 18.9 | 6278 | 22.457 | 16.159 |
| P-U3P90+TPU | 3.573 | 24.9 | 4786 | 45.200 | 21.705 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yin, S.; Liang, Y.; Lu, F.; Fu, J. Study on Acoustic and Mechanical Properties of AlSi7Mg/TPU Porous Interpenetrating Phase Composites. Coatings 2025, 15, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121388
Wang Y, Zhang M, Yin S, Liang Y, Lu F, Fu J. Study on Acoustic and Mechanical Properties of AlSi7Mg/TPU Porous Interpenetrating Phase Composites. Coatings. 2025; 15(12):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121388
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yajuan, Mingkang Zhang, Sihua Yin, Yifu Liang, Fengqing Lu, and Jisheng Fu. 2025. "Study on Acoustic and Mechanical Properties of AlSi7Mg/TPU Porous Interpenetrating Phase Composites" Coatings 15, no. 12: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121388
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, M., Yin, S., Liang, Y., Lu, F., & Fu, J. (2025). Study on Acoustic and Mechanical Properties of AlSi7Mg/TPU Porous Interpenetrating Phase Composites. Coatings, 15(12), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121388






