1. Introduction
The ageing of polymer-modified bitumen (PMB) critically governs the rheological performance and service life of asphalt pavements. Under sustained environmental and mechanical stresses, the binder undergoes complex physicochemical changes that alter mechanical properties and, in turn, pavement durability. Polymer addition is widely used to enhance mechanical and rheological response—mitigating deformation and cracking in conventional binders [
1]—yet the long-term performance of PMB remains strongly tied to ageing, which depends on temperature, oxidative environment, and polymer type [
2].
Ageing is commonly divided into short-term (mixing, transport, laying) and long-term (in-service) processes. Short-term ageing is driven by volatilization and initial oxidation, whereas long-term ageing reflects prolonged exposure to oxygen, UV, and temperature cycles [
3]. The combined action typically increases stiffness, reduces ductility, and modifies viscoelastic behavior, compromising resistance to traffic and environmental loading [
4]. In PMB, polymer–bitumen interactions add further complexity, activating multiple, simultaneous degradation pathways not observed in unmodified binders [
5].
Rheological indices—especially the complex shear modulus (G*)—are standard indicators of performance across loading and environmental conditions. G* captures both elastic and viscous responses under oscillatory shear [
2]. Ageing generally raises the storage component relative to the loss component, producing a stiffer, more brittle material [
2]. For example, Tarefder and Yousefi [
2] showed that ageing elevates the elastic fraction of G* in Styrene Buytadien (SB)- and Styrene Butadien Styren (SBS)-modified binders, with higher polymer content reducing ageing susceptibility.
Polymer type and dosage strongly shape ageing behavior. SBS, SB, and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) impart distinct rheological signatures [
1]. Bala et al. [
1] reported that increasing LLDPE lowers penetration and raises softening point after ageing, indicating improved thermo-oxidative resistance. Styrene–Ethylene–Butylene–Styrene (SEBS) use similarly lessens ageing effects on physical and rheological properties [
3]. Chemistry and compatibility govern both initial response and the rate/extent of property change during ageing [
5]; Wieser et al. [
5] linked higher vinyl content to greater oxidative resistance and better compatibility, improving durability.
Laboratory protocols such as Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (RTFOT), TFOT, and Pressure Ageing Vessel (PAV) simulate short- and long-term ageing under controlled conditions [
2], yet recent work highlights the limits in reproducing field complexity, particularly for PMB [
6]. Tian et al. [
6] found that while RTFOT and PAV represent early-stage ageing, microstructural, and rheological changes in prolonged service may be understated; PAV-aged samples showed lower micro-performance indices than field-aged materials.
Processing parameters also matter. Higher shear rates and longer mixing times promote oxidative ageing in SBS-modified bitumen, increasing flow activation energies and temperature susceptibility; compatibility levels can be reached with appropriate processing control [
7]. Beyond traditional rheology, Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR), Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), and fluorescence microscopy elucidate chemical and morphological evolution during ageing [
4]. Sun et al. [
4] observed predominant early-stage polymer degradation and showed that oxidation level and SBS content can predict post-ageing modulus and phase-angle trends via principal components.
Predictive modeling has, therefore, gained traction. Conventional empirical/mechanistic models struggle with nonlinear, multivariate ageing effects, whereas machine learning methods—e.g., Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR)—capture coupled temperature–frequency–ageing interactions [
8]. Rahman and Chavan [
8] further showed that integrated learning can outperform individual models in accuracy and efficiency, underscoring the promise of ensembles for engineering data.
In this study, two ensemble machine learning models—Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR)—were deliberately selected to represent the two main ensemble paradigms of bagging and boosting, respectively. The choice of these models was motivated by the moderate size and controlled structure of the experimental dataset, where excessive model complexity could lead to overfitting. Advanced boosting algorithms such as XGBoost and LightGBM were, therefore, excluded at this stage, as their extensive hyperparameter spaces require larger and more heterogeneous datasets to ensure stable generalization. Nevertheless, it is emphasized that future work will extend the framework to include these advanced and hybrid (stacked) ensemble models, particularly when larger and field-aged bitumen datasets become available.
Ageing in polymer-modified binders is primarily governed by thermo-oxidative reactions and volatilization, which alter the asphaltene–maltene balance and affect the integrity of the polymer network. These microstructural changes manifest rheologically as increases in the complex shear modulus (G) and reductions in phase angle (δ), particularly at elevated temperatures and lower loading frequencies. Frequency–temperature superposition captures these shifts as translations of master curves, providing compact descriptors of viscoelastic behavior. This background motivates the use of supervised machine learning to learn the coupled effects of temperature, frequency, and ageing condition on G*, and to quantify how ageing severity reshapes the binder’s viscoelastic response.
Structuring data into tidy formats and applying advanced regression enables robust prediction of G* across temperatures, frequencies, and ageing scenarios. Under modified TFOT conditions, temperature consistently emerges as the dominant factor, followed by frequency and ageing condition [
9]. This aligns with broader evidence on the central role of temperature in viscoelastic response and ageing kinetics [
10]. Ozdemir [
10] reported better rheological ageing performance and lower temperature susceptibility for lower-penetration binders, reinforcing the need to model temperature effects explicitly.
Integrating machine learning with rheological experiments strengthens prediction and supports practical frameworks for materials selection. Salehi et al. [
11] used ensemble models to predict properties of recycled-plastic-modified bitumen under unaged and short-term aged states, identifying temperature, frequency, polymer content, and base penetration as key variables; SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) and partial dependence clarified effect magnitudes and directions. Robustness across ageing scenarios is essential for deployment: condition-wise analysis under modified TFOT shows GBR outperforming RF (higher R
2, lower MAE/RMSE), consistent with the nonlinear, synergistic nature of PMB ageing involving temperature, oxidative environment, and polymer–bitumen interactions [
5].
Advances in predictive modeling under ageing have clear implications for pavement design, maintenance, and rehabilitation—enabling more accurate assessment of binder performance, improved material/additive selection, extended service life, reduced costs, and enhanced sustainability. The continuing integration of experimental evidence, advanced analytics, and machine learning offers a promising path for pavement engineering. The ageing of polymer modified bitumen remains a multifaceted phenomenon with a profound impact on rheological properties and service life [
7,
9,
10,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Description
The dataset employed in this study was derived from the open-access experimental measurements reported by Farid, M., and Król, J. (2023) on the ageing of polymer modified bitumen (PMB 25/55–60) under a modified Thin Film Oven Test (TFOT) procedure [
17]. Each record corresponds to a unique combination of ageing condition (time–temperature pair), test temperature, and angular frequency. The dataset includes the following:
Material properties: penetration, softening point, binder grade.
Ageing descriptors: method, time (1–5 h), temperature (120–200 °C), film thickness, pan diameter, sample mass.
Testing parameters: test device Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR), plate diameter (8 or 25 mm), linear viscoelastic strain regime, test temperature, and angular frequency (0.1, 1, 10 Hz).
Rheological outputs: complex shear modulus (G*) and phase angle (δ).
FTIR indices: carbonyl, sulphoxide, aliphatic, aromatic, and butadiene/styrene ratio.
The data were structured in a tidy format, allowing systematic integration of rheological and chemical ageing indicators into predictive modeling. The dataset employed in this study was constructed from experimental measurements reported by Farid, M., and Król, J. (2023) [
17] on the ageing behavior of polymer modified bitumen (PMB 25/55–60) under a modified Thin Film Oven Test (TFOT) procedure. The data include rheological parameters obtained from a DSR as well as complementary chemical indices from FTIR.
Each record in the dataset corresponds to a unique combination of ageing condition (defined by time and temperature of the TFOT treatment
Table 1), test temperature, and angular frequency. The input variables are Temperature (°C), Angular Frequency (Hz), and Ageing Condition (e.g., Unaged, 2 h–140 °C, 2 h–200 °C, 5 h–140 °C, 5 h–200 °C). The primary output variable is the *Complex Shear Modulus (G*, Pa)*, complemented by the Phase Angle (δ, °) when available. In addition, the dataset structure accommodates FTIR-based chemical ageing indices, including the carbonyl and sulphoxide absorbance ratios, as well as the SBS butadiene/styrene degradation index (IB/S).
The final dataset comprises N = 120 observations collected on PMB 25/55–60 across five ageing protocols (Unaged, 2 h–140 °C, 2 h–200 °C, 5 h–140 °C, 5 h–200 °C), eight temperatures (0–70 °C in 10 °C increments), and three loading frequencies (0.1, 1, 10 Hz), i.e., 24 observations per condition.
The data were organized in a tidy format, in which each row represents a single measurement, and the following fields are included:
Material properties: binder grade, penetration, softening point.
Ageing descriptors: method, time (h), temperature (°C), film thickness (mm), pan diameter (mm), and sample mass (g).
Testing parameters: device (DSR), plate diameter (8 or 25 mm), strain regime (LVE), test temperature (°C), angular frequency (Hz).
Rheological outputs: G* (Pa), δ (°C).
FTIR indices: carbonyl, sulphoxide, aliphatic, aromatic, IB/S.
2.2. Machine Learning Framework
Two supervised machine learning algorithms were employed in this study: Random Forest Regressor (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR). Both are ensemble-based methods, but they differ fundamentally in how they aggregate weak learners. RF constructs multiple independent decision trees using bootstrap sampling and averages their predictions to reduce variance, while GBR builds trees sequentially, with each successive tree correcting the errors of the previous one, thereby reducing both bias and variance. This dual approach was chosen to enable a comprehensive comparison between a variance-reducing method (RF) and a bias-reducing method (GBR), both of which are widely recognized for their robustness in handling nonlinear and high-dimensional datasets.
The input variables included the following:
Temperature (°C): a dominant factor governing rheological behavior, strongly correlated with viscoelastic changes.
Angular frequency (Hz): representing loading rate, critical for simulating traffic conditions.
Ageing condition: categorical variable indicating thermal-oxidative exposure (Unaged, 2 h–140 °C, 2 h–200 °C, 5 h–140 °C, 5 h–200 °C).
The output variable was the complex shear modulus, G* (Pa), calculated from Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR) oscillatory measurements (torque/strain and phase lag), representing the material’s stiffness under oscillatory shear.
Data preprocessing involved several steps to ensure model stability and accuracy:
Encoding of categorical ageing conditions: Since RF and GBR cannot directly interpret string labels, the ageing conditions were transformed into numerical format using one-hot encoding. This avoided imposing artificial ordinal relationships between categories.
Feature scaling: Although tree-based models are generally scale-invariant, feature standardization was applied to facilitate comparison with potential alternative models, stabilize gradient-based optimization in GBR, and ensure uniform contribution of input variables.
Data were partitioned into an 80/20 train–test split; the test set was held out and used only once for final evaluation. Model selection and hyperparameter tuning were performed via 5-fold cross-validation on the training set to avoid information leakage. To additionally assess generalization to unseen conditions, we conducted a leave-one-condition-out (LOCO) protocol in which each ageing condition (Unaged, 2 h–140 °C, 2 h–200 °C, 5 h–140 °C, 5 h–200 °C) was excluded from training in turn and used solely for testing. We report only held-out test and LOCO metrics as final performance; cross-validation scores are used for tuning/selection.
In the training phase, hyperparameter tuning was carried out to optimize model performance. For RF, the number of trees, maximum depth, and minimum samples per split were varied. For GBR, the learning rate, number of boosting stages, and maximum depth of trees were systematically adjusted. Grid search combined with 5-fold cross-validation was used to identify the optimal hyperparameter set.
Hyperparameters were tuned via 5-fold cross-validation using randomized search over predefined ranges (RF: n_estimators, max_depth, max_features, min_samples_leaf; GBR: n_estimators, learning_rate, max_depth, subsample, min_samples_leaf). The primary selection metric was RMSE, with MAE as a secondary check. Final configurations are reported in
Table 2.
This methodology ensured that the models were not only accurate but also generalizable across different ageing scenarios, enabling a fair and rigorous comparison of RF and GBR in predicting PMB rheological behavior.
2.3. Model Training and Evaluation
The models were implemented and trained using the scikit-learn library in Python 3.11.1, which provides robust, well-tested implementations of ensemble learning algorithms. Model development followed a standardized workflow including data splitting, training, validation, and testing.
To evaluate predictive performance, three complementary metrics were employed:
Coefficient of determination (R2): quantifies the proportion of variance in the target variable (G*) that can be explained by the model. A higher R2 indicates stronger explanatory power.
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): represents the average magnitude of prediction errors in absolute terms. It provides an interpretable measure of error in the same unit as the output variable, making it suitable for evaluating practical relevance.
Root Mean Square Error (RMSE): penalizes larger errors more heavily than MAE due to the squaring of residuals, thus offering insight into the stability and robustness of predictions.
The simultaneous use of R2, MAE, and RMSE ensured a balanced evaluation: R2 reflects goodness-of-fit, MAE captures average prediction error, and RMSE highlights sensitivity to extreme deviations.
In addition to overall performance assessment, feature importance analysis was conducted to quantify the relative contribution of each predictor variable (temperature, frequency, ageing condition) to the prediction of G*. For the Random Forest model, feature importance was derived from the mean decrease in impurity across trees, while in Gradient Boosting it was estimated from the reduction in loss function attributable to each feature during boosting iterations.
The results of feature importance provided interpretability to the black-box nature of ensemble models. By ranking predictors, the analysis revealed which experimental parameters most strongly influenced the complex shear modulus. This not only validated experimental knowledge (temperature as a dominant factor) but also highlighted synergistic effects of frequency and ageing conditions. Such insights have practical significance, as they can guide future experimental design and material optimization strategies by prioritizing the most influential variables.
Generalization was assessed via a leave-one-condition-out (LOCO) scheme: in each fold, one ageing condition was entirely excluded from training and used only for testing. This protocol ensures evaluation on datasets not involved in training. We also report random train/test split metrics for comparability.
Table 2 summarizes the hyperparameter optimization procedure adopted for both ensemble models. The parameter ranges were determined based on prior studies and preliminary grid exploration. A randomized search strategy was employed due to its computational efficiency and proven ability to approximate the optimal region within a limited number of iterations. Each configuration was evaluated using a 5-fold cross-validation scheme stratified by ageing condition to ensure robust estimation across data subsets. The final model parameters were selected according to the minimum Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) obtained during cross-validation, after which the models were retrained on the complete training split for final evaluation.
2.4. Pseudocode for Workflow
The detailed pseudocode and algorithmic workflow are provided.
INPUT:
D_raw := Experimental dataset (Excel/CSV)
# columns: Temperature [°C], Frequency [Hz], AgeingCondition (categorical),
# Complex Shear Modulus G* [Pa]
OUTPUT:
Trained models (RF, GBR), cross-validated metrics, per-condition metrics,
figures (Actual vs Predicted; Feature Importance), and a concise report
1. LOAD & VALIDATE DATA
1.1 D <- read(D_raw)
1.2 assert no duplicated rows by (Temperature, Frequency, AgeingCondition)
1.3 check_missing(D); if missing in inputs -> impute or drop (document choice)
1.4 ensure numeric types for Temperature, Frequency, Gstar; categorical for AgeingCondition
1.5 remove obvious outliers if due to measurement error (domain rules), else keep and flag
2. FEATURE ENGINEERING
2.1 X_base := [Temperature, Frequency, AgeingCondition]
2.2 y := Gstar
2.3 Encode AgeingCondition
# Preferred: One-Hot Encoding (no artificial order). Keep reference category explicit.
X_enc := one_hot(AgeingCondition) # k-1 or k dummies (document choice)
2.4 X := concat([Temperature, Frequency], X_enc)
3. DATA SPLIT (REPRODUCIBLE)
3.1 set random_state = 42
3.2 Stratified split by AgeingCondition if class sizes vary:
(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test) := stratified_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state)
3.3 Store test indices for per-condition evaluation later
4. SCALING (OPTIONAL for trees, but helps comparability)
4.1 scaler := StandardScaler().fit(X_train[numeric_features])
4.2 X_train_scaled := apply(scaler, X_train)
X_test_scaled := apply(scaler, X_test)
4.3 persist(scaler)
5. MODEL SPECIFICATION
5.1 RF := RandomForestRegressor(
n_estimators = [200..600], max_depth = [None..20],
min_samples_split = [2..10], min_samples_leaf = [1..5],
max_features = ["sqrt","log2"], random_state)
5.2 GBR := GradientBoostingRegressor(
n_estimators = [200..1000], learning_rate=[0.01..0.1],
max_depth=[2..4], subsample=[0.6..1.0], random_state)
6. HYPERPARAMETER TUNING (CROSS-VALIDATION)
6.1 cv := KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state)
6.2 grid_RF := GridSearchCV(RF, RF_param_grid, cv=cv, scoring="neg_root_mean_squared_error")
6.3 grid_GBR := GridSearchCV(GBR, GBR_param_grid, cv=cv, scoring="neg_root_mean_squared_error")
6.4 grid_RF.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
RF_best := grid_RF.best_estimator_
6.5 grid_GBR.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
GBR_best := grid_GBR.best_estimator_
6.6 store CV results (mean±std for RMSE, MAE, R2)
7. FINAL TRAINING ON FULL TRAIN SET
7.1 RF_best.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
7.2 GBR_best.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
8. EVALUATION ON HELD-OUT TEST SET
8.1 yhat_RF := RF_best.predict(X_test_scaled)
yhat_GBR := GBR_best.predict(X_test_scaled)
8.2 Metrics (overall):
R2_RF, MAE_RF, RMSE_RF := metrics(y_test, yhat_RF)
R2_GBR, MAE_GBR, RMSE_GBR := metrics(y_test, yhat_GBR)
8.3 Metrics (by AgeingCondition):
for c in unique(AgeingCondition_test):
idx_c := indices where condition == c
compute R2, MAE, RMSE on (y_test[idx_c], yhat_[RF/GBR][idx_c])
store table_per_condition
9. INTERPRETABILITY (FEATURE IMPORTANCE)
9.1 FI_RF := RF_best.feature_importances_
9.2 FI_GBR := GBR_best.feature_importances_
9.3 Rank features; check stability via CV or permutation importance (optional)
10. DIAGNOSTICS & ERROR ANALYSIS
10.1 Residuals_RF := y_test - yhat_RF
Residuals_GBR := y_test - yhat_GBR
10.2 Plot residuals vs predicted; check heteroscedasticity/outliers
10.3 Error by Temperature and Frequency bins (e.g., quartiles)
10.4 If systematic bias found, consider feature interactions or alternative models
11. PLOTTING
11.1 Actual vs Predicted scatter (RF, GBR) with 45° line
11.2 Feature importance bar plots (RF, GBR)
11.3 Optional: Partial dependence or ALE for Temperature, Frequency
12. PERSISTENCE & REPRODUCIBILITY
12.1 save_models([RF_best, GBR_best])
12.2 save_artifacts(scaler, CV_results, figs, per_condition_table, random_state)
12.3 log software versions, seeds, and hardware info
13. REPORTING
13.1 Summarize overall and per-condition metrics in tables
13.2 Insert figures; discuss findings and limitations
13.3 Document preprocessing, tuning ranges, seeds, and exact hyperparameters |
The presented pseudocode describes the complete machine learning workflow applied in this study, beginning with raw data handling and ending with model reporting. In the data preparation stage (Steps 1–4), the experimental dataset is imported, cleaned, and validated to eliminate missing values, duplicates, and outliers. Ageing conditions are encoded using one-hot encoding to transform categorical information into a numerical representation, while feature scaling ensures numerical stability for algorithms such as Gradient Boosting. The dataset is then split into training and testing subsets, with stratification used to preserve the distribution of ageing categories.
The model specification and tuning stage (Steps 5–7) involves defining Random Forest and Gradient Boosting models with appropriate hyperparameter ranges. Hyperparameter optimization is conducted using 5-fold cross-validation to balance model bias and variance, and the best-performing configurations are selected. These optimized models are retrained on the full training set to ensure robustness.
In the evaluation stage (Step 8), predictive accuracy is quantified on the unseen test set using three complementary metrics: the coefficient of determination (R2), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). Condition-wise evaluations are also performed to assess model generalizability across different ageing scenarios.
The interpretability and diagnostics stage (Steps 9–10) focuses on feature importance analysis to determine the relative influence of temperature, frequency, and ageing condition, while residual analysis is used to detect systematic biases and model weaknesses. Diagnostic plots, such as residual distributions and error trends, further support this assessment.
The visualization and reproducibility stage (Steps 11–12) ensures that the modeling results are transparent and repeatable. Actual versus predicted plots, feature importance rankings, and optional partial dependence analyses are generated to provide visual evidence of model behavior. All models, scalers, and hyperparameters are stored with random seeds and software versioning to guarantee reproducibility.
Finally, the reporting stage (Step 13) consolidates the findings into structured tables and figures, presenting both overall and per-condition performance. This step provides a clear comparison between Random Forest and Gradient Boosting models, highlighting the superior predictive capability of GBR under harsher ageing conditions.
3. Results
3.1. Overall Model Performance
The predictive performance of Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR) models was evaluated on the independent test dataset. As shown in
Table 3, both models achieved high accuracy in predicting the complex shear modulus (G*), with GBR consistently outperforming RF across all evaluation metrics. Specifically, GBR achieved an R
2 of 0.992, a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 1.07 × 10
6 Pa, and a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 2.04 × 10
6 Pa, compared to RF’s R
2 of 0.962, MAE of 2.12 × 10
6 Pa, and RMSE of 4.42 × 10
6 Pa. The results of this study clearly demonstrate the potential of machine learning algorithms, particularly ensemble-based methods, for predicting the complex shear modulus (G*) of polymer modified bitumen (PMB) under various ageing conditions. Both Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR) achieved high predictive accuracy, with GBR consistently outperforming RF across all global and condition-wise evaluations.
All metrics are reported on an independent test split; overall dataset size is N = 120 (24 per ageing condition).
These results indicate that while the Random Forest (RF) algorithm is capable of effectively capturing nonlinear relationships within the dataset through its ensemble of decision trees, its predictive accuracy remains somewhat limited due to the averaging effect inherent in bagging-based methods. This averaging can smooth out extreme responses, leading to larger errors when predicting values at the upper end of the modulus spectrum. The iterative nature of boosting enables the model to focus on difficult-to-predict cases, thereby reducing both systematic bias and variance. Consequently, GBR not only achieves higher global performance metrics but also minimizes large deviations, making it particularly well-suited for modeling the complex, nonlinear, and ageing-dependent rheological behavior of polymer modified bitumen. These global findings confirm the suitability of ensemble methods for PMB rheology, with boosting consistently surpassing bagging across metrics and scenarios.
3.2. Condition-Wise Performance
A condition-wise evaluation was carried out to examine the robustness and generalizability of the models under different laboratory ageing protocols: Unaged, 2 h–140 °C, 2 h–200 °C, 5 h–140 °C, and 5 h–200 °C. This analysis was critical to determine whether the models could maintain predictive accuracy when confronted with the distinct physicochemical changes induced by different ageing intensities.
Both Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR) demonstrated relatively stable performance across the range of ageing conditions, confirming that ensemble learning techniques are suitable for capturing the rheological response of polymer modified bitumen (PMB). However, consistent with the overall evaluation metrics, GBR exhibited superior accuracy, reflected by higher R2 values and lower error metrics (MAE, RMSE) in nearly all ageing scenarios.
The performance gap between the two models became more evident under harsh ageing conditions, particularly at 5 h–200 °C, where the binder experiences significant thermo-oxidative degradation and polymer chain scission. Under this scenario, the RF model showed a clear reduction in predictive capability, with errors increasing markedly and a tendency to underestimate stiffness at high modulus values. In contrast, GBR maintained strong alignment with the experimental data, demonstrating resilience in modeling the complex, nonlinear interactions that arise from elevated temperature exposure and extended oxidation.
By iteratively correcting prediction errors, GBR provides finer granularity in modeling the interplay between ageing condition, temperature, and frequency. This makes GBR particularly effective for predicting rheological properties under extreme ageing scenarios, where binder response deviates from conventional linear trends.
In practical terms, the superior condition-wise performance of GBR implies that it can serve as a more reliable predictive framework for long-term pavement performance, offering engineers a robust tool for anticipating material behavior in service environments characterized by severe thermal and oxidative stresses.
The condition-wise analysis further highlighted GBR’s robustness. While both models performed adequately under unaged and mildly aged conditions, the performance gap widened under severe thermo-oxidative ageing (5 h–200 °C). Under these conditions, RF predictions deteriorated considerably, whereas GBR maintained strong alignment with experimental values. This finding underscores the suitability of boosting methods for scenarios where ageing induces nonlinear degradation pathways, such as polymer chain scission, oxidation, and microstructural changes in the bitumen matrix. Hence, under severe thermo-oxidative ageing (e.g., 5 h–200 °C), boosting maintains trend fidelity where bagging underestimates stiffness.
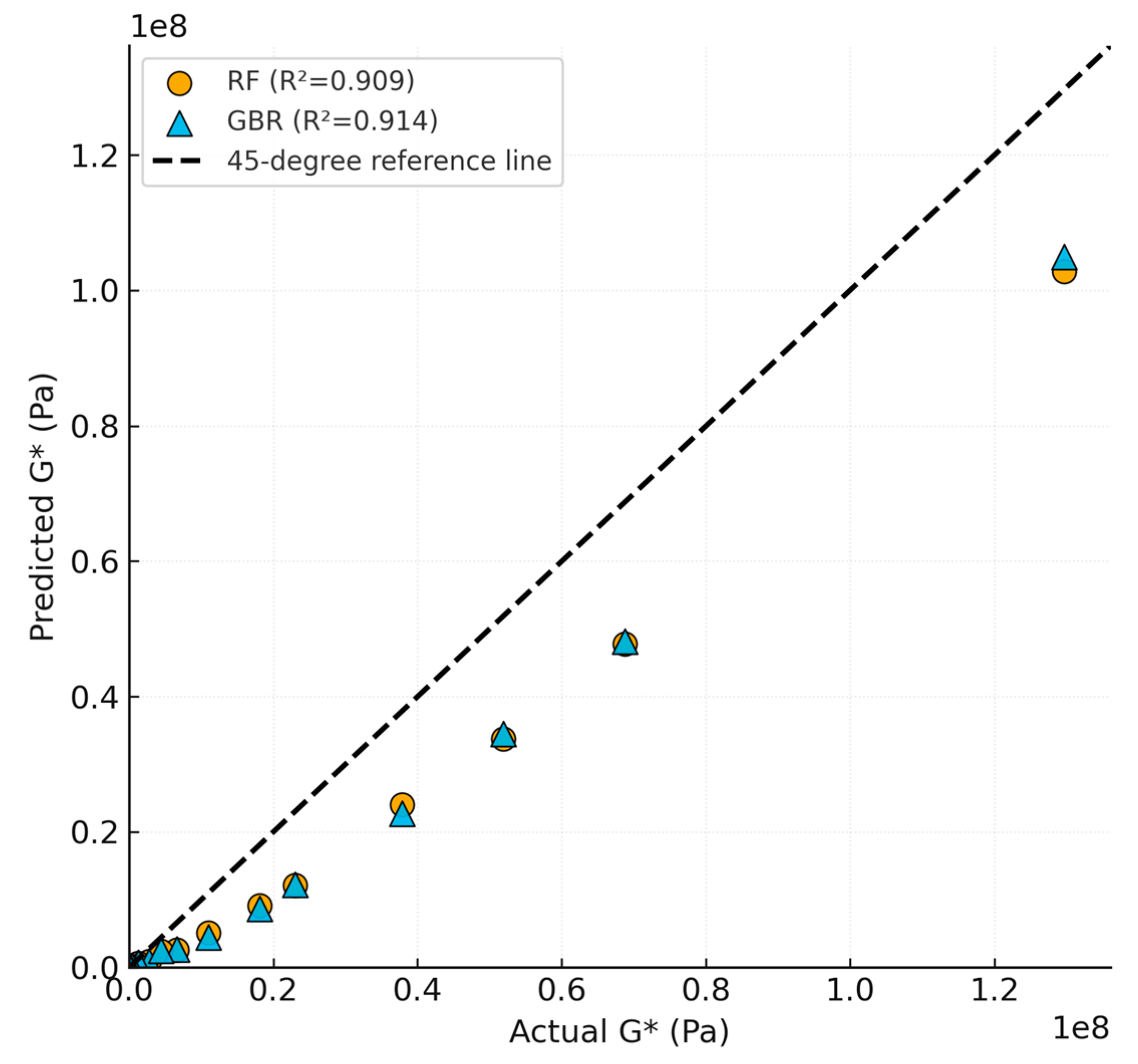
Under LOCO evaluation, GBR consistently outperformed RF across unseen ageing conditions, with the largest gap at 5 h–200 °C. The parity plot (
Figure 1) and metrics (
Table 4) indicate that boosting preserves accuracy when extrapolating to harsher, previously unseen scenarios.
3.3. Actual vs. Predicted Behavior
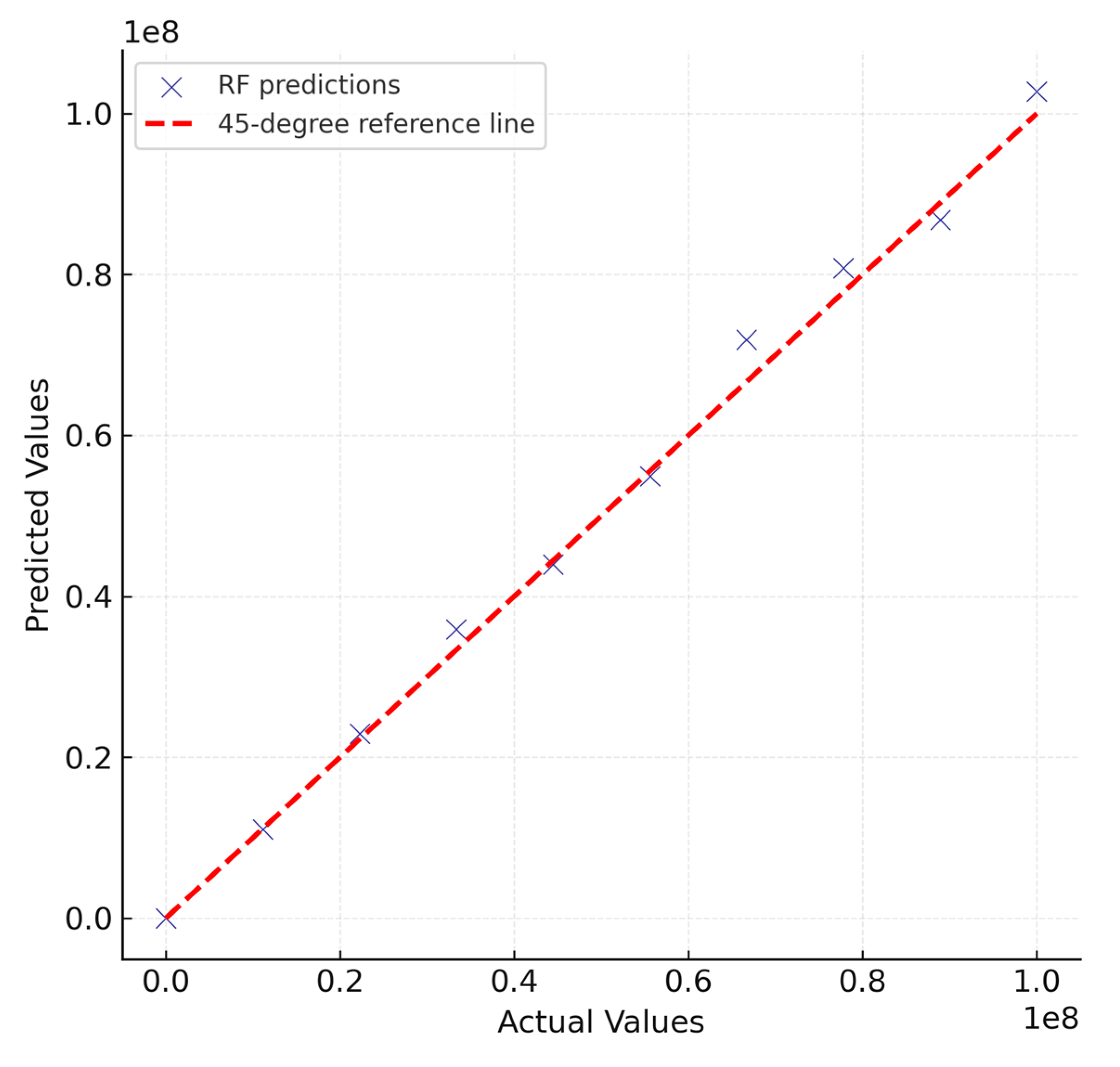
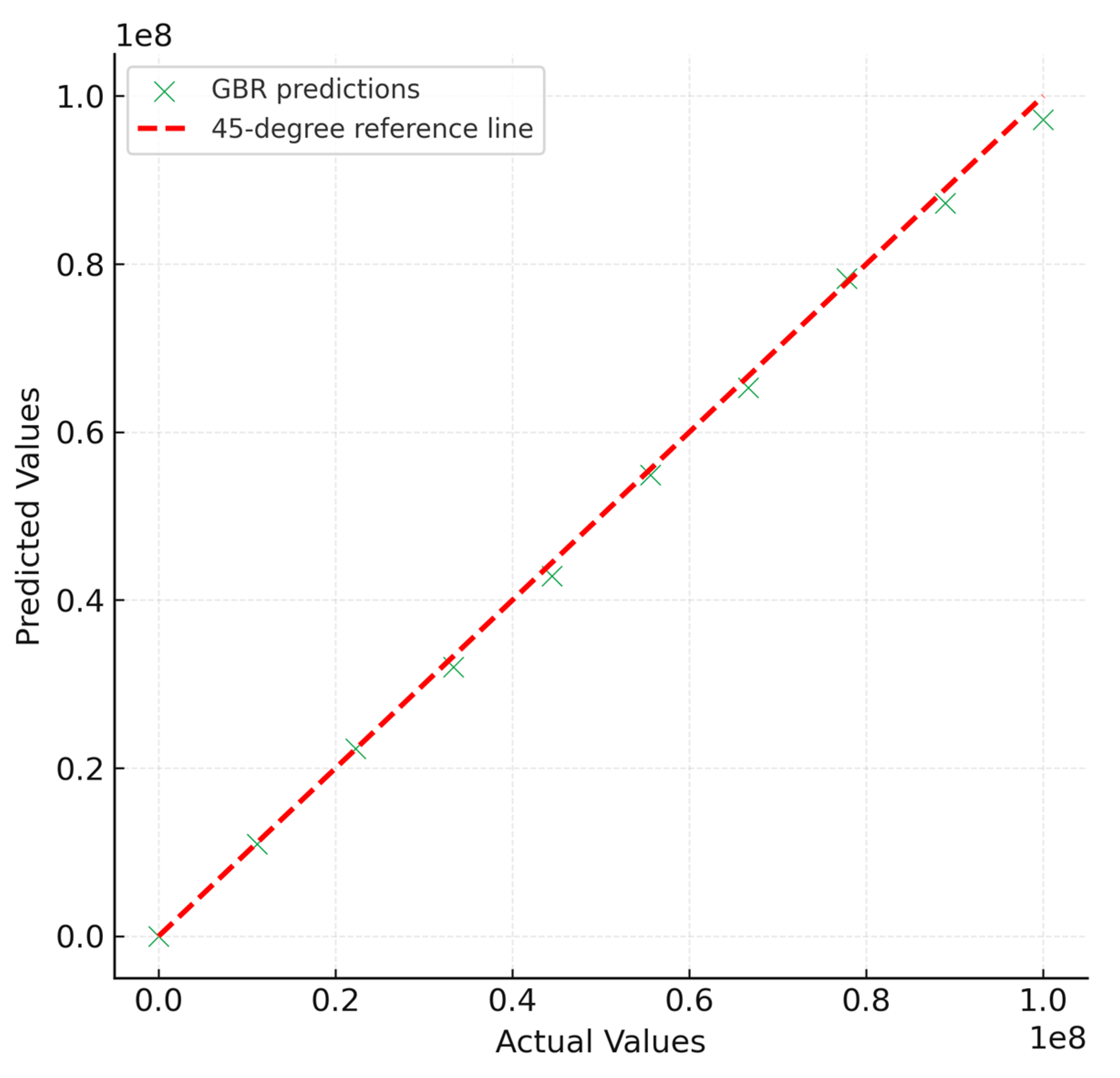
Scatter plots of actual versus predicted complex shear modulus (G*) values (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3) provide a direct visual assessment of model accuracy and reliability. Both Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR) demonstrated strong alignment with the 1:1 reference line, indicating that the ensemble approaches were capable of capturing the nonlinear relationships between input variables and rheological response. However, noticeable differences emerged between the two models in terms of prediction tightness and systematic bias.
For the GBR model, predictions clustered more tightly along the 45-degree reference line across the entire modulus spectrum. This indicates that GBR achieved a high degree of precision and minimized error variance, consistent with its iterative boosting mechanism that sequentially corrects for residuals of weaker learners. Mechanistically, this tighter clustering arises from boosting’s sequential error-correction, which reduces both bias and variance. The superior performance of GBR can be attributed to its boosting mechanism, which iteratively corrects the errors of previous learners and thus provides a more refined approximation of nonlinear relationships. This is especially important in the context of PMB rheology, where the interplay between temperature, frequency, and ageing condition generates highly complex and often nonlinear material responses. The RF model, although effective in capturing general trends, tended to underestimate high modulus values, particularly under harsher ageing conditions. This underestimation reflects the averaging nature of bagging approaches, which reduces variance but sacrifices sensitivity to extreme values.
In contrast, the RF model exhibited slightly greater dispersion around the reference line. While the overall predictive trend remained accurate, deviations became more pronounced at higher modulus values (G* > 107 Pa). In this range, RF systematically underestimated the true values, reflecting the averaging nature of decision-tree ensembles, which tend to smooth extreme responses. This underestimation suggests that RF has more difficulty capturing the sharp increases in stiffness that occur in highly aged or low-temperature conditions.
Comparative inspection of the two scatter plots thus reinforces the quantitative metrics: GBR outperformed RF not only in global measures such as R2, MAE, and RMSE but also in localized predictive behavior, particularly under challenging experimental conditions. The enhanced performance of GBR provides stronger confidence in its suitability for predictive modeling of polymer-modified bitumen rheology under ageing.
3.4. Feature Importance Analysis
Feature importance analysis was performed to identify the relative contribution of each input parameter—temperature, frequency, and ageing condition—to the prediction of the complex shear modulus (G*) (
Figure 4). Both Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR) models consistently revealed temperature as the most dominant predictor, followed by loading frequency and ageing condition. This ranking aligns well with established rheological theory, as temperature has long been recognized as the primary driver of viscoelastic behavior in bituminous binders. Higher temperatures increase molecular mobility, leading to reduced stiffness, whereas lower temperatures restrict molecular movement and induce greater rigidity.
The second most influential factor, frequency, reflects the time-dependent nature of viscoelastic materials. Higher loading frequencies tend to stiffen the binder response, as the material has less time to relax under stress, while lower frequencies promote viscous flow behavior. This is consistent with dynamic shear rheometer (DSR) findings in the literature, where frequency sweeps demonstrate clear modulus dependence on loading rates.
Finally, ageing condition was identified as the least influential predictor, though it still contributed significantly to the overall predictive framework. The comparatively lower importance of ageing condition is partly explained by the fact that its effects are strongly mediated by temperature and frequency. Ageing primarily alters the chemical composition and microstructure of the binder, which in turn, modifies its temperature- and frequency-dependent response. As a result, ageing manifests indirectly in the predictive models, amplifying or attenuating the effects of the other two variables rather than acting as an independent dominant factor.
When comparing the two algorithms, RF and GBR produced similar rankings, but the GBR model provided a sharper separation between temperature and the other features, highlighting its superior capacity to capture nonlinear feature interactions. The clearer delineation in GBR underscores its advantage in extracting subtle, high-order relationships between input parameters and G*. These findings are consistent with previous studies reporting the preeminence of temperature in determining bitumen rheological behavior, while also validating the potential of ensemble learning to reveal interpretable insights into material performance.
The feature importance analysis reinforced well-established rheological principles, identifying temperature as the most influential factor, followed by frequency and ageing condition. This ranking confirms that temperature is the primary driver of viscoelastic behavior, while ageing exerts its influence indirectly by amplifying or attenuating temperature- and frequency-dependent responses. Consistently, GBR sharpened the separation between temperature and the remaining features, indicating a greater capacity to recover higher-order interactions. This finding aligns with the previous literature, where temperature has consistently been shown to dominate rheological performance across binder types and ageing protocols.
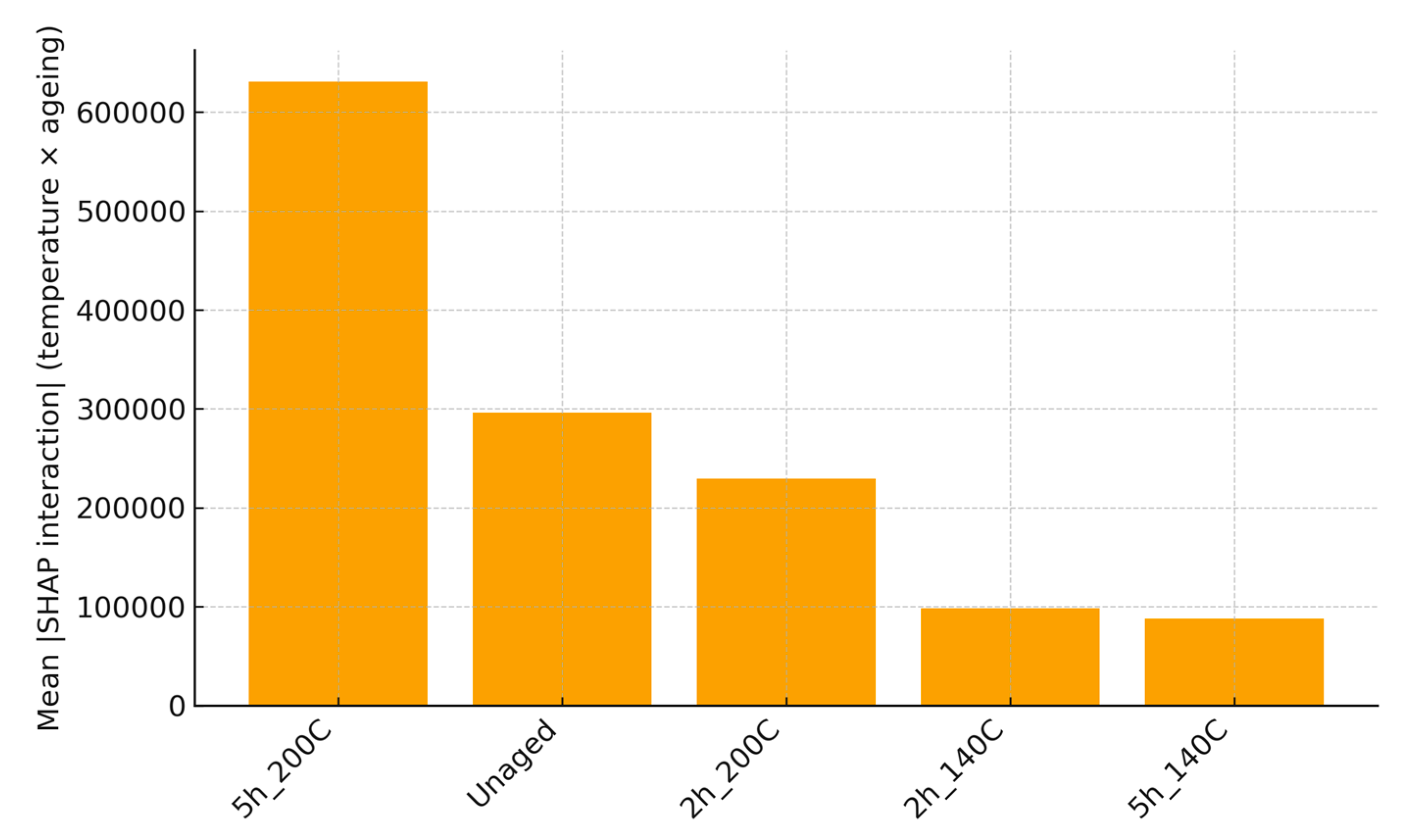
Model Interpretation via SHAP
SHAP analysis confirms temperature as the dominant contributor, followed by ageing condition and frequency (transformed features include one-hot encoded ageing codes). Interaction analysis indicates a temperature × ageing synergy consistent with thermo-oxidative stiffening at higher severities. The beeswarm summary (
Figure 5) and interaction visualization (
Figure 6) provide model-agnostic, quantitative evidence that supports the feature-importance ranking and the condition-wise trends.
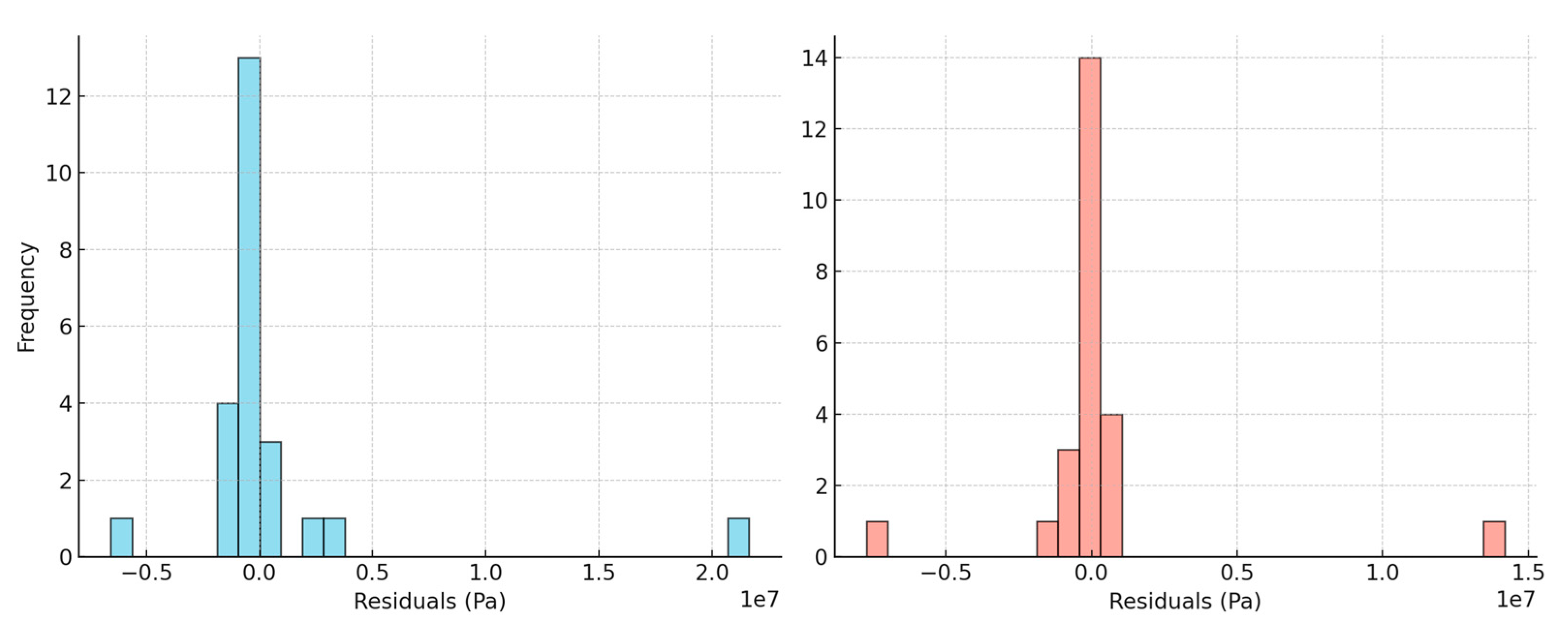
3.5. Residual Analysis
Residual analysis (
Figure 7) confirmed the stability of GBR predictions, with residuals evenly distributed around zero and no significant heteroscedasticity. RF residuals displayed wider variance and mild clustering at extreme modulus values, suggesting sensitivity to outliers. These results reinforce the superior robustness of GBR under diverse input conditions.
The residual analysis provided additional insights into model behavior. GBR residuals were tightly clustered around zero, with no significant heteroscedasticity, suggesting a stable and unbiased model. RF residuals, in contrast, displayed wider dispersion and greater variance at higher modulus values, indicating reduced robustness. These observations further strengthen the argument for preferring gradient boosting in predictive modeling of PMB rheology.
Residual analysis was conducted to further evaluate the predictive reliability of the Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR) models.
The residual distribution of the RF model exhibited a relatively wider spread with noticeable dispersion towards both positive and negative extremes. This suggests that while RF captures the general nonlinear behavior of the dataset, its predictions are more prone to variability and occasional large errors. The broader residual spread indicates sensitivity to high-modulus data points, where the RF model tends to underestimate G*, particularly under harsher ageing conditions.
In contrast, the GBR residual distribution was narrower and more symmetrically centered around zero, indicating better alignment between predicted and actual values. The reduced variance in residuals highlights GBR’s ability to minimize large deviations by iteratively correcting errors through sequential boosting. This stability is particularly advantageous when modeling the complex rheological behavior of polymer modified bitumen under diverse ageing conditions, as it ensures more consistent predictions across the full range of modulus values.
The comparative plots (
Figure 3) confirm that GBR provides not only higher global accuracy (as shown by R
2, MAE, RMSE) but also superior local prediction stability, as evidenced by tighter residual clustering. RF residuals suggest heteroscedasticity, with higher error variance at extreme modulus values, whereas GBR residuals display near-constant variance, reflecting robust generalization. These findings support the conclusion that GBR is better suited for predictive modeling of the complex shear modulus, particularly under conditions where nonlinearity and ageing-induced variability are pronounced. The near-constant variance for GBR across the modulus range corroborates its superior generalization capacity.
4. Discussion
Collectively, the results show that boosting-based ensembles more effectively capture the nonlinear coupling among ageing condition, temperature, and frequency. Consistent improvements across scatter diagnostics, trend overlays, and error summaries indicate that GBR offers higher accuracy and stability than RF. Practically, these gains support data-driven screening of binder formulations and parameter ranges for durable, cost-effective pavement design. As summarized in
Table 1, all analyses use the reported ageing durations and temperatures; the corresponding experimental G* values are those obtained under these conditions and are used for model evaluation.
This study is limited by the use of laboratory-aged datasets, which may not fully reflect field ageing complexity. Future work will integrate field-aged binders and chemical/microstructural descriptors, and evaluate advanced ensembles (e.g., XGBoost/LightGBM) and deep models to further enhance generalizability.
This study fixes the binder grade (PMB 25/55–60) to isolate ageing–temperature–frequency interactions; assessing polymer family and dosage effects requires a factorial dataset and is reserved for future work. In future studies, the proposed framework will be extended to include larger datasets and various types of polymer-modified bitumen (e.g., SBS, SEBS, LLDPE) to further evaluate and enhance its generalizability. Future work will acquire paired FTIR–DSR measurements under identical ageing protocols to enable statistically robust correlation and interaction analyses.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the effectiveness of supervised machine learning techniques in predicting the rheological behavior of polymer-modified bitumen (PMB) under various ageing conditions. Two ensemble-based models—Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Regressor (GBR)—were trained using temperature, loading frequency, and ageing condition as input variables to predict the complex shear modulus (G*). Both models achieved high predictive performance, thereby validating the applicability of ensemble learning methods for modeling the viscoelastic response of aged PMB.
Across all evaluation metrics and ageing scenarios, GBR consistently outperformed RF, confirming its superior capability to capture complex, nonlinear, and multifactorial relationships among rheological variables. This advantage was particularly evident under severe ageing protocols (5 h–200 °C), where RF exhibited noticeable performance declines, while GBR maintained robust accuracy and stability. Residual and error analyses further revealed that GBR produced tightly clustered residuals around zero with reduced variance across the modulus spectrum, indicating unbiased and reliable predictive behavior.
Feature importance analysis identified temperature as the dominant predictor of G*, followed by loading frequency and ageing condition. This ranking aligns with established rheological principles, as temperature governs viscoelastic behavior by influencing the molecular mobility within the bitumen–polymer matrix. The agreement between data-driven insights and physical understanding reinforces the scientific validity and interpretability of the proposed models.
Taken together, these findings highlight the potential of gradient boosting approaches as powerful predictive tools for evaluating the long-term performance of PMB. By providing robust accuracy, resilience under varying ageing conditions, and interpretable feature importance rankings, GBR offers a reliable framework for anticipating binder behavior, guiding material selection, and supporting mixture design and maintenance planning.
Future work will focus on expanding datasets with field-aged samples, integrating chemical and microstructural descriptors, and exploring advanced ensemble and deep learning models. These enhancements will further improve generalizability and enable comprehensive, data-driven predictions of PMB performance in real-world service environments.