Optimization of Gold Thin Films by DC Magnetron Sputtering: Structure, Morphology, and Conductivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
- •
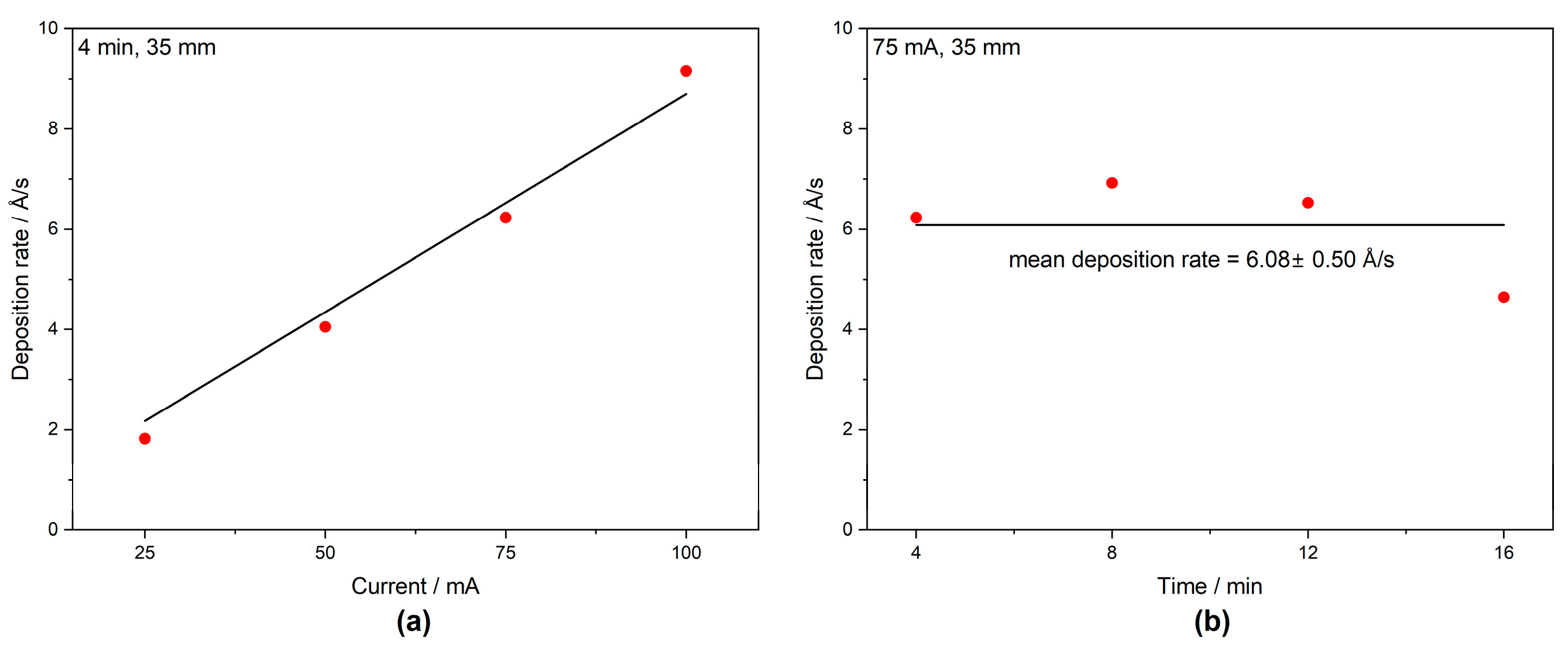
- Sputtering current—with the increase in sputtering current, the sputtering yield increases. More ions are generated and accelerated towards the target material, and more atoms are removed from the target surface. It leads to a faster deposition rate.
- •
- Deposition time—this does not influence the sputtering yield. With a longer deposition time, more ions are bombarding the target, so the total number of ejected atoms is greater, and a thicker film can be obtained, e.g., for CrN [21].
- •
- Target-substrate distance—shorter distance enhances the deposition rate, and the films with larger grains can be obtained [22]. At a higher distance, the deposition rate is slower, as sputtered atoms undergo more collisions with gas molecules. It is even more crucial at higher gas pressures [23]. At the same time, with the increase in target–substrate distance, the difference in particle concentration on the surface is lower, and the deposition uniformity is better [24].
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
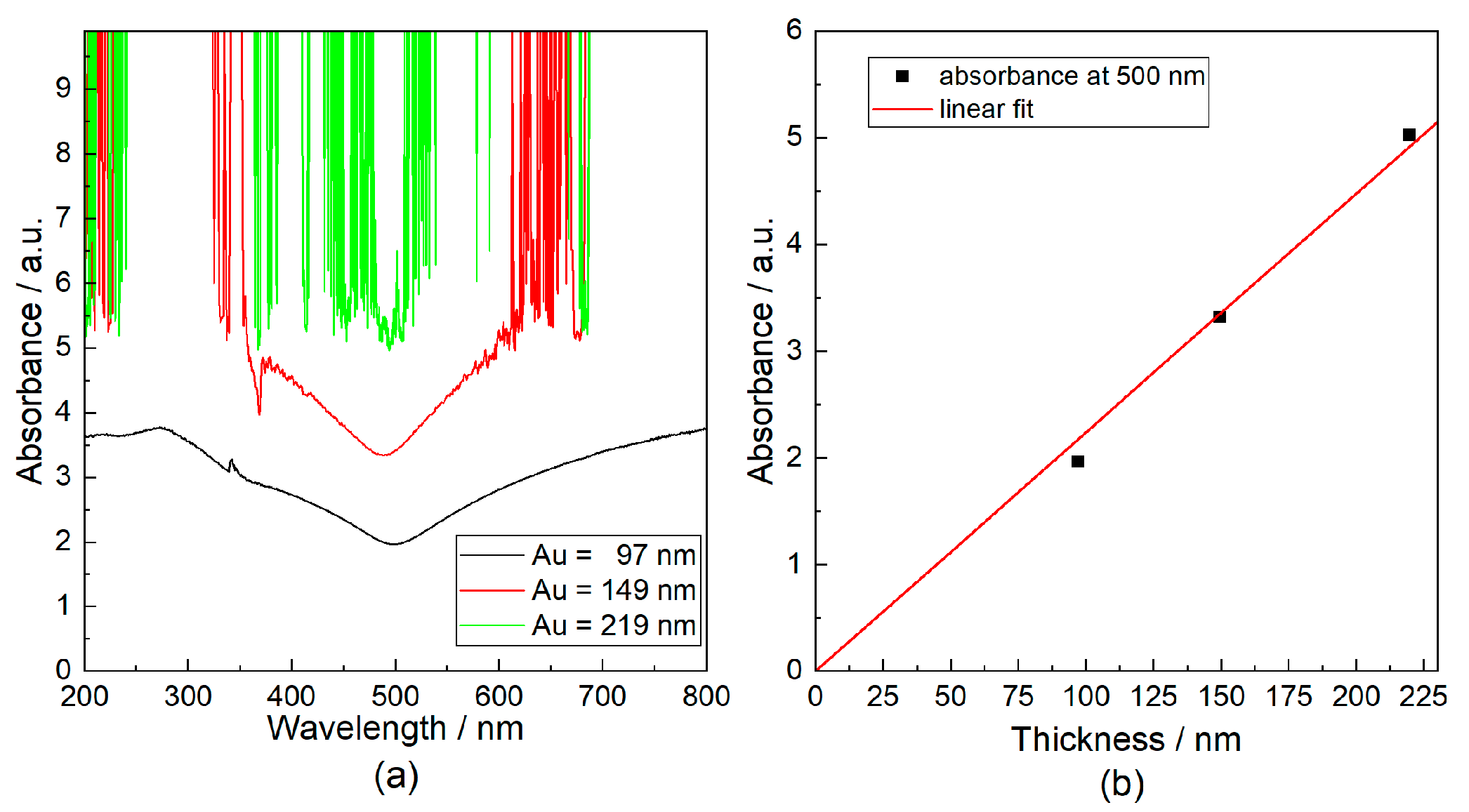
3.1. Thickness and Chemical Composition
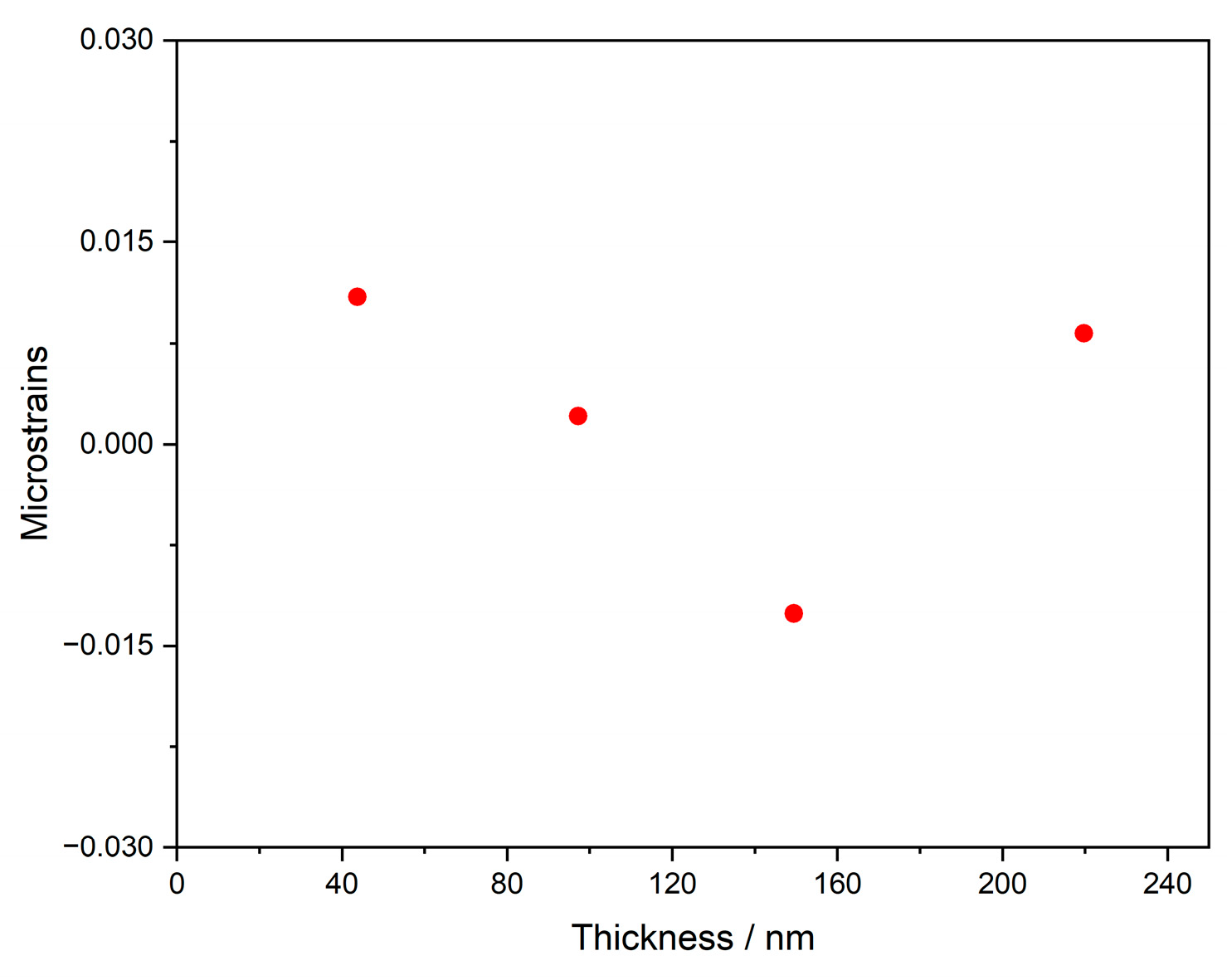
3.2. Structure
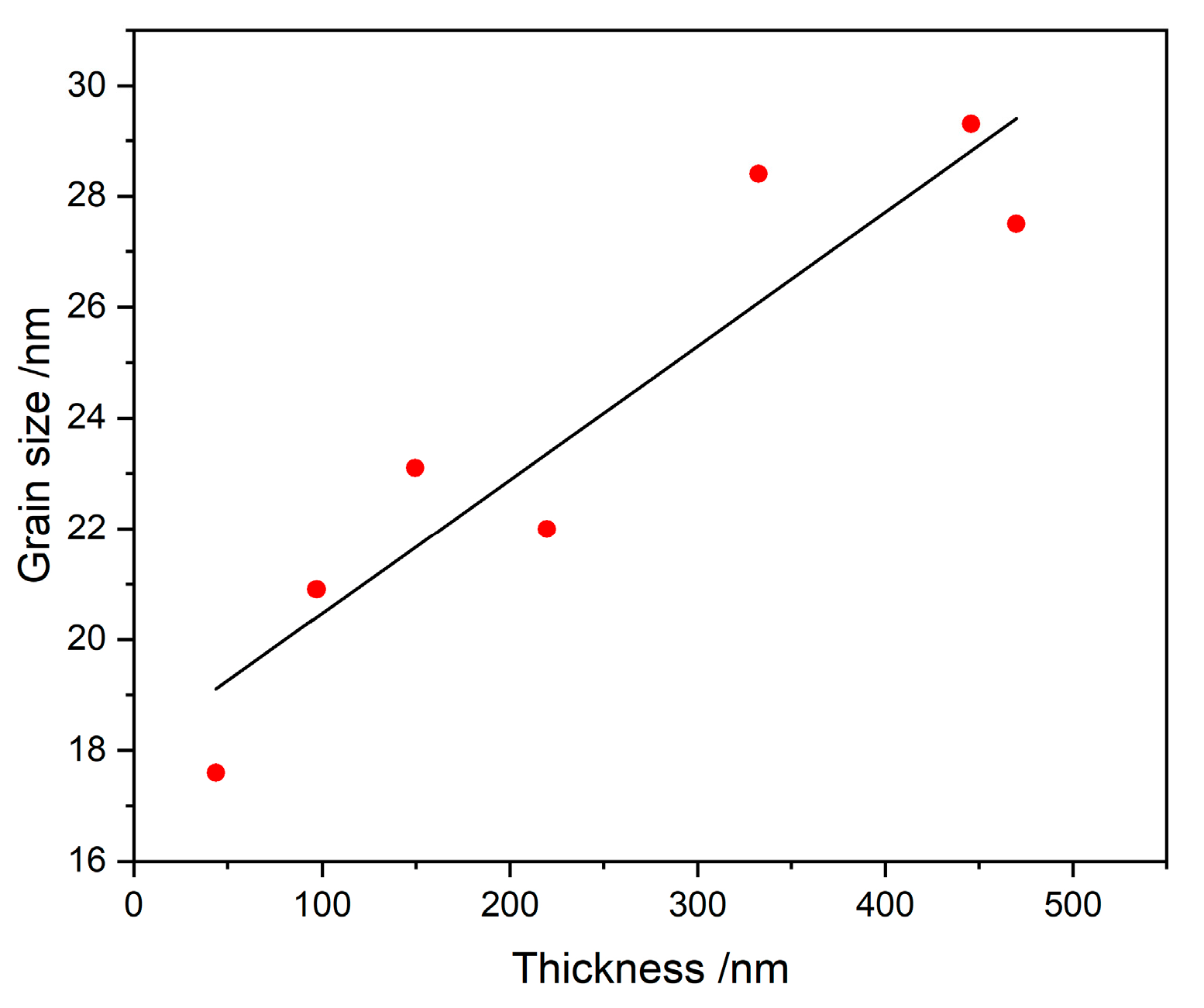
3.3. Morphology
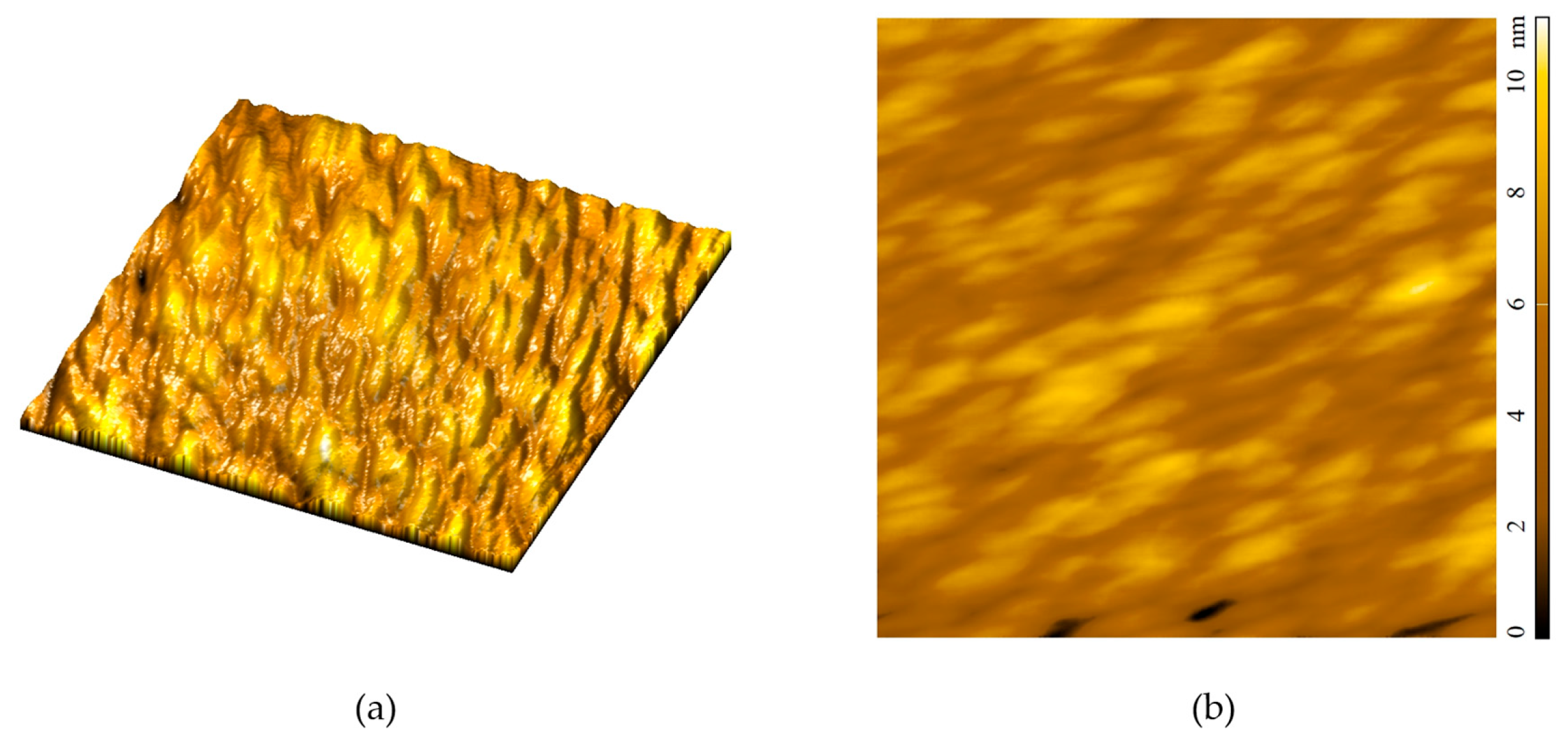
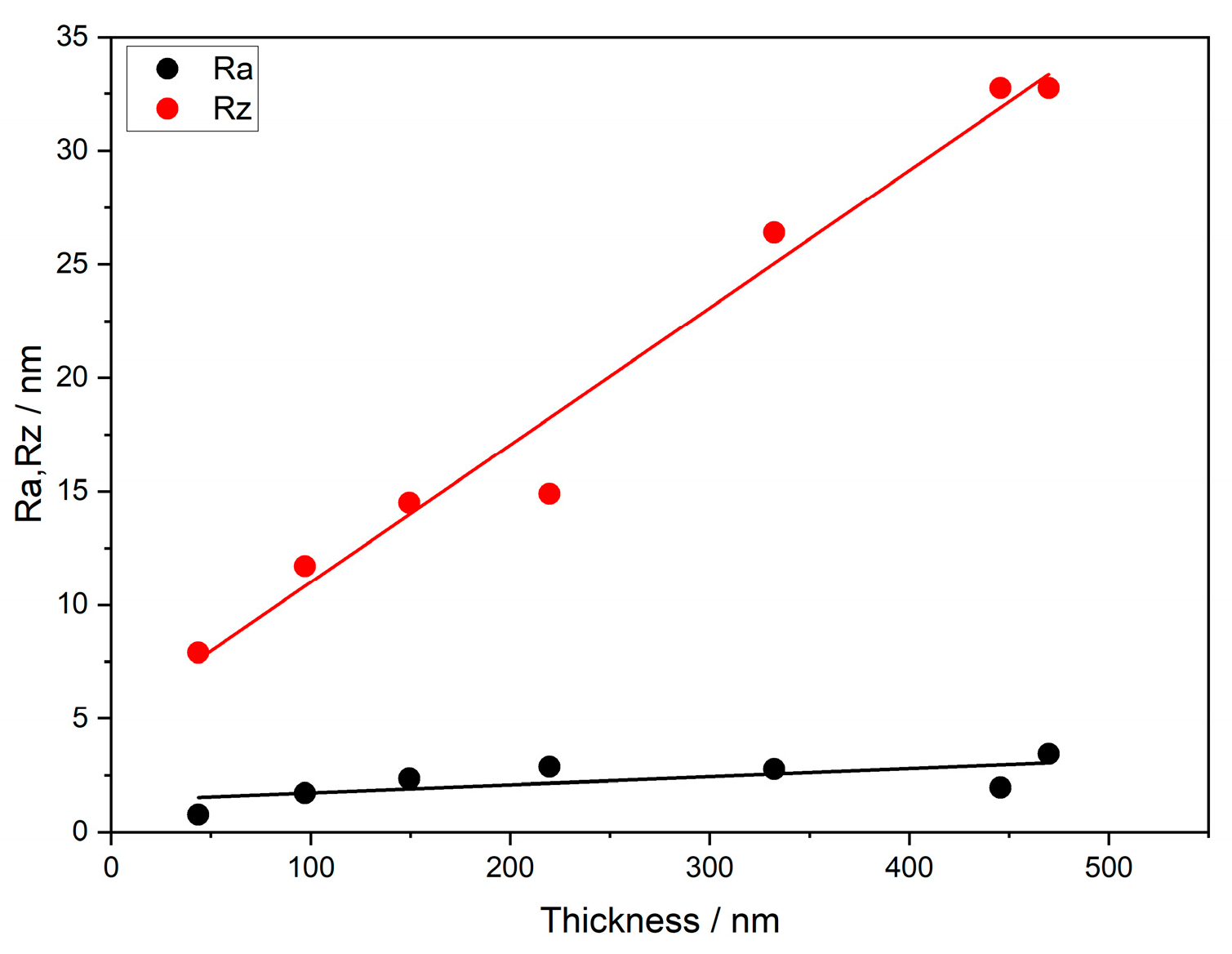
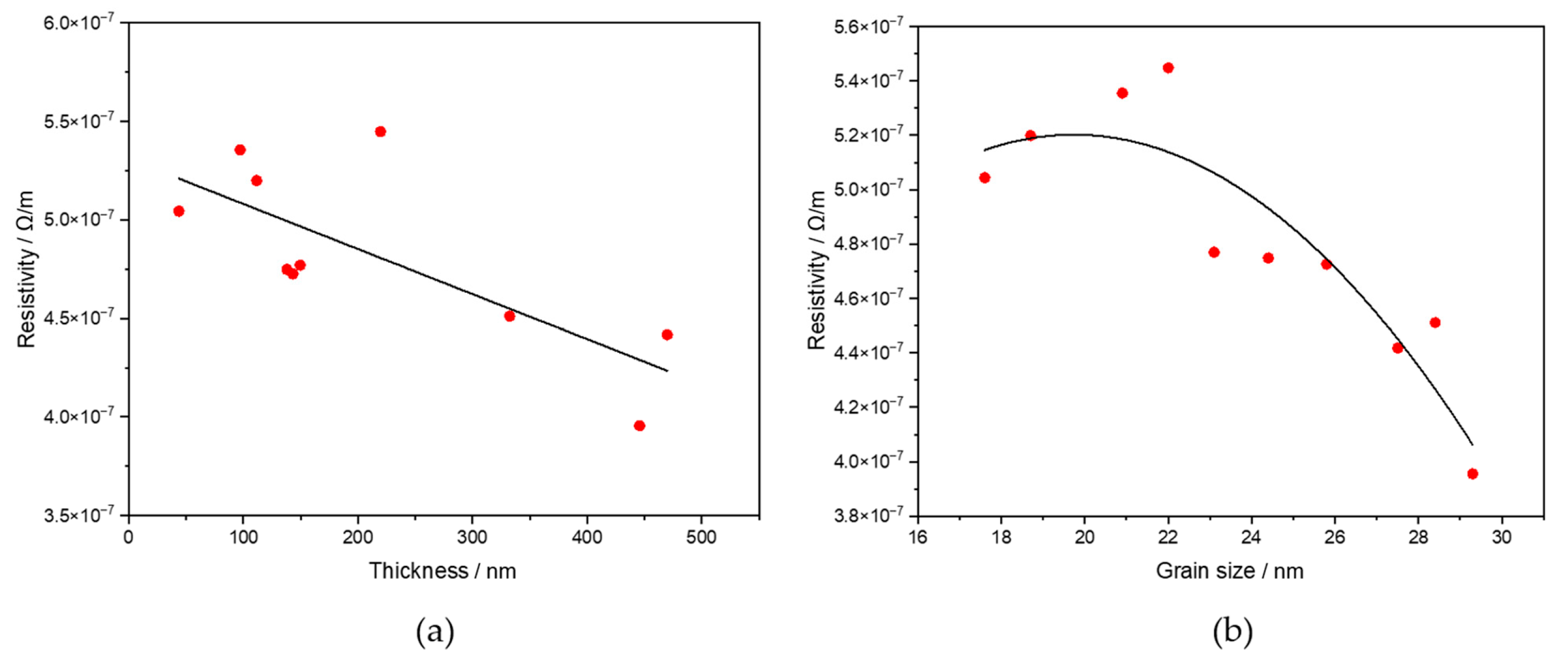
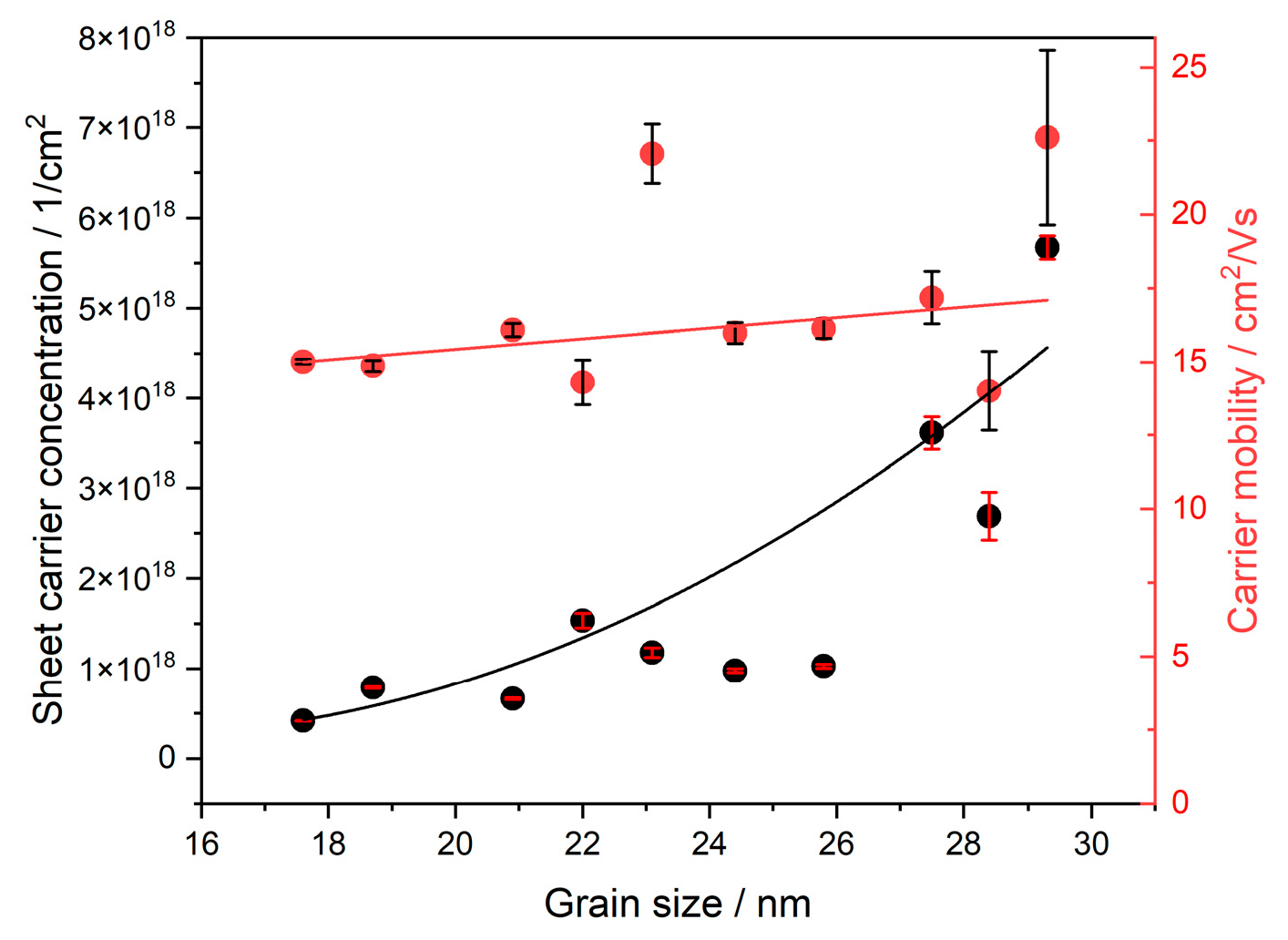
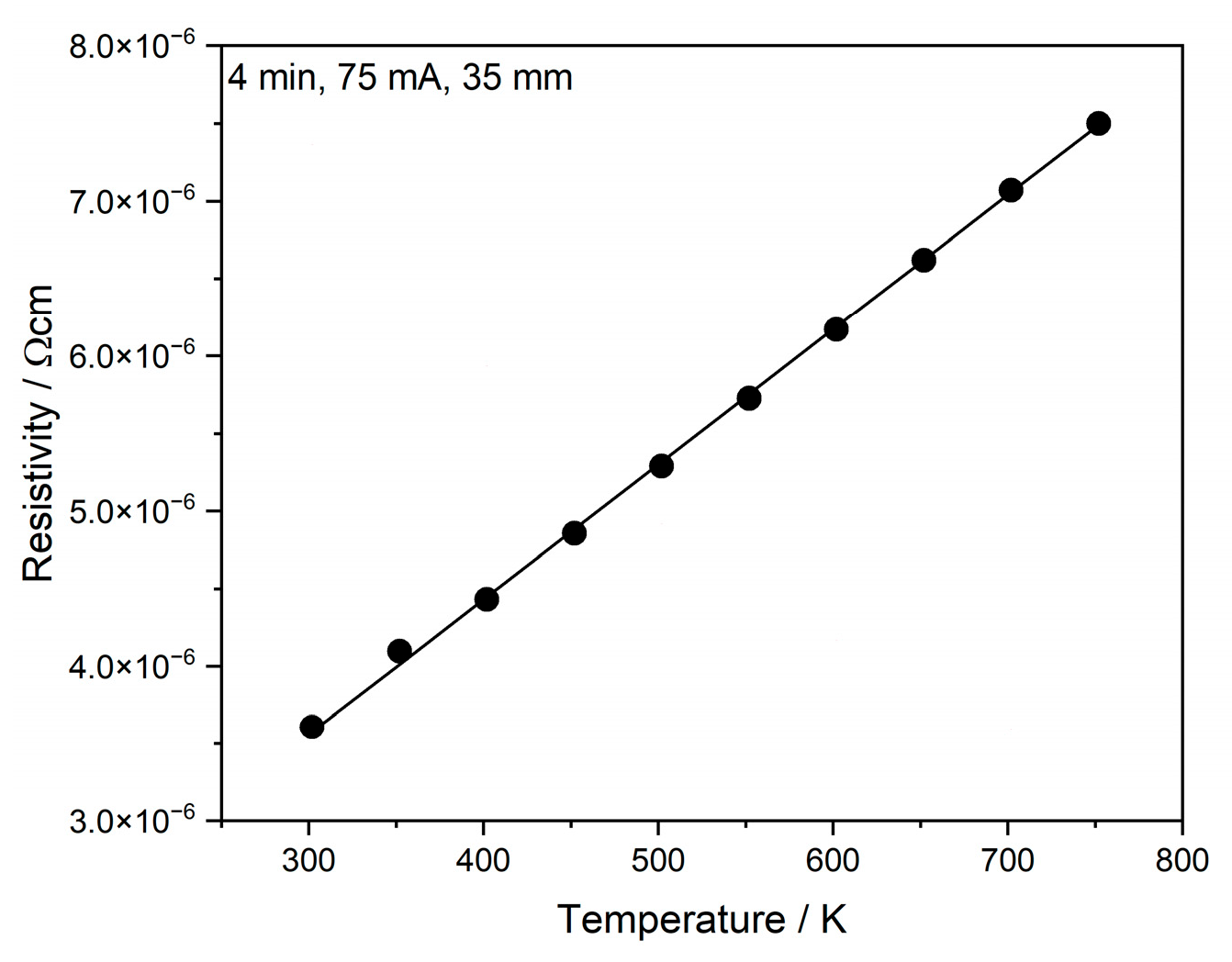
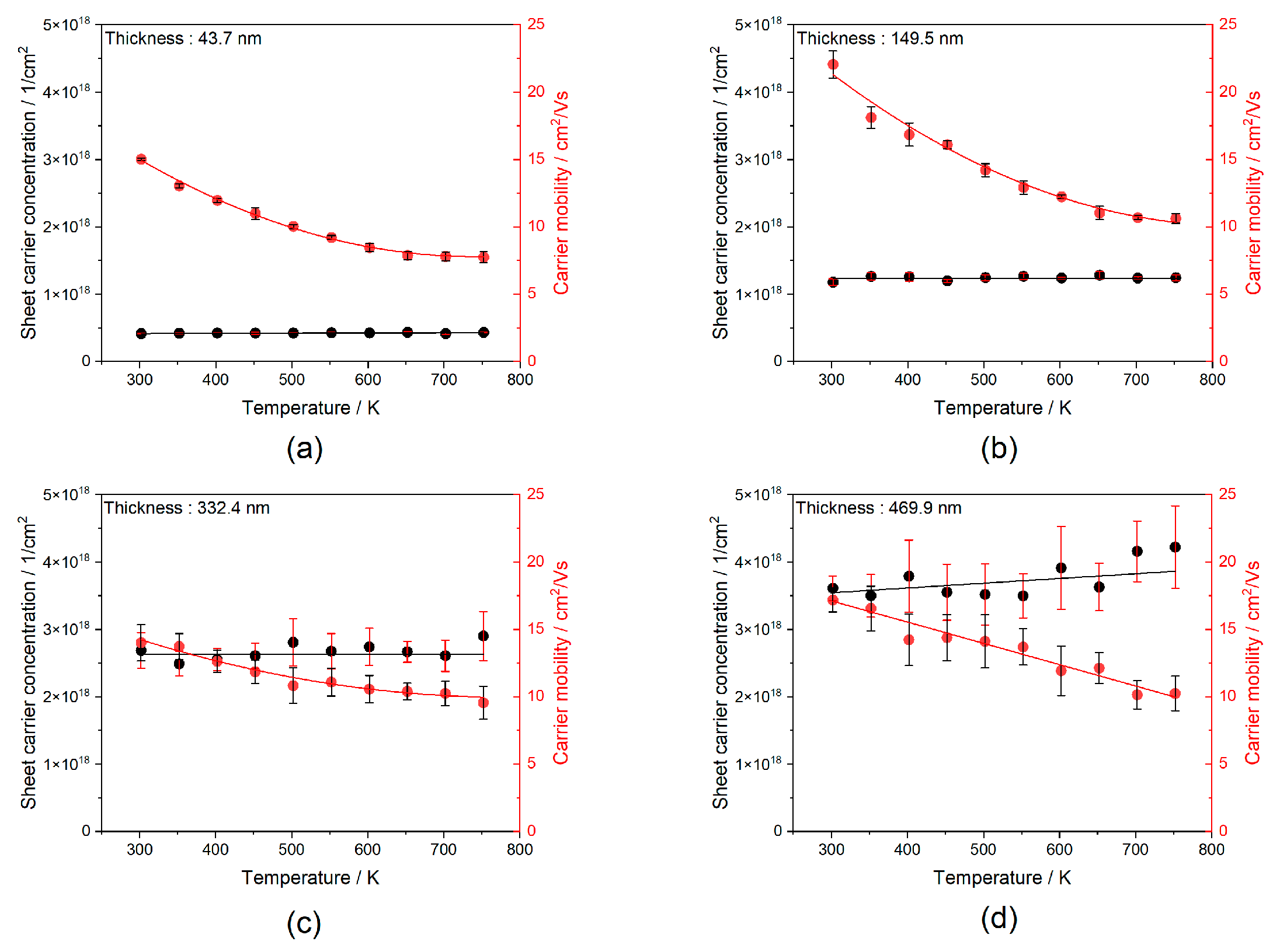
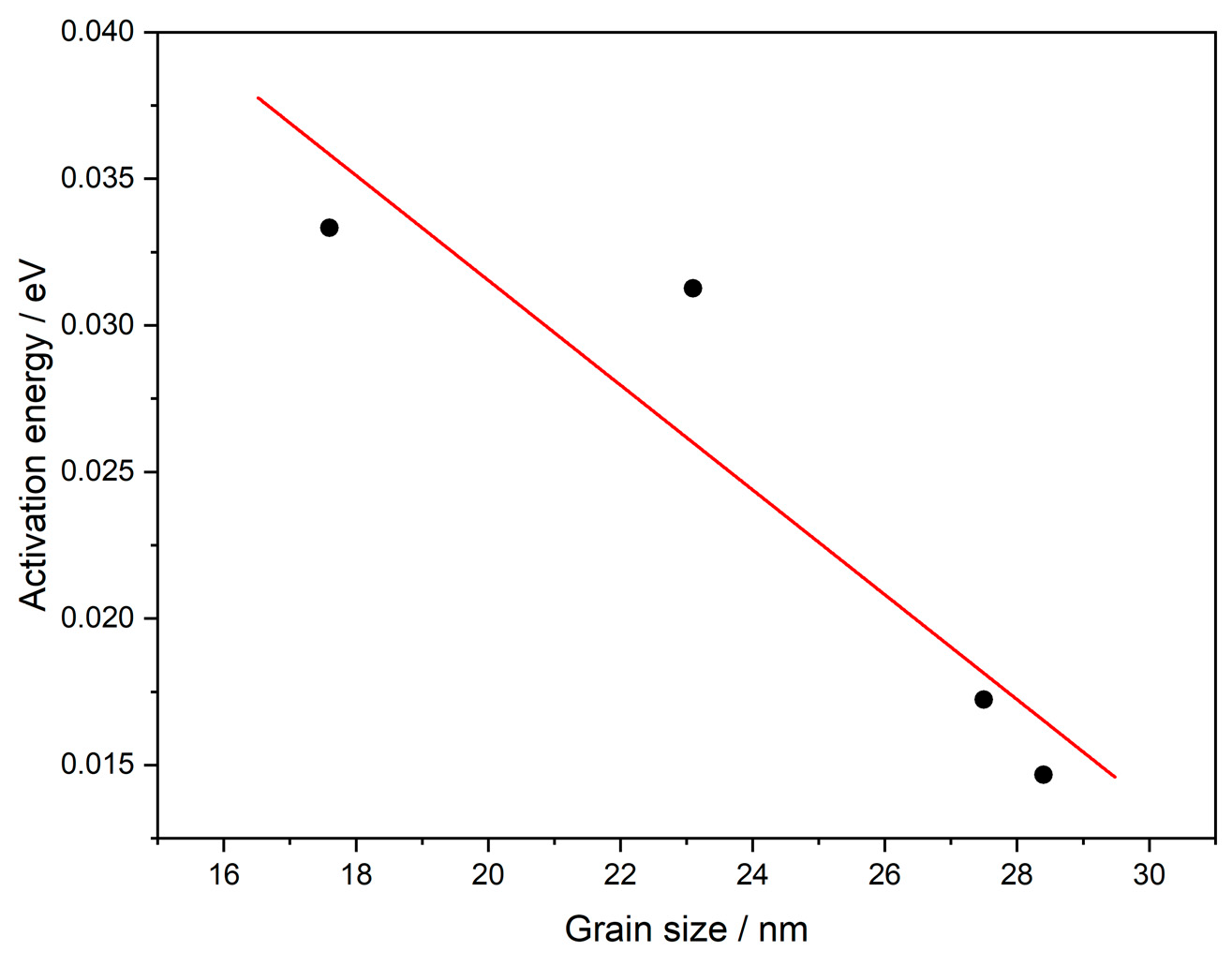
3.4. Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, L.D. Scope for new applications for gold arising from the electrocatalytic behaviour of its metastable surface states. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déronzier, T.; Morfin, F.; Massin, L.; Lomello, M.; Rousset, J.L. Pure nanoporous gold powder: Synthesis and catalytic properties. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 5287–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortari, A.; Maaroof, A.; Martin, D.; Cortie, M.B. Mesoporous gold electrodes for sensors based on electrochemical double layer capacitance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvítek, O.; Kopáček, V.; Švorčík, V. Gold nanostructures in gas chemical sensor technology. Chem. Listy 2018, 112, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Bulowski, W.; Knura, R.; Socha, R.P.; Basiura, M.; Skibińska, K.; Wojnicki, M. Thin Film Semiconductor Metal Oxide Oxygen Sensors: Limitations, Challenges, and Future Progress. Electronics 2024, 13, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulowski, W.; Socha, R.P.; Drabczyk, A.; Kasza, P.; Panek, P.; Wojnicki, M. Molecular Layer Doping ZnO Films as a Novel Approach to Resistive Oxygen Sensors. Electronics 2025, 14, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wu, X.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Bao, H. Suppressed Thermal Conductivity in Polycrystalline Gold Nanofilm: The Effect of Grain Boundary and Substrate. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2021, 38, 027202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.I.; Radwan, S.I.; Shehata, M.M.; Ghazy, O.A.; Saleh, H.H. Structural, optical and electrical properties of PVC/Au thin films prepared by sputtering process. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepička, P.; Kolská, Z.; Náhlík, J.; Hnatowicz, V.; Švořcík, V. Properties of Au nanolayers on polyethyleneterephthalate and polytetrafluoroethylene. Surf. Interface Anal. 2009, 41, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, S.I.; Rashad, A.M.; Tantawy, H.R.; Samad, S.A. Effect of Annealing and Ion Beam Irradiation on AC Electrical Properties for Gold Sputtered PM-355. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2022, 60, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švorčík, V.; Kvítek, O.; Lyutakov, O.; Siegel, J.; Kolská, Z. Annealing of sputtered gold nano-structures. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 102, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švorčík, V.; Siegel, J.; Sutta, P.; Mistrík, J.; Janicek, P.; Worsch, P.; Kolská, Z. Annealing of gold nanostructures sputtered on glass substrate. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 102, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Q.; Huang, Q.-S.; Qi, R.-Z.; Feng, Y.-F.; Feng, J.-T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.-B.; Wang, Z.-S. Effects of sputtering power and annealing temperature on surface roughness of gold films for high-reflectivity synchrotron radiation mirrors. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2019, 30, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libansky, M.; Zima, J.; Barek, J.; Reznickova, A.; Svorcik, V.; Dejmkova, H. Basic electrochemical properties of sputtered gold film electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 251, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casuse, T.Q.; Benavidez, A.; Plumley, J.B.; Tsui, L.-K.; Ali, A.-M.; Cerrato, J.M.; Garzon, F.H. DC Sputtered Ultralow Loading Gold Nanofilm Electrodes for Detection of As (III) in Water. ECS Sens. Plus 2022, 1, 014602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, C.; Xiao, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Xia, F.; Xiao, J. High sensitivity and fast response sensor based on sputtering Au tuned ZnFe2O4-SE for low concentration NH3 detection. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lü, J.; Song, X. Microstructure and electrical properties of ultrathin gold films prepared by DC sputtering. Vacuum 2010, 85, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, C.; Lützenkirchen-Hecht, D.; Frahm, R. Structural and electrical properties of thin d.c. magnetron-sputtered gold films deposited on float glass. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, X.-H.; Zhang, D.-L. Thickness dependence of grain size and surface roughness for dc magnetron sputtered Au films. Chin. Phys. B 2010, 19, 086802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, L.; Zhou, M.; Fan, X.; Ma, M. Preparation and spectral analysis of gold nanoparticles using magnetron sputtering and thermal annealing. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2014, 29, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A.; Bergström, J.; Burman, C.; Hogmark, S. Influence of deposition temperature and time during PVD coating of CrN on corrosive wear in liquid aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 146-147, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaveedeetrakul, A.; Witit-anun, N.; Boonamnuayvitaya, V. The role of target-to-substrate distance on the DC magnetron sputtered zirconia thin films’ bioactivity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2612–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuhrer, R.; Yeung, W.Y. Effect of target–substrate working distance on magnetron sputter deposition of nanostructured titanium aluminium nitride coatings. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; An, Q.; Fang, H. Monte Carlo simulation of deposition uniformity in the triple-target magnetron co-sputtering system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 646, 158914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.; Glaser, C.; Syed, M. Surface Morphology of Gold Thin Films using RF Magnetron Sputtering. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Technical Conference, SVC TechCon, Providence, RI, USA, 29 April–4 May 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kejzlar, J.; More-Chevalier, J.; Hruška, M.; Otta, J.; Fitl, P.; Novotný, M.; Poupon, M.; Hruška, P.; Prokop, D.; Cichoň, S.; et al. Black gold layers: Preparation via thermal evaporation, material and optical properties, and application potential for gas sensors. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 3280–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mech, K.; Kowalik, R.; Żabiński, P. Cu Thin Films Deposited by DC Magnetron Sputtering for Contact Surfaces on Electronic Components. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2011, 56, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rossnagel, S.M. Sputter deposition for semiconductor manufacturing. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1999, 43, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, W.D. Sputter Deposition; AVS: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sitko, R. Quantitative X-ray fluorescence analysis of samples of less than ‘infinite thickness’: Difficulties and possibilities. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2009, 64, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezher, S.; Dawood, M.; Kadhim, D.B. Optical Observations of Sputtered Au-nanostructures and Characterizations. J. Tech. 2024, 6, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Srivastava, A. Correlation Between Optical and Morphological Properties of Nanostructured Gold Thin Film. JSM Nanotechnol. Nanomed. 2016, 4, 1039. [Google Scholar]
- Dupré, L.; Buttard, D.; Leclere, C.; Renevier, H.; Gentile, P. Gold contamination in VLS-grown Si nanowires: Multiwavelength anomalous diffraction investigations. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4511–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viter, R.; Balevicius, Z.; Abou Chaaya, A.; Baleviciute, I.; Tumenas, S.; Mikoliunaite, L.; Ramanavicius, A.; Gertnere, Z.; Zalesska, A.; Vataman, V.; et al. The influence of localized plasmons on the optical properties of Au/ZnO nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 6815–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.C.; Sharma, S.; Pandey, K.K.; Gupta, P.; Rai, S.; Singh, R.; Chattopadhyay, M.K. Sputtering current driven growth and transport characteristics of superconducting Ti40V60 alloy thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2025, 137, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Allaq, A.H.; Tabassum, N.; Mohammed, Y.S.; Elmustafa, A.A. Sputtering-driven microstructure and mechanical behavior in NbMoTaW high-entropy alloy films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 340, 130694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Regodon, G.; Ferrer, F.J.; Rico, V.; Garcia-Martin, J.M.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Growth dynamics of nanocolumnar thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles. Nanotechnology 2024, 35, 095705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinský, P.; Slepička, P.; Hnatowicz, V.; Svorčík, V. Early stages of growth of gold layers sputter deposited on glass and silicon substrates. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, D.; Gasparotto, A.; Pierangelo, E.; Tondello, E. Nucleation and growth of gold nanoparticles deposited by RF-sputtering: An experimental study. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2004, 818, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, A.; Monteduro, A.G.; Rizzato, S.; Leo, A.; Di Natale, C.; Kim, S.S.; Maruccio, G. Advances in Materials and Technologies for Gas Sensing from Environmental and Food Monitoring to Breath Analysis. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2023, 7, 2200083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K. The conductivity of thin metallic films according to the electron theory of metals. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1938, 34, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, H.; Ghidelli, M.; Dehm, G. Approaches to Measure the Resistivity of Grain Boundaries in Metals with High Sensitivity and Spatial Resolution: A Case Study Employing Cu. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, M.E.; Gonzalez-Fuentes, C.A.; Henriquez, R.; Kremer, G.; Moraga, L.; Oyarzun, S.; Suarez, M.A.; Flores, M.; Munoz, R.C. Resistivity of thin gold films on mica induced by electron–surface scattering: Application of quantitative scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, H.; Lee, S.; Brink, T.; Ghidelli, M.; Dehm, G. Understanding Grain Boundary Electrical Resistivity in Cu: The Effect of Boundary Structure. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16607–16615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästle, G.; Boyen, H.G.; Schröder, A.; Plettl, A.; Ziemann, P. Size effect of the resistivity of thin epitaxial gold films. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 165414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkan, C.; Welland, M.E. Size effects in the electrical resistivity of polycrystalline nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14215–14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Zhang, X.; Cao, B.Y.; Fujii, M.; Takahashi, K.; Ikuta, T. Influence of grain boundary scattering on the electrical properties of platinum nanofilms. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 114102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, B.; Park, S.; Haverty, M.; Shankar, S.; Dunham, S.T. Simulation of grain boundary effects on electronic transport in metals, and detailed causes of scattering. Phys. Status Solidi B 2010, 247, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moors, K.; Sorée, B.; Magnus, W. Resistivity scaling in metallic thin films and nanowires due to grain boundary and surface roughness scattering. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 167, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.-G.; Zhang, D. Grain boundary resistivities of polycrystalline Au films. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 96, 17010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.; Lyutakov, O.; Rybka, V.; Kolská, Z.; Svorčík, V. Properties of gold nanostructures sputtered on glass. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendavid, A.; Martin, P.J.; Wieczorek, L. Morphology and optical properties of gold thin films prepared by filtered arc deposition. Thin Solid Film. 1999, 354, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.; Martin, E.; Cote, J.-M.; Sthal, F.; Gavoille, J.; Raschetti, M.; Oliveri, S. Low temperature dependence of resistivity in obliquely sputter-deposited gold thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 499, 131884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streletskiy, O.A.; Zavidovskiy, I.A.; Nischak, O.Y.; Dvoryak, S.V. Electrical conductivity and structural properties of a-C:N films deposited by ion-assisted pulse-arc sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2020, 701, 137948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridonov, J. Limits Of Measurement of Thickness and Elemental Composition with a Portable Xrf Analyzer. Univers. Tech. Sci. 2021, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, C.; Dargel, R. Determination of layer thickness with μXRF. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurlani, W.; Berretti, E.; Innocenti, M.; Lavacchi, A. Coating Thickness Determination Using X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Monte Carlo Simulations as an Alternative to the Use of Standards. Coatings 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcinai, S.; Ferretti, M. X-ray fluorescence-based methods to measure the thickness of protective organic coatings on ancient silver artefacts. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 149, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
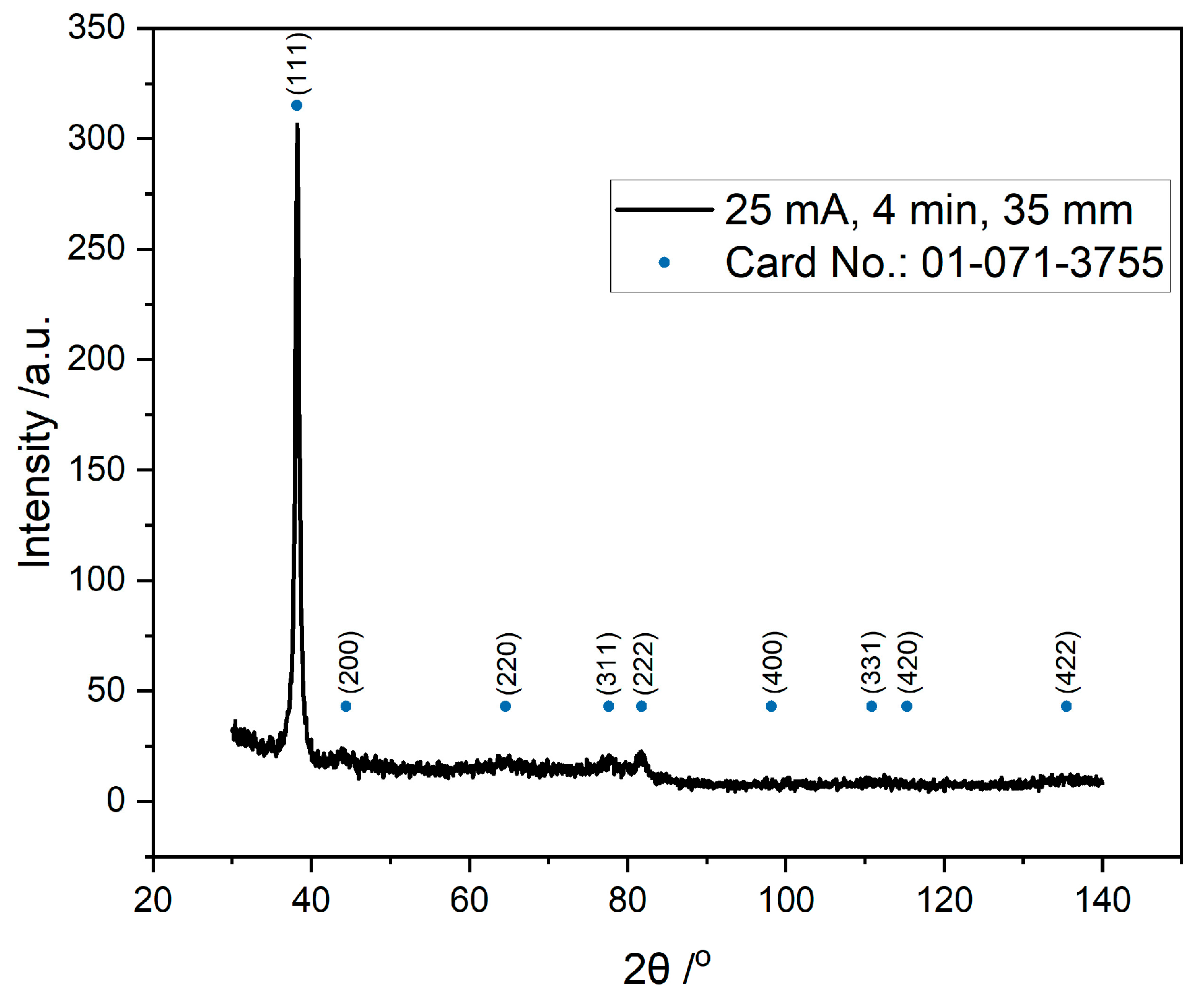
| Element Number | Element Symbol | Element Name | Atomic Conc. | Weight Conc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 79 | Au | Gold | 95.00% | 99.68% |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 5.00% | 0.32% |
| Current/mA | Distance/mm | Time/min | Substrate Weight/g | Substrate Weight with Au/g | Au Weight/g | Thickness/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 35 | 4 | 2.09480 | 2.09556 | 0.00076 | 43.7 |
| 50 | 35 | 4 | 2.08971 | 2.09140 | 0.00169 | 97.2 |
| 75 | 35 | 4 | 2.09578 | 2.09838 | 0.00260 | 149.5 |
| 100 | 35 | 4 | 2.09753 | 2.10135 | 0.00382 | 219.7 |
| 75 | 35 | 8 | 2.09454 | 2.10032 | 0.00578 | 332.4 |
| 75 | 35 | 12 | 2.09538 | 2.10355 | 0.00817 | 469.9 |
| 75 | 35 | 16 | 2.09512 | 2.10287 | 0.00775 | 445.7 |
| 75 | 33 | 4 | 2.10047 | 2.10241 | 0.00194 | 111.6 |
| 75 | 31 | 4 | 2.10063 | 2.10312 | 0.00249 | 143.2 |
| 75 | 29 | 4 | 2.09797 | 2.10037 | 0.00240 | 138.0 |
| Sample Thickness [nm] | Microstrains from W–H Analysis |
|---|---|
| 43.7 | 0.01094 |
| 97.2 | 0.00208 |
| 149.5 | −0.01261 |
| 219.7 | 0.00827 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulowski, W.; Skibińska, K.; Żabiński, P.; Wojnicki, M. Optimization of Gold Thin Films by DC Magnetron Sputtering: Structure, Morphology, and Conductivity. Coatings 2025, 15, 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111240
Bulowski W, Skibińska K, Żabiński P, Wojnicki M. Optimization of Gold Thin Films by DC Magnetron Sputtering: Structure, Morphology, and Conductivity. Coatings. 2025; 15(11):1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111240
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulowski, Wojciech, Katarzyna Skibińska, Piotr Żabiński, and Marek Wojnicki. 2025. "Optimization of Gold Thin Films by DC Magnetron Sputtering: Structure, Morphology, and Conductivity" Coatings 15, no. 11: 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111240
APA StyleBulowski, W., Skibińska, K., Żabiński, P., & Wojnicki, M. (2025). Optimization of Gold Thin Films by DC Magnetron Sputtering: Structure, Morphology, and Conductivity. Coatings, 15(11), 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111240








