Research on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Fiber Geopolymer Mortar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Programs
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportion Design
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Strength Test of Geopolymer Mortar
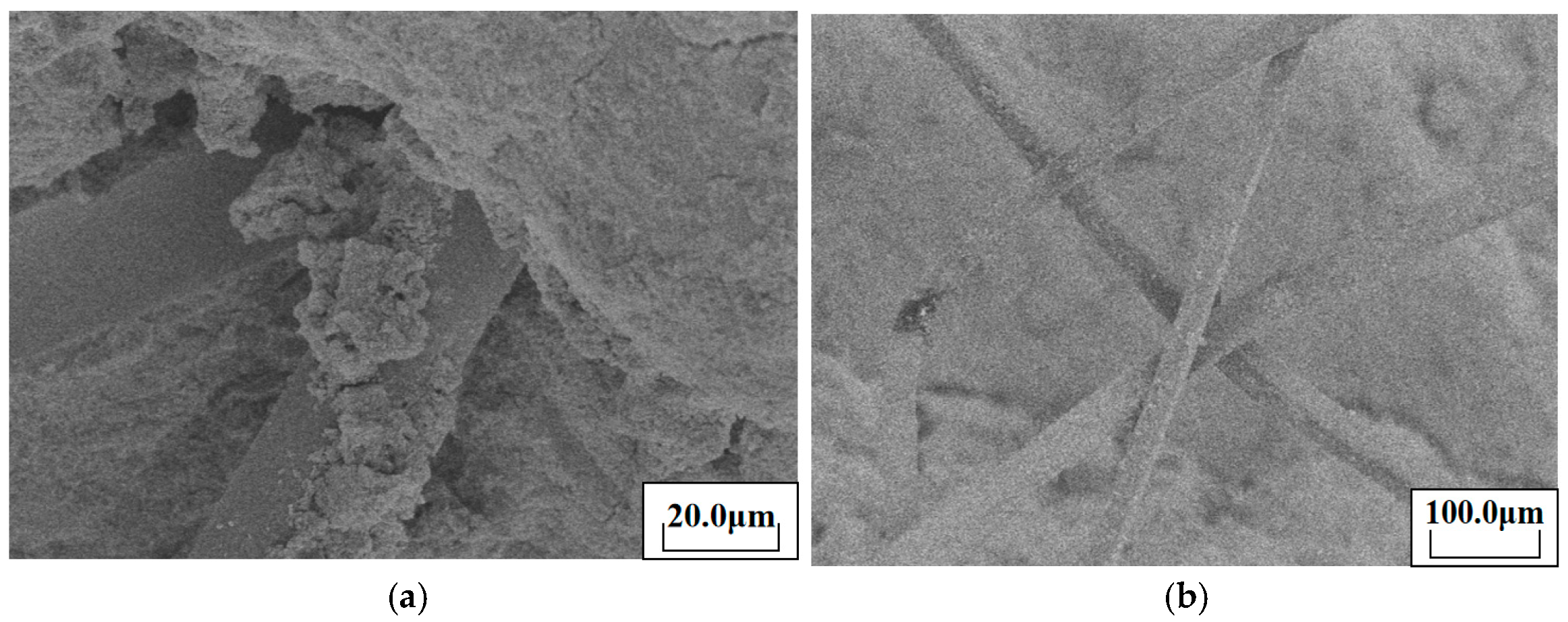
2.3.2. Microstructural Characterization
- (1)
- Molecular structure analysis
- (2)
- Microanalysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Properties of Geopolymer Mortar with Fibers
3.1.1. Research on Flexural Strength Test
3.1.2. Experimental Research on Compressive Strength
3.1.3. Comparative Analysis of Flexural-to-Compressive Ratio
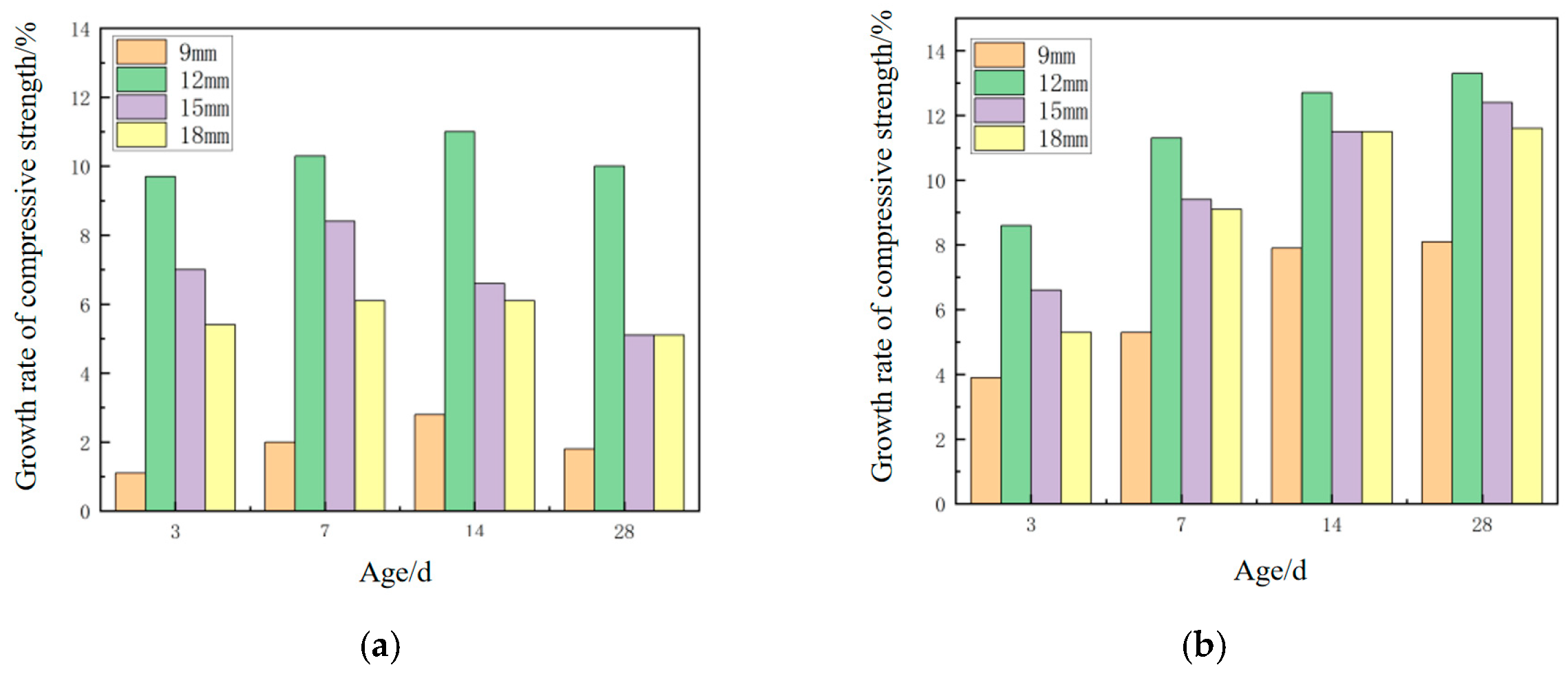
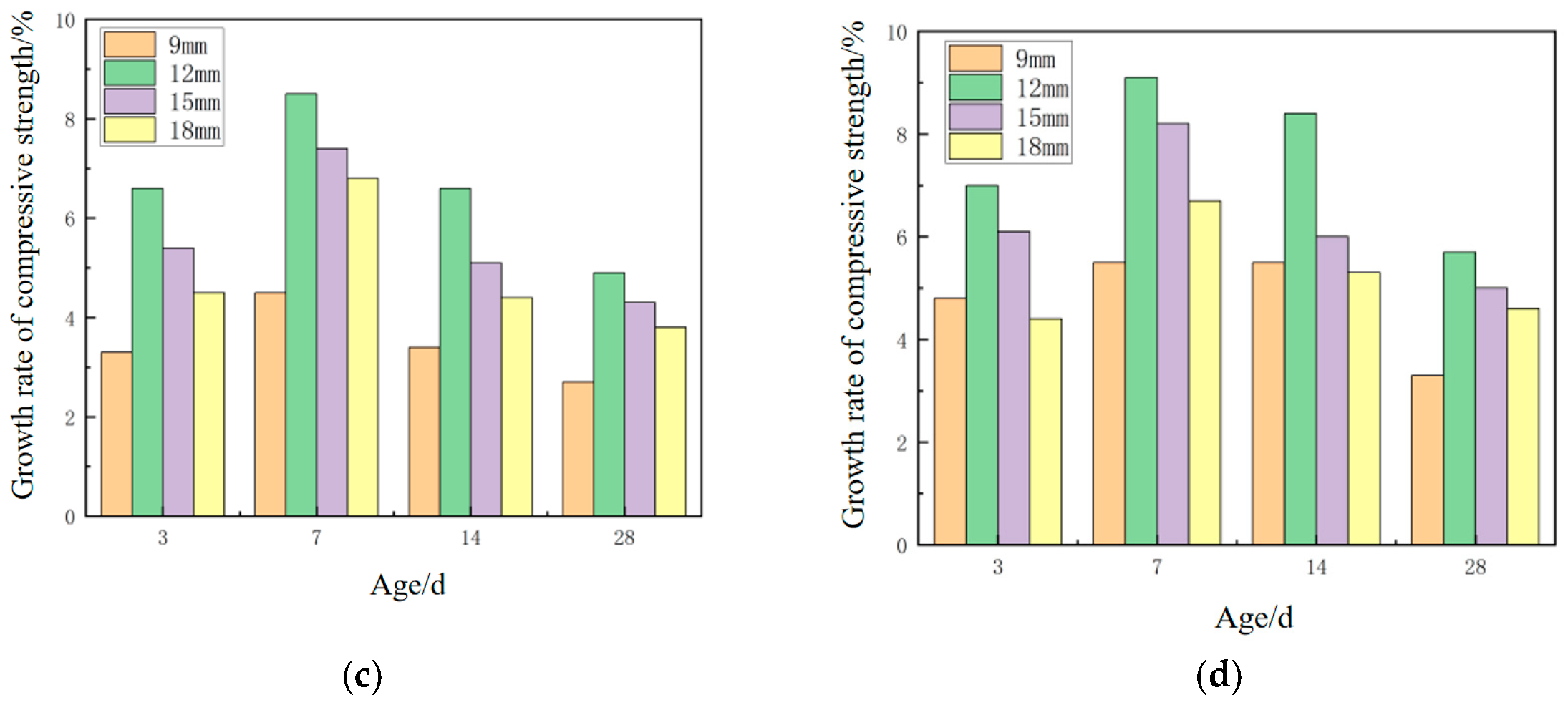
3.2. Mechanical Properties of Geopolymer Mortar Mixed with Fibers
3.2.1. Research on Flexural Strength Test
3.2.2. Research on Compressive Strength Test
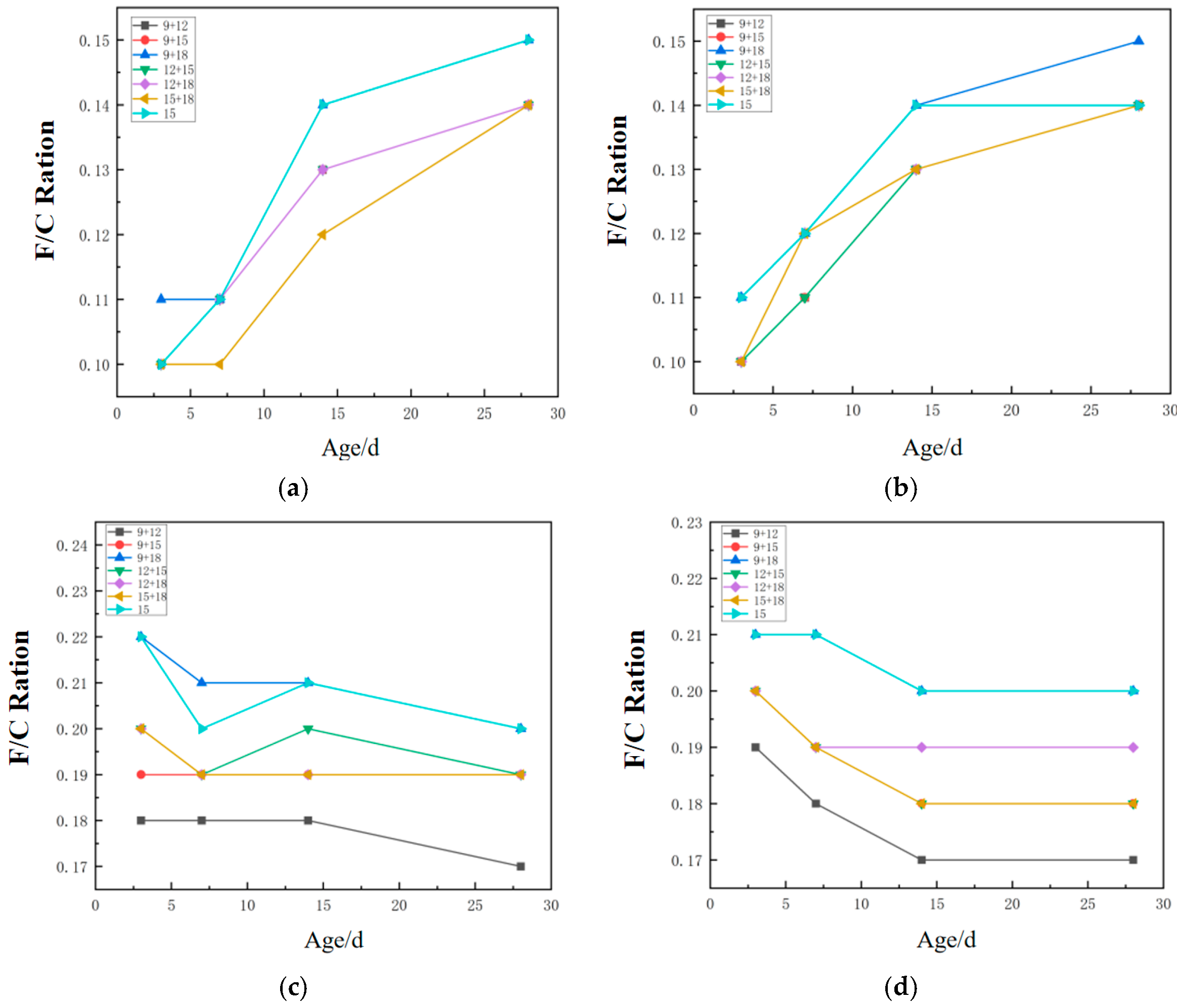
3.2.3. Comparative Analysis of Flexural-to-Compressive Ratio
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymer Mortar
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- By analyzing the strength variation laws of geopolymer mortars with different fiber lengths and mixing methods and combining this with SEM images to investigate the mechanical property mechanism of fiber-reinforced mortars, both approaches have improved the mechanical properties of geopolymer mortars.
- (2)
- When 15 mm fibers are incorporated individually into the geopolymer mortar, the bridging effect provided by the longer fibers significantly enhances flexural strength and toughness, achieving optimal performance in these properties. In contrast, 12 mm fibers exhibit superior dispersion homogeneity during mixing, resulting in minimal disruption to the matrix structure and a relatively minor reduction in workability. This favorable distribution contributes to a more effective enhancement of the matrix’s compressive load-bearing capacity, thereby yielding the highest compressive strength.
- (3)
- When 9 mm and 18 mm fibers are incorporated into the geopolymer mortar, the combined fiber reinforcement effect enhances the mechanical properties, resulting in superior performance compared to geopolymer mortars containing only a single fiber type.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Luo, Y.; Mei, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Gong, H. Mechanical properties of polypropylene fiber reinforced geopolymer-based reef limestone aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 483, 141739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, B.; Chen, W.; Ai, J.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Z. Investigating the influence of fibre type and content on the toughness and ductility of geopolymer mortar with acoustic emission technology. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 147, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Liu, C.; Shumuye, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zang, G. Effect of nano-silica on mechanical properties and microstructure of engineered geopolymer composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 156, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Zhang, M. Fiber-reinforced geopolymer composites: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 107, 103498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xu, J. Study on the Improvement Effect of Polypropylene Fiber on the Mechanical Properties and Freeze–Thaw Degradation Performance of High Fly Ash Content Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Slag Concrete. Polymers 2025, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Feng, Z.; Guo, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, P. Mechanical behavior and microscopic damage mechanism of hybrid fiber-reinforced geopolymer concrete at elevated temperature. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt B, 53851–53866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akid, A.; Hossain, S.; Munshi, M.; Elahi, M.; Sobuz, R.; Tam, V.; Islam, M. Assessing the influence of fly ash and polypropylene fiber on fresh, mechanical and durability properties of concrete. J. King Saud Univ.—Eng. Sci. 2023, 35, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Deng, J.; Hu, R.; Chen, M. Effect of Different Fibers on Shrinkage Properties and Bonding Properties of Geopolymer Mortar Repair Materials and Analysis of the Mechanism. Coatings 2023, 13, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Tao, J.; Shi, K. A review on interfacial bonding behavior between fiber and concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 105, 112455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, H.; Cornejo, M.; Espinoza, A.; García, E.; Ulloa, N. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of compressive strength of polypropylene fiber reinforced geopolymer mortars. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Kong, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, Z. Experimental investigation on the mechanical properties and microstructure of hybrid fiber reinforced recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 120488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tu, H.; Li, Y.; Weng, Y. Effect of fiber content and fiber length on the dynamic compressive properties of strain-hardening ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harle, S. Durability and long-term performance of fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composites: A review. Structures 2024, 60, 105881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Dan, H.; Tan, J.; Li, M.; Li, S. Optimization Design of MK-GGBS Based Geopolymer Repairing Mortar Based on Response Surface Methodology. Materials 2023, 16, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Tomsia, A.; Jiang, L.; Tang, B.; Cheng, Q. Stiff and tough PDMS-MMT layered nanocomposites visualized by AIE luminogens. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagopal, V.; Panicker, A.; Arathy, A.; Sandeep, S.; Pillai, S. Influence of fibers on the mechanical properties of cementitious composites—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, G.; Gupta, M.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Microstructures, mechanical properties and deformation mechanism of heterogeneous metal materials: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2026, 248, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, C.; Yoo, D.; Pan, R.; He, J.; Ke, L. Flexural and cracking behaviors of reinforced UHPC beams with various reinforcement ratios and fiber contents. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydrych, M.; Hýsek, Š.; Fridrichová, L.; Le Van, S.; Herclík, M.; Pechočiaková, M.; Le Chi, H.; Louda, P. Impact of Flax and Basalt Fibre Reinforcement on Selected Properties of Geopolymer Composites. Sustainability 2020, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zha, Q.; Li, S.; Cai, G.; Wu, D.; Zhai, C. Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Modified Clay. Molecules 2022, 27, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Kollo, L.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Prashanth, K. Selective laser melting of Cu–Ni–Sn: A comprehensive study on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and deformation behavior. Int. J. Plast. 2021, 138, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterweger, C.; Mayrhofer, T.; Piana, F.; Duchoslav, J.; Stifter, D.; Poitzsch, C.; Fürst, C. Impact of fiber length and fiber content on the mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of short carbon fiber reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, E.A.; Roether, J.A.; Schubert, D.W.; Redda, D.T.; Boccaccini, A.R. Hemp Fiber Reinforced Red Mud/Fly Ash Geopolymer Composite Materials: Effect of Fiber Content on Mechanical Strength. Materials 2021, 14, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Impact of Nano-CaCO3 and PVA Fiber on Properties of Fresh and Hardened Geopolymer Mortar. Buildings 2023, 13, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Cao, H.; Zhou, R. Study on the Reinforced Properties of Geopolymer Fibers with a Sustainable Development Role. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Fu, Q.; Yan, L.; Kasal, B. Characterization of interfacial properties between fibre and polymer matrix in composite materials—A critical review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 1441–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyaaldin, M.H.; Mosaberpanah, M.A.; Alzeebaree, R. Performance of Fiber-Reinforced Alkali-Activated Mortar with/without Nano Silica and Nano Alumina. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Tang, W.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Gao, P.; Zhan, B.; Yu, Q. Effect of short fibers on non-uniform strain distribution of geopolymer mortar under dry conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 459, 139768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Min, W.-L.; Chen, J.-J.; Wu, R.-J.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Xia, J. Performance characteristics of micro fiber-reinforced ambient cured one-part geopolymer mortar for repairing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 415, 135086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Peng, R.; Peng, X. Study on the Mechanical Properties of Fiber Reinforced Concrete Composite to Cryogenic Temperatures. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 17109–17132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, P.K.; Ilango, T.; Chezhiyan, S. A detailed study on the mechanical and durability properties of hybrid fibre reinforced concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21 Pt 1, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraş, M.M. Mechanical and fracture behavior of geopolymer composites reinforced with fibers by using nano-TiO2. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosuk, P.; Suksiripattanapong, C.; Hiroki, G.; Phoo-Ngernkham, T.; Thumrongvut, J.; Sukontasukkul, P.; Chindaprasirt, P. Performance of polypropylene fiber-reinforced cellular lightweight fly ash geopolymer mortar under wet and dry cycles. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17671–2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
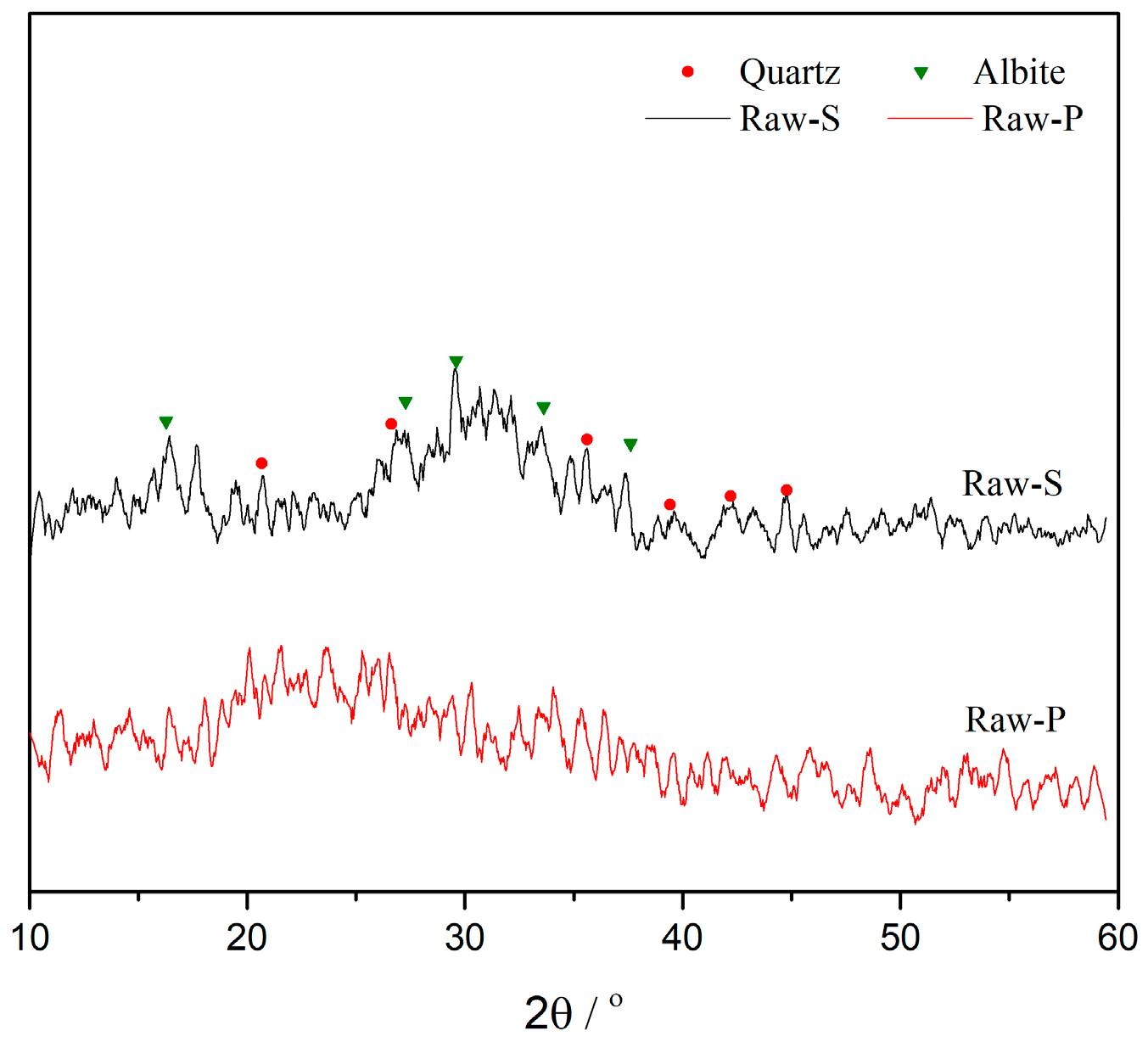

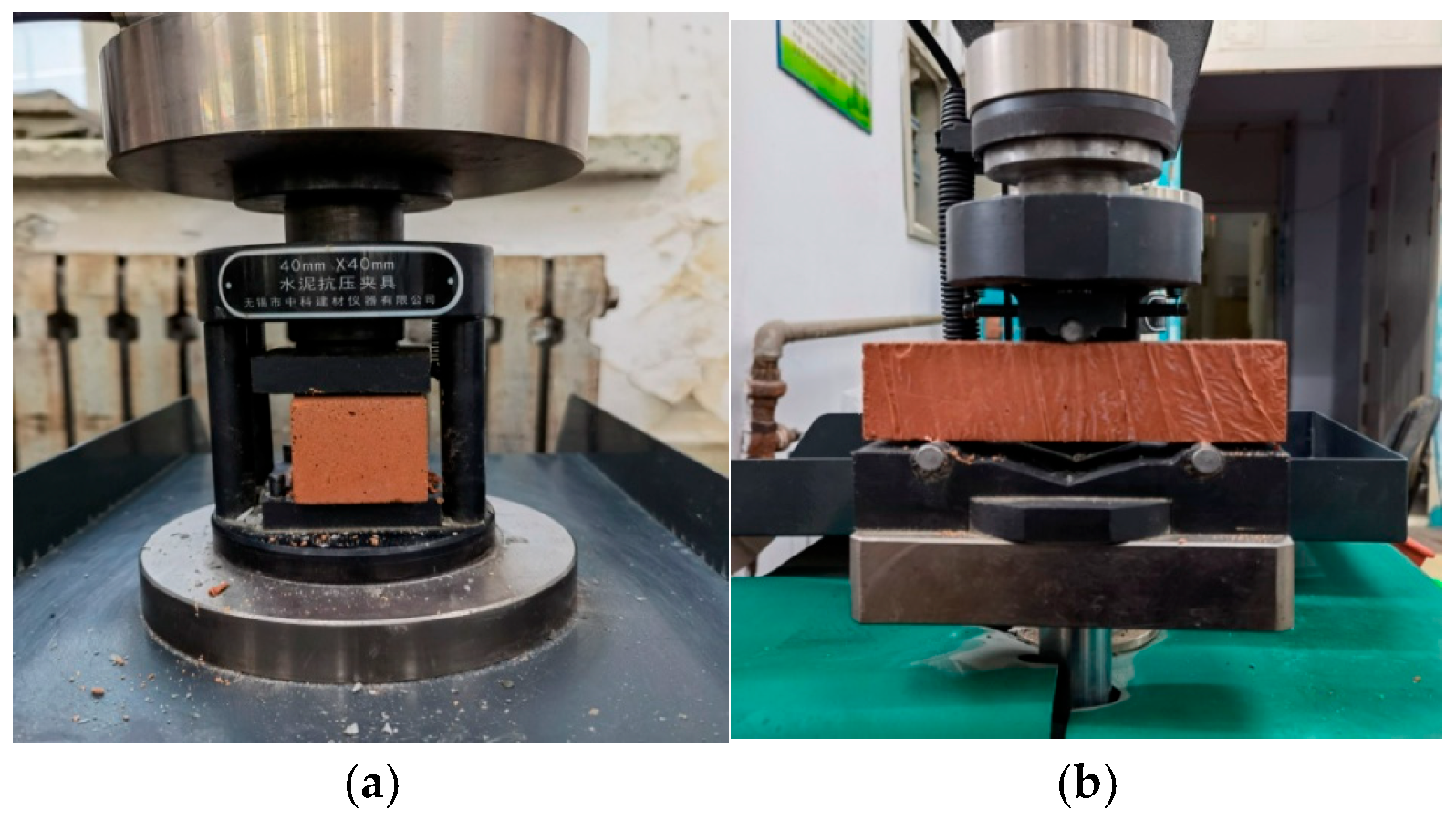






| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | TiO2 | CaO | Na2O | MgO | LoI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| content | 50.14 | 41.11 | 0.76 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 6.91 |
| Chemical Composition | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | SO3 | TiO2 | MnO | Fe2O3 | K2O | Na2O | SrO | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| content | 35.99 | 34.11 | 15.36 | 6.58 | 2.5 | 2.41 | 1.07 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.4 | 0.13 | - |
| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | MgO | SO3 | Na2O | P2O5 | SrO | LoI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| content (%) | 62.04 | 25.5 | 4.28 | 3.96 | 1.33 | 1.27 | 0.73 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.12 | - |
| Technical Parameters | Bulk Density (kg/m3) | Apparent Density (kg/m3) | Porosity (%) | Fineness Modulus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard sand | 1610 | 2570 | 37.4 | 2.4 |
| Technical Parameters | Na2O Content (%) | SiO2 Content (%) | Modulus | Density (kg/m3) | Brix Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured value | 8.5 | 26.5 | 3.1 | 1480 | 40 |
| Serial Number | Number | Na2SiO3 | NaOH | Silicoaluminate Materials | Water | Fiber/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metakaolin | Fly Ash | Slag | ||||||
| 1 | P100F0S0M1.4N16 | 221 | 31.6 | 269.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | — |
| 2 | 0.7 | |||||||
| 3 | P60F40S0M1.2N12 | 156.3 | 28.9 | 178.8 | 119.2 | 0 | 40.8 | — |
| 4 | 0.7 | |||||||
| 5 | P60F0S40M1.2N14 | 153.4 | 27.9 | 172.8 | 0 | 115.2 | 39.4 | — |
| 6 | 0.7 | |||||||
| 7 | P60F20S20M1.2N12 | 156.3 | 28.9 | 178.8 | 59.6 | 59.6 | 40.8 | — |
| 8 | 0.7 | |||||||
| Serial Number | Number | Fiber Length (mm) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 14 d | 28 d | |||
| 1 | P100F0S0M1.4N16 | —— | 1.8 | 3.6 | 5.3 | 6.0 |
| 2 | 9 | 1.9 | 3.9 | 6.0 | 6.5 | |
| 3 | 12 | 1.9 | 4.1 | 6.2 | 6.8 | |
| 4 | 15 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 6.5 | 7.0 | |
| 5 | 18 | 1.9 | 4.0 | 6.3 | 6.8 | |
| 6 | P60F40S0M1.2N12 | —— | 1.5 | 2.9 | 5.2 | 6.3 |
| 7 | 9 | 1.6 | 3.1 | 5.6 | 6.8 | |
| 8 | 12 | 1.7 | 3.3 | 6.1 | 7.1 | |
| 9 | 15 | 1.8 | 3.5 | 6.3 | 7.3 | |
| 10 | 18 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 6.0 | 7.1 | |
| 11 | P60F0S40M1.2N14 | —— | 4.5 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 7.7 |
| 12 | 9 | 4.8 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 8.2 | |
| 13 | P60F0S40M1.2N14 | 12 | 5.3 | 7.4 | 8.5 | 8.9 |
| 14 | 15 | 5.5 | 7.6 | 8.8 | 9.2 | |
| 15 | 18 | 5.1 | 7.3 | 8.4 | 8.8 | |
| 16 | P60F20S20M1.2N12 | —— | 4.3 | 6.0 | 7.2 | 8.0 |
| 17 | 9 | 4.5 | 6.8 | 8.2 | 8.6 | |
| 18 | 12 | 4.9 | 7.2 | 8.7 | 9.3 | |
| 19 | 15 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 8.9 | 9.7 | |
| 20 | 18 | 5.0 | 7.3 | 8.7 | 9.4 | |
| Serial Number | Number | Fiber Length (mm) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 14 d | 28 d | |||
| 1 | P100F0S0M1.4N16 | — | 18.5 | 35.8 | 42.6 | 45.0 |
| 2 | 9 | 18.7 | 36.5 | 43.8 | 45.8 | |
| 3 | 12 | 20.3 | 39.5 | 47.3 | 49.5 | |
| 4 | 15 | 19.8 | 38.8 | 45.4 | 47.3 | |
| 5 | 18 | 19.5 | 38.0 | 45.2 | 47.3 | |
| 6 | P60F40S0M1.2N12 | — | 15.2 | 26.5 | 41.7 | 45.8 |
| 7 | 9 | 15.8 | 27.9 | 45.0 | 49.5 | |
| 8 | 12 | 16.5 | 29.5 | 47.0 | 51.9 | |
| 9 | 15 | 16.2 | 29.0 | 46.5 | 51.5 | |
| 10 | 18 | 16.0 | 28.9 | 46.5 | 51.1 | |
| 11 | P60F0S40M1.2N14 | — | 24.2 | 35.2 | 40.8 | 44.6 |
| 12 | 9 | 25.0 | 36.8 | 42.2 | 45.8 | |
| 13 | 12 | 25.8 | 38.2 | 43.5 | 46.8 | |
| 14 | 15 | 25.5 | 37.8 | 42.9 | 46.5 | |
| 15 | 18 | 25.3 | 37.6 | 42.6 | 46.3 | |
| 16 | P60F20S20M1.2N12 | — | 22.8 | 32.8 | 41.5 | 46.0 |
| 17 | 9 | 23.9 | 34.6 | 43.8 | 47.5 | |
| 18 | 12 | 24.4 | 35.8 | 45.0 | 48.6 | |
| 19 | 15 | 24.2 | 35.5 | 44.0 | 48.3 | |
| 20 | 18 | 23.8 | 35.0 | 43.7 | 48.1 | |
| Serial Number | Number | Mixing Type (mm) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 14 d | 28 d | |||
| 1 | P100F0S0M1.4N16 | — | 1.8 | 3.6 | 5.3 | 6.0 |
| 2 | 9 + 12 | 1.9 | 3.9 | 5.7 | 6.5 | |
| 3 | 9 + 15 | 2.0 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 6.8 | |
| 4 | 9 + 18 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 6.8 | 7.3 | |
| 5 | 12 + 15 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 6.1 | 6.6 | |
| 6 | 12 + 18 | 2.0 | 4.1 | 6.2 | 6.9 | |
| 7 | 15 + 18 | 1.9 | 3.8 | 5.9 | 6.7 | |
| 8 | P60F40S0M1.2N12 | — | 1.5 | 2.9 | 5.2 | 6.3 |
| 9 | 9 + 12 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 5.5 | 6.6 | |
| 10 | 9 + 15 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 5.9 | 7.0 | |
| 11 | 9 + 18 | 1.9 | 3.7 | 6.8 | 7.8 | |
| 12 | 12 + 15 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 6.0 | 7.1 | |
| 13 | 12 + 18 | 1.7 | 3.5 | 6.3 | 7.3 | |
| 14 | 15 + 18 | 1.7 | 3.4 | 6.2 | 7.2 | |
| 15 | P60F0S40M1.2N14 | — | 4.5 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 7.7 |
| 16 | 9 + 12 | 4.7 | 6.7 | 7.8 | 8.0 | |
| 17 | 9 + 15 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 8.5 | 8.7 | |
| 18 | 9 + 18 | 5.9 | 8.3 | 9.5 | 9.6 | |
| 19 | 12 + 15 | 5.2 | 7.2 | 8.4 | 8.7 | |
| 20 | 12 + 18 | 5.4 | 7.6 | 8.8 | 9.0 | |
| 21 | 15 + 18 | 5.3 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 9.0 | |
| 22 | P60F20S20M1.2N12 | — | 4.3 | 6.0 | 7.2 | 8.0 |
| 23 | 9 + 12 | 4.4 | 6.3 | 7.5 | 8.3 | |
| 24 | 9 + 15 | 5.1 | 7.2 | 8.4 | 9.2 | |
| 25 | 9 + 18 | 5.8 | 8.3 | 9.6 | 10.3 | |
| 26 | 12 + 15 | 4.8 | 6.8 | 8.0 | 8.8 | |
| 27 | 12 + 18 | 5.3 | 7.5 | 8.8 | 9.6 | |
| 28 | 15 + 18 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 8.6 | 9.4 | |
| Serial Number | Number | Mixing Type (mm) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 14 d | 28 d | |||
| 1 | P100F0S0M1.4N16 | — | 18.5 | 35.8 | 42.6 | 45.0 |
| 2 | 9 + 12 | 18.7 | 36.5 | 44.5 | 46.5 | |
| 3 | 9 + 15 | 19.5 | 38.6 | 46.8 | 48.5 | |
| 4 | 9 + 18 | 20.5 | 39.9 | 48.5 | 50.2 | |
| 5 | 12 + 15 | 19.5 | 38.0 | 45.5 | 47.6 | |
| 6 | 12 + 18 | 20.0 | 38.8 | 48.0 | 48.3 | |
| 7 | 15 + 18 | 19.6 | 38.5 | 47.3 | 48.5 | |
| 8 | P60F40S0M1.2N12 | — | 15.2 | 26.5 | 41.7 | 45.8 |
| 9 | 9 + 12 | 15.5 | 27.5 | 43.8 | 47.3 | |
| 10 | 9 + 15 | 16.0 | 28.8 | 45.9 | 49.0 | |
| 11 | 9 + 18 | 16.8 | 29.8 | 48.0 | 52.0 | |
| 12 | 12 + 15 | 16.0 | 28.3 | 46.5 | 50.1 | |
| 13 | 12 + 18 | 16.5 | 29.3 | 47.1 | 50.8 | |
| 14 | 15 + 18 | 16.3 | 29.1 | 46.3 | 50.4 | |
| 15 | P60F0S40M1.2N14 | — | 24.2 | 35.2 | 40.8 | 44.6 |
| 16 | 9 + 12 | 25.7 | 37.5 | 42.4 | 46.0 | |
| 17 | 9 + 15 | 26.7 | 39.3 | 44.5 | 46.8 | |
| 18 | 9 + 18 | 27.3 | 40.2 | 46.1 | 48.2 | |
| 19 | 12 + 15 | 25.8 | 38.5 | 43.0 | 46.5 | |
| 20 | 12 + 18 | 27.3 | 39.8 | 45.3 | 47.3 | |
| 21 | 15 + 18 | 27.1 | 39.5 | 45.0 | 47.0 | |
| 22 | P60F20S20M1.2N12 | — | 22.8 | 32.8 | 41.5 | 46.0 |
| 23 | 9 + 12 | 23.7 | 35.0 | 43.8 | 48.2 | |
| 24 | 9 + 15 | 26.1 | 37.9 | 47.0 | 50.9 | |
| 25 | 9 + 18 | 26.8 | 39.5 | 47.6 | 51.6 | |
| 26 | 12 + 15 | 24.6 | 35.9 | 45.0 | 49.3 | |
| 27 | 12 + 18 | 26.5 | 38.9 | 47.3 | 51.3 | |
| 28 | 15 + 18 | 26.2 | 38.5 | 47.0 | 51.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, C.; Song, Z. Research on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Fiber Geopolymer Mortar. Coatings 2025, 15, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111239
Xing Z, Li Z, Wang P, Li C, Song Z. Research on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Fiber Geopolymer Mortar. Coatings. 2025; 15(11):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111239
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Zhiqiang, Zekang Li, Peng Wang, Chao Li, and Zeming Song. 2025. "Research on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Fiber Geopolymer Mortar" Coatings 15, no. 11: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111239
APA StyleXing, Z., Li, Z., Wang, P., Li, C., & Song, Z. (2025). Research on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Fiber Geopolymer Mortar. Coatings, 15(11), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111239





