An Overview of Metallic Abradable Coatings in Gas Turbine Engines
Abstract
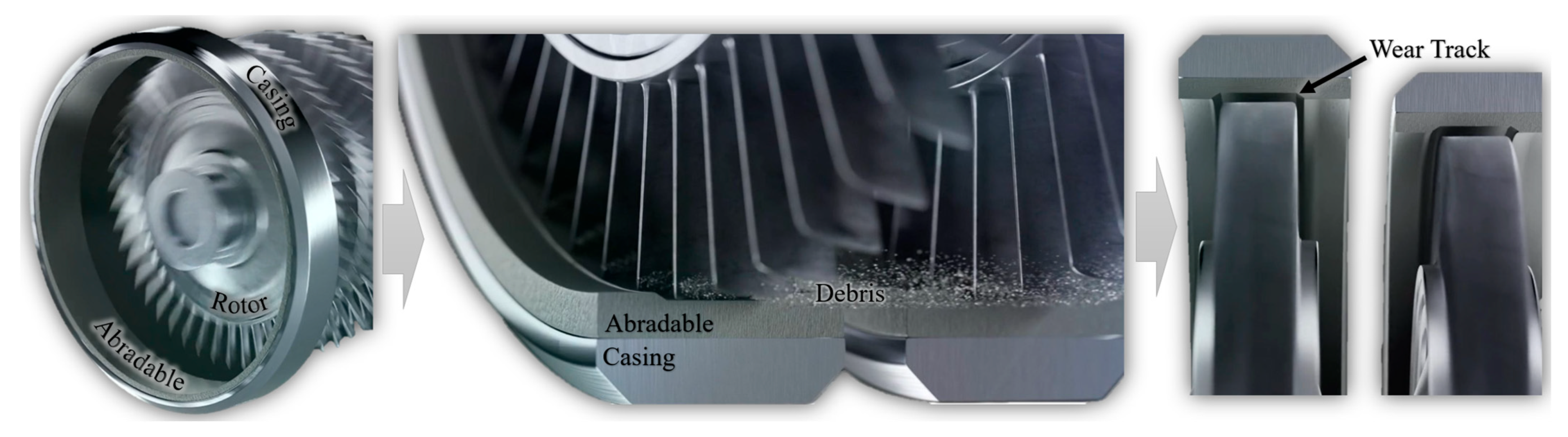
1. Introduction
2. Abradable Materials
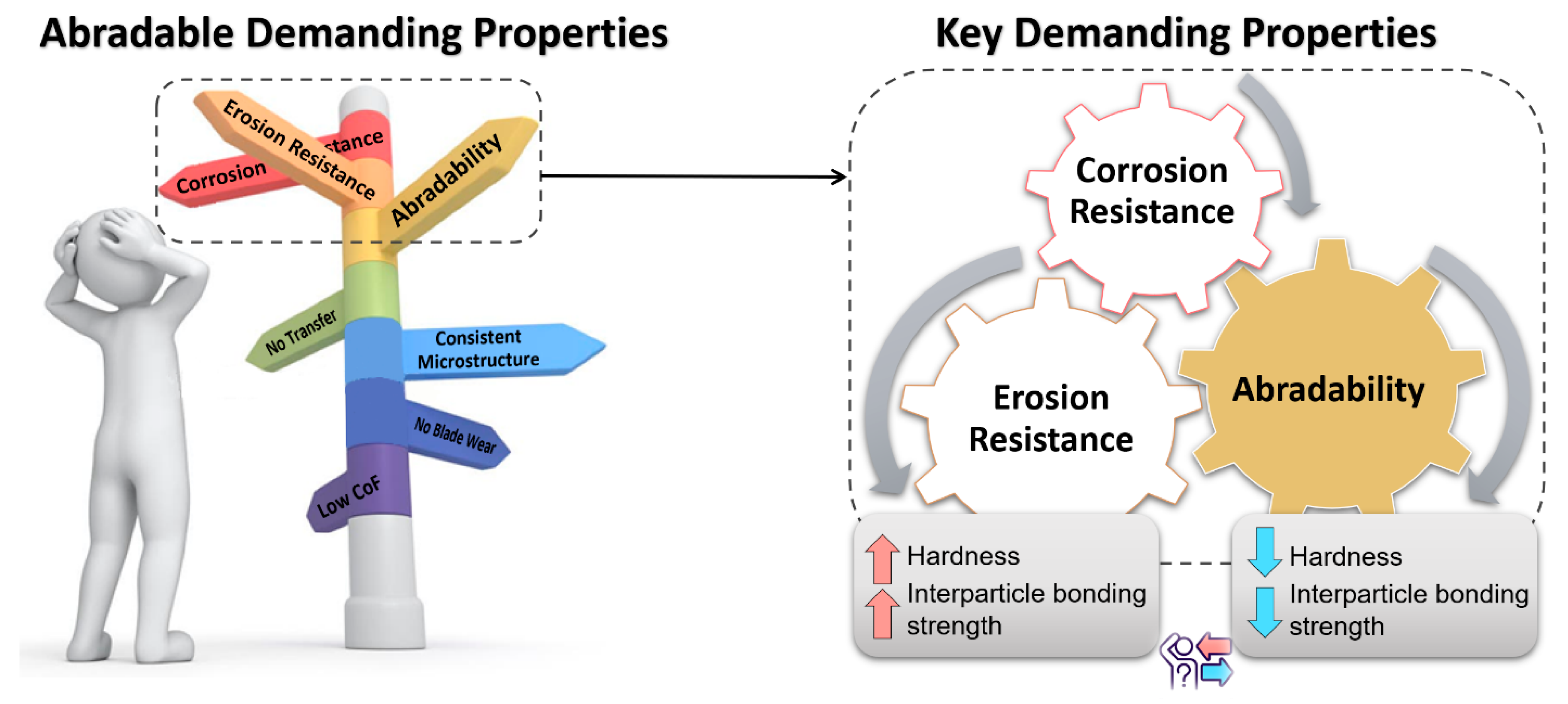
- Be readily abradable but mechanically stable;
- Exhibit corrosion and oxidation resistance;
- Have a low coefficient of friction;
- Resist erosion from gas flows and solid particles;
- Present a consistent microstructure;
- Minimize wear of blade tips or knife edges;
- Avoid material transfer between the blade and the abradable;
- Disintegrate into fine particles, large debris can potentially damage the engine;
- The rubbing process should break the bond between particles rather than melting them;
- Maintain a smooth post-wear surface to reduce aerodynamic losses.
2.1. Classification
2.1.1. Polymer Materials
2.1.2. Ceramic Materials
2.1.3. Metallic Materials
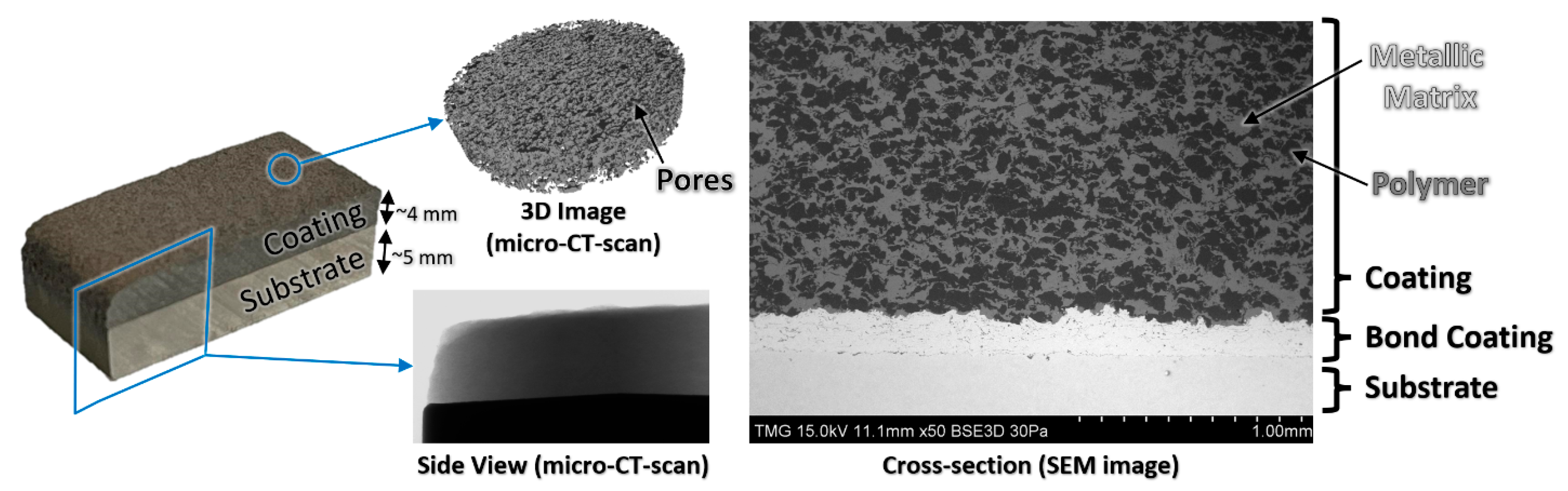
2.2. Manufacturing Process
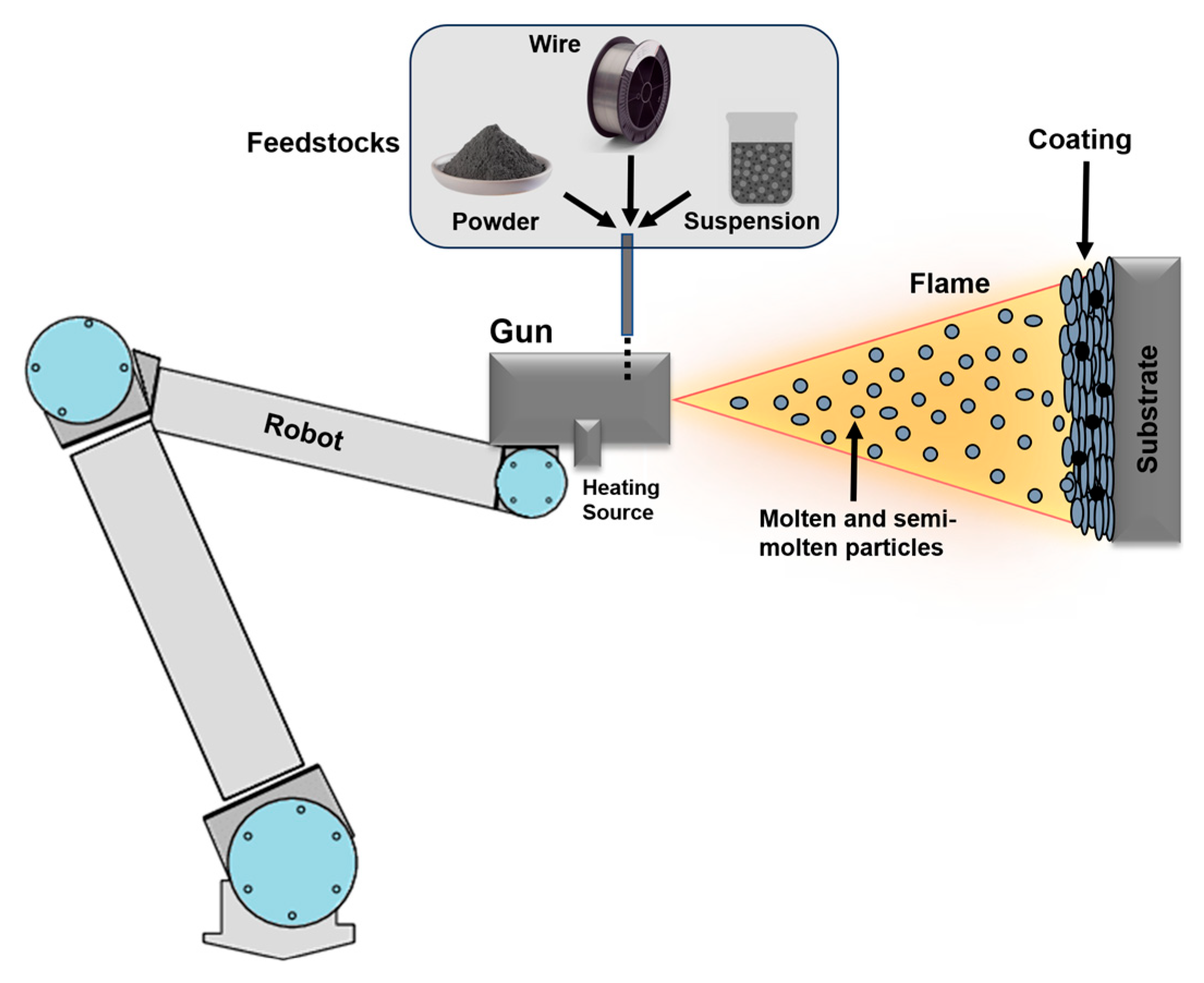
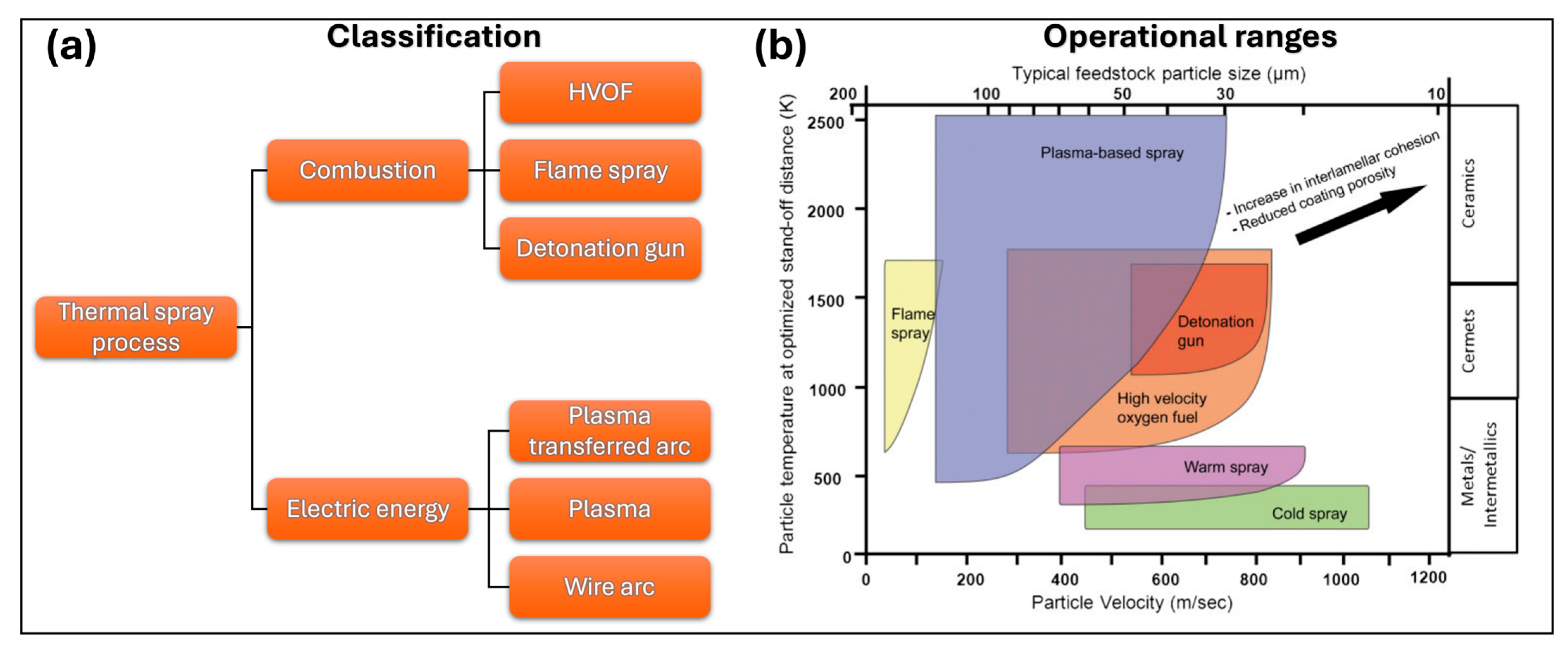
3. Thermal Spray Deposition Process
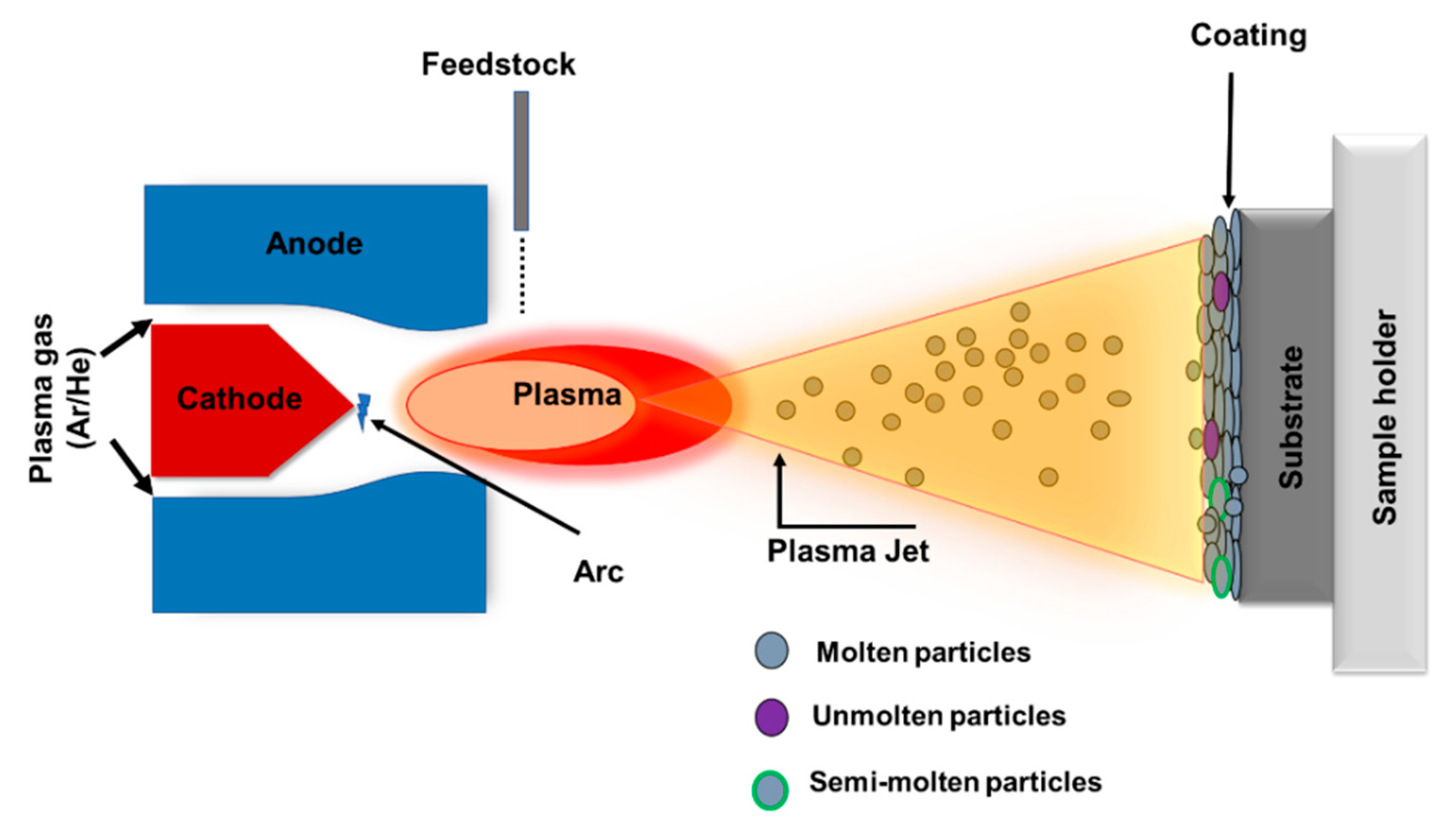
3.1. Atmospheric Plasma Spray (APS)
4. Metallic-Based Abradable Coatings
4.1. Coatings Requirements
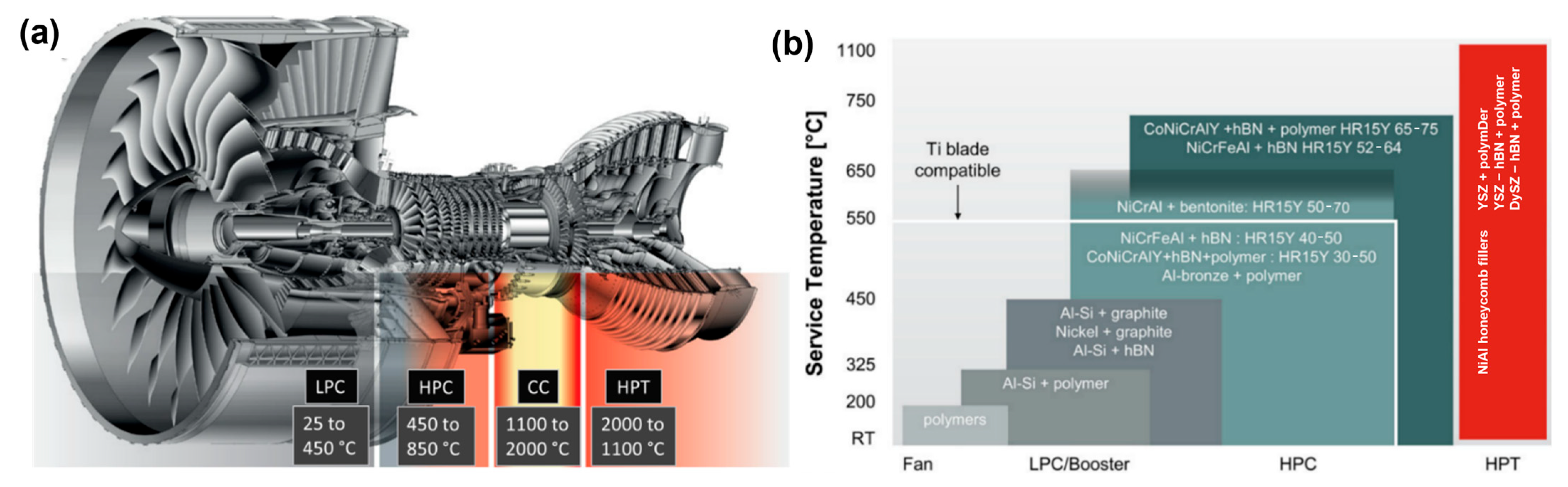
4.2. Temperature-Based Categorization of Metallic Abradable Coatings
5. Abradability Evaluation
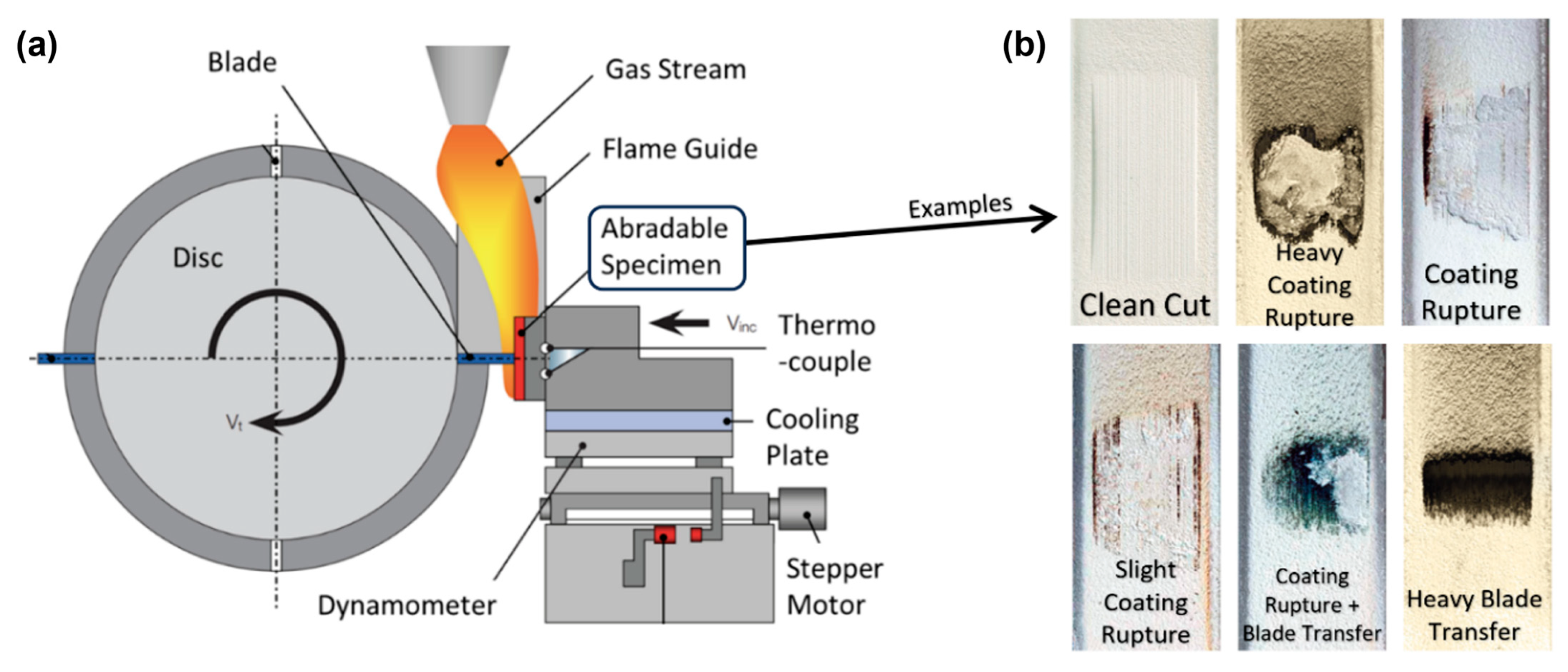
5.1. Conventional Tribological Tests and Limitations
5.2. High-Speed Abradable Test Rigs
6. Conclusions
- The abradability of metallic coatings is critically influenced by the optimization of coating composition, engineered microstructure, and thermal stability, which must be tailored to specific operational temperature regimes.
- Distinct metallic matrix systems, including AlSi, Ni, Co, and Cu-based alloys, demonstrate performance advantages that are strongly dependent on their operational temperature and intended abradability characteristics.
- High-speed abradable test rigs provide a controlled and instrumented environment for reproducing engine-representative blade–coating interactions, enabling the quantitative assessment of reaction forces, wear mechanisms, and coating degradation.
- The integration of materials science principles, tribological insights, and advanced experimental methodologies constitutes a robust framework for the development, validation, and optimization of next-generation abradable coatings.
- The design and implementation of multi-layer or functionally graded abradable coatings to extend operational performance across wider temperature ranges.
- The application of computational modeling and machine learning approaches to enable predictive material design and process optimization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorfman, M.R.; Dwivedi, G.; Dambra, C.; Wilson, S. Perspective: Challenges in the Aerospace Marketplace and Growth Opportunities for Thermal Spray. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, U.; Olmes, S.; Simeon, A. Sealing Technology: Rub Test Rig for Abrasive/Abradable Systems. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–17 May 2007; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cao, X.; Chen, W.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Dong, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, M. A comprehensive review of thermally sprayed abradable sealing coatings: Focusing on abradability. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasripoor, F.; Schmid, R.K.; Dorfman, M.R.; Russo, L. A Review of Clearance Control Wear Mechanisms for Low Temperature Aluminium Silicon Alloys. In Proceedings of the ITSC 1998, Nice, France, 25–29 May 1998; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiarowski, M.W.; Leo, R.; Scholten, C.; Blake, J. Steam Turbine Modernization Solutions Provide a Wide Spectrum of Options to Improve Performance; Siemens Power Generation: Munich, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Borel, M.O.; Nicoll, A.R.; Schläpfer, H.W.; Schmid, R.K. The wear mechanisms occurring in abradable seals of gas turbines. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1989, 39–40, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounazef, M.; Guessasma, S.; Ait Saadi, B. The wear, deterioration and transformation phenomena of abradable coating BN–SiAl–bounding organic element, caused by the friction between the blades and the turbine casing. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 3375–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwicke, C.U.; Lau, Y.-C. Advances in Thermal Spray Coatings for Gas Turbines and Energy Generation: A Review. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMasi-Marcin, J.T.; Gupta, D.K. Protective coatings in the gas turbine engine. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1994, 68–69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.; Mudasar, M.; Kashif, A. Criteria for Abradable Coatings to Enhance the Performance of Gas Turbine Engines. J. Mate Sci. Metall. 2021, 2, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Irissou, E.; Dadouche, A.; Lima, R.S. Tribological Characterization of Plasma-Sprayed CoNiCrAlY-BN Abradable Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2014, 23, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, N.; Watson, M.; Marshall, M. The influence of material properties on the wear of abradable materials. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, K.; Arendarchuck, B.E.; Rivadeneira, F.R.E.; de Castilho, B.C.N.M.; Moreau, C.; Stoyanov, P. Design and Development of Cost-Effective Equipment for Tribological Evaluation of Thermally Sprayed Abradable Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2024, 34, 852–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metco, O. Rapid Validation of Turbomachinery Abradable Systems Using Oerlikon Metco’s Rub-Test Facility. In SF-0029.0—Abradable Testing; Oerlikon: Zürich, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimov, E.; Watson, M.; Hadjisoteriou, A.; Marshall, M. Investigation of wear mechanisms in AlSi-polyester abradable—Ti(6Al4V) blade contacts using stroboscopic imaging. Wear 2022, 494–495, 204207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Liu, T.; Cheng, X.; Shen, J.; Li, C. The Influence of Composition and Microstructure on the Abradability of Aluminum-Based Abradable Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2017, 26, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metco, O. Thermally sprayed abradable coating technology for sealing in gas turbines. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference “The Future of Gas Turbine Technology”, Brussels, Belgium, 17–18 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Shen, J.; Yu, Y.G.; Ren, X.J.; Xuan, H.J.; Liu, T. Progress on Facilities and Methodology to Evaluate Abradable Seal Coatings. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 690–693, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoul, B.; Batailly, A.; Legrand, M.; Stainier, L.; Cartraud, P. Abradable Coating Removal in Turbomachines: A Macroscopic Approach Accounting for Several Wear Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition. Volume 7B: Structures and Dynamics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–19 June 2015; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. V07BT32A012. [Google Scholar]
- Chupp, R.E.; Ghasripoor, F.; Turnquist, N.A.; Demiroglu, M.; Aksit, M.F. Advanced Seals for Industrial Turbine Applications: Dynamic Seal Development. J. Propuls. Power 2002, 18, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, R.E.; Hendricks, R.C.; Lattime, S.B.; Steinetz, B.M.; Aksit, M.F. Turbomachinery Clearance Control; Glenn Research Center: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2007. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20070005016 (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- FELTMETALTM Abradable Seals—Technetics. Available online: https://technetics.com/resources/video-library/?wchannelid=6dz3bth5yd&wmediaid=g08vko9zm3 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Dadouche, A.; Conlon, M.J.; Dmochowski, W.; Liko, B.; Bedard, J.-P. Experimental Evaluation of Abradable Seal Performance at High Temperature. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2008: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. Volume 5: Structures and Dynamics, Parts A and B, Berlin, Germany, 9–13 June 2008; ASMEDC: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrinzi, E.; Giovannetti, I.; Sheng, N.; Leblanc, L. Development of New Abradable/Abrasive Sealing Systems for Clearance Control in Gas Turbines. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 Turbine Blade Tip Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 30 September–3 October 2013; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. V001T05A004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, A.; Saxena, K.K.; Rajak, D.K.; Sehgal, S. Multi-Scale and Multifunctional Coatings and Interfaces for Tribological Contacts, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; ISBN 978-1-03-263534-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.S.; Marple, B.R.; Dadouche, A.; Dmochowski, W.; Liko, B. Nanostructured Abradable Coatings for High Temperature Applications. In Proceedings of the ITSC2006, Seattle, WA, USA, 15–18 May 2006; pp. 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madabadi, N. Development of Polymeric Abradable Coatings for Aero Engine Applications. Master’s Thesis, Concordia University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sporer, D.; Wilson, S.; Giovannetti, I.; Refke, A.; Giannozzi, M. On The Potential of Metal and Ceramic Based Abradables in Turbine Seal Applications. In Proceedings of the 36th Turbomachinery Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 11–13 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Zou, Y.; Yu, S.; Xie, E.; Zhao, Q.; Ye, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Ceramic-based abradable sealing coatings for advanced aeroengines: Materials design, structural strategies, and multifunctional performance. Extreme Mater. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flitney, R. Seals and Sealing Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 105–288. ISBN 978-0-08-099416-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S. Abradable Thermal Spray Applications and Technology. In Thermal Spray Technology; ASM Handbook; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.-Q.; Shi, Q.-S.; Liu, M.-J.; Li, G.-R.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, G.-J. Lightweight epoxy-based abradable seal coating with high bonding strength. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 69, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.-Q.; Li, W.; Shi, Q.-S.; Chen, L.; Yang, G.-J. Self-lubricating epoxy-based composite abradable seal coating eliminating adhesive transfer via hierarchical design. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorban, M.; Stoyanov, P.; Lima, R.S. A Comprehensive Review of High-Temperature Ceramic Abradable Coatings Used in Aero and Industrial Gas Turbines. In Proceedings of the ITSC 2025, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5–8 May 2025; pp. 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, K.; Rivadeneira, F.R.E.; Nair, R.B.; Barnett, B.; Moreau, C.; Stoyanov, P. Influence of hBN on the abradable performance of AlSi-based coatings: Bridging the gap between tribological assessment and abradability testing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 489, 131060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillieu, A.; Rahimov, E.; Marshall, M. The role of thermal properties in the wear mechanisms of an AlSi-polyester abradable. Wear 2025, 562–563, 205618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, R.; Pellegrino, A.; Bennett, C.; Rouse, J.; Agyakwa, P.; Zumpano, G. Influence of Temperature, Strain Rate, and Condition on the Mechanical Response of an AlSi-PES Abradable. Exp. Mech. 2025, 65, 1259–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R. Gas turbine coatings—An overview. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2012, 26, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawley, J.D. Overview of Zirconia with Respect to Gas Turbine Applications. 1 March 1984. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19840013672 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Li, C.; Chai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Du, F.; Yan, W.; Yan, G.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y. Effect of calcium carbonate on the thermal shock behavior of YSZ-based abradable sealing coatings. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 8408–8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gao, S.; Xue, W.; Wu, B.; Zhang, J.; Duan, D. High-Speed Rubbing Behavior Between Nickel-Based Superalloy Blades and Ceramic-Based Abradable Coatings. Tribol. Lett. 2023, 71, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.K.; Ghasripoor, F.; Dorfman, M.; Wei, X. An Overview of Compressor Abradables. In Proceedings of the 1st International Thermal Spray Conference, ITSC 2020, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–11 May 2000; pp. 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendarchuck, B.E.; Bertuol, K.; Rivadeneira, F.; de Castilho, B.C.N.M.; Barnett, B.; Moreau, C.; Stoyanov, P. Tribological evaluation of Cu-based abradable coating. Wear 2025, 570, 206034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, A.; Fathi, B.; Elkoun, S.; Rodrigue, D.; Soldera, A. Impact of compression molding conditions on the thermal and mechanical properties of polyethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.E.; Evans, W.J. Freestanding abradable coating manufacture and tensile test development. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Lugscheider, E.; Zwick, J.; Ernst, F.; Sporer, D.; Hopkins, N.; Hertter, M.; Matejicek, J. Microstructure and Properties of New Abradable Seal Coatings for Compressor Applications. In Proceedings of the ITSC2006, Seattle, WA, USA, 15–18 May 2006; pp. 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvette, J.; Hia, I.L.; Pierre, J.; Chenier, G.; Farahani, R.D.; Piccirelli, N.; Therriault, D. Non-Planar Multiprocess Additive Manufacturing of Multifunctional Composites. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, G.; Cui, X.; Xu, Y. Yttrium-Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics Fabrication through Material Extrusion 3D Printing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 7584–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Ou, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, Z.; Zheng, P.; Guo, X. Microstructure and Properties of Hot Pressing Sintered SiC/Y3Al5O12 Composite Ceramics for Dry Gas Seals. Materials 2024, 17, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padture, N.P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawłowski, L. The Science and Engineering of Thermal Spray Coatings, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-471-49049-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bertuol, K.; Ribas, M.T.; Mayer, A.R.; Pukasiewicz, A.G.M.; Siqueira, I.B.a.F.; Chicoski, A.; de Souza, M.J. Study of HVOF Parameter Influence on Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Cr3C2-25NiCr Coatings. In Proceedings of the ITSC2019, Yokohama, Japan, 26–29 May 2019; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimi, A.S. Obtenção de Superligas NiCrAIY Nanoestruturadas por Moagem de Alta Energia e Sua Aplicação por Aspersão Térmica Hipersônica (HVOF). Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Brazil.
- Sidhu, T.S.; Prakash, S.; Agrawal, R.D. Studies on the properties of high-velocity oxy-fuel thermal spray coatings for higher temperature applications. Mater. Sci. 2005, 41, 805–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossard, S. Microstructural Analysis of Thermal Spray Coatings by Electron Microscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, UNSW Sydney, Kensington, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Meghwal, A.; Anupam, A.; Murty, B.S.; Berndt, C.C.; Kottada, R.S.; Ang, A.S.M. Thermal Spray High-Entropy Alloy Coatings: A Review. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2020, 29, 857–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, K. Análise da Influência de Parâmetros de Shot Peening na Dureza Superficial, Rugosidade e Tensão Residual em aço ASTM A743-CA6NM—Analysis of the Influence of Shot Peening Parameters on Surface Hardness, Roughness and Residual Stress in Steel ASTM A743-CA6NM. Bachelor’s Thesis, Federal University of Technology—Parana, Ponta Grossa, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.R.; Bertuol, K.; Siqueira, I.B.A.F.; Chicoski, A.; Váz, R.F.; de Sousa, M.J.; Pukasiewicz, A.G.M. Evaluation of cavitation/corrosion synergy of the Cr3C2-25NiCr coating deposited by HVOF process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, K. Estudo do Efeito Sinérgico Cavitação/Erosão em Revestimentos de Carboneto de Cromo e Tungstênio Depositados por Aspersão Térmica de Alta Velocidade—Study of Synergistic Cavitation/Erosion Effect on Chromium and Tungsten Carbide Coatings Deposited by High Velocity Oxy-Fuel. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, T.C.; Hackett, C.M.; Settles, G.S. Independent control of HVOF particle velocity and temperature. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2002, 11, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Prasad, C.D.; Hanumanthappa, H. Role of Thermal Spray Coatings on Erosion, Corrosion, and Oxidation in Various Applications: A Review. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2024, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, A.S.M.; Berndt, C.C. A review of testing methods for thermal spray coatings. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 179–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metco, O. Atmospheric Plasma Spray Solutions. Plasma Solut. 2022, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, C.P.; Vicenzi, J. Protection against Erosive Wear Using Thermal Sprayed Cermet: A Review. In Protection Against Erosive Wear Using Thermal Sprayed Cermet; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–77. ISBN 978-3-642-21986-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugscheider, E.; Barimani, C.; Eckert, P.; Eritt, U. Modeling of the APS plasma spray process. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 7, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, J.; Marshall, M.B. High speed wear testing of an abradable coating. Wear 2012, 294–295, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Gao, S.; Duan, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Effects of blade material characteristics on the high-speed rubbing behavior between Al-hBN abradable seal coatings and blades. Wear 2018, 410–411, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlikon Metco, Material Product Data Sheet—CoNiCrAlY-BN/Polyester Abradable Thermal Spray Powders. Available online: https://mymetco.oerlikon.com/en-us/product/metco2043 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Jech, D.; Čelko, L.; Komarov, P.; Ziegelheim, J.; Česánek, Z.; Schubert, J. The Role of Different Atmospheric Plasma Spray Parameters on Microstructure of Abradable AlSi-Polyester Coatings. Solid State Phenom. 2017, 270, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmeera, A.K.; Jadhav, P.; Lande, C. Effect of Change in Material Properties of the Abradable Coating on the Wear Behavior of It—Microstructure Model-Based Analysis Approach. Lubricants 2025, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Tan, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Sun, J. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of NiCrAl–NiC abradable sealing coating system in NaCl solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 316, 129059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maozhong, Y.; Baiyun, H.; Jiawen, H. Erosion wear behaviour and model of abradable seal coating. Wear 2002, 252, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqallaf, J.; Ali, N.; Teixeira, J.A.; Addali, A. Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour and Protective Coatings for Gas Turbine Compressor Blades—A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvi, B.; Roy, M. Elevated temperature erosion of abradable seal coating: Original scientific paper. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 12, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.E. Mechanical characterisation of AlSi-hBN, NiCrAl-Bentonite, and NiCrAl-Bentonite-hBN freestanding abradable coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3268–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendarchuck, B.E.; Bertuol, K.; Rivadeneira, F.; de Castilho, B.C.N.M.; Barnett, B.; Moreau, C.; Stoyanov, P. Unveiling the influence of nickel on the erosion and the tribological performance of AlSi-based abradable coatings. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 22266–22282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, R.E.; Hendricks, R.C.; Lattime, S.B.; Steinetz, B.M. Sealing in Turbomachinery. J. Propuls. Power 2006, 22, 313–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, D.; Singh, D.; Kumar Sharma, S. Thermal Characteristics and Tribological Performances of Solid Lubricants: A Mini Review. In Advances in Rheology of Materials; Dutta, A., Muhamad Ali, H., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-83769-996-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.; Menezes, P.L. Self-Lubricating Materials for Extreme Condition Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, W.; Wang, W.; Tang, C. A review on the preparation and application of BN composite coatings. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aussavy, D. Processing Characterization and Modeling of Thermomechanical Properties of Threee Abradable Coatings: NiCrAl-Bentonite, CoNiCrAlY-BN-Polyester, and YSZ-Polyester. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Technologie de Belfort-Montbeliard, Belfort, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Yu, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D. Effect of Microstructure Refining on the Thermal Stability and Wear Resistance of Abradable AlSi-Polyester Coating. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Matthews, A. Investigation of abradable seal coating performance using scratch testing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.; Marshall, M. Wear mechanisms at the blade tip seal interface. Wear 2018, 404–405, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiba, S.; Faure, L.; Philippon, S.; Papasidero, J. Experimental Investigation of the Mechanical Behavior of an AlSi-PE Abradable Coating at High Strain Rates for a Large Range of Temperatures. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2020, 6, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinet, B.; Cappella, A.; Philippon, S.; Montebello, C. Effect of temperature on wear mechanisms of an aluminium—Based abradable coating for aircraft engines after a dynamic interaction with a Ti6Al4V blade. Wear 2020, 446–447, 203202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Hou, Y. The Influence of Incursion Rate on Abradability of AlSi-hBN Abradable Seal Coating. In Proceedings of the International Thermal Spray Conference, ITSC 2024, Milan, Italy, 29 April–1 May 2024; pp. 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gao, S.; Xue, W.; Wu, B.; Duan, D. Structural design and high temperature tribological behavior of a new turbine blade tip protective coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 457, 129316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.; Nicoll, A.R. Advances in Abradable Coatings for Gas Turbines. In Proceedings of the ASME 1994 International Gas Turbine and Aeroengine Congress and Exposition, The Hague, The Netherlands, 13–16 June 1994; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. V005T12A010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, K.; Arendarchuck, B.; Rivadeneira, F.; Nolte, L.; Lehner, M.; Barnett, B.; Moreau, C.; Stoyanov, P. Assessment of AlSi-based abradable coatings with hBN and MoCr additives for aerospace conditions: A novel high-temperature rig approach. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2026, 168, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Wietheger, W.; Heinemann, H.; Dokhanchi, S.R.; Rom, M.; Visconti, G. Prediction of Particle Properties in Plasma Spraying Based on Machine Learning. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, K.; Rivadeneira, F.; Arendarchuck, B.; Nair, R.B.; Barnett, B.; Moreau, C.; Stoyanov, P. Effect of Mo and Cr on abradability and tribological performance of AlSi-based abradable coatings. Wear 2025, 571, 205837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metco, O. Thermal Spray Materials Guide. 2015. Available online: https://www.ahtstlab.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/ThermalSprayMaterialsGuide.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Zavareh, M.A.; Doustmohammadi, E.; Sarhan, A.A.D.M.; Karimzadeh, R.; Moozarm Nia, P.; Al/Kulpid Singh, R.S. Comparative study on the corrosion and wear behavior of plasma-sprayed vs. high velocity oxygen fuel-sprayed Al8Si20BN ceramic coatings. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 12180–12193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoun, H.I.; Grosdidier, T.; Seichepine, J.-L.; Goran, D.; Aourag, H.; Coddet, C.; Zwick, J.; Hopkins, N. Improvement of thermally sprayed abradable coating by microstructure control. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Zhang, J.P.; Pei, Z.L.; Liu, J.H.; Li, W.H.; Gong, J.; Sun, C. Investigation on high-speed rubbing behavior between abrasive coatings and Al/hBN abradable seal coatings. Wear 2020, 456–457, 203389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, G.; Kumaran, S.; Rao, T.S. Sliding Wear Behavior of Al-Si/Graphite Composite. Tribol. Trans. 2010, 54, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Matthews, A. Evaluation of abradable seal coating mechanical properties. Wear 2009, 267, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilemany, J.M.; Navarro, J.; Lorenzana, C.; Vizcaino, S.; Miguel, J.M. Tribological Behaviour of Abradable Coatings Obtained by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying (APS). In Proceedings of the International Thermal Spray Conference 2001, Singapore, 28–30 May 2001; pp. 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Shen, J.; Xuan, H.; Hu, Y.; Hong, W. Evaluation of an AlSi-polyester abradable seal coating performance using high-temperature and high-velocity abrasion tests. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2016, 230, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutasim, Z.; Hsu, L.; Wong, E. Evaluation of plasma sprayed abradable coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1992, 54–55, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cuny, M.; Philippon, S.; Chevrier, P.; Garcin, F. Experimental Measurement of Dynamic Forces Generated during Short-Duration Contacts: Application to Blade-Casing Interactions in Aircraft Engines. Exp. Mech. 2014, 54, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddenberg, K.; Kock, B.; Dorfman, M.; Russo, L.; Nestler, M. A New Aluminium Silicon-Boron Nitride Abradable for Compressor Components. In Proceedings of the ITSC 1998, Nice, France, 25–29 May 1998; pp. 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jońca, J.; Malard, B.; Soulié, J.; Sanviemvongsak, T.; Selezneff, S.; Vande Put, A. Oxidation behaviour of a CoNiCrAlY/h-BN based abradable coating. Corros. Sci. 2019, 153, 170–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chappel, D.; Howe, H.; Vo, L. Abradable seal testing—Blade temperatures during low speed rub event. In Proceedings of the 37th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 8–11 July 2001; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Zois, D.; Wilson, S.; Dorfman, M.R. Investigation of High Temperature Compressor Abradable Coatings for Gas Turbine Applications. In Proceedings of the ITSC2018, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–4 December 2001; pp. 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Song, Q.H.; Li, J.J.; Sun, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.F. Reaction mechanism comparison of AlSi-polyester and aluminum bronze/polyester plasma spraying. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2021, 16, 1411–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Guo, D.; Cheng, X.-W.; Liu, J.-M.; Yu, Y.-G. Corrosion behaviour of NiCrFeAl-hBN seal coatings in oxidation environments at a high temperature. Rare Met. 2021, 40, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, Y.; Mutasim, Z.; Coe, M. Abradable Coatings for Low-Temperature Applications. In Proceedings of the ITSC2001, Singapore, 28–30 May 2001; pp. 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.E. The Sensitivity of Abradable Coating Residual Stresses to Varying Material Properties. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2009, 18, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappella, A.; Philippon, S.; Pinheiro, L. Micro-Ct and Ai-Based Analysis of Induced Changes in Porosity of Alsi-Pe Abradable Coatings Due to Short-Term Loading and High Temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 514, 132518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Tian, J.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, A. Interactions between blades and abradable coatings: A numerical approach considering geometrical nonlinearity. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 191, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bender, F. Fundamentals of Friction Modeling; ASPE—The American Society of precision Engineering: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2010; Volume 48, ISBN 978-1-887706-53-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Hu, X.; Lancaster, D.; Sun, X.; Joost, W. Modeling deformation and failure in AlSi-polyester abradable sealcoating material using microstructure-based finite element simulation. Mater. Des. 2022, 219, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padova, C.; Barton, J.; Dunn, M.J.; Manwaring, S.; Young, G.; Adams, M., Jr.; Adams, M. Development of an Experimental Capability to Produce Controlled Blade Tip/Shroud Rubs at Engine Speed; ASME American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Marshall, M.; Lewis, R. Investigating Al-Si base abradable material removal mechanism with axial movement in labyrinth seal system. Wear 2022, 510–511, 204496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, R.E.; Lau, Y.-C.; Ghasripoor, F.; Baldwin, D.J.; Ng, C.; McGovern, T.; Berkeley, D. Development of Higher Temperature Abradable Seals for Gas Turbine Applications. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2004: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, Vienna, Austria, 14–17 June 2004; ASMEDC: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuol, K.; Rivadeneira, F.; Nair, R.; Stoyanov, P. Advancing Abradable Evaluation: A Comprehensive Review and Development of an Innovative Cost-Effective Methodology. In Proceedings of the 27th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering, Florianópolis, Brazil, 4–8 December 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandard, R.; Witz, J.-F.; Boidin, X.; Fabis, J.; Desplanques, Y.; Meriaux, J. Interacting force estimation during blade/seal rubs. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Polymeric [10,25,27,30] | Ceramic [26,28,29] | Metallic [10,28,31] |
|---|---|---|
| Widely investigated materials | ||
| Epoxy-based [27,32,33] | ZrO2- 7Y2O3 [26,29,34] | AlSi + 40Polyester [35,36,37] |
| Alternative materials | ||
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | DySZ-based | Co-based alloys |
| Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | YAG-based | Ni-based alloys |
| Polyamideimide (PAI) | Yb-based | Cu-based alloys |
| Manufacturing Method | Characteristics | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Compression molding | Higher processing pressures during polymer melt forming may enhance mechanical properties and increase crystallinity, leading to denser, harder-to-cut, and stronger materials [27,44]. | Polymers and composites |
| Sintering | Aids to grain growth at elevated temperatures, improving bonding strength while redistributing internal defects, yet retaining controlled porosity [26,29]. | Ceramics and composites |
| Thermal spray | Exhibit strong anisotropy, as splats solidify in layered sequences where particle shape and inter-splat bonding largely govern the resulting properties [31,45]. | Metals and composites |
| Abradable Materials (Metallic-Based) | Operating Temperature [93] | Description [93] | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum-based Alloy | AlSi + BN | <450 °C | Good erosion resistance | [4,16,67,75,94,95,96] |
| AlSi + Graphite | <480 °C | Balance of abradability and erosion resistance | [83,97,98,99] | |
| AlSi + Polymer | <325 °C | Balance of abradability and erosion resistance | [15,16,69,100,101,102] | |
| AlSi + Polyester + BN | <325 °C | Balance of abradability and erosion resistance | [103] | |
| Cobalt-based Alloy | CoNiCrAlY + BN + Polyester | <750 °C | Great corrosion resistance | [11,26,71,74,104,105,106] |
| Copper-based Alloy | CuAl (Al+ Bronze) + Polyester | <650 °C | Good corrosion resistance | [80,101,107] |
| Nickel-based Alloy | Ni + Graphite | <480 °C | Balance of lubricity and erosion resistance | [83,98,99,105,106] |
| NiCrAl + Bentonite | <650 °C | Good erosion resistance | [75,81,95,106] | |
| NiCrFeAl + BN | <815 °C | Balance of lubricity and erosion resistance | [106,108,109] | |
| Category | Type | Key Parameters | Units | Main Measurement Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | Input | Blade speed | [rpm or m/s] | Tachometer/encoder/high-speed camera |
| Incursion rate | [μm/s or μm/pass] | Linear displacement/laser sensor/high-speed camera | ||
| Incursion depth | [μm] | Laser sensor/profilometry/gauges | ||
| Operating temperature | [°C] | Thermocouples/IR pyrometer | ||
| Output | Blade Wear | [µm, % loss] | Optical surface analysis/profilometry/scale/stroboscopic image | |
| Coating Wear | [µm, mm3/Nm] | Optical surface analysis/profilometry/scale | ||
| Rub Grooves profile | [μm] | Profilometry/roughness tester | ||
| Reaction Forces | [kN] | Load cell/strain gauges/force transducer | ||
| Rubbing Temperature | [°C] | Thermocouples/IR pyrometer/IR camera | ||
| Qualitative | Input | Abradable material | - | EDS/X-ray/RAMAN |
| Blade material | - | EDS/X-ray/RAMAN | ||
| Output | Adhesive Transfer | - | SEM/optical surface analysis | |
| Wear Mechanism | - | SEM/optical surface analysis | ||
| Densification | - | SEM/optical surface analysis | ||
| Debris Characteristics | - | Laser-diffractometer/SEM/EDS | ||
| Rub Grooves Characteristics | - | SEM/optical surface analysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertuol, K.; Arendarchuck, B.E.; Stoyanov, P. An Overview of Metallic Abradable Coatings in Gas Turbine Engines. Coatings 2025, 15, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101216
Bertuol K, Arendarchuck BE, Stoyanov P. An Overview of Metallic Abradable Coatings in Gas Turbine Engines. Coatings. 2025; 15(10):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101216
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertuol, Kaue, Bruno Edu Arendarchuck, and Pantcho Stoyanov. 2025. "An Overview of Metallic Abradable Coatings in Gas Turbine Engines" Coatings 15, no. 10: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101216
APA StyleBertuol, K., Arendarchuck, B. E., & Stoyanov, P. (2025). An Overview of Metallic Abradable Coatings in Gas Turbine Engines. Coatings, 15(10), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101216







