The Influence of the Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Parameters of the Mg-AZ31B Alloy on the Micromechanical and Sclerometric Properties of Oxide Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Material
2.2. Research Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
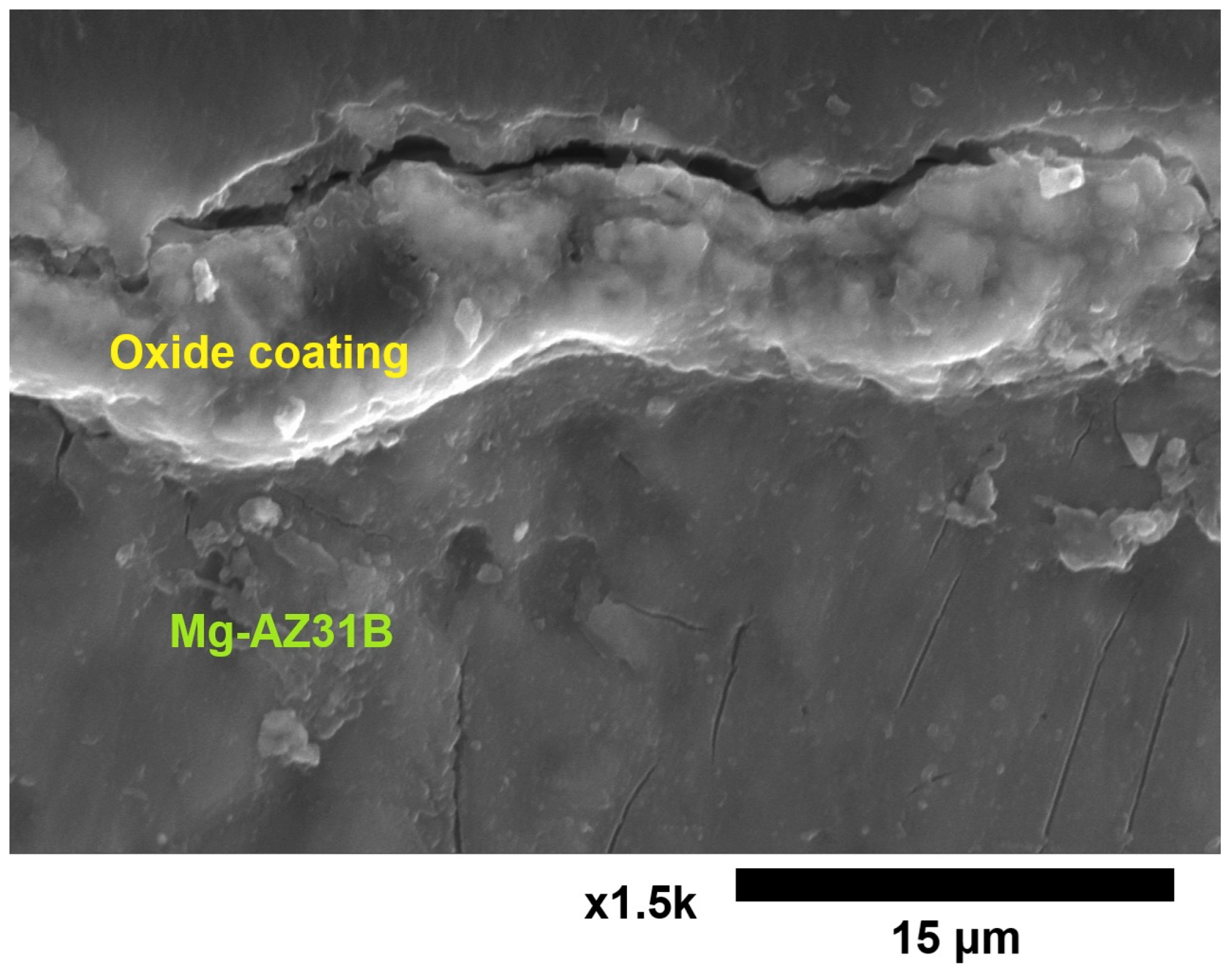
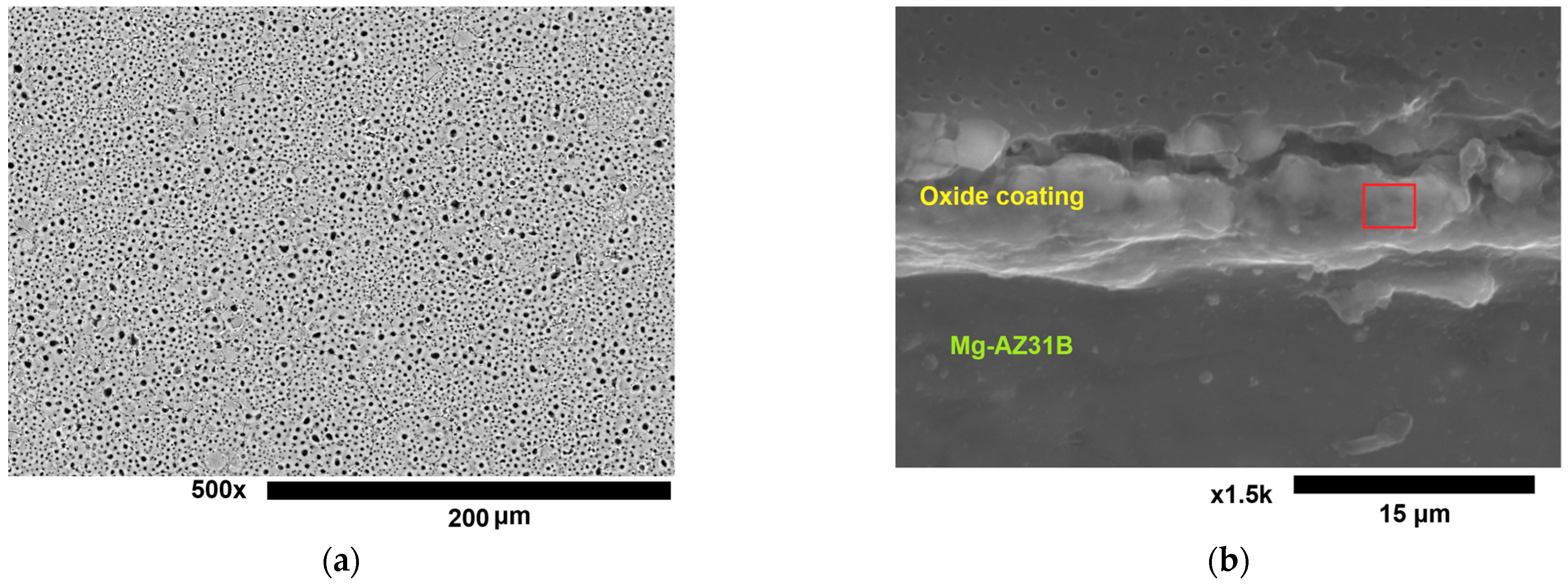
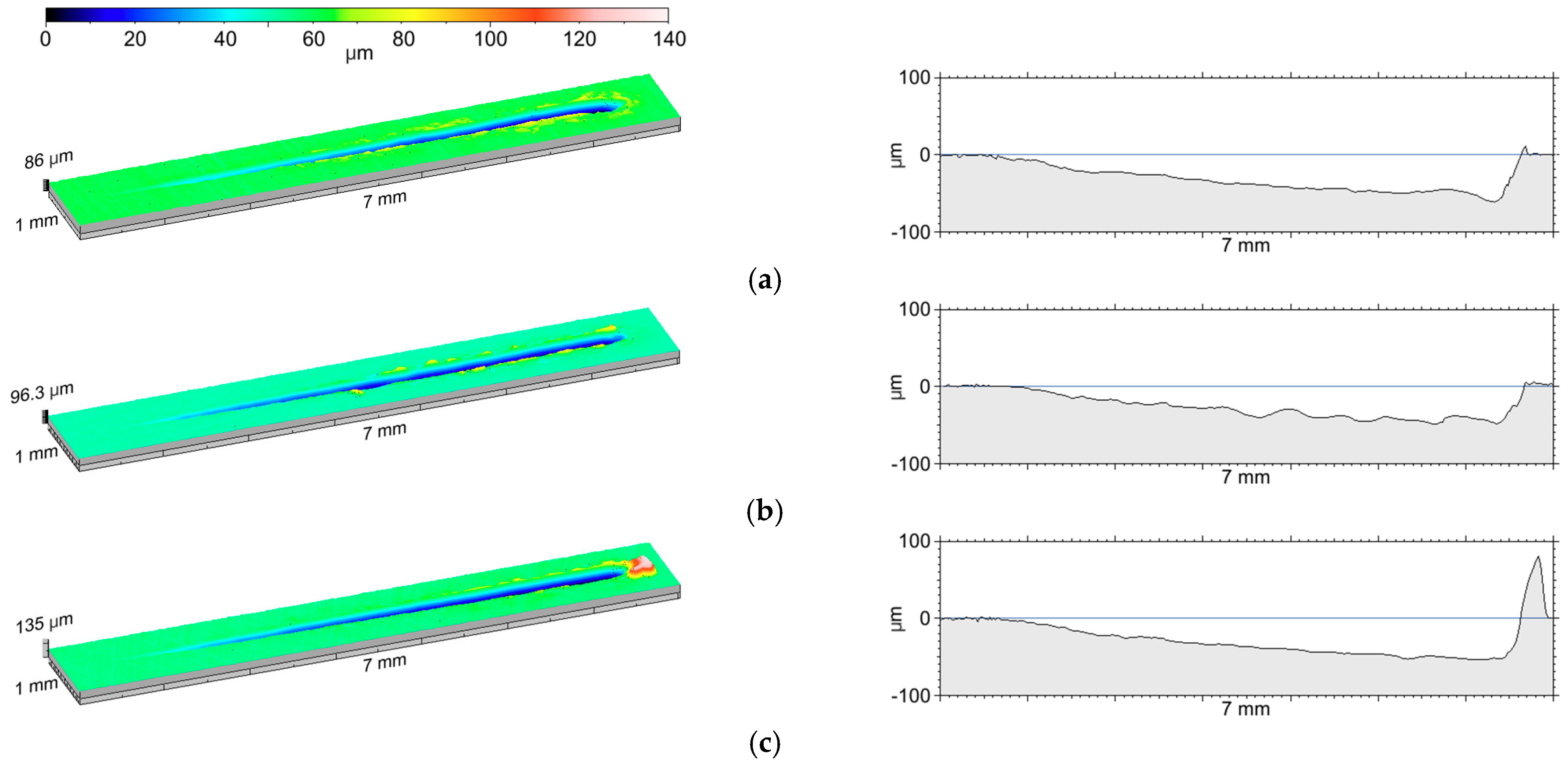
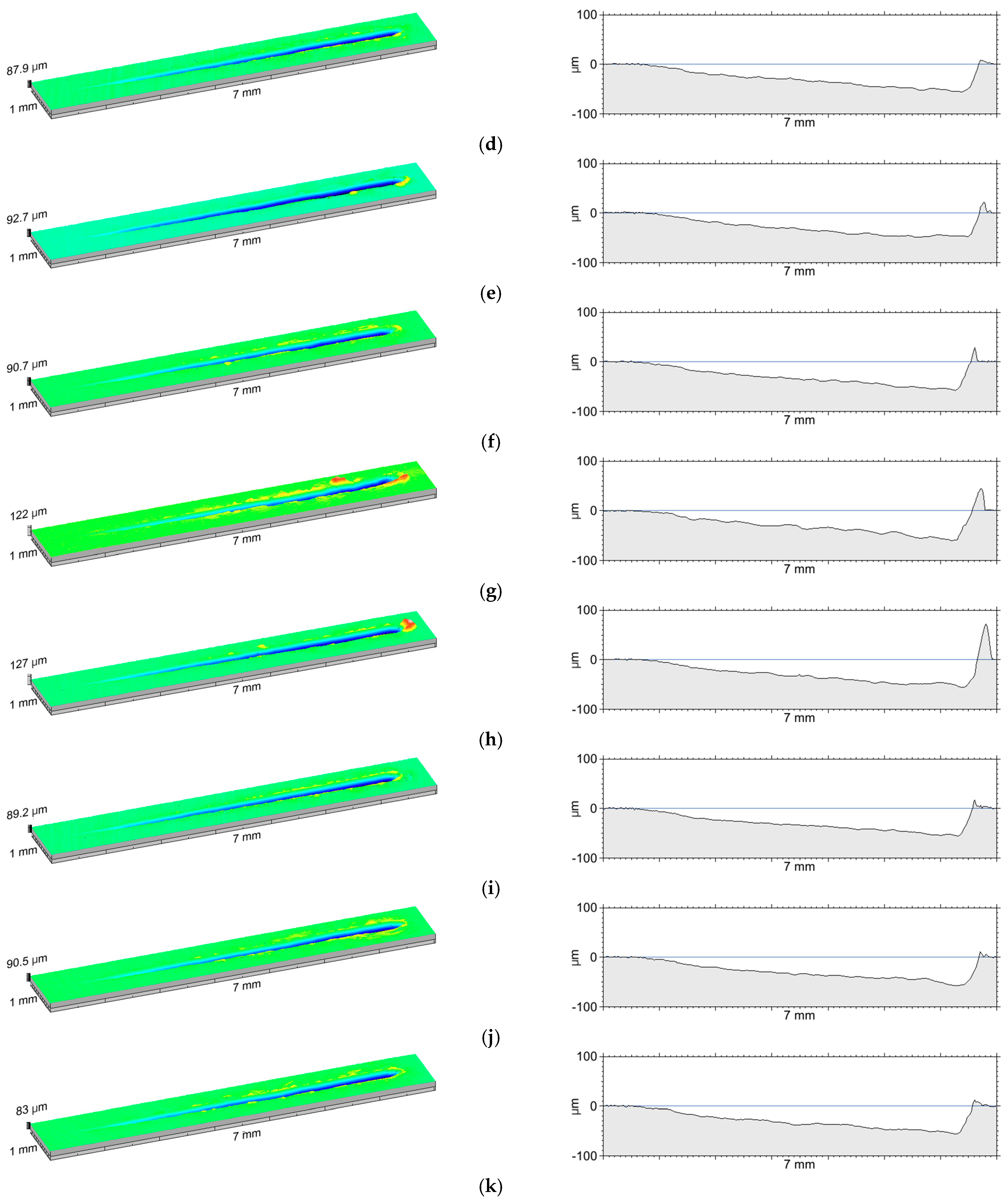
3.1. The Thickness of the Oxide Coating
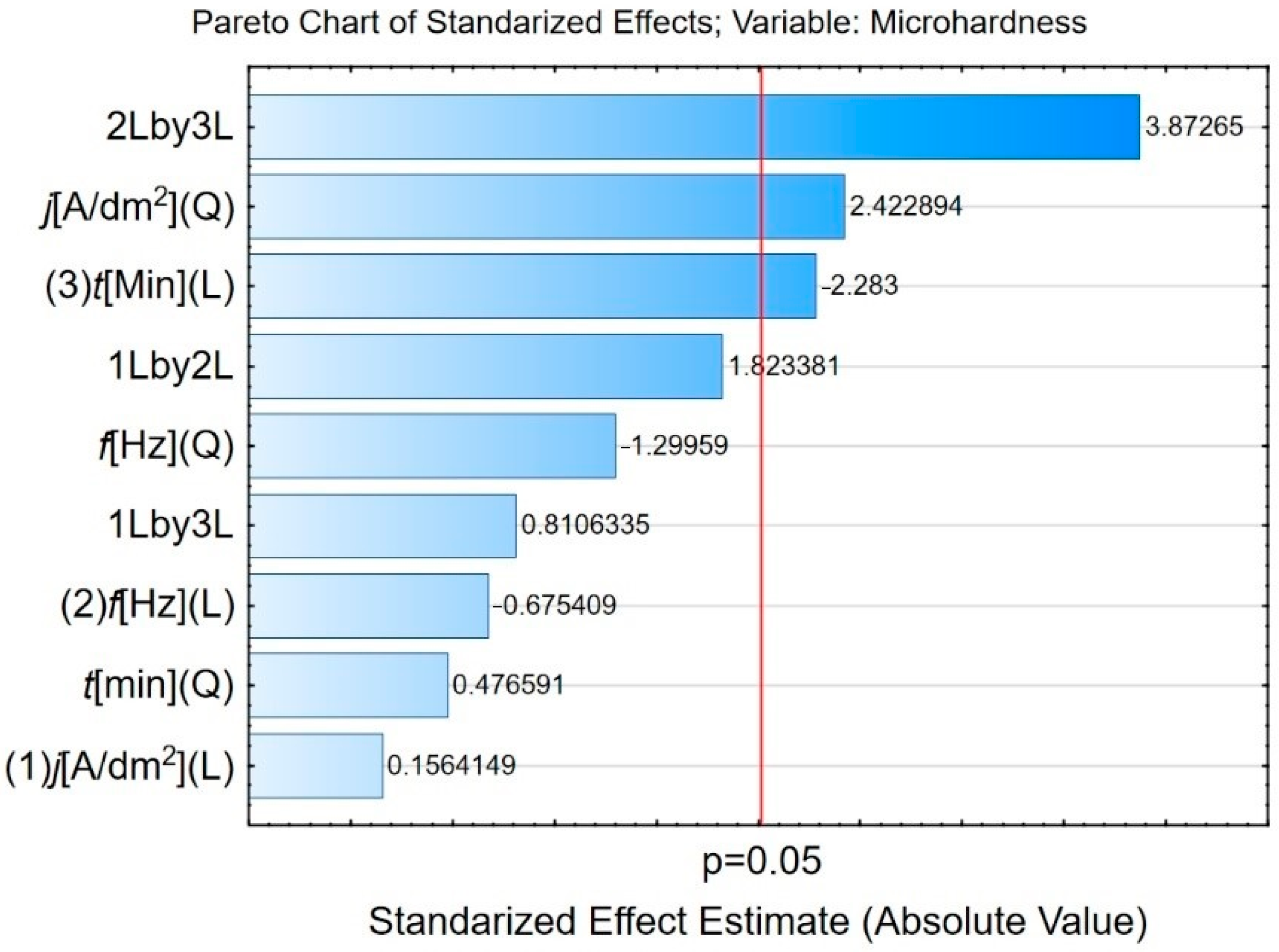
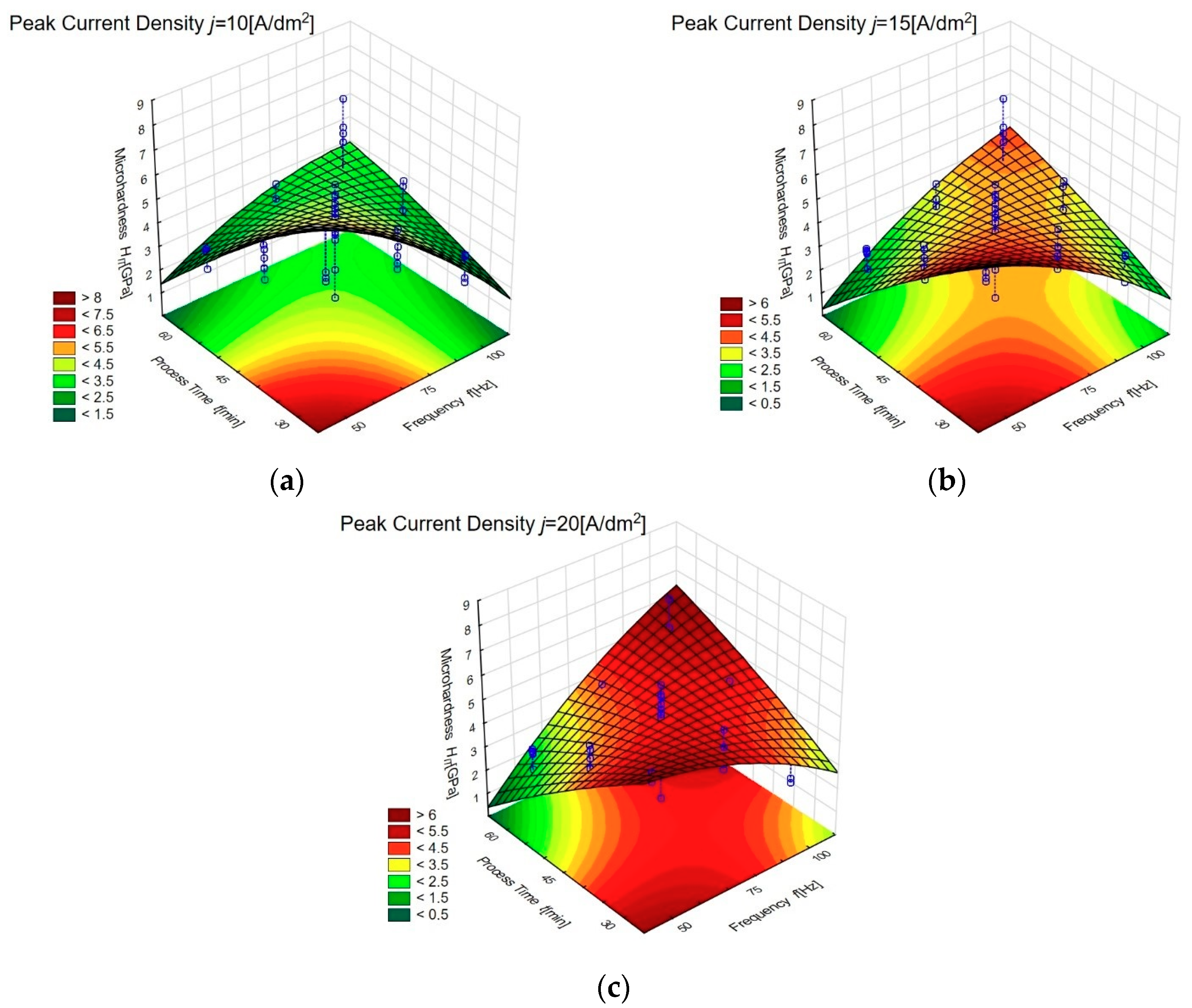
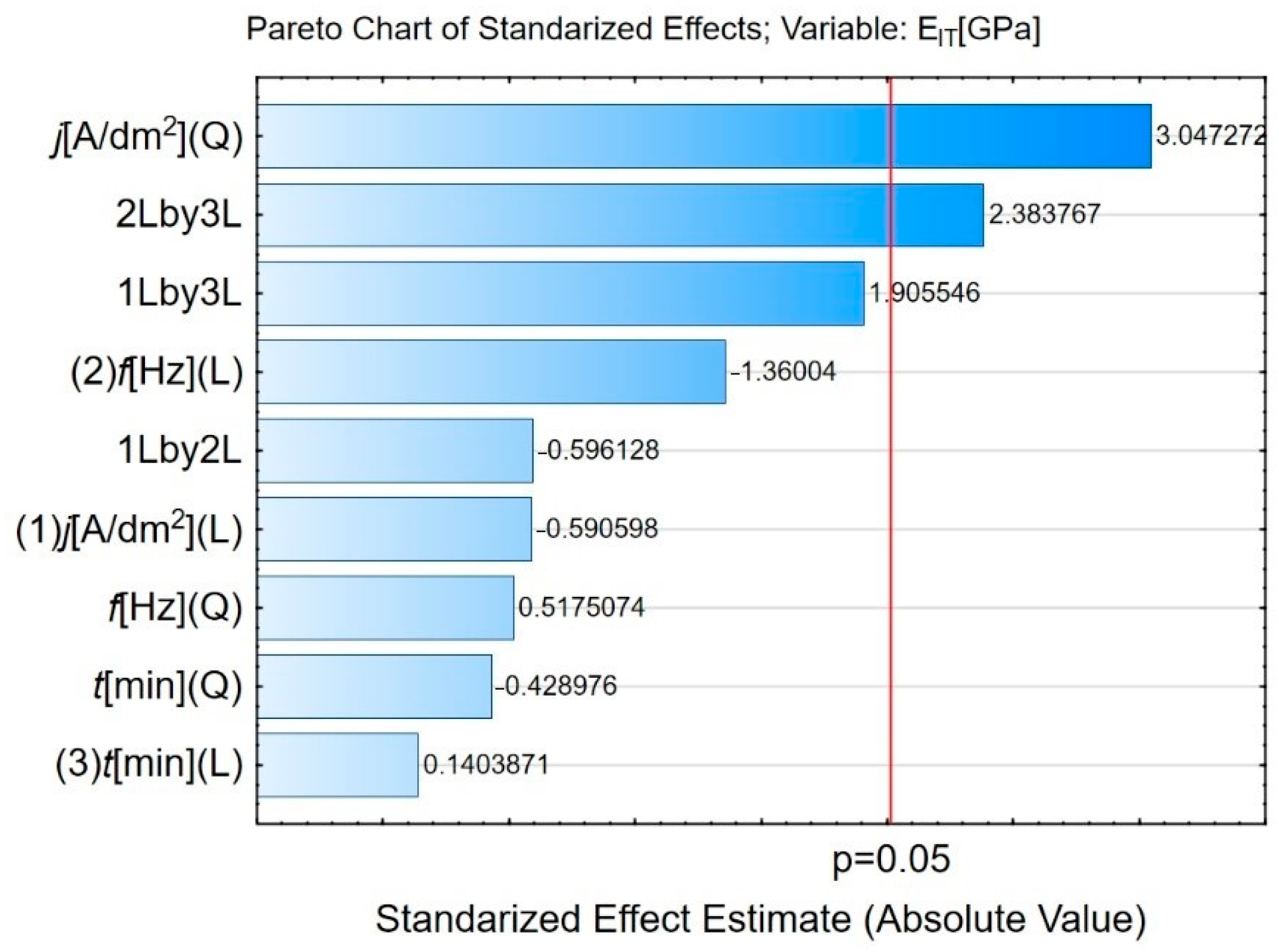
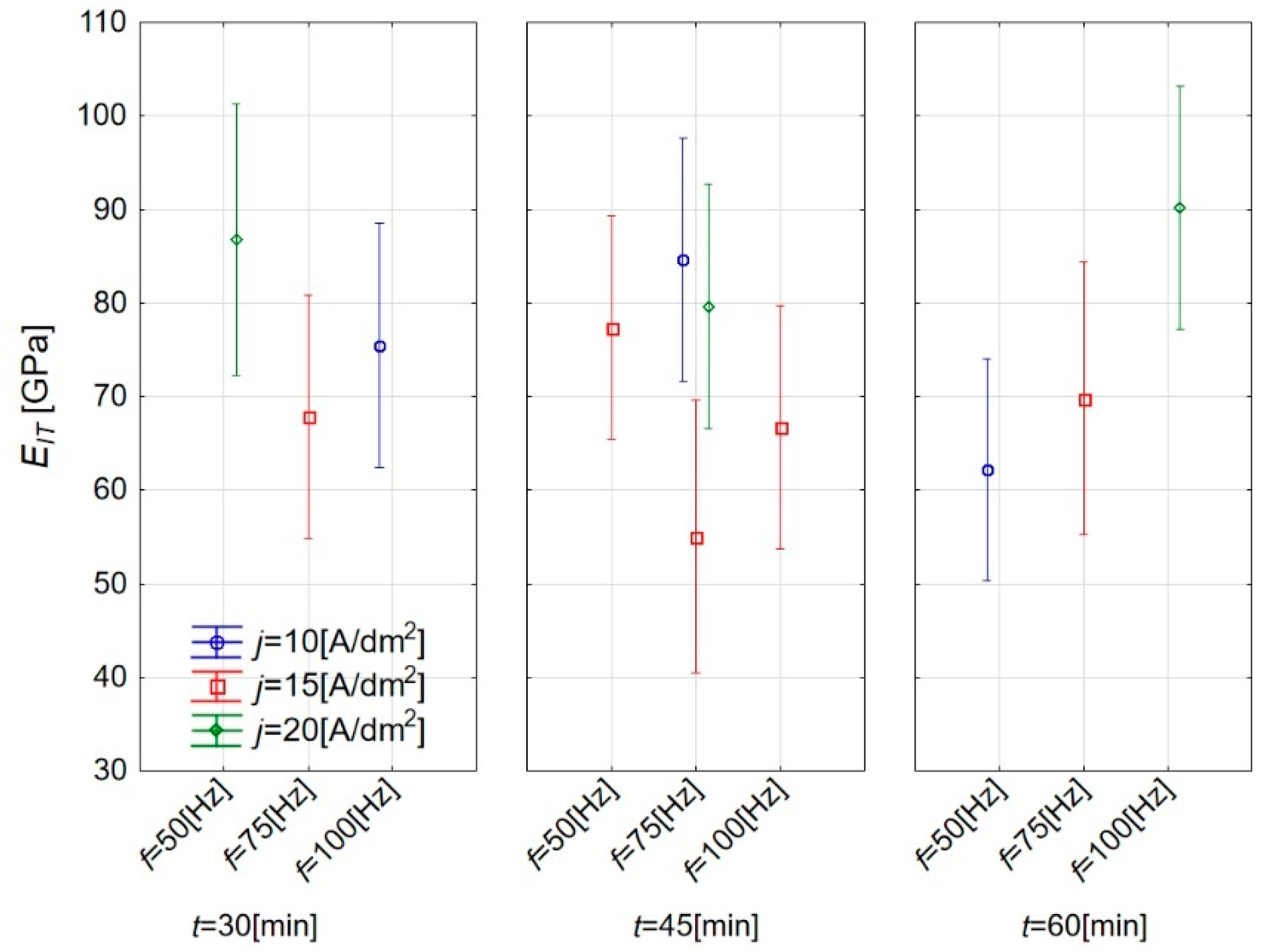
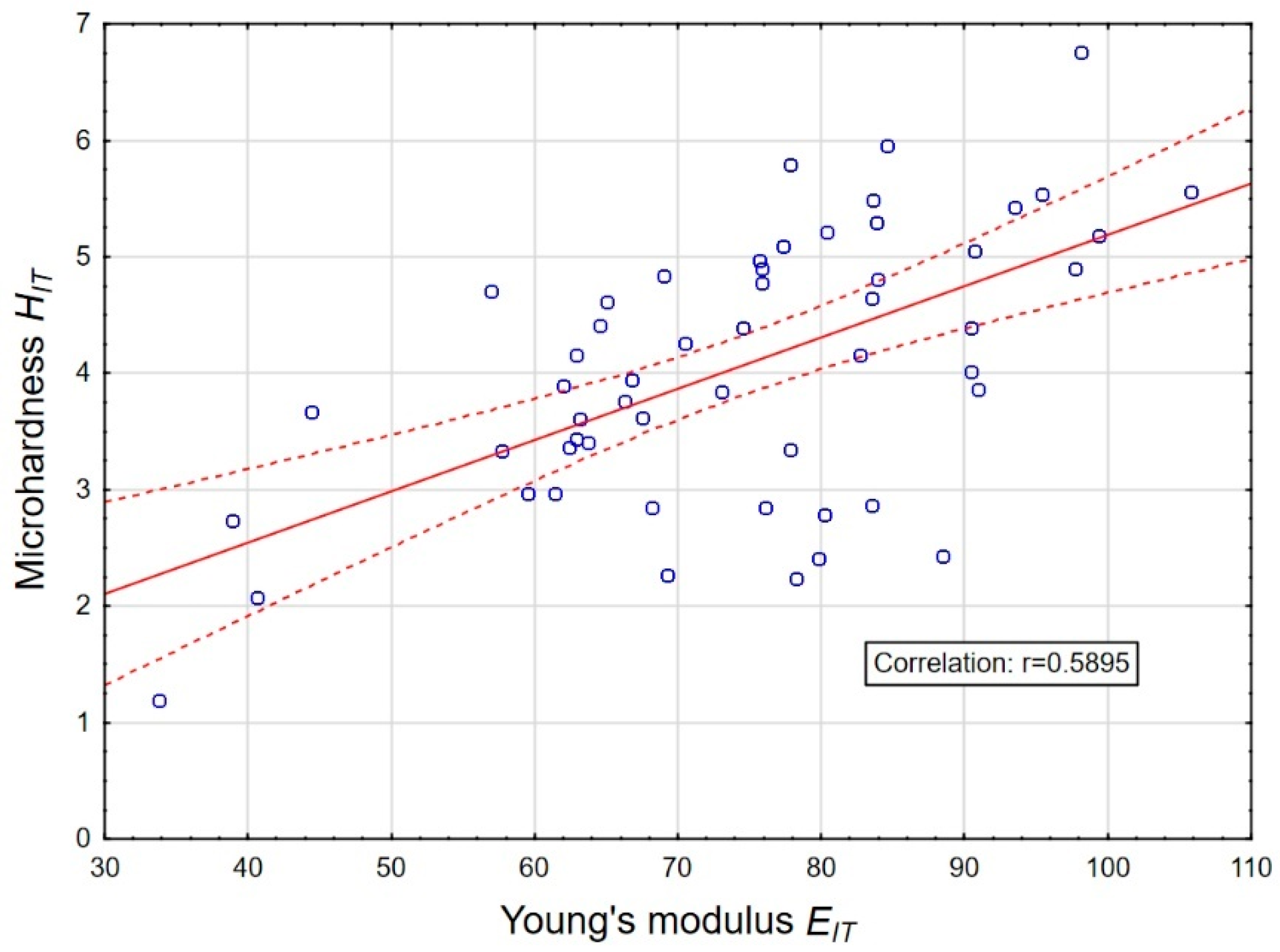
3.2. Influence of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation on Micromechanical Properties
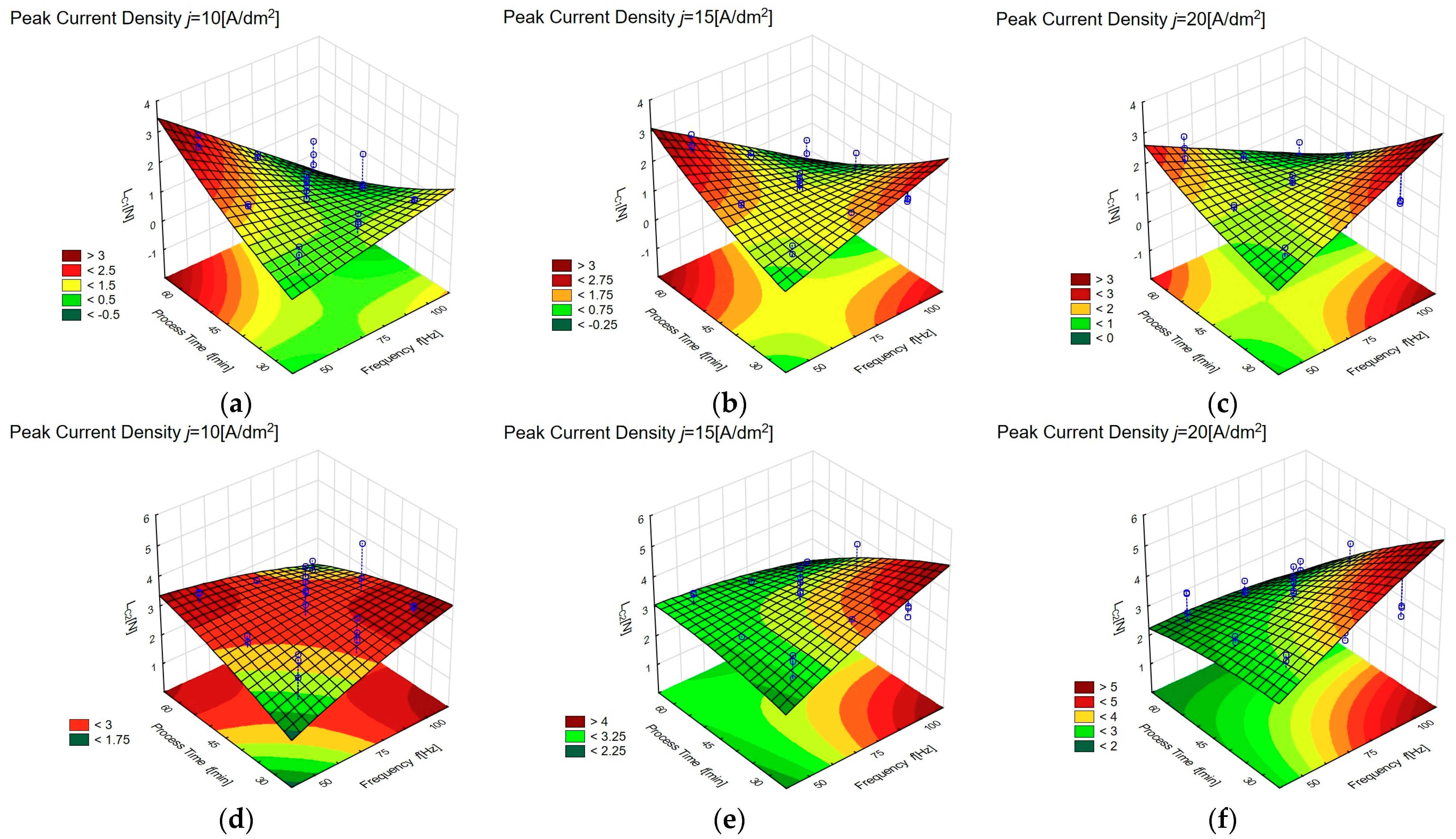
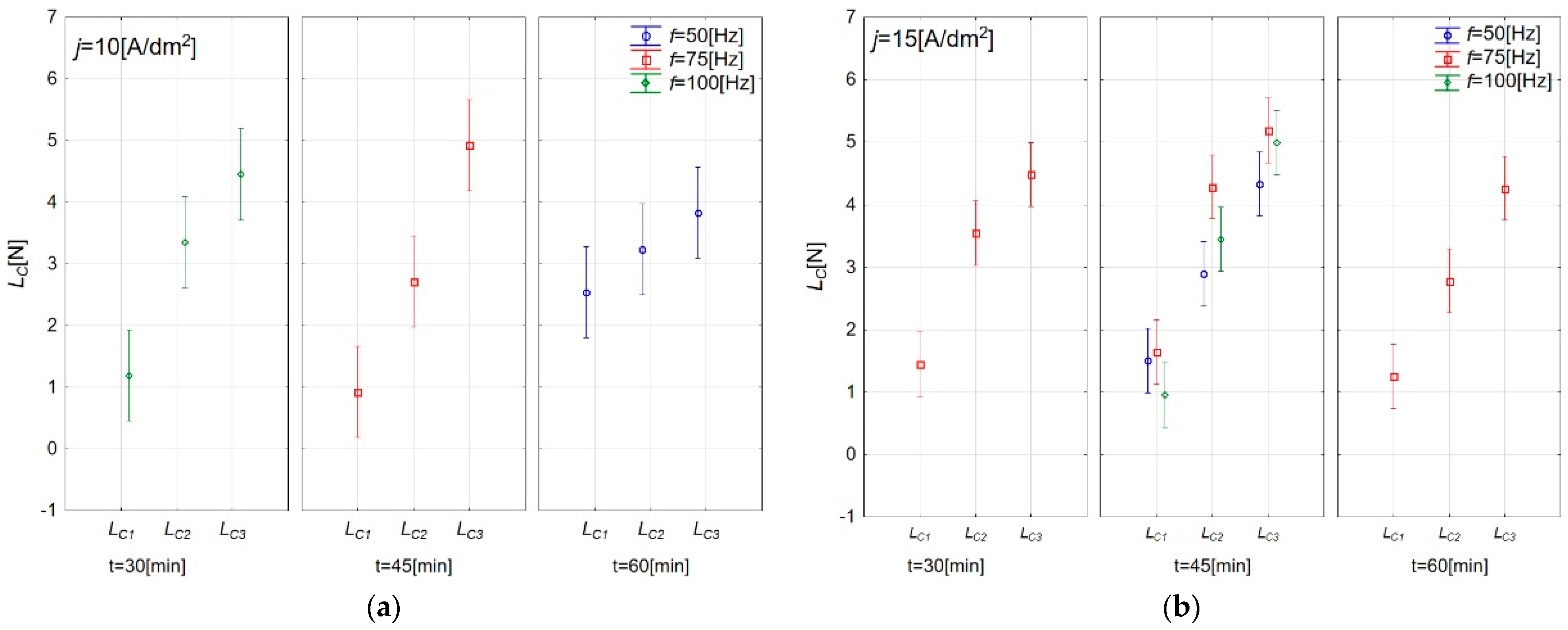
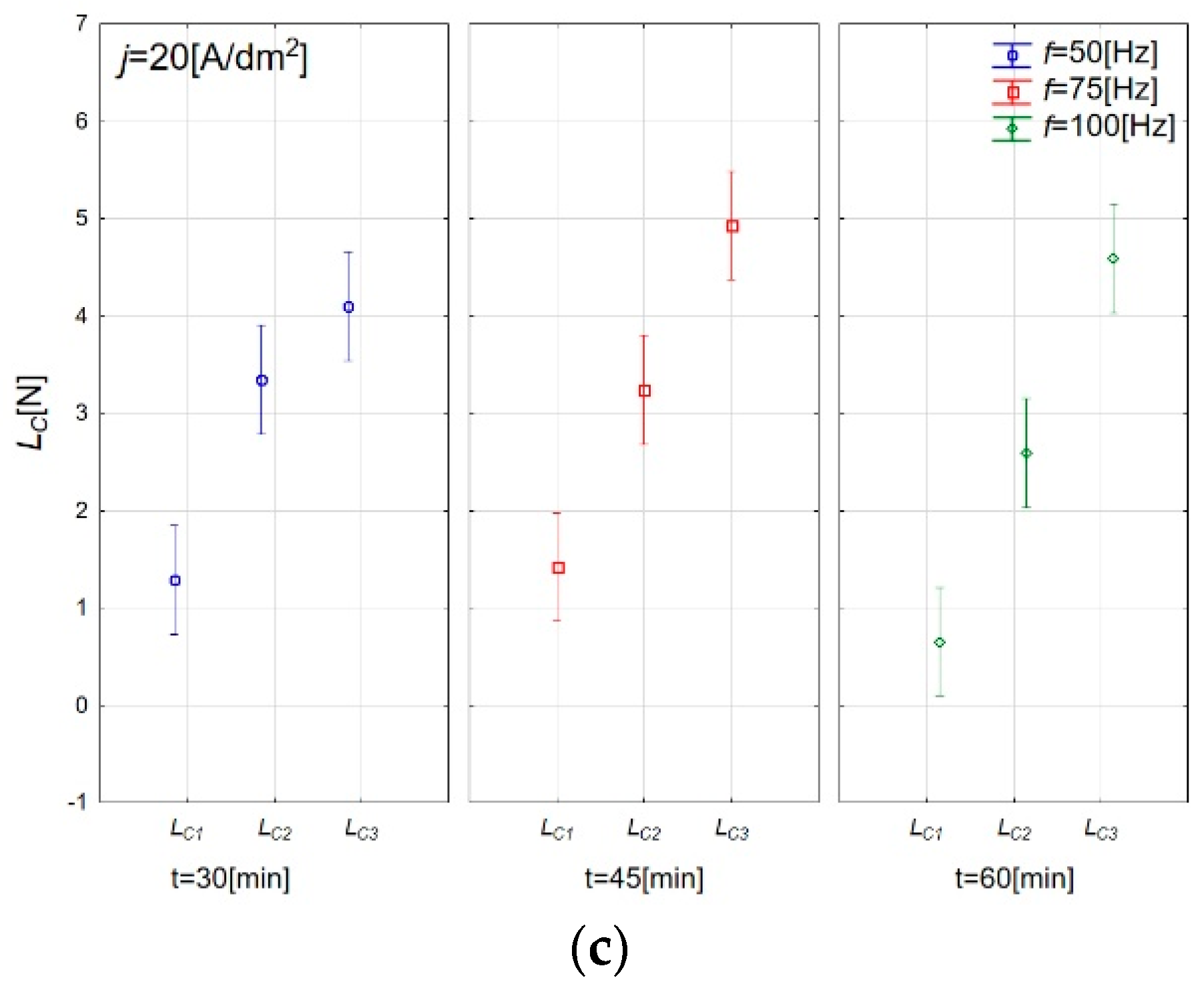
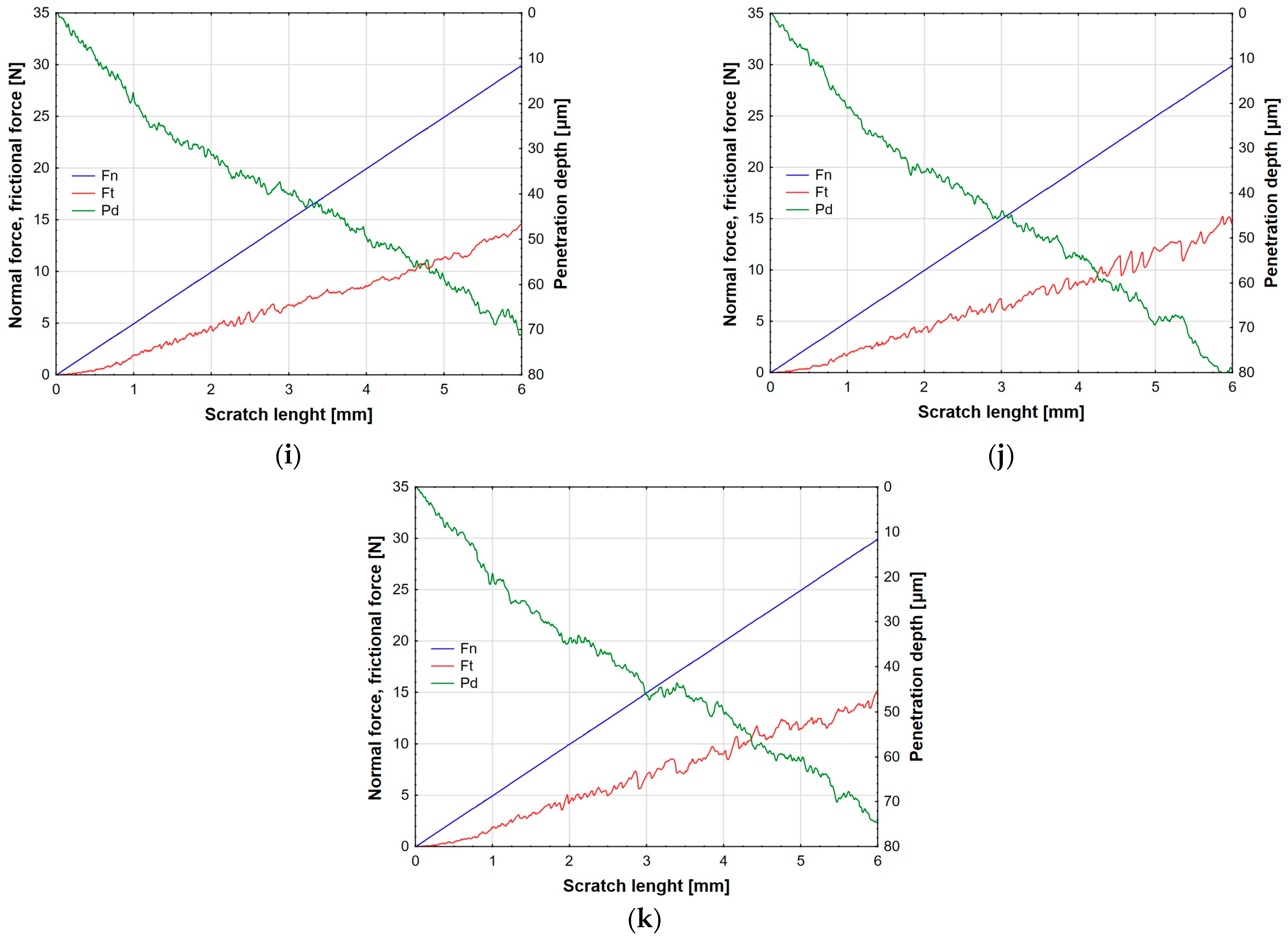
3.3. Adhesive Properties of Anodic Oxide Coatings
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huo, H.; Gao, Y.; Zuo, P.; Wang, J.; Yin, G. Achieving high-energy-density magnesium/sulfur battery via a passivation-free Mg-Li alloy anode. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 50, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandlöbes, S.; Friák, M.; Korte-Kerzel, S.; Pei, Z.; Neugebauer, J.; Raabe, D. A rare-earth free magnesium alloy with improved intrinsic ductility. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10458–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.L.; Zhang, G.R.; Venter, T.; Biesalski, M.; Etzold, B.J. Towards best practices for improving paper-based microfluidic fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 298, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barylski, A.; Aniołek, K.; Dercz, G.; Matuła, I.; Rak, J.; Mazur, I. The Effect of Changes in the Aging Temperature Combined with Deep Cryogenic Treatment on the Structure, Phase Composition, and Micromechanical Properties of the WE43 Magnesium Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ye, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Suo, T.; Deng, Q.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q. Development of mechanical properties in AZ31 magnesium alloy processed by cold dynamic extrusion. Mater. Charact. 2021, 182, 111535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Development and application of magnesium alloy parts for automotive OEMs: A review. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2023, 11, 15–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F. The History of Biodegradable Magnesium Implants: A Review. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waizy, H.; Diekmann, J.; Weizbauer, A.; Reifenrath, J.; Bartsch, I.; Neubert, V.; Schavan, R.; Windhagen, H. In Vivo Study of a Biodegradable Orthopedic Screw (MgYREZr-Alloy) in a Rabbit Model for up to 12 Months. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 28, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golroudbary, S.R.; Makarava, I.; Repo, E.; Kraslawski, A.; Luukka, P. Magnesium Life Cycle in Automotive Industry. Procedia CIRP 2022, 105, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Nie, X.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A.; Dowey, S.J. Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Raja, V.S.; Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Kainer, K.U. Study of the structure and corrosion behavior of PEO coatings on AM50 magnesium alloy by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3513–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedźwiedź, M.; Bara, M.; Korzekwa, J.; Kaptacz, S.; Sowa, M.; Olesiński, A.; Simka, W. Tribological Properties and Surface Wettability of Coatings Produced on the Mg-AZ31B Alloy by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation. Coatings 2024, 14, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulabifard, A.; Rahmati, M.; Raeissi, K.; Hakimizad, A.; Santamaria, M. The Effect of Electrolytic Solution Composition on the Structure, Corrosion, and Wear Resistance of PEO Coatings on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Coatings 2020, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Ahn, B.-H.; Jeong, Y.S.; Song, J.I.; Koo, B.H. The influence of various additives on the properties of PEO coatings formed on AZ31 Mg Alloy. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2016, 23, 1650006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Muhaffel, F.; Sun, G.; Cimenoglu, H.; Alpas, A.T. Role of counterfaces with DLC and N-based coatings on frictional behaviour of AZ31 magnesium alloy subjected to plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 397, 125997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sravya, T.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Abdulhakim, A.; Gupta, M. Mechanical properties of magnesium-rare earth alloy systems: A review. Metals 2015, 5, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cakmak, E.; Tekin, K.C.; Malayoglu, U.; Shrestha, S. The effect of substrate composition on the electrochemical and mechanical properties of PEO coatings on Mg alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutsaylyuk, V.; Student, M.; Posuvailo, V.; Student, O.; Hvozdets’kyi, V.; Maruschak, P.; Zakiev, V. The role of hydrogen in the formation of oxide-ceramic layers on aluminum alloys during their plasma-electrolytic oxidation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1682–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazenbiller, E.; Mansoor, S.; Konchakova, N.; Serdechnova, M.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Blawert, C.; Höche, D. Computational damage modelling of PEO coated extruded magnesium tested in slow strain rate configuration. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 446, 128758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Gennari, C.; Franceschi, M.; Brunelli, K. Influence of silicon morphology on direct current plasma electrolytic oxidation process in AlSi10Mg alloy produced with laser powder bed fusion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egdio, G.D.; Tonelli, L.; Morri, A.; Boromei, I.; Shashkov, P.; Martini, C. Influence of Anodizing by Electro-Chemical Oxidation on Fatigue and Wear Resistance of the EV31A-T6 Cast Magnesium Alloy. Coatings 2023, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdu, S.; Bayramoğlu, S.; Demirtaş, A.; Usta, M.; Üçışık, A.H. Characterization of AZ31 Mg Alloy coated by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Vacuum 2013, 88, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.H.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Niu, E.W.; Pang, H.; Zou, B.; Yang, S.Z. Investigation of plasma electrolytic oxidation process on AZ91D magnesium alloy. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X.; Jiang, Z.H.; Li, G.Y.; Jiang, Q.; Lian, J.S. Electroless Ni-P/Ni-B duplex coatings for improving the hardness and the corrosion resistance of AZ91D magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 4949–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.S.; Yen, C.A.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, J.W. Effects of processing parameters on the adhesion and corrosion resistance of oxide coatings grown by plasma electrolytic oxidation on AZ31 magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietraszek, J. Response surface methodology at irregular grids based on Voronoi scheme with neural network approximator. In Neural Networks and Soft Computing, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Neural Networks and Soft Computing, Zakopane, Poland, 11–15 June 2002; Physica: Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Pietraszek, J.; Goroshko, A. The Heuristic Approach to the Selection of Experimental Design, Model and Valid Pre-Processing Transformation of DoE Outcome. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 874, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14577-4; Metallic Materials—Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Materials Parameters—Part 4: Test Method for Metallic and Non-Metallic Coatings. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19252:2008; Plastics—Determination of Scratch Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 20502:2005; Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Determination of Adhesion of Ceramic Coatings by Scratch Testing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- ASTM C1624-22(2022); Standard Test Method for Adhesion Strength and Mechanical Failure Modes of Ceramic Coatings by Quantitative Single Point Scratch Testing. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM D7027-20(2020); Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Scratch Resistance of Polymeric Coatings and Plastics Using an Instrumented Scratch Machine. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.







| Sample | Controlled Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On a Natural Scale | On a Standard Scale | |||||
| Peak Current Density jpeak (A/dm2) | Frequency f (Hz) | Process Time t (min) | ×1 | ×2 | ×3 | |
| A | 10 | 50 | 60 | −1 | −1 | 1 |
| B | 20 | 50 | 30 | 1 | −1 | −1 |
| C | 10 | 100 | 30 | −1 | 1 | −1 |
| D | 20 | 100 | 60 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| E | 10 | 75 | 45 | −1 | 0 | 0 |
| F | 20 | 75 | 45 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| G | 15 | 50 | 45 | 0 | −1 | 0 |
| H | 15 | 100 | 45 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| I | 15 | 75 | 30 | 0 | 0 | −1 |
| J | 15 | 75 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| K | 15 | 75 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sample | Instantaneous Power P | Energy Consumed W |
|---|---|---|
| [W] | [Wh] | |
| A | 51.25 | 51.25 |
| B | 63.79 | 31.89 |
| C | 26.61 | 13.31 |
| D | 34.74 | 34.74 |
| E | 43.21 | 32.41 |
| F | 66.44 | 49.83 |
| G | 39.97 | 29.98 |
| H | 42.28 | 31.71 |
| I | 60.53 | 30.27 |
| J | 31.87 | 31.87 |
| K | 41.05 | 30.79 |
| Mg | Si | O | Al | Na |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49.75 | 26.38 | 18.10 | 3.52 | 1.09 |
| Sample | Oxide Layers Thickness d (μm) | Standard Deviation (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 8.49 | 0.23 |
| B | 8.46 | 0.32 |
| C | 8.30 | 0.37 |
| D | 8.25 | 0.49 |
| E | 7.96 | 0.53 |
| F | 8.85 | 0.48 |
| G | 8.34 | 0.50 |
| H | 7.82 | 0.49 |
| I | 8.21 | 0.42 |
| J | 8.07 | 0.44 |
| K | 8.36 | 0.67 |
| Sample | HIT (GPa) | Standard Deviation (GPa) | EIT (GPa) | Standard Deviation (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.71 | 0.32 | 62.16 | 19.10 |
| B | 4.96 | 0.56 | 86.82 | 6.28 |
| C | 2.74 | 0.56 | 75.49 | 9.49 |
| D | 5.48 | 0.77 | 90.12 | 9.89 |
| E | 4.85 | 0.90 | 84.70 | 14.81 |
| F | 4.93 | 0.44 | 79.66 | 12.86 |
| G | 4.13 | 0.54 | 77.38 | 10.54 |
| H | 3.81 | 0.77 | 74.32 | 19.64 |
| I | 4.83 | 0.64 | 67.91 | 9.265 |
| J | 3.64 | 0.60 | 69.81 | 14.04 |
| K | 2.96 | 0.98 | 55.02 | 20.21 |
| Sample | Lc1 (N) | Standard Deviation (N) | Lc2 (N) | Standard Deviation (N) | Lc3 (N) | Standard Deviation (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.54 | 0.36 | 3.24 | 0.39 | 3.83 | 0.31 |
| B | 1.28 | 0.15 | 3.34 | 0.39 | 4.01 | 0.23 |
| C | 1.19 | 0.06 | 3.35 | 0.20 | 4.45 | 0.15 |
| D | 0.65 | 0.41 | 2.59 | 0.28 | 4.59 | 0.16 |
| E | 0.92 | 0.44 | 2.72 | 0.51 | 4.93 | 0.22 |
| F | 1.42 | 0.45 | 3.24 | 0.85 | 4.93 | 0.45 |
| G | 1.50 | 0.33 | 2.89 | 0.24 | 4.33 | 0.31 |
| H | 0.95 | 0.63 | 3.50 | 1.00 | 4.99 | 0.14 |
| I | 1.44 | 0.19 | 3.54 | 0.37 | 4.48 | 0.39 |
| J | 1.25 | 0.26 | 2.78 | 0.22 | 4.26 | 0.38 |
| K | 1.64 | 0.03 | 4.28 | 0.26 | 5.19 | 0.12 |
| Sample | Ra (µm) | Standard Deviation (µm) | Rz (µm) | Standard Deviation (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.420 | 0.025 | 2.460 | 0.164 |
| B | 0.447 | 0.024 | 2.492 | 0.105 |
| C | 0.388 | 0.047 | 2.332 | 0.232 |
| D | 0.479 | 0.069 | 2.773 | 0.311 |
| E | 0.396 | 0.056 | 2.363 | 0.335 |
| F | 0.480 | 0.064 | 2.780 | 0.321 |
| G | 0.444 | 0.058 | 2.545 | 0.270 |
| H | 0.384 | 0.051 | 2.300 | 0.241 |
| I | 0.460 | 0.038 | 2.648 | 0.231 |
| J | 0.470 | 0.048 | 2.706 | 0.241 |
| K | 0.389 | 0.060 | 2.299 | 0.278 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niedźwiedź, M.; Bara, M.; Korzekwa, J.; Barylski, A.; Kaptacz, S. The Influence of the Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Parameters of the Mg-AZ31B Alloy on the Micromechanical and Sclerometric Properties of Oxide Coatings. Coatings 2024, 14, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111446
Niedźwiedź M, Bara M, Korzekwa J, Barylski A, Kaptacz S. The Influence of the Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Parameters of the Mg-AZ31B Alloy on the Micromechanical and Sclerometric Properties of Oxide Coatings. Coatings. 2024; 14(11):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111446
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiedźwiedź, Mateusz, Marek Bara, Joanna Korzekwa, Adrian Barylski, and Sławomir Kaptacz. 2024. "The Influence of the Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Parameters of the Mg-AZ31B Alloy on the Micromechanical and Sclerometric Properties of Oxide Coatings" Coatings 14, no. 11: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111446
APA StyleNiedźwiedź, M., Bara, M., Korzekwa, J., Barylski, A., & Kaptacz, S. (2024). The Influence of the Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Parameters of the Mg-AZ31B Alloy on the Micromechanical and Sclerometric Properties of Oxide Coatings. Coatings, 14(11), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111446








