Rapid Thermal Processing of Kesterite Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodhouse, M.; Jones-Albertus, R.; Feldman, D.; Fu, R.; Horowitz, K.; Chung, D.; Jordan, D.; Kurtz, S. On the Path to SunShot: The Role of Advancements in Solar Photovoltaic Efficiency, Reliability, and Costs; NREL/TP-6A20-65872; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2016. Available online: http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy16osti/65872.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Richter, A.; Hermle, M.; Glunz, S.W. Reassessment of the Limiting Eciency for Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2013, 3, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Hayato, K.; Wataru, Y.; Toru, I.; Katsunori, K.; Kunihiro, N.; Toshihiko, U.; Daisuke, A.; Masanori, K.; Hisashi, U.; et al. Silicon heterojunction solar cell with interdigitated back contacts for a photoconversion efficiency over 26%. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kimoto, Y.; Yasaki, Y.; Kato, T.; Sugimoto, H. Cd-Free Cu(In, Ga)(Se, S)2 Thin-Film Solar Cell With Record Efficiency of 23.35%. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2019, 9, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biplab, S.R.I.; Ali, M.H.; Moon, M.M.A.; Pervez, M.F.; Rahman, M.F.; Hossain, J. Performance enhancement of CIGS-based solar cells by incorporating an ultrathin BaSi2 BSF layer. J. Comput. Electron. 2020, 19, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Ochoa, M.; Lai, H.; Kothandaraman, R.; Fu, F.; Carron, R. Efficiency boost of bifacial Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin-film solar cells for flexible and tandem applications with silver-assisted low-temperature process. Nat. Energy 2023, 8, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranthman, M.P.; Wong-Ng, W.; Bhattacharya, R.N. Semiconductor Materials for Solar Photovoltaic Cells; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-20331-7. [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri, H.; Sasaguchi, N.; Hando, S.; Hoshino, S.; Ohashi, J.; Yokota, T. Preparation and evaluation of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films by sulfurization of E-B evaporated precursors. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1997, 49, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repins, I.L.; Romero, M.J.; Li, J.V.; Wei, S.-H.; Kuciauskas, D.; Jiang, C.-S.; Beall, C.; DeHart, C.; Mann, J.; Hsu, W.-C.; et al. Kesterite Successes, Ongoing Work, and Challenges: A Perspective From Vacuum Deposition. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2013, 3, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Winkler, M.T.; Gunawan, O.; Gokmen, T.; Todorov, T.K.; Zhu, Y.; Mitzi, D.B. Device Characteristics of CZTSSe Thin-Film Solar Cells with 12.6% Efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanyuk, Y.E.; Haass, S.G.; Giraldo, S.; Placidi, M.; Tiwari, D.; Fermin, D.J.; Hao, X.; Xin, H.; Schnabel, T.; Kauk-Kuusik, M.; et al. Doping and alloying of kesterites. J. Phys. Energy 2019, 1, 044004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; He, M.; Green, M.A.; Sun, K.; Hao, X. A Critical Review on the Progress of Kesterite Solar Cells: Current Strategies and Insights. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Duan, B.; Lou, L.; Xin, H. Elemental de-mixing-induced epitaxial kesterite/CdS interface enabling 13%-efficiency kesterite solar cells. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, K.; Yuan, X.; Huang, J.; Green, M.A.; Hao, X. Emergence of flexible kesterite solar cells: Progress and perspectives. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2023, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmo, K.; Altosaar, M.; Pilvet, M.; Mikli, V.; Grossberg, M.; Danilson, M.; Raadik, T.; Kauk-Kuusik, M.; Josepson, R.; Krustok, J. The effect of Ag alloying of Cu2(Zn,Cd)SnS4 on the monograin powder properties and solar cell performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 24281–24291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljina, J.; Zhang, R.; Ganchev, M.; Raadik, T.; Volobujeva, O.; Altosaar, M. Formation of Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber layers for solar cells by electrodeposition annealing route. Thin Solid Films 2013, 537, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurr, R.; Hölzing, A.; Jost, S.; Hock, R.; Voß, T.; Schulze, J.; Kirbs, A.; Ennaoui, A.; Lux-Steiner, M.; Weber, A.; et al. The crystallisation of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cell absorbers from coelectroplated Cu-Zn-Sn precursors. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 2465–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomé, P.M.P.; Fernandez, P.A.; da Cunha, A.F. Morphological and structural characterization of Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin films grown by selenization of elemental precursor layers. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 2531–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganchev, M.; Iljina, J.; Kaupmees, L.; Raadik, T.; Volobujeva, O.; Altosaar, M.; Mere, A.; Raudoja, J.; Mellikov, E. Phase composition of selenized Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin films determined by X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 7394–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.A.; Salomé, P.M.P.; da Cunha, A.F. Growth and Raman scattering characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 2519–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.S.; Parkin, I.P.; Hardy, A.M.E.; Clark, R.J.H.; Hibbert, T.G.; Molloy, K.C. Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition of Tin Sulfides (SnS, Sn2S3, and SnS2) on Glass. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmrich, M.; Haeuseler, H. Lattice Vibration-Spectra Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Spectrosc. 1991, 47, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altosaar, M.; Raudoja, J.; Timmo, K.; Danilson, M.; Grossberg, M.; Krustok, J.; Mellikov, E. Cu2Zn1−xCdxSn(Se1−y Sy)4 solid solutions as absorber materials for solar cells. Phys. Status Solidi A 2008, 205, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossberg, M.; Krustok, J.; Raudoja, J.; Timmo, K.; Altosaar, M.; Raadik, T. Photoluminescence and Raman study of Cu2ZnSn(SexS1−x)4 monograins for photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films 2010, 519, 7403–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-M.; Hyun, M.-H.; Nam, S.; Lee, D.; O, B.; Lee, K.-S.; Yu, P.Y.; Choi, Y.D. Resonant Raman scattering measurements of strains in ZnS epilayers grown on GaP. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 9429–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.A.; Salome, P.M.P.; da Cunha, A.F. A study of ternary Cu2SnS3 and Cu3SnS4 thin films prepared by sulfurizing stackedmetal precursors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 215403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, H.R.; Humphreys, R.G.; Zwick, U.; Cardona, M. Infrared and Raman spectra of the IV–VI compounds SnS and SnS2. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 15, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, S.; Weber, A.; Honkimäki, V.; Schock, H.-W. In-situ investigation of the kesterite formation from binary and ternary sulphides. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, W.; Nitsche, R. Tetrahedral quaternary chalcogenides of the type Cu2 II IV S4(Se4). Mater. Res. Bull. 1974, 9, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.G.; da Cunha, A.F.; Fernandes, P.A.; Teixeira, J.P.; Sousa, R.A.; Leitão, J.P. Effect of rapid thermal processing conditions on the properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films and solar cell performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 126, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scragg, J.J.S.; Choubrac, L.; Lafond, A.; Ericson, T.; Platzer-Björkman, C. A low-temperature order-disorder transition in Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 041911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.; Choubrac, L.; Lafond, A.; Guillot-Deudon, C.; Jobic, S. Solid-State NMR and Raman Spectroscopy to Address the Local Structure of Defects and the Tricky Issue of the Cu/Zn Disorder in Cu-Poor, Zn-Rich CZTS, Materials. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 8646–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
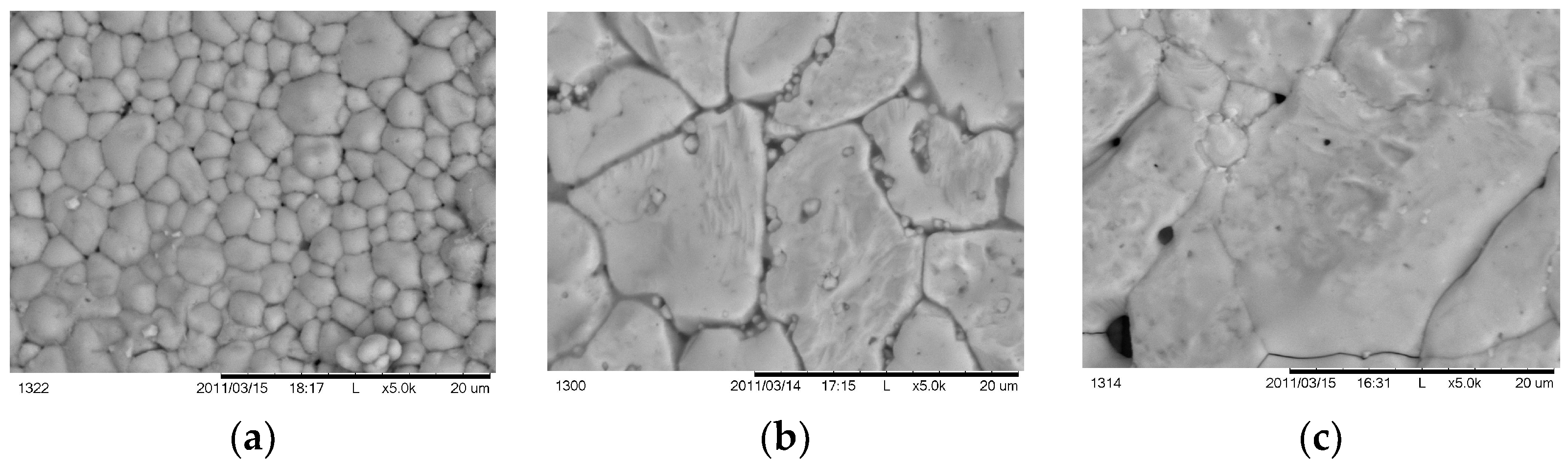
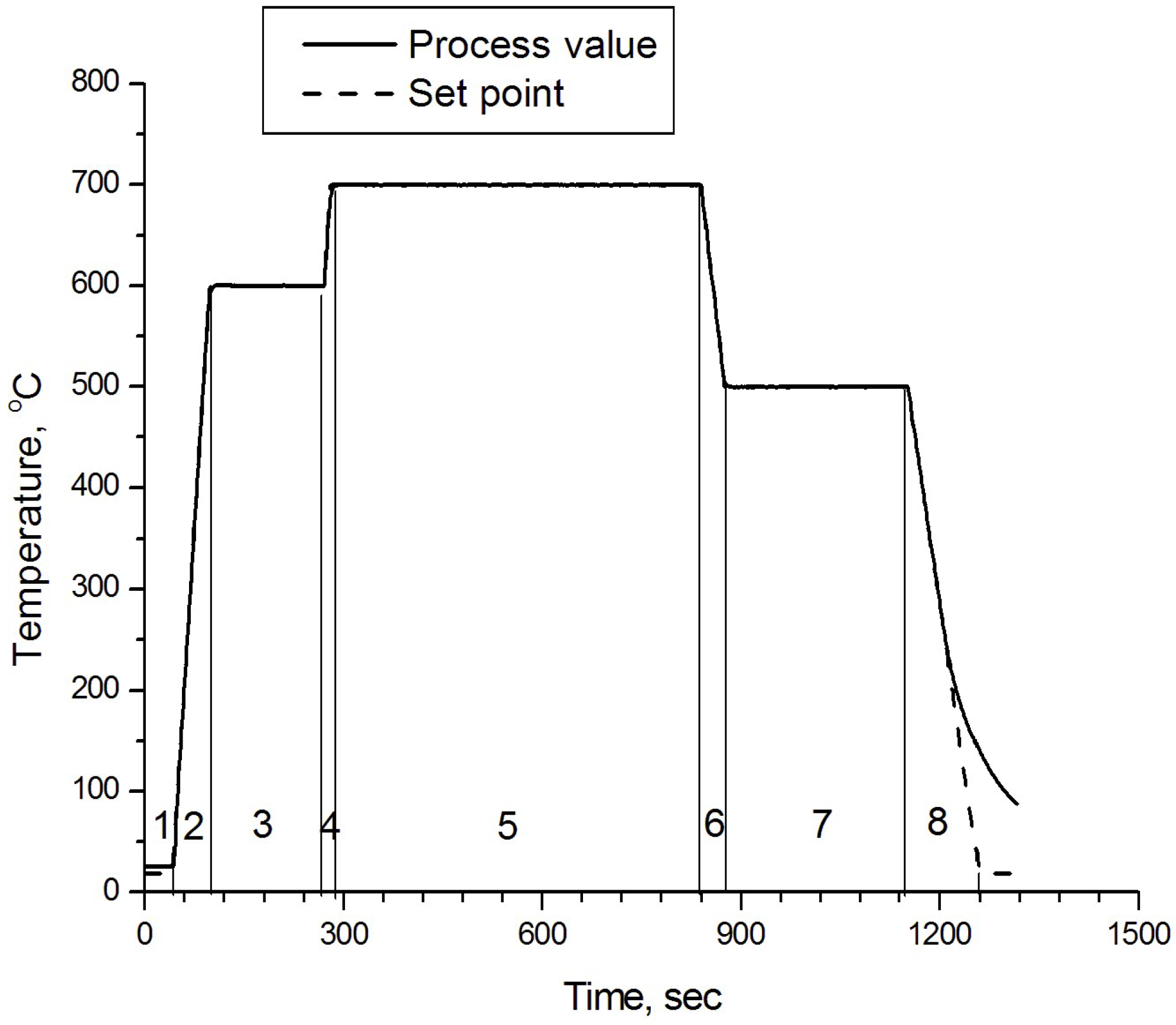


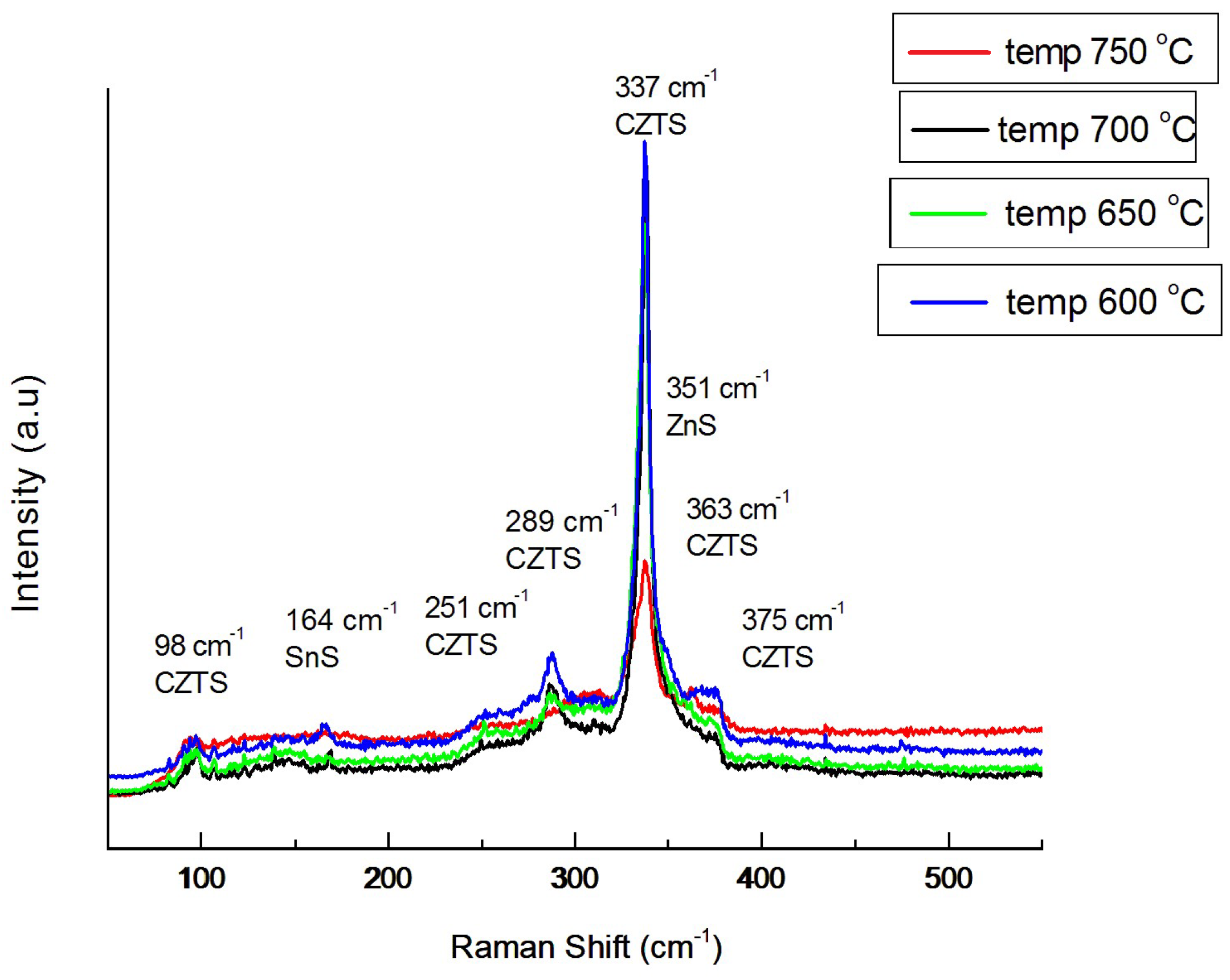
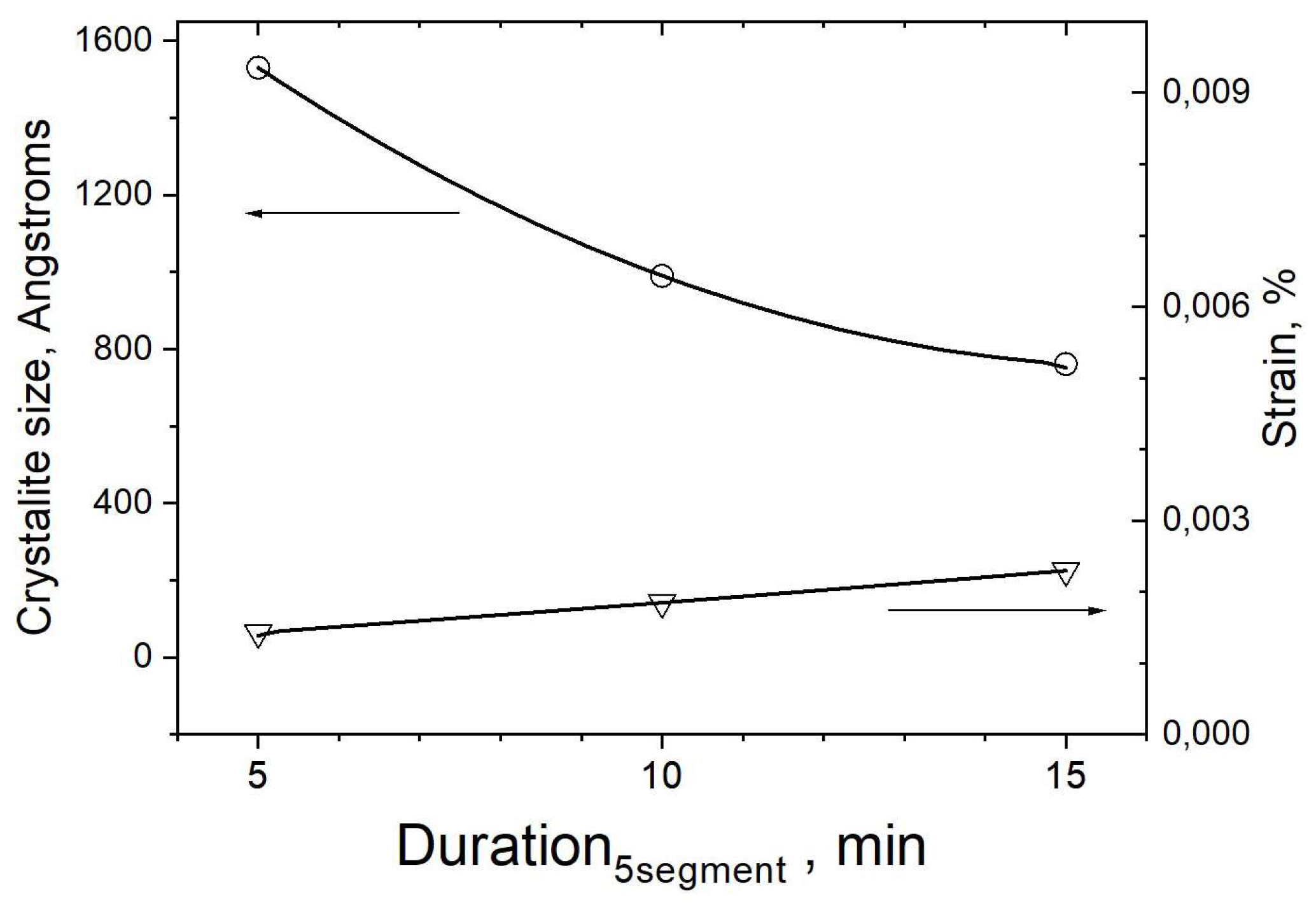
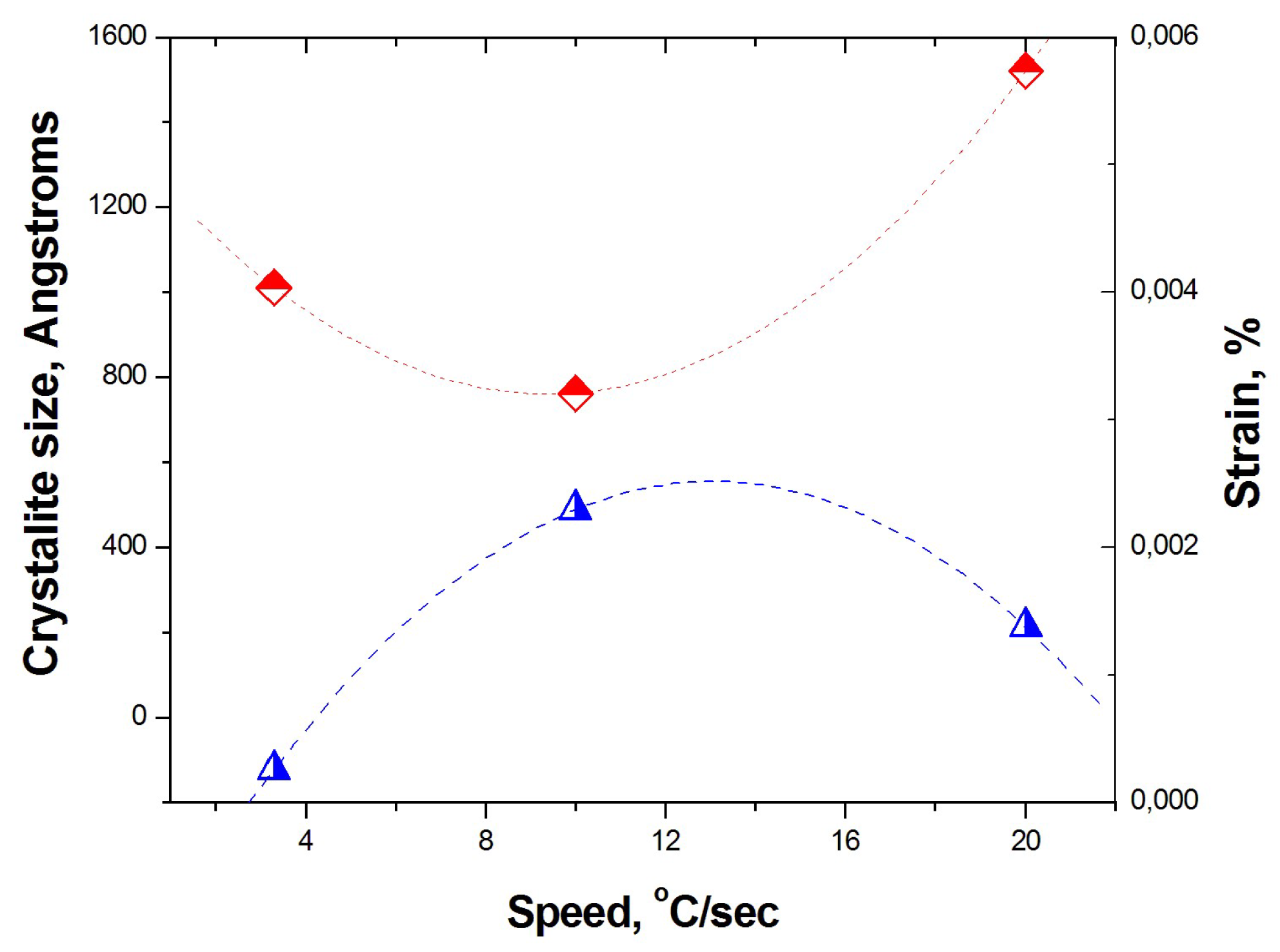
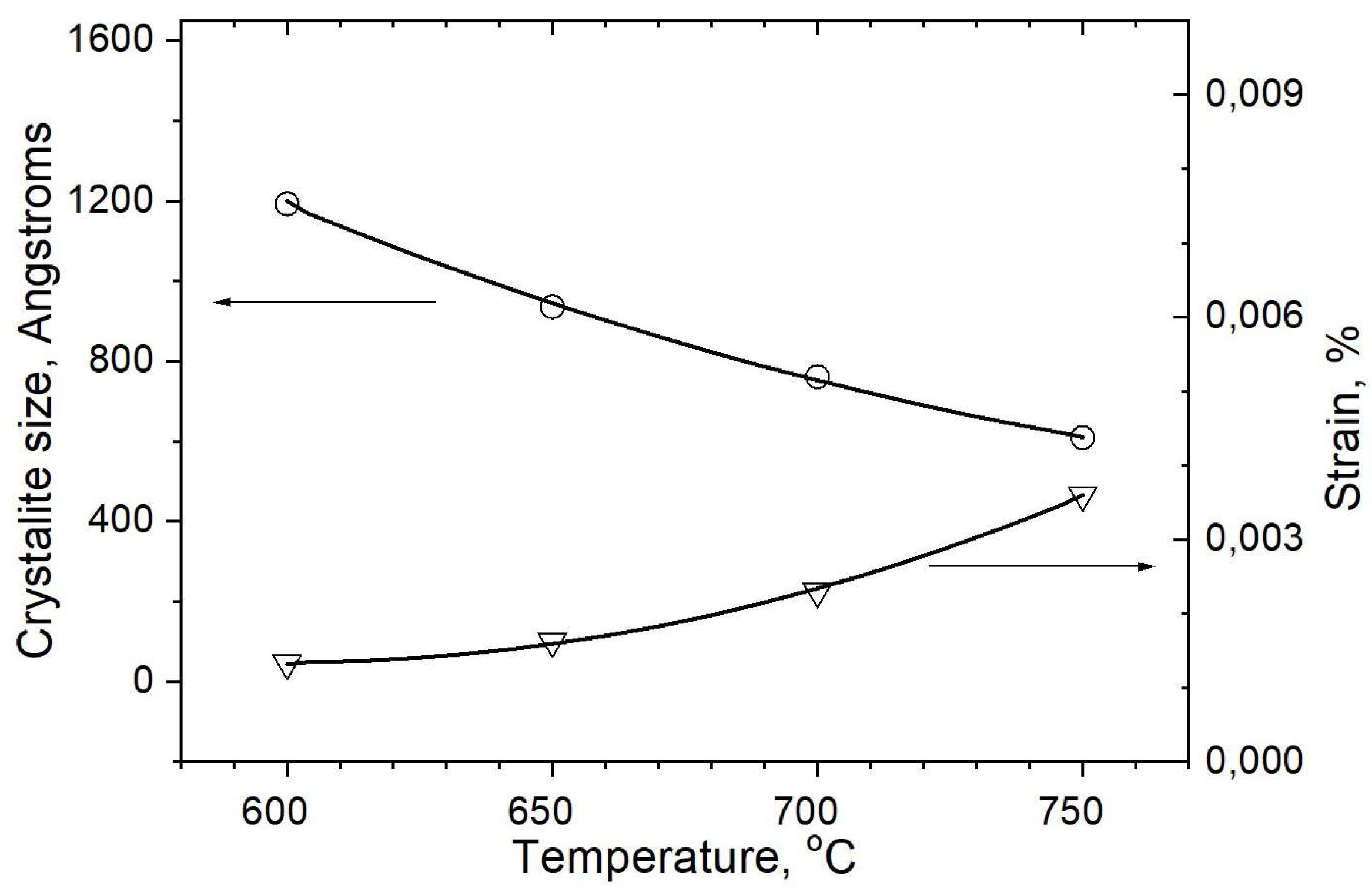
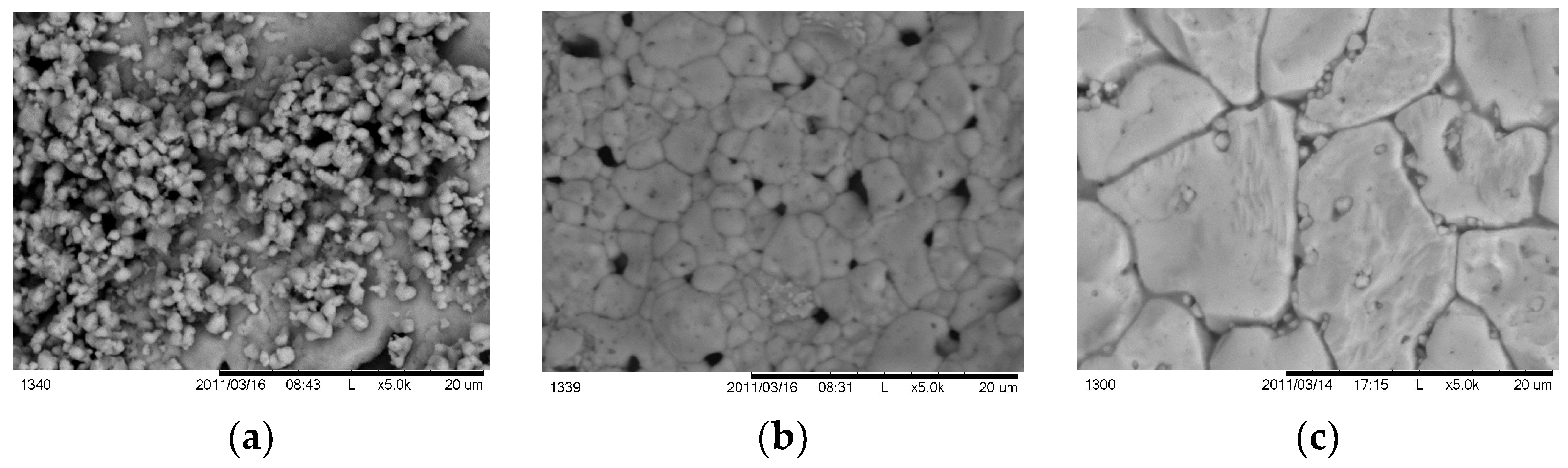


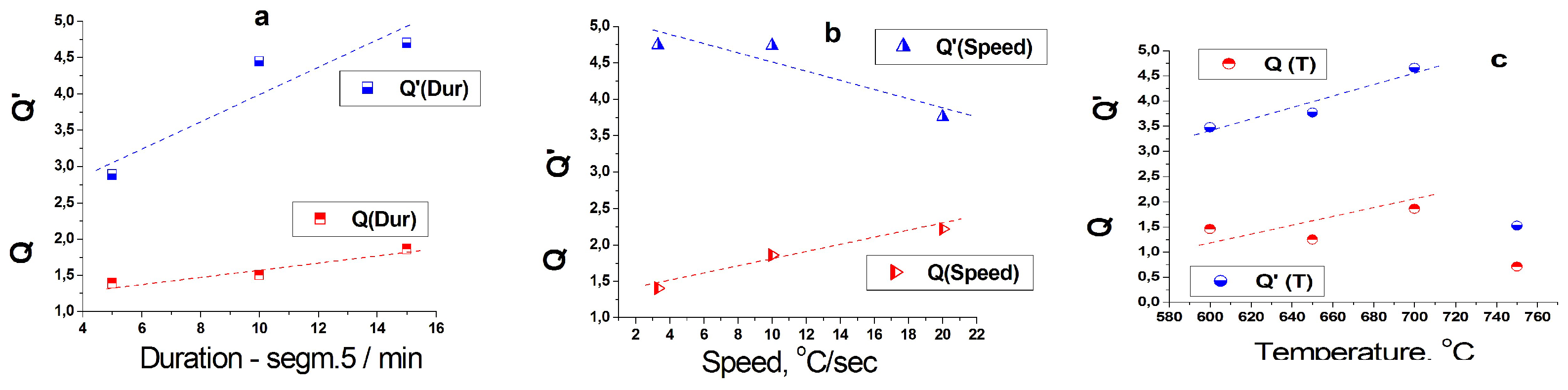
| Probe | Base | Duration | Duration | Speed Fast | Speed Slow | T °C 750 °C | T °C 650 °C | T °C 600 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 Seg | 19 °C 10 s | 19 °C 10 s | 19 °C 10 s | 19 °C 10 s | 19 °C 10 s | 19 °C 10 s | 19 °C 10 s | 19 °C 10 s |
| 2 Seg | 600 °C 1 min | 600 °C 1 min | 600 °C 1 min | 600 °C 30 s | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 1 min | 600 °C 1 min | 600 °C 1 min |
| 3 Seg | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 3 min | 600 °C 3 min |
| 4 Seg | 700 °C 10 s | 700 °C 10 s | 700 °C 10 s | 700 °C 5 s | 700 °C 30 s | 750 °C 10 s | 650 °C 5 s | 600 °C 5 s |
| 5 Seg | 700 °C 15 min | 700 °C 10 min | 700 °C 5 min | 700 °C 15 min | 700 °C 15 min | 700 °C 15 min | 700 °C 15 min | 700 °C 15 min |
| 6 Seg | 500 °C 40 s | 500 °C 40 s | 500 °C 40 s | 500 °C 20 s | 500 °C 2 min | 500 °C 45 s | 500 °C 15 s | 500 °C 15 s |
| 7 Seg | 500 °C 5 min | 500 °C 5 min | 500 °C 5 min | 500 °C 5 min | 500 °C 5 min | 500 °C 5 min | 500 °C 5 min | 500 °C 5 min |
| 8 Seg | 19 °C 2 min | 19 °C 2 min | 19 °C 2 min | 19 °C 1 min | 19 °C 10 min | 19 °C 2 min | 19 °C 2 min | 19 °C 2 min |
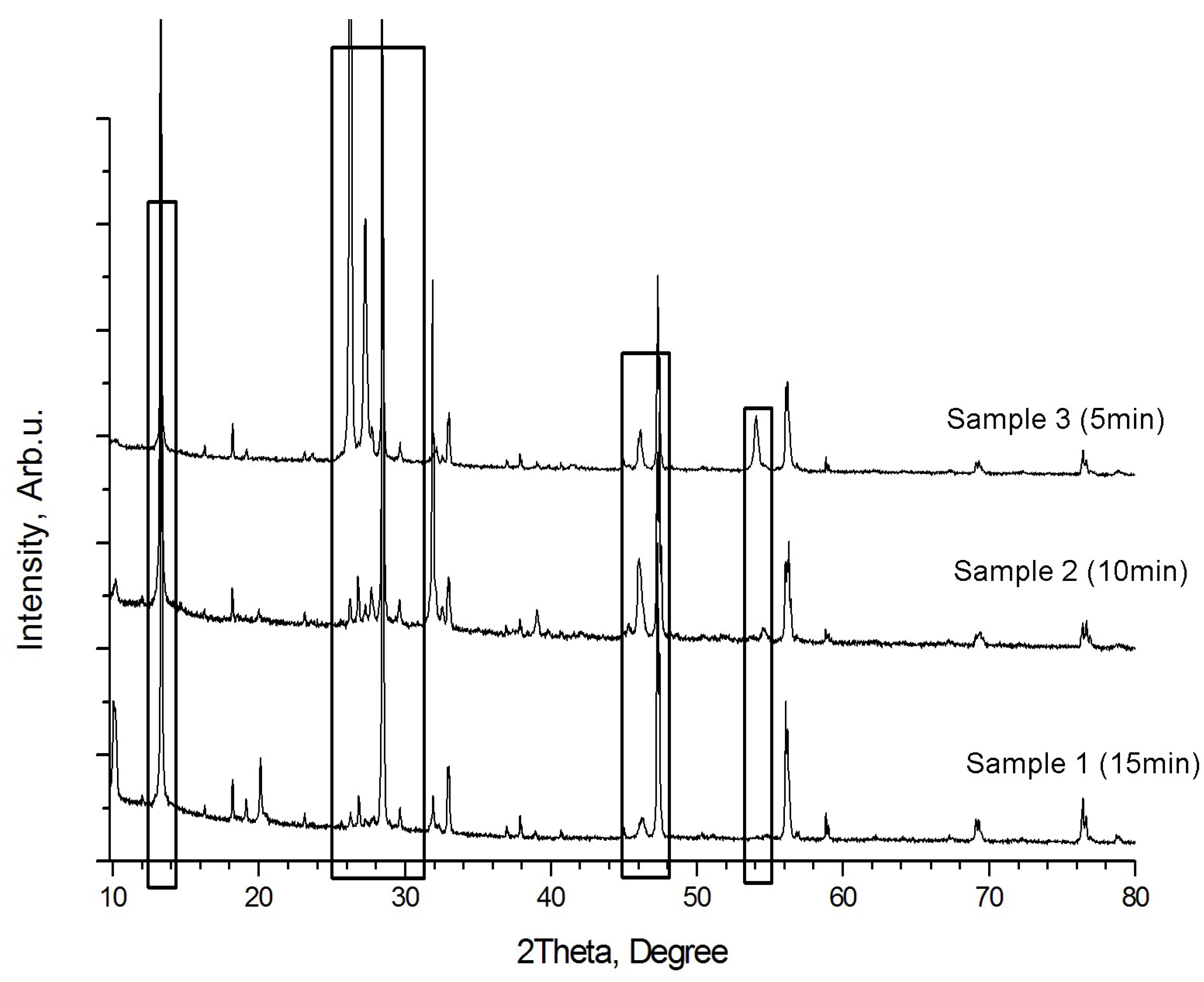
| Sample | Process | Cu2ZnSnS4 Kesterite-4122 | ZnS h | SnS | CuS Covellite | Cu7S4 Roxbyite | Cu2S digenite | ZnS h | ZnS h | ZnS(W) 0688h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
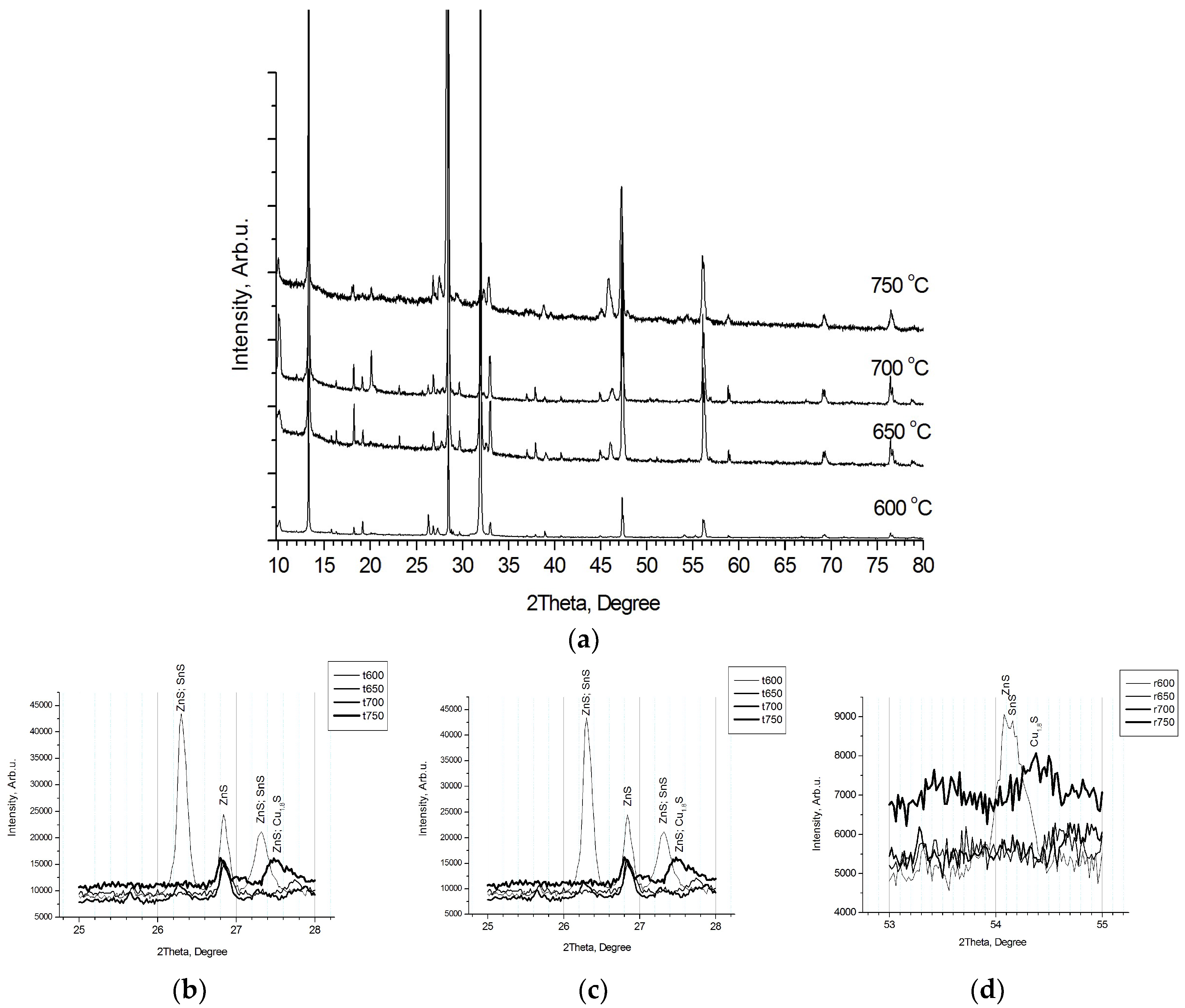
| 1 | Base 15 min, 700 °C | ●+ | ●2201+ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊− | ●2424 | ●2195 | ◊ |
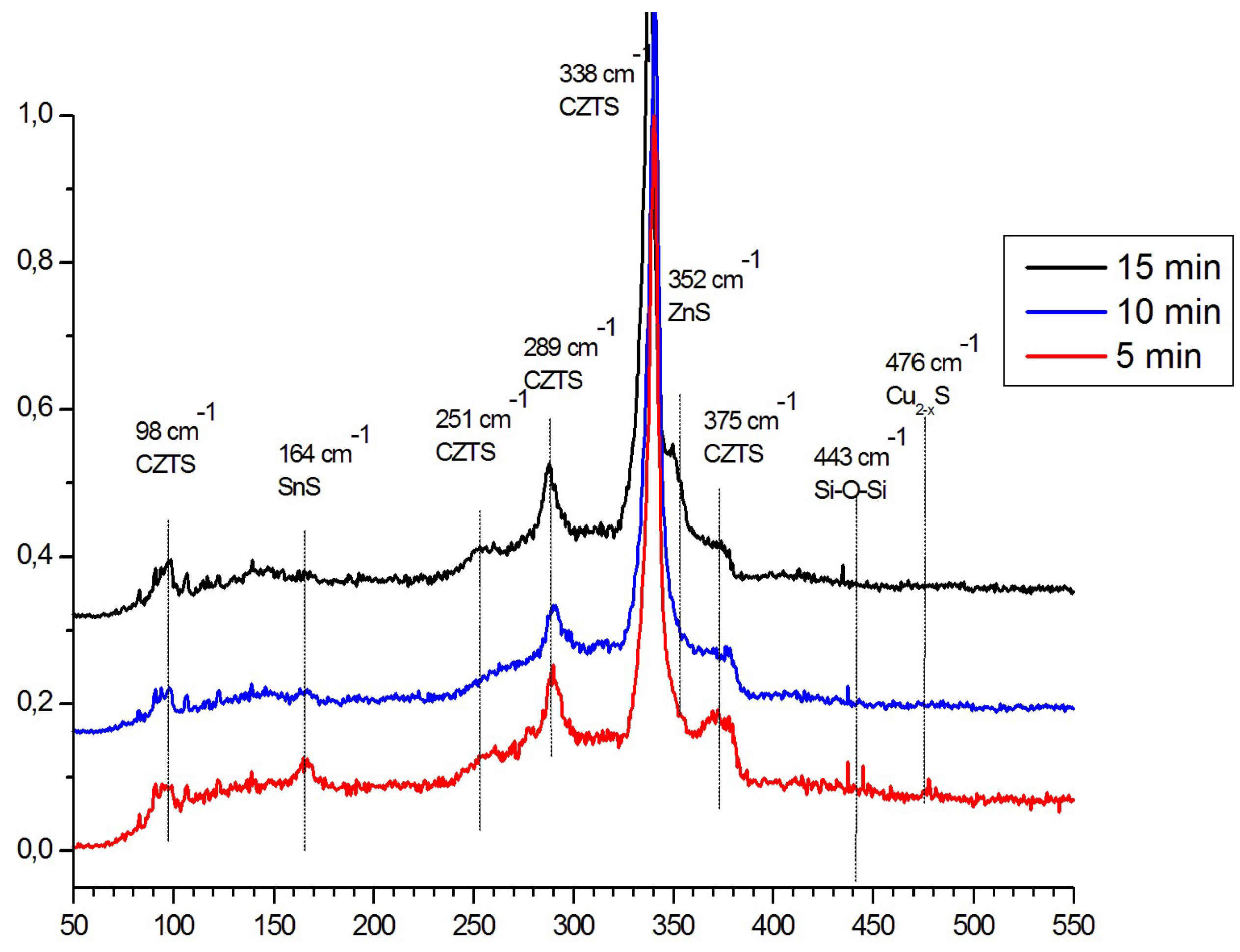
| 2 | Time—10 min | ●+ | ●2347 | ●+ | ● | ● | ◊− | ◊ | ◊ | ● |
| 3 | Time—5 min | ●+ | ◊ | ●+ | ● | ● | ◊− | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ |
| 4 | Speed—Fast | ●+ | ●4998+ | ● | ◊ | ◊ | ◊± | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ |
| 5 | Speed—Slow | ●+ | ●6022+ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ |
| 6 | Temp—750 °C | ●+ | ●2140 | ◊− | ◊ | ◊ | ●9133/− | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ |
| 7 | Temp—650 °C | ●+ | ●4989 | ●+ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊± | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ |
| 8 | Temp—600 °C | ●+ | ●6009 | ●+ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ |
| 1 | Base—700 °C | ●+ | ●2201+ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊ | ◊± | ●2424 | ●2195 | ◊ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganchev, M.; Spasova, S.; Raadik, T.; Mere, A.; Altosaar, M.; Mellikov, E. Rapid Thermal Processing of Kesterite Thin Films. Coatings 2023, 13, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081449
Ganchev M, Spasova S, Raadik T, Mere A, Altosaar M, Mellikov E. Rapid Thermal Processing of Kesterite Thin Films. Coatings. 2023; 13(8):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081449
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanchev, Maxim, Stanka Spasova, Taavi Raadik, Arvo Mere, Mare Altosaar, and Enn Mellikov. 2023. "Rapid Thermal Processing of Kesterite Thin Films" Coatings 13, no. 8: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081449
APA StyleGanchev, M., Spasova, S., Raadik, T., Mere, A., Altosaar, M., & Mellikov, E. (2023). Rapid Thermal Processing of Kesterite Thin Films. Coatings, 13(8), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081449







