Influence of Silver-Coated Tool Electrode on Electrochemical Micromachining of Incoloy 825
Abstract
1. Introduction
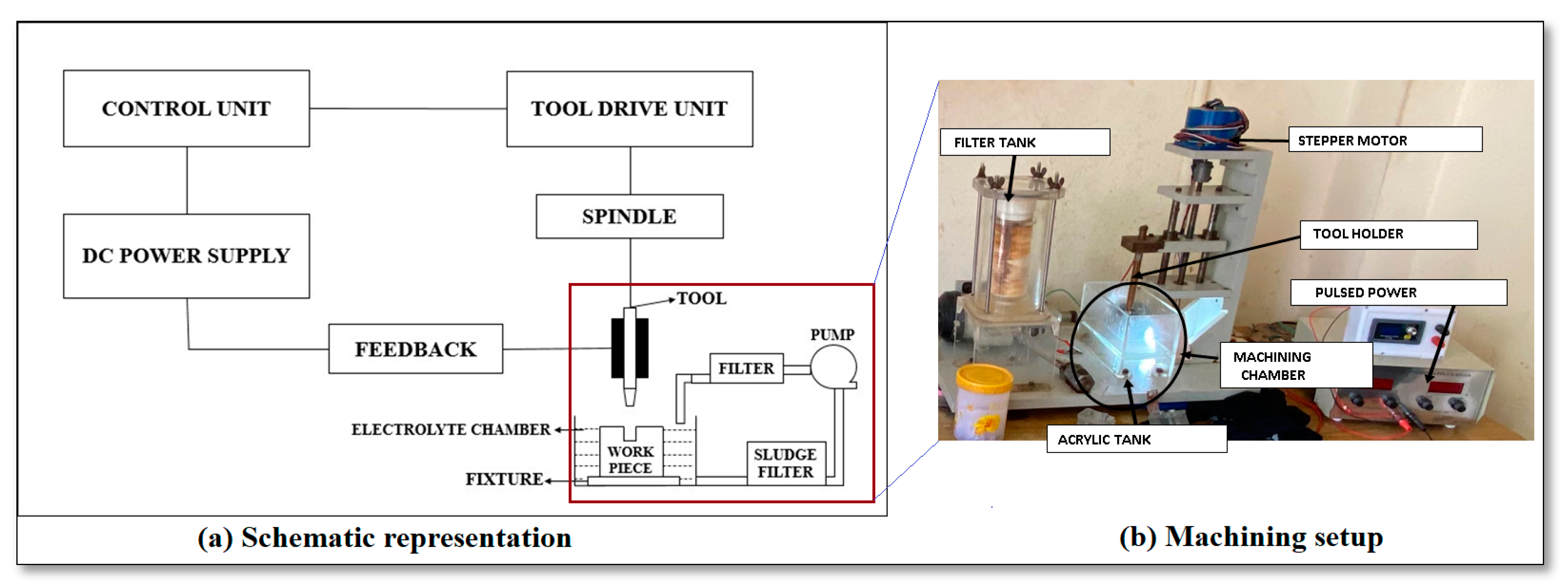
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Workpiece and Electrode
2.2. Electroplating Arrangement for Ag-Coated Copper Electrode
2.3. Selection of Electrolyte
2.4. Selection of the Process Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Analysis of Ag-Coated and Uncoated Copper Tool Electrode
3.2. Electrical Conductivity Analysis of Ag-Coated and Uncoated Copper Tool Electrode
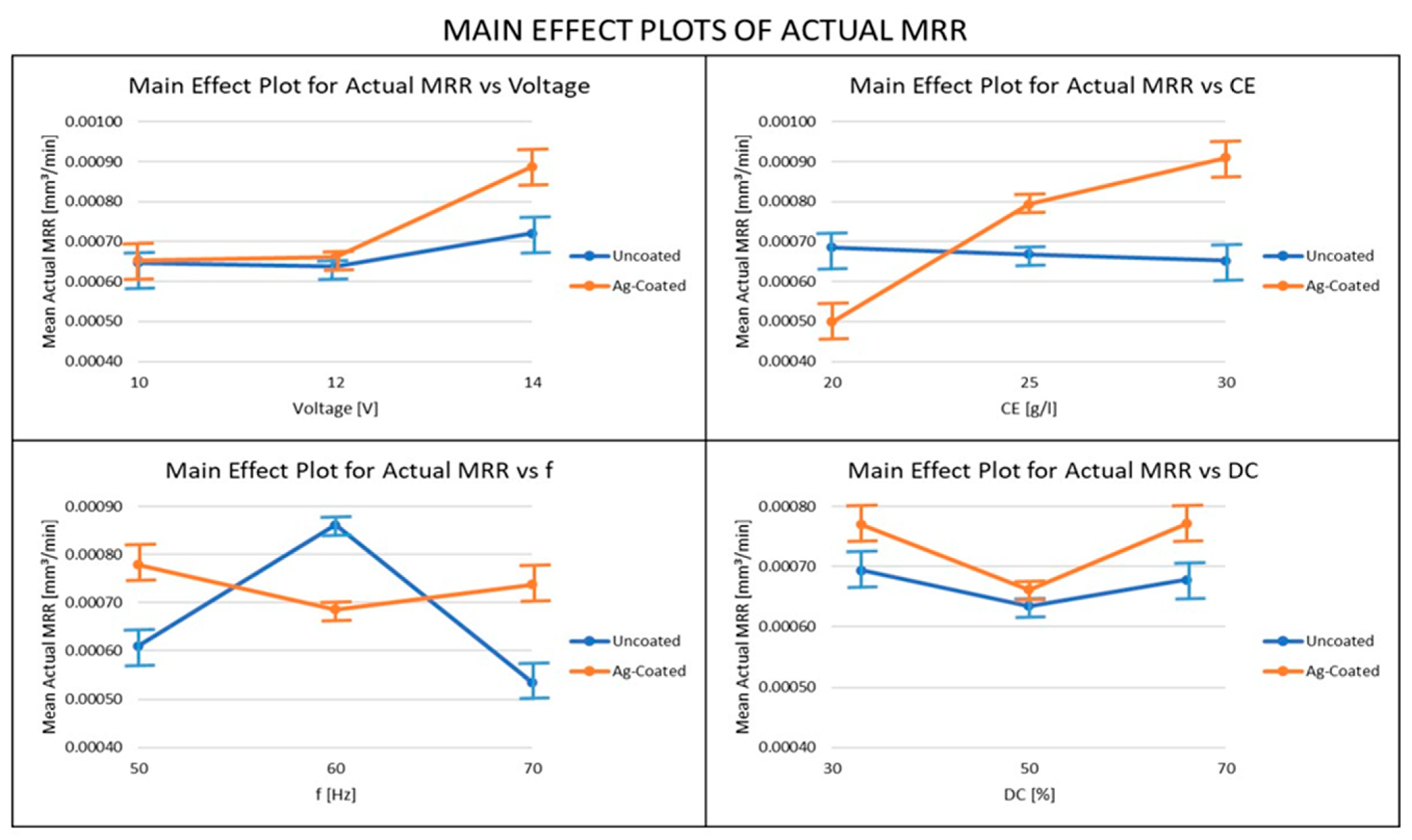
3.3. Influence of Ag-Coated Electrode and Process Parameters on Actual MRR
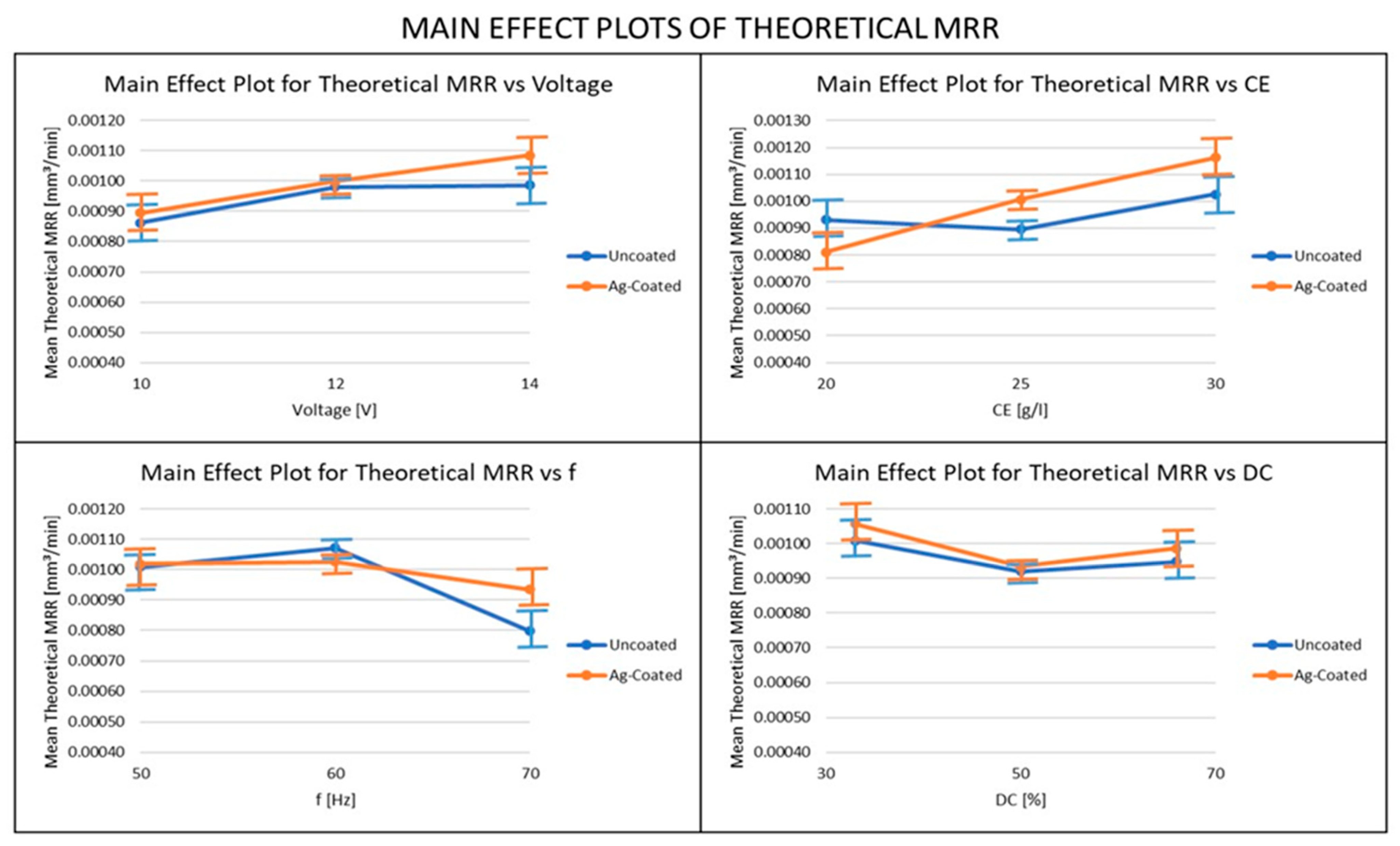
3.4. Influence of Ag-Coated Electrode and Process Parameters on Theoretical MRR
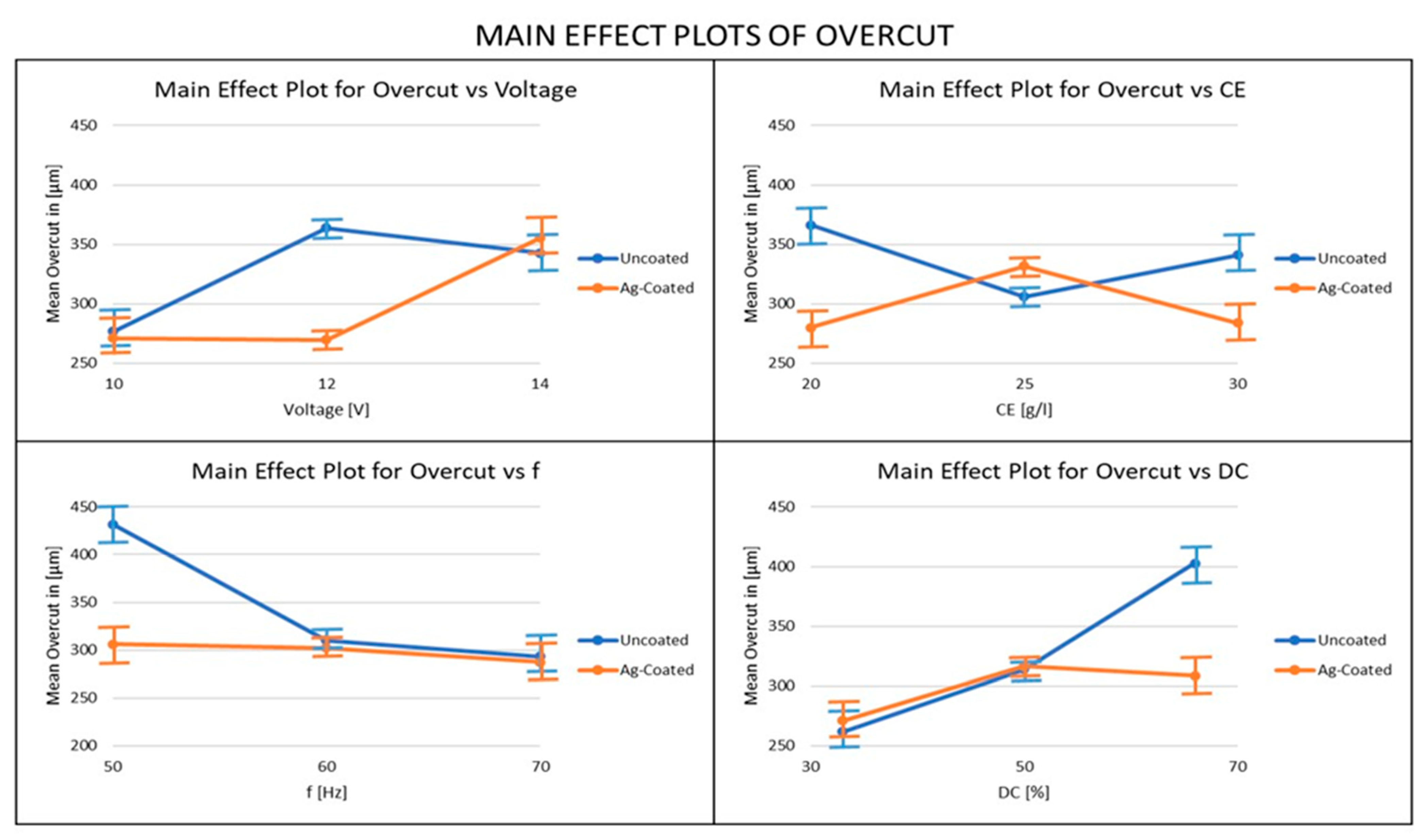
3.5. Influence of Ag-Coated Electrode and Process Parameters on Overcut
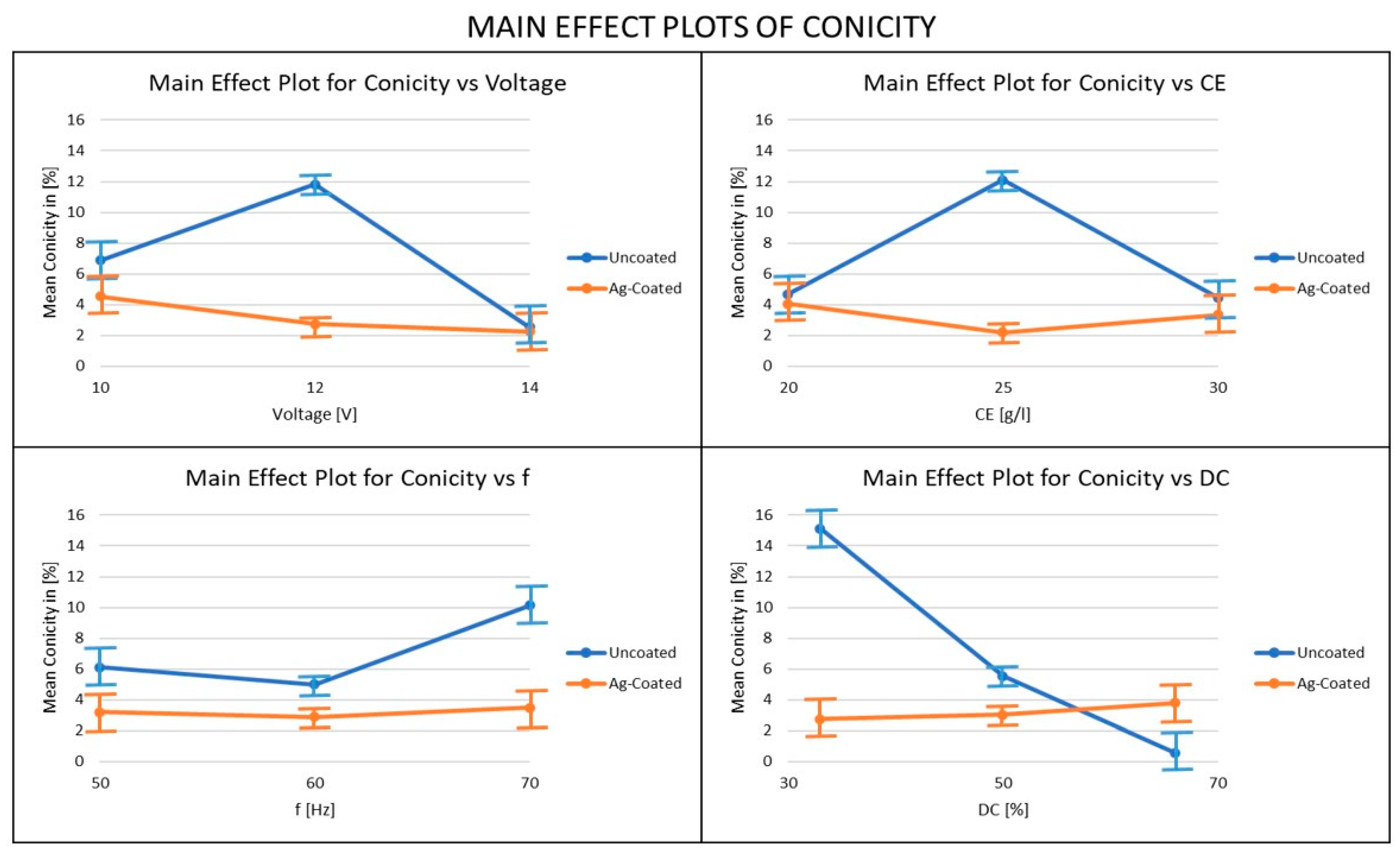
3.6. Influence of Ag-Coated Electrode and Process Parameters on Conicity
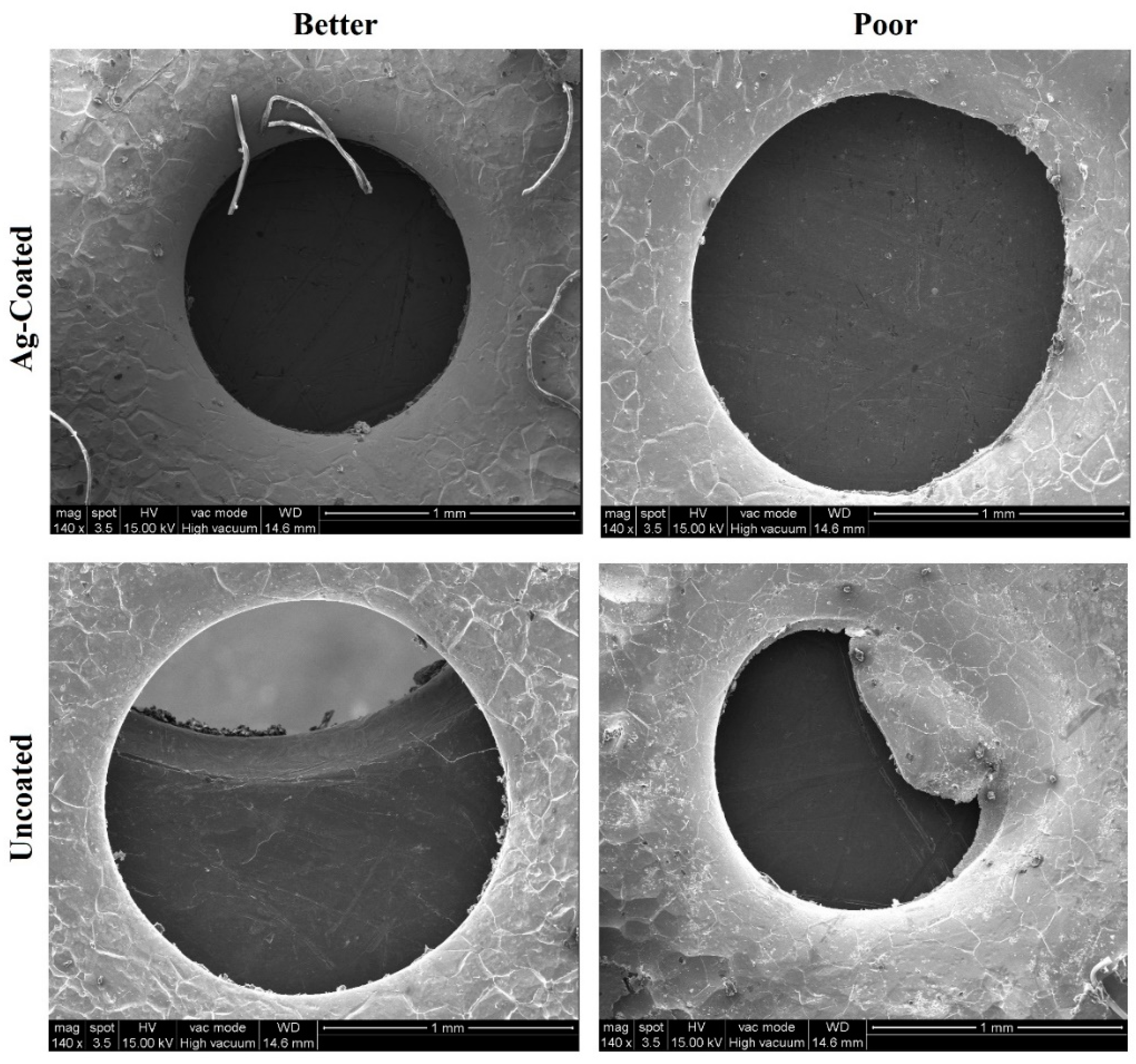
3.7. SEM Analysis of the Workpiece Specimen and Tool Electrode
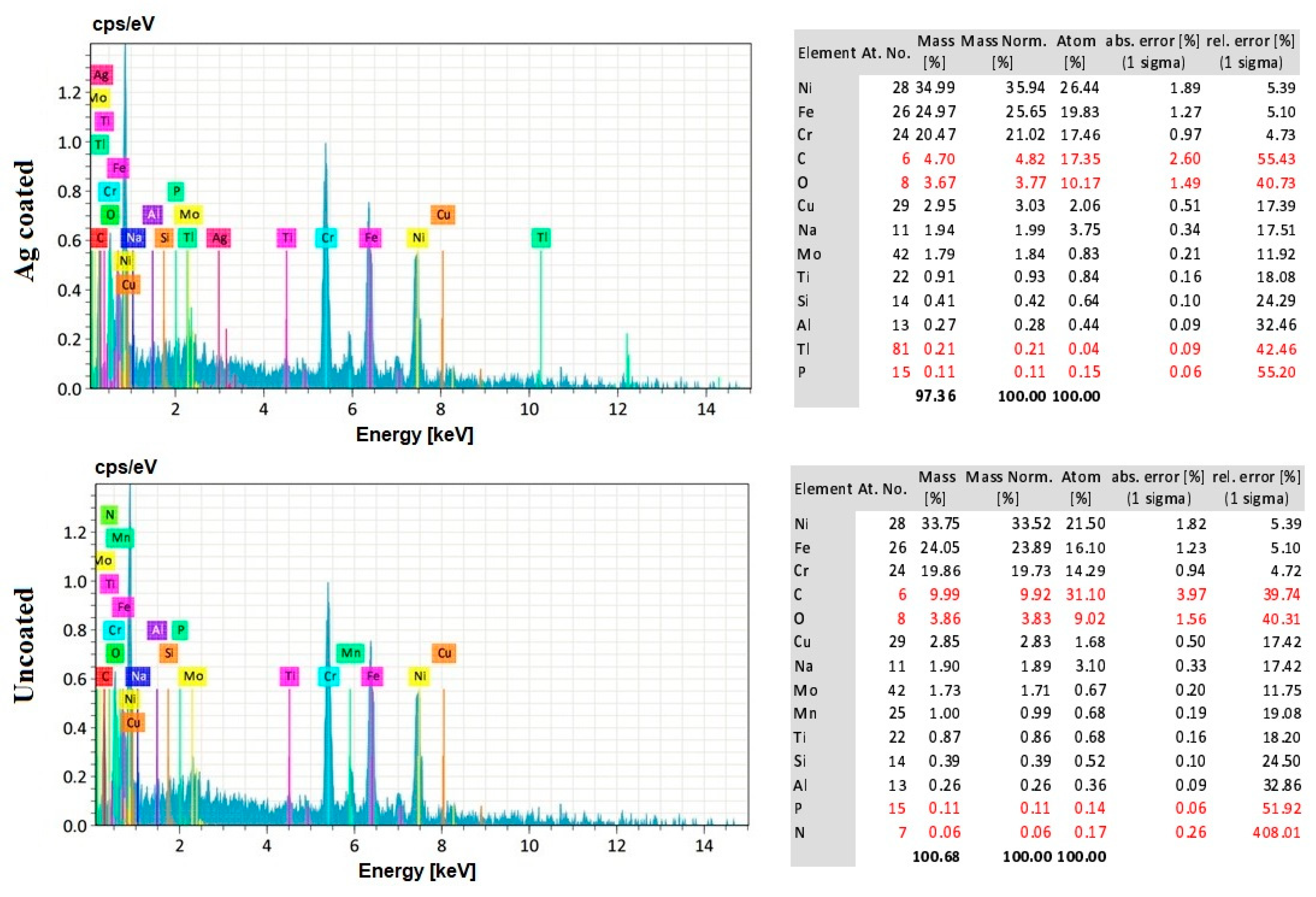
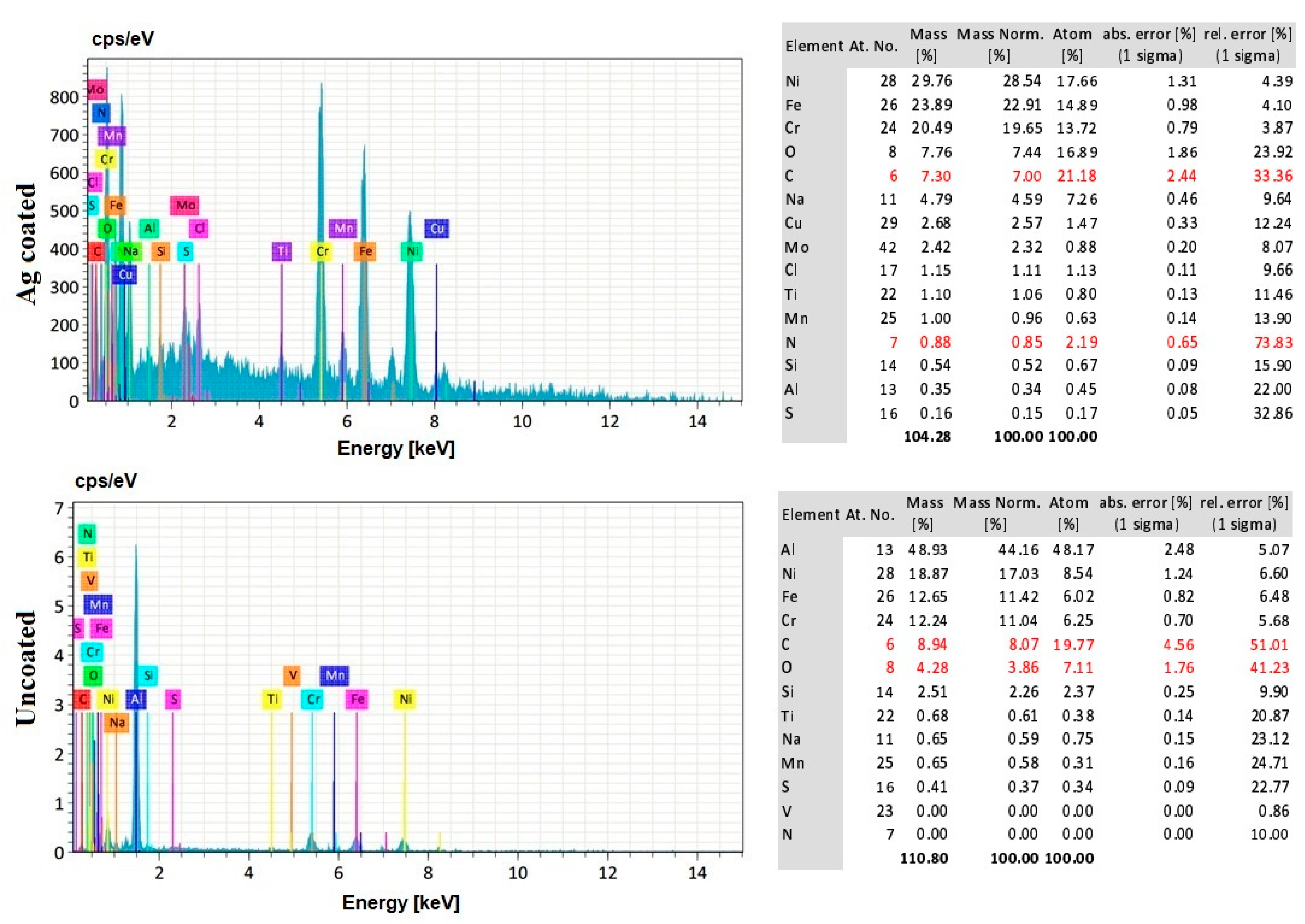
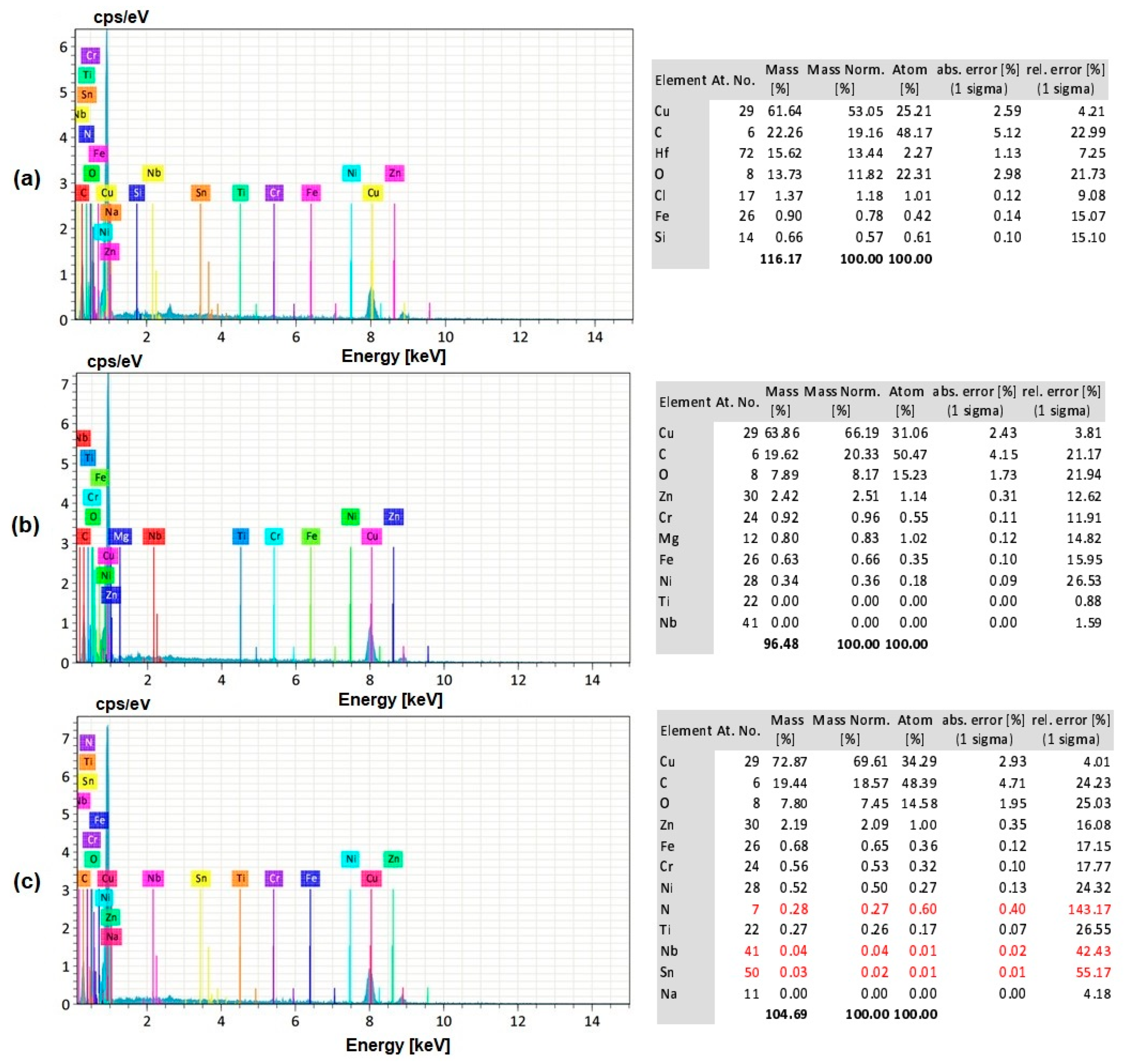
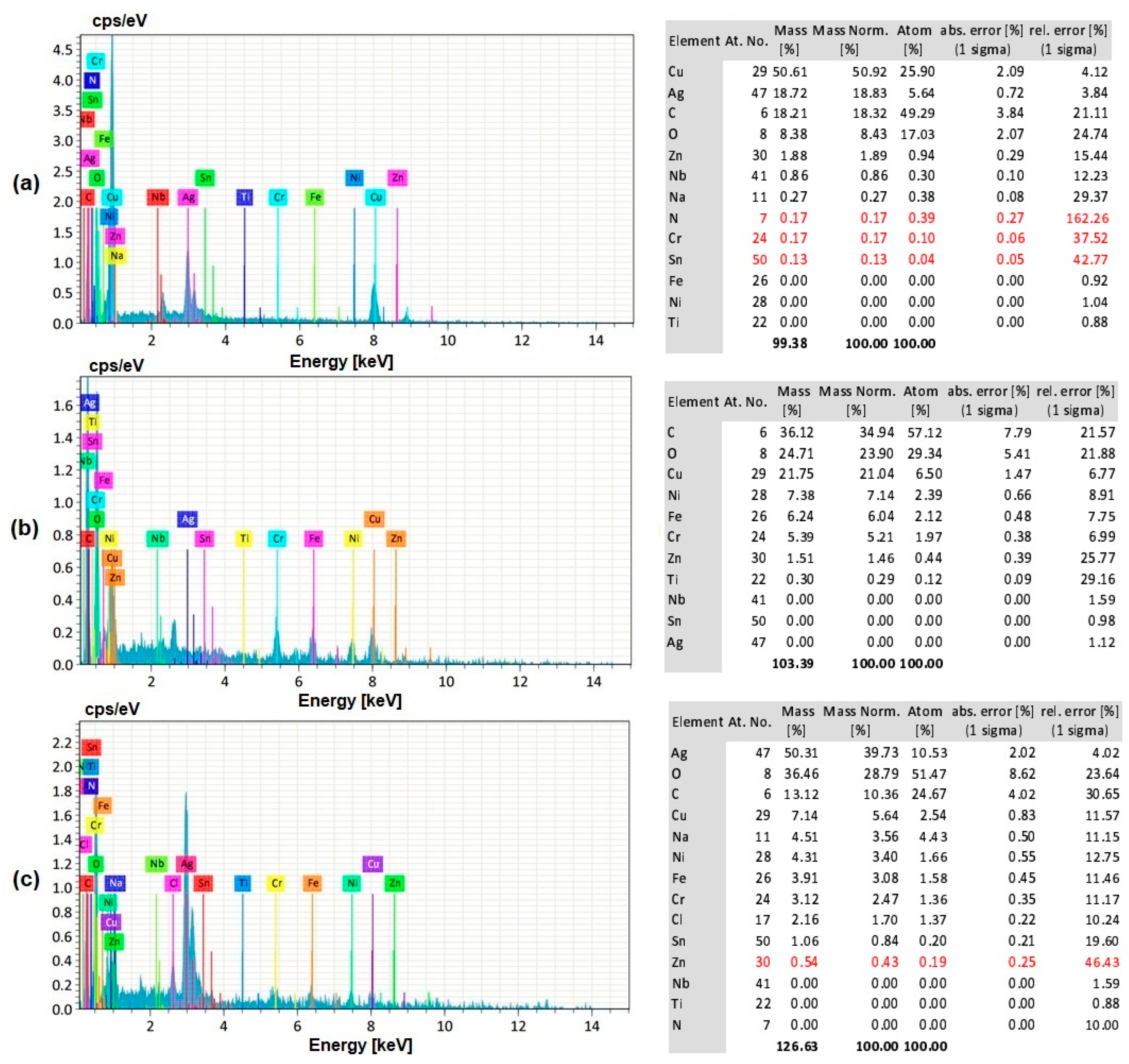
3.8. EDS Analysis of the Workpiece Specimen and Tool Electrode
4. Conclusions
- The MRR obtained using the Silver-coated copper tool was higher than the uncoated tool electrode in most cases, because of the high electrical conductivity obtained in the Silver-coated copper tool electrode. For both the actual and theoretical MRR, the pulse frequency was the most important parameter when the uncoated electrode was used, whereas the electrolyte concentration was the most important parameter, when the coated electrode was used. From these results, it can be recommended that, in order to achieve higher productivity in the ECMM process, a coated electrode and high values of voltage, electrolyte concentration, and duty cycle should be used, along with relatively low-frequency values.
- The overcut results obtained using the silver-coated copper tool electrode were better when compared to the uncoated tool electrode, since the Silver-coated copper tool electrode has a fine grain structure that restricts the flow of electrons. For the overcut, the most important parameter was the duty factor when the uncoated electrode was used and the voltage when the coated electrode was used. From these results, it can be recommended that, in order to achieve lower overcut, a coated electrode and low values of voltage, electrolyte concentration, and duty cycle should be used, along with high-frequency values.
- The conicity levels are generally higher with an uncoated copper tool electrode. For conicity, when the uncoated electrode was used the duty factor was the most important parameter, whereas when the coated electrode was used, the voltage was the most important parameter. In order to minimize conicity, it is recommended that a coated electrode should be used at high voltage, moderate electrolyte concentration, low frequency, and low-duty cycle conditions.
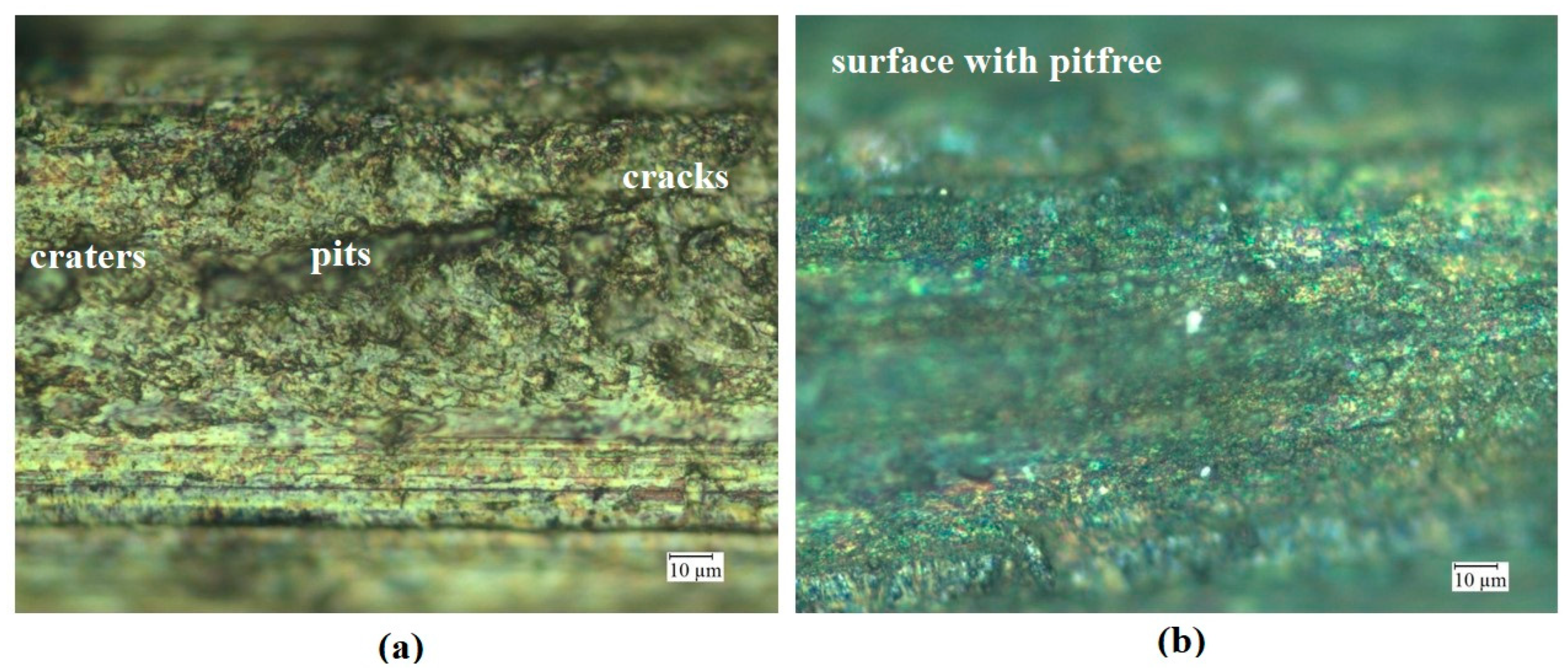
- The silver-coated copper tool electrode tends to have fewer cracks, pit formations, and corroded regions than the uncoated copper tool electrode because of silver coating, which acted as a corrosion shield when coming into contact with carbon contented electrolyte dissolution.
- The EDS analysis revealed that when a silver-coated copper tool electrode was used, it could produce fewer particles of tool electrode over the machined surface without affecting real constituents of the workpiece specimens. Under harsher conditions, the embedment of workpiece elements on the tool electrode is increased. Finally, the removal of Ag coating was correlated to the energy input, mainly represented by the duty cycle, as higher amount of Ag was removed at lower duty cycle values, when the energy is applied in a shorter duration.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kangazian, J.; Sayyar, N.; Shamanian, M. Influence of Microstructural Features on the Mechanical Behavior of Incoloy 825 Welds. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2017, 6, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Lao, Z.; Wei, H.; Li, J.; Bei, H.; Zhang, Z. Site Occupancy of Alloying Elements in Γ′ Phase of Nickel-Base Single Crystal Superalloys. Intermetallics 2020, 121, 106772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-N.; Bor, H.-Y.; Chang, L. The Effects of Carbon Content on the Microstructure and Elevated Temperature Tensile Strength of a Nickel-Base Superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3741–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Devarasiddappa, D. Development of ANN Modelling for Estimation of Weld Strength and Integrated Optimization for GTAW of Inconel 825 Sheets Used in Aero Engine Components. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.C. The Superalloys, Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, C.; Stoloff, N.S.; Hagel, W.C. (Eds.) Superalloys II; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Moiduddin, K.; Mian, S.M.; Alkhalefah, H.; Umer, U. Performance Analysis of Electrochemical Micro Machining of Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy under Different Electrolytes Concentrations. Metals 2021, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Kalaichelvan, K. Influence of Process Parameters on Machinability of Inconel 718 by Electrochemical Micromachining Process using TOPSIS Technique. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 7945–7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajurkar, K.P.; Sundaram, M.M.; Malshe, A.P. Review of Electrochemical and Electrodischarge Machining. Procedia CIRP 2013, 6, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Moiduddin, K.; Alkhalefah, H.; Mahalingam, S.; Karmiris-Obratański, P. Multiobjective Optimization of Heat-Treated Copper Tool Electrode on EMM Process Using Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) Algorithm. Materials 2022, 15, 4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Geethapriyan, T.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Shanmugam, R.; Ramoni, M. Influence of heat-treated Cu-Be electrode on machining accuracy in ECMM with Monel 400 alloy. Arch. Civil. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, C.; Wang, G.; Qu, N.; Zhu, D. A Study of Electrochemical Machining of Ti-6Al-4V in NaNO3 Solution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harugade, M.; Kavade, M.V.; Hargude, N. Effect of Electrolyte Solution on Material Removal Rate in Electrochemical Discharge Machining. IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2013, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Manikandan, N.; Kumanan, S.; Sathiyanarayanan, C. Multiple Performance Optimization of Electrochemical Drilling of Inconel 625 Using Taguchi Based Grey Relational Analysis. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Duraisamy, S.; Palanisamy, P.; Veeramani, A. Optimization of the Machining Parameters in the Electrochemical Micro-Machining of Nickel. Mater. Tehnol. 2018, 52, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Kalaichelvan, K.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Rajadurai, A. Performance analysis of process parameters on machining α-β titanium alloy in electrochemical micromachining process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B J. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 232, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Kong, Q.; Tong, H.; Zhong, H. Silicon-Based Tool Electrodes for Micro Electrochemical Machining. Precis. Eng. 2018, 52, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, R.; Ramoni, M.; Thangamani, G.; Thangaraj, M. Influence of Additive Manufactured Stainless Steel Tool Electrode on Machinability of Beta Titanium Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, K.; Hayashi, A.; Hirai, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ota, M. Drilling of Microholes Using Electrochemical Machining. Precis. Eng. 2018, 54, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithu, M.A.H.; Fantoni, G.; Ciampi, J.; Santochi, M. On How Tool Geometry, Applied Frequency and Machining Parameters Influence Electrochemical Microdrilling. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, A.K.; Sundaram, M.M.; Rajurkar, K.P. Use of Coated Microtools in Advanced Manufacturing: An Exploratory Study in Electrochemical Machining (ECM) Context. J. Manuf. Process. 2012, 14, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, B.; Malapati, M.; Munda, J.; Sarkar, A. Influence of Tool Vibration on Machining Performance in Electrochemical Micro-Machining of Copper. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, B.; Bhattacharyya, B. Generation of Microfeatures on Stainless Steel by Electrochemical Micromachining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, B.; Mäder, T.; Fürderer, B.; Nestler, D.; Reinecke, H. Carbon Fibres Used as Electrode Tools for Micro-Electrochemical Machining. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Composite Materials, Edinburgh, UK, 27–31 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, D. Experimental Research on Electrochemical Machining of Titanium Alloy Ti60 for a Blisk. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2016, 29, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanigaivelan, R.; Arunachalam, R. Study on Influence of Tool Design on Electrochemical Micromachining. Manuf. Technol. Today 2011, 10, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Anasane, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, B. Experimental Investigation into Micromilling of Microgrooves on Titanium by Electrochemical Micromachining. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, S.; Arularasu, M.; Ganesan, K. A Study on Electrochemical Micromachining of Super Duplex Stainless Steel for Biomedical Filters. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 7, 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyappan, S.; Sivakumar, K. Experimental Investigation on the Performance Improvement of Electrochemical Machining Process Using Oxygen-Enriched Electrolyte. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 75, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.K.; Thomas, B. A Comparative Study of Electrochemical Machining Process Parameters by Using GA and Taguchi Method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 263, 062038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttarwar, S.S.; Chopde, I.K. A Study of Influence of Electrochemical Process Parameters on the Material Removal Rate and Surface Roughness of SS AISI 304. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Res. 2013, 3, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Kalaichelvan, K. Experimental Investigation of Electrochemical Micromachining Process Parameters on Pure-Titanium Using Taguchi-Grey Relational Analysis. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2016, 852, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Kalaichelvan, K.; Muthuramalingam, T. Influence of Coated Tool Electrode on Drilling Inconel Alloy 718 in Electrochemical Micro Machining. Procedia CIRP 2016, 46, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Thangamani, G.; Kalaichelvan, K. Multi Performance Optimization of Electrochemical Micro-Machining Process Surface Related Parameters on Machining Inconel 718 Using Taguchi-Grey Relational Analysis. Metall. Ital. 2016, 2016, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nugroho, A.W.; Sudarisman; Nurahman, M.B.; Septiaji, P. Overcut and material removal rate on electrochemical machining of aluminum and stainless steel using isolated brass electrode. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference of Industrial, Mechanical, Electrical, Chemical Engineering (ICIMECE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 6–7 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Padhan, S.; Das, S.R. Analysis on hole overcut during micro-EDM of Inconel 718. Mater. Today Proceed. 2022, 56, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, T. Experimental investigation of machined hole and optimization of machining parameters using electrochemical machining. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4354–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, M.; Chavoshi, S.Z. Prediction and analysis of radial overcut in holes drilled by electrochemical machining process. Cent. Eur. J. Eng. 2013, 3, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, S.; Hiremath, S.S. Machining of holes on SS316L with solid and hollow tool electrodes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2022, 37, 1859–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, J.; Hariharan, P. Investigation of electrochemical machining on SS304 using NaCl and NaNO3 as electrolyte. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2022, 37, 1790–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Teimouri, R.; Baseri, H. Study of tool wear and overcut in EDM process with rotary tool and magnetic field. Adv. Tribiol. 2012, 2012, 895918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machno, M.; Matras, A.; Szkoda, M. Modelling and analysis of the effect of EDM-Drilling parameters on the machining performance of Inconel 718 using the RSM and ANNs methods. Materials 2022, 15, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, G.; Merla, C. Workpiece and electrode influence on micro-EDM drilling performance. Precis. Eng. 2014, 38, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Pei, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Analysis of surface quality of multi-film cooling holes in nickel-based single crystal superalloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekkumar, P.; Soundrapandian, E.; Tajdeen, A.; Prashanth, T. Experimental study of Electrochemical micromachining on Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy. In Advances in Materials Research. Springer Proceedings in Materials; Kumaresan, G., Shanmugam, N.S., Dhinakaran, V., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, M.; Shan, H.S. A review of electrochemical macro- to micro-hole drilling processes. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machno, M.; Bogucki, R.; Szkoda, M.; Bizoń, W. Impact of the deionized water on making high aspect ratio holes in the Inconel 718 Alloy with the use of Electrical Discharge Drilling. Materials 2020, 13, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, N.H.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Tran, V.D. Effect of ultrasonic low frequency vibration and its direction on machinability in WEDM process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2022, 37, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Moiduddin, K.; Akash, R.; Krishnan, S.; Mian, S.H.; Ameen, W.; Alkhalefah, H. Influence of process parameters on dimensional accuracy of machined Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) alloy in Laser Beam Machining Process. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2020, 132, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Elements | Ni | Fe | Cr | Mo | Cu | Ti | C | Mg | Si | S | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (%) | 42.2 | 30.89 | 19.9 | 2.74 | 1.637 | 0.81 | 0.022 | 0.71 | 0.36 | 0.001 | 0.116 |
| Chemical | Concentration |
|---|---|
| AgNO3 | 15 g/L |
| KCL | 15 g/L |
| Na2S2O3 | 40 g/L |
| C4H4O2Na2 | 30 g/L |
| Exp No. | Applied Voltage [V] | Electrolyte Concentration [g/L] | Frequency [Hz] | Duty Cycle [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 33 |
| 2 | 10 | 25 | 60 | 50 |
| 3 | 10 | 30 | 70 | 66 |
| 4 | 12 | 20 | 60 | 66 |
| 5 | 12 | 25 | 70 | 33 |
| 6 | 12 | 30 | 50 | 50 |
| 7 | 14 | 20 | 70 | 50 |
| 8 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 66 |
| 9 | 14 | 30 | 60 | 33 |
| Electrode | Electrical Conductivity [Ω−1/mm] | |
|---|---|---|
| Before Machining | After Machining | |
| Uncoated | 31.41 | 2.93 |
| Ag coated | 34.58 | 3.48 |
| S. No | V [V] | CE [g/L] | f [Hz] | DC [%] | Actual MRR [mm3/min] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoated | Ag Coated | |||||
| 1 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 33 | 0.00063 | 0.000499 |
| 2 | 10 | 25 | 60 | 50 | 0.000805 | 0.000592 |
| 3 | 10 | 30 | 70 | 66 | 0.000505 | 0.00087 |
| 4 | 12 | 20 | 60 | 66 | 0.000858 | 0.000415 |
| 5 | 12 | 25 | 70 | 33 | 0.000529 | 0.00076 |
| 6 | 12 | 30 | 50 | 50 | 0.000529 | 0.000809 |
| 7 | 14 | 20 | 70 | 50 | 0.000569 | 0.000584 |
| 8 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 66 | 0.000671 | 0.001029 |
| 9 | 14 | 30 | 60 | 33 | 0.000923 | 0.001051 |
| S. No | V [V] | CE [g/L] | f [Hz] | DC [%] | Theoretical MRR [mm3/min] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoated | Ag Coated | |||||
| 1 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 33 | 0.00098 | 0.000804 |
| 2 | 10 | 25 | 60 | 50 | 0.000921 | 0.000882 |
| 3 | 10 | 30 | 70 | 66 | 0.000804 | 0.001 |
| 4 | 12 | 20 | 60 | 66 | 0.001078 | 0.000843 |
| 5 | 12 | 25 | 70 | 33 | 0.000804 | 0.001019 |
| 6 | 12 | 30 | 50 | 50 | 0.001058 | 0.001137 |
| 7 | 14 | 20 | 70 | 50 | 0.000784 | 0.000784 |
| 8 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 66 | 0.00096 | 0.001117 |
| 9 | 14 | 30 | 60 | 33 | 0.001215 | 0.001352 |
| S. No | V [V] | CE [g/L] | f [Hz] | DC [%] | Overcut [μm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoated | Ag Coated | |||||
| 1 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 33 | 284.5 | 232.4 |
| 2 | 10 | 25 | 60 | 50 | 223.3 | 325.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 30 | 70 | 66 | 330.0 | 255.2 |
| 4 | 12 | 20 | 60 | 66 | 429.9 | 264.4 |
| 5 | 12 | 25 | 70 | 33 | 246.3 | 264.2 |
| 6 | 12 | 30 | 50 | 50 | 415.6 | 280.4 |
| 7 | 14 | 20 | 70 | 50 | 302.6 | 343.4 |
| 8 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 66 | 448.4 | 405.7 |
| 9 | 14 | 30 | 60 | 33 | 277.3 | 316.2 |
| S. No | V [V] | CE [g/L] | f [Hz] | DC [%] | Conicity [Degree] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoated | Ag Coated | |||||
| 1 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 33 | 11.55 | 4.98 |
| 2 | 10 | 25 | 60 | 50 | 8.27 | 3.06 |
| 3 | 10 | 30 | 70 | 66 | 0.80 | 5.60 |
| 4 | 12 | 20 | 60 | 66 | 0.86 | 3.92 |
| 5 | 12 | 25 | 70 | 33 | 27.93 | 1.60 |
| 6 | 12 | 30 | 50 | 50 | 6.67 | 2.73 |
| 7 | 14 | 20 | 70 | 50 | 1.64 | 3.25 |
| 8 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 66 | 0.07 | 1.88 |
| 9 | 14 | 30 | 60 | 33 | 5.86 | 1.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thangamani, G.; Thangaraj, M.; Anand, P.I.; Jayakumar, M.; Karkalos, N.E.; Papazoglou, E.L.; Karmiris-Obratański, P. Influence of Silver-Coated Tool Electrode on Electrochemical Micromachining of Incoloy 825. Coatings 2023, 13, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050963
Thangamani G, Thangaraj M, Anand PI, Jayakumar M, Karkalos NE, Papazoglou EL, Karmiris-Obratański P. Influence of Silver-Coated Tool Electrode on Electrochemical Micromachining of Incoloy 825. Coatings. 2023; 13(5):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050963
Chicago/Turabian StyleThangamani, Geethapriyan, Muthuramalingam Thangaraj, Palani Iyamperumal Anand, Mani Jayakumar, Nikolaos E. Karkalos, Emmanouil L. Papazoglou, and Panagiotis Karmiris-Obratański. 2023. "Influence of Silver-Coated Tool Electrode on Electrochemical Micromachining of Incoloy 825" Coatings 13, no. 5: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050963
APA StyleThangamani, G., Thangaraj, M., Anand, P. I., Jayakumar, M., Karkalos, N. E., Papazoglou, E. L., & Karmiris-Obratański, P. (2023). Influence of Silver-Coated Tool Electrode on Electrochemical Micromachining of Incoloy 825. Coatings, 13(5), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050963










