Abstract
Silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) are a promising material for nanomedicine technology. SiNPs are considered a powerful tool for drug delivery, functional coatings and films, and biomolecule separation due to their stability, biocompatibility, and accessible surface modification. Herein, the synthesis of SiNPs and SiNPs nylon 6 (SiNPs-Nylon) coated nanocomposites was proposed. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) were used for morphology, size, and stability analysis. Anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) loading to the nanocomposites and pH-dependent release experiments are presented. DOX-loaded nanocomposites with high drug capacities of up to 258 μg/mg (DOX/SiNPs) and 493 μg/mg (DOX/SiNPs-Nylon) show effective inhibition of A549 and HEK 293FT cell lines. The IC50 values were 0.08 ± 0.01 µM in terms of DOX amount and recalculated as 0.31 ± 0.04 µg/mL in terms of the concentration of SiNPs for the HEK 293FT cells. Therefore, silica nanocomposites have a high potential for cancer treatment.
1. Introduction
Silica nanoparticles or silicon dioxide nanoparticles (SiNPs) are widely used for various biological applications [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. SiNPs are cost-effective and excellent drug-delivery agents due to intrinsic properties such as high stability, large pore volume, ease of synthesis and surface modification, and good tissue biocompatibility for oral and intravenous injection [4,6,7,9,11,12,13,18,20,24]. The size, morphology, and structure of SiNPs and pores can be fine-tuned [5,17,22]. Due to the above properties, SiNPs are promising candidates for designing multifunctional biomedical tools, including delivery systems for therapy and biosensors [25,26,27,28,29]. However, it is difficult to obtain a non-toxic and stable SiNPs core with a high capacity for therapeutics. Many parameters should be considered for nanomedicine applications, including size, surface energy, and possible interactions with biopolymers which highly alters biodistribution.
SiNPs may serve as stimuli-responsive carriers for the delivery area [2,30]. pH variations from plasma (~7.4) to the extracellular media of tumors (5–6) allow producing effective pH-sensitive SiNPs for cancer treatment such as breast, lung, and colorectal cancer [11,20,31,32]. However, pH-mediated triggered delivery of drugs is a feature area requiring a share of art in design development. Porous SiNP was used for various drug-loading, including doxorubicin (DOX). DOX is an effective chemotherapeutic drug against various cancers [33,34]. Although DOX is associated with various side effects, it is widely used in clinical practice [33,34]. Many works are focused on the synthesis of smart DOX-loaded nanoparticles to reduce their harmful effects [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. However, DOX-loaded SiNPs in the published works show only low-efficient drug binding (µg/mg, DOX/SiNPs): 1–10 [44,45,46,47,48,49,50], 15–20 [51,52], 50–75 [4,27,53,54], 98 [55], 177 [56]. For further extended biological research, the excellent capacity of the drug is required. Moreover, the drug should release only in tumor cells. SiNPs can be functionalized for chemical detection, diagnostic tool, and biosensing [2,3,57]. Possible surface modification opens the doorway for various applications and smart construction production [19,58]. Nylon 6 is a frequently used polyamide for nanocomposite synthesis [58,59,60,61,62,63,64]. Due to high biocompatibility, stability, and toughness, nylon 6 is used for medical plastic material production and nanoparticle coating [58,65,66,67].
Herein, we present the synthesis procedures to obtain DOX-loaded silica nanocomposites (SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX) for cancer treatment. SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon have a high capacity of up to 258 and 493 μg/mg (DOX/silica). The perspectives of silica-DOX for cancer treatment were shown on lung cancer cell line A549 and human embryonic kidney cells HEK 293FT by cytotoxicity test (MTT test). The IC 50 values were estimated in comparison to the free DOX drug. The high DOX-loaded SiNPs-Nylon may highly contribute to the drug resistance of cancer treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES), sodium acetate (NaOAc), and Nylon 6 were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Co (St. Louis, MO, USA). 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol (TFE), 3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT), arginine hydrochloride were acquired from Panreac Química (Barcelona, Spain). DOX was purchased from Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (Petach Tikva, Israel). The 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine was obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antimycotic antibiotic solution were purchased from GIBCO, Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Acetonitrile, hexane, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), ethanol, and acetic acid were obtained from Reachim (Moscow, Russia). Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (HTAB) were purchased from Helicon (Moscow, Russia). The nutrient medium for cells (RPMI-1640, aqueous ammonia) was obtained from Aurat (Moscow, Russia). Milli-Q water was used for the synthesis.
2.2. Characterization of SiNPs, SiNPs-Nylon, SiNPs-DOX, and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX
The dynamic light scattering (DLS) and ζ-potential studies were carried out on a Malvern Zetasizer Nano device (Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK) in deionized water (~250 µg/mL) at 25 °C. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were conducted on a Jem−1400 device (Jeol, Tokyo, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 80 kV. A drop of a sample was allowed to adsorb for 1 min on a copper grid covered with formvar film. The images were captured by a side-mounted Veleta digital camera (EM SIS, Muenster, Germany). FT-IR analysis was carried out in KBr pellets using a Varian 640-IR-spectrometer (Varian, LA, USA). The DOX loading and release characterization was done according to Section 2.6 and Section 2.7.
2.3. SiNPs Synthesis
The synthetic procedures for SiNPs were adapted from Rao et al. (TEOS, NH3 method) [68], Masalov et al. (with L-arginine hydrochloride) [69], and Vazquez et al. (CTAB/HTAB) [70]. Briefly, to the 0.01–0.2 M alcoholic solution of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), 28% ammonia was added to a concentration of 1 M at 25 °C under sonication in an ultrasound bath. Sonication was continued for 60 min to get a white suspension [68]. Incubation was carried out for 12 h. The SiNPs were centrifuged for 10 min at 13,400 rpm. The precipitate was washed four times with 98 % ethanol.
To the 3.5 mL of 6 mM, an aqueous solution of L-arginine hydrochloride heated to 60 °C, 0.5 mL of TEOS/n-hexane in a volume ratio of V(hexane):V(TEOS) = 6:5 solution was added dropwise. The incubation was carried out for 12 h at 60 °C under stirring (300 rpm). Three fractions were obtained and marked as an organic fraction, intermediate fraction, and aquatic fraction. The fractions were separated using a micropipette. The SiNPs were separated by centrifugation (10 min, 7000 rpm). The precipitate was washed three times with 98% ethanol before the size analysis.
To the 25 mg/mL cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) or hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (HTAB) aqueous solution, 25 µL/ml triethanolamine was added. The solution was incubated for 1 h under stirring (1400 rpm) at 95 °C. Afterward, 75 μL/mL of TEOS was added dropwise and stirred for 1 h (1400 rpm) at 40 °C. The SiNPs were separated by centrifugation (13,400 rpm) for 10 min. The precipitate was washed four times with 98 % ethanol before the size analysis.
2.4. Nylon-Coated SiNPs Synthesis (SiNPs-Nylon)
A 1 mL of 2.2 mM ethanol solution of (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES) was added to the 1 mg of SiNPs under stirring (1400 rpm) for 2 h at 25 °C. The modified nanoparticles were separated by centrifugation and washed with 98 % ethanol (3 × 1 mL). Afterward, 1 mL of a cyanuric chloride solution (10 mg/mL) in CH3CN was added to the precipitate under stirring (1400 rpm) for 2 h at 25 °C. The SiNPs were collected by centrifugation and washed with CH3CN (3 × 3 mL) and 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (1 × 3 mL). To the surface active SiNPs 10–15 mg/mL in trifluoroethanol, 4% nylon 6 solution in trifluoroethanol was added. The incubation was carried out for 12 h under stirring (1400 rpm) at 25 °C. The SiNPs-Nylon was centrifuged (13,400 rpm) for 5 min and washed using trifluoroethanol (3 × 1 mL) and water (1 × 1 mL). The SiNPs-Nylon is stable during storage for at least 7 months. The SiNPs-Nylon retains colloidal stability without significant size changes (data not shown).
2.5. SiNPs Stability
The stability of SiNPs was analyzed in 1 mL of 100 mM acetate buffer (pH from 4.0 to 6.0), 10 mM PBS (pH 7.4), and 50% fetal bovine serum at 25 °C under stirring (750 rpm). The aliquot was collected and analyzed by DLS. The initial solution was remixed. The nanoparticles were counted as stable during the storage for at least two-three months in deionized water. The nanoparticles should retain at least 1 week’s stability in buffer/salt conditions for biomedical applications.
2.6. Doxorubicin-Loaded SiNPs
The DOX loading (50–500 µg/mL) on the SiNPs (0.05–1.0 mg) was carried out in 1 mL of 10 mM sodium borate buffer (pH 8.0). The solution was incubated at 25 °C under stirring (700 rpm) for 12 h. Afterward, the SiNPs were centrifugated, and the solution was completely withdrawn. The SiNPs were washed with 10 mM borate buffer pH 8.5 (3 × 1 mL). The DOX concentration in the discarded solution was measured by UV (λ = 480 nm). The drug amount bound to the SiNPs was determined as capacity E µg/mg (DOX/SiNPs) and calculated according to the formula: E = (DOX0-DOX)/N. The DOX0and DOX represent the initial amount of DOX in the discard solution (µg), respectively, and N denotes the amount of SiNPs (mg).
2.7. Doxorubicin Release from SiNPs
The DOX release from 0.2 mg DOX-loaded SiNPs was measured in 1 mL of 100 mM acetate buffer (pH from 3.0 to 7.0) at 25 °C (or varying in the range from 15 to 45 °C) under stirring (750 rpm). At various time points, the SiNPs were centrifuged, and the aliquot was collected, followed by re-mixing. The concentration of the released DOX was measured spectrophotometrically (λ = 480 nm) and by fluorescence (λex = 480 nm, λem = 590 nm) using a Clariostar plate reader (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany). The amount of the released DOX was calculated using a serial dilution of a DOX standard solution.
2.8. The Cytotoxicity Assay (MTT Test)
Lung adenocarcinoma A549 and human embryonic kidney HEK 293FT cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco’s Minimum Essential Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS (Invitrogen), penicillin (100 units/mL), streptomycin (100 μg/mL), and 1% GlutaMAX in a humidified at 37.0 ± 1.0 °C, 5.0 ± 0.5% CO2 incubator. Exponentially growing cells were plated in a 96-well plate (4 × 103 ± 0.5 × 103 cells per well) and incubated overnight. Afterward, the cells were treated with media containing nanocomposites and incubated for 48 h at 37.0 ± 1.0 °C in a 5.0% ± 0.5% of CO2 atmosphere. The medium was removed from the wells, and 100 µL of an MTT solution (0.25 mg/mL in the culture medium containing 1% of an antimycotic antibiotic solution) was added and incubated at 37 °C for 4 h. The medium was removed, and formazan was dissolved in 0.1 mL of DMSO. The absorbance at 570 nm (peak) and 620 nm (baseline) was read using a microplate reader Multiscan EX (Thermo Electron Corporation, Waltham, MA, USA). Cells treated with medium-supplemented PBS buffer instead of the nanoparticles’ solution were used as a 100% viability control. Results were expressed as a percentage of the control values. All measurements were repeated not less than three times, and the standard deviation was calculated.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of SiNPs
The SiNPs synthesis was held using several synthetic approaches, which are related to tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) hydrolysis [68,69,70]. However, for the drug delivery area, the nanoparticles’ size has to be obtained higher than 10–20 nm and less than 100–150 nm. Small nanoparticles ~ 10 nm are rapidly excreted by the renal system. Too-high-sized nanoparticles (> 200 nm) do not pass through capillaries. Some optimizations of the synthesis conditions are required to achieve the optimal nanoparticles surface charge and size, which are important for cell internalization and tissue delivery. The primarily used methods for SiNPs synthesis are Stober’s process (TEOS hydrolysis in aqueous ammonia media) and the microemulsion method, which involves the formation of micelles [1]. The synthetic procedures for SiNPs were adapted from Vazquez et al. (method 1 using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) or hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (HTAB) aqueous solutions in the presence of triethanolamine) [70], Masalov et al. (method 2 in a microemulsion with L-arginine hydrochloride) [69], and Rao et al. (method 3 using TEOS alcohol solution with aqueous NH3) [68]. For the SiNPs synthesis, the methods optimization data are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Hydrodynamic diameter, polydispersity index (PDI), and variable parameters for SiNPs synthesis.
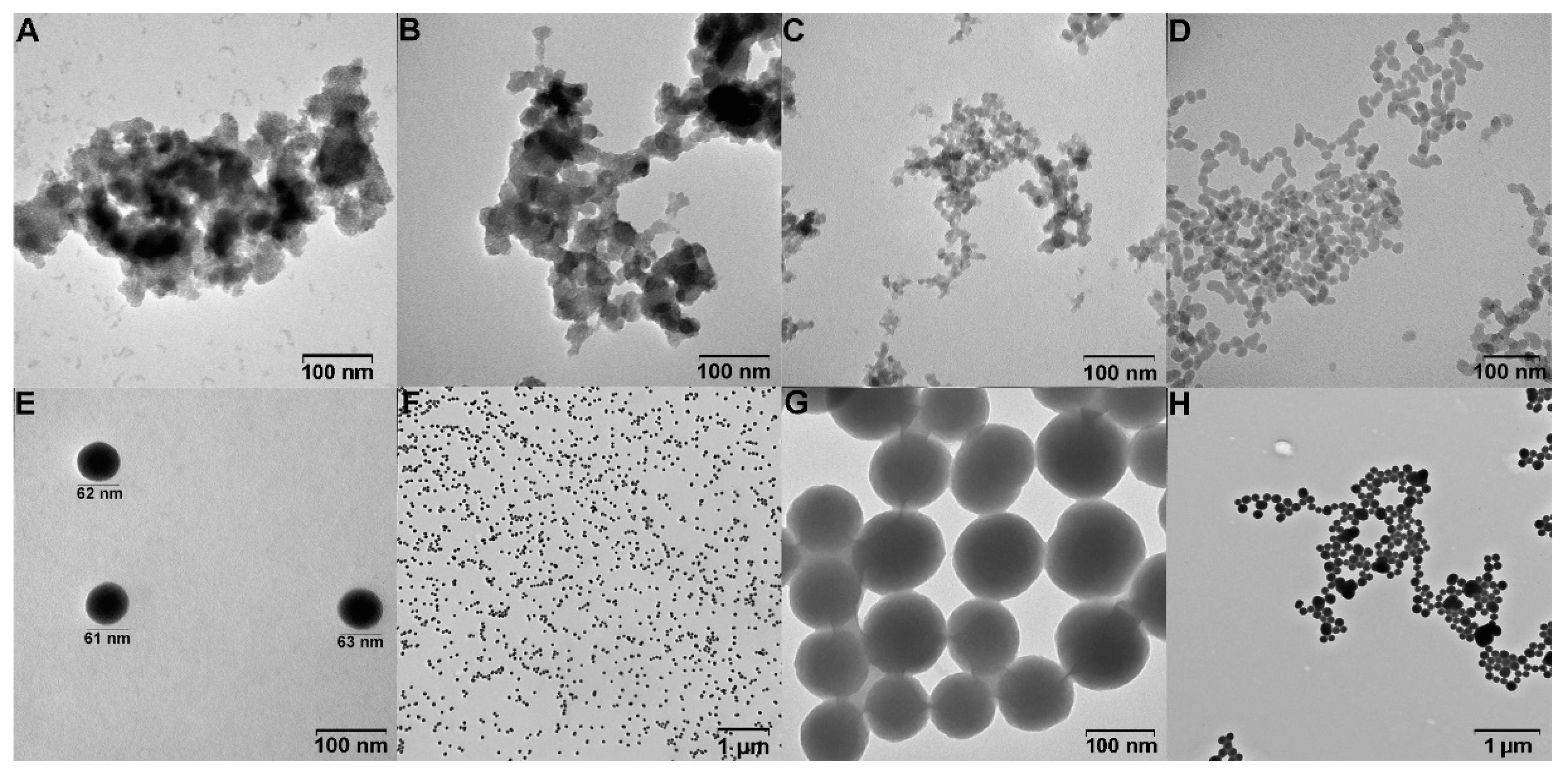
The nanoparticles’ size was investigated using dynamic light scattering (DLS, Table 1) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, Figure 1) methods. The method one procedure in the presence of triethanolamine and CTAB or HTAB yields pronounced porous high-sized agglomerates of the particles shown by TEM (Figure 1A,B) and DLS (Table 1). However, the average size of SiNPs 370–450 nm is not suitable for further drug-loading experiments. Three fractions of SiNPs were obtained using the second approach in a microemulsion (water/hexane) in the presence of L-arginine (Table 1). SiNPs with the smallest size were analyzed using TEM. The TEM image (Figure 1C) indicates a high degree of aggregation. Moreover, SiNPs obtained by the microemulsion method don’t retain the size and PDI in an aqueous solution during storage. The small-sized spherical particles were obtained for nanoparticles obtained by method three (Table 1, Figure 1D–H). For the 0.018–0.040 M TEOS, the nanoparticles have optimal size for biological applications. The PDI is a measure of the heterogeneity of a sample based on size. For Rao et al. synthetic procedure, PDI is lower than 0.13, which shows high homogeneity of the samples. The synthesis with 0.018 M TEOS yields the SiNPs with hydrodynamic diameter by DLS 63 ± 1 nm (ζ-potential of −28.6 ± 2 mV) with low PDI values of 0.09 ± 0.01 (Figure S1). Increasing the reaction volume from 1 mL to 50 mL doesn’t lead to significant changes in nanoparticle size and PDI (Figure S2). A similar synthesis with 0.040 M TEOS shows a little agglomeration process (Figure 1D). For further studies, the smallest monodisperse SiNPs with 0.018 M TEOS conditions were selected.

Figure 1.
TEM images of SiNPs obtained by method 1 with CTAB (A) and HTAB (B); (C) SiNPs obtained by method 2; SiNPs obtained by method 3 with 0.040 M TEOS (D), 0.018 M TEOS (E,F), 0.200 M TEOS (G,H).
The nanoparticle stability in an aqueous solution is an essential factor for biomedicine. The stability of SiNPs was analyzed in acetate buffer (pH from 3.0 to 7.0), PBS buffer (pH 7.4), and 50% FBS. The SiNPs are stable in an aqueous solution during storage for one year without agglomeration (Figures S3 and S4). In the acetic buffer (pH 4.0 and 5.0), SiNPs show almost the same average size as initial nanoparticles for not less than one week (Figures S5 and S6). SiNPs at pH 6.0 and 7.4 immediately resized from 63 nm to 73–75 nm, and no changes for 1 week of storage were observed (Figures S7 and S8). For the model experiment using FBS, SiNPs size immediately increases to 82 ± 3 nm, PDI = 0.30 ± 0.01 (Figures S9 and S10), which may be associated with the nanoparticle’s protein corona formation. No changes and aggregation processes occurred after 10 days of storage (Figure S11). The high stability, as well as the scalability of the synthesis procedure, shows the perspectives of SiNPs by the adapted method 3.
3.2. SiNPs and Nylon 6 Nanocomposite Synthesis
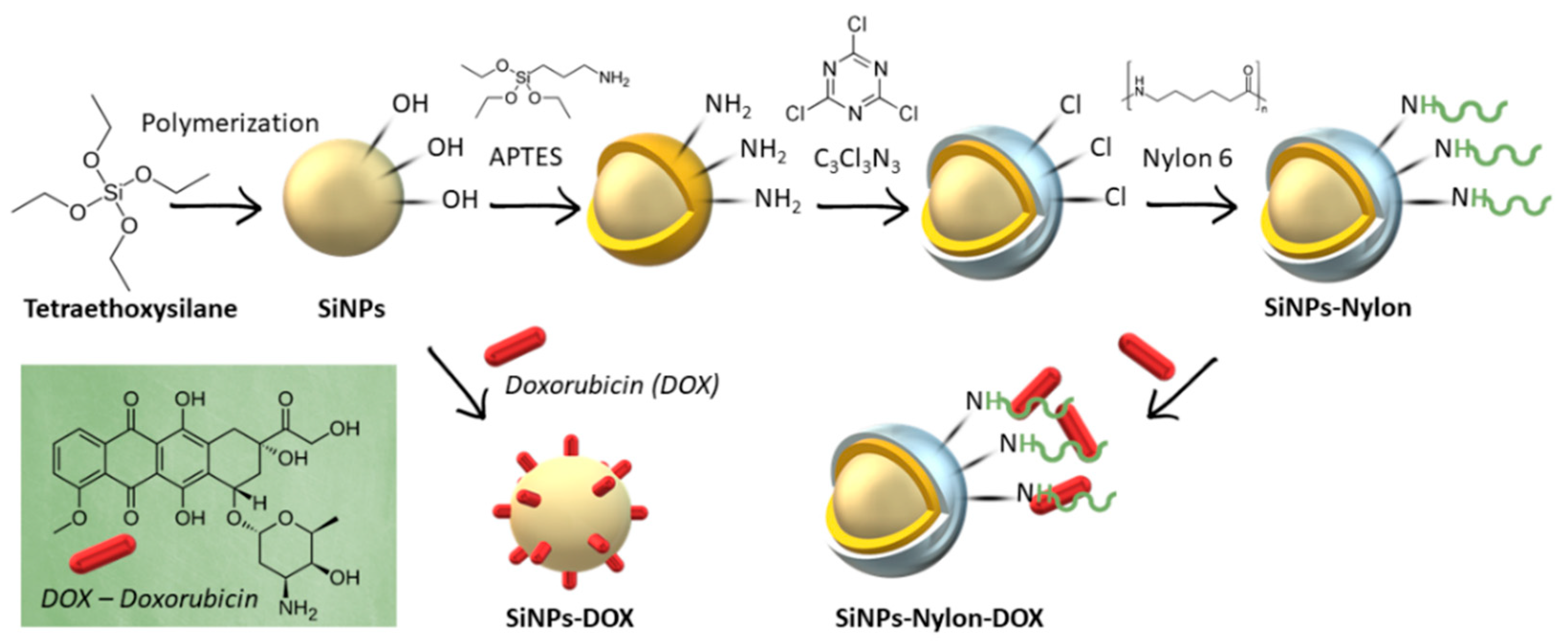
The SiNPs and nylon 6 nanocomposite (SiNPs-Nylon) was synthesized by the widely used 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) method [71,72,73,74] with subsequent cyanuric chloride reaction. In the next stage, nylon 6 was conjugated on the activated SiNPs surface (Figure 2).
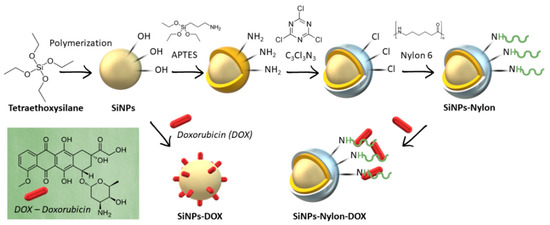
Figure 2.
Synthesis of nylon 6-coated SiNPs (SiNPs-Nylon) and DOX-loaded SiNPs (SiNPs-DOX) or SiNPs-Nylon (SiNPs-Nylon-DOX). APTES–(3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane; C3Cl3N3 –2,4,6-Trichloro-1,3,5-triazine (cyanuric chloride).
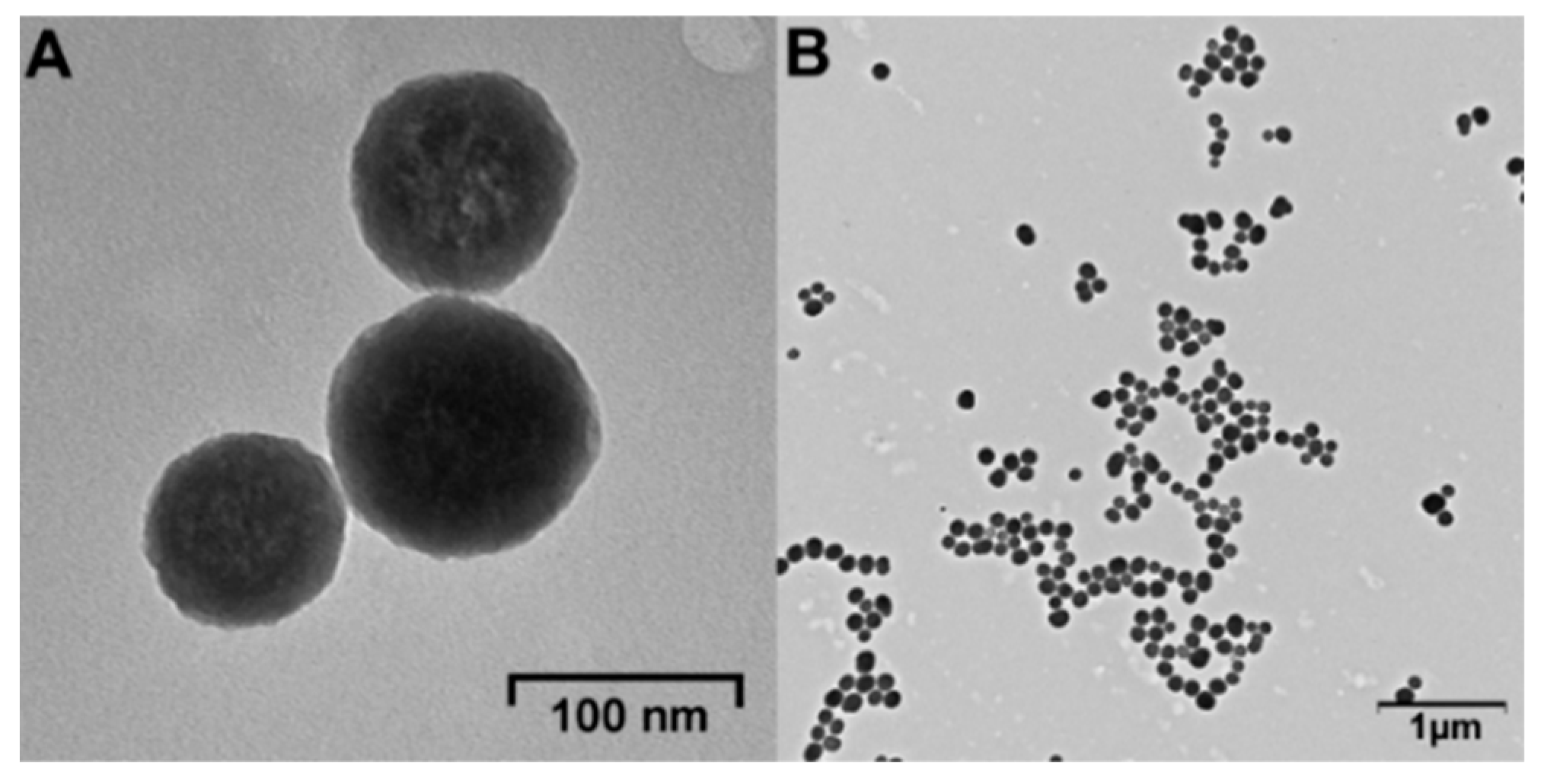
The FT-IR spectra of the SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon were recorded. To confirm the surface functionalization. The characteristic peaks, assigned to symmetric (495 and 810 cm−1) and asymmetric (1101 cm−1) Si-O-Si stretching, and stretching vibrations of Si-OH (948 cm−1) can be identified in the spectra (Figure S12) [45,75]. The FT-IR spectra of SiNPs-Nylon show some additional bands, which can be attributed to nylon 6. Among them is a characteristic band 1652 cm−1 corresponding to the C=O stretching of the amide group. A qualitative reaction with N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Phenazinium ion was done for SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon. A colored blue violet product was formed in the nylon presence (Figure S13). The DLS and TEM data of SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon indicate the increase in the size without any agglomeration (Table 2, Figure 3). The hydrodynamic diameter of SiNPs-Nylon was 110 ± 2 nm. TEM images show a high surface-to-volume structure with individual spherical structures (Figure 3). The SiNPs-Nylon is stable during storage for at least 7 months at 4 °C. The SiNPs-Nylon retains colloidal stability without significant size changes evaluated by DLS.

Table 2.
Hydrodynamic diameter and polydispersity index (PDI) of SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon obtained by DLS.

Figure 3.
TEM image of SiNPs-Nylon. High magnification (A) and low magnification images (B).
3.3. Anticancer Drug Doxorubicin Loading
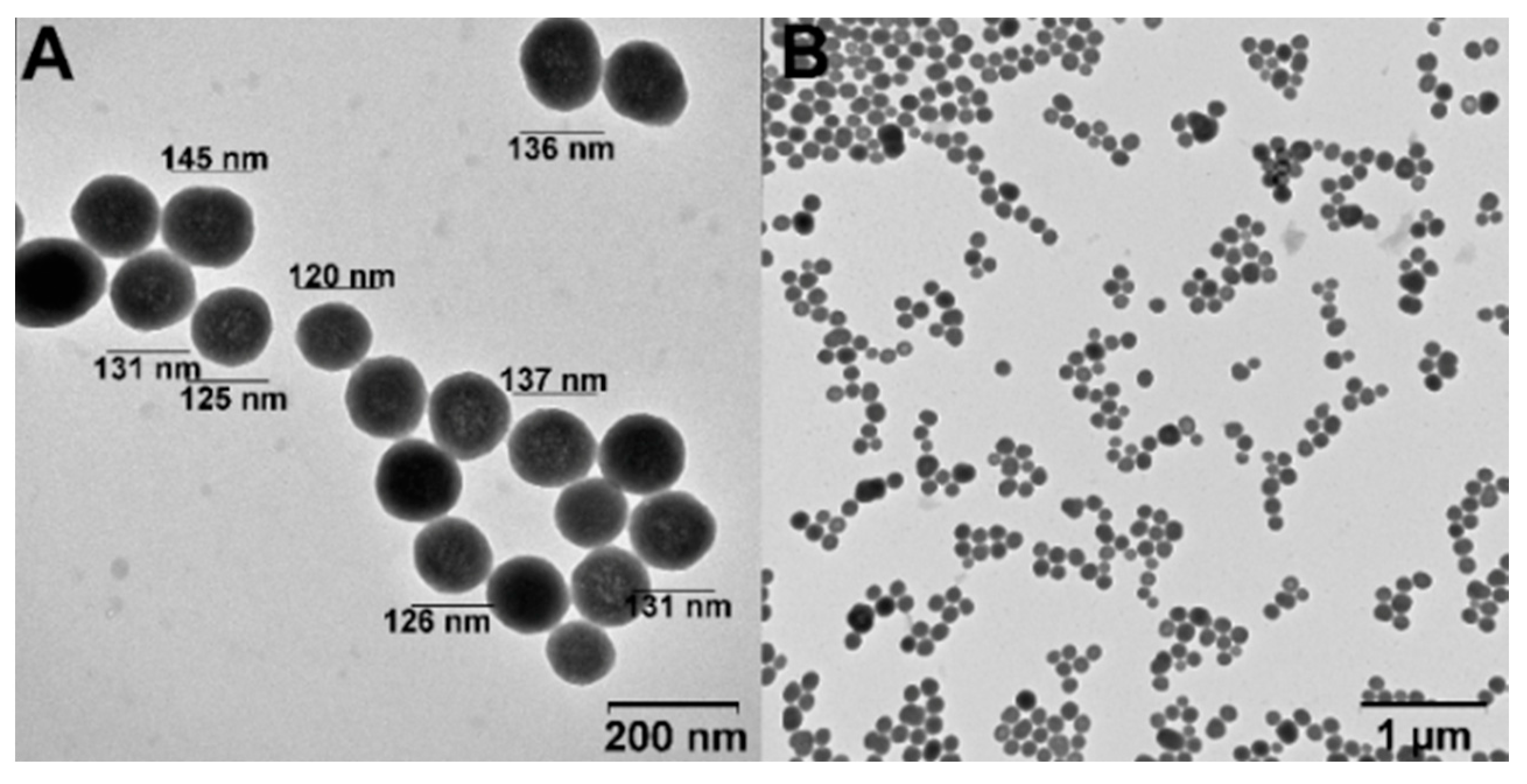
The adsorption of DOX on SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon was studied by UV-vis. spectroscopy and fluorescence. DOX has an absorption maximum of 480 nm, which confers a convenient drug-loading traceability. For drug-loading, we have used the sodium borate buffer (pH 8.0) and adopted a previously published procedure [41]. The amount of DOX bound to the SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon was calculated as the difference between the initial and after-incubation DOX amount. The experimental variation, capacity data, and loading efficiency for SiNPs are presented in Table 3. The highest capacity was calculated as 258 µg / mg (DOX/SiNPs). However, the drug loading efficiency is only 52%. The capacity of SiNPs is much higher than was obtained in the works [4,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. Previously, we obtained a high DOX capacity for CaCO3 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles [36,41]. Such a high capacity is probably associated with a good porous spatial structure of nanoparticles, which was analyzed by TEM (Figure 4). The proposed condition for DOX-loading may be used elsewhere. For SiNPs-Nylon, DOX-loading capacity is presented in Table 3. The highest obtained capacity was calculated as 493 µg / mg (DOX/SiNPs-Nylon), which is 2-fold higher than for SiNPs. Nylon 6 represents two different polarity domains in the chemical structure. Both the polar amide group and the non-polar hydrocarbon chain can interact with the amphiphilic drug DOX favoring its sorption. For the maximum DOX loading capacity on the SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon, nanoparticles size immediately increases to 147 ± 5 nm (PDI = 0.232 ± 0.002) and 137 ± 2 nm (PDI = 0.209 ± 0.002), respectively. ζ-potential changes from −28.6 ± 2 mV to 0.01 ± 0.08 for SiNPs-DOX.

Table 3.
DOX loading SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon capacity.
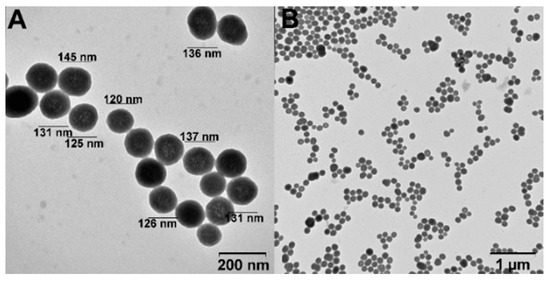
Figure 4.
TEM image of SiNPs-DOX. The high (A) and low (B) magnification images.
3.4. Doxorubicin Release
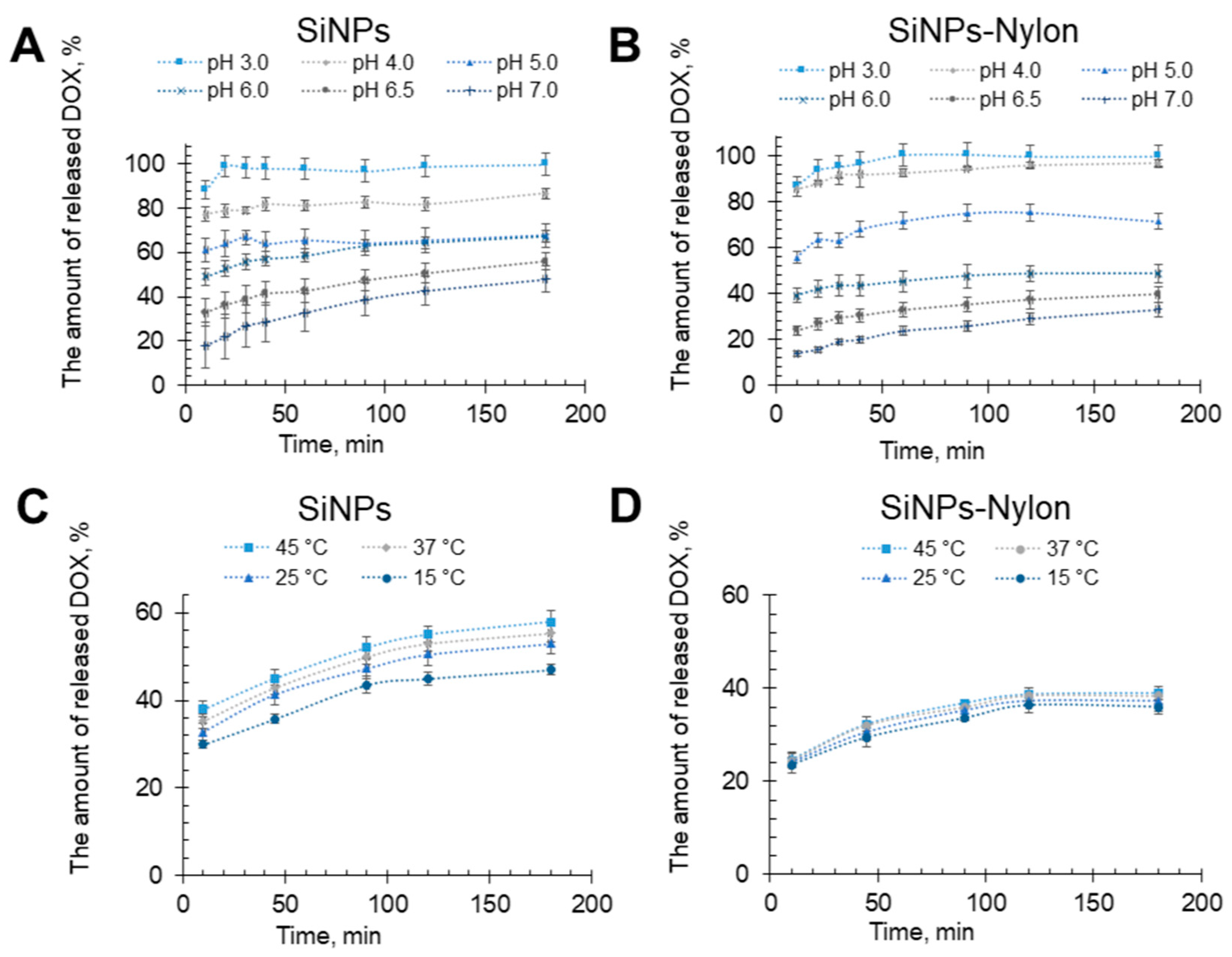
The DOX release efficiency experiments from the SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX were carried out in sodium acetate buffer with pH from 3.0 to 7.0 at 25 °C (Figure 5A,B) and pH of 6.5 at 15–45 °C (Figure 5C,D). The pH range was chosen from physiological plasma pH ~7 to acidic. A pH of ~4.5–5 can be found in the cancer tissue microenvironment and endosomes. The SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX show the pH-dependent DOX release. At neutral pH, the release is low. It becomes extremely high (Figure 5A,B) in acidic pH. For example, at pH 5, the release is ~60% for SiNPs. It should be noted that DOX release efficiency for SiNPs at pH 5 and 6 is almost the same. For SiNPs-Nylon, the efficiency at pH 5 is significantly higher than at pH 6, which is better for selective DOX release in tumor cells. Despite SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX having similar drug release at acidic pH, SiNPs-Nylon-DOX has higher drug capacity and consequently higher quantitative DOX release. Moreover, DOX release efficiency slightly increases with temperature (Figure 5C,D), which shows the potential of SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX for further in vivo experiments. The drug release enhancement during temperature increase was previously shown for silica and Fe3O4@SiO2 nanocomposites [76,77,78]. DOX is a principally hydrophobic molecule that can form electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding. We assumed that drug molecules pushed out the water, interacting with the nylon 6 or silica surface in the case of SiNPs. Nylon 6 represents two possible force interactions. DOX may interact with polar amide groups by hydrogen bonds and under van der Waals forces with a hydrophobic hydrocarbon backbone. Silica nanoparticles effectively load DOX principally by electrostatic interactions [79]. Therefore, different interaction mechanisms and possible silica nanoparticle size changes provide diverse DOX release efficiency during temperature increases.
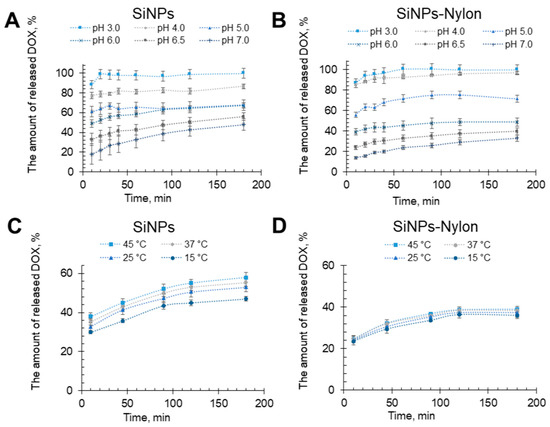
Figure 5.
DOX release from SiNPs-DOX (A,C) and SiNPs–Nylon-DOX (B,D) at pH 3.0–7.0 at 25 °C (up) and pH 6.5 at 15–45 °C (bottom). The SiNPs-Nylon-DOX with a capacity of 493 µg/mg (size 137 ± 2 nm by DLS) and SiNPs-DOX 258 µg/mg (size 147 ± 5 nm by DLS) were used for DOX release studies. All values are given as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) values. All measurements were repeated not less than three times.
3.5. Cellular Toxicity Study of SiNPs-DOX
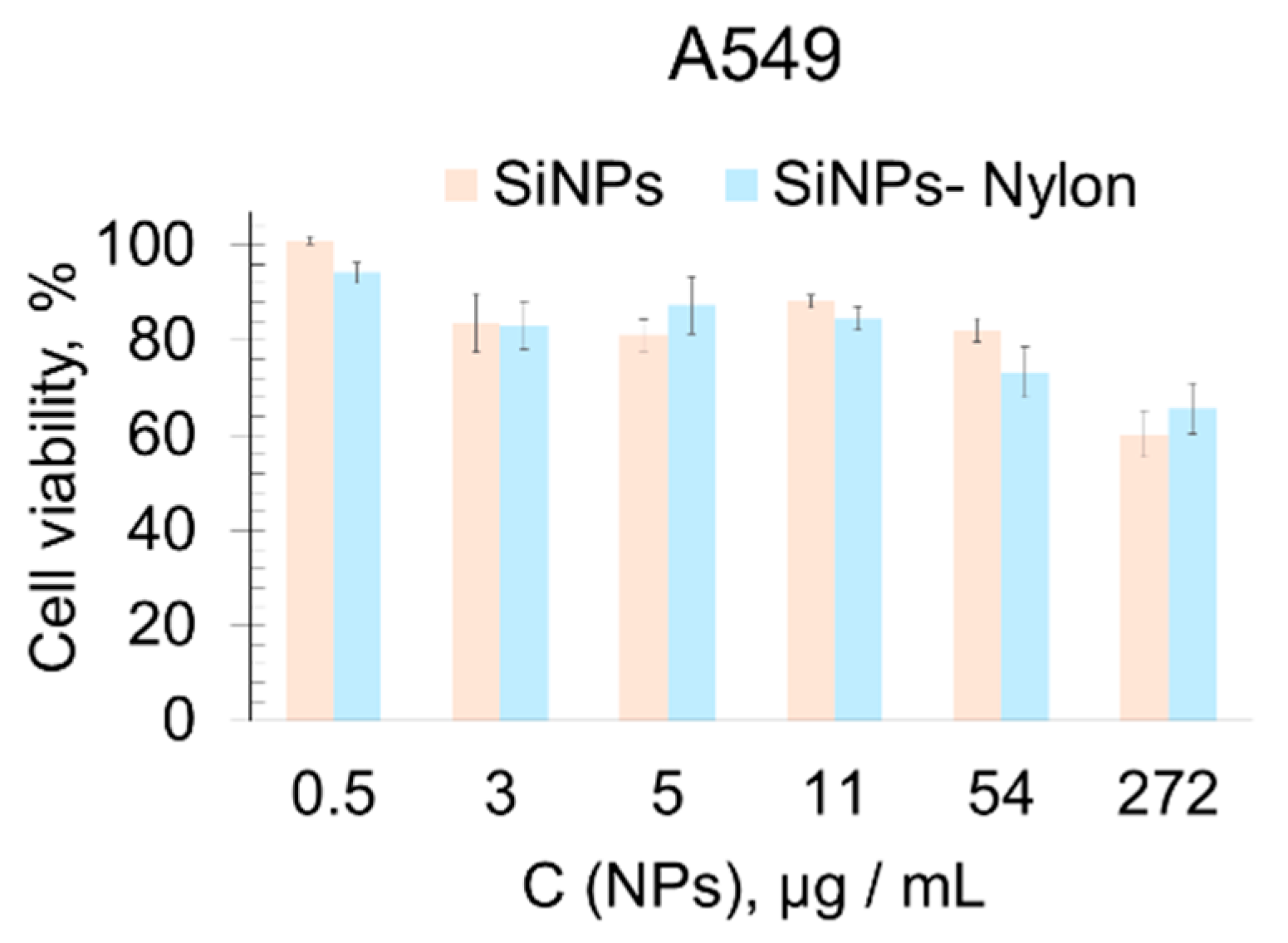
The cytotoxicity of the SiNPs, SiNPs-Nylon, SiNPs-DOX, and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX were assessed in the primary used 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) method [80]. The cell viability experiment was conducted using a widely used A549 human lung carcinoma cell line, and human embryonic kidney cells were transformed with large T-antigen SV40 (HEK 293FT). For the MTT test, various amounts of SiNPs, SiNPs-Nylon, SiNPs-DOX, SiNPs-Nylon-DOX, and DOX were incubated with the cells for 48 h (Figure 6 and Figure 7). The SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon show no acute toxicity up to 50 µg/mL (Figure 6), which indicates the perspectives of silica nanocomposites for drug-delivery application.
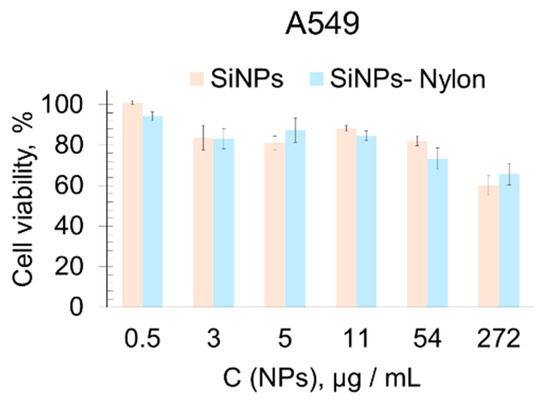
Figure 6.
Cell viability assay (MTT test). A549 cell lines were incubated for 48 h with SiNPs (size 63 ± 1 nm by DLS) and SiNPs-Nylon (size 110 ± 2 nm by DLS). Cells treated with medium-supplemented PBS buffer instead of the nanoparticles’ solution were used as a 100% viability control. All values are given as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) values. All measurements were repeated not less than three times.
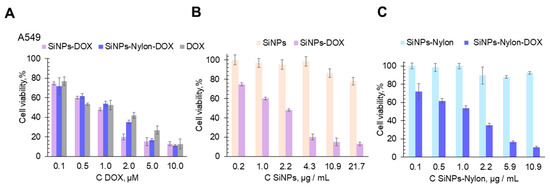
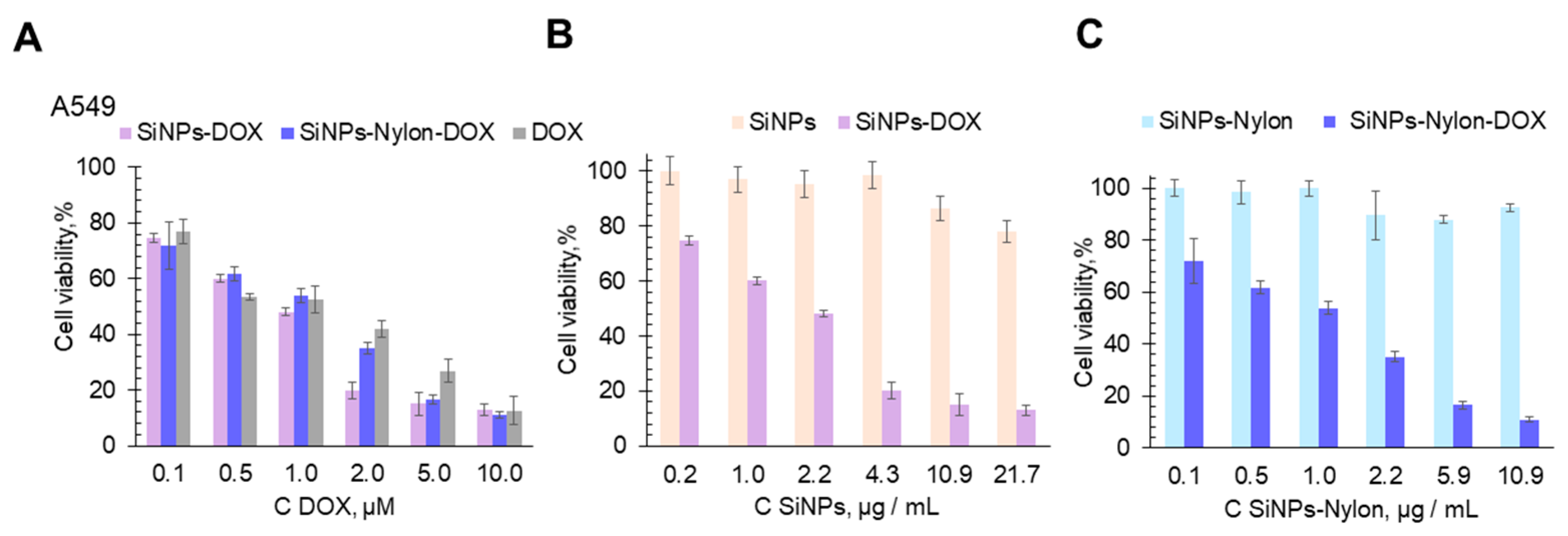
Figure 7.
Cell viability assay (MTT test). A549 cell line was incubated for 48 h with SiNPs, SiNPs-Nylon, SiNPs-Nylon-DOX, SiNPs-DOX, and DOX. Cells treated with medium-supplemented PBS buffer instead of the nanoparticles’ solution were used as a 100% viability control. Cells were incubated with the same amount of free DOX or the DOX loaded on SiNPs (A) or with the same mass of SiNPs and SiNPs–DOX (B), SiNPs-Nylon and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX (C). The SiNPs-Nylon-DOX with a capacity of 493 µg/mg (size 137 ± 2 nm by DLS) and SiNPs-DOX 258 µg/mg (size 147 ± 5 nm by DLS) were used for cell viability studies. All values are given as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) values. All measurements were repeated not less than three times.
SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX show good inhibition of cell proliferation (Figure 7). SiNPs-DOX, SiNPs-Nylon-DOX, and DOX have almost the same toxic effect per drug concentration (Figure 7A). However, cell viability for SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX per nanocomposite mass is not the same (cf. Figure 7B,C). The SiNPs-Nylon-DOX shows a higher toxicity effect (Figure 7C), which may be explained by the higher than for SiNPs-DOX drug capacity. In comparison to the A549 cell line, HEK 293FT is more affected by SiNPs-DOX and DOX (cf. Figure 7 and Figure S14), which is explained by the different susceptibility of cells to external influences.
The calculated IC50 values of SiNPs-DOX, SiNPs-Nylon-DOX, and DOX are presented in Table 4. For example, the IC50 value of SiNPs-DOX was 0.98 ± 0.05 µM in terms of DOX concentration and recalculated as 3.8 ± 0.3 µg/mL in terms of the amount of the nanoparticles for the A549 cell line. The IC50 value for SiNPs-DOX for the experiments with HEK 293FT cells is much lower, equal to 0.08 ± 0.01 µM in terms of DOX amount and recalculated as 0.31 ± 0.04 µg/mL in terms of the concentration of the nanoparticles. For the SiNPs-Nylon-DOX, the IC50 value per DOX concentration is similar to SiNPs-DOX. However, for the SiNPs-Nylon-DOX, the IC50 value is lower, equal to 2.3 ± 0.2 µg/mL in terms of the amount of the nanocomposite. The obtained results demonstrate the higher therapeutic potential of SiNPs-Nylon-DOX. However, further investigation in the context of drug loading, metabolism, and extended toxicity is required.

Table 4.
The IC50 values of SiNPs-DOX and SiNPs-Nylon-DOX for the A549 cell line per DOX or nanoparticles concentration.
4. Conclusions
Herein, we presented a smart pH-responsible drug release construction based on silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) and Nylon 6-coated SiNPs (SiNPs-Nylon) for cancer treatment. The synthesized SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon were characterized by TEM and DLS. In the tested wide concentration range of 0.5–50 µg/mL, SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon demonstrated no toxicity to the A549 cell line. The proposed drug loading method provides a high doxorubicin capacity of 258 μg/mg (DOX/SiNPs) and 493 μg/mg (DOX/SiNPs-Nylon). SiNPs-Nylon composite has shown good DOX extraction behavior in aqueous solution. The DOX-loaded SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon showed good suppression of cancer cell growth. For example, the IC50 values of SiNPs-Nylon-DOX were calculated as 1.12 ± 0.08 µM in terms of DOX amount and recalculated as 2.3 ± 0.2 µg/mL in terms of the nanoparticles’ concentration for A549 cells. The SiNPs-Nylon-DOX demonstrates excellent drug release efficiency in the acidic pH values, which can be found in the tumor microenvironment. Moreover, SiNPs-Nylon-DOX is more stable than SiNPs-DOX in neutral pH. The SiNPs-Nylon has great potential for drug delivery and cancer treatment. The porous silica nanocomposites have good perspectives in the smart drug delivery area.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/coatings13020324/s1, Figure S1: DLS size distribution data (Number, Volume, and Intensity) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS; Figure S2: DLS size distribution data (Number, Volume, and Intensity) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS in 50 mL synthesis conditions; Figure S3: DLS size distribution data (Number, Volume, and Intensity) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS after one year storage; Figure S4: DLS size distribution data (Number) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS after synthesis (up) and after one year storage (bottom); Figure S5: DLS size distribution data (Number) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS diluted in 100 mM sodium acetate buffer pH 4 (up), and after 7 days (bottom); Figure S6: DLS size distribution data (Number) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS diluted in 100 mM sodium acetate buffer pH 5, and after 7 days; Figure S7: DLS size distribution data (Number) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS in 100 mM sodium acetate buffer pH 6, and after 7 days; Figure S8: DLS size distribution data (Number) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS diluted in 10 mM phosphate-buffered saline pH 7.4, and after 7 days; Figure S9: DLS size distribution data (Number, Volume) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS diluted in fetal bovine serum; Figure S10: DLS size distribution data (Number, Volume) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS diluted in fetal bovine serum (after 10 days); Figure S11: DLS size distribution data (Number) for method Rao et al. with 0.018 M TEOS diluted in fetal bovine serum, and after 10 days; Figure S12: The FT-IR spectra of SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon; Figure S13: Scheme of the qualitative reaction of the nylon determination in SiNPs and SiNPs-Nylon with N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-phenazinium ion; Figure S14: Cell viability assay. HEK 293FT cell line was incubated for 48 h with SiNPs, SiNPs–DOX, and DOX.
Author Contributions
Data curation and investigation, V.P., Y.P. and E.D.; conceptualization, E.D. and A.C.; writing—original paper, A.C. and V.P.; writing—review and editing, E.D.; supervision, D.P.; funding acquisition, A.C., E.D. and D.P.; project administration, D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (grant No. 22-24-00996).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data that support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Selvarajan, V.; Obuobi, S.; Ee, P.L.R. Silica Nanoparticles—A Versatile Tool for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.; Ghoran, S.H.; Niakan, M.H.; Jamali, K.; Moeini, Z.; Jangjou, A.; Izadpanah, P.; Amani, A.M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle: Heralding a Brighter Future in Cancer Nanomedicine. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 319, 110967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, M.; Gil, S.; Gaviña, P.; Costero, A.M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Chemical Detection: From Small Species to Large Bio-Molecules. Sensors 2022, 22, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racles, C.; Zaltariov, M.; Peptanariu, D.; Vasiliu, T.; Cazacu, M. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica as Doxorubicin Carriers and Cytotoxicity Boosters. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Dai, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Guo, B.; Huang, L. Recent Advances of Mesoporous Silica as a Platform for Cancer Immunotherapy. Biosensors 2022, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slapak, E.J.; El Mandili, M.; Bijlsma, M.F.; Spek, C.A. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Literature Overview. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi, M.; Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Delivery of Repurposed Anthelmintics for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Botella, P.; Rivero-Buceta, E. Silica-Based Stimuli-Responsive Systems for Antitumor Drug Delivery and Controlled Release. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzeciak, K.; Chotera-ouda, A.; Bak-sypien, I.I.; Potrzebowski, M.J. Mesoporous Silica Particles as Drug Delivery Systems—The State of the Art in Loading Methods and the Recent Progress in Analytical Techniques for Monitoring These Processes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frickenstein, A.N.; Hagood, J.M.; Britten, C.N.; Abbott, B.S.; McNally, M.W.; Vopat, C.A.; Patterson, E.G.; Maccuaig, W.M.; Jain, A.; Walters, K.B.; et al. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Properties and Strategies for Enhancing Clinical Effect. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isa, E.D.M.; Ahmad, H.; Rahman, M.B.A.; Gill, M.R. Progress in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Agents for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouaitah, K.; Lojkowski, W. Delivery of Natural Agents by Means of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres as a Promising Anticancer Strategy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moodley, T.; Singh, M. Current Stimuli-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E.; Wahl, R. Nanoparticles: Promising Auxiliary Agents for Diagnosis and Therapy of Thyroid Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontón, I.; del Rio, A.M.; Gómez, M.G.; Sánchez-García, D. Preparation and Applications of Organo-Silica Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Targeted Stimuli-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Bacterial Infection Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, E.B. Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chircov, C.; Spoială, A.; Păun, C.; Crăciun, L.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Turculeƫ, S.C. Mesoporous Silica Platforms with Potential Applications in Release and Adsorption of Active Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barui, S.; Cauda, V. Multimodal Decorations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids in Oncology: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Butler, K.S.; Zink, J.I.; Brinker, C.J. Synthetic Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles: Toxicity, Biomedical and Environmental Implications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 886–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembuan, C.; Oliveira, H.; Graf, C. Effect of Different Silica Coatings on the Toxicity of Upconversion Nanoparticles on RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, V.; Dmitrienko, E.; Chubarov, A. Magnetic Nanocomposites and Imprinted Polymers for Biomedical Applications of Nucleic Acids. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osminkina, L.A.; Timoshenko, V.Y. Porous Silicon as a Sensitizer for Biomedical Applications. Open Mater. Sci. 2016, 3, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osminkina, L.A.; Nikolaev, A.L.; Sviridov, A.P.; Andronova, N.V.; Tamarov, K.P.; Gongalsky, M.B.; Kudryavtsev, A.A.; Treshalina, H.M.; Timoshenko, V.Y. Porous Silicon Nanoparticles as Efficient Sensitizers for Sonodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 210, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximchik, P.V.; Tamarov, K.; Sheval, E.V.; Tolstik, E.; Kirchberger-Tolstik, T.; Yang, Z.; Sivakov, V.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Osminkina, L.A. Biodegradable Porous Silicon Nanocontainers as an Effective Drug Carrier for Regulation of the Tumor Cell Death Pathways. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 6063–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceroni, P.; Chao, Y.; Crucho, C.; De Cola, L.; Fucikova, A.; Goyal, A.; Joo, J.; Kamali, A.R.; Osminkina, L.; Silvestrini, S.; et al. Silicon Nanostructures for Sensing and Bioimaging: General Discussion. Faraday Discuss. 2020, 222, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongalsky, M.B.; Sviridov, A.P.; Bezsudnova, Y.I.; Osminkina, L.A. Biodegradation Model of Porous Silicon Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-Responsive Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, S.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, R.; Wang, R.; et al. Silica Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications and Toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xue, Z.; Yasin, A.; He, Y.; Chai, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, K. Colorectal Cancer and Adjacent Normal Mucosa Differ in Apoptotic and Inflammatory Protein Expression. Eng. Regen. 2021, 2, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritharan, S.; Sivalingam, N. A Comprehensive Review on Time-Tested Anticancer Drug Doxorubicin. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidi, E.; Brunham, L.R. Regulated Cell Death Pathways in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, D.; Cameron, A.; MacDonald, B.; Nganou, C.; Scheller, H.; Marsh, J.; Beale, S.; Lu, M.; Shan, Z.; Kaliaperumal, R.; et al. Adsorption of Doxorubicin on Citrate-Capped Gold Nanoparticles: Insights into Engineering Potent Chemotherapeutic Delivery Systems. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19611–19619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, V.; Poletaeva, Y.; Pyshnaya, I.; Pyshnyi, D.; Dmitrienko, E. Designing PH-Dependent Systems Based on Nanoscale Calcium Carbonate for the Delivery of an Antitumor Drug. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, N.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X. Folic Acid-Decorated β-Cyclodextrin-Based Poly(ε-Caprolactone)-Dextran Star Polymer with Disulfide Bond-Linker as Theranostic Nanoparticle for Tumor-Targeted Mri and Chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, F.; Nisticò, R.; Magnacca, G.; Matencio, A.; Khazaei Monfared, Y.; Trotta, F. Magnetic Composites of Dextrin-Based Carbonate Nanosponges and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Potential Application in Targeted Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, S.; Albukhaty, S.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Almalki, F. Design and Synthesis of Multi-Functional Superparamagnetic Core-Gold Shell Coated with Chitosan and Folate Nanoparticles for Targeted Antitumor Therapy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.M.; Leonel, A.G.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Carvalho, I.C.; Krambrock, K.; Mansur, H.S. Bifunctional Magnetopolymersomes of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Carboxymethylcellulose Conjugated with Doxorubicin for Hyperthermo-Chemotherapy of Brain Cancer Cells. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2102–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovrigina, E.; Chubarov, A.; Dmitrienko, E. High Drug Capacity Doxorubicin-Loaded Iron Oxide Nanocomposites for Cancer Therapy. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, U.A.; Raza, A.; Ali, S.; Saeed, R.F.; Akhtar, N. Doxorubicin-Loaded Gold Nanorods: A Multifunctional Chemo-Photothermal Nanoplatform for Cancer Management. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, S.; Shahzad, K.; Saeed, T.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Abbasi, B.H.; Ahmad, N.; Khalid, W.; Atif, M.; Ali, Z.; Abbasi, R. Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity in Vitro of Surface-Functionalized Drug-Loaded Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 1339–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatami, F.; Matin, M.M.; Danesh, N.M.; Bahrami, A.R.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. Targeted Delivery System Using Silica Nanoparticles Coated with Chitosan and AS1411 for Combination Therapy of Doxorubicin and AntimiR-21. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nadaf, A.H.; Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Jawarneh, S.; Bardaweel, S.; Mahmoud, N.N. Folic Acid-Hydrophilic Polymer Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Target Doxorubicin Delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; Huo, Q.; Xie, N. Tumour-Targeted and Redox-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Controlled Release of Doxorubicin and an SiRNA against Metastatic Breast Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yao, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhong, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, N.; Zhai, Z.; Yang, S.; et al. Therapeutic Effect of Doxorubicin-Chlorin E6-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Combined with Ultrasound on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Lewik, G.; Ratcliffe, J.C.; Choi, C.H.J.; Mäkilä, E.; Tong, W.Y.; Voelcker, N.H. Systematic Evaluation of Transferrin-Modified Porous Silicon Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin to Glioblastoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33637–33649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Hua, L.; Guo, Z.; Sun, L. One-Pot Green Synthesis of Doxorubicin Loaded-Silica Nanoparticles for in Vivo Cancer Therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, A.; Zahid, F.; Zhan, G.; Yi, P.; Yang, H.; Gan, L.; Yang, X. Polyaspartic Acid-Anchored Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for PH-Responsive Doxorubicin Release. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Song, X.; Zhou, J.; Ouyang, X.; Li, J.; Deng, D. Virus-like Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Combination Therapy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Chen, F.; Sun, K.; An, P.; Sun, C.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, B. A Novel PH-Responsive Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle (HMSN) System Encapsulating Doxorubicin (DOX) and Glucose Oxidase (GOX) for Potential Cancer Treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Bai, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X. Optimized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery System with Removable Manganese Oxide Gatekeeper for Controlled Delivery of Doxorubicin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 592, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Shan, X.; Han, Y.; Jin, H.; Gao, Y. Study of PH-Responsive and Polyethylene Glycol-Modified Doxorubicin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 5997–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, T.; Singh, M. Sterically Stabilised Polymeric Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Improve Doxorubicin Efficiency: Tailored Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ping, Y.; Miao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Qu, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J. PEG/PEI-Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as Delivery Carriers for Doxorubicin: Synthesis, Characterization, and in Vitro Evaluation. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1728–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hao, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.C.; Zou, G.; Liang, X.-J. Multifunctional hybrid silica nanoparticles for controlled doxorubicin loading and release with thermal and pH dual response. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakova, A.; Chubarov, A.; Dmitrienko, E. Magnetic Nylon 6 Nanocomposites for the Microextraction of Nucleic Acids from Biological Samples. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tjiu, W.W.; Liu, T.; Lui, W.Y.; Phang, I.Y.; Zhang, W.D. Dramatically Enhanced Mechanical Performance of Nylon-6 Magnetic Composites with Nanostructured Hybrid One-Dimensional Carbon Nanotube-Two-Dimensional Clay Nanoplatelet Heterostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 3392–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.Z.; Safari, Z.; Madady, N. Synthesis of Co3O4@SiO2 Core/Shell–Nylon 6 Magnetic Nanocomposite as an Adsorbent for Removal of Congo Red from Wastewater. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3199–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.Y.; Kim, K.; Kim, C.K.; Kang, E. Reinforcement of Nylon 6,6/Nylon 6,6 Grafted Nanodiamond Composites by in Situ Reactive Extrusion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghambari, H.; Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Saraji, M.; Cárdenas, S. Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites for the Microextraction of Benzophenones from Water Samples. Molecules 2019, 24, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, K.; Khan, I.; Ahad, M.; Shah, T.; Sadiq, M.; Zada, A.; Zada, N. Preparation of ZnO/Nylon 6/6 Nanocomposites, Their Characterization and Application in Dye Decolorization. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrienko, E.V.; Bulushev, R.D.; Haupt, K.; Kosolobov, S.S.; Latyshev, A.V.; Pyshnaya, I.A.; Pyshnyi, D.V. A Simple Approach to Prepare Molecularly Imprinted Polymers from Nylon-6. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakiba, M.; Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Khosravi, F.; Jouybar, S.; Bigham, A.; Zare, M.; Abdouss, M.; Moaref, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Nylon—A Material Introduction and Overview for Biomedical Applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 3368–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S. Silica Nanoparticles-Nylon 6 Composites: Synthesis, Characterization and Potential Use as Sorbent. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfuz, H.; Hasan, M.; Dhanak, V.; Beamson, G.; Stewart, J.; Rangari, V.; Wei, X.; Khabashesku, V.; Jeelani, S. Reinforcement of Nylon 6 with Functionalized Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced Tensile Strength and Modulus. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 445702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; El-hami, K.; Kodaki, T.; Matsushige, K.; Makino, K. A Novel Method for Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface 2005, 289, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masalov, V.M.; Sukhinina, N.S.; Emel’chenko, G.A. Synthesis of Monodisperse Silica Nanoparticles via Heterogeneous Tetraethoxysilane Hydrolysis Using L-Arginine as a Catalyst. Inorg. Mater. 2018, 54, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, Y.; Vazquez, N.I.; Gonzalez, Z. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Sol–Gel as Nanocontainer for Future Drug Delivery Applications. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. 2017, 6, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, K.; Ozmen, M.; Ersoz, M. Immobilization of Albumin on Aminosilane Modified Superparamagnetic Magnetite Nanoparticles and Its Characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 71, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. Charge-Reversal APTES-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with High Drug Loading and Release Controllability. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17166–17175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Acosta, J.R.; Silva, J.A.; Fernández-Izquierdo, L.; Díaz-Castañón, S.; Ortiz, M.; Zuaznabar-Gardona, J.C.; Díaz-García, A.M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs) with Potential Applications in Plasmid DNA Isolation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 545, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Goh, P.; Rezaei, M.; Arzhandi, D.; Ismail, N. Aptes and Teos Modified Binary Recyclable Hybrid Fe3O4@GO Nanocomposite for Photocatalytic Dye Removal. J. Teknol. 2018, 80, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Tang, F.; Li, L. The Shape Effect of PEGylated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on Cellular Uptake Pathway in Hela Cells. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 162, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjaoui, Z.; Jamal Al Dine, E.; Kulmukhamedova, A.; Bezdetnaya, L.; Soon Chang, C.; Schneider, R.; Mutelet, F.; Mertz, D.; Begin-Colin, S.; Quilès, F.; et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded Thermoresponsive Superparamagnetic Nanocarriers for Controlled Drug Delivery and Magnetic Hyperthermia Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 30610–30620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggannavar, G.B.; Hiremath, C.G.; Achari, D.D.; Pangarkar, V.G.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Development of Doxorubicin-Loaded Magnetic Silica-Pluronic F-127 Nanocarriers Conjugated with Transferrin for Treating Glioblastoma across the Blood-Brain Barrier Using an in Vitro Model. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8017–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervault, A.; Dunn, A.E.; Lim, M.; Boyer, C.; Mott, D.; Maenosono, S.; Thanh, N.T.K. Doxorubicin Loaded Dual PH- and Thermo-Responsive Magnetic Nanocarrier for Combined Magnetic Hyperthermia and Targeted Controlled Drug Delivery Applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12152–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nghiem, T.H.L.; Nguyen, D.T.; Tran, T.T.H.; Vu, D.; Nguyen, T.B.N.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, M.H. Optical Properties of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Load and Release on Silica Nanoparticle Platform. Molecules 2021, 26, 3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).