Abstract
The corrosion of steel structures in aggressive marine environments is a vital issue that induces significant degradation of their performance and lifespan. Herein, three arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings with varied Al contents of 0 wt.%, 15 wt.%, and 50 wt.% were deposited onto a hull steel substrate. The effect of Al content on the long-term corrosion protection performance of ZnAl coatings left in a chloride-containing solution for 840 h was systematically investigated. The evolutions of open-circuit potential, polarization curves, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of different ZnAl coatings during the long-term immersion test were examined. The morphologies and phase constitutions of the corrosion products were characterized. The results indicated that the corrosion rate of ZnAl coatings decreased as the Al content increased, and the ZnAl50 coating exhibited the most superior long-term corrosion protection performance. Moreover, for the three ZnAl coatings with an Al contents varying from 0 to 50%, their corrosion rate increased with immersion time in the initial 360 h due to the formation of the unstable and porous corrosion product ZnO; after 360 h immersion, their corrosion rate decreased with the prolonging of immersion time. This was revealed to be related to the formation of different corrosion products. ZnO and stable Al2O3 were the main corrosion products for the pure Zn coating and ZnAl15 coating, respectively. Al2O3 and powerful layered double hydroxide Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O were found to be the dominant corrosion products of the ZnAl50 coating, which was responsible for its remarkable long-term corrosion protection performance.
1. Introduction
Steel is one of the most widely employed structural materials in marine environment due to its various advantages including excellent mechanical and welding properties, cost-effectiveness, and so on. The corrosion of steel equipment and structures in marine environment is a major issue that urgently requires solving, deteriorating their service performance and lifespan significantly [1]. That is, the exposure of steel structures in aggressive chloride-containing environments always leads to their severe corrosion and thus the degradation of their properties. Therefore, the development of anti-corrosion measures is of significant importance.
Numerous efforts have been made to improve the anti-corrosion performance of steel. The deposition of protective coatings on steel structures has been proved to be an effective and economical method to inhibit or mitigate their corrosion. Among them, sacrificial metallic coatings, such as Zn, Al, and ZnAl alloys coatings, are considered to be one of the most efficient, promising, and widely used approaches for protecting steel structures against aggressive marine corrosion [2,3,4,5]. In general, sacrificial metallic coatings provide effective corrosion protection for steel substrates through three mechanisms: the barrier effect of metallic coating itself, cathodic protection as a sacrificial anode, and the barrier effect of the corrosion products of the metallic coatings [6,7]. Nevertheless, pure Zn or pure Al coatings could hardly offer long-lasting corrosion protection for steel structures [7,8,9]. In the case of the pure Zn coating, its corrosion products are generally loose and not stable in marine environments, eventually leading to the rapid and continuous corrosion of Zn [6,10]. In terms of pure Al coatings, although its corrosion products, i.e., primary Al2O3 passivation film, are dense and stable in ambient environments, they are inclined to pitting corrosion and becoming damaged in chloride-containing marine environments, which impairs the protection effect of Al coatings, thus resulting in the corrosion of the substrate. Moreover, in the passive state, Al coatings behave as noble coatings, which cannot offer cathodic protection to the steel substrate [10,11].
To cope with the long-term corrosion protection issue of pure Zn and Al coatings, Al is always added to Zn coatings as an alloying element to develop ZnAl alloy coatings. ZnAl alloy coatings combine the advantages of pure Zn and pure Al, i.e., the sacrificial anode protection performance of Zn and the passivation effect of Al, thus favoring long-lasting corrosion protection for steel substrates [6,12,13]. As for the deposition of sacrificial ZnAl coatings, hot dipping, electroplating, and thermal spraying are the commonly used coating preparation methods. For the ZnAl coatings fabricated via varied surface treatment methods, their corrosion resistance is primarily derived from the protective effect of corrosion products, which are mainly influenced by the alloy composition and coating microstructure [6,14]. For instance, the corrosion product of hot-dipped ZnAl55 coating was demonstrated to be Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O, which could effectively inhibit further corrosion of the coating [15]. Moreover, for the electroplated ZnAl10 coating, its corrosion protection effect was revealed to attributable to the formation of an Al2O3 layer on the coating surface. As one of the most important surface treatment technologies, thermal spray, which includes plasma spray, arc spray, high velocity oxygen-fuel (HVOF) et al., these methods have been widely used to deposit protective coatings. For instance, plasma spray depends on the dissociation and ionization of working gases to form a high-temperature plasma jet and thus to deposit various types of materials [16,17]. Moreover, arc spray has been the main method used to fabricate ZnAl alloy coatings owing to its numerous merits including economical energy saving, cost effectiveness, high deposition efficiency, on-site flexibility, and so on [18,19]. Arc-sprayed ZnAl alloy coatings have been reported to demonstrate better corrosion resistance than pure Zn and pure Al coatings [7,20,21]. For example, Kuroda et al. [20] conducted an 18 year marine field test for arc-sprayed Zn, Al, and ZnAl13 alloy coatings to investigate their corrosion protection performance for steel pipes. Their results showed that the pure Zn coating started to degrade in immersed portion after 7 years. The Al coating could provide corrosion protection in general conditions, though not in the splash zone. On the contrary, the ZnAl13 alloy coatings performed well, providing corrosion protection even after 18 years of exposure in all conditions, regardless of whether sealed or not. Wu et al. [7] deposited Zn, Al, and ZnAl coatings on a carbon steel surface via arc spraying and the corrosion resistance of different coatings was studied through electrochemical methods. The results indicated that the ZnAl alloy coating exhibited the best corrosion resistance for a steel substrate. Lee et al. [21] fabricated Zn and ZnAl15 alloy coatings on carbon steel using the plasma arc thermal spray process to investigate their corrosion behavior in artificial seawater. Results showed that the ZnAl15 alloy coating presented better corrosion protection performance for the steel substrate compared to the single Zn coating. This has been explained as being correlated with their different corrosion products. That is, the corrosion product of the single Zn coating, primarily Zn(OH)2, is loose and porous, which could hardly prevent the penetration of corrosive media toward substrate. Conversely, the Al element in the ZnAl15 alloy coating facilitated the formation of simonkolleite, hydrozincite, and Zn–Al layered double hydroxide, which could effectively seal the defects in the coating and resist the ingress of the solution toward the substrate. Liu et al. [22] studied the corrosion mechanism of arc-sprayed Zn and ZnAl alloy coatings systematically. They concluded that the ZnAl alloy coating exhibited better corrosion protection capability than the Zn coating owing to the remarkable self-sealing effect of the corrosion products of the ZnAl coating.
The composition of the ZnAl alloy coating, i.e., the Al content, is a key factor significantly influencing the morphology and constitutions of the corrosion products, thus determining the corrosion resistance of the coating. Nevertheless, few studies have aimed to investigate the influence of Al content on the long-term corrosion behavior of thermal-sprayed ZnAl alloy coatings systematically. Moreover, currents studies mainly focused on the corrosion behavior of ZnAl alloy coatings with relatively low Al content, e.g., less than 15 wt.%. In general, ZnAl alloys with higher Al content are difficult to obtain due to the formation of brittle phases during the alloying process of ZnAl alloys with high Al composition [23]. Zhu et al. [24] deposited three types of arc-sprayed ZnAl alloy coatings with Al contents of 15.9, 21.1, and 30.1 wt.% to investigate the effect of Al content on their electrochemical behavior. Results revealed that the corrosion resistance of the ZnAl alloy coatings improved with the increase in Al content. However, the underlying mechanism was not demonstrated. Hu et al. [25] compared the corrosion protection performance of new, patented arc-sprayed ZnAl alloy coatings with Al fractions of 15, 30, and 50 wt.%. They concluded that the ZnAl alloy coating with 30% Al composition demonstrated the lowest corrosion rate owing to the effective protection of its compact and stable corrosion products. Nonetheless, the investigation was not that systematic and the results require further confirmation.
Therefore, in this study, arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings with Al contents of 0, 15 wt.%, and 50 wt.% were deposited onto a hull steel substrate. The effect of Al content on the microstructure, long-term corrosion performance, and the correlating corrosion mechanism of ZnAl coatings in a 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution were systematically investigated. The corrosion protection performances of different types of coatings were examined using electrochemical methods. The morphologies and chemical compositions of the corrosion products were determined using SEM and EDS. The XRD evolution of corrosion products during long-term immersion test was examined to clarify their corrosion mechanisms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coating Preparation
A commercial high-speed arc spray system (CMD-AS3000, Beijing Xindi Surface Technology Equipment Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) was used to deposit ZnAl coatings with Al compositions of 0, 15 wt.%, and 50 wt.%, which were hereinafter defined as pure Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings, respectively. Pure Zn wires (purity: 99.9%, diameter: Φ2.8 mm), ZnAl15 alloy wires (chemical compositions: Al: 14.5 wt.%, Zn: 85.5 wt.%, diameter: Φ2.8 mm), and ZnAl50 alloy wires (chemical compositions: Al: 49.5 wt.%, Zn: 50.5 wt.%, diameter: Φ2.8 mm) were utilized as feedstock materials to fabricate the Zn coating, ZnAl15 coating, and ZnAl50 coating, respectively. The Zn and ZnAl alloy wires were provided by Jiangsu Linlong New Materials Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China. A typical hull steel, 921A, with dimensions of 20 mm × 20 mm × 2 mm was used as the substrate. The chemical composition of the 921A substrate is listed in Table 1. Before coating deposition, the steel substrates were firstly ultrasonically cleaned in acetone, followed by grit blasting. The arc-sprayed Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings with thicknesses of ~300 μm were obtained a spraying voltage and current of 26 V and 180 A, respectively. The compressed air pressure and spraying distance were 0.55 MPa and 200 mm, respectively.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of 921A hull steel substrate.
2.2. Coating Characterization
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Zeiss Auriga, Oberkochen, Germany) was used to characterize the cross-sectional microstructure of the arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings and the surface morphologies of the corrosion products. The chemical compositions of the sprayed coatings and the coatings after the immersion test were analyzed using an Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS) equipped on the SEM. The phase constitutions of the arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings with varied Al contents and their corrosion products were examined via X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Bruker D8 advance, Hanau, Germany) with a Cu kα X-ray. The XRD was performed at a scanning angle ranging from 10° to 90° with a scanning speed of 10°/min and scanning step of 0.02° per step. Image analysis method was conducted on the cross-sectional images of arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings to measure their apparent porosities. Ten images were analyzed for each coating to obtain the average porosity value.
2.3. Long-Term Soaking Test
A long-term soaking test was performed for the arc-sprayed Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings to investigate the effect of Al content on the long-term corrosion protection behavior of ZnAl alloy coatings. The long-term soaking test was conducted in a 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution at ambient temperature. After immersion for 120 h, 360 h, 600 h, and 840 h, coating samples were taken out from the soaking solution and used for the following electrochemical test, SEM characterization, and XRD testing to reveal the influence of the Al content on the corrosion mechanism of ZnAl coatings. Prior to the soaking test, the surface of the coatings was ground and polished firstly, followed by sealing their back and side faces with epoxy resin, exposing the coating surface only. The soaking solution was changed every 2 to 3 days.
2.4. Electrochemical Test
The electrochemical test was conducted on an electrochemical workstation (CHI760, CH Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) to reveal the corrosion behavior of ZnAl coatings with different Al contents. A three-electrode system was utilized for the electrochemical test. The working electrode, reference electrode, and counter electrode were the coating sample, a saturated calomel electrode (SCE), and a platinum plate, respectively. The exposed surface area of the coating sample used for the electrochemical test was 1 cm2. The open circuit potential (OCP), potentiodynamic polarization curves, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were measured in sequence. Firstly, OCP versus time was measured. Then, the potentiodynamic polarization curve was tested, which started from −0.5 V, corresponding to the OCP, and terminated at a potential of +0.6 V relative to the OCP value with a potential scanning rate of 0.5 mV/s. At last, EIS was tested at the corrosion potential value with an amplitude of 10 mV. The scanning frequency of EIS ranged from 0.01 Hz to 100 kHz, and Zsimpwin software v 3.60 was used to fit the EIS data. Three samples were examined for each coating to obtain the average values.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Coating Microstructure
Figure 1 demonstrates the cross-sectional SEM images of the arc-sprayed Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings. It is observed that all the three types of sprayed coatings exhibited dense microstructures with good bonding and good adherence to the steel substrate. Furthermore, the three coatings presented uniform lamellar structures, which is a typical characteristic of thermal-sprayed coatings [26,27]. Some small black inclusions were found to be distributed within the coatings, which were verified to be oxides formed during the spraying process via EDS. Moreover, different contrast regions were observed within the ZnAl50 coatings. The regions with bright-white and dark-grey contrasts were confirmed to be a Zn-rich phase and Al-rich phase, respectively, using EDS analysis, whereas no distinct contrast difference was found within the ZnAl15 coating. This will be explained in detail in the following.

Figure 1.
Cross-sectional microstructure of arc-sprayed Zn coating (a,b), ZnAl15 coating (c,d), and ZnAl50 coating (e,f). (b,d,f) are the enlarged images of (a,c,e), respectively.
Additionally, pores and inter-lamellar un-bonded interfaces were apparently observed within the arc-sprayed Zn and ZnAl coatings. These pores and un-bonded interfaces mainly originated from two aspects: one is the insufficient filling and wetting of molten droplets towards pores, and the other is due to the formation of oxides during the spraying process, which hinders effective bonding between lamellae [28,29,30]. The interconnection of the pores and un-bonded interfaces distributed within the coatings would promote the formation of through-thickness pores, thus favoring the penetration of corrosive media towards the substrate and impairing the barrier effect of the coating itself [31]. The apparent porosities of the arc-sprayed Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings were examined to evaluate their barrier effect. As listed in Table 2, apparently, the ZnAl15 coating demonstrated the lowest porosity of 3.2% and the pure Zn coating exhibited the highest porosity of 5.6%. That is to say, the Al content within the ZnAl coatings exhibited a significant influence on the coating porosity. In the case of the pure Zn coating, the Zn droplets melted early during the spraying process due to the metal’s relatively low melting point (419.5 °C), which led to severe oxidation of Zn droplets and finally poor interface bonding and high porosity. This is further confirmed by the high oxygen content within the Zn coating, as listed in Table 2. For the ZnAl15 alloy coating, the addition of the alloying element Al into Zn resulted in an increased melting point of the ZnAl alloy and decreased oxidation during the spraying process, owing to the higher melting point of Al (660.3 °C) compared to Zn. In this way, low porosity was achieved. Nevertheless, when the Al content increased to 50%, i.e., for the ZnAl50 alloy coating, its porosity increased instead compared to that of the ZnAl15 coating. This can be explained as follows: the high Al content led to a relatively high melting point of the ZnAl50 coating, which would in turn hinder the sufficient melting of particles and thus the filling of pores. Moreover, Al is more inclined to oxidation than Zn since the Gibbs free energy for Al to form oxides is lower than that of Zn [32]. The above two reasons resulted in the higher porosity of the ZnAl50 coating than that of the ZnAl15 coating.

Table 2.
Chemical compositions and porosities of three arc-sprayed coatings.
The chemical compositions and phase constitutions of the arc-sprayed Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings were examined using EDS and XRD. As shown in Table 2, the chemical compositions of the three types of coatings were found to be comparable to that of the feedstock wires, indicating that there was no apparent elemental loss during the spraying process. Figure 2 presents the XRD results of the three arc-sprayed coatings. In the case of the as-sprayed pure Zn coating, only the Zn phase (PDF card No. 65-3358) was detected. For the as-sprayed ZnAl15 and ZnAl50 coatings, both Zn-rich and Al-rich phases (PDF card No. 65-2869) were identified. Moreover, the Zn-rich phase was found to be the primary phase for the ZnAl15 coating. When the Al content increased to 50%, i.e., in the case of the ZnAl50 coating, the Al-rich phase turned to be the dominant phase. Since the amount of Al-rich phase was low, distinct contrast differences would not be found in the ZnAl15 coating, which was in accordance with the SEM results shown in Figure 1c.
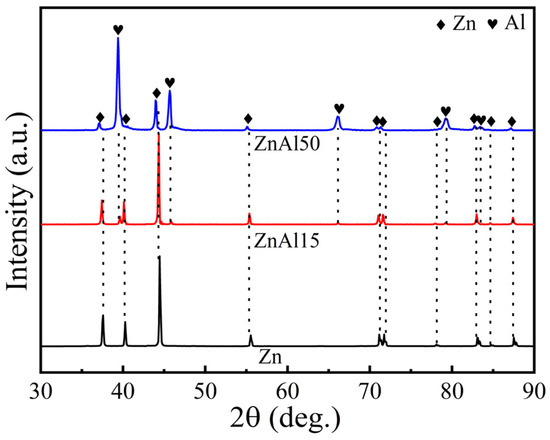
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of arc-sprayed Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings.
3.2. Long-Term Electrochemical Behavior of Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 Coatings
An electrochemical test over a long-lasting period was conducted for the arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings with Al contents varied from 0 to 50%. The evolution of OCP, polarization curves, and EIS during the long-term soaking process was examined to demonstrate the effect of Al content on the long-term protection performance for steel substrates. As can be seen from Figure 3, all the three types of ZnAl coatings exhibited similar OCP variation tendency with the prolonging of the immersion period. That is, for each coating, the OCP values moved to a negative direction in the first 360 h and then shifted to a positive direction after 360 h. Additionally, as shown in Figure 3 and the results listed in Table 3, after immersion for 840 h, the OCP values for the three types of coatings decreased in the following sequence: ZnAl50 coating > ZnAl15 coating > Zn coating. Moreover, it is found from Figure 4 that the corrosion potential of the three coatings during the long-term soaking test presented similar evolution tendencies to that of OCP. Since OCP and corrosion potential of a coating represent its corrosion tendency in thermodynamics, it is suggested that the corrosion tendency of ZnAl coatings decreased as the Al content increased from 0 to 50%. Furthermore, it could be inferred that the corrosion tendency of all the three coatings increased in the initial 360 h and then decreased until 840 h. Noteworthy, the OCP and corrosion potential of the three ZnAl coatings with Al contents of 0, 15%, and 50% were always much lower than the corrosion potential of −0.71V for the 921A steel substrate throughout the long-term soaking test. This indicates that the arc-sprayed Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings acted as sacrificial anodes to protect the steel substrate all through the immersion test.

Figure 3.
Variation of OCP after immersion for various periods for different coatings: (a) Zn coating; (b) ZnAl15 coating; and (c) ZnAl50 coating.

Table 3.
Electrochemical parameters for different coating samples.
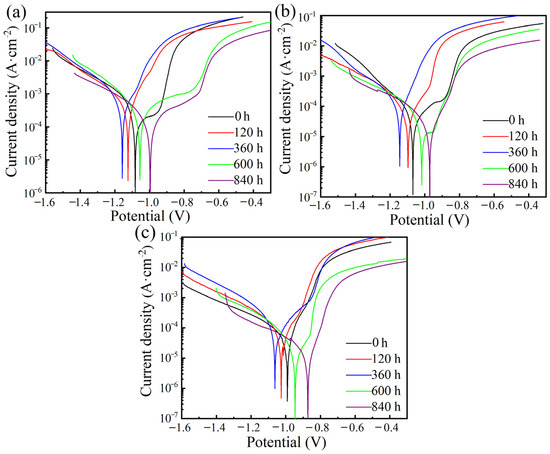
Figure 4.
Variation of potentiodynamic polarization curves after immersion for various periods for (a) Zn coating, (b) ZnAl15 coating, and (c) ZnAl50 coating.
Corrosion current density is another key factor usually used to evaluate the coating corrosion rate. In general, higher corrosion current density suggests a higher corrosion rate [33,34]. It is obviously found from Figure 4 and Table 3 that, after long-term immersion testing for 840 h, the corrosion current densities of the ZnAl coatings decreased with the increase in Al content. The ZnAl50 coating demonstrated the lowest corrosion current density of 9.05 μA/cm2, which is approximately two orders of magnitude lower than that of the pure Zn coating. This fact indicates that the corrosion protection ability of the ZnAl coating improves as the Al content increases from 0 to 50%. In other words, a higher Al content contributes to a lower corrosion rate and greater corrosion protection performance in the 840 h soaking test. Moreover, for each coating, the corrosion current density increased in the initial 360 h soaking period; after 360 h, this value began to decrease as the soaking test continued, which is in accordance with the corrosion potential results. These results suggest that the corrosion rate of each coating increased in the first 360 h and then slowed down after 360 h. This may be due to the variation of the dominant corrosion mechanism before and after 360 h for the Zn, ZnAl15, and ZnAl50 coatings, which will be discussed in detail in the following section.
EIS was measured to further clarify the long-term corrosion behavior of different coatings. Figure 5 shows the evolution of Nyquist plots during 840 h of immersion for the three different coatings. The Nyquist plots consisted of two capacitive loops at high frequency and low frequency, respectively. In general, a larger diameter of the capacitive loop means a lower corrosion rate [33,35,36]. Thus, it is indicated from Figure 5 that for each coating, at the early corrosion stage, the diameter of the capacitive loop decreased in the first 360 h. From 360 h to 840 h, the diameter of the capacitive loop increased. As observed from the phase angle Bode plots shown in Figure 6, two time constants were observed, corresponding to the two semi-circle loops in the Nyquist plots. Therefore, the generally used equivalent electrical circuit of Rs(Qc(Rc(QdlRct))) (Figure 7) was employed to fit the EIS data and the fitted results of EIS were listed in Table 4. Rs is the solution resistance; Qdl represents the constant phase element correlated to the inner double layer capacitance; Qc and Rc are the constant phase element and resistance related to the corrosion product film; Rct is the charge transfer resistance. It is well known that Rct and impedance modulus value at low frequency |Z|f = 0.01 Hz are two important factors frequently used to evaluate the corrosion activity. Greater Rct and |Z|f = 0.01 Hz values usually represent lower corrosion rates [37,38]. As shown in Figure 8 and Table 4, the Rct and |Z|f = 0.01 Hz values presented similar tendencies during the long-term immersion test, i.e., they tended to decrease over the initial 360 h and then underwent an increasing tendency after 360 h. These results indicate that the corrosion rate increased in the first 360 h and then decreased after 360 h, which is consistent with the corrosion current density results shown in Figure 4. Additionally, when comparing the Rct and |Z|f = 0.01 Hz values among ZnAl coatings with varied Al contents, it is obviously found that the Zn coating demonstrated the lowest Rct and |Z|f = 0.01 Hz values and the ZnAl50 coating exhibited highest Rct and |Z|f = 0.01 Hz values after the long-term immersion test. This fact further confirms that the corrosion protection ability of the ZnAl coating improved as the Al content increased from 0 to 50%.

Figure 5.
Nyquist plots after immersion for various periods for (a) Zn coating, (b) ZnAl15 coating, and (c) ZnAl50 coating.
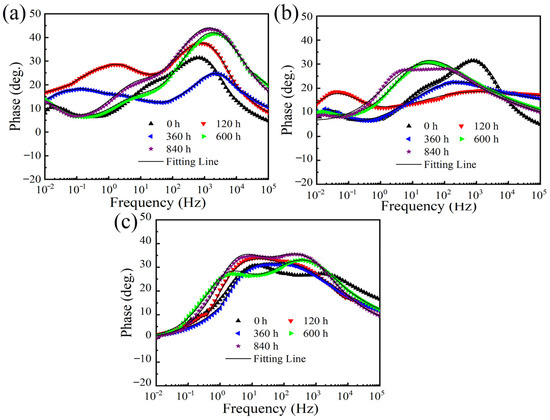
Figure 6.
Phase angle Bode plots after immersion for various periods for (a) Zn coating, (b) ZnAl15 coating, and (c) ZnAl50 coating.
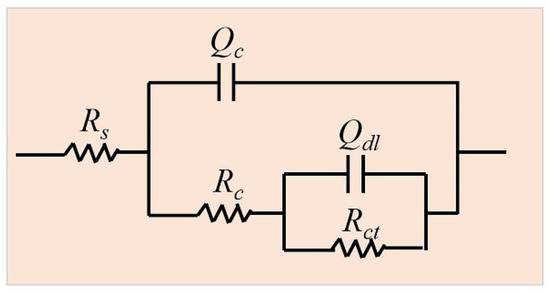
Figure 7.
Equivalent electrical circuit employed for EIS data fitting.

Table 4.
EIS data obtained from EIS plots after fitted by equivalent circuit diagram.
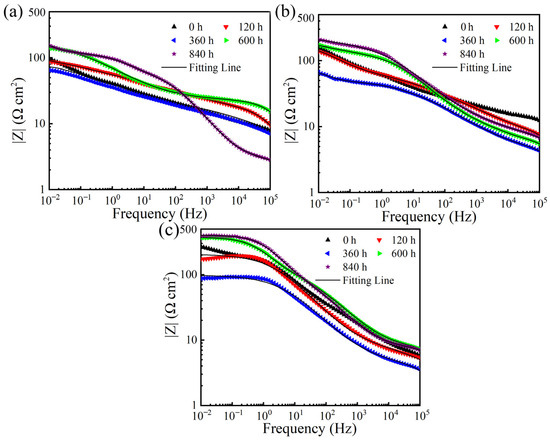
Figure 8.
Impedance modulus Bode plots after immersion for various periods for (a) Zn coating, (b) ZnAl15 coating, and (c) ZnAl50 coating.
3.3. Effect of Al Content on the Corrosion Mechanism of Arc-Sprayed ZnAl Coatings
In order to reveal the effect of Al content on the corrosion mechanism of the arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings with Al contents varying from 0 to 50%, XRD evolutions of the corrosion products during the long-term soaking test were examined, and the results are shown in Figure 9. For the pure Zn coating, during the initial 360 h immersion, ZnO (PDF card No. 36-1451) was found to be the primary corrosion product, and the amount of ZnO increased with the prolonging of the immersion period in the first 360 h. This can be explained as follows: at this stage, the activation dissolution of Zn was the dominant corrosion mechanism. It has been reported that the corrosion protection ability of corrosion products was mainly attributed to their effective inhibition of the surface redox reaction. ZnO is usually loose and porous and could not provide effective barrier effect; more importantly, ZnO is a semi-conductor, which could hardly hinder the redox reaction [3,6]. Therefore, ZnO is generally an undesirable corrosion product that demonstrates poor corrosion protection performance. In this way, the corrosion rate of the Zn coating increased gradually in the initial stage. After 360 h, it is found from Figure 9a that the amount of ZnO began to decrease. This phenomenon may be due to the transformation of ZnO to zinc salts such as hydrozincite and simonkolleite, which are usually found to be the corrosion products of Zn in chloride-containing solutions [8,9]. Nevertheless, the diffraction peaks of hydrozincite or simonkolleite were not identified, which is likely due to their low amounts at the coating surface. These zinc slats are slightly soluble in aqueous solutions and present denser and more stable characteristics than that of ZnO; moreover, they could mitigate redox reactions to some extent. Thus, after 360 h, it can be inferred that, attributed to the presence of zinc salts such as hydrozincite or simonkolleite at the Zn coating surface, the corrosion protection performance would be improved and its corrosion rate would be thus decreased, which is consistent with the electrochemical test results. However, from a long-term perspective, zinc salts like hydrozincite and simonkolleite are not that stable, as they might convert to ZnO in an alkaline solution and are incapable of offering long-term corrosion protection.
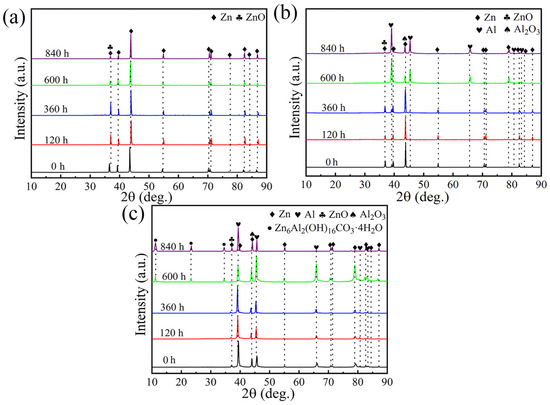
Figure 9.
Evolution of XRD patterns of different coatings during long-term soaking test. (a) Zn coating; (b) ZnAl15 coating; (c) ZnAl50 coating.
In the case of the ZnAl15 coating, as shown in Figure 9b, for the initial 360 h, ZnO was also the dominant corrosion product, as with the Zn coating, indicating that the dissolution of Zn is the primary corrosion mechanism at this stage. As shown in Figure 2, both the Al-rich phase and Zn-rich phase existed in the as-sprayed ZnAl15 coating. Galvanic cells would be formed between the Al-rich and Zn-rich phases, promoting the preferential dissolution of the Zn-rich phase to form ZnO. Since ZnO could not provide effective corrosion protection, the corrosion rate of the ZnAl15 coating increased at this stage. During the second corrosion stage, i.e., after 360 h, as can be seen from Figure 9b, the Al-rich phase began to be the dominant phase instead of the Zn-rich phase. This could be explained as follows: after 360 h, most of the Zn-rich phase at the coating surface had dissolved, leaving the Al-rich phase to become the primary phase. This fact is in accordance with the EDS results (Table 5), which indicated that the Zn/Al mass ratio at the coating surface was 0.86 after 840 h immersion, which is significantly deviated from the original 5.7 Zn/Al ratio in the as-sprayed ZnAl15 coating. In this way, the Al-rich phase started to dissolve to form Al2O3 (PDF card No. 50-1496), as indicated in Figure 9b. The corrosion product Al2O3 is dense, stable, and an excellent insulator, facilitating superior corrosion protection for the under-layered coating to some extent [39], which resulted in a gradual decrease in the corrosion rate of the ZnAl15 coating after 360 h.

Table 5.
Chemical compositions of the coating surface for different types of coatings after 840 h immersion.
For the ZnAl50 coating, its corrosion also consisted of two stages. In the primary 360 h, similar to the ZnAl15 coating, ZnO was the primary corrosion product owing to the preferential dissolution of the Zn-rich phase. Since ZnO could not provide powerful corrosion protection, the corrosion rate thus increased with the extension of the immersion period. After 360 h, apart from the Zn-rich phase, Al-rich phase, and Al2O3 phase, the diffraction peaks of Zn6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O (PDF card No. 38-0486), a type of layered double hydroxide (LDH), were also detected. Moreover, with the increase in the soaking time, the amount of LDH increased. LDH is formed due to the co-deposition of Zn ions and Al ions in the aqueous solution, and is proven to be a superior and desirable corrosion product that could effectively prevent further corrosion of the steel substrate. The remarkable corrosion protection capability of LDH is mainly derived from two aspects: on the one hand, LDH is more stable and insoluble in chloride-containing aqueous solutions compared to ZnO and zinc salts, and the redox rate of the ZnAl coating could be thus mitigated in the presence of LDH. On the other hand, LDH is generally dense and compact, acting as a superior protective barrier inhibiting further corrosion of the coating [6,21]. Therefore, the presence of both Al2O3 and LDH at the surface of the ZnAl50 alloy coating contributed to the drastically decreased corrosion rate and remarkable long-term corrosion protection performance for the steel substrate. This was also confirmed through the EDS results shown in Table 5, which indicate that the mass ratio of Zn/Al at the coating surface is 0.88, which is only slightly different from the Zn/Al ratio of ~1 in the as-sprayed ZnAl50 alloy coating. This fact suggests that the dissolving of Zn is effectively inhibited and the corrosion products are relatively stable in the aqueous solution.
The corrosion product morphologies of the Zn coating, ZnAl15 coating, and ZnAl50 coating after soaking in 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution for 840 h were characterized via SEM to further reveal their long-term corrosion mechanisms. As shown in Figure 10, after 840 h immersion, the ZnAl coatings with Al contents of 0, 15%, and 50% presented significantly different corrosion morphologies. For the pure Zn coating, its corrosion product, ZnO (as confirmed by XRD in Figure 9a), was loose and porous as expected, exhibiting a granular and nanosheet morphology consistent with the reported morphology of ZnO [8]. In the case of the ZnAl15 coating, discontinuous granular and flocculent corrosion products were formed on the coating surface, which have been confirmed to be mostly Al2O3. In addition, some pores and cracks were still observed on the coating surface. On the contrary, for the ZnAl50 coating, instead of porous corrosion products, dense and uniform corrosion products were observed and defects such as pores and cracks on the coating surface essentially disappeared.
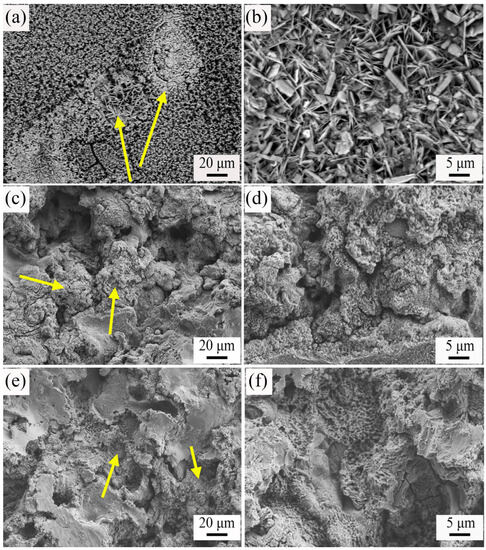

Figure 10.
Corrosion morphologies of different coatings after 840 h immersion. (a,b) Zn coating; (c,d) ZnAl15 coating; (e,f) ZnAl50 coating. (b,d,f) are the corresponding enlarged images of (a,c,e), respectively. The yellow arrows inserted in (a,c,e) denote the corrosion products.
On the basis of the above results, the long-term corrosion behavior and corrosion mechanism of arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings with Al content ranged from 0 to 50% could be summarized as follows. In general, the corrosion of the ZnAl coatings with Al contents varying from 0 to 50% was composed of two main stages. At the first stage, in approximately ten days, the activation dissolving of Zn phase was the dominant corrosion mechanism for all three ZnAl coatings. However, the loose and porous corrosion product ZnO could hardly hinder the further corrosion of the inner coating. Thus, the corrosion rates of the Zn and ZnAl coatings continuously increase with prolonging of the immersion period at the initial stage.
At the second stage, ZnO was still the primary corrosion product for the Zn coating, which could not inhibit the extensive dissolving of Zn and therefore was unable to provide long-term corrosion protection for the steel substrate. In this way, the pure Zn coating presented the worst corrosion protection behavior for the steel substrate. For the ZnAl15 and ZnAl50 coatings, new and powerful corrosion products were formed. In terms of the ZnAl15 coating, due to the addition of Al, stable and dense Al2O3 turned out to be the dominant corrosion product, which could block a fraction of pores, i.e., exhibiting a self-healing effect, and impede the dissolving of the Zn-rich phase to some extent. Nevertheless, due to the low Al content in the ZnAl15 alloy coating, the amount of the formed Al2O3 layer was low and it was unable to form a continuous protective barrier layer; thus, its protection effect was limited. When the Al content increased to 50%, i.e., for the ZnAl50 coating, besides Al2O3, LDH was also formed since the high Al content favors the formation of LDH. The relatively stable, compact, and uniform corrosion product LDH could construct a continuous and powerful barrier layer on the coating surface. Moreover, the corrosion products Al2O3 and LDH presented effective self-healing to block the pores within the coating. In this way, the most powerful and excellent long-term corrosion protection for the inner coating and substrate could be realized with the ZnAl50 coating. Thus, the long-term corrosion protection performance of the arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings improved with the increase in Al content.
To sum up, the effect of Al content on the long-term corrosion mechanisms of arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings could be summarized as follows. The variation of corrosion resistance among ZnAl coatings with different Al contents was principally derived from the formation of different corrosion products. The Al content within the arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings significantly influenced their corrosion protection performance via affecting the type and amount of corrosion products. In other words, with the increase in Al content within ZnAl coating, the corrosion product varied from loose, porous, and instable ZnO to stable and dense Al2O3, and finally compact and powerful LDH. Thus, the corrosion protection effect offered by the corrosion products improved gradually with increased Al content within the ZnAl coating.
4. Conclusions
Arc-sprayed ZnAl coatings with varied Al contents of 0, 15wt.%, and 50 wt.% were fabricated on a hull steel substrate. The effect of Al content on the microstructure and long-term corrosion behavior of the ZnAl coatings was systematically investigated. The underlying corrosion mechanism was revealed. The main conclusions are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- The ZnAl15 coating presented the densest microstructure, with a porosity of 3.2%, and the pure Zn coating demonstrated the highest porosity of 5.6%, which was related to the melting and oxidation state of the droplets during spraying process.
- (2)
- The long-term electrochemical test results indicated that the corrosion rate of the ZnAl coatings decreased as the Al content increased. The ZnAl50 coating demonstrated the most remarkable and effective corrosion protection capability for the steel substrate during the long-term soaking test in a chloride-containing aqueous solution. Additionally, all three types of ZnAl coatings with Al contents varying from 0 to 50% exhibited similar corrosion tendencies during the long-term immersion test. That is, in the initial 360 h, their corrosion rate increased; after 360 h immersion, their corrosion rate decreased instead.
- (3)
- The effect of Al content on the corrosion resistance of ZnAl coatings was revealed to primarily result from its influence on the corrosion products. At the initial stage, porous and unstable ZnO was proven to be the main corrosion product for the three ZnAl coatings, which resulted in their increased corrosion rates with the prolonging of the immersion period. After 360 h, ZnO was still the dominant corrosion product of the pure Zn coating, whereas single, dense, and stable Al2O3 was revealed to be the dominant corrosion product for the ZnAl15 coating, and both Al2O3 and compact, continuous LDH were revealed to be the corrosion products for the ZnAl50 coating, contributing to their decreased corrosion rates. The excellent long-term corrosion protection performance of the ZnAl50 coating originated from the powerful barrier effect and self-healing effect of the stable and compact corrosion product LDH.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.T.; methodology, Y.D., F.Z. and H.Z.; validation, S.C., K.X. and Z.W.; investigation, Y.D., F.Z., Z.W. and S.C.; resources, J.T. and S.X.; writing-original draft preparation, Y.D.; writing-review and editing, F.Z., S.X. and J.T.; supervision, K.X., S.X. and J.T.; project administration, S.X. and J.T.; funding acquisition, Y.D. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Equipment Pre-Research Field Foundation (grant number JZX7Y20220244100601) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 52001280).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Jiangsu Linlong New Materials Co., Ltd. for providing metallic wires.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Olugbade, T.O.; Ojo, O.T.; Omiyale, B.O.; Olutomilola, E.O.; Olorunfemi, B.J. A review on the corrosion fatigue strength of surface-modified stainless steels. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2021, 43, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.S.; Li, Z.L.; Zhao, X.S.; Xin, Y.L.; Ma, L.; Sun, M.X.; Li, X.B. Degradation behavior of arc-sprayed zinc aluminum alloy coatings for the vessel yongle in the south China sea. Coatings 2023, 13, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasoda, R.D.; Huang, Y.; Qi, X.N. Corrosion performance of wire arc deposited zinc aluminum pseudo alloy and zinc 15 aluminum alloy coatings on steel in chloride environment. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 1918–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Texier-Mandoki, N.; Crusset, D.; Sabot, R.; Creus, J.; Refait, P. Corrosion behavior and sacrificial properties of Zn and Zn-Al coatings in conditions simulating deep geological disposal of radioactive waste at 80 °C. Coatings 2022, 12, 1044–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshtaghi, M.; Safyari, M.; Mori, G. Hydrogen absorption rate and hydrogen diffusion in a ferritic steel coated with a micro- or nanostructured ZnNi coating. Electrochem. Commun. 2022, 124, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, S.; Liao, J.S. Long-term corrosion protection of arc spray Zn-Al-Si coating system in dilute chloride solutions and sulfate solutions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 302, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.P.; Sun, G.Q.; Wang, Q.Q.; Lin, S. Preparation, wear resistance, and corrosion performance of arc-sprayed Zn, Al, and Zn-Al coatings on carbon steel substrates. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonabi, S.F.; Ashrafizadeh, F.; Sanati, A.; Nahvi, S.M. Structure and corrosion behavior of arc-sprayed Zn-Al coatings on ductile iron substrate. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2018, 27, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Singh, J.K.; Ismail, M.A.; Bhattacharya, C. Corrosion mechanism and kinetics of Al-Zn coating deposited by arc thermal spraying process in saline solution at prolong exposure periods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3399–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, X.Y. Anticorrosion mechanism and application status of arc-sprayed Zn-Al alloy coating. Hot Work. Technol. 2014, 43, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Panossian, Z.; Mariaca, L.; Morcillo, M.; Flores, S. Steel cathodic protection afforded by zinc, aluminium and zinc/aluminium alloy coatings in the atmosphere. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 190, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.L.; Zhang, T.; Gong, F.Y. Study on properties of cold-sprayed Al-Zn coating on s135 drill pipe steel. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9209465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Singh, J.K.; Park, J.H. Pore blocking characteristics of corrosion products formed on aluminum coating produced by arc thermal metal spray process in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Li, H.R.; Wang, Z.; Song, H.W.; Li, Y.G. Development of hot-dip galvanized coating on steel surface. Mater. Prot. 2019, 52, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Seré, P.R.; Zapponi, M.; Elsner, C.I.; Sarli, A.R.D. Comparative corrosion behaviour of 55Aluminium–zinc alloy and zinc hot-dip coatings deposited on low carbon steel substrates. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Baeva, M.; Testrich, H.; Kewitz, T.; Foest, R. Effect of a Spatially Fluctuating Heating of Particles in a Plasma Spray Process. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifutdinov, A.I. Numerical study of various scenarios for the formation of atmospheric pressure DC discharge characteristics in argon: From glow to arc discharge. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 094008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idir, A.; Younes, R.; Bradai, M.A.; Sadeddine, A.; Baiamonte, L.; Pintaude, G. Correlation of tensile properties of arc-sprayed coatings and easy testing methods. Coatings 2023, 13, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, T.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Tsai, K.C.; Lu, W.F.; Huang, J.Y.; Liu, T.Y. Thermal spray coatings of Al, ZnAl and inconel 625 alloys on SS304L for anti-saline corrosion. Coatings 2019, 9, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, S.; Kawakita, J.; Takemoto, M. An 18-year exposure test of thermal-sprayed Zn, Al, and Zn-Al coatings in marine environment. Corrosion 2006, 62, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Singh, J.K. Deposition and corrosion studies of plasma arc thermal sprayed Zn and 85Zn–15Al films on steel surface. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 19650–19665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Z.X.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.X.; Xu, B.S. Study on self-sealing mechanism of Zn and Zn-Al coating based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. China Surf. Eng. 2005, 2, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.Q.; Xiao, K.; Dong, C.F.; Li, X.G. Corrosion behaviour of Zn-Al pseudo-alloy coating on carbon steel in chloride environments. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 567, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Xu, B.S.; Chen, Y.X. Effect of Al content on electrochemical corrosion behavior of arc sprayed Zn-Al coatings. China Surf. Eng. 2011, 24, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.M.; Zhang, P.Z.; Wei, D.B.; Su, F. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of arc sprayed Zn-xAl (x = 15, 30, 50) alloy coatings in NaCl solution. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1065f7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.J.; Yao, S.W.; Luo, X.T.; Li, C.X.; Li, C.J. An effective approach for creating metallurgical self-bonding in plasma-spraying of NiCr-Mo coating by designing shell-core-structured powders. Acta Mater. 2016, 110, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.J.; Xu, K.W.; Hu, J.H.; Zhang, S.J.; Cao, G.Q.; Shao, G.S. Durable self-polishing antifouling Cu-Ti coating by a micron-scale Cu/Ti laminated microstructure design. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 79, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.J.; Luo, X.T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y.Q.; Li, C.X.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.J. Mo-alloyed stainless steel coating with improved cavitation erosion resistance by plasma spraying a specially designed core-shell-structured powder. Wear 2023, 528, 204961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.S.; Luo, X.T.; Sun, Y.Q.; Ren, Y.; Li, C.J. Atmospheric plasma-sprayed CuNiInB coatings of high fretting wear performance enabled by oxide-free metallic droplet deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 464, 129537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.T.; Chang, S.F.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Cheng, K.C.; Hsu, K. Influence of feedstock in the formation mechanism of cold-sprayed copper coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.J.; Wei, Y.K.; Li, C.X.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.J. Effect of post-spray shot peening treatment on the corrosion behavior of NiCr-Mo coating by plasma spraying of the shell-core-structured powders. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2018, 27, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.Y.; Luo, X.T.; Ge, Y.; Li, C.J. Enhancing the hot-corrosion resistance of atmospheric plasma sprayed Ni-based coatings by adding a deoxidizer. Mater. Des. 2021, 211, 110154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.K.; Li, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.T.; Li, C.J. Corrosion resistant nickel coating with strong adhesion on AZ31B magnesium alloy prepared by an in-situ shot-peening-assisted cold spray. Corros. Sci. 2018, 138, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, M.C.; Luo, Q.; Fan, H.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Lu, H.S.; Chou, K.C.; Wang, X.L.; Li, Q. Influence of alloyed magnesium on the microstructure and long-term corrosion behavior of hot-dip Al–Zn–Si coating in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2016, 104, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Zhou, S.G.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, C.T.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.P. Enhancing anti-corrosion and antifouling properties of Cu/GLC composite film for marine application. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 375, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.S.; Cinca, N.; Dosta, S.; Cano, I.G.; Guilemany, J.M.; Caires, C.S.A.; Benedetti, A.V. Corrosion resistance and antibacterial properties of copper coating deposited by cold gas spray. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 361, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.H.; Chen, F.; Xiang, S.R.; Zhou, J.L.; Song, Z.W.; Yu, G. Studies of several pickling and activation processes for electroless Ni-P plating on AZ31 magnesium alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, D115–D123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavian, M.; Attar, M.M. Another approach in analysis of paint coatings with EIS measurement: Phase angle at high frequencies. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 4152–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safyari, M.; Mori, G.; Ucsnik, S.; Moshtaghi, M. Mechanisms of hydrogen absorption, trapping and release during galvanostatic anodization of high-strength aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).