Abstract
The work studies the influence of the silver dopant (<0.5 at.%) on the structure and mechanical properties of porous TiNi alloys obtained by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. These alloys are of high scientific and practical interest in medicine. The presence of silver in the TiNi alloy will ensure improved cytocompatibility and antibacterial properties. The TiNi porous alloys with 0.2 and 0.5 at.% Ag nanoparticles have multiphase composition. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of the obtained alloys showed that an increase in the silver content is accompanied by a quantitative decrease in the austenite phase TiNi(B2) and an increase in the martensite phase TiNi(B19’), as well as in secondary phases Ti2Ni, Ti4Ni2O. Evenly distributed silver nanoparticles up to 10 nm were found in the surface layer by transmission electron microscopy. The results of the scanning electron microscopy showed that inclusions containing silver are located mainly in the zones of Ti2Ni peritectic crystallization. The mechanical characteristics were studied by means of compression tests and it was found that with an increase in the silver dopant, the elastic modulus and elastic limit decrease, but the maximum deformation to fracture increases significantly. It was found that with an increase in the volume fraction of silver, the plastic properties of the alloy increase. No dependency of the tensile strength on the amount of silver was found.
1. Introduction
Currently, TiNi-based alloys are of high scientific and practical interest [1,2]. The unique properties of the TiNi alloys such as shape memory effect, superelasticity, strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance make them highly biocompatible compared to other alloys, which ensures their wide use in medicine. Various doping additives introduced into the TiNi composition give it various structure-phase states and effectively influence its physical and mechanical characteristics [3,4,5]. In work [3], aluminum was added into the porous TiNi alloy to improve the physical and mechanical properties and make it possible to use as an implantation material. In [4], the authors determined the range of silver content for the production of TiNi-Ag wires. It was found that the optimal balance between strength, ductility, and shape memory parameters was achieved at a silver concentration of 0.1 at.%. In a study of the silver effect on cell viability in cast TiNiAg alloys, results showed that silver in small amounts (0.1–0.2 at.%) is favorable for cell adhesion, and increases the cell viability level by more than 30% [6].
Porous TiNi alloys are well integrated into biological tissues and at the same time they remain permeable to biological fluids. Therefore, porous TiNi alloys are used as an effective osteoplastic material [7,8]. Nowadays, the implant industry pays special attention to materials with antimicrobial activity which prevent infection [9]. Among the metals with antimicrobial properties, silver has attracted the interest of many researchers due to its high biocidal activity. Silver has bactericidal activity at concentrations up to 35 parts per billion [9,10] without any toxic effect on mammalian cells. For the Ag particles in the range of 20–30 nm, optimal characteristics of antibacterial activity, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance were achieved [11,12]. In addition, the bacteria showed a low propensity to develop resistance to silver. But the results of studies on the antimicrobial efficacy of silver alloys are often inconclusive and conflicting.
Regarding the studies on TiNiAg alloys, there are mainly works on cast titanium nickelide alloys. TiNi alloys with the Ag concentration from 0.5 to 9 at.% are of particular interest in medicine. The presence of silver in the alloy ensures the improved cytocompatibility and antibacterial properties of TiNi [13,14,15,16,17] as well as increases the yield strength and tensile strength [18,19]. The shape memory effect of TiNi alloys was studied at the Ag concentration of 1.4 at.% [14]. Martensitic transformations, as well as microhardness, were mainly considered in the range of 0.6–1.9 at.% Ag [20,21,22,23]. The effect low silver content (<0.5 at.%) has on the structure, mechanical characteristics, and deformability of porous TiNiAg alloys has not been fully studied. No study was found on Ag addition during the production of porous TiNi alloys by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. There are few studies on adding Ag during the sintering of porous TiNi alloys, as well as on modifying the surface of porous TiNi alloys using Ag. Ag addition reduces the Young’s modulus of the porous TiNi alloy, which results in a greater similarity to the Young’s modulus of the human bone, as well as an increase in the maximum deformation of the alloy [24].
The aim of this work is to study the effect silver dopant has on the structure and physical and mechanical properties of porous TiNi alloys obtained by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS).
The authors believe that the silver addition in the nanopowder form will provide antibacterial properties while maintaining the high functional characteristics of the porous-permeable NiTi. This will create a new material with a suitable microenvironment for osteogenesis and an antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effect in order to counteract the development of infection at the interface of the implant-biological tissue.
2. Materials and Methods
Two powder mixtures were prepared for the study, each containing the main part of nickel PNK OT-4, titanium PTOM-2, titanium nickelide PN45T55OM, and silver nanopowder dopant with an average particle size of 8 nm and the concentration of 0.2 at.% Ag and 0.5 at.% Ag. To distribute the dopant more evenly, silver nanopowder was mixed with nickel powder in equal amounts, then the main part of the nickel and titanium powders was added to the resulting mixture in small portions and mixed. The TiNiAg alloy samples were obtained by the SHS method in a flow reactor in the flowing argon atmosphere to prevent the mixture oxidation during heating and the oxidation of the synthesized alloy during cooling. The synthesis was initiated by an electric arc, after preheating the reactor to a stable temperature of 520 °C. After the synthesis reaction was passed, the reactor with the obtained porous alloys was cooled by immersion in water at room temperature.
The phase composition and structure of the alloys were studied with a Shimadzu XRD-6000 diffractometer in CuKα radiation. X-ray diffraction patterns were indexed with the PowderCell 2.4 full-profile analysis program and compared with the PDF 4+ database. The volume fractions of the phases were estimated by full-profile analysis based on calculations in relation to the intensities ratio of diffraction reflections using the POWDER CELL 2.4 program and the PDF-4+ database. The lattice parameters and micro-stresses were calculated with precision using the POWDER CELL 2.4 software. SEM images of porous TiNiAg samples were obtained with a scanning electron microscope (TESCAN ORSAY HOLDING, Brno, Czech Republic) with a Tescan MIRA 3 LMU Schottky cathode equipped with an Oxford Instruments Ultim Max 40 energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (Oxford Instruments, High Wycombe, UK).
The structure of the samples in cross-section geometry was studied using transmission electron microscopy at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV using the JEOL JEM-2100 (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) electron microscope at the Center for Collective Use Nanotech, Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The study of mechanical properties was performed on an Instron 5969 (Instron, a division of Illinois Tool Works Inc., Norwood, IL, USA) setup using a compression loading scheme. Samples for compression with geometric dimensions 6 mm × 3 mm × 3 mm were cut from the workpiece with an electric spark machine. Uniaxial compression loading was carried out at a room temperature of 24 °C. When studying the mechanical properties of each composition, at least 5 samples were tested.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results
3.1.1. XRD of Cross Sections TiNiAg Specimens
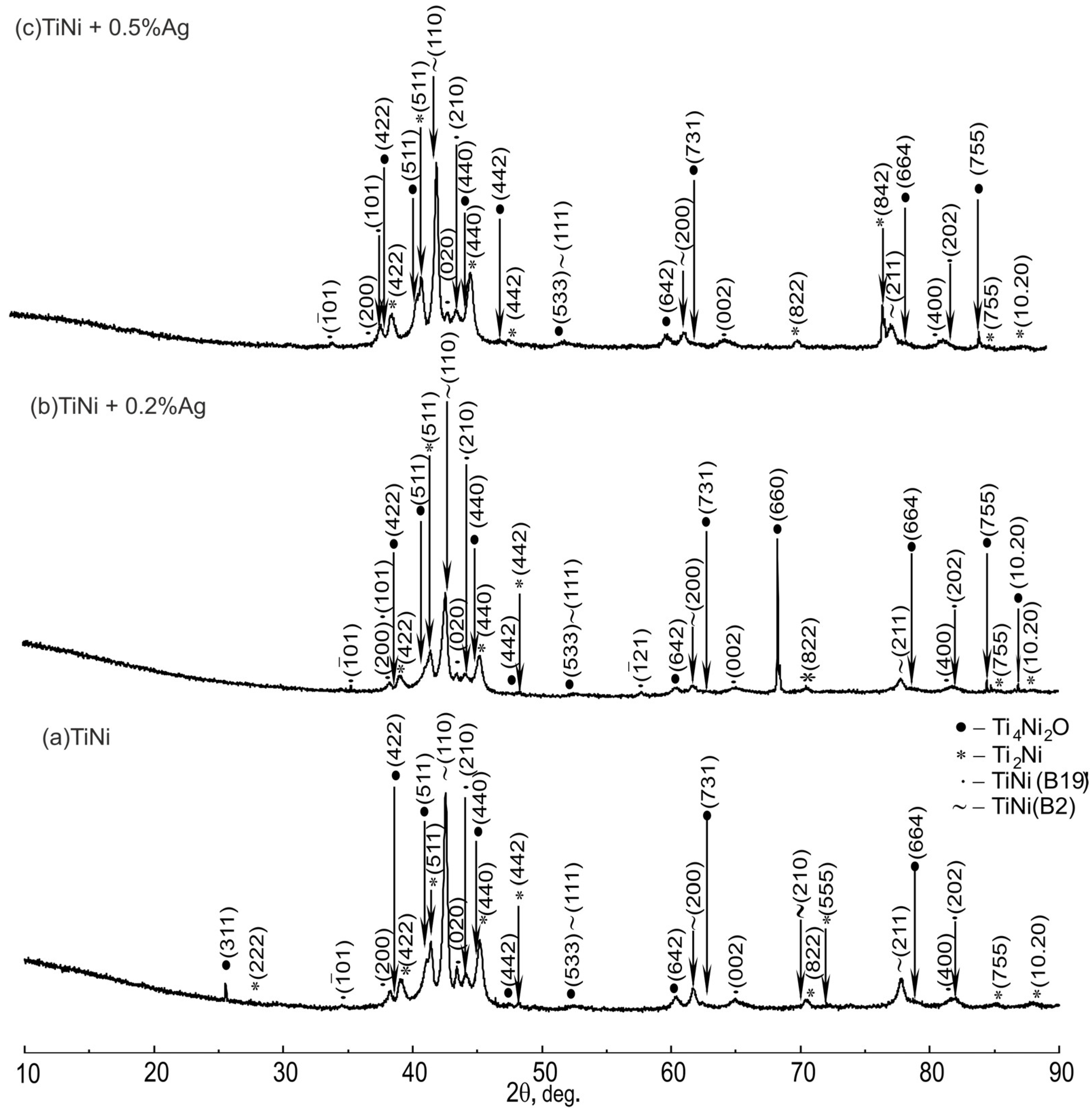
Figure 1 shows X-ray diffraction patterns of TiNi samples containing Ag. The phase composition of the studied alloys consists of Ti4Ni2O, Ti2Ni, TiNi(B19’), and TiNi(B2) phases. Due to the small amount of silver, no Ag-based phases were found.
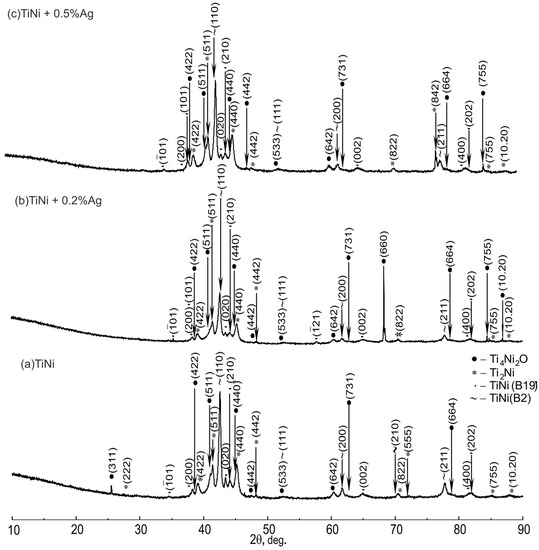
Figure 1.
X-ray diffractograms of SHS–TiNi porous alloys specimens: (a) TiNi; (b) TiNi + 0.2% Ag; (c) TiNi + 0.5% Ag.
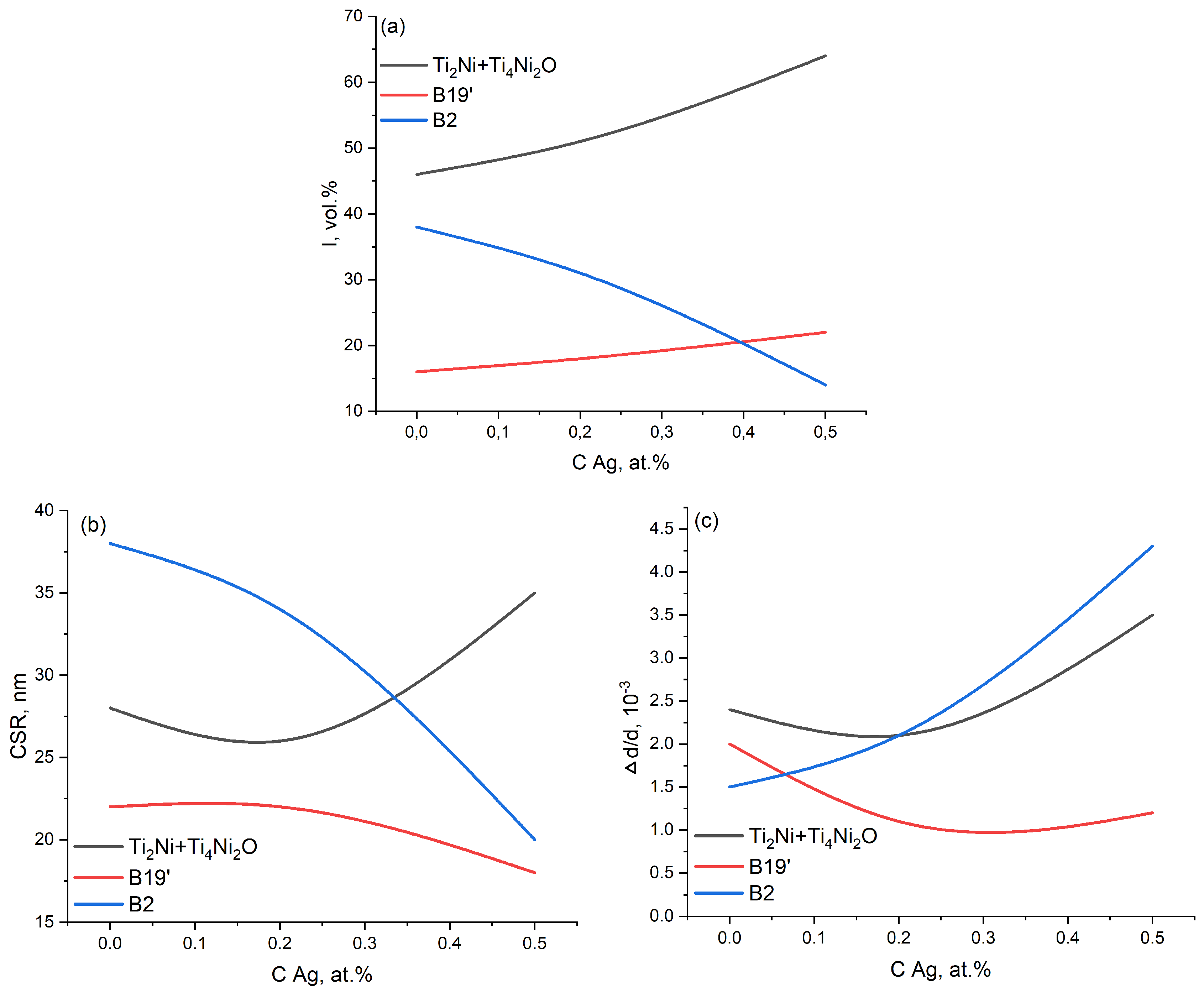
Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of TiNiAg alloys shows an increase in the volume fraction of the TiNi martensitic phase with the B19’ structure, Ti2Ni, Ti4Ni2O secondary phases, and a decrease in the fraction of the TiNi austenite phase with the B2 structure with increasing silver content (Table 1 and Figure 2a).

Table 1.
X-ray analysis of TiNiAg alloys.
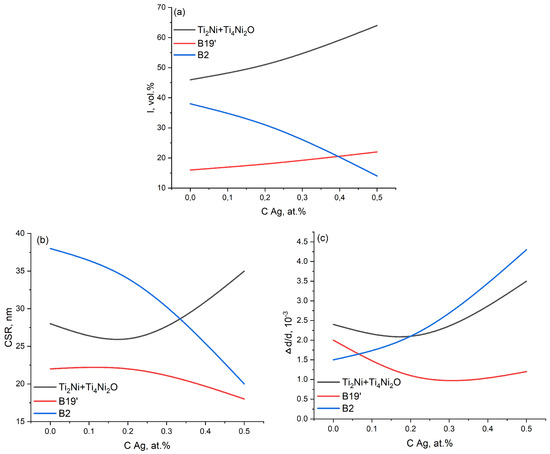
Figure 2.
Concentration dependence according to the results of X-ray diffraction analysis of TiNiAg: (a) volume fraction of the phases; (b) CSR values; (c) microdistortions.
Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis showed microdistortions of all the phases in the TiNiAg alloy system. It can be assumed, and it follows from Table 1, that silver is probably incorporated into the crystal lattice of both the B2 and Ti2Ni phases, since the greatest microdistortion of these lattices is observed, especially in the B2 phase (Figure 2c).
3.1.2. SEM Study of Polished TiNiAg Samples
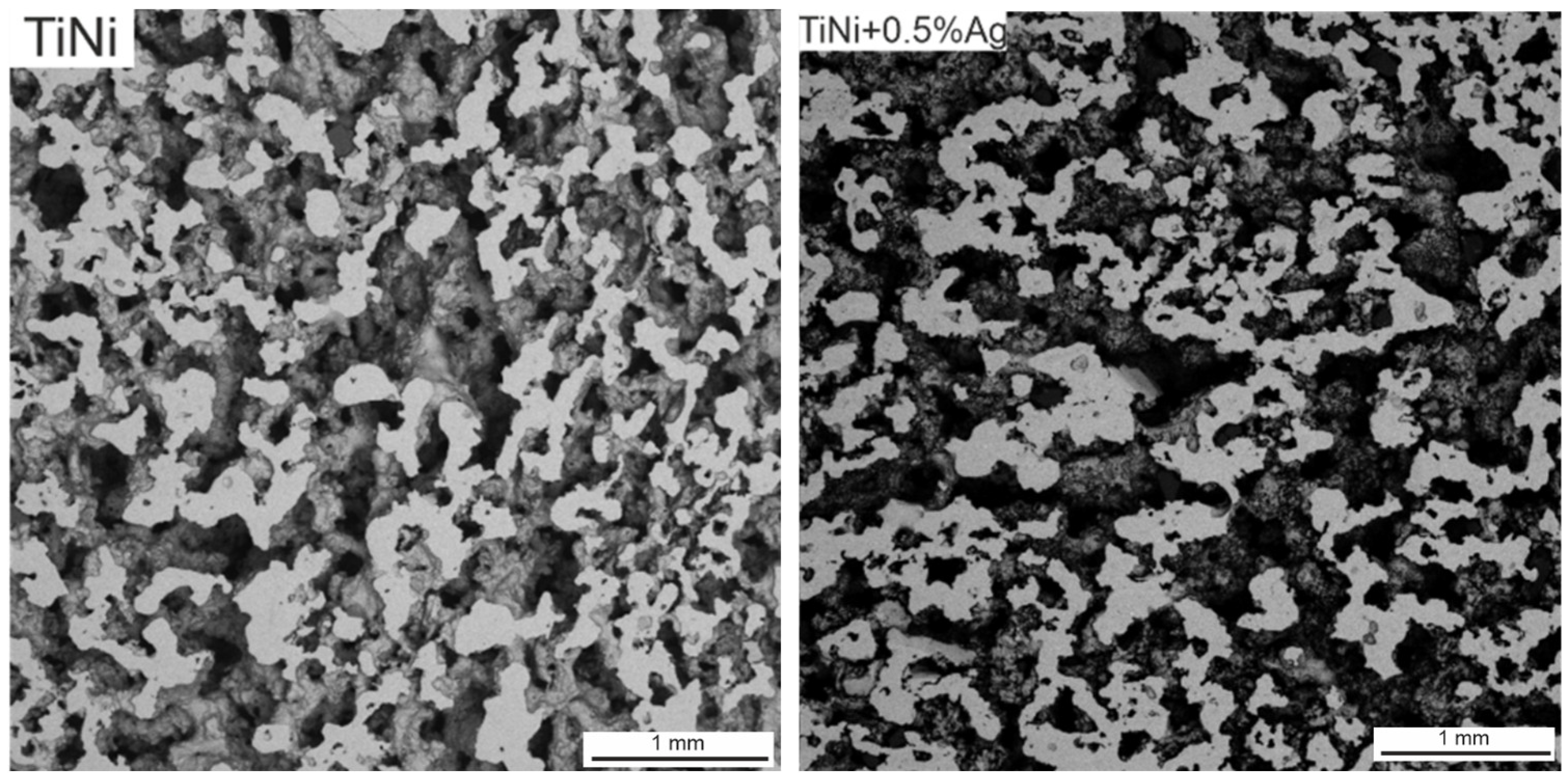
With an increase in the silver content, the porosity of the samples did not change and accounted for 62% ± 2% (Figure 3).
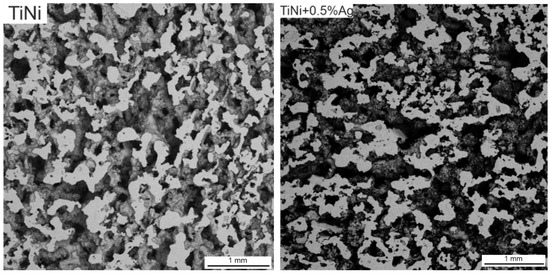
Figure 3.
The cross-sectional SEM image of SHS–TiNi porous alloys specimens.
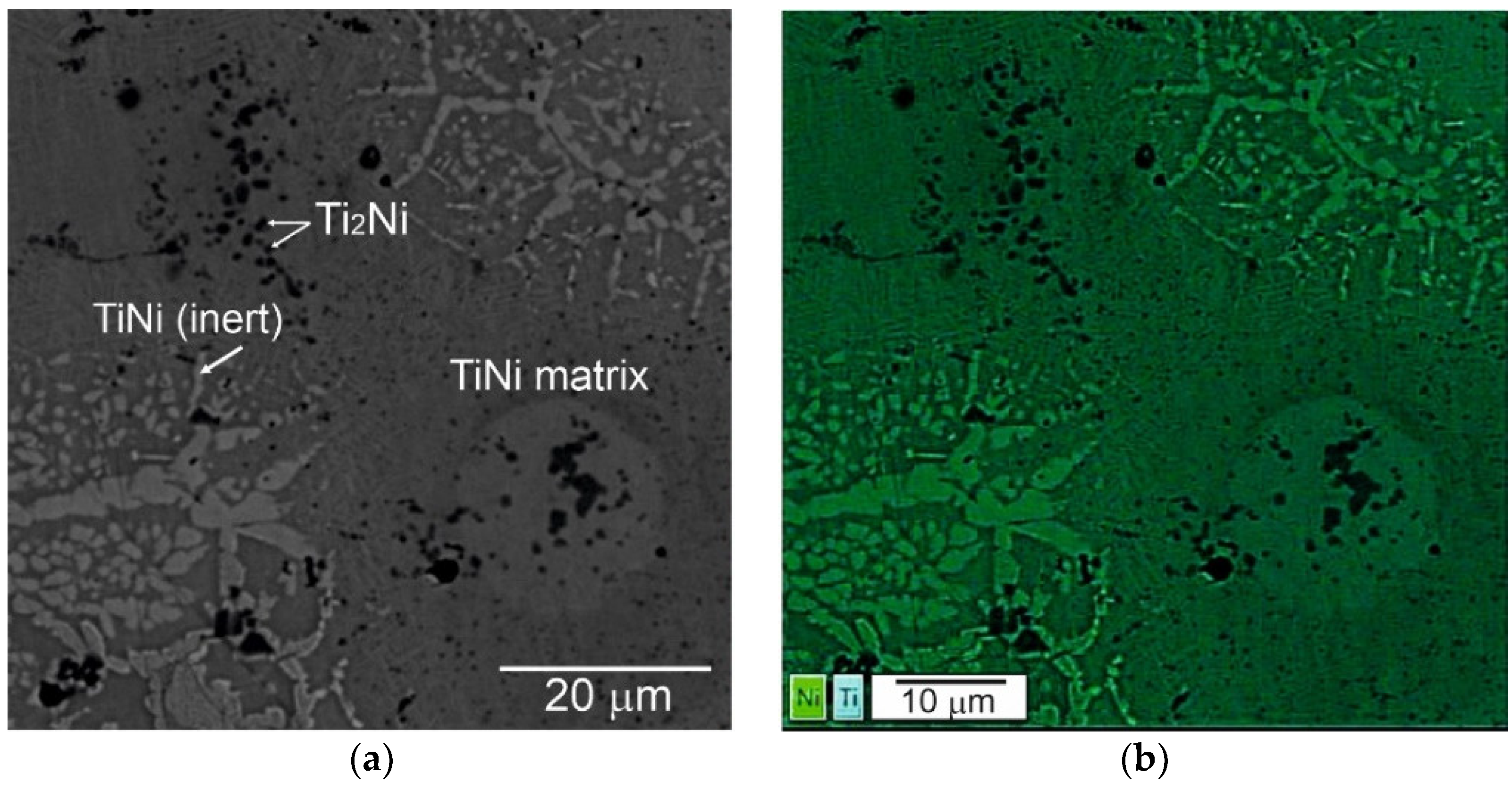
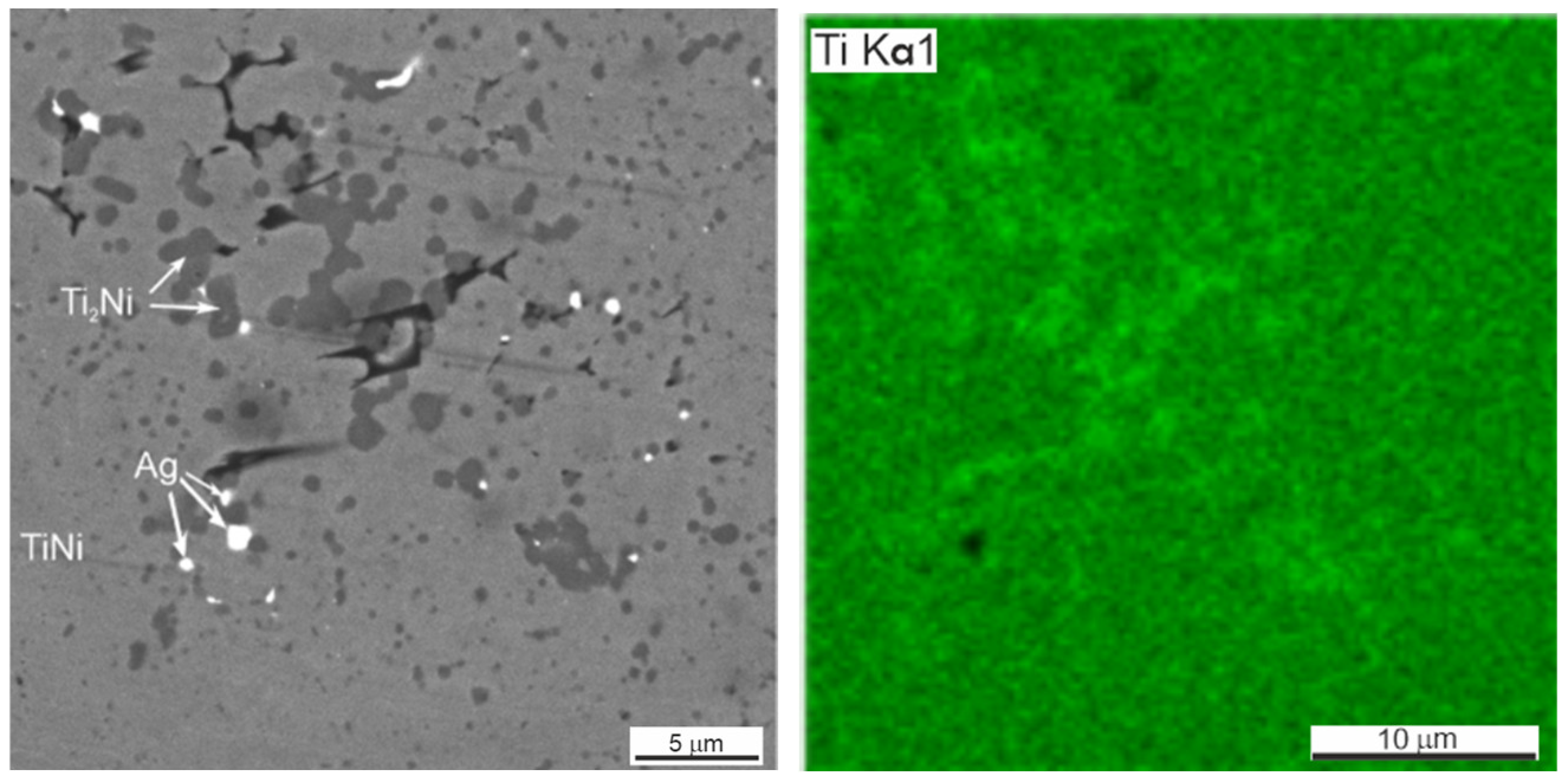
Apart from titanium and nickel powders, the mixture includes TiNi powder PN55T45OM. It is not possible to distinguish the TiNi powder which does not participate in the synthesis reaction from the TiNi phase after SHS by X-ray diffraction. At the same time, the SEM study of the phase and elemental composition of porous alloys made it possible to do this. Phase 1 enriched with nickel forms a residual skeleton of the inert powder particles which partially dissolve in the reaction melt (Figure 4, Table 2).
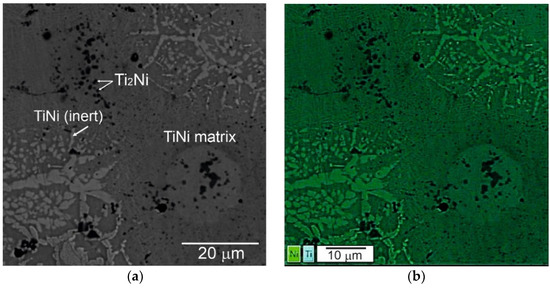
Figure 4.
SEM image (a) and EDS elemental mapping (b) of initial porous TiNi alloy.

Table 2.
Elemental composition of phases in TiNi SHS alloys.
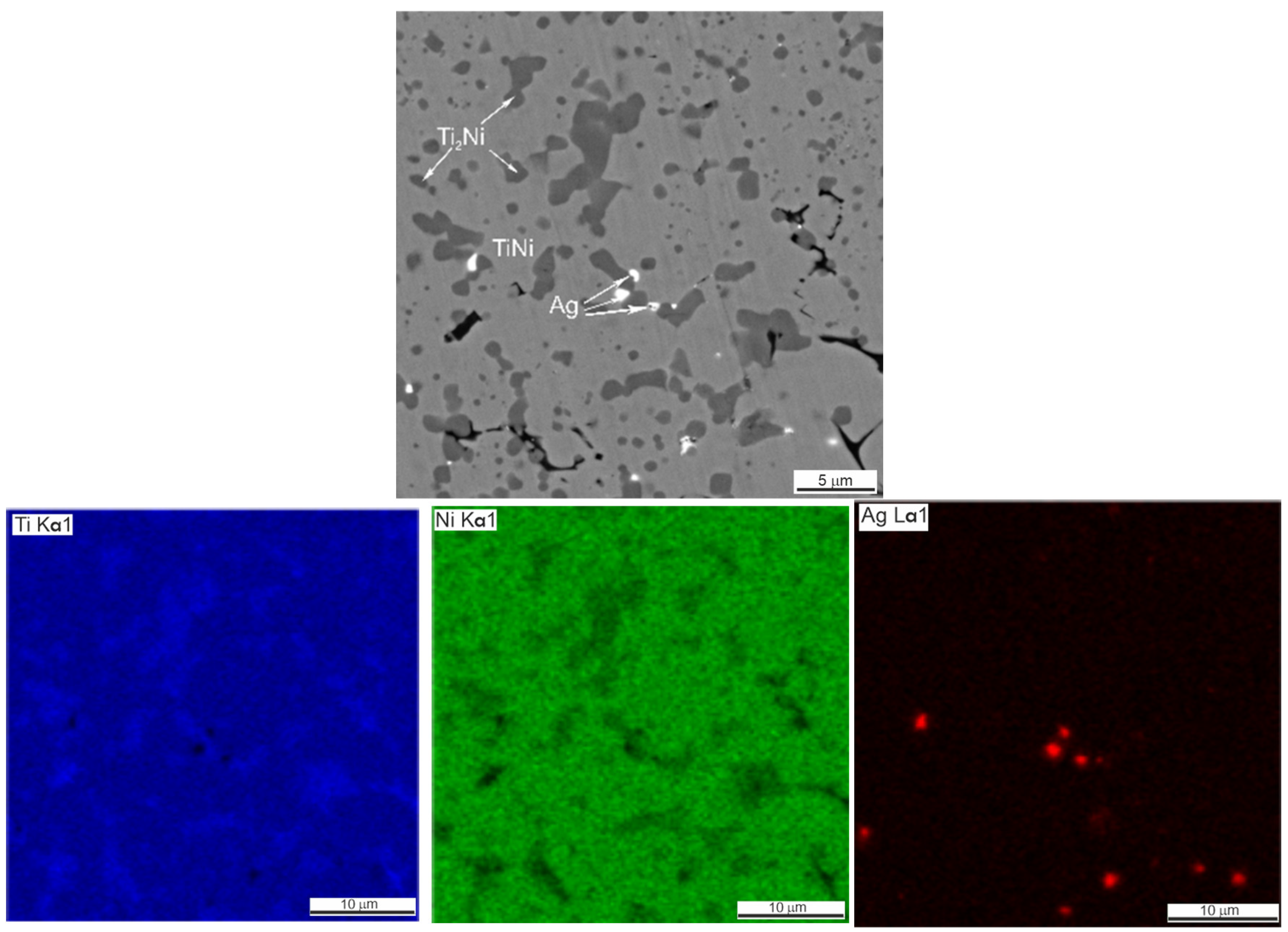
The presence of silver in the form of light inclusions up to 0.1 µm was detected on the SEM–EDS maps of element distribution in porous SHS alloys TiNi + 0.2% Ag, TiNi + 0.5% Ag (Figure 5 and Figure 6, Table 3 and Table 4). The localization of silver particles is predominantly on the particles of the Ti2Ni or Ti4Ni2O phases.
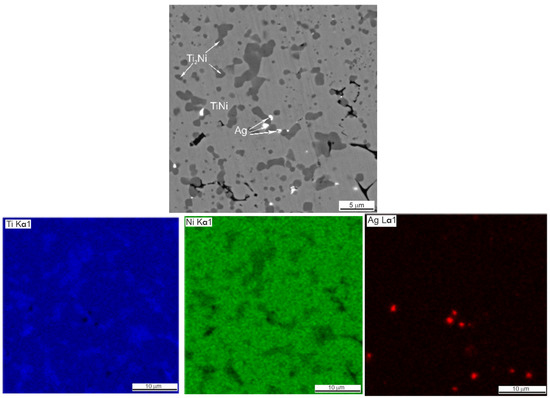
Figure 5.
SEM image and EDS elemental mapping of porous SHS TiNi + 0.2% Ag.
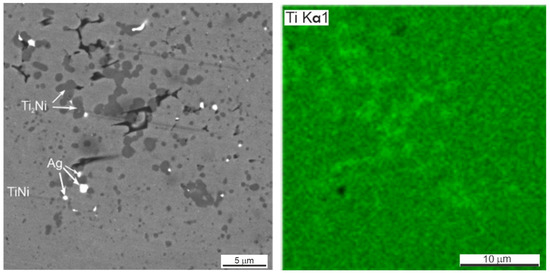
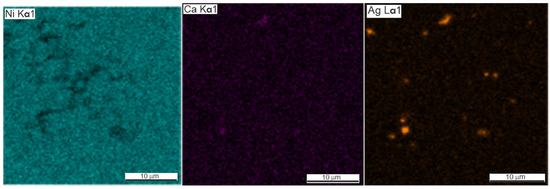
Figure 6.
SEM image and EDS elemental mapping of porous SHS alloy TiNi + 0.5% Ag.

Table 3.
Elemental composition of phases in SHS alloys TiNi + 0.2% Ag.

Table 4.
Elemental composition of phases in SHS alloys TiNi + 0.5% Ag.
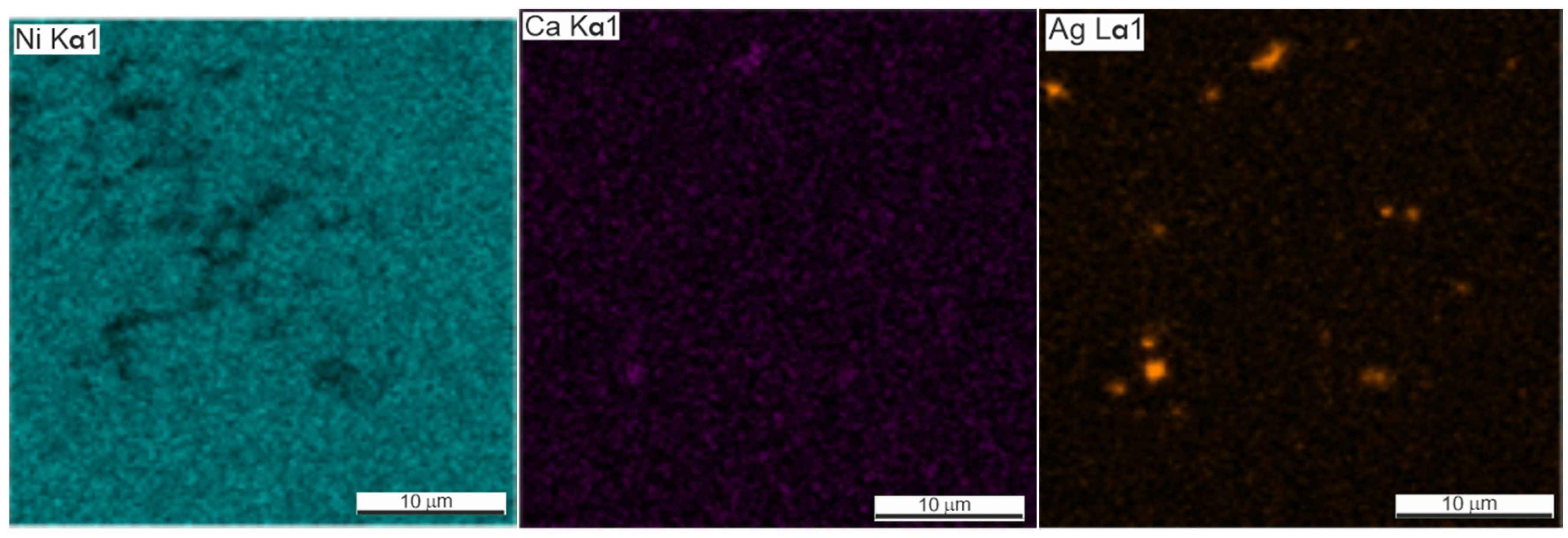
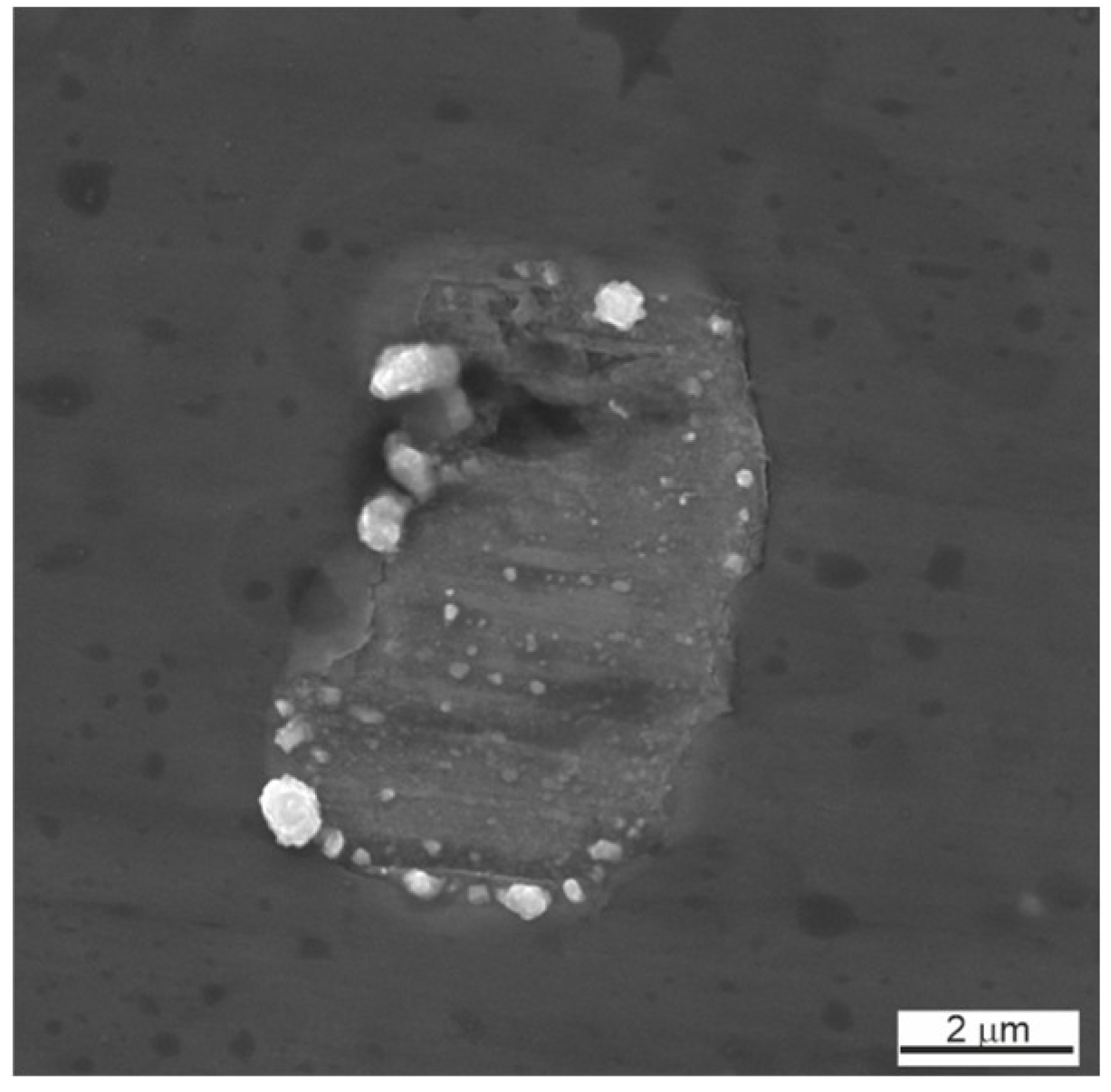
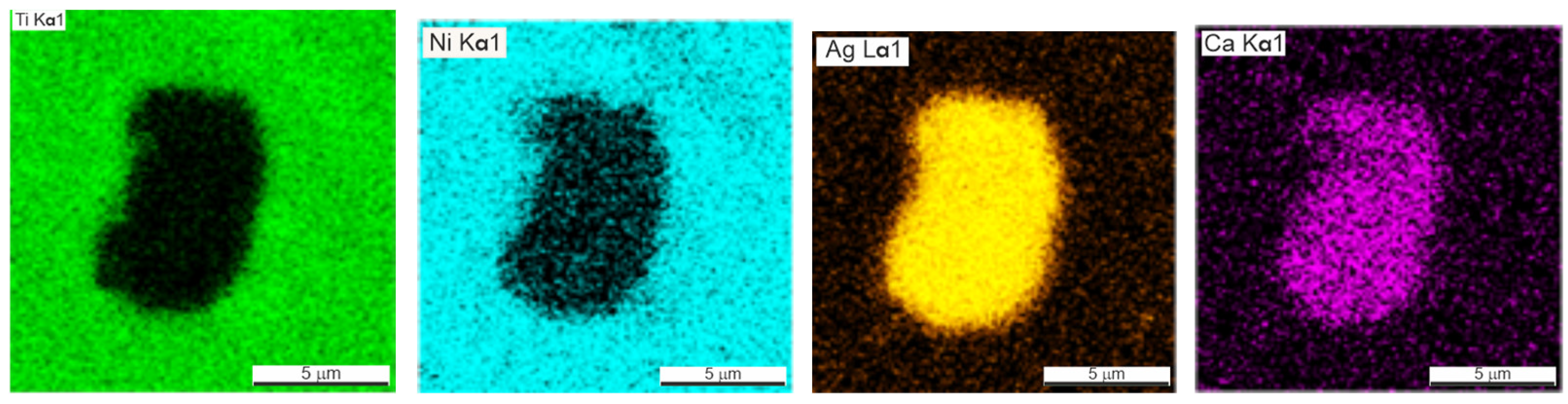
Silver was found not only in the form of subnanocrystalline particles but also in the composition of larger, up to 7 μm, intermetallic inclusions of the Ca–Ag system (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Calcium is a residual technological impurity, which is used in the production of titanium powder by calcium hydride reduction. Elemental EDS mapping showed the presence of Ca and Ag in the form of inclusions of 5–10 µm. Most of the inclusions are in the form of the chemical compound AgxCay containing Ag less than 1 µm.
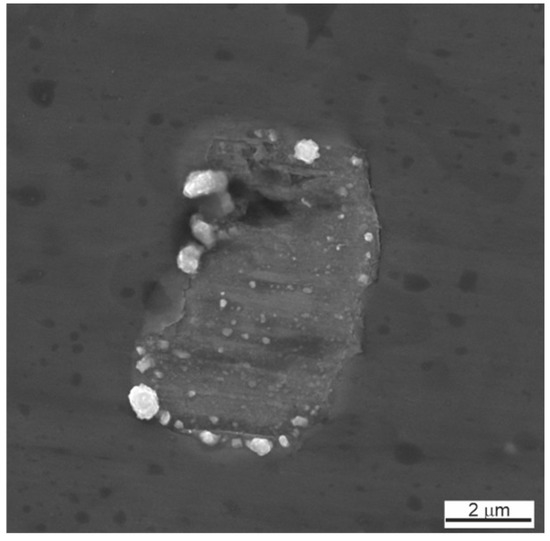

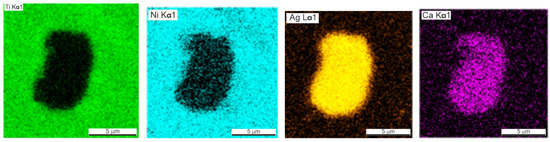
Figure 7.
SEM image of the microstructure and EDS mapping of the element composition of the pure silver phase in the porous TiNi + 0.5% Ag alloy.
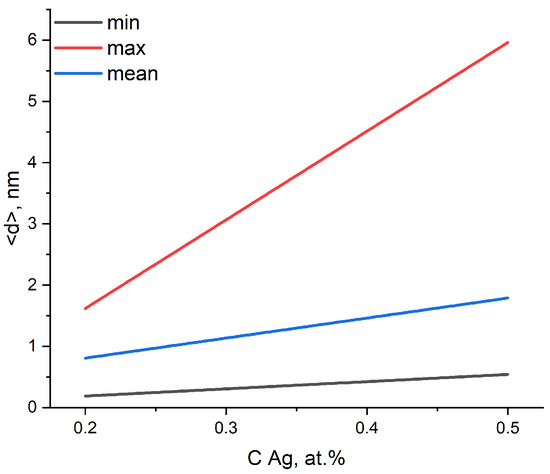
Figure 8.
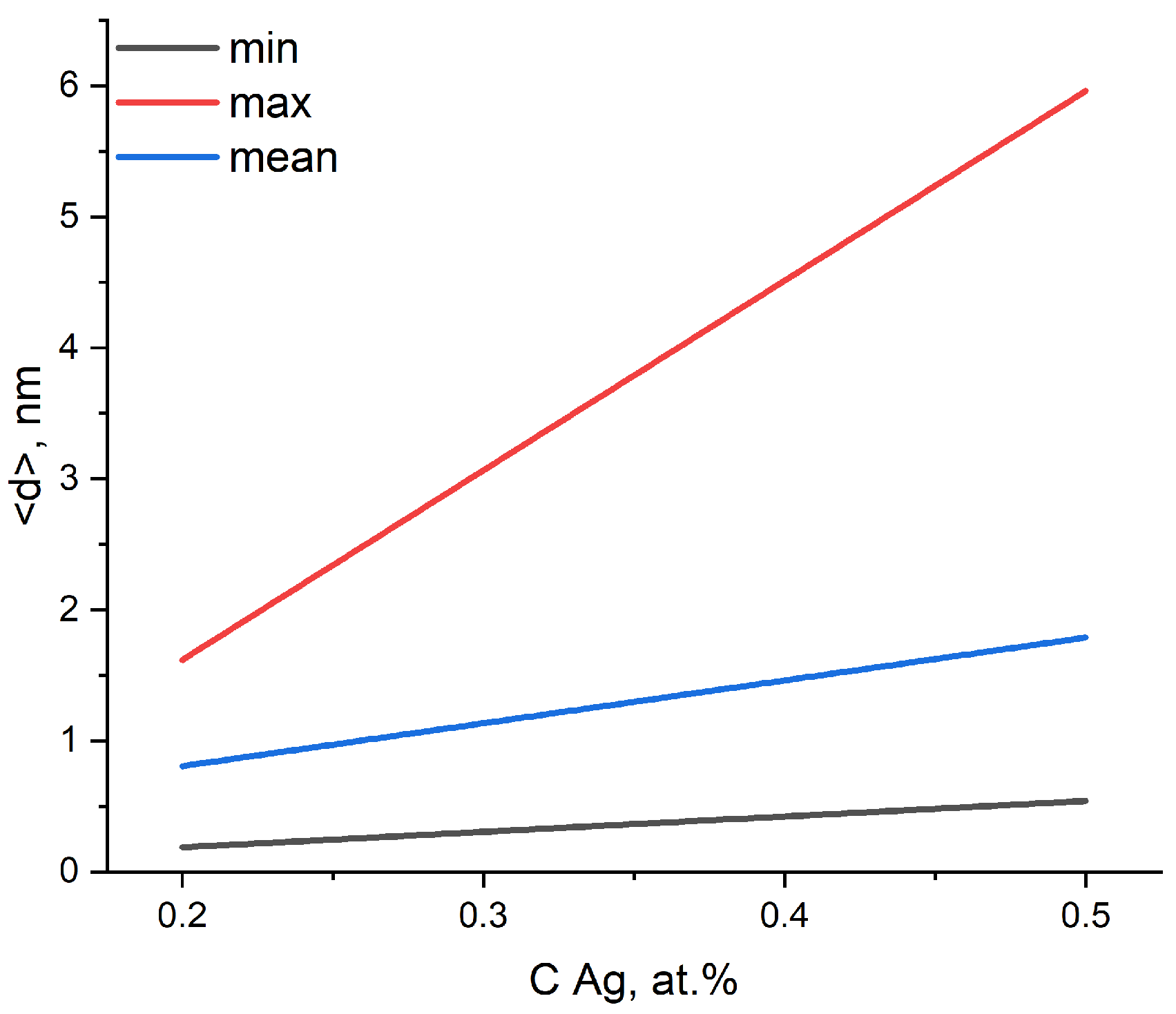
The dependence of the particle size containing silver on the Ag dopant concentration.
Ag and Ca form a number of chemical compounds [25] which contain some of the detected Ag in a dissolved state. Some amount of the unreacted Ag was found in a free state or in the compound with the predominant content of silver, Ag9Ca2, Ag7Ca2.
The results of the EDS mapping of TiNiAg (0.2–0.5) samples showed that inclusions containing silver are located mainly in the zones of Ti2Ni peritectic crystallization. The temperature of Ti2Ni peritectic crystallization is about 950 °C, while the crystallization of all Ag–Ca system compounds occurs in the range of 750–910 °C. With an increase in the Ag concentration in the alloy from 0.2% to 0.5%, the size of agglomerates from inclusions containing Ag increases from 0.2 to 6 µm (Table 5 and Figure 8).

Table 5.
The size of agglomerates of inclusions with silver.
3.1.3. TEM Image and EDS Elemental Mapping of Cross-Section of TiNiAg Alloy
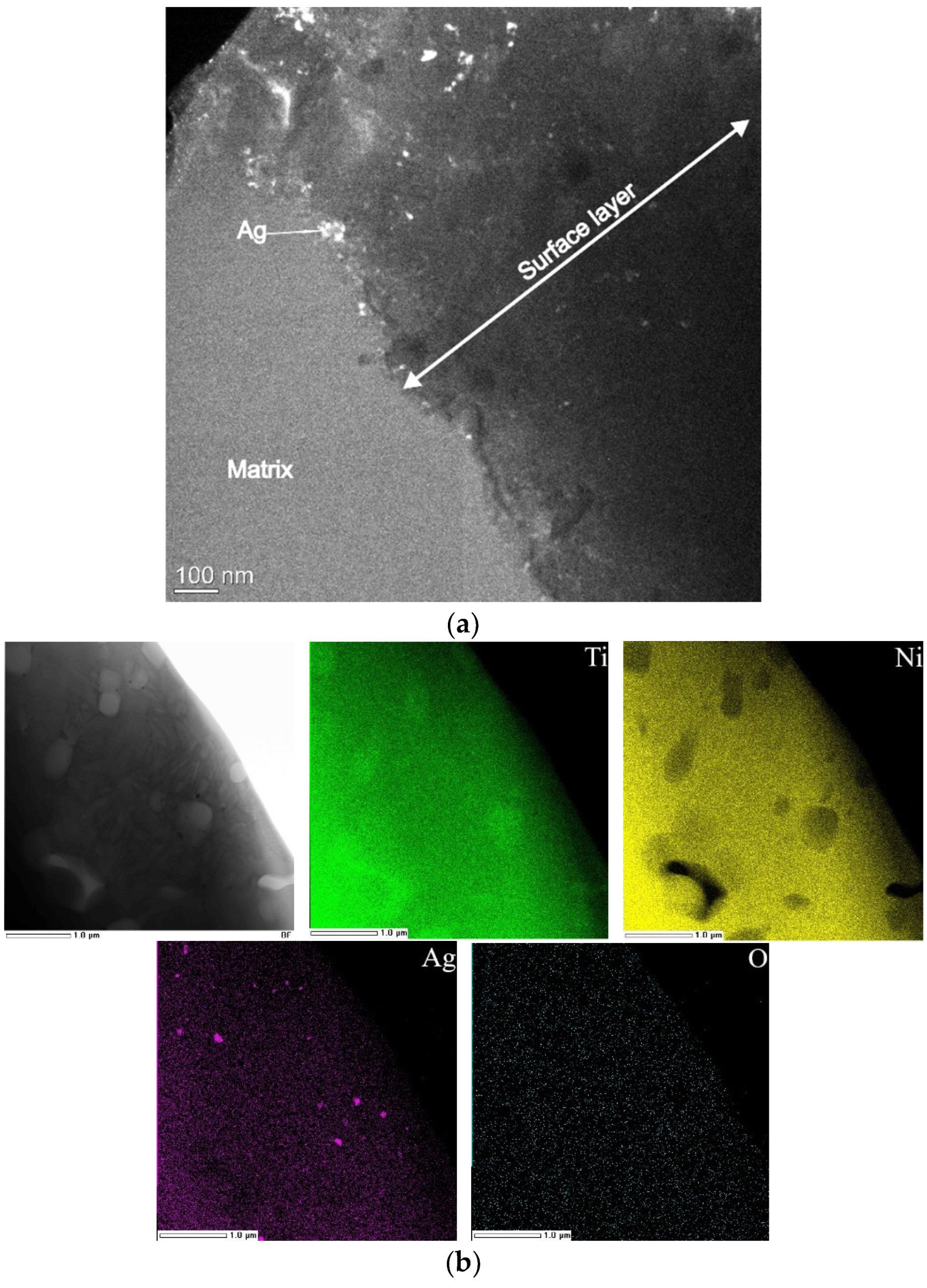
According to the results of transmission electron microscopy of TiNiAg(0.2–0.5) samples in the cross-section geometry, silver was found in the form of nanoparticles up to 10 nm in the surface layer of Ti4Ni2O (Figure 9). Moreover, they were found not in agglomerates, but in the form of isolated particles evenly distributed over the entire surface layer. Importantly, silver was found in the matrix in large inclusions up to 2 µm. Other authors have found Ag in the form of dispersed particles on the surface of ternary TiNiAg alloys [13,14], and also [4,26] showed the solubility limit of silver in a TiNi solid solution up to 0.26 wt.%.
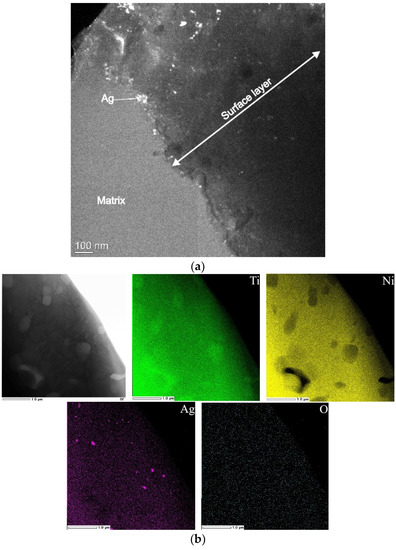
Figure 9.
TEM image of TiNiAg sample in the cross-section geometry (a); TEM–EDS elemental mapping of TiNiAg matrix (b).
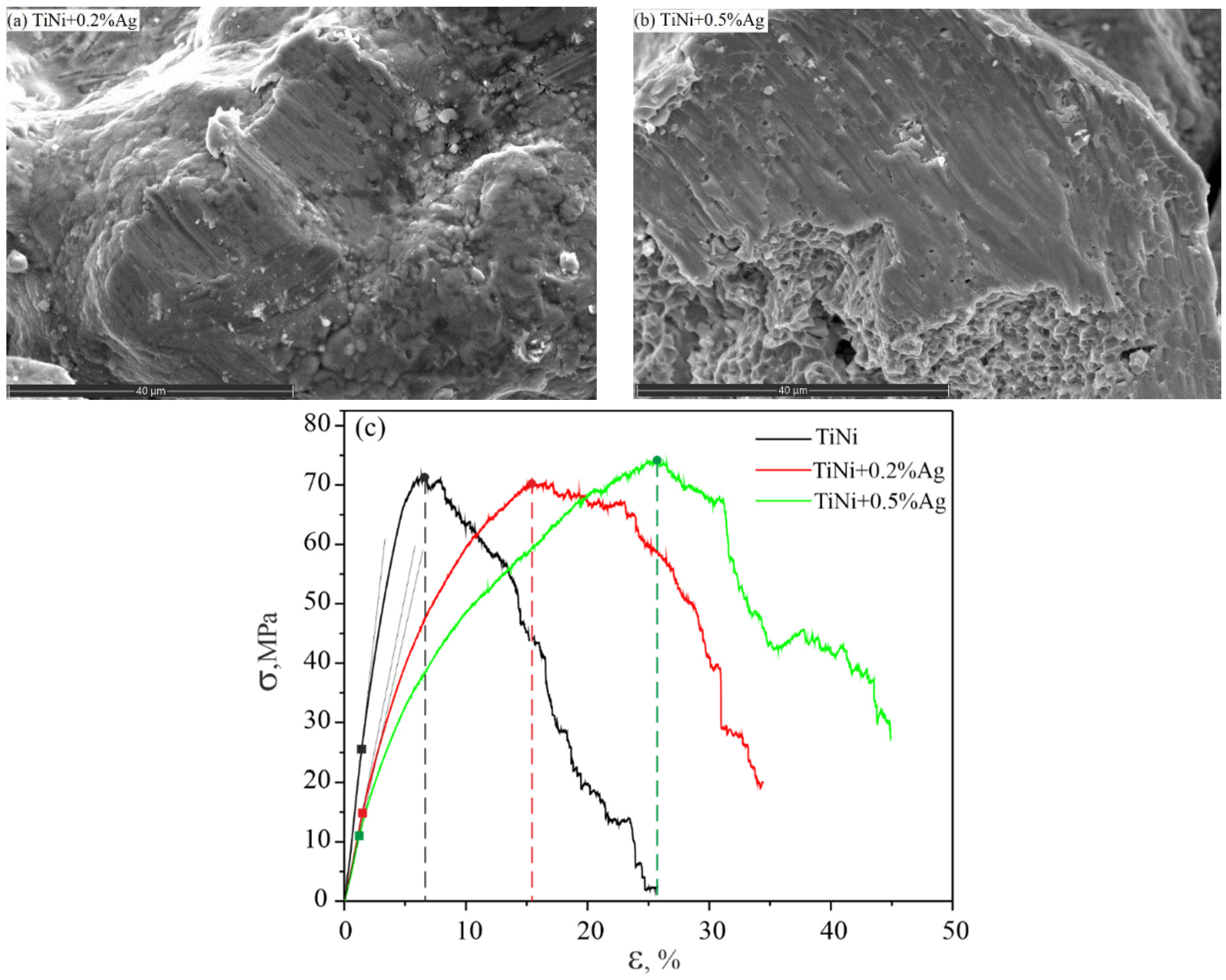
The mechanical properties of porous alloys were studied under a compression loading scheme. The stress–strain dependence of the TiNiAg system alloys is characterized by the absence of a martensitic plateau, and the porous alloy deforms elastoplastically. With an increase in the silver content, the strength properties do not change and the ultimate strength is 70 ± 4 MPa (Figure 10 and Table 6). The elastic limit decreases from 26 to 11.5 MPa, the elastic modulus decreases from 1700 to 950 MPa. The maximum strain to fracture in compression of porous TiNiAg alloys increased from 7% to 27% with increasing silver concentration. SEM images of fracture surfaces taken after compression testing showed that the alloy with the silver content 0.2 at.% and 0.5 at.% is partially in a martensitic state, which can be proved by the presence of the areas of quasi-cleavage and plastic shear traces.
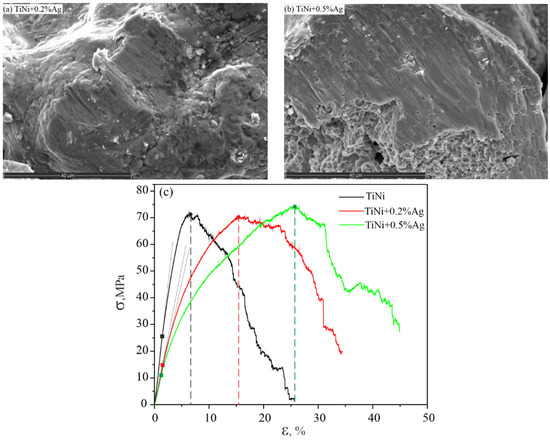
Figure 10.
The fracture surface of the alloy sample for TiNi + 0.2% Ag (a); TiNi + 0.5% Ag (b); σ-ε dependence for the alloys of the TiNiAg system (c).

Table 6.
Mechanical properties of porous TiNiAg alloys.
3.2. Discussion
Silver dissolves in the TiNi(B2) phase of the porous alloy to a limited extent, up to 0.1 at.%, although other authors found that the solubility of silver in the cast alloy does not exceed 0.26 at.% [13,14]. Silver crystallizes in its pure form. Silver particles were found in the matrix in the zones of peritectic crystallization of the Ti2Ni phase in the form of large particles. In the surface Ti4Ni2O layer, silver particles crystallized in the nanocrystalline state evenly over the entire surface layer.
Out of the three alloying elements, Ag is known to have a significantly different electronic structure compared to Ni and Ti. Moreover, Ag atoms significantly differ in size in comparison with Ni atoms. Thus, different electron shell structures of the Ag, Ni, and Ti atoms cause the difference in the structure of the binary state diagrams of the Ag-Ni, Ag-Ti, and Ni-Ti systems. The behavior of the electronic subsystem correlates with the phase diagrams of the binary Ti-Ag alloy state, in which Ti and Ag in the Ti-Ag system can form solid solutions based on the initial components (Ag), (αTi), (βTi) and two intermetallic compounds AgTi and AgTi2 at 1020 ± 5 and 940 °C. In the Ni-Ag system with a simple monotectic system, Ni and Ag are practically insoluble in each other on the state diagram. The maximum solubility of Ni in Ag is 0.102 at.%, and the maximum solubility of Ag in Ni is about 1 at.% and decreases with decreasing temperature [4,6,27,28,29].
In the Ag-Ti system, there are solid solutions based on alloy-forming elements (Ag), (αTi), and (βTi) with wide areas of homogeneity (Figure 1) [27,28]. Moreover, the solubility of Ag in (βTi) reaches 15 at.% at 1020 °C. The solubility of Ti in (Ag) is much lower and corresponds to 5 at.%. In the area of stoichiometric compositions Ag2Ti and AgTi, peritectic reactions form compounds with tetragonal syngonies with space symmetry groups I4/mmm and P4/ptt, respectively. In the Ag-Ti system, the eutectoid transformation (βTi)↔(αTi) + AgTi2 takes place on the Ti side. On the Ag side, a eutectic transformation is observed.
The phase diagram of Ag-Ni is characterized by the presence of monotectic and eutectic equilibria [29] (Figure 1). The eutectic point is located at a composition of 99.679 at.% Ag at 960 °C. Ni in Ag dissolves very slightly (on the order of 0.1 at.%). The maximum solubility of Ag in Ni is not high and amounts to ~1 at.%, and it decreases with decreasing temperature.
The state diagram of the Ti-Ni binary system is characterized by the formation of three intermetallic compounds Ti2Ni, TiNi, and TiNi3. Three compounds are formed in the system: Ti2Ni, TiNi, and TiNi3. The Ti2Ni compound is formed by a peritectic reaction. The TiNi and TiNi3 compounds crystallize from the melt with an open maximum. The TiNi compound has a homogeneity area which has a width range from 49.5 to 57 at.% Ni at 1118 °C and with decreasing temperature the area width narrows. There are three eutectic, one peritectic, and one eutectoid transformations in the Ni-Ti system. The solubility of Ni in Ti depends on the crystal structure and reaches 8 at.% in (βTi). Whereas in (αTi) the solubility of Ni is not high and is equal to 0.2 at.%. The (Ni) based solid solution region is quite wide and reaches a maximum value of 13.9 at.% at a temperature of 1304 °C and narrows with decreasing temperature.
According to the results of mechanical testing of porous TiNiAg alloys, a similar effect on mechanical characteristics was found in the study of the effect silver has on TiNiAg wires [4]. The study revealed an improvement in the mechanical characteristics of alloys in TiNiAg wires with an increase in the silver content [21]. In the studied case, an increase in plasticity can be associated with the change in the ratio of titanium and nickel in the B2 phase. The change in the matrix composition results in martensite formation, which causes plastic strain when the alloy is deformed at room temperature. The increase in plasticity is apparently caused by the appearance of a secondary Ag phase in the alloy matrix, which is softer and more plastic.
Studies of the structure and mechanical properties of porous NiTi alloys doped with silver have shown positive prerequisites for further research. Moreover, in the future, studies of physical properties, superelastisity effect, biocompatibility, and antibacterial effect of porous TiNiAg alloys will be carried out, which are important characteristics for the use of the alloy for medical purposes.
4. Conclusions
Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of the obtained alloys showed that an increase in the silver content is accompanied by a quantitative decrease in the austenite phase TiNi(B2) and an increase in the martensite phase TiNi(B19’), as well as in secondary phases Ti2Ni, Ti4Ni2O. Microdistortions of all the phases in the TiNiAg alloy system indicate that silver is incorporated into the crystal lattice of both the B2 and Ti2Ni phases. EDS analysis showed that silver dissolves in the TiNi(B2) phase of the porous alloy to a limited extent, up to 0.1 at.%.
The results of the EDS mapping of TiNiAg samples with 0.2 and 0.5 at.% Ag showed that inclusions containing silver are located mainly in the zones of Ti2Ni peritectic crystallization. With an increase in the Ag concentration in the alloy from 0.2% to 0.5%, the size of agglomerates from inclusions containing Ag increases from 0.2 to 6 µm. In the surface layer of the Ti4Ni2O phase, evenly distributed silver nanoparticles up to 10 nm were found.
It was found that with an increase in the volume fraction of silver, the plastic properties of the alloy increase, while the compressive strength does not change and accounts for 70 ± 4 MPa. Obviously, the increase in the plasticity of the porous TiNi alloy from 7% to 27% is caused by the formation of soft and plastic inclusions with silver in the matrix of the TiNi alloy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.L. and Y.Y.; methodology, V.L. and A.M.; validation, E.M. and G.B.; formal analysis, V.L., A.M. and Y.Y.; investigation, V.L., G.B. and A.M.; resources, E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, V.L., A.M. and Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, E.M. and G.B.; visualization, G.B.; project administration, E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Tomsk State University Development Programme (Priority-2030).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The structure research was carried out with the equipment of Tomsk Regional Core Shared Research Facilities Center of National Research Tomsk State University (Grant of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation No. 075-15-2021-693 (No. 13.RFC.21.0012)).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggeler, G.; Hornbogen, E.; Yawny, A.; Heckmann, A.; Wagner, M. Structural and functional fatigue of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 378, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monogenov, A.N.; Marchenko, E.S.; Baigonakova, G.A.; Yasenchuk, Y.F.; Garin, A.S.; Volinsky, A.A. Improved mechanical properties of porous nitinol by aluminum alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 918, 165617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigonakova, G.A.; Marchenko, E.S.; Chekalkin, T.L.; Kang, J.H.; Weiss, S.; Obrosov, A. Influence of silver addition on structure, martensite transformations and mechanical properties of TiNiAg alloy wires for biomedical application. Materials 2020, 13, 4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchenko, E.S.; Baigonakova, G.A.; Gunther, V.E. Effect of alloying of titanium nickelide-based alloys with group v elements (Vanadium, niobium) on their mechanical properties. Russ. Metall. 2018, 2018, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, E.S.; Baigonakova, G.A.; Kokorev, O.V.; Klopotov, A.A.; Iuzhakov, M.M. Phase equilibrium, structure, mechanical and biocompatible properties of TiNi-based alloy with silver. Mater. Res. Express. 2019, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbogen, E. Microstructure and Thermo-Mechanical Properties of NiTi Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2004, 455, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-J.; Lu, N.-H.; Chen, C.-H. Mechanical and elastocaloric effect of aged Ni-rich TiNi shape memory alloy under load-controlled deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 788, 139554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratten, J.; Nazhat, S.N.; Blaker, J.J.; Boccaccini, A.R. In vitro attachment of Staphylococcus epidermidis to surgical sutures with and without Ag-containing bioactive glass coating. J. Biomater. Appl. 2004, 19, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.; Proctor, C.; Kabler, P. Bactericidal effects of low concentrations of silver. J. Am. Waterworks Assoc. 1962, 54, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gutierrez, F.; Olive, P.L.; Banuelos, A.; Orrantia, E.; Nino, N.; Sanchez, E.M.; Ruiz, F.; Bach, H.; Av-Gay, Y. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic effect of silver and titanium nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Lu, Z.; Qin, G.; Zhang, E. Effect of nano/micro-Ag compound particles on the bio-corrosion, antibacterial properties and cell biocompatibility of Ti-Ag alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Q.; Cui, L. Introduction of antibacterial function into biomedical TiNi shape memory alloy by the addition of element Ag. Acta Biomater 2011, 7, 2758–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.-T.; Joo, U.-H.; Park, G.-H.; Hwang, C.-J.; Kim, K.-N. Effect of silver addition on the properties of nickel-titanium alloys for dental application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater 2006, 76, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kim, Y.-W.; Nam, T.-H. Transformation behavior and superelastic properties of Ti-Ni-Ag scaffolds prepared by sintering of alloy fibers. Scr. Mater 2018, 153, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, S.; Tillmann, W. Influence of Ag on antibacterial performance, microstructure and phase transformation of NiTi shape memory alloy coatings. Vacuum 2019, 164, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhou, W.-T.; Wang, C.; Ii, S.; Chiang, H.-S.; Hsueh, C.-H. TiNiCuAg shape memory alloy films for biomedical applications. J. Allo. Compd. 2018, 738, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.; Álvares, O.J. Designing NiTiAg shape memory alloys by vacuum arc remelting: First practical insights on melting and casting. Shape Mem. Superelast. 2018, 4, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, E.S.; Baigonakova, G.; Gyunter, V.E. The effect of silver doping on the structure and shape memory effect in biocompatible tini alloys. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2018, 44, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.-J.; Noh, J.-P.; Yeom, J.-T.; Kim, J.-I.; Nam, T.-H. Martensitic transformation behavior of Ti–Ni–Ag alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kim, E.-S.; Kim, Y.-W.; Nam, T.-H. Microstructures and martensitic transformation behavior of superelastic Ti-Ni-Ag scaffolds. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 82, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-Y.; Chun, S.-J.; Kim, N.-S.; Cho, J.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Yeom, J.-T.; Nam, T.-H.; Kim, J.-I. Martensitic transformation behavior in Ti–Ni–X (Ag, In, Sn, Sb, Te, Tl, Pb, Bi) ternary alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 5064–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Pang, G.; Sun, B.; Meng, X.; Cai, W. The microstructure and martensitic transformation behaviors in Ti-Ni-Hf -X (Ag, Sn) high temperature shape memory alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 756, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Hamzah, E.; Saud, S.N.; Nazim, E.M.; Bahador, A. Silver additions influence on biomedical porous Ti-Ni SMAs fabricated by microwave sintering. J. Teknol. 2018, 80, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baren, M.R. The Ag−Ca (Silver-Calcium) system. Bull. Alloy. Phase Diagrams. 1988, 9, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamponi, C.; Wuttig, M.; Quandt, E. Ni–Ti–Ag shape memory thin films. Scr. Mater 2007, 56, 1075–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyakishev, N.P. Diagrams of the State of Binary Metal Systems: Handbook; Volume 3; ASM International: Almere, the Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.L.; Bhansali, K.J. The Ag−Ti (silver-titanium) system. Bull. Alloy. Phase Diagr. 1983, 4, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, M.; Nash, P. The Ag−Ni (silver-nickel) system. JPE 1987, 8, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).