Photocatalytic Treatment of Methyl Orange Dye Wastewater by Porous Floating Ceramsite Loaded with Cuprous Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Required Materials and Reagents
2.2. Characterization and Testing of Samples
2.3. Synthesis of Cu2O
2.4. Preparation of Porous Floating Ceramsite Loaded with Cu2O
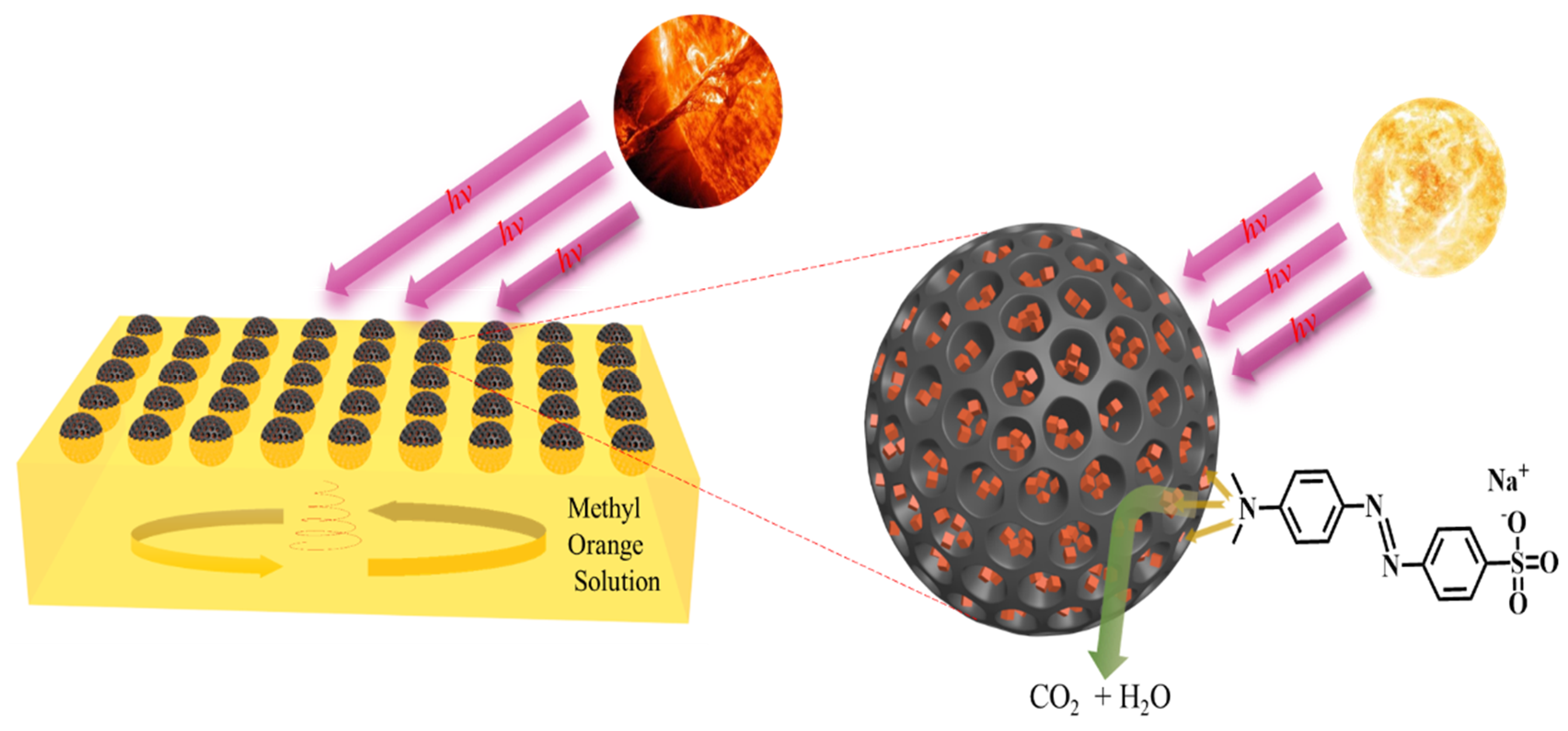
2.5. Evaluating the Degradation Effect of MO
2.6. Experimental Procedure for Photocatalytic Degradation of MO
3. Results and Discussion
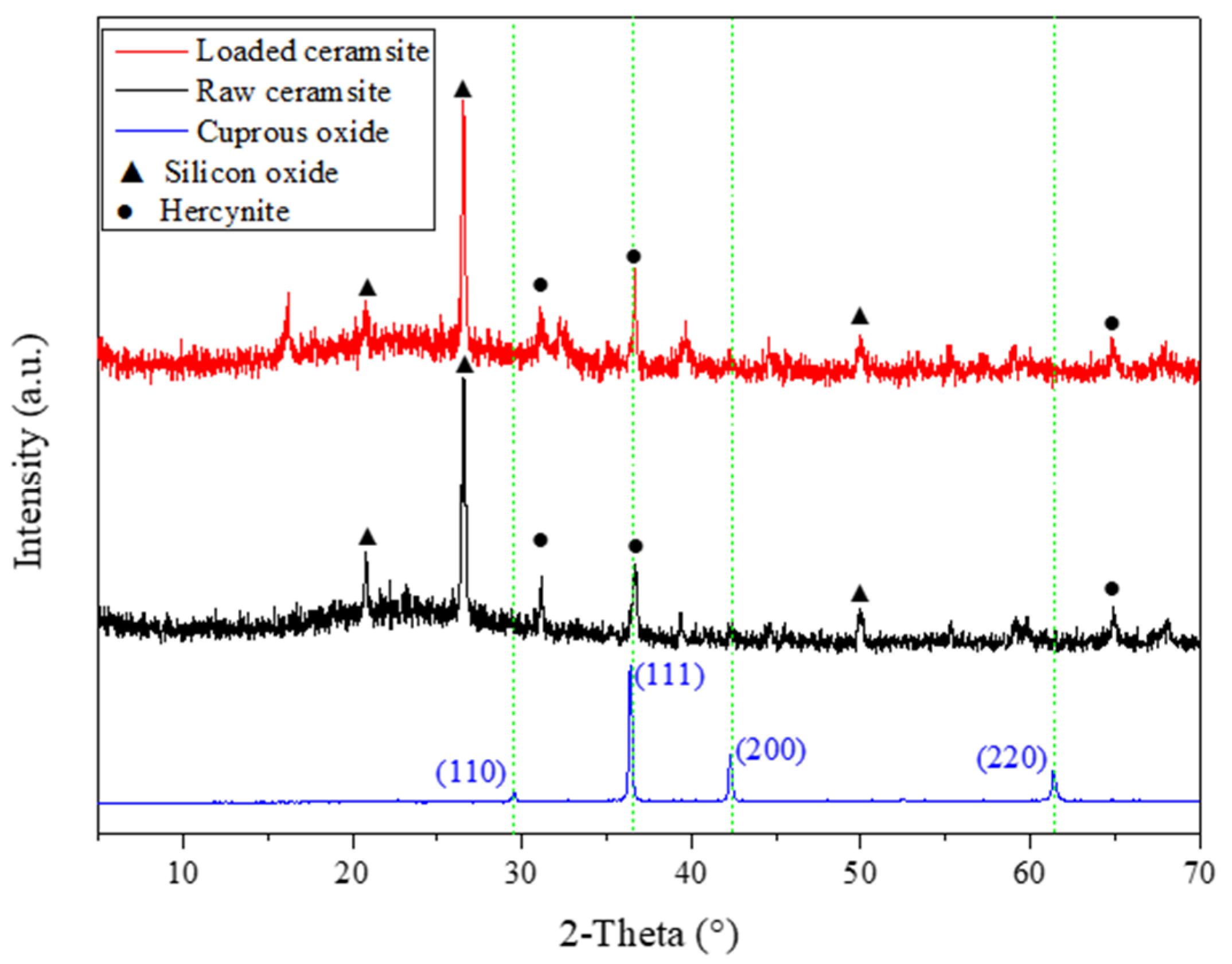
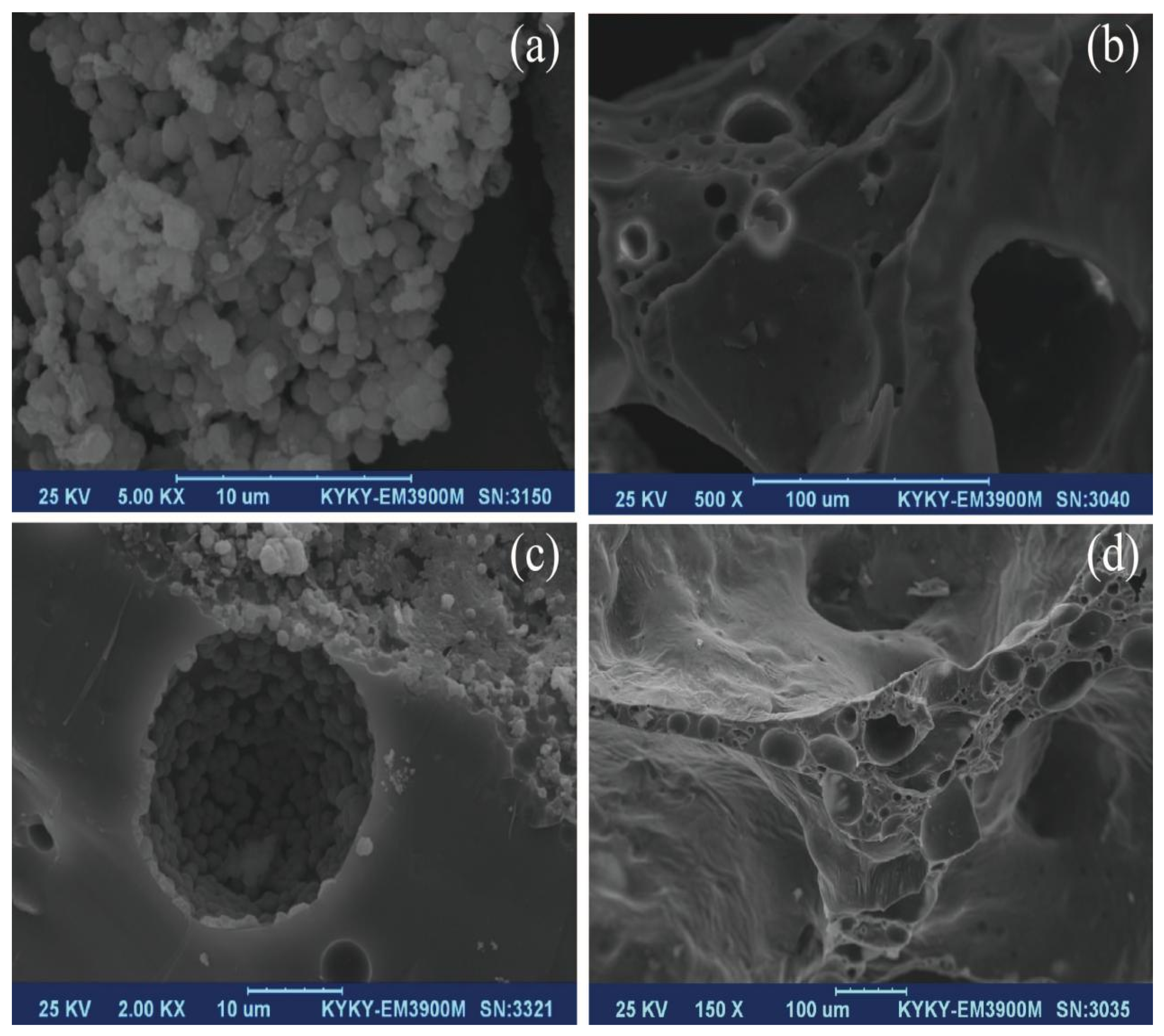
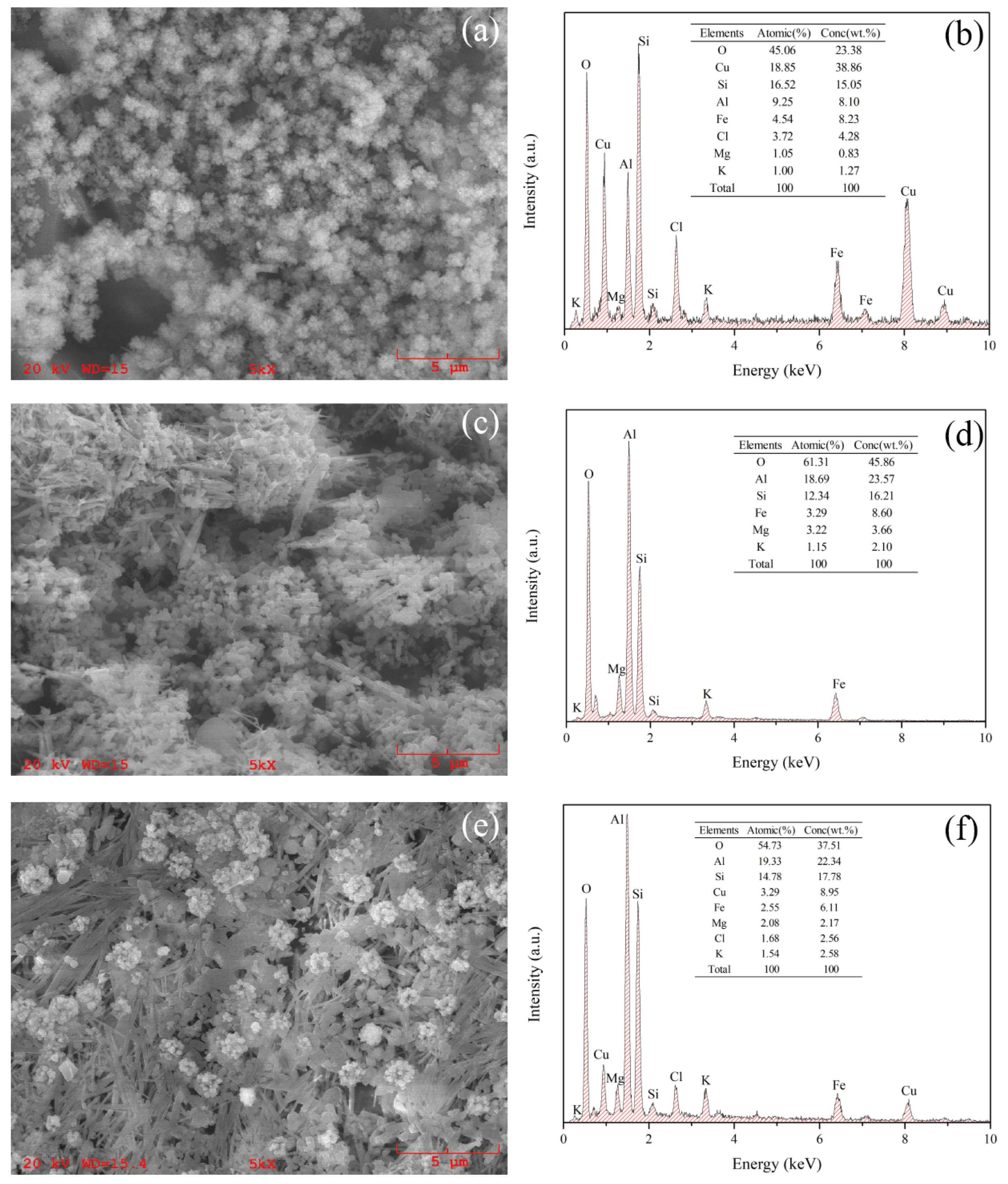
3.1. Characterization of Various Products
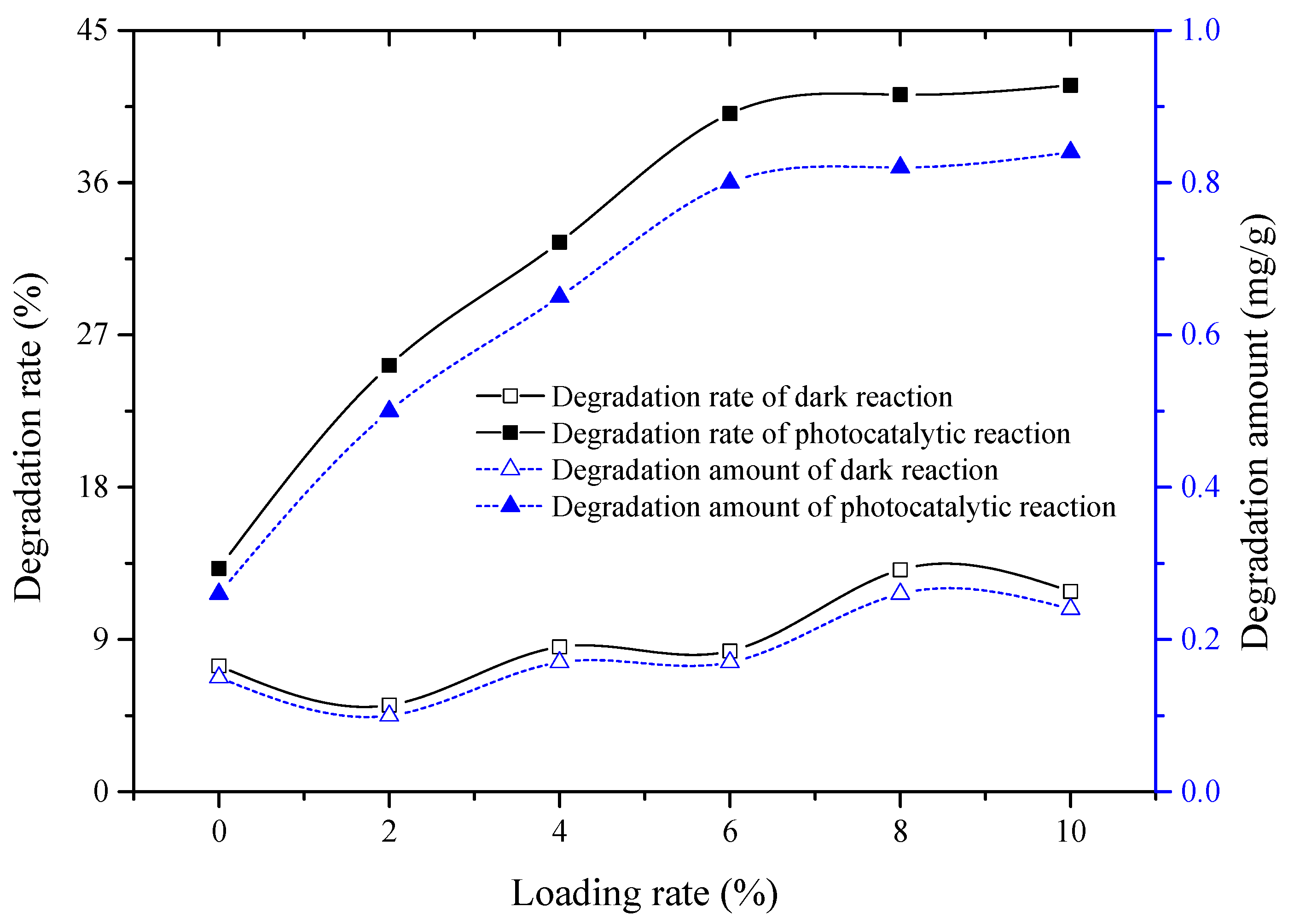
3.2. Effect of Cuprous Oxide Loading
3.3. Effect of PFCC Dosage
3.4. Effect of Reaction Time
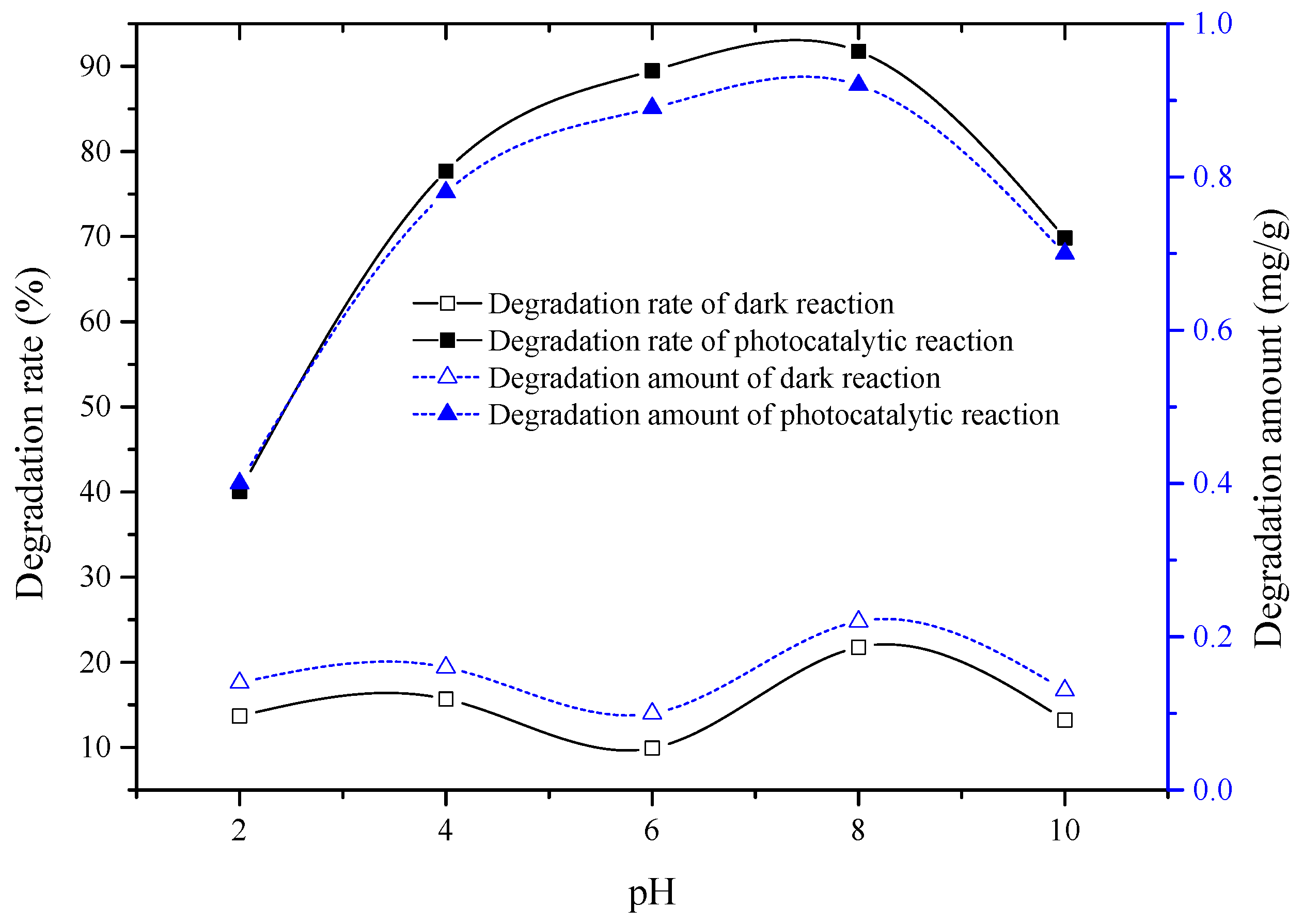
3.5. Effect of Solution pH
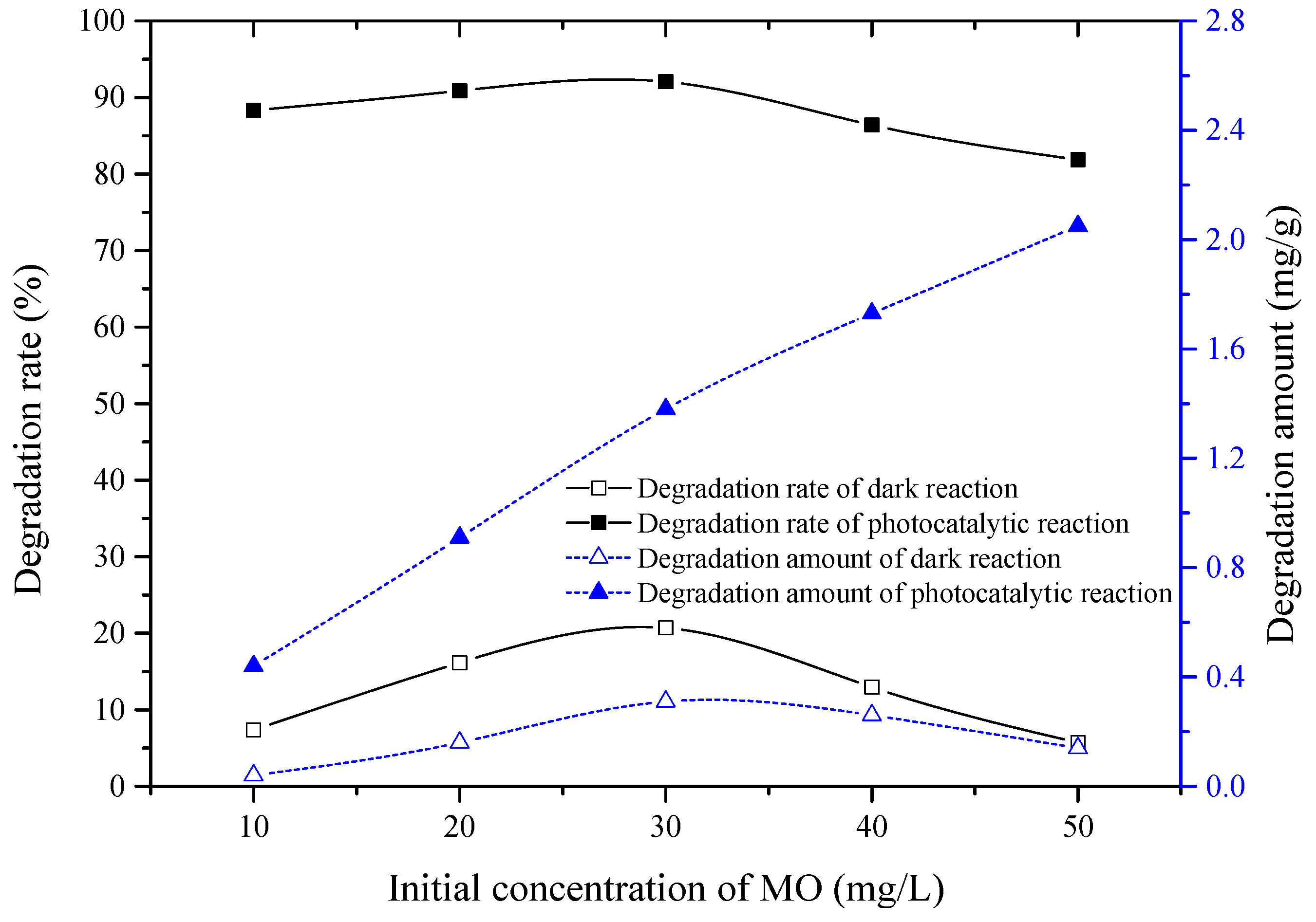
3.6. Effect of Initial Concentration of MO
3.7. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis
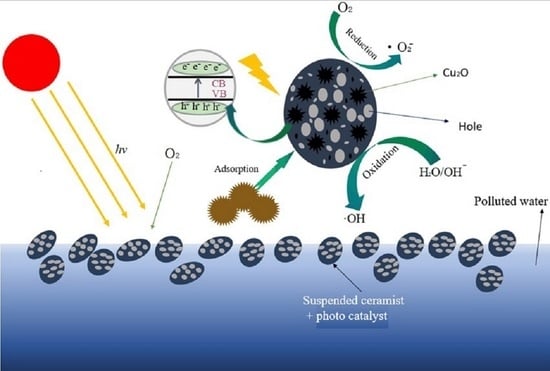
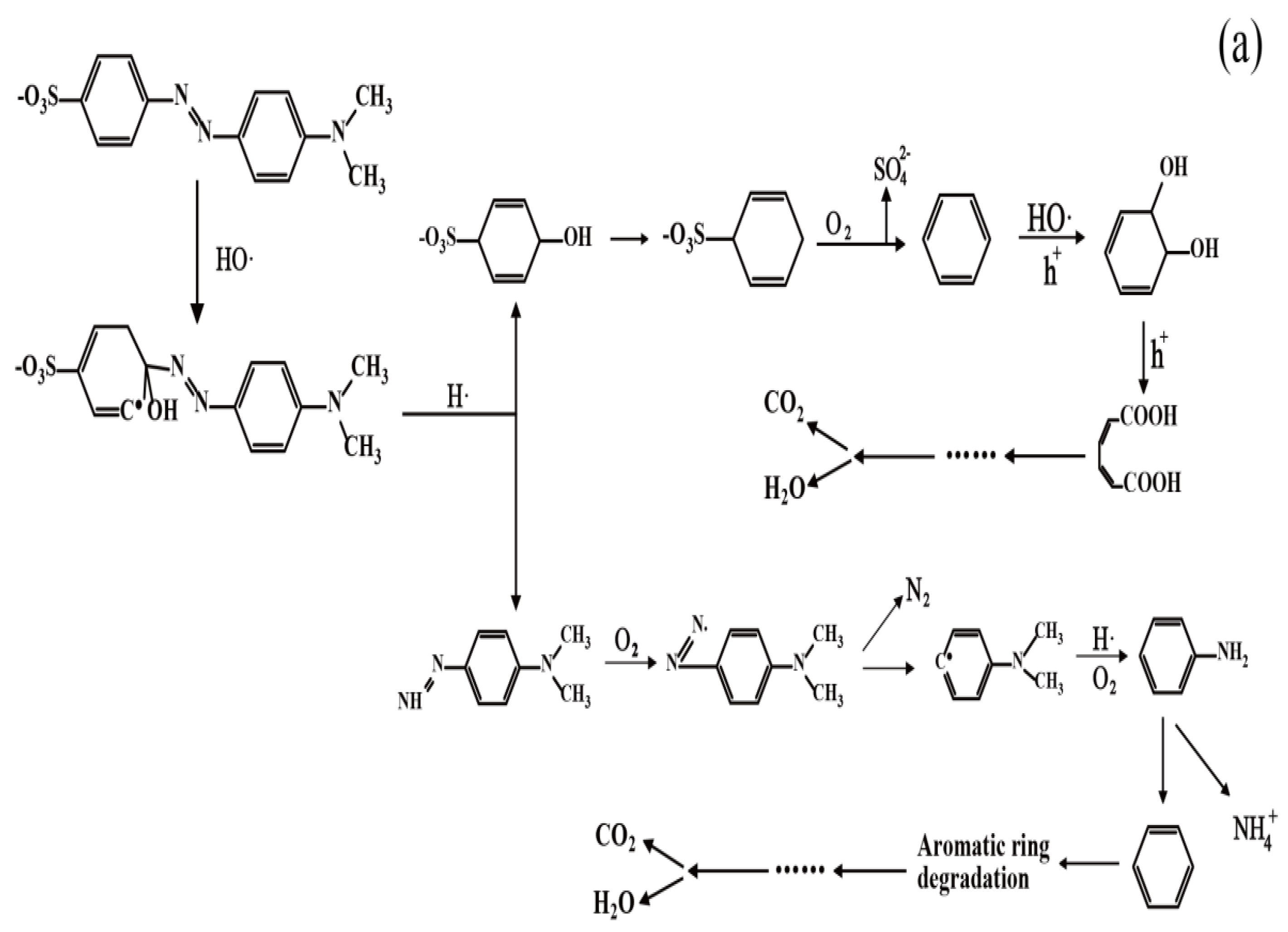
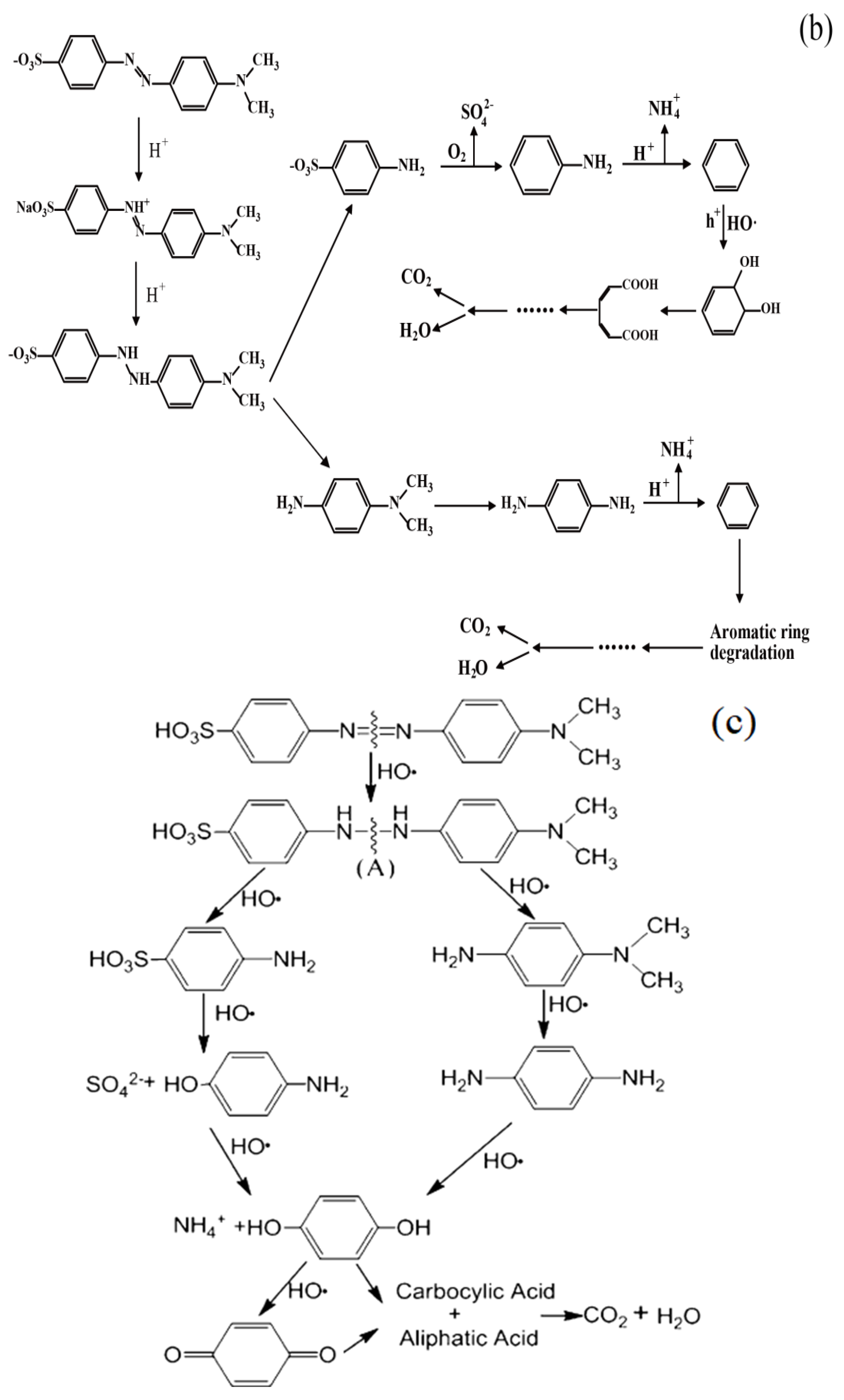
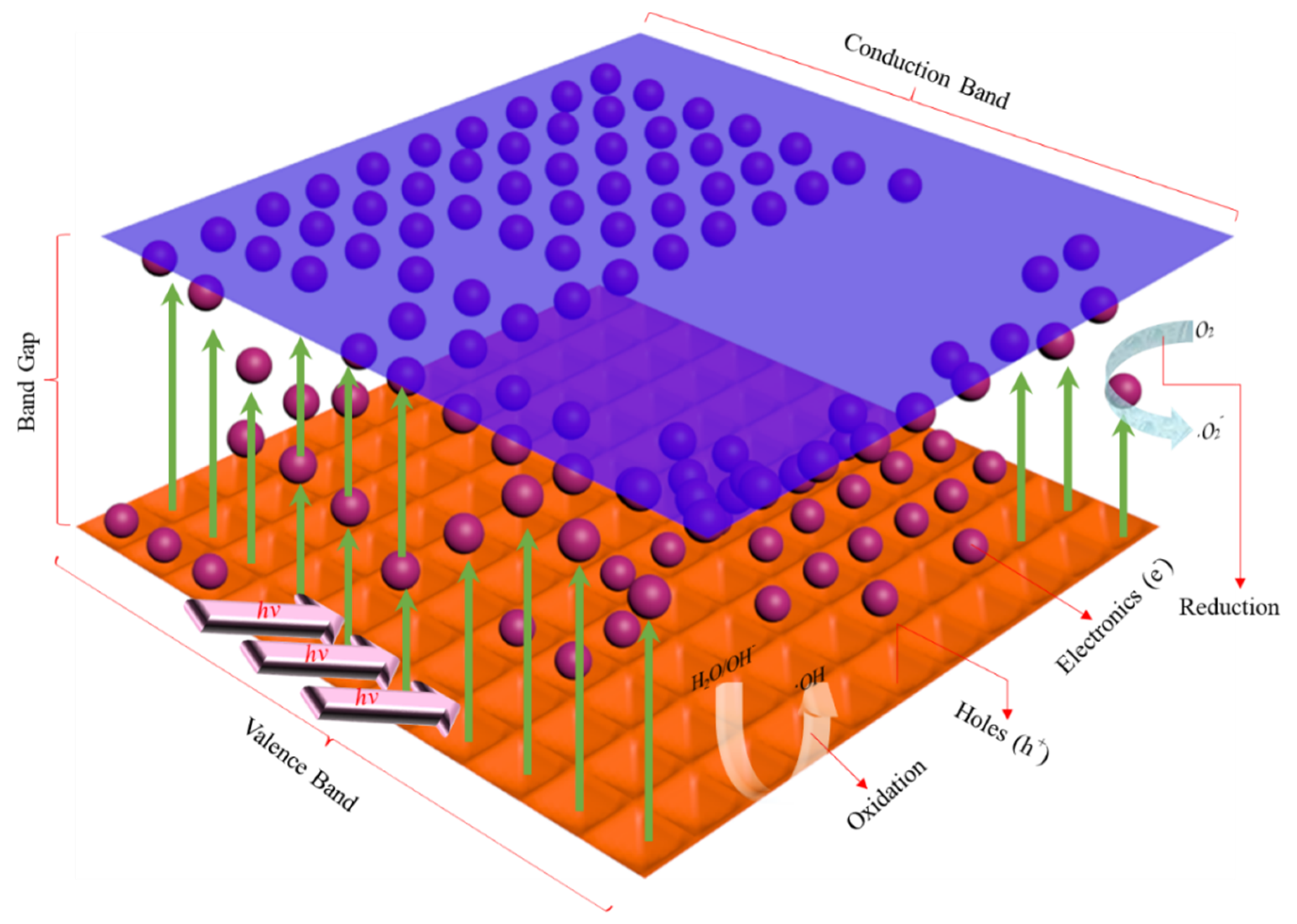
3.8. Discussion on the Degradation Mechanism of MO
- (1)
- Degradation mechanism of superoxide free radicals [36]:e− + O2 → •O2−O2− + H+ → HO2•2HO2• → O2 + H2O2H2O2 + ·O2− → •OH + OH− + O2H2O2 +•OH → H2O + HO2HO2• + •OH → H2O + O2
- (2)
- Degradation mechanism of hydroxyl radicals [37]:hν + Cu2O → h+ + e− + Cu2OOH− + h+ → HO•H2O + h+ → H+ + HO•O2 + 2H2O + 2e− → H2O2 + 2OH−Cu2+ + H2O2 → Cu+ + O2−• + 2H+Cu++ H2O2 → Cu2+ + OH− + HO•
- (3)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, M.; Yao, J. Acid-promoted synthesis of UiO-66 for highly selective adsorption of anionic dyes: Adsorption performance and mechanisms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 499, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.-B.; Bae, S.-S.; Kim, E.-T. Efficient Visible-Light Photocatalysis of TiO2-δ Nanobelts Utilizing Self-Induced Defects and Carbon Doping. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnagiris, S.; Medvids, A.; Lelis, M.; Milcius, D.; Antuzevics, A. Black carbon-doped TiO2 films: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 382, 111941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Adsorption of aqueous neodymium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, and yttrium ions onto nZVI-montmorillonite: Kinetics, thermodynamic mechanism, and the influence of coexisting ions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 33521–33537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, H.; Mahmood, Q.; Pervez, A.; Bhatti, Z.A.; Baig, S.A. Comparative decolorization of dyes in textile wastewater using biological and chemical treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.; Jadhav, A.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.M. Developments in the chemistry of reactive dyes and their application processes. Color. Technol. 2014, 130, 382–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maučec, D.; Šuligoj, A.; Ristić, A.; Dražić, G.; Pintar, A.; Tušar, N.N. Titania versus zinc oxide nanoparticles on mesoporous silica supports as photocatalysts for removal of dyes from wastewater at neutral pH. Catal. Today 2018, 310, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Time-delayed photocatalysis enhanced microbial nitrate reduction via solar energy storage in carbon nitrides. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 127904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.S.; Bhagwat, A.D.; Mahajan, C.M. Synthesis of Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) Nanoparticles—A Review. J. Nano- Electron. Phys. 2016, 8, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Chen, W.; Xu, H.; Geng, N.; Cai, Y. Preparation of TiO2/grapheme composite with appropriate N-doping ratio for humic acid removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 613–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kim, H.; Ong, M. T Characterization of stone powder sludge foams and their application to wastewater treatment: Role of pore connectivity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Song, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. TiO2−x/CoOx Photocatalyst Sparkles in Photothermocatalytic Reduction of CO2 with H2O Steam. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 243, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Two-photon Induced NIR Active Core-Shell Structured WO3/CdS for Enhanced Solar Light Photocatalytic Performance. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 272, 118979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Fang, J.; Deng, B. Preparation and Evaluation of GAC-Based Iron-Containing Adsorbents for Arsenic Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3833–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, W.; Zeng, G. Recent advances in round-the-clock photocatalytic system: Mechanisms, charac terization techniques and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2019, 39, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Chang, Y.; Shang, C. Removal of natural organic matter using surfactant-modified iron oxide-coated sand. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florent, M.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Detoxification of mustard gas surrogate on ZnO2/g-C3N4 composites: Effect of surface features’ synergy and day-night photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 272, 119038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mang, L.; Guang, H.X.; Xiao, D.Z. Surface modification of porous suspended ceramsite used for water treatment by activated carbon/Fe3O4 magnetic composites. Environ. Technol. 2013, 15, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, W.P.; Logan, B.E. Enhanced transport of bacteria in porous media by sediment-phase and aqueous-phase natural organic matter. Water Res. 1996, 30, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D. The Preparation of Visible-Light-Responsive Photocatalyst and the Study on Its Degradation Effect on Organic Pollutants; Beijing Jiaotong University: China, Beijing, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, S.; Bajaj, H.C.; Tayade, R.J. Recent advances based on the synergetic effect of adsorption for removal of dyes from waste water using photocatalytic process. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 65, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Research on Preparation and Properties of Visible-Light-Activity Photocatalyst; Dalian University of Technology: Dalian, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Muthu, S.S. Sustainable Innovations in Textile Chemistry and Dyes; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Jiao, J.; Mei, X. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of cuprous oxides. Solid State Sci. 2010, 12, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Supported Cuprous Oxide. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alajlani, Y.; Placido, F.; Barlow, A.; Chu, H.O.; Song, S.; Rahman, S.U.; de Bold, R.; Gibson, D. Characterisation of Cu2O, Cu4O3, and CuO mixed phase thin films produced by microwave-activated reactive s puttering. Vacuum 2017, 144, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozanov, L. Kinetic equations of non-localized physical adsorption in vacuum for Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Vacuum 2021, 189, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, Z.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Xu, B.; Hu, L.; Cui, H.; Ruan, S.; Zeng, Y.-J. Bio-inspired carbon doped graphitic carbon nitride with booming photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 246, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, V.; Obregón, S.; Patrón-Soberano, O.A.; Terashima, C.; Fujishima, A. An approach to the photocatalytic mechanism in the TiO2-nanomaterials microorganism interface for the control of infectious processes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Wang, W.W.; Dong, F.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Han, L.; Luo, X.D.; Huang, J.T.; Feng, Z.J.; Chen, Z.; Jia, G.H.; et al. Recent Advances in Noncontact External-Field-Assisted Photocatalysis: From Fundamentals to Applications. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4739–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Shuai, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, D. Progress and challenges in photocatalytic disinfection of waterborne Viruses: A review to fill current knowledge gaps. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, A.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Esrafili, M.D.; Mermer, O. Experimental and theoretical study of TiO2 based nanostruc tured semiconducting humidity sensor. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 8362–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Dan, Y. Visible Light Induced Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange by Polythiophene/TiO2 Composite Particles. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 213, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhou, C.Y.; Ma, Z.B.; Yang, X.M. Fundamentals of TiO2 Photocatalysis: Concepts, Mechanisms, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, Y. A Highly Crystalline Perylene Imide Polymer with the Robust Built-In Electric Field for Efficient Photocatalytic Water Oxidation. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1907746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafaela, B.P.; Marcelino, C.; Amorim, C. Towards visible-light photocatalysis for environmental applications: Band-gap engi neering versus photons absorption—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4155–4170. [Google Scholar]
- Smazna, D.; Shree, S.; Polonskyi, O.; Lamaka, S.; Baum, M.; Zheludkevich, M.; Faupel, F.; Adelung, R.; Mishra, Y.K. Mutual interplay of ZnO micro- and nanowires and methylene blue during cyclic photocatalysis process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Haritash, A.K. Photocatalytic degradation of Amoxicillin inpharmaceutical wastewater: Apotential tool to manage residual antibiotics. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Xu, H.; Zuo, S.; Xiao, Y.; Li, D.; Xia, D. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange on Cu2O-g-C3N4 heterojunction catalyst. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2018, 38, 552–558. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelraheem, W.H.M.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Dionysiou, D.D. Solar light-assisted remediation of domestic wastewater by NB- TiO2 nanoparticles for potable reuse. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 269, 118807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, H.; Mahmood, A.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Yip, A. Photocatalysts for degradation of dyes in industrial effluents: Opportunities and challenges. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



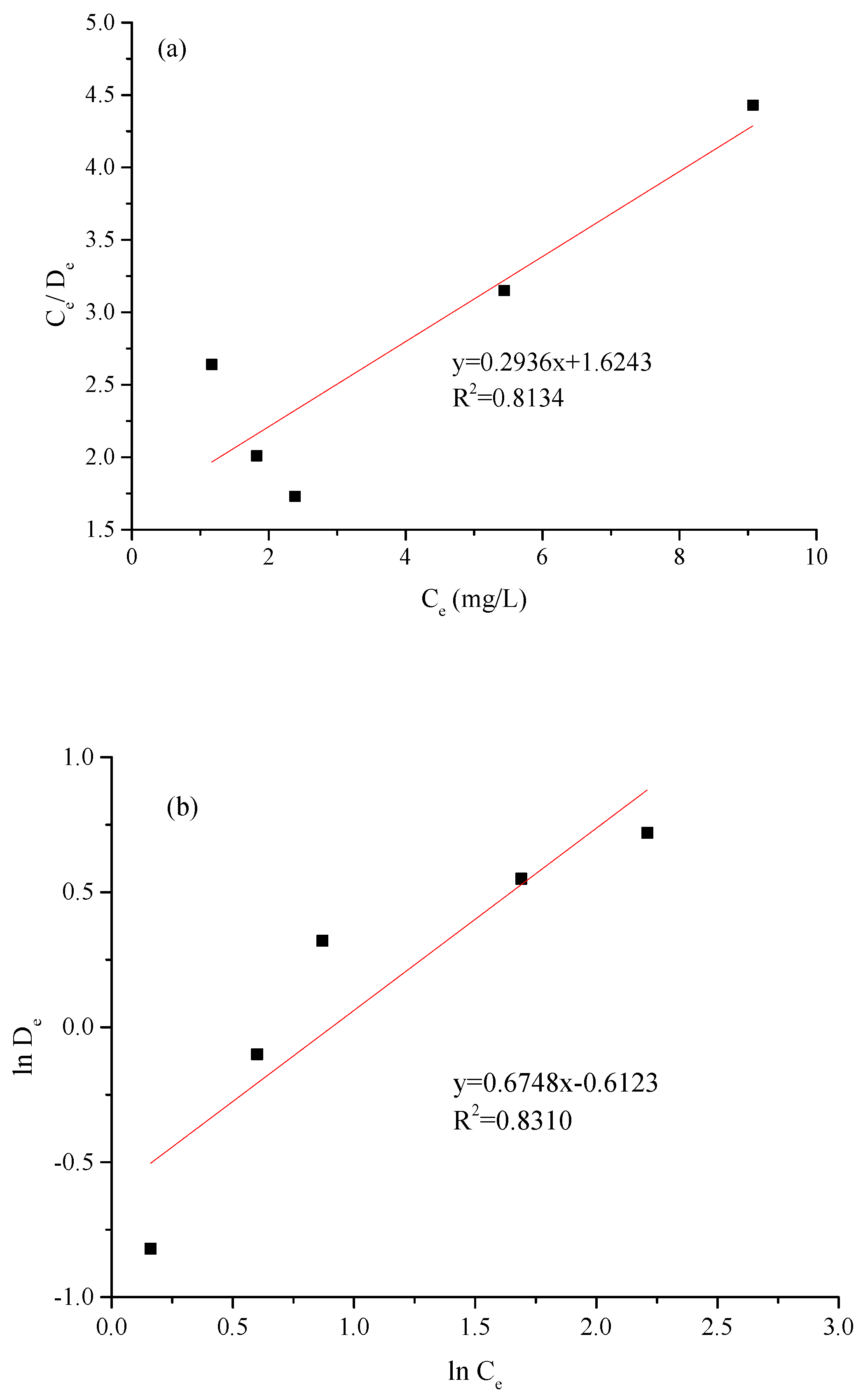
| Isotherm Models | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Dm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | n | KF (mg/g) | R2 |
| Values | 3.41 | 0.1808 | 0.8134 | 1.48 | 0.5421 | 0.8310 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Cao, T.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, H.; Yu, M. Photocatalytic Treatment of Methyl Orange Dye Wastewater by Porous Floating Ceramsite Loaded with Cuprous Oxide. Coatings 2022, 12, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020286
Cheng Y, Cao T, Xiao Z, Zhu H, Yu M. Photocatalytic Treatment of Methyl Orange Dye Wastewater by Porous Floating Ceramsite Loaded with Cuprous Oxide. Coatings. 2022; 12(2):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020286
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yue, Ting Cao, Zhiguo Xiao, Haijie Zhu, and Miao Yu. 2022. "Photocatalytic Treatment of Methyl Orange Dye Wastewater by Porous Floating Ceramsite Loaded with Cuprous Oxide" Coatings 12, no. 2: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020286
APA StyleCheng, Y., Cao, T., Xiao, Z., Zhu, H., & Yu, M. (2022). Photocatalytic Treatment of Methyl Orange Dye Wastewater by Porous Floating Ceramsite Loaded with Cuprous Oxide. Coatings, 12(2), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020286