Stabilization of Sandy Soils by Bentonite Clay Slurry at Laboratory Bench and Pilot Scales
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Program
2.1. Soil Properties
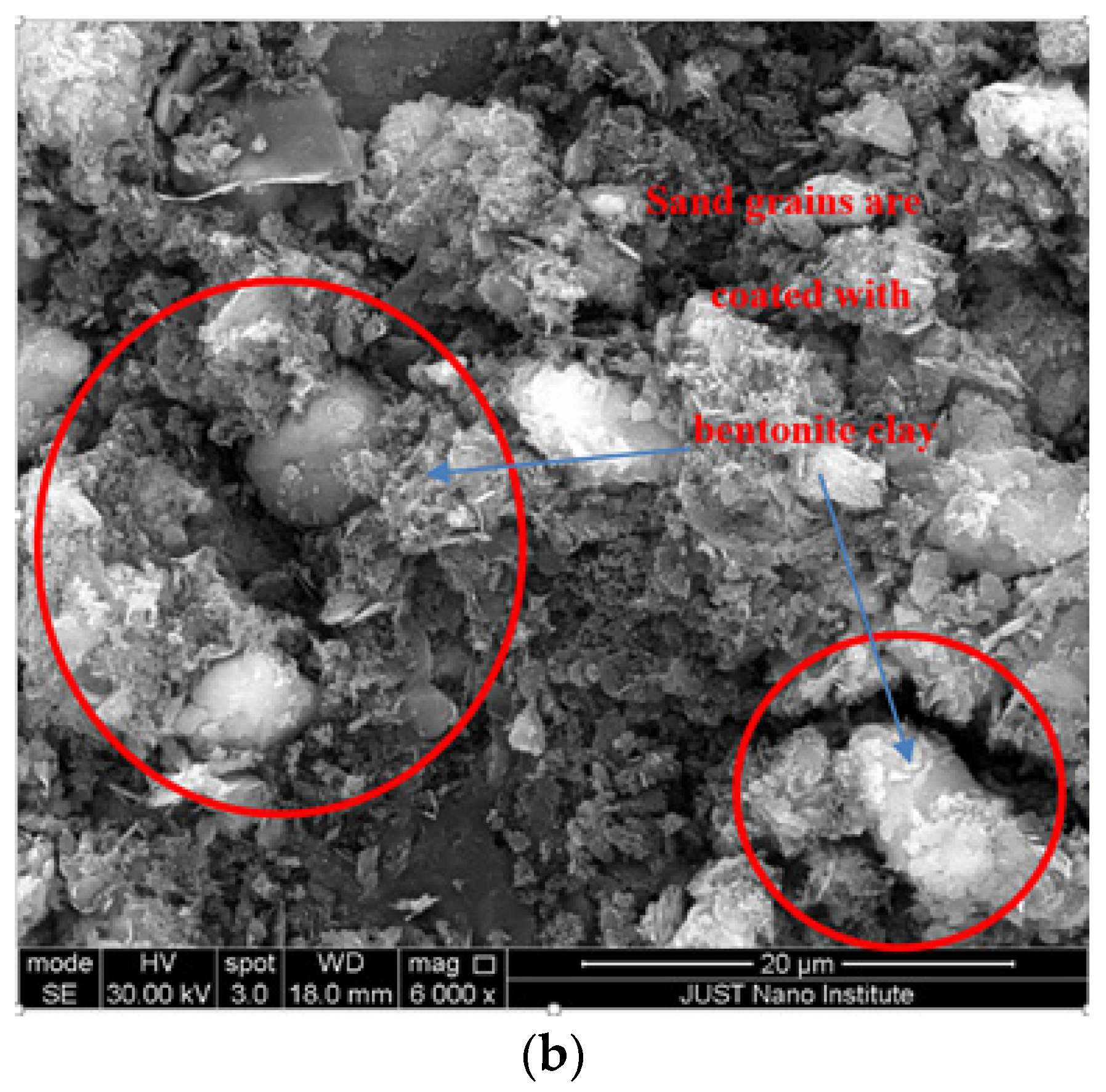
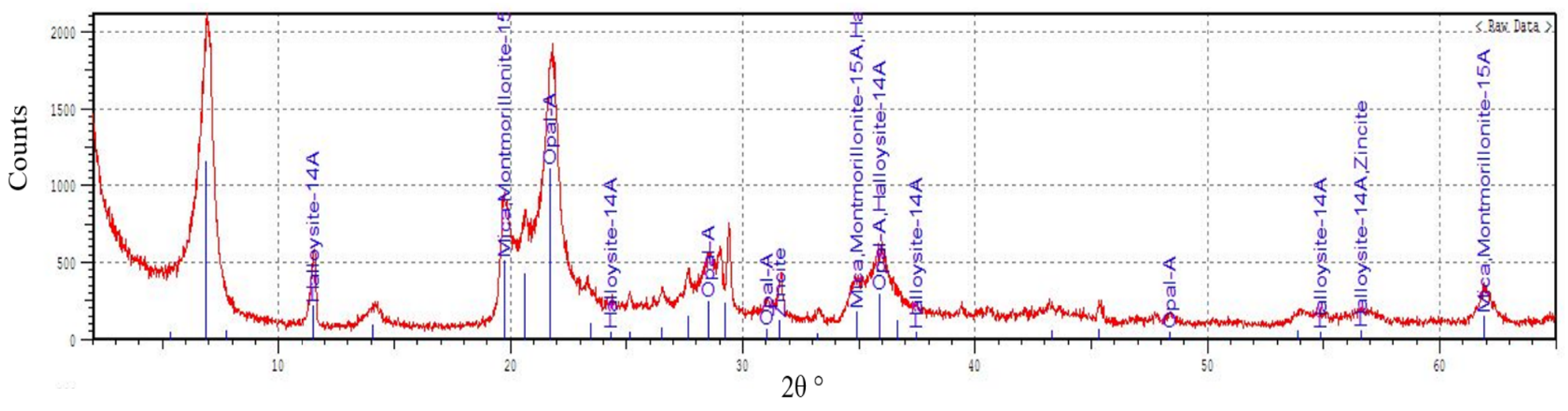
2.2. Additive Properties
3. Experimental Program
3.1. Bentonite Clay–Water Slurry Preparation
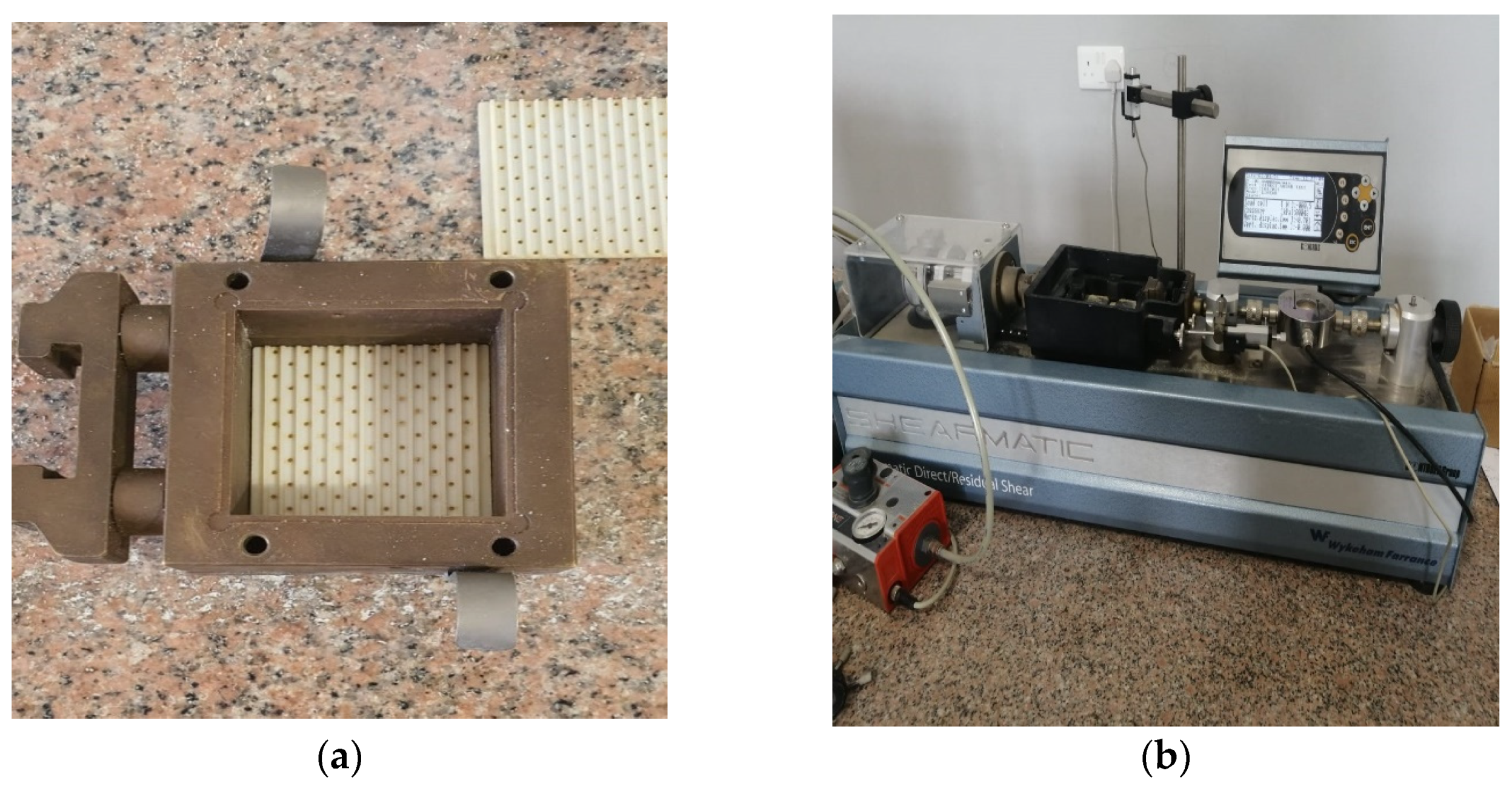
3.2. Direct Shear Test
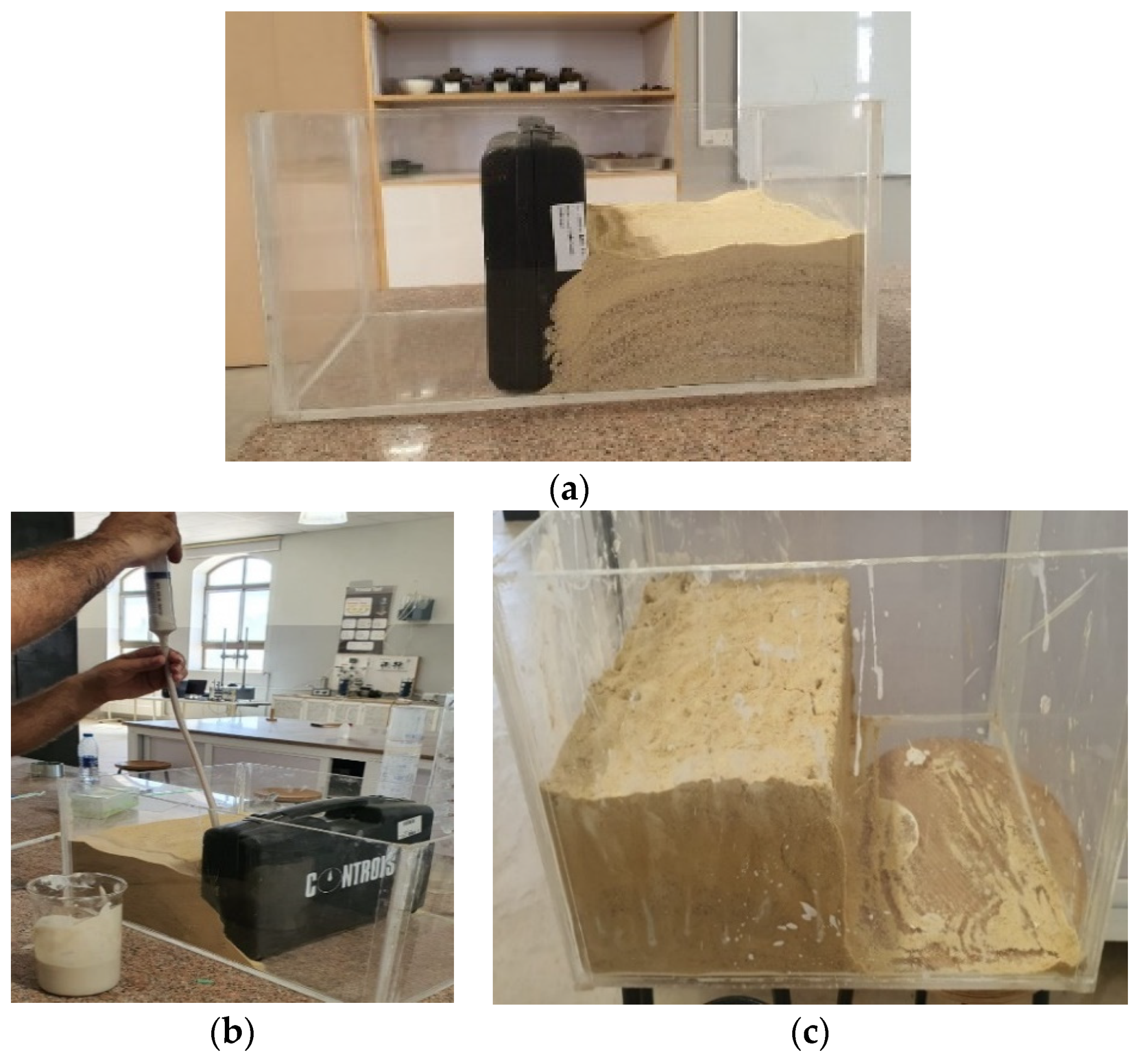
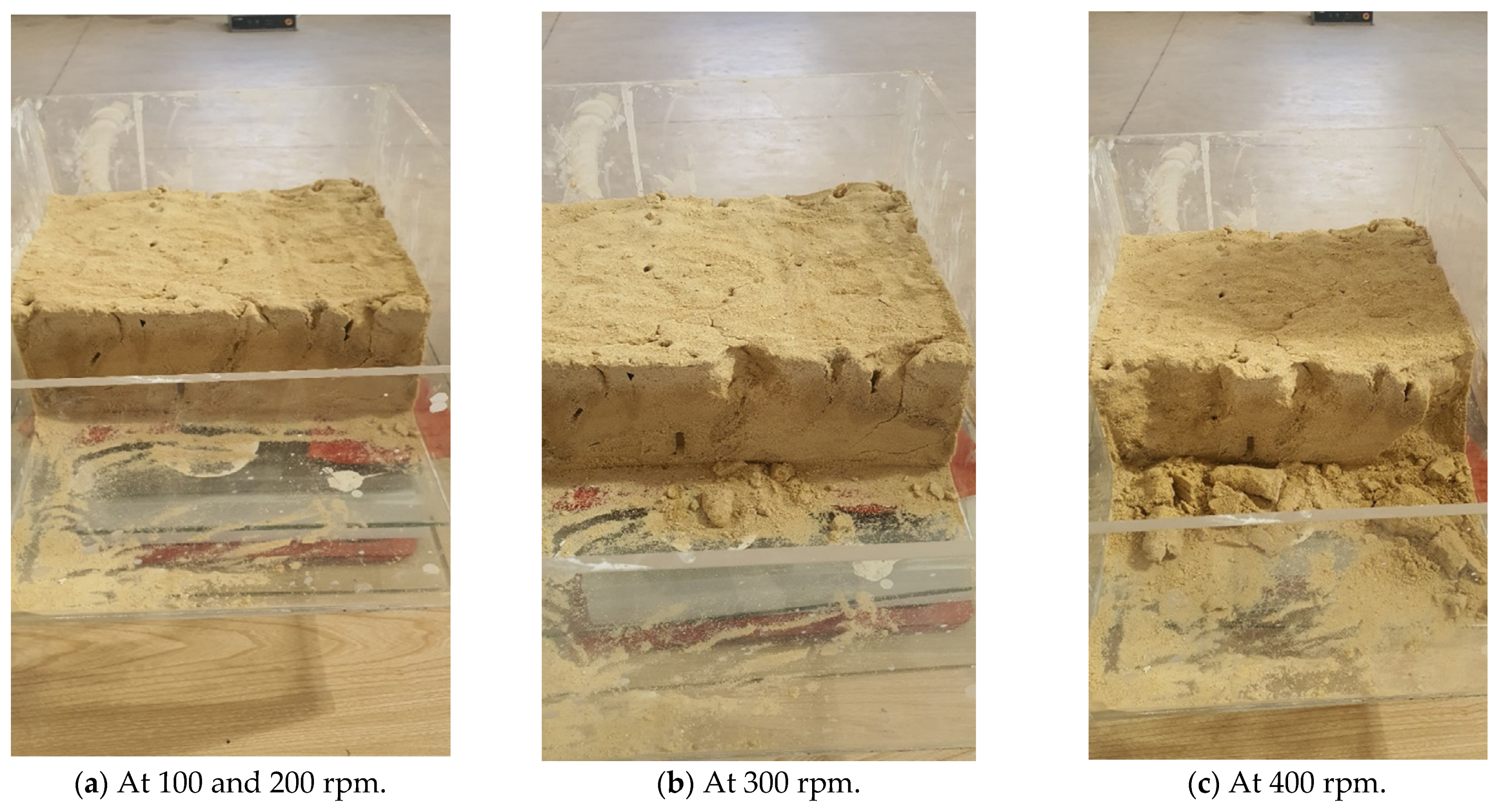
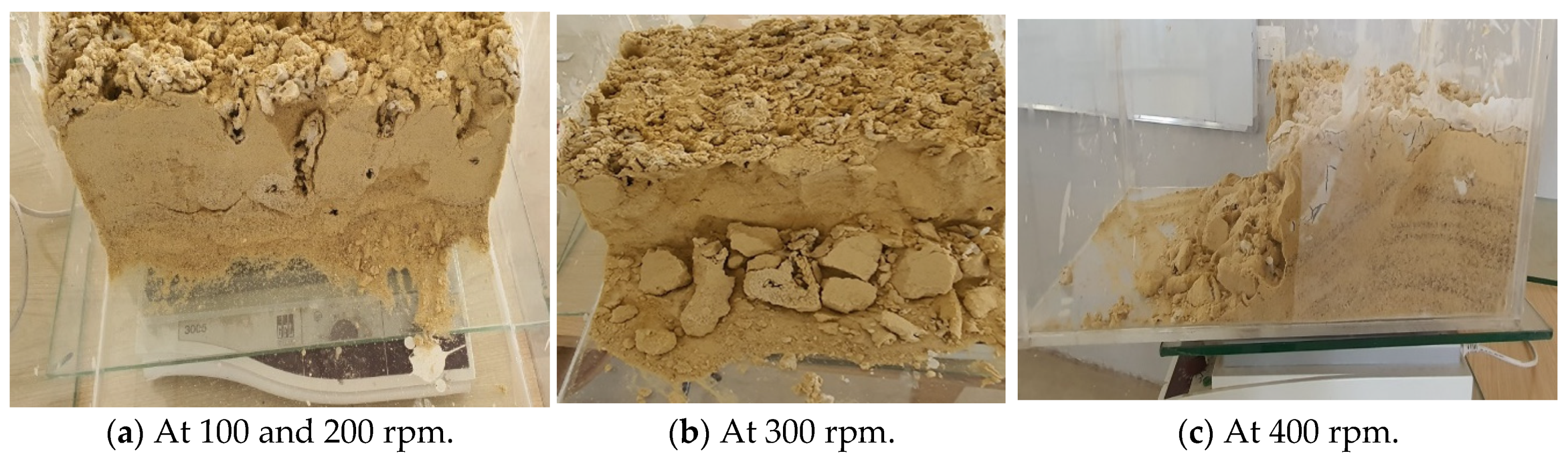
3.3. Pilot Scale
4. Results and Discussion
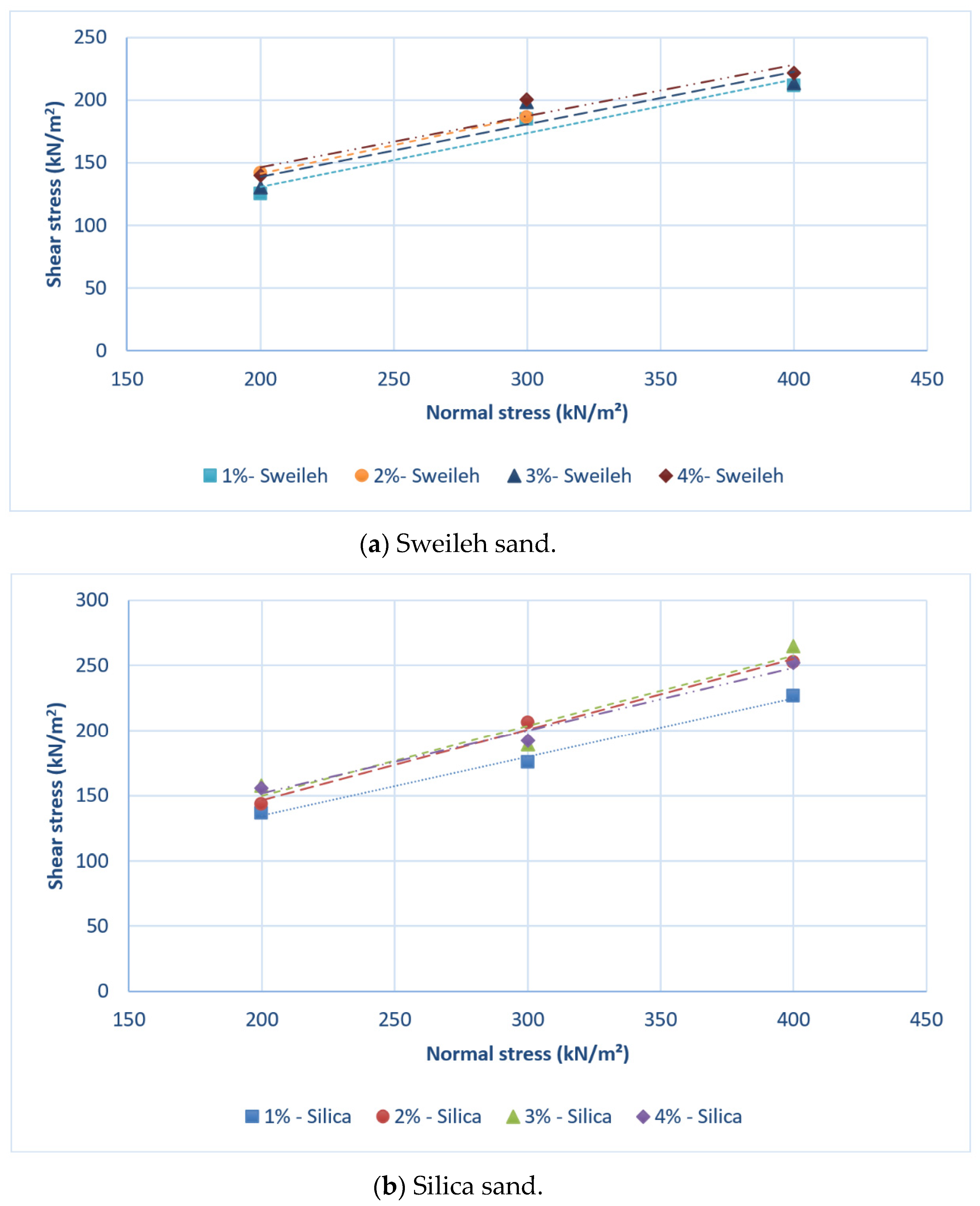
4.1. Optimum Volume of Water to Be Added
4.2. Optimum Amount of Bentonite Clay to Be Used in the Slurry
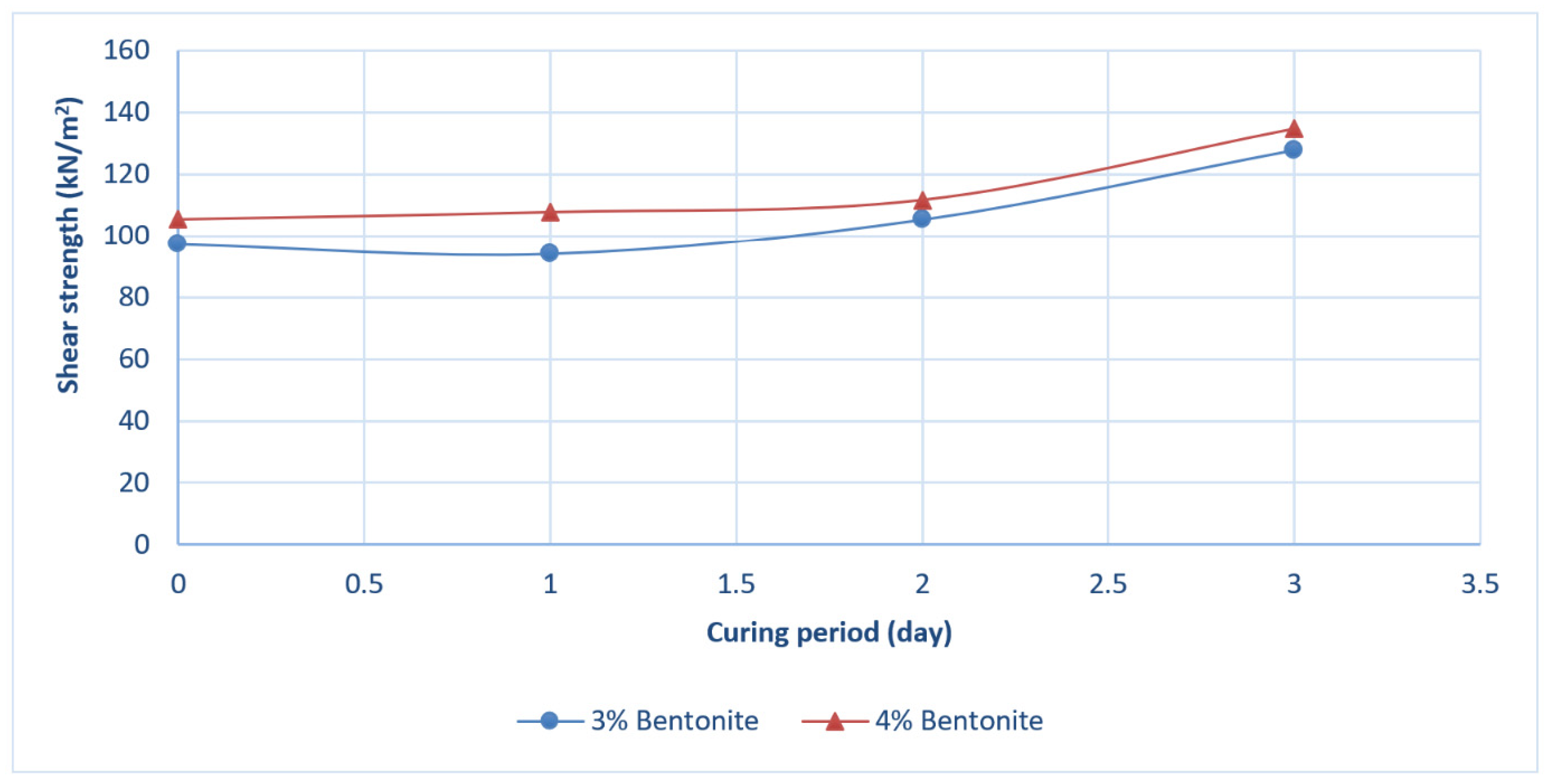
4.3. Curing Stage for Stabilized Sand with 3% and 4% Bentonite Clay–Water Slurry
4.4. Comparison between Current Study Results and Other Similar Studies
5. Conclusions
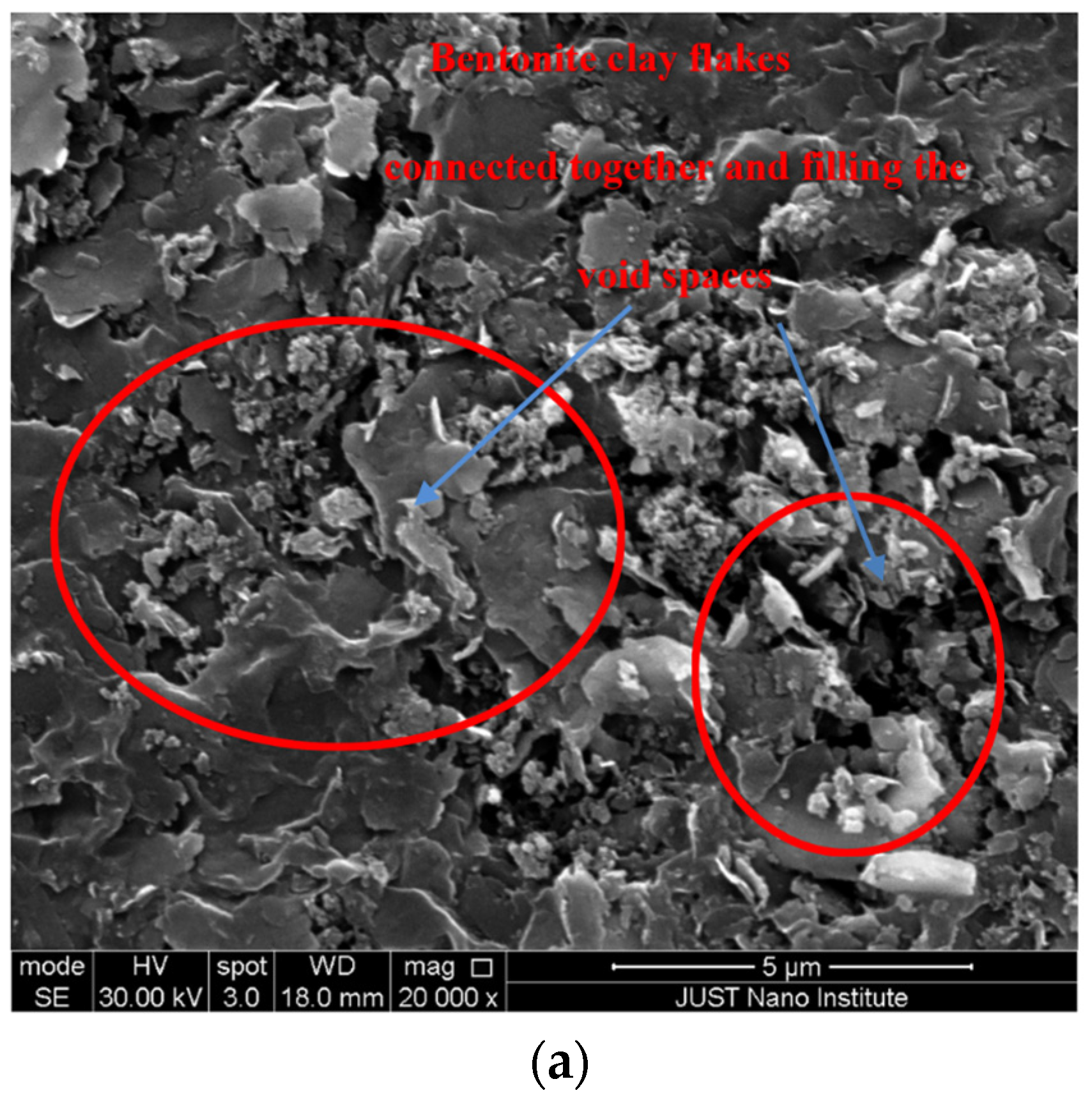
- Bentonite clay powder can be considered as a good stabilizing agent as it fills the voids between sand particles, and decreases the amount of free water in the voids resulting in an increase of sand mass strength.
- Slurry composed of 10.4% of water and 4% of bentonite clay by dry weight of sand is the optimum volume to be added for the stabilization process of Sweileh sand. For silica sand 3% bentonite content by dry weight of sand can be used as the optimum amount for slurry preparation.
- Three days curing time increased the shear strength of the stabilized Sweileh sand with bentonite clay–water slurry by 31.6% and 27.9% for stabilization with 3% and 4% bentonite clay, respectively, compared to no curing time after stabilization.
- Stabilized sandy soil with eco-friendly bentonite clay–water slurry offers an excellent resistance to mechanical shaking.
- The cohesion of stabilized sand by bentonite clay–water slurry increased with a slight decrease in the internal friction angle of sand, which is in line with previous studies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komine, H.; Ogata, N. Experimental Study on Swelling Characteristics of Sand-Bentonite Mixture for Nuclear Waste Disposal. Soils Found. 1999, 39, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khdair, A.I.; Khdair, S.I.; Abu-Rumman, G.A. Dataset on some soil properties improvement by the addition of olive pomace. Data Brief 2019, 24, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammedi, A.; Ebadi, T.; Ahmadi, M. Effect of bentonite addition on geotechnical properties of oil-contaminated sandy soil. J. Civ. Eng. Constr. 2018, 7, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta, N.K.; Wayal, A.S.; Hiranandani, P. Stabilization of dune sand with ceramic tile waste as admixture. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2013, 2, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, S.; Viana de Fonseca, A.; Bangaru, S. Silty sand stabilized with different binders. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayal, A.S.; Ameta, N.K.; Purohit, D.G. Dune sand stabilization using bentonite and lime. J. Eng. Res. Stud. 2012, 3, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.-X.; Gong, W.; Xie, H.; Liu, B.-L.; Chen, H.-L. Chemical sand stabilization: A review of material, mechanism, and problems. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2015, 4, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.T.; Daw, G.P.; Shotton, P.G.; James, A.N. Paper 5 The properties of bentonite slurries used in diaphragm walling and their control. In Diaphragm Walls & Anchorages; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 1975; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Czaban, J.; Siebielec, G.; Czyż, E.; Niedźwiecki, J. Effects of Bentonite Addition on Sandy Soil Chemistry in a Long-Term Plot Experiment (I); Effect on Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, N.; Siddiqua, S. Stabilization of silty sand using bentonite-magnesium-alkalinization: Mechanical, physicochemical and microstructural characterization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 183, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueddouda, M.K.; Lamara, M.; Aboubaker, N.; Taibi, S. Hydraulic conductivity and shear strength of dune sand-bentonite mixtures. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2008, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, M.R. Geotechnical Properties of Soil-Ball Milled Soil Mixtures. Nanotechnology in Construction 3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaiez, H.; Taiba, A.C.; Mahmoudi, Y.; Belkhatir, M. Shear characteristics of fly ash improved sand as an embankment material for road infrastructure purpose. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2021, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfiq, A. Improvement of Sandy Soil Properties by Using Bentonite. Kufa J. Eng. 2009, 1, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbar, A.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H. Effect of slag and bentonite on shear strength parameters of sandy soil. Geomech. Eng. 2018, 15, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhwani, B.; Seethalakshmi, P.; Sachan, A. Use of commercially available bentonite clay for treatment of micaceous sand. J. Geotech. Transp. Eng. 2020, 6. Available online: http://jgtte.com/issues/11/Issue%2011%20-1.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Lei, H.; Liu, X.; Shi, F.; Ma, C. Infiltration behaviour into sand of bentonite slurry with guar gum. Géotechnique Lett. 2022, 12, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Bezuijen, A. Pressure infiltration characteristics of bentonite slurry. Géotechnique 2018, 69, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelbaum, D.; Shackelford, C. Hydraulic Conductivity of Bentonite Slurry Mixed Sands. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 1941–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. D3080/D3080M-11; Standard Test Method for Direct Shear Test of Soils under Consolidated Drained Conditions. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- Bahmani, S.H.; Huat, B.B.; Asadi, A.; Farzadnia, N. Stabilization of residual soil using SiO2 nanoparticles and cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, Z.H.; Taha, M.R. A review of stabilization of soils by using nanomaterials. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 576–581. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; He, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, H.; Chu, J.; Xiao, Y. Strength and Permeability of Bentonite-Assisted Biocemented Coarse Sand. Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 58, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



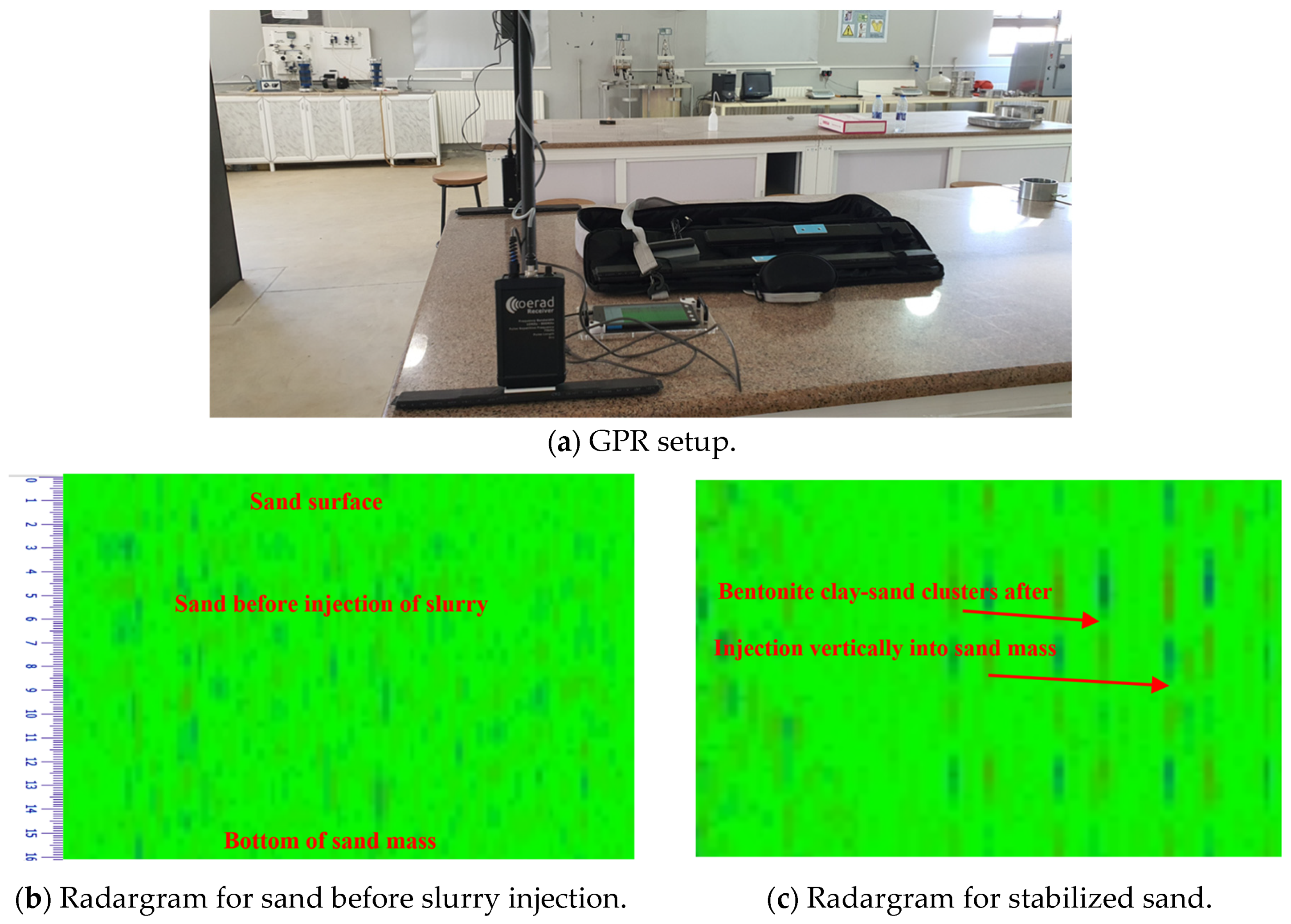


| Sand | Natural Sweileh Sand | Natural Silica Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Friction angle (°) | 26.31 | 30.75 |
| Cohesion (kN/m2) | 33.11 | 26.14 |
| Element | Percent |
|---|---|
| Si | 68.5 |
| Al | 12.4 |
| Ca | 4.9 |
| Cl | 3.4 |
| Fe | 3.4 |
| Na | 2.4 |
| Mg | 2.1 |
| S | 1.4 |
| K | 0.9 |
| Ba | 0.2 |
| Mn | 0.1 |
| Ti | 0.08 |
| P | 0.04 |
| Zn | 0.02 |
| Cr | 0.02 |
| Ni | 0.009 |
| Rb | 0.008 |
| Bentonite Content % | 0% | 1% | 2% | 3% | 4% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sweileh Sand | Silica Sand | Sweileh Sand | Silica Sand | Sweileh Sand | Silica Sand | Sweileh Sand | Silica Sand | Sweileh Sand | Silica Sand | |
| Friction angle (°) | 26.31 | 30.75 | 23.29 | 24.33 | 25.47 | 28.51 | 22.67 | 28.22 | 22.29 | 25.83 |
| Cohesion (kN/m2) | 33.11 | 26.14 | 44.46 | 44.11 | 40.35 | 37.70 | 55.43 | 42.70 | 64.36 | 54.75 |
| Shear strength (kN/m2) | 82.55 | 85.63 | 87.52 | 89.33 | 87.98 | 92.02 | 97.19 | 96.37 | 105.36 | 103.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bani Baker, M.; Abendeh, R.; Sharo, A.; Hanna, A. Stabilization of Sandy Soils by Bentonite Clay Slurry at Laboratory Bench and Pilot Scales. Coatings 2022, 12, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121922
Bani Baker M, Abendeh R, Sharo A, Hanna A. Stabilization of Sandy Soils by Bentonite Clay Slurry at Laboratory Bench and Pilot Scales. Coatings. 2022; 12(12):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121922
Chicago/Turabian StyleBani Baker, Mousa, Raed Abendeh, Abdulla Sharo, and Adel Hanna. 2022. "Stabilization of Sandy Soils by Bentonite Clay Slurry at Laboratory Bench and Pilot Scales" Coatings 12, no. 12: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121922
APA StyleBani Baker, M., Abendeh, R., Sharo, A., & Hanna, A. (2022). Stabilization of Sandy Soils by Bentonite Clay Slurry at Laboratory Bench and Pilot Scales. Coatings, 12(12), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121922







