Influence of the Current Regime during Electrodeposition in a Cr(III)-Containing Fe-Cr-Ni Electrolyte on the Near-Surface pH, Alloy Composition, and Microcrack Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
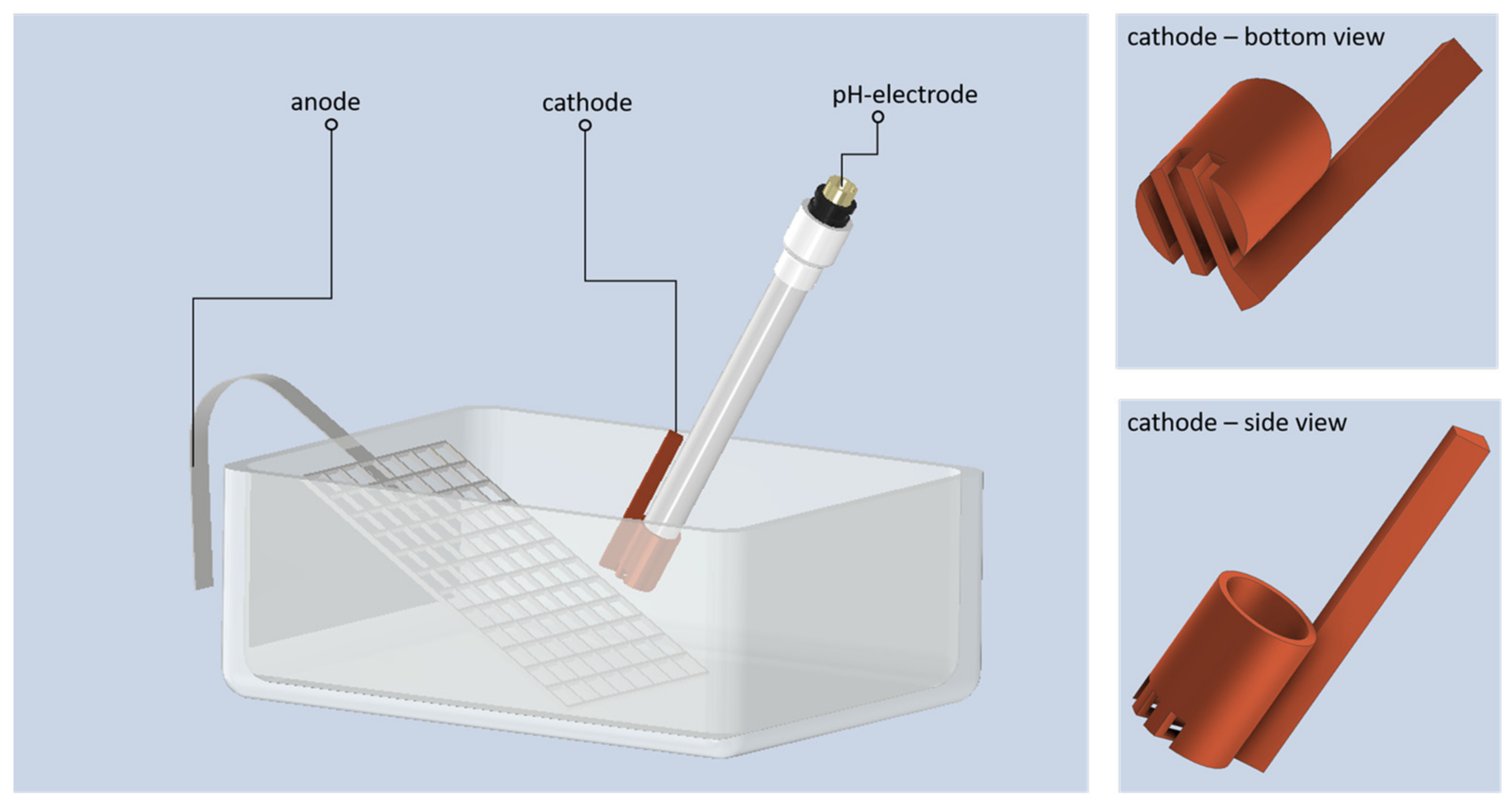
2.1. Substrate Preparation, Electrodepostion and In Situ pH Measurement
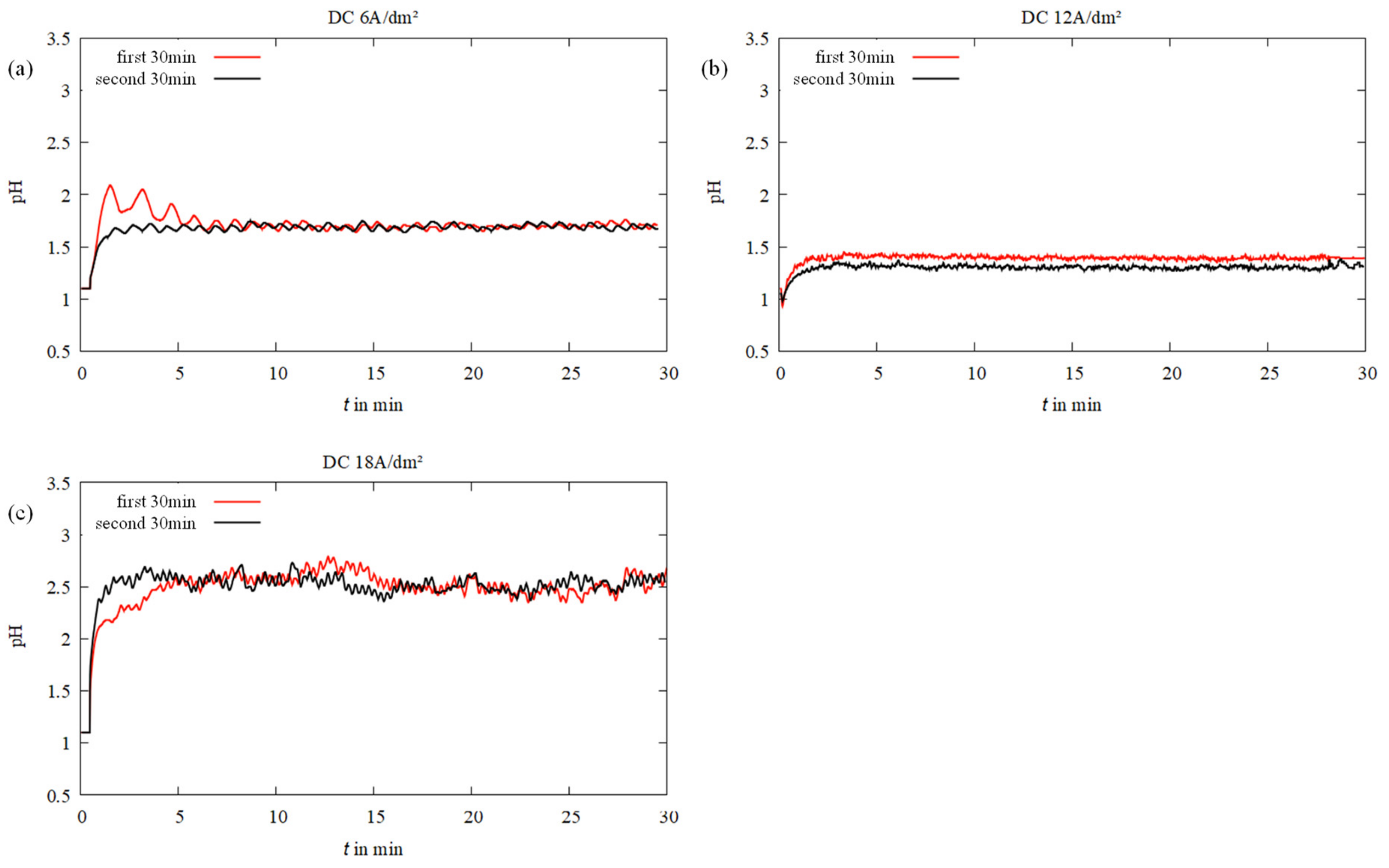
- DC: 6 A/dm2 (DC_6), 12 A/dm2 (DC_12), 18 A/dm2 (DC_18)
- Stepped DC at 12 A/dm2:
- ton = 10 s, toff = 10 s (Step_10/10)
- ton = 10 s, toff = 5 s (Step_10/5)
- ton = 5 s, toff = 2 s (Step_5/2)
- ton = 2 s, toff = 1 s (Step_2/1)
- PC at 12 A/dm2: ton = toff = 10 ms, f = 50 Hz, on/off ratio 1:1 (PC)
- For the alloy composition and microcracking behavior studies, the effective coating time for each sample was 120 min. For each current mode, three test samples (No. 1–3) were electrodeposited successively in the same electrolyte for two hours effective coating time each to investigate possible electrolyte aging and its influences on the composition and layer thickness of the alloy. For the studies of samples DC_12, Step_10/5, and PC, samples from the previous study were used, which were also manufactured under the exact conditions mentioned in [13].
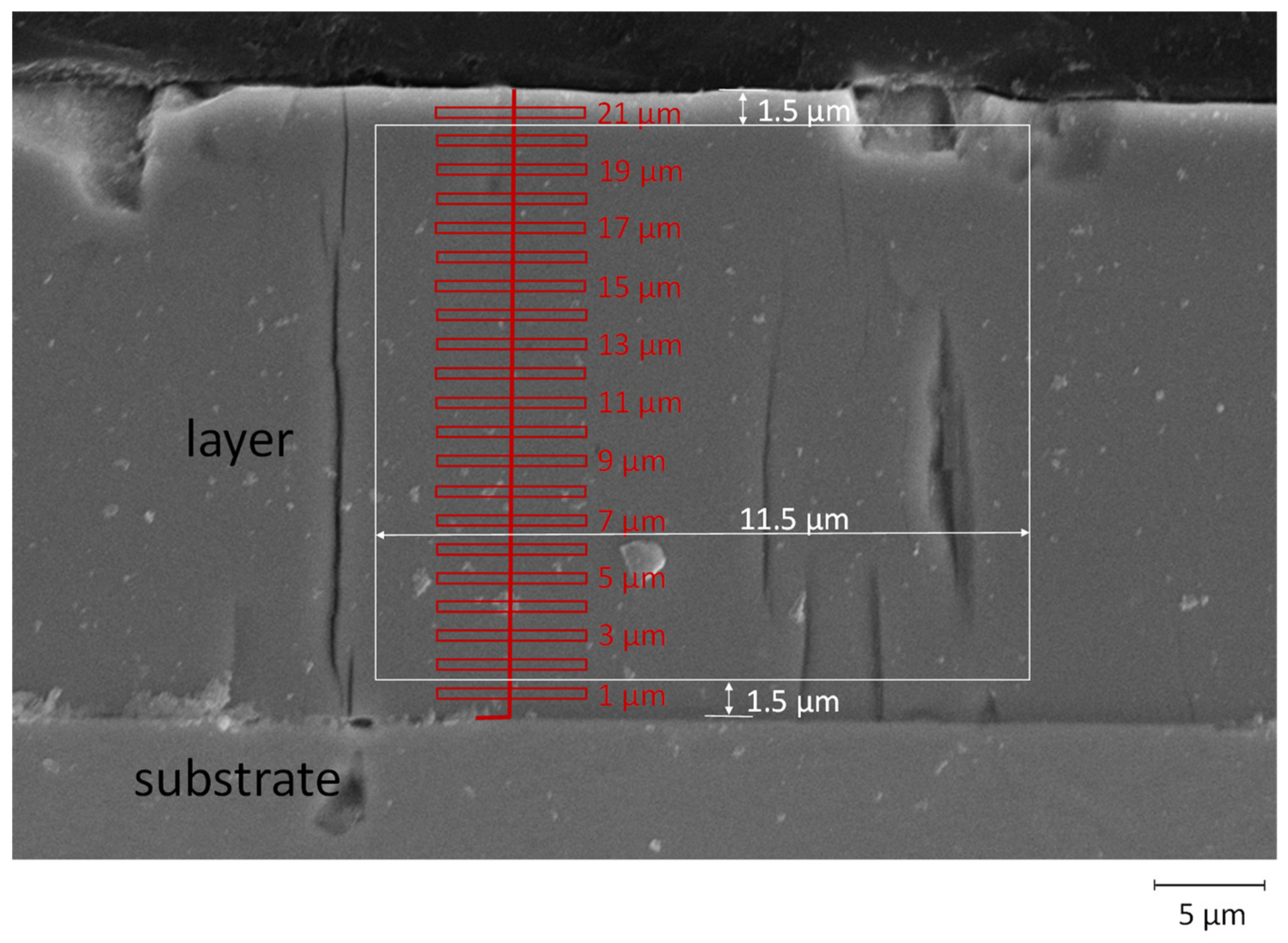
2.2. Layer Characterization
3. Results
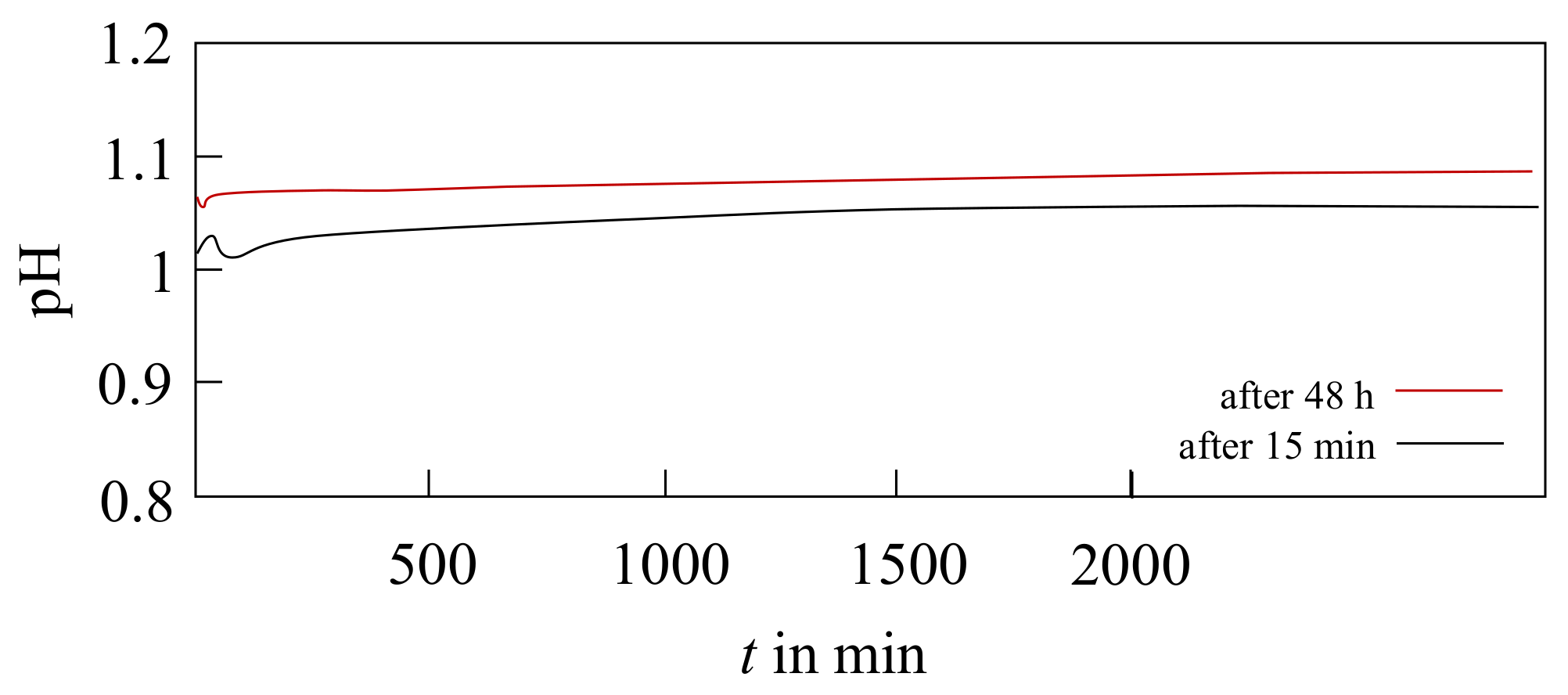
3.1. Electrolyte Lifetime
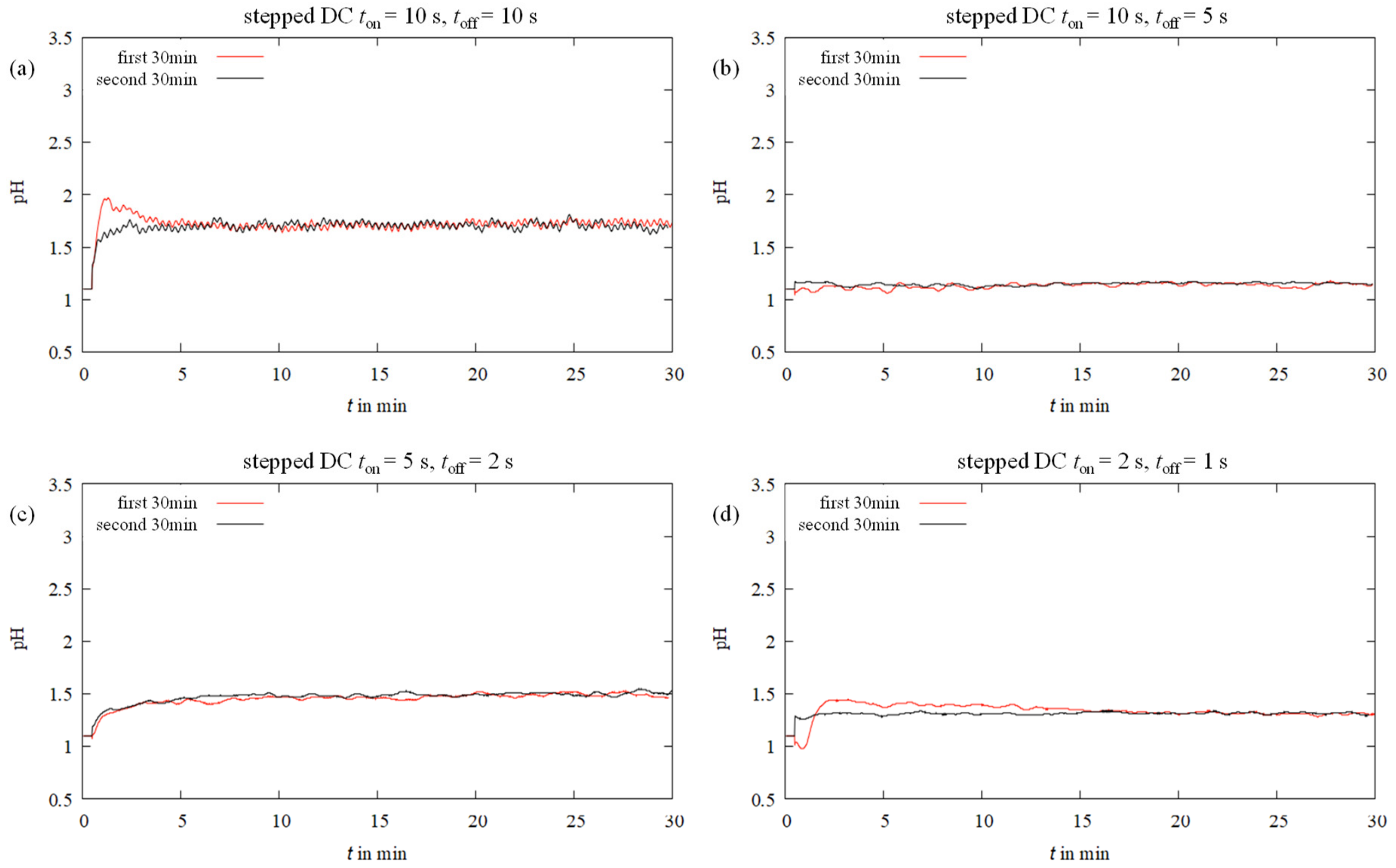
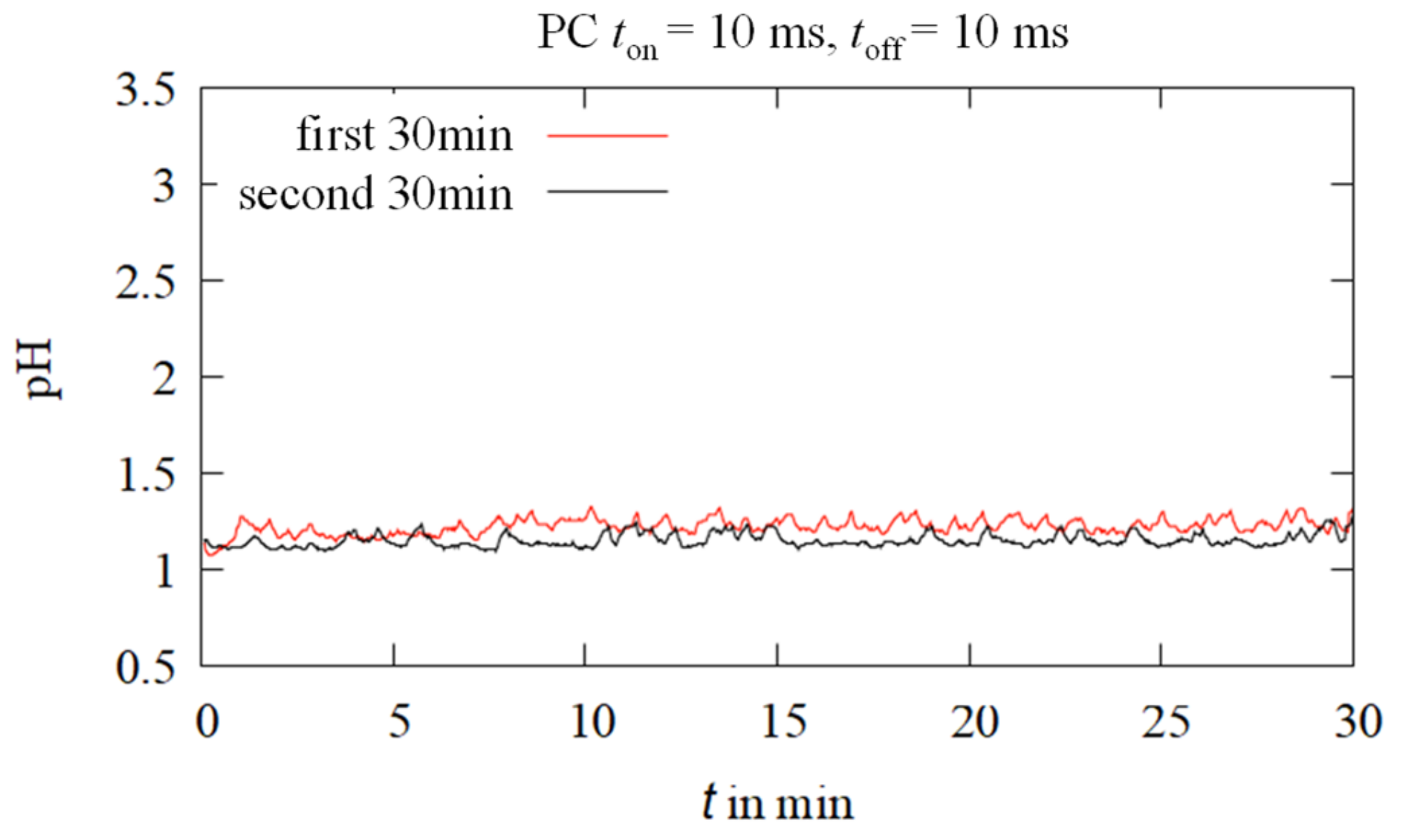
3.2. Near-Surface pH In Situ Curves during Electrodeposition
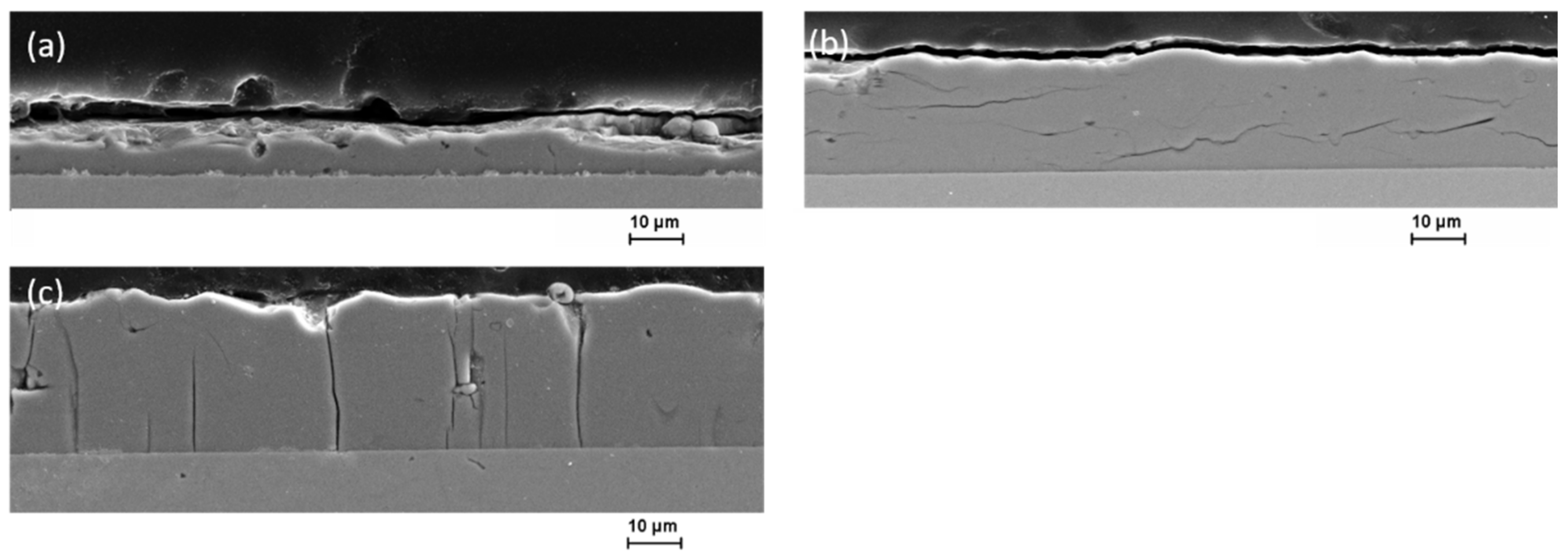
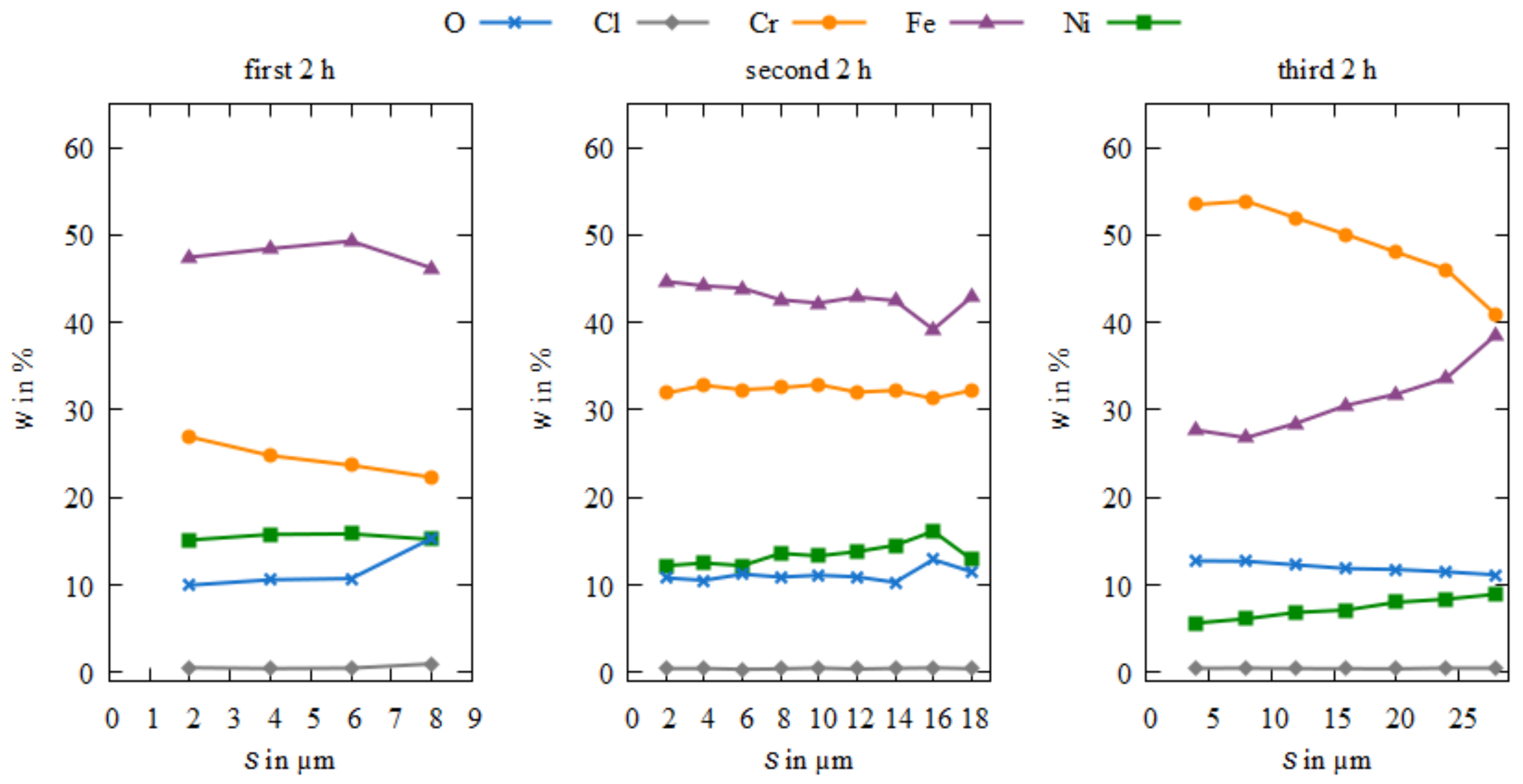
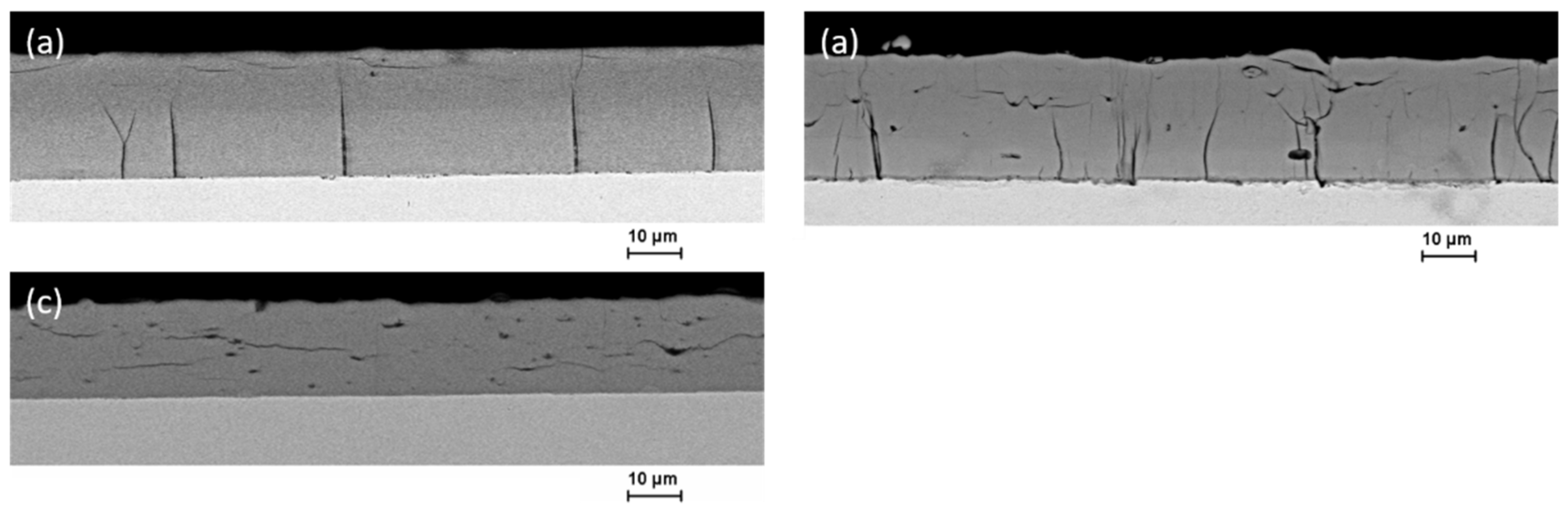
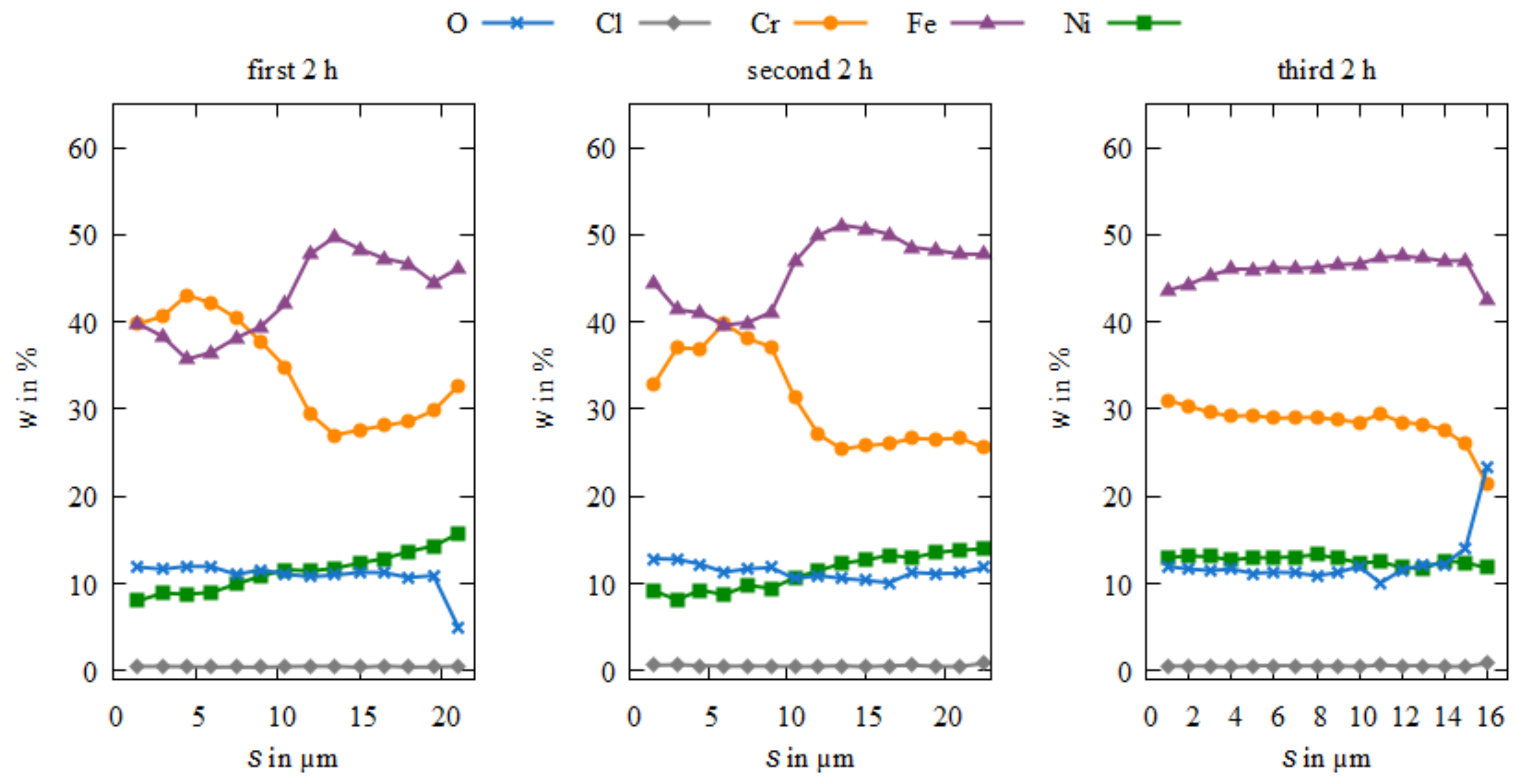
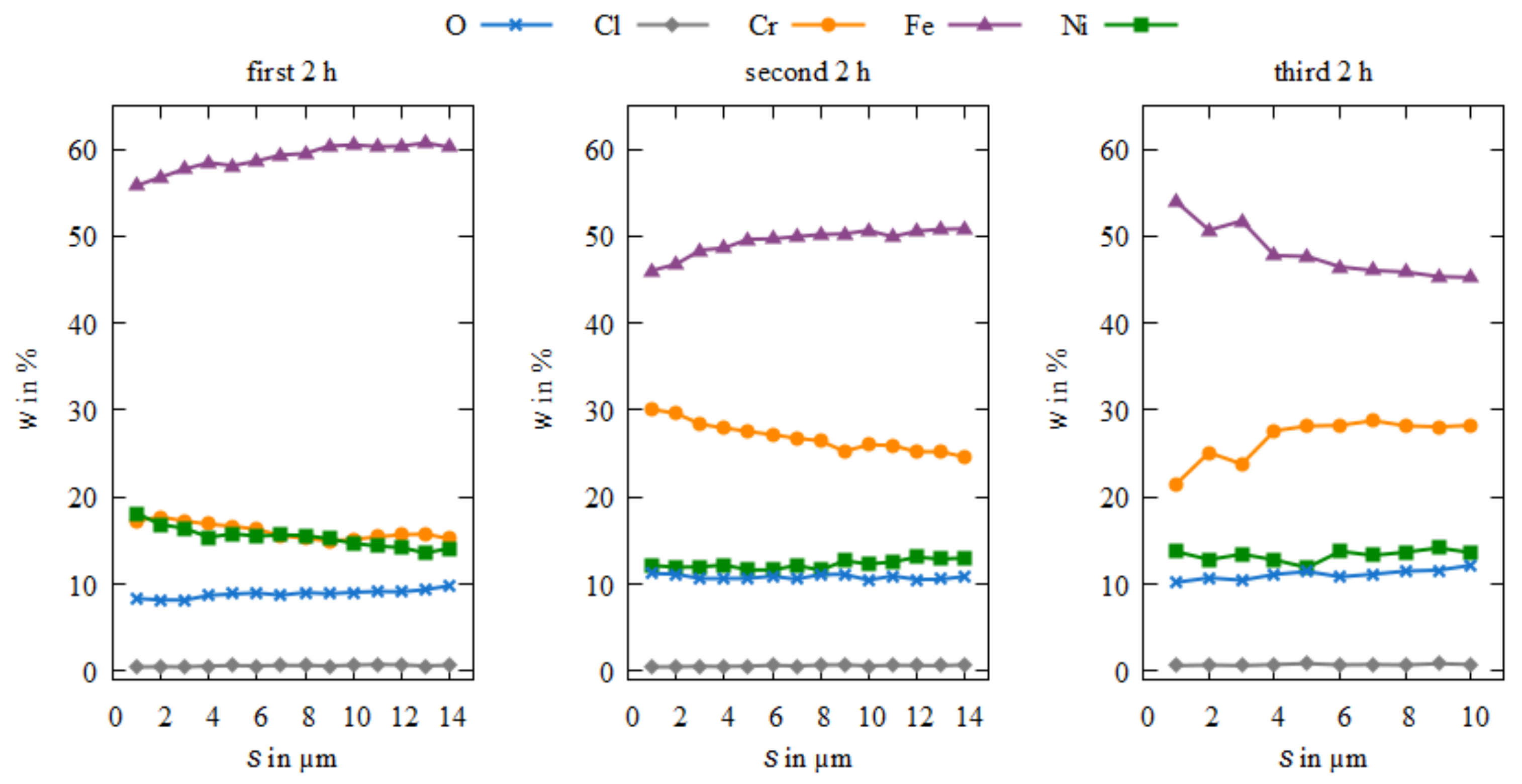
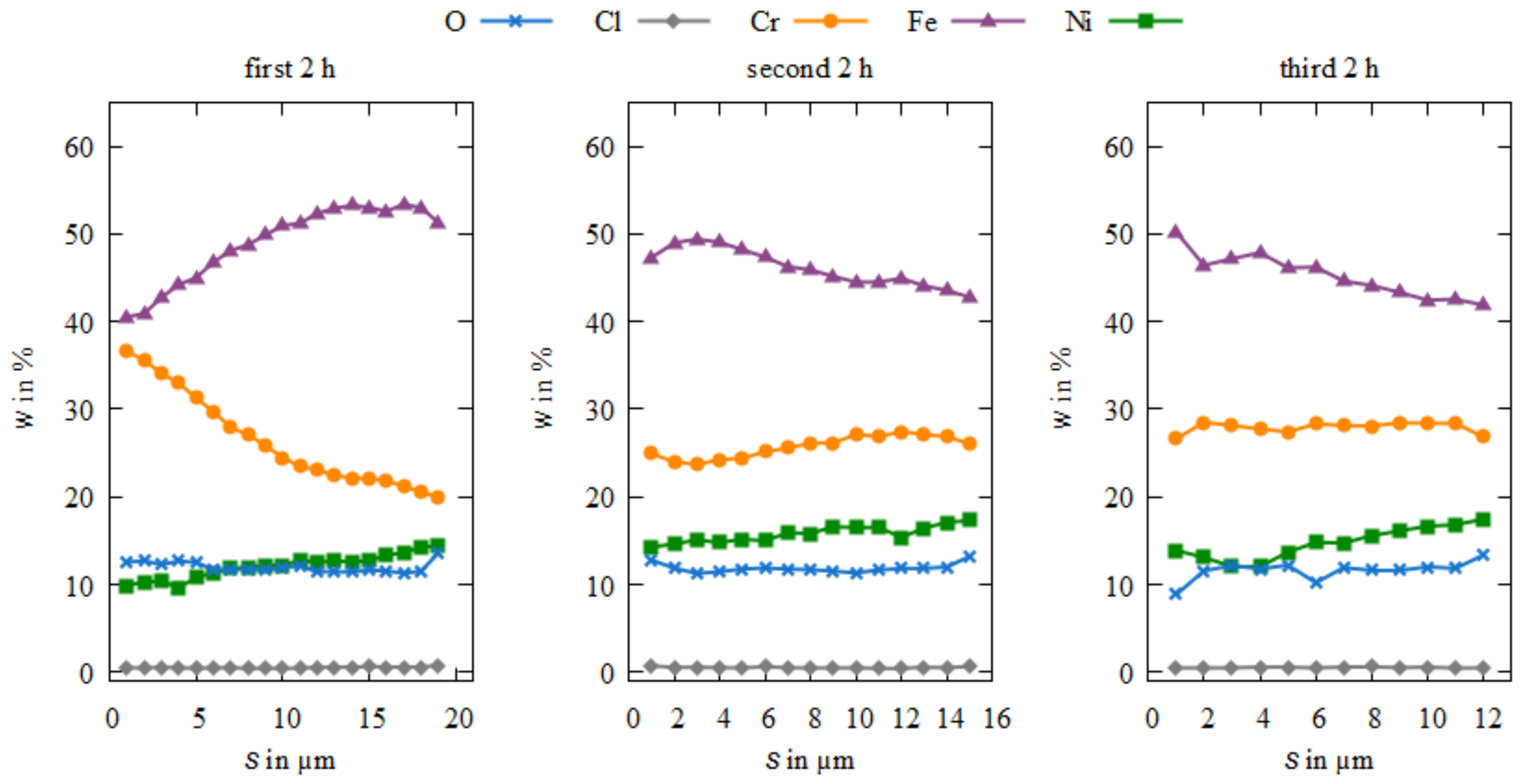
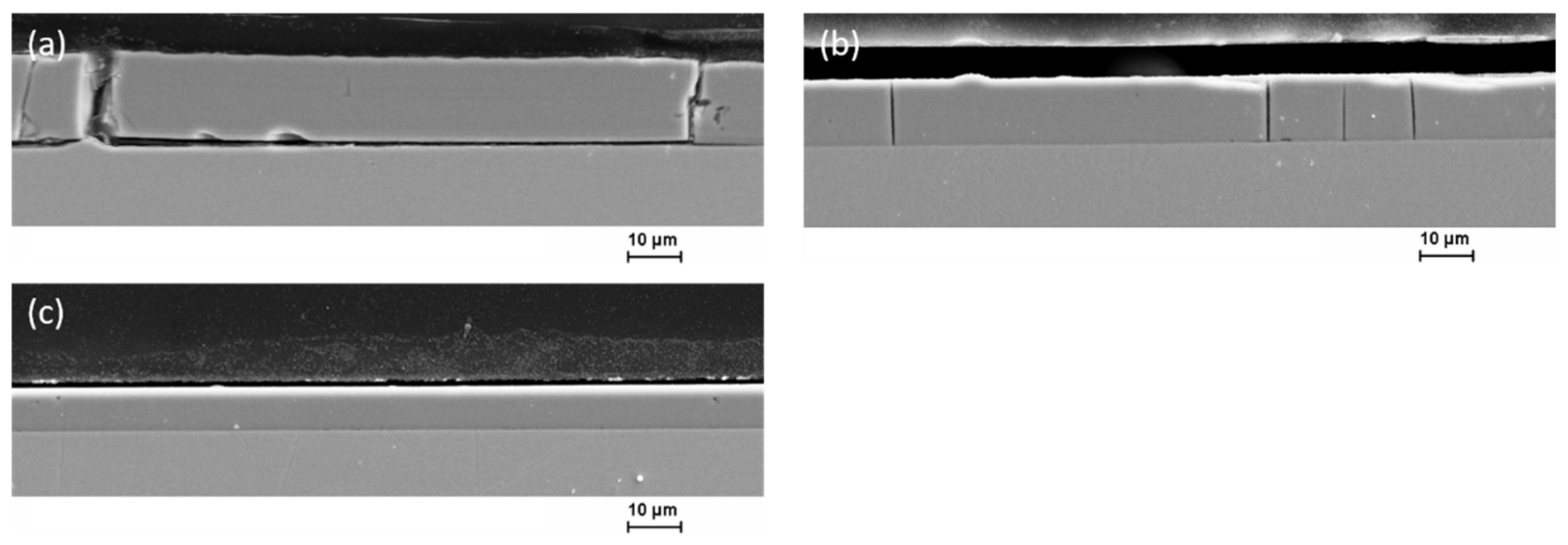
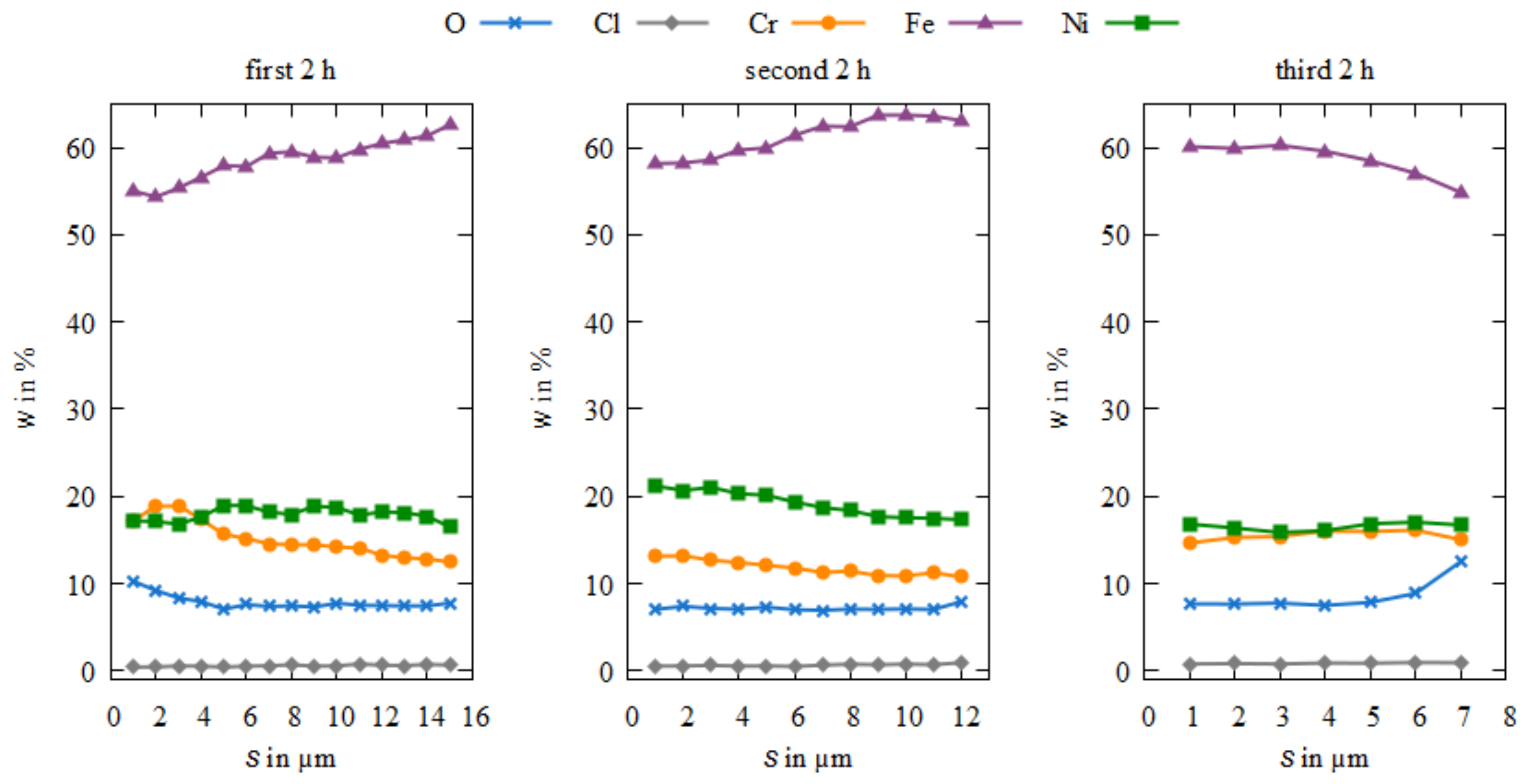
3.3. Microstructure and Element Composition of the Coatings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simão, J.; Aspinwall, D.K. Hard chromium plating of EDT mill work rolls. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 92–93, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Massler, O.; Kafexhiu, F.; Sedlacek, M. Crack density and tribological performance of hard-chrome coatings. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACh), Establishing a European Chemicals Agency, Amending Directive 1999/4. 2017, 10, 1–21. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/1907/2021-10-01 (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Pfeiffer, W.; Koplin, C.; Reisacher, E.; Wenzel, J. Residual stresses and strength of hard chromium coatings. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 681, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Connick, R.E. Hydrolytic polymerization of chromium(III). 1. Two dimic specis. Inorg. Chem. 1981, 1443, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharif, M.; McDougall, J.; Chisholm, C.U. Electrodeposition of thick chromium coatings from an environmentally acceptable chromium (III)-glycine complex. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 1999, 77, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabe, D.R. The role of hydrogen in metal electrodeposition processes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1997, 27, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhold, V.; Höhlich, D.; Dittes, A.; Mehner, T.; Lampke, T. Electrodeposition of FeCrNi and FeCr alloys and influence of heat treatment on microstructure and composition. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1147, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Yoon, S.; Guillonneau, G.; Zhang, Y.; Frantz, C.; Niederberger, C.; Weidenkaff, A.; Michler, J.; Philippe, L. The electrodeposition of FeCrNi stainless steel: Microstructural changes induced by anode reactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 26375–26384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sherik, A.; Erb, U.; Palumbo, G.; Aust, K. Deviations from hall-petch behaviour in as-prepared nanocrystalline nickel. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1992, 27, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.L.; Hsu, C.J.; Hsu, I.M.; Chang, J.T. Electroplating of Ni-Cr on steel with pulse plating. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1992, 1, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, K.; Dole, N.; Karadavut, O.; Hernandez, F.R.; Hall, T.D.; Taylor, E.J.; Brankovic, S.R. Crack free Cr coatings from Cr3+ electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 012504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhold, V.; Höhlich, D.; Mehner, T.; Lampke, T. Electrodeposition of thick and crack-free Fe-Cr-Ni coatings from a Cr (III) electrolyte. Coatings 2022, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, F.I.; Protsenko, V.S.; Butyrina, T.E.; Krasinskii, V.A.; Baskevich, A.S.; Kwon, S.C.; Lee, J.Y. Electrodeposition of nanocrystalline chromium coatings from cr(iii)-based electrolyte using pulsed current. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2011, 47, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimbach, M.; Tschaar, C.; Schmidt, U.; Bund, A. Electrochemical characterization of chromium deposition from trivalent solutions for decorative applications by EQCM and near-surface pH measurements. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 270, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, E.; Hasegawa, M.; Staubli, S.; Pellicer, E.; Herrmann, I.K.; Sort, J.; Michler, J.; Philippe, L. Electrodeposition of amorphous Fe-Cr-Ni stainless steel alloy with high corrosion resistance, low cytotoxicity and soft magnetic properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, E.; Manzano, C.V.; Pellicer, E.; Sort, J.; Ulfig, R.M.; Mischler, S.; Michler, J.; Philippe, L. “Green” Cr(III)-glycine electrolyte for the production of FeCrNi coatings: Electrodeposition mechanisms and role of by-products in terms of coating composition and microstructure. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25762–25775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertero, E.; Manzano, C.V.; Bürki, G.; Philippe, L. Stainless steel-like FeCrNi nanostructures via electrodeposition into AAO templates using a mixed-solvent Cr(III)-based electrolyte. Mater. Des. 2020, 190, 108559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelkhani, H.; Arshadi, M.R. Properties of Fe-Ni-Cr alloy coatings by using direct and pulse current electrodeposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chemicals | Formula | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (mol/L) | (g/L) | ||
| Iron(II) chloride | FeCl2·4H2O | 0.03 | 5.96 |
| Chromium(III) chloride | CrCl3·6H2O | 0.40 | 106.58 |
| Nickel(II) chloride | NiCl2·6H2O | 0.20 | 33.28 |
| Glycine | C2H5NO2 | 0.40 | 30.03 |
| Ammonium chloride | NH4Cl | 0.50 | 26.75 |
| Boric acid | H3BO3 | 0.15 | 9.27 |
| Sodium chloride | NaCl | 0.50 | 29.22 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Effective coating time (min) | 120 |
| Temperature (°C) | 23 |
| Anode-cathode distance (mm) | 20 |
| Area ratio anode: cathode | 6:1 |
| Bath volume (mL) | 250 |
| Bath movement (rpm) | 150 |
| pH | 1.1 |
| Samples | Layer Thickness Microcrack Density | Coating 1 | Coating 2 | Coating 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC_6 | d (µm) | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 15.1 ± 2.8 | 12.5 ± 2.8 |
| Md | not measurable | 26 | 59 | |
| DC_12 | d (µm) | 10.2 ± 1.2 | 15.4 ± 2.3 | 30 ± 5 |
| Md | 31 | 28 | 50 | |
| DC_18 | d (µm) | 27 ± 5 | 26.6 ± 2.3 | 20 ± 4 |
| Md | 52 | 71 | 78 |
| Samples | Layer Thickness Microcrack Density | Coating 1 | Coating 2 | Coating 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step_2/1 | d (µm) | 18.1 ± 1.8 | 17.9 ± 1.3 | 12.5 ± 2.0 |
| Md | 42 | 21 | 16 | |
| Step_5/2 | d (µm) | 16.5 ± 1.5 | 17.8 ± 2.6 | 14 ± 4 |
| Md | 28 | 31 | 26 | |
| Step_10/5 | d (µm) | 22.5 ± 1.4 | 14.1 ± 2.1 | 16.2 ± 1.9 |
| Md | 56 | 0 | 22 | |
| Step_10/10 | d (µm) | 13.1 ± 0.5 | 13 ± 4 | 22.8 ± 1.3 |
| Md | 36 | 21 | 47 |
| Samples | Layer Thickness Microcrack Density | Coating 1 | Coating 2 | Coating 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | d (µm) | 15.3 ± 1.2 | 12.5 ± 1.1 | 6.7 ± 1.2 |
| Md | 24 | 26 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meinhold, V.; Höhlich, D.; Mehner, T.; Lampke, T. Influence of the Current Regime during Electrodeposition in a Cr(III)-Containing Fe-Cr-Ni Electrolyte on the Near-Surface pH, Alloy Composition, and Microcrack Behavior. Coatings 2022, 12, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101569
Meinhold V, Höhlich D, Mehner T, Lampke T. Influence of the Current Regime during Electrodeposition in a Cr(III)-Containing Fe-Cr-Ni Electrolyte on the Near-Surface pH, Alloy Composition, and Microcrack Behavior. Coatings. 2022; 12(10):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101569
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeinhold, Vanessa, Dominik Höhlich, Thomas Mehner, and Thomas Lampke. 2022. "Influence of the Current Regime during Electrodeposition in a Cr(III)-Containing Fe-Cr-Ni Electrolyte on the Near-Surface pH, Alloy Composition, and Microcrack Behavior" Coatings 12, no. 10: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101569
APA StyleMeinhold, V., Höhlich, D., Mehner, T., & Lampke, T. (2022). Influence of the Current Regime during Electrodeposition in a Cr(III)-Containing Fe-Cr-Ni Electrolyte on the Near-Surface pH, Alloy Composition, and Microcrack Behavior. Coatings, 12(10), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101569







