Abstract
Burning loss of graphene in the high-temperature plasma-spraying process is a critical issue, significantly limiting the remarkable performance improvement in graphene reinforced ceramic coatings. Here, we reported an effective approach to enhance the graphene retention, and thus improve the performance of plasma-sprayed alumina/graphene nanoplatelets (Al2O3/GNPs) coatings by heat treatment of agglomerated Al2O3/GNPs powders. The effect of powder heat treatment on the microstructure, GNPs retention, and electrical conductivity of Al2O3/GNPs coatings were systematically investigated. The results indicated that, with the increase in the powder heat treatment temperature, the plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings exhibited decreased porosity and improved adhesive strength. Thermogravimetric analysis and Raman spectra results indicated that increased GNPs retention from 12.9% to 28.4%, and further to 37.4%, as well as decreased structural defects, were obtained for the AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings, respectively, which were fabricated by using AG powders without heat treatment, powders heat-treated at 850 °C, and powders heat-treated at 1280 °C. Moreover, the electrical conductivities of AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings exhibited 3 orders, 4 orders, and 7 orders of magnitude higher than that of Al2O3 coating, respectively. Powder heat treatment is considered to increase the melting degree of agglomerated alumina particles, eventually leaving less thermal energy for GNPs to burn; thus, a high retention amount and structural integrity of GNPs and significantly enhanced electrical conductivity were achieved for the plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings.
1. Introduction
Plasma spraying is a popular technique to fabricate various protective coatings in surface engineering, owing to its cost-effective qualities, large-scale fabrication, high deposition efficiency, flexibility, etc. [1,2]. Among the various materials which could be sprayed, plasma-sprayed alumina (Al2O3) coating is widely used in corrosion and wear resistance applications due to its chemical stability, high hardness and elastic modulus, excellent wear resistance, etc. [3,4,5]. Nevertheless, the poor electrical conductivity of Al2O3 coating restricts its potential usage in electronic components, electromagnetic shielding, heating elements, electro discharging machining, etc. [6,7,8]. Thus, the development of methods to enhance the electrical conductivity of plasma-sprayed Al2O3 coating is of significant importance.
The incorporation of nano-sized secondary phases is known to be an effective approach to improve a variety of material properties [9,10,11]. Graphene has been proven to be an ideal nano-filler, owing to its various attractive and outstanding properties, such as its high surface area, excellent mechanical properties, and high electrical and thermal conductivity [12,13,14]. Nevertheless, the single-layered graphene offers some intrinsic challenges and drawbacks as well, mainly its relatively high cost, poor wetting ability, and difficulty in dispersion, limiting its wider application. Graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs), which consist of dozens of layers of stacked graphene, are a promising substitute for single-layered graphene, to be used as reinforcements, and thus have attracted extensive research attention. GNPs have been proved to preserve most of the remarkable properties of graphene together with relatively low production cost as compared to graphene [11,15,16]. Therefore, the incorporation of GNPs is an economical and promising approach to improve the variety of ceramic performance. In particular, the incorporation of GNPs has led to a tremendous improvement in the mechanical properties of ceramic composites [17,18,19]. For example, Walker et al. [17] have fabricated a silicon nitride (Si3N4) ceramic composite with the addition of ~1.5 vol.% GNPs through spark plasma sintering. The results indicated that the fracture toughness of Si3N4 increased significantly, by up to ~235% (from ~2.8 to ~6.6 MPam1/2), and the toughening mechanism was revealed to be crack bridging, GNPs pull out and crack deflection. Ahmad et al. [18] revealed that the incorporation of 0.75 wt.% GNPs resulted in a 45% increase in the fracture toughness of the Al2O3 composite through high-frequency induction heat sintering. Liu et al. [19] have proved that the addition of 0.78 vol.% GNPs to Al2O3 matrix led to a 30.75% and 27.2% increase in its flexural strength and fracture toughness, respectively. Likewise, GNPs have also shown great potential to improve the electrical conductivity of the ceramic matrix. For instance, a very low GNP loading of 0.22 wt.% contributed to the increase in the electrical conductivity of the alumina matrix by up to eight orders of magnitude [7]. Wang et al. [6] fabricated a GNPs/Al2O3 composite by spark plasma sintering. The results showed that the electrical conductivity of the composite was remarkably improved through the addition of ~2 wt.% GNPs due to the formation of a GNPs electrical pathway in the matrix.
Nevertheless, the research into the reinforcement of thermal-sprayed ceramic coatings by GNPs is much more complicated and limited due to the high processing temperature, as well as the oxidizing atmosphere involved in the thermal spraying process, which needed to be specifically considered. The harsh processing conditions of thermal spraying inevitably results in burning, thermal degradation, and structural damage in GNPs, eventually leading to difficulty retaining GNPs within thermal-sprayed coatings [20,21,22,23]. For instance, Garcia et al. [23] reported that ~60% of the GNPs burned and only around 40% of the GNPs were preserved from the high temperature (~3000 °C) during flame-spraying of the GNPs/YAS (Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2) coating. The same authors [22] also reported that only 16% of the initial GNPs were retained after flame spraying by using a higher melting point YAS.
Although the incorporation of GNPs into thermal-sprayed ceramic coatings was demonstrated to improve their mechanical, thermal, and electrical performance to some extent [15,21,23], it is important to develop methods to suppress the burning and thermal degradation of GNPs during the thermal spraying process, thus retaining as many GNPs with high structural integrity as possible, to perform and realize the full potential of GNPs. Even though using low-pressure thermal spraying would be a promising approach to cope with the burning issue of GNPs through isolating GNPs from an oxidizing atmosphere, these techniques are limited in practical engineering due to the high cost of the vacuum apparatus. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, the works relating to the reinforcement of plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings by GNPs were mainly focused on improving the performance of the ceramic/GNPs composite coatings. Nevertheless, few works have concentrated on the approaches preventing GNPs from burning and thermal degradation during the plasma-spraying process.
In this study, we reported an effective approach to reduce the thermal degradation of GNPs during the plasma-spraying process through heat treatment of Al2O3/GNPs composite powders. The Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings were fabricated by plasma-spraying Al2O3/GNPs agglomerated powders with different heat-treatment conditions. The retention and thermal degradation of GNPs within the plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings were examined by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Raman spectrometer. The effects of the Al2O3/GNPs powder heat-treatment on the microstructure, GNPs retention, and the electrical conductivity of the plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings were systematically investigated. The major objective of this study was to provide a promising and effective approach to enhance the retention and structural integrity of GNPs in the thermal spraying process, eventually achieving an Al2O3/GNPs coating with significantly improved electricity conductivity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock Preparation
Commercial Al2O3 powders with a nominal size of 60 nm and 400 nm (Yingrui Science and Technology Ltd., Anhui, China), and multi-layered graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) with a nominal length of 5–10 μm and thickness of less than 10 nm (Figure 1), were used as raw materials. The Al2O3/GNPs composite feedstock powders were prepared by a spray-drying process. Prior to spray drying, nano-sized Al2O3 powders (the ratio (in wt.%) of 60 nm Al2O3 to 400 nm Al2O3 was optimized to 3:2) and 1 wt.% GNPs were evenly dispersed in an aqueous organic binder PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) to form a slurry. The proportion (in wt.%) of Al2O3, GNPs, and PVA in the slurry was 98.65%, 1%, and 0.35%, respectively. The reason for using a mixture of Al2O3 powders with two sizes was to facilitate the uniform dispersion of nano-sized Al2O3 and the adsorption of GNPs on Al2O3 particles within slurry. Then, the slurry was spray-dried to obtain spherical Al2O3/GNPs composite powders with a size range from 15 to 45 μm. The spray-dried Al2O3/GNPs powders without any further heat treatment were referred to as AG powders. In order to investigate the effect of powder heat treatment on the GNPs retention and performance of Al2O3/GNPs coatings, a portion of spray-dried Al2O3/GNPs powders were heat-treated. The heat treatment of AG powders was performed under argon atmosphere for 2 h at 850 °C and 1280 °C, respectively, with a heating rate of 5 °C min−1. The AG powders, heat-treated at 850 and 1280 °C, were referred to as AG850 and AG1280 powders, respectively. For comparison, commercial fuse-crushed Al2O3 powders with a size range of 15–45 μm were also used for coating deposition to investigate the effect of GNPs incorporation on the electrical conductivity of Al2O3 coating.
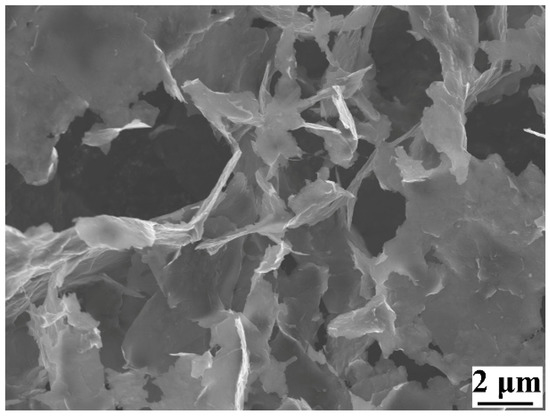
Figure 1.
Surface morphology of GNPs.
2.2. Coating Preparation
Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 powders, were used as feedstock for the fabrication of plasma-sprayed Al2O3 coating and three types of Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings, i.e., AG, AG850, and AG1280AG coatings, respectively, using a commercial plasma spraying system (ZB-80X, Hangtian Zhenbang, Beijing, China). Grit-blasted 304L stainless steel (nominal composition in wt.%: Cr: 18~20; Ni: 9~12; C: ≤0.03; Si: ≤1; Mn: ≤2; P: ≤0.045; Fe: Bal.) with a size of Ø20 × 2 mm was used as substrate. Each coating had a thickness of ~300 μM, and the plasma-spraying parameters are listed in Table 1. After the plasma-spraying process, in order to obtain a cross-section coating sample, the round coating samples were cut in the middle perpendicular to the coating surface with a precision sample cutting machine. After that, the sample was mounted, ground with SiC emery paper up to 2000 grit, then mirror-polished to a 0.02 μM finish with silica polishing agent.

Table 1.
Plasma spray parameters.
2.3. Coating Characterization
The surface morphologies of feedstock, cross-sectional microstructure and fracture surface morphologies of the four types of plasma-sprayed coatings were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, ZEISS SIGMA 500, Jena, Germany). The phase compositions of the feedstock and plasma-sprayed coatings were characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Rigaku Ultima IV system, Tokyo, Japan) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å) under a working voltage of 40 kV and current of 40 mA. In order to investigate the retention and structural degradation of graphene in the plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings, Raman spectra of the pristine GNPs and the GNPs retained within each coating were examined on the coating surface by Raman spectrometer (LabRAM HREvo, Montpellier, France) with a laser excitation wavelength of 532 nm at room temperature. Raman spectra at ten different random locations were obtained for each coating to obtain the average ID/IG value.
To quantitatively characterize the interface bonding within Al2O3 and three types of Al2O3/GNPs composite coating, the apparent porosities of the four types of coating were measured by the image analysis method, conducted on their cross-sectional images. Ten images taken randomly were used to obtain the average porosity value for each coating. The adhesive strengths of the four types of plasma-sprayed coating were measured through pull-off test, according to the widely used ASTM C633-13 standard [24]. Cylindrical specimens made of 304 L stainless steel, with a length of 50 mm and diameter of 25.4 mm, were used. First, the flat surface of the cylindrical specimen was grit-blasted and coated with plasma-sprayed coatings. Then, another, identical cylindrical specimen without coating deposition was glued to the coated cylinder with resin glue. After resin curing, the glued cylinders were mounted in a tensile test machine and pulled at a rate of 0.1 MPa s−1 until failure. Five samples were tested for each coating to obtain an average adhesive strength value.
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
In order to investigate the effect of powder heat treatment on the retention of GNPs within plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, TA449F3, Selb, Germany) was conducted for the AG, AG 850, and AG1280 coatings and their corresponding feedstock powders. The weight loss versus heating temperature of each coating or powder was recorded during the heating process, which was performed in oxygen atmosphere at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 up to 1200 °C. Prior to the test, the substrate was ground off with emery paper to obtain a free-standing coating. Then, these free-standing coatings were ground into powder with a mortar and pestle for the TGA test. Five samples were tested for each type of coating and powder to obtain the average GNPs amount within coating and feedstock, respectively.
2.5. Electrical Conductivity Test
The electrical conductivities of four types of coating were examined by AC impedance spectroscopy method [20] conducted on an electrochemical workstation (Biologic VMP3B-20, Seyssinet-Pariset, France). The four types of coating were first deposited on 304 L stainless steel substrate with a size of Ø20 × 2 mm; then, the substrate was ground off to obtain free-standing coating samples with a diameter of Ø20 mm and thickness of ~600 μm. Prior to the test, silver paint with a diameter of 10 mm was painted symmetrically on both sides of the coating surface. Two platinum lead wires were connected to each surface using silver paint, then dried overnight at 180 °C. During the impedance test, the frequency was set from 0.1 to 100 kHz with an AC amplitude of 10 mV. The electrical conductivity was then obtained from the impedance values [25]. Three samples were tested for each type of coating to achieve an average electrical conductivity value.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Powders
The surface morphologies of the Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 powders are presented in Figure 2. The as-received, fuse-crushed Al2O3 powders exhibited an angular and dense structure. The three types of Al2O3/GNPs agglomerated powder, i.e., AG, AG850, andAG1280 powders, exhibited a spherical shape with a uniform particle size range of 15–45 μm after undergoing the spray-drying process. As can be seen from the higher magnification images of AG, AG850, and AG1280 powders (Figure 2d,f,h), transparent graphene nanoplatelets, similar to that observed in the pristine GNPs (Figure 1), were found to be enclosed and wrapped into nanostructured alumina particles. Figure 3 presents the sintering morphologies of the Al2O3/GNPs powders with and without heat treatment. Evidently, for the AG powders without heat treatment, the nano-sized alumina particles were loosely connected to each other. For the AG850 powder heat-treated at 850 °C, a slight sintering was observed among the alumina particles. As the heat treatment temperature increased to 1280 °C, sintering necks among nano-sized alumina particles were obviously observed, indicating evident sintering within the AG1280 powders. Thus, with the increase in the powder heat treatment temperature, the sintering effect of alumina particles was enhanced, in favor of the thermal conduction and melting of powders during the in-flight process. This will be discussed in more detail later.
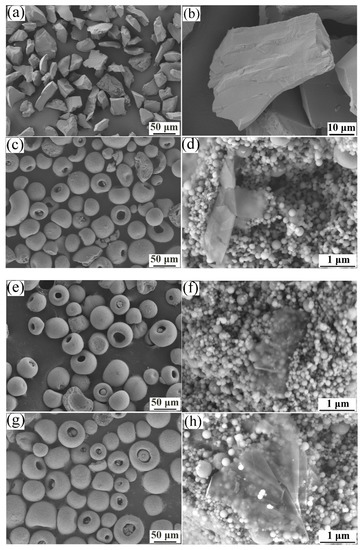
Figure 2.
Morphologies of four types of feedstock: (a,b) Al2O3 powder; (c,d) AG powder; (e,f) AG850 powder; and (g,h) AG1280 powder. Left and right images are taken at a low and high magnification, respectively.
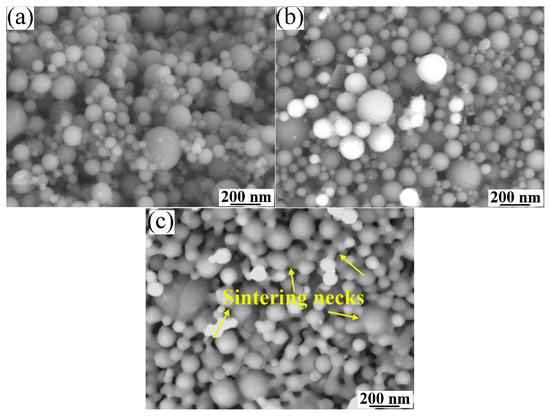
Figure 3.
Surface morphologies of (a) AG powder; (b) AG850 powder; and (c) AG1280 powder.
3.2. Effect of Powder Heat Treatment on the Microstructure of the Plasma-Sprayed Al2O3/GNPs Composite Coatings
Figure 4 presents the cross-sectional microstructure of the plasma-sprayed Al2O3, AG, AG 850, and AG1280 composite coatings. All four types of coating exhibited a homogenous microstructure with good interface bonding between the coating and substrate. In the case of the AG coating (Figure 2b), deposited by plasma-spraying AG powders without heat treatment, a relatively high number of voids with a large size of tens of micrometers were observed. Nevertheless, for the AG850 (Figure 2c) and AG1280 (Figure 2d) composite coatings fabricated by plasma-spraying of heat-treated AG850 and AG1280 powders, they appeared to become denser with fewer and smaller voids than that of the AG coating. Moreover, as the heat-treatment temperature for the AG powder increased from 850 to 1280 °C, large-scaled voids disappeared, and the coating density was further enhanced in the case of the AG 1280 coating. This is also confirmed by the cross-sectional microstructure of the Al2O3/GNPs coatings at a higher magnification (Figure 5). It is notable that the AG 1280 coating also exhibited a denser microstructure than that of the Al2O3 coating (Figure 4a and Figure 5a).
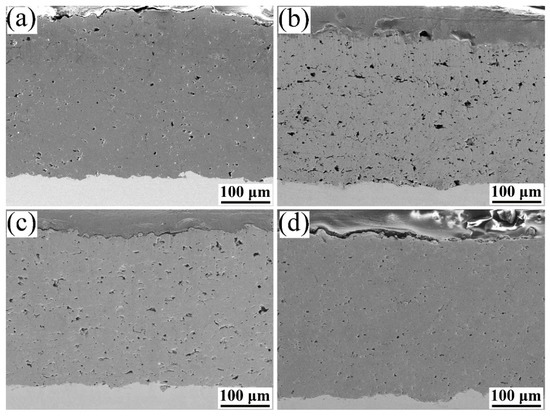
Figure 4.
Microstructure of the polished cross-section for different coatings: (a) Al2O3 coating; (b) AG coating; (c) AG850 coating; and (d) AG1280 coating.
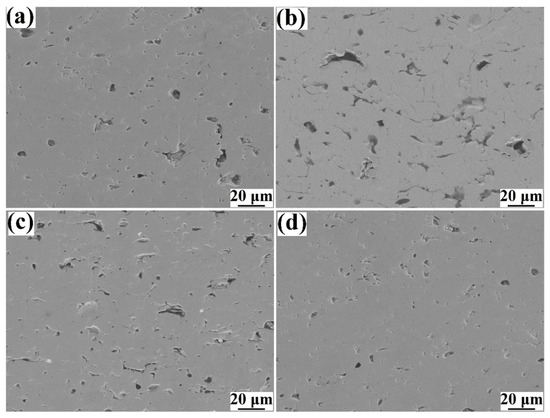
Figure 5.
Cross-sectional microstructure at a higher magnification for the four types of coatings: (a) Al2O3 coating; (b) AG coating; (c) AG850 coating; (d) AG1280 coating.
To quantitatively characterize the interface boning within the four types of coating, their apparent porosities were examined, and the results are demonstrated in Figure 6 and Table 2. The AG coating created using AG powders without heat treatment exhibited the highest porosity of ~6.8%, which was much higher than the 3.4% and 1.6% for the AG850 and AG1280 coatings, respectively. Therefore, it is indicated that, with the increase in the heat treatment temperature for the AG powders, the coating porosity decreased significantly, and the coating density was correspondingly enhanced. This result is consistent with the cross-sectional microstructure results demonstrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5. It is notable that the porosity of 6.8% for the present AG coating is comparable to the 5.6% porosity of the reported plasma-sprayed Al2O3/0.5 wt.%GNPs composite coating using spray-dried Al2O3/GNPs powder without further powder heat treatment [20].
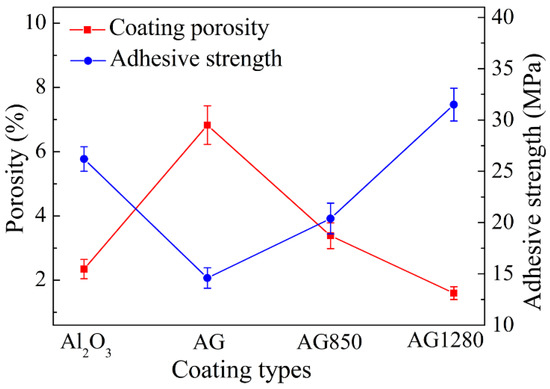
Figure 6.
Porosities and adhesive strengths of four types of coatings.

Table 2.
Apparent porosities and adhesive strengths of Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings.
The adhesive strength of a coating refers to the bonding strength between a coating and substrate, which represents its resistance to spalling off under service loading in practical applications, eventually influencing the long-term service of a coating. Therefore, the adhesive strength of the four types of plasma-sprayed coatings were measured, and the results are shown in Figure 6 and listed in Table 2. Apparently, the adhesive strength of the plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings increased with the increase in heat treatment temperature for AG powders. In particular, the AG 1280 composite coating exhibited a strong adhesive strength of ~31.5 MPa, which was comparable to the adhesive strength of the reported plasma sprayed Al2O3 coating with the deposition and assistance of the middle bonding layer [26,27].
The fracture surface morphologies of the plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings were characterized to check the retention of GNPs within these coatings, and the results are shown in Figure 7. Graphene nanoplatelets, exhibiting dimensions close to that in the original pristine GNPs (Figure 1), were found to be homogenously, and successfully incorporated into the AG (Figure 7a), AG850 (Figure 7b), and AG1280 coatings (Figure 7c). Evidently, for the AG coating, a large amount of partially molten (PM) regions were present within the coating, indicating the low melting degree of AG powders during the in-flight process. This is likely resulted from the poor thermal conduction of AG powders without heat treatment, eventually leading to the porous nanostructure in the original AG feedstock retained within the AG coating. That is, most of the agglomerated AG powders were only sintered in solid state during the plasma-spraying process, especially for the core of the powder [28]. Consequently, a porous structure with plenty of voids was obtained for the AG coating. Nevertheless, in terms of the AG 850 coating (Figure 7b), the proportion of the fully molten (FM) region was enhanced compared to that of the AG coating. Likewise, the FM region was further increased within the AG1280 coating and the nanostructure in the original agglomerated feedstock basically disappeared (Figure 7c). These results revealed that, with the increase in the powder heat-treatment temperature, a higher melting degree of powder during their in-flight process was achieved, resulting in improved coating density.
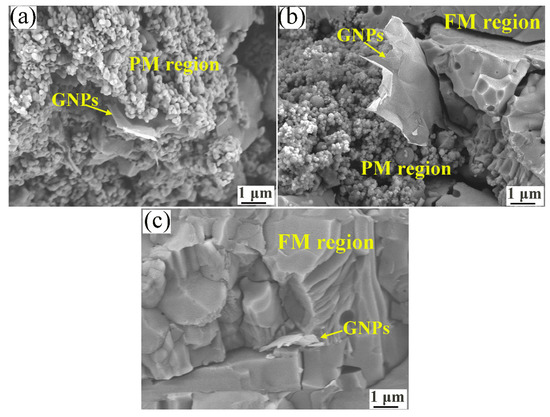

Figure 7.
Fracture surface morphologies of (a) AG coating; (b) AG850 coating; and (c) AG1280 coating.
Notably, it is also demonstrated from Figure 7 that GNPs were mainly located at the interface between lamellae. This is probably due to the poor wetting of GNPs to liquid droplets, together with the buoyancy effect resulting from the smaller GNPs density compared to that of alumina [23]. As a result, this leads to GNPs expelling to the droplet surface after droplet melting during the in-flight process. Consequently, GNPs become caught and trapped between lamellae upon impact to the substrate. On the other hand, the pulling-out characteristic of GNPs was observed from the fracture surface of coatings (Figure 7), which would facilitate the bridging effect of GNPs between lamellae and, thus, the formation of an electrical network throughout the coatings.
XRD analysis was conducted for the plasma-sprayed Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings, as well as their corresponding feedstock, to investigate the effect of powder heat treatment on the phase constitution of the coatings. As shown in Figure 8, only characteristic peaks of α-Al2O3 were detected within all four types of Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 feedstock. In the case of the four types of plasma-sprayed coating, typical diffraction peaks of γ-Al2O3 phase were also detected, apart from the α-Al2O3 phase, compared to that of the corresponding feedstock. This phenomenon was reported to be attributed to the rapid non-equilibrium solidification of molten α-Al2O3 splats during the formation of lamellae [4,28,29]. Moreover, the content of the γ-Al2O3 phase within the coating exhibited an evident upward trend with the increase in the heat-treatment temperature of the feedstock. This is because, for the AG1280 coating, a majority of the original alumina melted, to transform into γ-Al2O3 during their rapid solidification process. On the contrary, in terms of the AG coating, the low melting degree of AG powders during the spray process resulted in a large amount of α-Al2O3 phase in the feedstock remaining in the resultant coating. This is consistent with the above-demonstrated fracture surface results for different coatings. Notably, diffraction peaks of graphene were not detected for the four types of feedstock and coatings, due to their very small incorporation quantities. Moreover, the XRD peaks of Al4C3 phase were also not observed, indicating the absence of reaction between alumina and graphene during the plasma-spraying process.
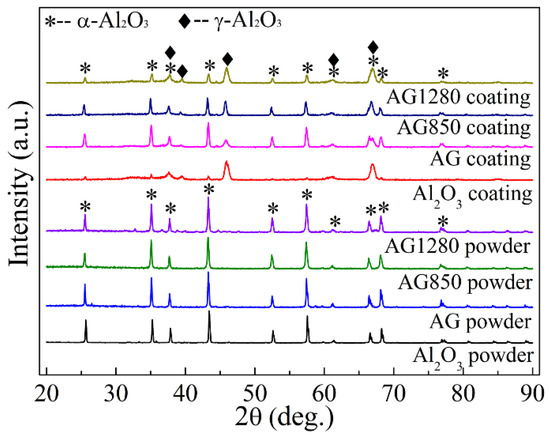
Figure 8.
XRD patterns of plasma sprayed Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings and their corresponding feedstock.
It is well-known that plasma-sprayed coatings are formed by the successive impact of molten or semi-molten droplets, followed by flattening, rapid cooling, and solidification processes. Plasma-sprayed coatings are generally characteristic of voids distributed within a coating, which could be divided into three types on the basis of the voids’ dimensions, i.e., three-dimensional (3D) type, two-dimensional (2D) type, and micro-crack type. The 3D-type voids are coarse voids, ranging in size from a sub-micrometer to more than 10 μm, which are considered to result from the entrainment of gas or insufficient filling of molten droplets to a substrate or previously deposited deposit [30,31]. In the case of the plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings, with the increase in heat treatment temperature for powders, the occurrence of sintering necks within the nano-structured alumina particles enhanced thermal conduction throughout the agglomerated droplets; thus, a high melting degree of alumina was obtained during the in-flight process. This promoted a sufficient filling of voids by molten droplets upon impact on the substrate or pre-deposited lamellae. Consequently, a decreased porosity, improved interface bonding and coating density was achieved, e.g., for the AG 1280 coating. In contrast, for the AG powders without heat treatment, there were no sintering necks, but only many pores existed among the nano-structured alumina particles, hindering their thermal conduction during the in-flight process and, thus, a low melting degree was obtained for AG powders. Finally, after impacting onto the substrate, a high porosity and poor interface bonding was obtained for the AG coating. The well-molten AG1280 droplets would facilitate the retention of GNPs within the coating, and this will be discussed in the next section. Notably, when compared to the plasma-sprayed Al2O3 coating deposited by plasma spraying of commercial fuse-crushed Al2O3 powders, the AG1280 coating exhibited a much denser microstructure, less porosity, and stronger adhesive strength. This is likely attributed to the dispersion of GNPs within the AG1280 coating and the contribution of highly thermally conductive GNPs (thermal conductivities of GNPs and Al2O3 are ~5000 and 10 W/mK, respectively) to heat transfer during the in-flight process.
3.3. Effect of Powder Heat Treatment on the Retention and Thermal Degradation of GNPs within Al2O3/GNPs Coatings
TGA was performed to quantitatively characterize the GNPs retention within the AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings and, therefore, to investigate the effect of powder heat treatment on the GNPs retention of plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings. Figure 9 presents the TGA data of the AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings, compared with that of their corresponding feedstock. Evidently, for each type of feedstock and coating, their weight loss during the heating process of TGA test appeared in two temperature regions. One is the weight loss between ~100–500 °C, which was considered to be primarily due to the burning of organic adhesives added in the spray-drying process, together with the evaporation of residual water within powder. The other is the weight loss between 500 and 900 °C, which is a typical combustion temperature range for graphene [22,23]. Thus, the weight loss occurring between 500 and 900 °C in TGA results represents the GNPs remaining in the feedstock or coating. It is indicated from Figure 9 that GNPs were successfully retained from the high-temperature plasma jet and retained in the three types of Al2O3/GNPs coating. In addition, the GNPs contents within the AG, AG850, and AG1280 feedstock powders (Figure 9a) were 0.93 wt.%, 0.88 wt.%, and 0.86 wt.%, respectively, which were slightly lower than the 1 wt.% that added into the initial Al2O3/GNPs mixture before spray-drying. The small loss fraction of GNPs mainly occurred during the powder fabrication process, e.g., GNPs adhered on the powder mixture container and GNPs loss during heat treatment process. Apparently, the GNPs amounts within the resultant plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG 1280 coatings were 0.12 wt.%, 0.25 wt.%, and 0.32 wt.%, respectively (Figure 9b), which were lower than that in the corresponding feedstock. Only 0.12 wt.% GNPs were retained within the AG coating compared to the 0.93 wt.% of GNPs within AG feedstock, indicating that a majority of GNPs burned up during the plasma-spraying process. It is notable that the large difference in mass loss among AG, AG850, and AG 1280 powders between ~100 and 500 °C during TGA test (Figure 9a) was likely due to the difference in their moisture content, since they were fabricated using the same adhesive ratio.
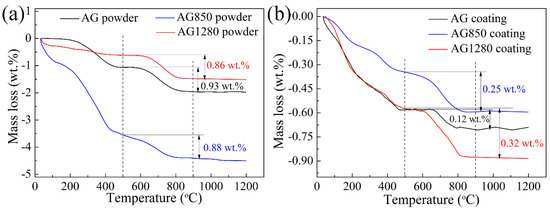
Figure 9.
TGA results of different Al2O3/GNPs feedstock powders (a) and Al2O3/GNPs coatings (b).
The retention percentages of GNPs for the three types of plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings (the ratio of GNPs amount within coating to that within their corresponding feedstock powders) were calculated, and the results are shown in Figure 10 and listed in Table 3. Evidently, the GNPs retention after the plasma-spraying process increased as follows: 12.9% for AG coating < 28.4% for AG850 coating < 37.2% AG1280 coating. These results revealed that powder heat treatment significantly increases the retention of GNPs within plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings. In addition, a higher heat treatment temperature causes more GNPs to be preserved after the high-temperature plasma-spraying process. Notably, the GNPs retention of 37.2% for the AG1280 coating is comparable to that of the reported 40% for flame-sprayed YAS/2.3 wt.% GNPs coating [23]. Taking account of the harsh processing conditions and much higher temperature (~10,000 °C) [31] during plasma spraying than that of the flame spraying (~3000 °C) [23], more GNPs would be retained by using heat-treated agglomerated powders. Moreover, the retention of GNPs within AG, AG850, and AG 1280 coatings was further confirmed through direct observation from optical images (Inserts in Figure 10). As the heat treatment temperature of powder increased, the coating color turned to dark black, representing that the higher GNPs content was incorporated within the coating. This result is consistent with the TGA results.
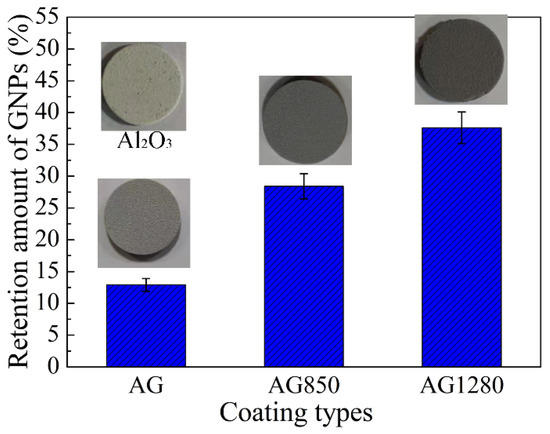
Figure 10.
The retention percentages of GNPs for the plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG1280 coating. The inserts are the optical images for the four types of coating.

Table 3.
The retention percentages of GNPs for different coatings.
Raman spectra analysis was performed for the plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG 1280 coatings, compared with that of the initial GNPs, to examine the structural degradation of GNPs during the high-temperature plasma-spraying process. Figure 11 showed that three typical bands, D band at 1350 cm−1, G band at 1580 cm−1, and 2D band at 2700 cm−1, were presented for all three types of coating, further confirming the presence and retention of GNPs within the coatings. The G band is the main in-plain vibrational mode of the graphitic lattice and is presented in all graphitic nanostructures. The D band is a ring-breathing vibrational mode, related to the structural defects and disorder formed in graphene. The intensity ratio of D band to G band, i.e., the ID/IG is generally an indicator of defects within graphene layers in GNPs [20,28,32,33]. Thus, the ID/IG value is often used to quantify the defectiveness in GNPs, as it varies with the amount of disorder. As shown in Table 4, a small value of ID/IG of 0.13 was obtained for the pristine GNPs, indicating its high structural integrity and few defects. Nevertheless, in terms of the plasma-sprayed coatings, the ID/IG value increased compared to that within the original GNPs, which is indicative of the increased number of defects formed within the coatings. Moreover, as predicted, the ID/IG value increased as follows: 0.34 of AG1280 coating < 0.57 of AG850 coating < 0.71 of AG coating, suggesting the increased defects and disorder within GNPs. These results reveal that powder heat treatment suppresses the thermal degradation and structural defectiveness of GNPs within plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings, and a higher powder heat treatment temperature improves the structural integrity of GNPs.
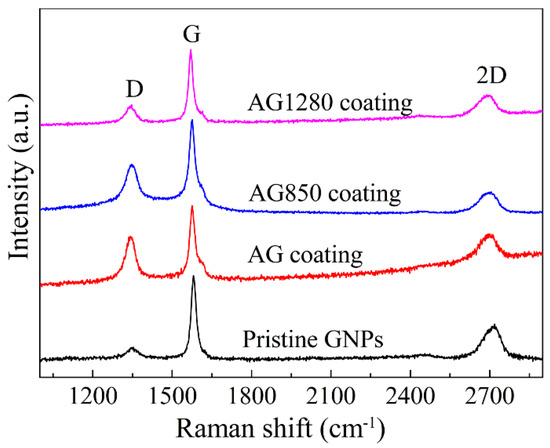
Figure 11.
Raman spectra of GNPs and plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings.

Table 4.
ID/IG values for pristine GNPs and plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings.
The effect of powder heat treatment on the GNPs retention within plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs coatings could be explained as follows: on one hand, in the case of the AG coating by plasma-spraying of AG powder without heat treatment, as demonstrated above, poor thermal conduction among nanostructured alumina particles leads to the low melting degree of powders, thus resulting in a lower amount of energy being absorbed by the AG feedstock during the plasma-spraying process. In this way, during spraying, there would be a high amount of heat available in plasma jet for the combustion and burning of GNPs, thus leading to a lower retention amount and high defects of GNPs within the AG coating. On the contrast, for the AG1280 coating using AG1280 powder with a higher heat-treatment temperature, sufficient melting was achieved for the alumina particles during the in-flight process, retaining less heat energy for GNPs to damage and degrade, compared to that of the AG coating, thus resulting in a high GNPs retention amount and less GNPs structural degradation. On the other hand, for the AG agglomerated powders with a higher heat treatment temperature, the surrounding sintered alumina particles would initially protect GNPs from exposure to an oxidizing atmosphere and high temperature, further facilitating GNPs retention.
3.4. Effect of Powder Heat Treatment on the Electrical Conductivity of Al2O3/GNPs Coatings
Figure 12 presents the electrical conductivities of plasma-sprayed Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings. Evidently, the electrical conductivity of the coating increased with the increase in the powder heat-treatment temperature. That is, the electrical conductivity of the Al2O3/GNPs coating increased from 1.24 × 10−9 S m−1 of Al2O3 coating to 1.18 × 10−6, 7.68 × 10−5, and 2.06 × 10−2 S m−1 for the AG, AG850, and AG1280 coating, respectively, i.e., ~3 orders, 4 orders, and 7 orders of magnitude higher than that of Al2O3 coating. This is mainly due to the improved interface bonding and well-preserved GNPs within the Al2O3/GNPs coatings using AG powders with a high heat-treatment temperature. It has been reported that the electrical conductivity of plasma-sprayed coatings is primarily dependent on their inter-lamellar bonding [20,34,35,36]. In general, the current conduction is interrupted by the un-bonded interfaces, leading to the poor electrical conductivity of plasma-sprayed coatings compared to the corresponding bulk materials. In terms of the AG1280 coating, its high density, low porosity, and good inter-lamellar interface bonding contributed to its smooth electrical conduction. Moreover, the GNPs trapped between lamellae acted as bridges, favoring electrical conduction between lamellae. The well-dispersed GNPs may also form a connected network throughout the entire coating, allowing for the current flow across the GNPs–GNPs contacts [23]. In contrast, in the case of the AG coating, its weak interface bonding and few preserved GNPs resulted in a low electrical conductivity. Notably, the limited increase in the electrical conductivity of AG1280 coating compared to the reported values is likely due to the few added GNPs [20,23].
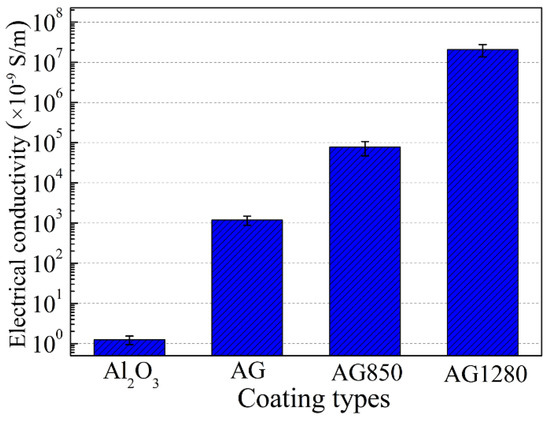
Figure 12.
Electrical conductivities of Al2O3, AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings.
In sum, heat treatment for the Al2O3/GNPs agglomerated powders is an effective approach to suppress the significant burning and thermal degradation of GNPs during the plasma-spraying process, eventually favoring the retention and structural integrity of GNPs within the Al2O3/GNPs coating. That is, heat treatment for the AG powders improves the melting degree of alumina particles, consequently leading to little thermal energy being available for the GNPs to combust. In this way, a large retention amount and few structural defects for GNPs could be achieved for the Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings by plasma-spraying Al2O3/GNPs powders with a high heat-treatment temperature, e.g., for the AG1280 coating. Although it is believed that the coating density could also, to some extent, be improved by the employment of higher plasma-spray power, the GNPs would suffer from much more burning under a higher plasma jet; thus, this may not be an appropriate approach to enhance the retention of GNPs. The incorporation of other types of graphene with a higher electrical conductivity could also be used to further enhance the electrical conductivity of ceramic coatings. For instance, Lee et al. [37,38] reported microporous 3D graphene-like carbons with remarkably high electrical conductivity of ~106 S m−1, which was higher than the 105 S m−1 of conventional graphene nanoplatelets fabricated by microwave explosion method [20]. In the future, an investigation into the effect of powder heat treatment on the mechanical properties of Al2O3/GNPs coatings would be conducted and presented. Furthermore, heat treatment at a temperature higher than 1280 °C will be applied to the Al2O3/GNPs powders to investigate whether an Al2O3/GNPs coating with higher GNPs retention and higher electrical conductivity could be achieved.
4. Conclusions
In this study, plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs (AG) coatings, using agglomerated AG powders with different heat-treatment conditions, were fabricated. The effect of powder heat treatment on the coating microstructure, GNPs retention, and, consequently, the electrical conductivity of Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings were systematically investigated and the underlying mechanism was revealed. The main conclusions can be drawn as follows:
- (1)
- With the increase in the heat treatment temperature for the AG feedstock powders, the corresponding plasma-sprayed Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings presented decreased porosity and improved adhesive strength. Moreover, GNPs were found to be well-dispersed at inter-lamellar interfaces within the plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings;
- (2)
- As the powder heat treatment temperature increased, enhanced GNPs retention from 12.9% to 28.4%, and further to 37.4%, as well as decreased structural defects of GNPs, were achieved for the AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings, respectively. This is mainly related to less thermal energy being available for GNPs to combust, resulting from the high melting degree of alumina particles during the in-flight process;
- (3)
- The electrical conductivities of the plasma-sprayed AG, AG850, and AG1280 coatings exhibited a remarkable increase of ~3 orders, 4 orders, and 7 orders of magnitude higher than that of the Al2O3 coating. The enhanced electrical conductivity of Al2O3/GNPs composite coatings with the increase in powder heat-treatment temperature is attributed to the improved interface bonding within the coating, as well as the contribution of retained GNPs, e.g., electrical conductive bridging between lamellae and electrical conductive networks formed by GNPs throughout the coatings.
The powder heat treatment strategy presented in this study provides a promising and effective approach to enhance GNPs retention in thermal-sprayed GNPs-reinforced ceramic coatings, and thus significantly improve their electrical conductivity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W., S.X. and J.T.; validation, X.W., S.X. and J.T.; investigation, X.W., S.X., K.X., L.H., D.W. and J.T.; resources. S.X. and J.T.; writing—original draft preparation, X.W. and S.X.; writing—review and editing, X.W., S.X., K.X., L.H., D.W. and J.T.; supervision, S.X. and J.T.; project administration: S.X. and J.T.; funding acquisition, X.W., S.X. and J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52001280), the Key Research Project of Henan Province (No. 20A430029), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M682339).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Kai Wang for his fruitful co-operation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, S.Q.; Zhou, J.Z.; Sun, K.T.; Yang, H.L.; Cai, W.C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Wu, S.J.; Li, H. Microstructural charactistics of plasma sprayed NiCrBSi coatings and their wear and corrosion behaviors. Coatings 2021, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Islam, A.; Mukherjee, B.; Richter, J.; Arold, T.; Niendorf, T.; Keshri, A.K. Plasma sprayed lanthanum zirconate coating over additively manufactured carbon nanotube reinforced Ni-based composite: Unique performance of thermal barrier coating system without bondcoat. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 550, 149397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, M.; Latka, L.; Sokolowski, P.; Toma, F.L.; Myalska, H.; Denoirjean, A.; Ageorges, H. Microstructural, mechanical and tribological properties of finely grained Al2O3 coatings obtained by SPS and S-HVOF methods. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 404, 126463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Li, C.J.; Yang, G.J. Influence of deposition temperature on the microstructures and properties of plasma-sprayed Al2O3 coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Khodair, Z.T.; Khadom, A.A. Preparation, characterization and application of Al2O3 nanoparticles for the protection of boiler steel tubes from high temperature corrosion. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 26945–26955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.F.; Fan, Z.J.; Yan, J.; Wei, T. Preparation of graphene nanosheet/alumina composites by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, A.; Rocha, V.G.; Alonso, B.; Fernández, A.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, C.F.; Torrecillas, R.; Zurutuza, A. Graphene for tough and electroconductive alumina ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 3201–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momohjimoh, I.; Saheb, N.; Hussein, M.A.; Laoui, T.; Al-Aqeeli, N. Electrical conductivity of spark plasma sintered Al2O3–SiC and Al2O3-carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 16008–16019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.; Kar, S.; Paul, S.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P. Carbon nanotube reinforced HVOF sprayed WC-Co coating. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balani, K.; Zhang, T.; Karakoti, A.; Li, W.Z.; Seal, S.; Agarwal, A. In situ carbon nanotube reinforcements in a plasma-sprayed aluminum oxide nanocomposite coating. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gómez, A.; Nistal, A.; García, E.; Osendi, M.I.; Belmonte, M.; Miranzo, P. The decisive role played by graphene nanoplatelets on improving the tribological performance of Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 glass coatings. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakah, R.R.; Huang, F.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jing, L. Comparative study of corrosion properties of different graphene nanoplate/epoxy composite coatings for enhanced surface barrier protection. Coatings 2021, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Shen, Z.G.; Zhang, W.; Yi, M.; Ma, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.X.; Zhao, Y.Z. Graphene coating for enhancing the atom oxygen erosion resistance of kapton. Coatings 2020, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Cai, W.W.; An, J.; Kim, S.; Nah, J.; Yang, D.X.; Piner, R.; Velamakanni, A.; Jung, I.; Tutuc, E.; et al. Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 2009, 324, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Q.; Xie, Y.T.; Li, K.; Huang, L.P.; Huang, S.S.; Zhao, B.Z.; Zheng, X.B. Microstructure and wear behavior of graphene nanosheets-reinforced zirconia coating. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12821–12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscia, U.; Longo, A.; Palomba, M.; Sorrentino, A.; Barucca, G.; Bartolomeo, A.D.; Urban, F.; Ambrosone, G.; Carotenuto, G. Influence of the thermomechanical characteristics of low-density polyethylene substrates on the thermoresistive properties of graphite nanoplatelet coatings. Coatings 2021, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.S.; Marotto, V.R.; Rafiee, M.A.; Koratkar, N.; Corral, E.L. Toughening in graphene ceramic composites. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3182–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Islam, M.; Subhani, T.; Zhu, Y.Q. Characterization of GNP-containing Al2O3 nanocomposites fabricated via high frequency-induction heat sintering route. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, H.X.; Jiang, K. Mechanical properties of graphene platelet-reinforced alumina ceramic composites. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 6215–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Mukherjee, B.; Sribalaji, M.; Rahman, O.S.A.; Arunkumar, P.; Babu, K.S.; Keshri, A.K. Role of hybrid reinforcement of carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets on the electrical conductivity of plasma sprayed alumina coating. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4508–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W.; Rance, G.A.; Xu, F.; Hussain, T. Alumina-graphene nanocomposite coatings fabricated by suspension high velocity oxy-fuel thermal spraying for ultra-low-wear. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Nistal, A.; Osendi, M.I.; Miranzo, P. Superior performance of ablative glass coatings containing graphene nanosheets. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Nistal, A.; Khalifa, A.; Essa, Y.; Escalera, F.M.; Osendi, M.I.; Miranzo, P. Highly electrically conducting glass-graphene nanoplatelets hybrid coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 17656–17662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM, C633-13. Standard Test. Method for Adhesion or Cohesion Strength of Thermal Spray Coatings 2013; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Herle, J.V.; Mcevoy, A.J.; Thampi, K.R. Conductivity measurements of various yttria-stabilized zirconia samples. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 3691–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.L.; Li, S.J.; Hou, G.L.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhou, H.D.; Chen, J.M. Mechanical and tribological properties of nano/micro composite alumina coatings fabricated by atmospheric plasma spraying. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5319–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S. An evaluation of plasma-sprayed coatings based on Al2O3 and Al2O3–13wt.% TiO2 with bond coat on pure titanium substrate. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, B.; Rahman, O.S.A.; Islam, A.; Sribalaji, M.; Keshri, A.K. Plasma sprayed carbon nanotube and graphene nanoplatelets reinforced alumina hybrid composite coating with outstanding toughness. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 727, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.G.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, G.; Wang, Z.X. Microstructure and properties of Al2O3/TiO2 nanostructured ceramic composite coatings prepared by plasma spraying. J. Alloy Compd. 2012, 544, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Ohmori, A. Relationships between the microstructure and properties of thermally sprayed deposits. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2002, 11, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, R. The relationship between the mechanism of formation, microstructure and properties of plasma-sprayed coatings. Thin Solid Films 1981, 83, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, F.; Rance, G.A.; Thomas, J.; Hussain, T. A low-friction graphene nanoplatelets film from suspension high velocity oxy-fuel thermal spray. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 025216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ding, S.Y.; Zheng, W.G.; Li, W.Y.; Li, H. Microstructure and anti-wear and corrosion performances of novel UHMWPE/graphene-nanosheet composite coatings deposited by flame spraying. Polym. Advan. Technol. 2013, 24, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, W.Y.; Liao, H.L.; Li, C.J.; Li, C.X.; Coddet, C. Microstructure and electrical conductivity of atmospheric plasma-sprayed LSM/YSZ composite cathode materials. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2007, 16, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Li, C.X.; Wang, M. Effect of spray parameters on the electrical conductivity of plasma-sprayed La1−xSrxMnO3 coating for the cathode of SOFCs. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 198, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liao, H.L.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, G.; Coddet, C.; Li, C.J.; Li, C.X.; Ning, X.J. Characterization of YSZ solid oxide fuel cells electrolyte deposited by atmospheric plasma spraying and low pressure plasma spraying. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2006, 15, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, K.; Kang, S.H.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.K.; Ryoo, R.; Park, J.Y. Extremely high electrical conductance of microporous 3D graphene-like zeolite-templated carbon framework. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11460–11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, T.; Kwon, Y.; Seo, Y.; Song, J.; Park, J.K.; Lee, H.; Park, J.Y.; Ihee, H.; Cho, S.J.; et al. Lanthanum-catalysed synthesis of microporous 3D graphene-like carbons in a zeolite template. Nature 2016, 535, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).