Facile Preparation of Superhydrophobic Membrane Inspired by Chinese Traditional Hand-Stretched Noodles
Abstract
1. Introduction
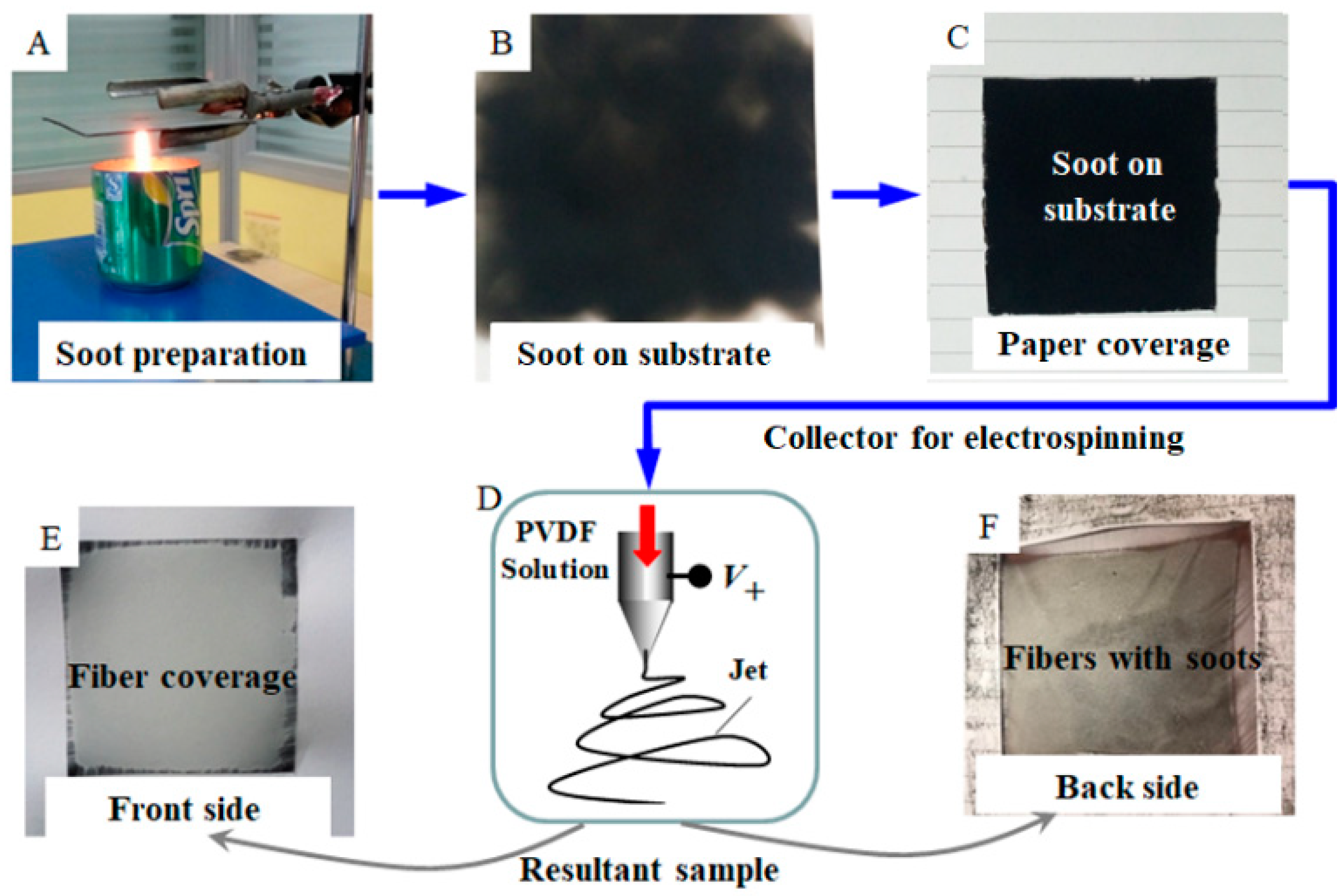
2. Materials and Methods
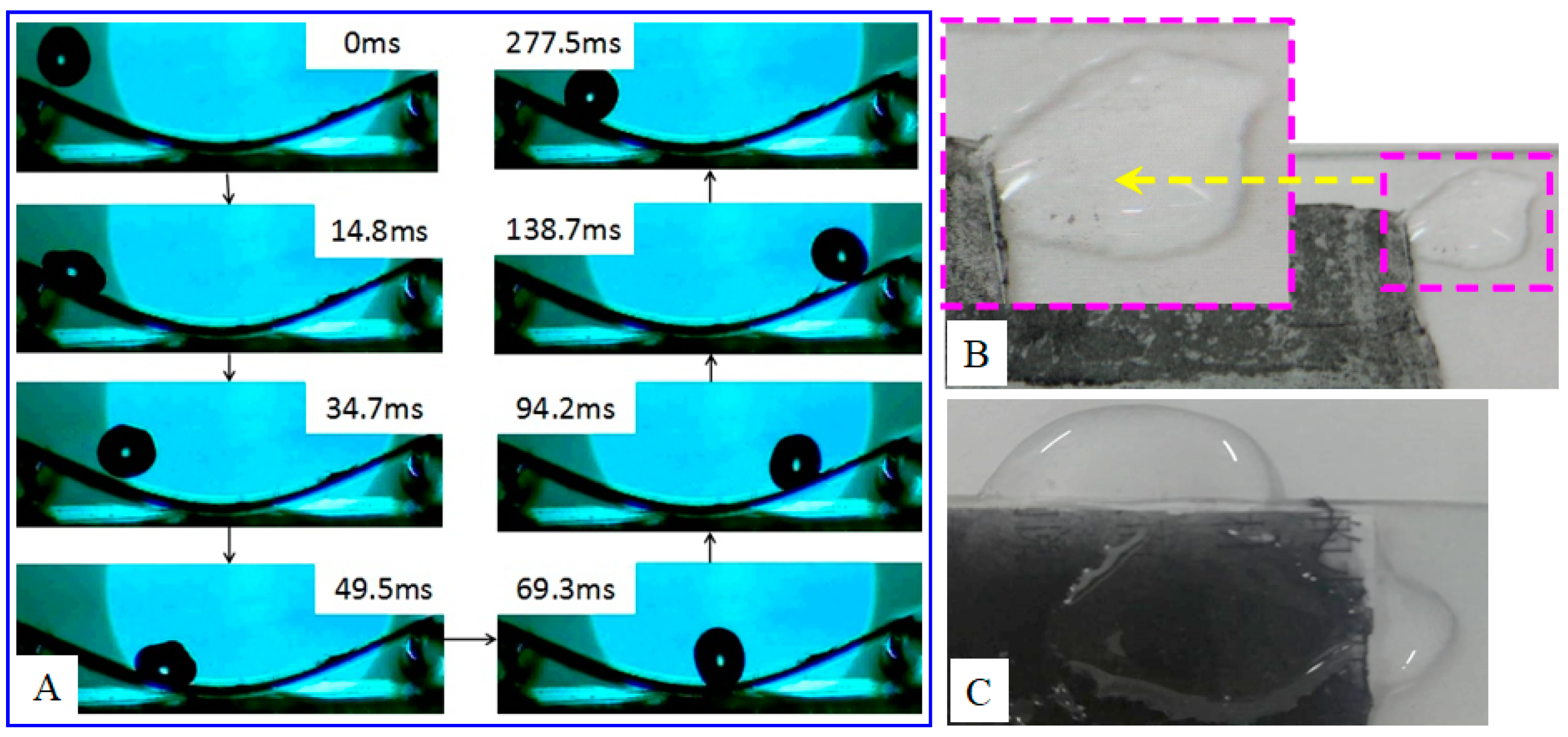
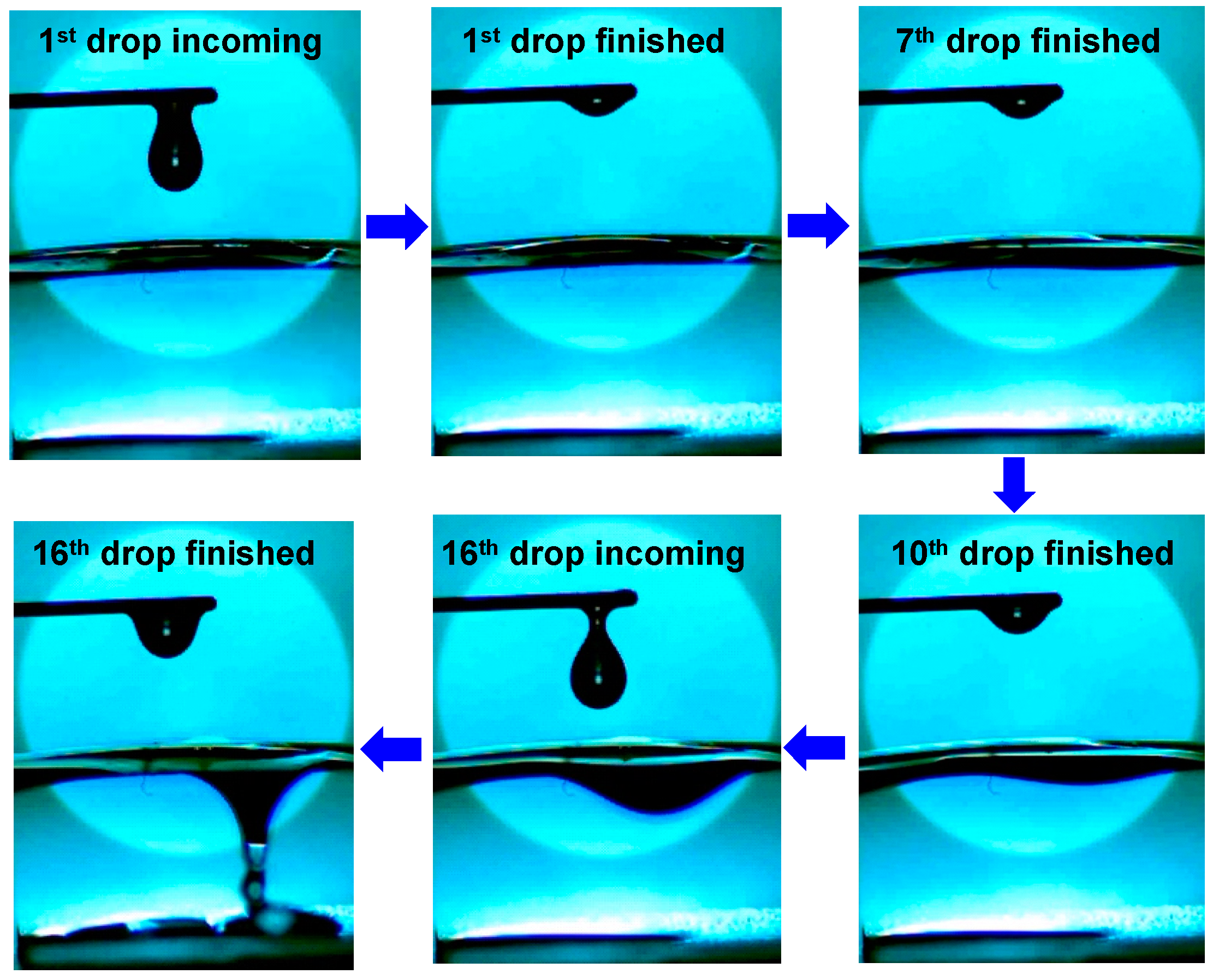
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Kumar, S.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A Review on Superhydrophobic Polymer Nanocoatings: Recent Development and Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 2727–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic polymeric superhydrophobic surfaces and nanostructures: From fabrication to appli-cations. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3338–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. A review on special wettability textiles: Theoretical models, fabrication technologies and multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y.; Demirel, A.L.; Avcı, Y.; Mert, O. Transformation of a Simple Plastic into a Superhydrophobic Surface. Science 2003, 299, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Verho, T.; Ras, R.H.A. Moving superhydrophobic surfaces toward real-world applications. Science 2016, 352, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-M.; Reinhoudt, D.; Crego-Calama, M. What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent pro-gress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, M. Engineering biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces of electrospun nanomaterials. Nano Today 2011, 6, 510–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuraje, N.; Khan, W.S.; Lei, Y.; Ceylan, M.; Asmatulu, R. Superhydrophobic electrospun nanofibers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1929–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahtan, T.F.; Gondal, M.A.; Dastageer, M.A.; Kwon, G.; Ezazi, M.; Al-Kuban, M.Z. Thermally Sensitized Membranes for Crude Oil–Water Remediation under Visible Light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48572–48579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Tuteja, A. The design and applications of superomniphobic surfaces. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibrous materials: A versatile medium for effective oil/water separation. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymers 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koombhongse, S.; Liu, W.; Reneker, D.H. Flat polymer ribbons and other shapes by electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.I.; Moon, H.S.; Lyoo, W.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Superhydrophobicity of PHBV fibrous surface with bead-on-string structure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 320, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospun porous cellulose acetate fibers from volatile solvent mixture. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, J.T.; Marquez, M.; Xia, Y. Highly Porous Fibers by Electrospinning into a Cryogenic Liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1436–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, D.; Kang, D.; Jiang, X. Fabrication of Necklace-like Structures via Electrospinning. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alayande, S.O.; Dare, E.O.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Akinlabi, A.K.; Aiyedun, P.O. Superhydrophobic and superoleophillic sur-face of porous beaded electrospun polystrene and polysytrene-zeolite fiber for crude oil-water separation. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2016, 92, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Xu, Z.; Cai, X.; Xu, L.; Sun, D. New Insight into Gap Electrospinning: Toward Meter-long Aligned Nanofibers. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13788–13793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-J.; Liao, J.-D.; Li, A.-J.; Chen, C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Xu, Y.-H. Relationship between wettabilities and chemical compositions of candle soots. Fuel 2014, 128, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. New insight into the soot nanoparticles in a candle flame. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4700–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Xiong, J.; Huang, J.; Zheng, T.; Cai, X. Facile transformation of soot nanoparticles into nanoporous fibers via single-step electrospinning. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 085212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulay, M.; Chauhan, A.; Patel, S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Halder, A.; Vaish, R. Candle soot: Journey from a pollutant to a functional material. Carbon 2019, 144, 684–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Hu, X.; Zheng, G.; Lv, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Sun, D.; et al. Spectroscopic evidence for a high fraction of ferroelectric phase induced in electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24952–24958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, W.D.; Brown, F.E. The Determination of Surface Tension (Free Surface Energy), and the Weight of Falling Drops: The Surface Tension of Water and Benzene by the Capillary Height Method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1919, 41, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, M.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Fabrication of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber membranes by electro-spinning for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, W.; Zeng, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Improved desalination properties of hydrophobic GO-incorporated PVDF electrospun nanofibrous composites for vacuum membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.; Yarin, A.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solu-tions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Bending instability in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, F.; Sun, D. Alignment of electrospun fibers using the whipping instability. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, P.; Alessandro, M.; Ramsier, R.D.; Chase, G.G. Continuous Electrospinning of Aligned Polymer Nanofibers onto a Wire Drum Collector. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Zhu, P.; Cai, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, F. Electrospinning of PVDF nanofibrous membranes with controllable crystalline phases. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 120, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Li, Y.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hierarchically Structured Superoleophobic Surfaces with Ultralow Contact Angle Hysteresis. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5838–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Wu, Q.; Shi, W.; Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cui, F. Polyamidoamine dendrimer grafted forward osmosis membrane with superior ammonia selectivity and robust antifouling capacity for domestic wastewater concentration. Water Res. 2019, 153, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. Separating small amount of water and hydrophobic solvents by novel superhydrophobic copper meshes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 6002–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, X.; She, H.; Yang, Y.; Zha, F. Superhydrophobic meshes that can repel hot water and strong corrosive liquids used for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7638–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Mu, P.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Pine powders-coated PVDF multifunctional membrane for highly efficient switchable oil/water emulsions separation and dyes adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Guo, X.; Zheng, G.; Guo, Z. Superhydrophobic Shish-kebab Mem-brane with Self-Cleaning and Oil/Water Separation Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9866–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, D. Superhydrophobic membranes on metal substrate and their corrosion protection in different corrosive media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Tang, L.; Tong, W.; Xiong, D. Fabrication of robust and scalable superhydrophobic surfaces and investigation of their anti-icing properties. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Lu, D.; Xu, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Xu, L.; Cai, X.; Lin, L. 2D → 3D conversion of superwetting mesh: A simple but powerful strategy for effective and efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Lu, M.; Chen, S.; Cai, C.; Yao, Z.; Cui, W.; Fan, C.; Liu, S. Beeswax-inspired superhydrophobic electrospun mem-branes for peritendinous anti-adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, X.; Yang, L.; Lin, T.; Lei, T. Facile Preparation of Superhydrophobic Membrane Inspired by Chinese Traditional Hand-Stretched Noodles. Coatings 2021, 11, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020228
Cai X, Huang J, Lu X, Yang L, Lin T, Lei T. Facile Preparation of Superhydrophobic Membrane Inspired by Chinese Traditional Hand-Stretched Noodles. Coatings. 2021; 11(2):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020228
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xiaomei, Junjie Huang, Xizhao Lu, Le Yang, Tianliang Lin, and Tingping Lei. 2021. "Facile Preparation of Superhydrophobic Membrane Inspired by Chinese Traditional Hand-Stretched Noodles" Coatings 11, no. 2: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020228
APA StyleCai, X., Huang, J., Lu, X., Yang, L., Lin, T., & Lei, T. (2021). Facile Preparation of Superhydrophobic Membrane Inspired by Chinese Traditional Hand-Stretched Noodles. Coatings, 11(2), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020228





