Abstract
A facile approach inspired by Chinese traditional hand-stretched noodle-making process has been demonstrated for the preparation of superhydrophobic membrane for the first time. Unlike standard electrospinning, a metal substrate that is covered with superhydrophobic nanopowders is utilized to collect fibers during electrospinning. Experimental results show that the proposed method can make some nanopowders stick on the fiber surface to endow electrospun membranes with superhydrophoboic property, especially as the substrate is heated. This noodle-making-like electrospinning process is believed to provide a novel and simple way for the fabrication of superhydrophobic membrane, which should further broaden the application of electrospinning technique.
1. Introduction
Since the first report of “lotus effect” in 1997 [1], research interests in superhydrophobicity have grown explosively [2,3,4]. It is now broadly accepted that superhydrophobic surfaces normally possess two key characteristics: low surface energy and hierarchically rough surface [5,6,7]. Therefore, the strategy for fabricating superhydrophobic surfaces is either to improve the surface roughness of a low surface energy material or to decrease the surface energy of a rough-surface material [5,6,8].
To build rough surface textures, various approaches have been proposed, such as template synthesis, phase separation, chemical vapor deposition, thermal sensitization, electrochemical deposition, electrospinning, and dip coating [2,9,10,11,12]. Among these approaches, electrospinning is a powerful technique to fabricate nanofibrous membranes with varied surface morphologies [9,13,14,15]. Special nanofibrous morphologies, such as beads-on-a-string [16], ribbon-like [17], porous [18], and necklace-like structures [19], have been demonstrated to increase hydrophobic property. For instance, Alayande et al. prepared the porous polystrene and polysytrene-zeolite fibers with the beads-on-a-string structure via electrospinning [20]. The electrospun fibers have excellent superhydrophobic surface with a water contact angle (WCA) of 160° and an oil contact angle of 0°. However, the surface morphology of electrospun fibers changes with different solution parameters (such as the viscosity and conductivity) and varied processing parameters (such as the applied voltage, feed rate, the distance between spinneret and collector, and environmental conditions). These parameters for a special fibrous morphology are not easy to determine. On the other hand, those electrospun fibers with special morphologies often show poor mechanical properties [9], which are undesirable in practical use.
Inspired by Chinese traditional hand-stretched noodle-making process, during which the noodles are stretched and then sprinkled with flours to prevent adhesion, here we report a facile approach to prepare superhydrophobic membranes by electrospinning nanofibers onto the substrate that is covered with (super)hydrophobic nanopowders. This approach can make some nanopowders stick on the fiber surface such that the electrospun nanofibrous membranes have great superhydrophobic property. Furthermore, nanopowders may be stick better and even become embedded in the nanofibers by heating the substrate. This improved electrospinning process is very meaningful for the membrane applications.
2. Materials and Methods
Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF; an electroactive polymer that we have widely investigated previously [21,22]) and candle soot were chosen for the solution electrospinning and superhydrophobic nanopowders, respectively. The preparation of candle soot and superhydrophobic PVDF membranes is illustrated in Figure 1. A piece of metal sheet was placed above the center flame of a burning paraffin candle (Figure 1A) and was adjusted accordingly to obtain superhydrophobic soot nanoparticles (Figure 1B) [23,24]. The soot particles prepared in this way were found to have an average particle size less than 50 nm, as reported in our previous work [25] and summarized in a very recent review paper [26]. A piece of paper with a square-shaped opening was placed on the sheet of metal that was covered with the soot (Figure 1C) and used as a collector for the electrospinning experiment.
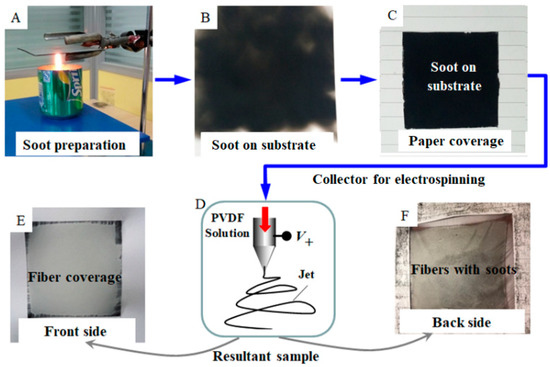
Figure 1.
Process for the preparation of candle soot and superhydrophobic poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes: (A) an image presenting the collection of candle soot via holding sheet metal on the flame, (B) a photo of sheet metal covered with the candle soot, (C) a piece of paper (with a square-shape opening) sticking to the sheet metal, and (D) the schematic electrospinning process taking the paper and metal as the substrate, on which there is the deposited fibrous membrane. The soot is pasted on the back side (F) of the membrane rather than the front side (E).
A vertical setup was utilized for the electrospinning (Figure 1D), the procedure of which is detailed in our previous study [27]. Briefly, 0.979 g of PVDF powder was dissolved in mixed solvents with 6 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and 4 mL of acetone. The solution was prepared via continuous magnetic stirring at 30 °C for more than 6 hours in a parafilm-sealed frosted glass bottle. Before the electrospinning process, the as-prepared solution was degassed to remove bubbles and the solution feed rate was controlled by a precision pump (NE-300). During the electrospinning experiments, the sheet of metal (with the soot deposition and the paper coverage) was grounded (Figure 1C) as a collector and placed on a heater. The applied voltage was kept at 7.0 kV, the solution feed rate was 500 μL/h, and the distance between the spinneret and collector was 10 cm. The electrospinning experiments were conducted in air atmosphere with the relative humidity between 55% and 60%.
The surface morphology of the electrospun fibers with or without soot was examined using scanning electron microscopes (SEM, SU70 and XL 30, Hitach, Tokyo, Japan). The wetting characterization was performed on a contact angle analyzer (JC2000D3, Zhongchen Digital Technic Apparatus, Shanghai, China) using a distilled water droplet (9 μL). The solution surface tension was obtained according to the drop weight method proposed by Harkins et al. [28], where deionized water (71.8 dyn/cm) was used as the reference solution. The rolling behavior of water droplets and the spreading and permeating behaviors of hydraulic oil droplets on the as-prepared electrospun membrane with soot were recorded using a high-speed camera (MIRO M110, Vision Research, Wayne, NJ, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1E,F shows the front side and back side of the deposited membrane. It is clearly observed that the soot is stuck to the back side of fibrous membrane and there is no soot on its front side. Figure 2 demonstrates the surface morphologies of both sides of the membrane. A great amount of candle soot is adhered to the fibers on the back side of the membrane (Figure 2A), especially to the outermost layer of fibers that present a lettuce-like hierarchical structure (Figure 2B). Such a hierarchical structure improves the surface roughness of the PVDF membrane (PVDF is a low surface energy material), and thus the membrane of the back side becomes superhydrophobic (WCA of 158°, inset in Figure 2A no soot on the fibers (Figure 2C,D), such that the WCA is only 131° (inset in Figure 2C) [29,30].
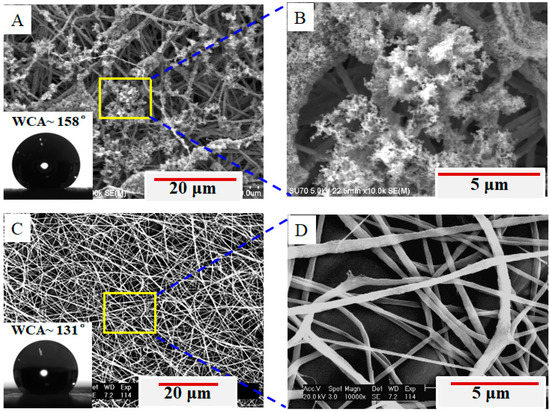
Figure 2.
SEM images and water contact angle (WCA) (inset) of the electrospun fibrous membrane for different sides: (A) the back side showing the electrospun membrane with soot on the surface fibers and thus becoming superhydrophobic (WCA~158°, inset), and enlarged SEM image (B) of fibers as indicated in subfigure (A). (C) The front side showing the electrospun membrane with no soot on fibers and only presenting as hydrophobic (WCA~131°, inset), and enlarged SEM image (D) of fibers as indicated in (C).
The above result may be understood from the formation of nanofibrous membrane. During electrospinning process, a charged jet causes bending instability after traveling in a short straight line (~1 cm) [31,32], which allows the charged electrospinning jet to experience an extremely high draw ratio (the ratio of a starting diameter of the electrospinning jet and the diameter of a produced nanofiber) of 60,000 within milliseconds (~50 ms) [32,33]. As the jet travels and the solvent evaporates in air, a continuous and long nanofiber (estimated to be many kilometers [34]) is randomly deposited to generate a non-woven fabric. Sometimes, electrospinning may also fabricate aligned nanofibrous membranes on special collectors [35,36]. As such, the fibers deposited early on the collector have an opportunity to touch the soot. The residual solvent within fibers [37] favors the soot stuck to the ultrafast incoming fibers. Therefore, a lettuce-like hierarchical structure is observed in nanofibers of the first deposition, which makes the membrane become superhydrophobic on the back side.
Figure 3A displays the sequential snapshots of a water droplet rolling on the superhydrophobic membrane surface under an applied frame rate of 1000 fps. The membrane was prepared on the unheated substrate and fixed on an arch-shaped sheet of PET for the rolling test. During the rolling experiment, a tap water droplet (12 μL) is dropped from a height of about 1 cm to the membrane surface. The impact velocity of droplet is equal to 1.41 m/s and the membrane is tilted at an angle of 30°. As shown in Figure 3, the droplet takes less than 300 ms to complete the first round-trip rolling after falling on the surface. However, the droplet has only one bounce at 34.7 ms and stops rolling after three rolling cycles, owing to a rapid consumption of the potential energy [38]. On the other hand, the rolling of the droplet may take some soot away from the as-electrospun membrane surface (Figure 3B) and leads to a decrease in hydrophobicity and an increase in water adhesion.
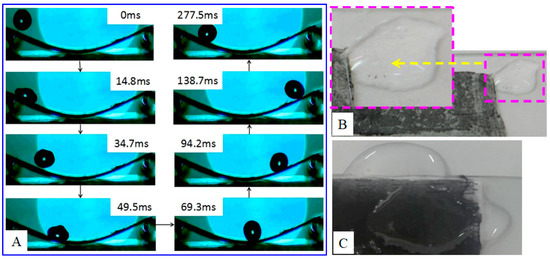
Figure 3.
(A) The snapshots for the rolling process of a 12 μL tap water droplet on an arc-shaped as-electrospun membrane, which is prepared on an unheated substrate; (B) a small number of candle soot nanoparticles taken away from the superhydrophobic membrane surface by water droplets; and (C) a trace of (or sometimes no visible) soot running off from the membrane, which is prepared on the heating substrate during electrospinning.
In order to prevent the soot being taken away from the fibrous membrane, we heated the substrate during electrospinning. The heating temperature was set to 80 or 120 °C, which is less than the burning point (130 °C) of the paper substrate and higher than 70 °C for changing the fiber morphology [37]. Compared with the superhydrophobic electrospun fibrous membrane collected on unheated substrate (Figure 3B), the as-electrospun membrane collected on heating substrate (Figure 3C) may hold the soot tightly on the fiber surface such that the membrane may keep superhydrophobic for long time. As reported previously, heating the collector during electrospinning could result in fibers being crosslinked or even fused together (depending on the heating temperature) [37], which is also shown in our experiment with heating temperature up to either 80 or 120 °C (Figure 4). This crosslink and fusion can allow more soot to be better stuck on or even embedded in the fibers, and thus it is hopeful to fabricate a hydrophobicity-durable electrospun membrane for future applications, indicating that the collector heating treatment during electrospinning can prevent the candle soot taking away from the superhydrophobic membrane.
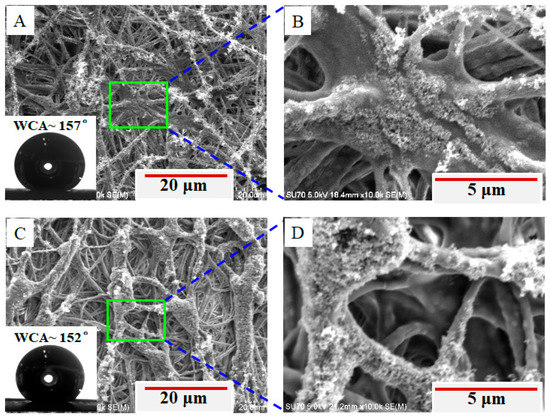

Figure 4.
SEM images and WCA (inset) of as-electrospun fibrous membranes deposited on the heating substrate with the soot: (A) at the heating temperature of up to 80 °C and the enlarged image (B) of fibers as indicated in subfigure (A), and (C) at the heating temperature of up to 120 °C and enlarged image (D) of fibers as indicated in subfigure (C). The insets show WCAs of the corresponding membranes.
Based on the SEM morphology and the WCA of the electrospun fiber membranes, the classic Wenzel and Cassie–Baxter, or their combined modes, can be used to interpret the wetting differences between these membranes [39,40,41]. It is well known that PVDF is a commercially available fluoropolymer with low surface energy, and therefore the electrospun PVDF fiber membrane collected using the conventional collector (with no soot deposition) is smooth (top in Figure 5A) and shows hydrophobicity (131°, Figure 2C). This wetting property can be interpreted via the Wenzel model, where the water droplet is considered to penetrate the membrane pore (bottom in Figure 5A). Interestingly, when using the collector with candle soot deposition, a hierarchically rough surface can be formed on the fiber surface (top in Figure 5B,C). In these cases, the electrospun membranes possesses the two key characteristics (i.e., low surface energy and hierarchically rough surface) for becoming superhydrophobic. As a result, the Cassie–Baxter model or the combined model of Cassie–Baxter and Wenzel states may be used for the interpretation, depending on the membrane morphology and the corresponding WCA. However, at present, it is unable to determine which model is better for it. Yet, according to the prior works, a possible mode (bottom in Figure 5B,C) is proposed for this noodle-making-like electrospinning process.
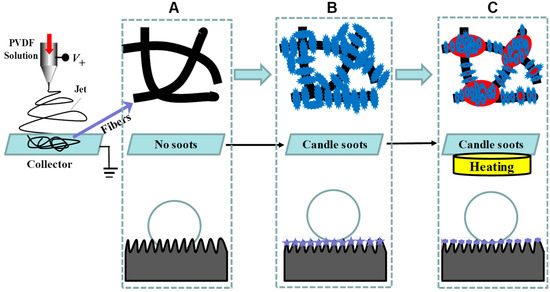
Figure 5.
Schematic illustrating the resultant electrospun fibers and the corresponding wetting states: (A) smooth fibers collected on a conventional substrate without soot and Wenzel model for a wetting droplet, (B) fibers collected on an unheated substrate covered with candle soot and Cassie–Baxter model for a droplet, and (C) fibers collected on a heating substrate covered with candle soot and combined model for a droplet.
Figure 6 shows the wetting properties of the electrospun membrane (that was obtained via heating the collector up to 80 °C) by subjecting it to droplets of various liquids. All aqueous droplets (H2SO4, juice, and milk) still exhibit good spherical shapes even after 2 h, except for the milk droplet slightly losing its sphericity after 5 min (possibly due to the different compositions in milk that contains protein, fat, lactose, and minerals besides water). Among these aqueous droplets, H2SO4 seems to keep the most perfect spherical size, which can be attributed to its largest surface tension (73.5 dyn/cm) as compared to the other two droplets. In contrast, the oil droplets spread over the membrane after they touched the membrane surface, suggesting superoleophilicity of the membrane. As shown in Figure 5, n-hexadecane spreads much faster than hydraulic oil, which is closely related to the huge difference in their viscosities (n-hexadecane 3.36 cP and hydraulic oil 190 cP), although the surface tension of the both also shows some difference (n-hexadecane 27.2 dyn/cm and hydraulic oil 29.7 dyn/cm). In fact, n-hexadecane began to spread immediately it touched the membrane surface, suggesting the potential use of the membrane in the separation of low viscosity oil/water mixtures [42,43]. On the other hand, the long-time superhydrophobicity off concentrated H2SO4 solution further reveals the possible use of the membrane to separate oil/water mixtures under harsh conditions [44,45].
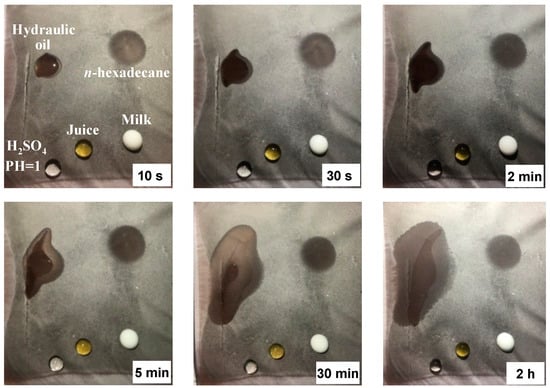
Figure 6.
The evolution of various liquid droplets (~0.15 mL) on the electrospun membrane collected on a heating substrate at different time: (a) 10 s, (b) 30 s, (c) 2 min, (d) 5 min, (e) 30 min, and (f) 2 h. The surface tensions are 29.7, 27.2, 40.5, 31.9, and 73.5 dyn/cm for hydraulic oil, n-hexadecane, milk, juice, and H2SO4, respectively. The viscosities are 3.36 cP for n-hexadecane and 190 cP for hydraulic oil.
As the spreading and permeability of high-viscosity oil (e.g., hydraulic oil, 190 cP) takes a comparatively long period, one may be interested whether leaking can occur on such a membrane. To figure out the permeability, the electrospun membrane (obtained by heating collector/substrate up to 80 °C) of thickness in the range of 100 to 125 μm was tailored into square (2 cm × 2 cm), and its two ends were, respectively, sandwiched between two parallel plates. As shown in Figure 7, the leaking of hydraulic oil occurs until the 16th droplet has landed on the as-prepared square surface, the reason of which can be attributed to the slow permeation of the oil due to its high viscosity. In fact, when the first oil droplet (~15 μL) was dropped on the membrane surface, it spread quickly on the surface, but no visible leak was observed (top middle). As the incoming droplet was increased however, the spreading gradually slowed down. With the 7th droplet dropping on the surface, the oil leaking was initiated as evidenced by the deformation of the membrane bottom surface (top right), indicating that the oil permeation was in progress with the droplet contacting the membrane surface. As the droplet accumulated on the surface, a remarkable leak of the oil was observed when the 15th droplet had landed on the surface (bottom middle). The above observations suggest the possibility of use of this membrane in the separation of low-viscosity oil/water mixtures.
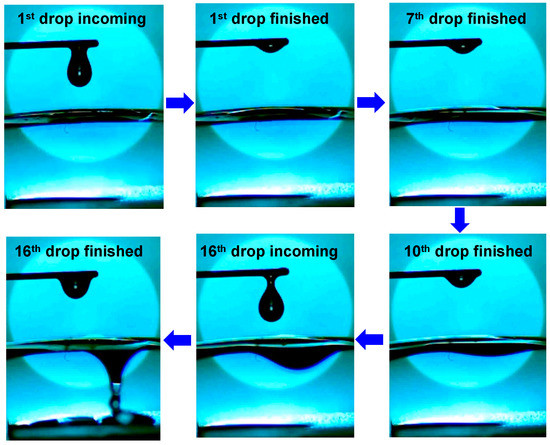
Figure 7.
Snapshots of spreading and permeating behavior of high-viscosity oil (hydraulic oil: ~190 cP) droplets (~13 μL) continuously dropped on the square (2 cm × 2 cm) 120 μm thick electrospun membrane that was obtained by heating collector/substrate up to 80 °C. The snapshots were clipped from a high-speed camera recording at 400 frames per second.
From the process of formation of superhydrphobic membrane, i.e., via the deposition of electrospun nanofibers on a substrate that is covered with (super)hydrophobic nanoparticles (a process like noodle making), it is believed that the improved process could be applied to more hydrophobic polymers, such as polyurethane (PU), polycaprolactone (PCL), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), for the production of superhydrophobic membranes. More (super)hydrophobic nanoparticles are also useful for the process, such as SiO2, TiO2, and ZnO. We believe that further improvement of this process is very hopeful to explore high-performance superhydrophobic membranes for a myriad of applications, such as self-cleaning [46], anti-corrosion [47], anti-icing [48], oil/water separation [49], and anti-adhesion [50].
4. Conclusions
A facile method has been demonstrated for the preparation of superhydrophobic membrane via electrospinning nanofibers onto the substrate that is covered with (super)hydrophobic nanopowders. Results reveal that such a method can make some nanopowders stick on the fiber surface to show superhydrophobicity. When heating the substrate during the nanofiber deposition process, more nanopowders can be better stuck on or even embedded in the nanofibers without sacrificing the superhydrophobicity of the membrane. These facts lead to the prediction that even more electrospun fibrous membranes with good superhydrophobicity could be obtained via this noodle-making-like electrospinning process, so long as hydrophobic polymers and (super)hydrophobic nanoparticles are properly chosen, which is of great significance for superwetting fiber-based membranes for oil/water separation.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, X.L. and L.Y.; Funding acquisition, T.L. (Tianliang Lin); Investigation, X.C. and J.H.; Project administration, T.L. (Tingping Lei). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2020J01709), Youth Innovation Fund of Xiamen City (No. 3502Z20206010), the Foundation from Department of Science and Technology of Fujian Province (No. 2019L3008), and Distinguished Young Scholars of Fujian Province (No. 2018J06014).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Kumar, S.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A Review on Superhydrophobic Polymer Nanocoatings: Recent Development and Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 2727–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic polymeric superhydrophobic surfaces and nanostructures: From fabrication to appli-cations. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3338–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. A review on special wettability textiles: Theoretical models, fabrication technologies and multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y.; Demirel, A.L.; Avcı, Y.; Mert, O. Transformation of a Simple Plastic into a Superhydrophobic Surface. Science 2003, 299, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Verho, T.; Ras, R.H.A. Moving superhydrophobic surfaces toward real-world applications. Science 2016, 352, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-M.; Reinhoudt, D.; Crego-Calama, M. What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent pro-gress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, M. Engineering biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces of electrospun nanomaterials. Nano Today 2011, 6, 510–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuraje, N.; Khan, W.S.; Lei, Y.; Ceylan, M.; Asmatulu, R. Superhydrophobic electrospun nanofibers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1929–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahtan, T.F.; Gondal, M.A.; Dastageer, M.A.; Kwon, G.; Ezazi, M.; Al-Kuban, M.Z. Thermally Sensitized Membranes for Crude Oil–Water Remediation under Visible Light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48572–48579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Tuteja, A. The design and applications of superomniphobic surfaces. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibrous materials: A versatile medium for effective oil/water separation. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymers 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koombhongse, S.; Liu, W.; Reneker, D.H. Flat polymer ribbons and other shapes by electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.I.; Moon, H.S.; Lyoo, W.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Superhydrophobicity of PHBV fibrous surface with bead-on-string structure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 320, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospun porous cellulose acetate fibers from volatile solvent mixture. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, J.T.; Marquez, M.; Xia, Y. Highly Porous Fibers by Electrospinning into a Cryogenic Liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1436–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, D.; Kang, D.; Jiang, X. Fabrication of Necklace-like Structures via Electrospinning. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alayande, S.O.; Dare, E.O.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Akinlabi, A.K.; Aiyedun, P.O. Superhydrophobic and superoleophillic sur-face of porous beaded electrospun polystrene and polysytrene-zeolite fiber for crude oil-water separation. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2016, 92, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Xu, Z.; Cai, X.; Xu, L.; Sun, D. New Insight into Gap Electrospinning: Toward Meter-long Aligned Nanofibers. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13788–13793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-J.; Liao, J.-D.; Li, A.-J.; Chen, C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Xu, Y.-H. Relationship between wettabilities and chemical compositions of candle soots. Fuel 2014, 128, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. New insight into the soot nanoparticles in a candle flame. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4700–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Xiong, J.; Huang, J.; Zheng, T.; Cai, X. Facile transformation of soot nanoparticles into nanoporous fibers via single-step electrospinning. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 085212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulay, M.; Chauhan, A.; Patel, S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Halder, A.; Vaish, R. Candle soot: Journey from a pollutant to a functional material. Carbon 2019, 144, 684–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Hu, X.; Zheng, G.; Lv, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Sun, D.; et al. Spectroscopic evidence for a high fraction of ferroelectric phase induced in electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24952–24958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, W.D.; Brown, F.E. The Determination of Surface Tension (Free Surface Energy), and the Weight of Falling Drops: The Surface Tension of Water and Benzene by the Capillary Height Method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1919, 41, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, M.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Fabrication of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber membranes by electro-spinning for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, W.; Zeng, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Improved desalination properties of hydrophobic GO-incorporated PVDF electrospun nanofibrous composites for vacuum membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.; Yarin, A.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solu-tions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Bending instability in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, F.; Sun, D. Alignment of electrospun fibers using the whipping instability. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, P.; Alessandro, M.; Ramsier, R.D.; Chase, G.G. Continuous Electrospinning of Aligned Polymer Nanofibers onto a Wire Drum Collector. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Zhu, P.; Cai, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, F. Electrospinning of PVDF nanofibrous membranes with controllable crystalline phases. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 120, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Li, Y.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hierarchically Structured Superoleophobic Surfaces with Ultralow Contact Angle Hysteresis. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5838–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Wu, Q.; Shi, W.; Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cui, F. Polyamidoamine dendrimer grafted forward osmosis membrane with superior ammonia selectivity and robust antifouling capacity for domestic wastewater concentration. Water Res. 2019, 153, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. Separating small amount of water and hydrophobic solvents by novel superhydrophobic copper meshes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 6002–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, X.; She, H.; Yang, Y.; Zha, F. Superhydrophobic meshes that can repel hot water and strong corrosive liquids used for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7638–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Mu, P.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Pine powders-coated PVDF multifunctional membrane for highly efficient switchable oil/water emulsions separation and dyes adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Guo, X.; Zheng, G.; Guo, Z. Superhydrophobic Shish-kebab Mem-brane with Self-Cleaning and Oil/Water Separation Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9866–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, D. Superhydrophobic membranes on metal substrate and their corrosion protection in different corrosive media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Tang, L.; Tong, W.; Xiong, D. Fabrication of robust and scalable superhydrophobic surfaces and investigation of their anti-icing properties. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Lu, D.; Xu, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Xu, L.; Cai, X.; Lin, L. 2D → 3D conversion of superwetting mesh: A simple but powerful strategy for effective and efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Lu, M.; Chen, S.; Cai, C.; Yao, Z.; Cui, W.; Fan, C.; Liu, S. Beeswax-inspired superhydrophobic electrospun mem-branes for peritendinous anti-adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
