Abstract
Surface topography and physical-chemical properties usually play a key-role in both osseointegration improvement and bacterial colonization reduction over the surface of dental implants. The aim of this study is to compare the chemical and bacteriological behavior of two different acid passivation surface treatments on titanium c.p. grade 3 used for dental implant manufacturing. Surface roughness was evaluated using White Light Interferometry (WLI) in order to determine different roughness parameters such as average roughness (Sa), the spacing parameter (Sm) and the hybrid parameter of surface index area (SIA). Contact angle (CA) and surface free energy (SFE) were evaluated in order to establish the surface wettability of the different groups of samples. Titanium ion-release from the different samples was also been analyzed in Hank’s solution medium at 37 °C by using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) at different immersion times. Bacterial viability adhesion assays were done using S. sanguinis (CECT 480, Spain) as a bacterial strain model of primary colonizer in oral biofilm formation. The bacteria attachment and morphology on Ti surfaces were determined using a live/dead staining method after 4 h of incubation and further analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Acid passivation surface treatments produced a statistically-significant (p < 0.05) roughness increase in all the evaluated parameters (Sa, Sm, SAI). The treatment with citric acid decreased the static contact angle (CA) and caused an increase in surface free energy (SFE) with a high polarization and oxidizing character. These physical-chemical surface characteristics obtained by means of citric acid passivation caused the bactericidal behavior as it has been proved in bacterial studies.
1. Introduction
Surface topography and physical-chemical properties play a very important role to improve osseointegration and to reduce bacterial colonization. In order to enhance the implant–bone interface and its clinical performance, we have different techniques like grid-blasting, acid-etched, porosity by sintering, oxidized, plasma-sprayed, apatite-coated treatments, as well as a combination of these procedures [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Treatments aiming at the decrease of bacterial impacts such as the application of nanosilver particles, biofunctionalization with peptides or oxidizer agents with antibacterial character, have also been studied [9,10,11,12,13,14].
The surface characteristics of a dental implant, include its chemistry, wettability, roughness, charge, energy, zero potential, crystallinity, the nature and thickness of its oxide layer as well as surface residual stresses, influence on the osseointegration and its microbiology behavior. The optimization of these properties is the key to the success of the titanium dental implant [15,16,17,18,19,20] Anodisation is an oxidation reaction obtained by electrochemical method or by chemical reaction to promote the increase of the thickness of protective layers. Several studies showed that an artificial increase of the oxide produces stronger and more effective osseointegration and also showed an important increase in the corrosion resistance [1,2,8,9]. The role of titanium oxide and the physico-chemical characteristics of the surface remain poorly understood.
Implants and prostheses based on titanium are generally acid etched after surface treatment for passivation. This treatment serves to increase the thickness of the oxide layer, increasing the corrosion resistance of the galvanic couples with the metal of the abutment as well as to exert an integral cleaning on the titanium surface. This treatment for many implants is performed with hydrochloric acid as it is less aggressive than sulfuric acid and gives good results. However, Htet et al. [21] demonstrated that citric acid had a bactericide character using laser treatment. The titanium bur with citric acid group exhibited statistically significantly greater improvement in vertical bone height than the Er:YAG laser group and significantly better bone-to-implant contact than the photodynamic therapy (PDT) group and the bur-alone group. The authors demonstrated that the chemical treatment with citric acid proved to be the most effective treatment for disinfection of the anodized implant surface.
Several antimicrobial agents were tested but there is no consensus in relation to the chemotherapeutic agent to optimize the decontamination and the inhibition of the bacteria adhesion. The objectives of this study were to evaluate different surface properties: thickness of the passivated film, roughness, contact angle, surface energy, titanium ion release by citric acid anodization and their effect on the microbial effect on titanium dental implants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Five different series of 5 mm in diameter and 2 mm thick flat disks of commercially pure (CP) titanium Grade 2 (KLEIN SA, Bienne, Switzerland) provided by SOADCO (Escaldes Engordany, Andorra) were used. The chemical products were purchased in Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Anodization Treatment
The treatments applied to the titanium samples presented four stages: grid-blasting, cleaning, passivation and sterilisation (Table 1). Grid-blasting was carried out with a blasting machine (MPA-5, Barcelona, Spain) at 0.25 MPa of pressure during the time required for saturation of the roughness of the samples. The saturation was determined using the ALMEN method [22].

Table 1.
Summary of the titanium sample treatments.
After blasting, the samples were cleaned following a standard sequential protocol: (1) sonication in acetone, 15min; (2) 3 × 3 h washings in 1,5 M NaCl; (3) 3 × 3 h washings in 0,15 M NaCl; (4) 3 × 3 h washings in distilled water; (5) 3 × 3 h washings in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7,4. Finally, all samples were steam-sterilized by autoclave at 121 °C for 30 min using an autoclave SELECTA model Sterilmax (SELECTA, Barcelona, Spain).
2.3. Observation by Focused Ion Beam-Scanning Electron Microscope (FIB-SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) of the Passivated Films
The cutting of the cross section of the Ti disk surface was made with the FIB-SEM electronic microscope model Neon40 (Zeiss, Jena, Germany), by means of a platinum layer on the surface to prevent damage to the surface when cutting. The obtained lamella had an approximate thickness of 200 nm.
By means of the TEM, the thickness of the passivation layer was accurately measured. A JEOL 2011 microscope was used, at 200 kV, with an Ultrascan cat camera (CCD cat 895 USC 4000). For the image analysis, 5 images of 400,000 magnification were taken and the passivate layer thickness was determined by Image J.
2.4. Interferometric Microscopy
Surface roughness was evaluated by using a white light interferometer microscope Wyko model NT1100 (IM, Wyko, Veeco, Tuxon, AZ, USA) in vertical scanning interferometry mode (VSI). Roughness data was analyzed withWyko Vision 4.10 software (Veeco Instruments, Plainview, NY, USA). The measurements were made in triplicates to characterize the amplitude parameter Sa (average roughness), the spacing parameter Sm (the mean spacing) and the hybrid parameter index area SAIndex (real surface area/nominal surface area). They were described in correlation with the biological response
2.5. Wettability and Surface Free Energy
Contact angle (CA) and surface free energy (SFE) were evaluated in order to establish the surface wettability of the different groups of samples.
Static contact angles were measured with two different reference liquids, ultra-distilled water (WA) Milli-Q grade (Millipore Milli-Q, Merck Millipore Corporation, Darmstadt, Germany) and di-iodomethane (DIIO) (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), as polar and non-polar liquids, respectively.
The contact angle of liquids on surfaces was measured using a contact angle analyzer equipment (Contact Angle System OCA15 plus; Dataphysics instrument Company, Filderstadt, Germany) by using the traditional sessile drop measuring method.
For CA measurements, 3 µL of liquid drops was placed on the surface of a flat disk-shaped samples with plane-parallel faces. Liquid droplets were backlighted by LEDs through ground glass and CA were measured within 3s after the settlement of the droplets, capturing the drop image by a video camera and analyzing it by using the SCA20 software (Dataphysics instrument Company, Filderstadt, Germany).
At least one CA measurement was acquired on the surface from 5 different samples at room temperature (T = 25 °C), with a constant volume drop of 3 μL, dispensed with a dose rate of 1 μL/min by using a screw-driven precise dosing mechanism, and the mean values were used for analysis.
The SFE values with its dispersive and polar components for the solid surfaces (Equation (1)) were estimated using the Owens–Wendt–Rabel–Kaelble (OWRK) model after CA measurements [23,24,25],
where is due to the interactions arising from induced and dipole–dipole forces (London or ”dispersion”), and is the ”polar” component arising from interaction between permanent dipoles [26,27].
2.6. Ion Release
At least five different flat disk-shaped samples (n = 5) of each group of samples (n = 3) were completely immersed in a glass-containers with Hank’s solution. All sample glass-holders were tightly sealed to prevent evaporation of the liquid testing solution during the incubation test conducted in a Memmert incubator oven model BE500 (MEMMERT Gmbh, Germany). Moreover, all containers were previously acid cleaned by using 2% ultra-pure nitric solution (Suprapur, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and finally rinsed with ultra-distilled water Milli-Q grade (Millipore Milli-Q, Merck Millipore Corporation, Darmstadt, Germany) in order to prevent any contamination.
The exposed surface of the samples and the volume of the solution fluid remained constants during the course of the ion release test, the latest was also kept constant in 5 mL, based on an extraction medium weight/volume ratio of 0.2 g/mL, according to the ISO 10993-5 Standard specifications [28].
All the 5 mL of solution was extracted at 5 different times in order to both analyze and quantify the titanium ions released to the liquid medium as a function of time. All the extracted medium samples were filtered using 0.22 μm filters before diluting in 2% ultra-pure nitric solution (Suprapur, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany).
Titanium-released quantification was carried out by using high resolution inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) using Perkin Elmer Optima 320RL equipment (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). These measurements were carried out at 5 different time points (1, 3, 7, 14 and 21 days) of incubation at 37 °C. Calibration standards were prepared by serial dilution containing Ti at 7 different concentrations from 1 ppb to 1 ppm using elemental stock solutions (NIST). Each solution extract was analyzed in triplicate.
2.7. Bacterial Culture
Bacterial adhesion assays were carried out using the bacterial strain S. sanguinis. S. sanguinis was chosen as a model of the primary colonizer in biofilm formation and was obtained from Coleccion Espanola de Cultivos Tipo (CECT 480, Spain). Bacteria were grown overnight at 37 °C in Todd-Hewitt (TH) broth (Scharlab SL, Barcelona, Spain). The optical density of each bacterial suspension was measured at 600 nm (OD600) and adjusted to around 0.2, corresponding to a bacterial concentration of 108 colony-forming unit (CFU)/mL. The assays were performed in static conditions, using three replicates for each condition. After sterilization with ultraviolet (UV) irradiation for 10 min and washing twice with PBS, samples were transferred to a 48-well plate and incubated with 40 µL of S. sanguinis at during 4 h at 37 °C. After incubation time, the samples were washed three times with PBS and 100 μL of LIVE/DEAD BackLight Bacterial Viability Kit (ThermoFisher, Barcelona, Spain).
The viability of bacteria was measured using a LIVE/DEAD BackLight Bacterial Viability Kit (ThermoFisher, Barcelona, Spain). The samples were incubated at room temperature in the dark for 15 min and the attached bacteria were visualized using a Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA software using the multiple comparison Fisher’s test to determine statistically significant differences between groups (p < 0.05). Each data point represents mean ± standard deviation (SD) of at least three independent experiments.
3. Results
Figure 1 shows the passivation films by means of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. These were films obtained in the rough material by means of hydrochloric acid and citric acid etch.
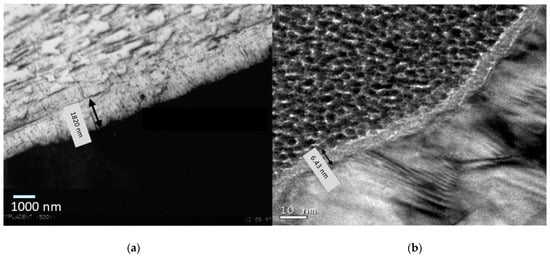
Figure 1.
Passivation film obtained by acid etching: (a) hydrochloric acid and (b) citric acid.
An important difference in the thickness of the oxide layer can be observed since with hydrochloric acid it is 1.8 micrometers and for citric acid it is 6.4 nm. This fact is due to the fact that hydrochloric acid is a very strong acid and therefore the attack on titanium is much more aggressive than a weak acid like citric acid [28,29,30].
Interferometric 3D-roughness of the different Ti samples are shown in Table 2. The differences were quantified by calculating the roughness parameters Sa, Sm and index area. As shown on Figure 2, the results of the roughness measurements confirmed a statistically-significant (p < 0.05) increase of the roughness when the samples are etched by acid in both cases. Hydrochloricacid is more concentrated, consequently the roughness is bigger than that of citric acid. The same trend is shown by the spacing parameter Sm. The index area parameter indicates the increase of real area compared to the nominal area of the sample due to roughness. As expected, the higher roughness leads to a higher index area.

Table 2.
Roughness parameters of the titanium treated samples.
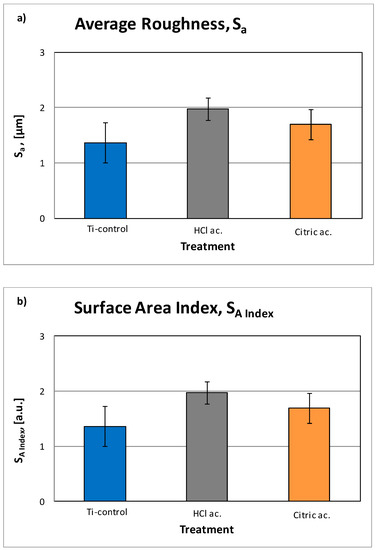
Figure 2.
Roughness parameters: (a) average roughness (Sa) and (b) surface area index (SA Index).
The CA and SFE calculation are shown on (Table 3). The grit-blasting treatment decreased surface wettability, and, therefore, increased the CA. This effect was particularly pronounced for those surfaces grit-blasted with Al2O3 [2,28]. Results showed the highest contact angle for the samples treated with hydrochloric acid and the lowest for citric acid anodization (Figure 3). The control and citric acid treatment do not present significance statistical differences.

Table 3.
Values (mean ± standard deviation) of contact angle of water (WA) and diiodomethane (DIIO), and the estimated surface energy (ϒ) with their polar (ϒP) and dispersive (ϒD) components, for each surface treatment.
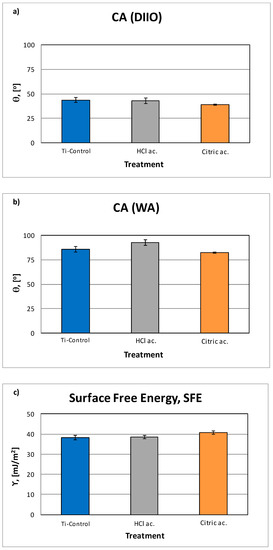
Figure 3.
Contact angle (CA) results for Di-iodomethane (a) and ultra-distilled water (b), as well as surface free energy (SFE) results for all groups of samples (c).
Regarding the dispersive components of SFE, the polar component tends to decrease when increasing the acid character. There are significant differences between the polar component of the control surfaces with respect to the anodized samples, and between the values obtained with hydrochloric acid and citric acid [15,16,17,18,29,30].
Titanium ion release can be observed in Figure 4. The analysis of the ion-release curves presented in Figure 4 shows less titanium released ions in the titanium control group of samples. This is due to the fact that the acid attack after blasting causes an increase in surface roughness and the samples treated with hydrochloric and citric acid have a greater specific surface area and therefore a greater release of ions. As hydrochloric acid is more aggressive, it produces more roughness, more specific surface area exposed to the release liquid medium and therefore greater release. The titanium oxide layer is capable of reducing the release but because it is porous it cannot inhibit the release of ions to the physiological environment.
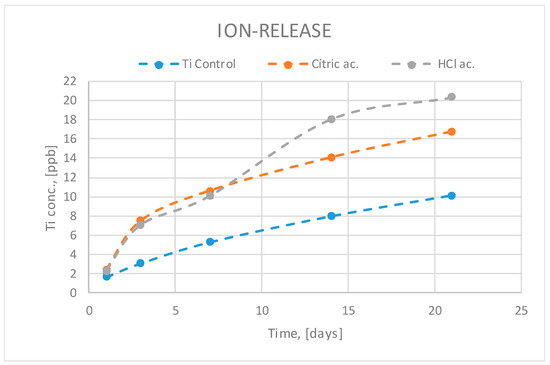
Figure 4.
Titanium ion release at different times as a function of surface treatment.
The total amount of bacterial biofilm over the different titanium surfaces is shown in Table 4. There are statistically significant differences in total bacterial amount when comparing all groups (p < 0.05). The attachment and viability of S. sanguinis on the passivated samples was determined using a live/dead staining after 4 h of incubation. Figure 5 shows the images of live/dead bacteria of control, HCl passivated and citric passivated. Figure 6 indicates the percentage of surface coverage by live bacteria on control and passivated samples (HCl, citric acid). On untreated surfaces, a high bacterial colonization was observed, with a total surface coverage of 68%. In comparison, the area covered by bacteria was drastically reduced to 26% on citric acid and 52% on hydrochloric acid (p < 0.05). Interestingly, the citric acid treatment statistically increased the antibacterial properties of the hydrochloric acid (0.85% of surface coverage vs. 0.47% for HCl and 0.22% for citric acid).

Table 4.
Number of S. sanguinis bacteria after 4 h and the ratio of S. sanguinis adhered compared to unpassivated samples.

Figure 5.
Microscope images of bacteria stained using the Live/Dead® BacLight bacterial viability kit which allows the assessment of the bacterial viability on each condition. Live: green and dead: dark red.
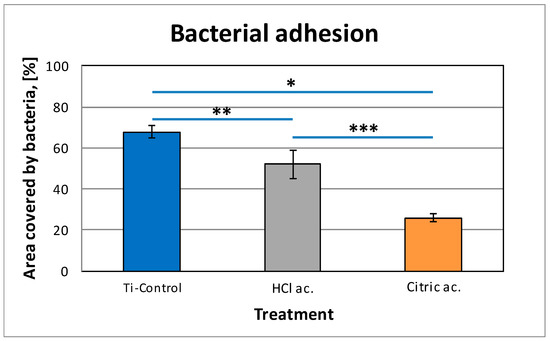
Figure 6.
Live/dead staining of S. S. sanguinis on control and passivated samples (HCl, citric acid). Symbols (*, **, ***) indicate statistical differences between conditions with p < 0.05.
The ratio of bacteria attached to the surface (Table 4) confirmed a significant decrease with HCl passivated samples compared to Ti (only 34.54% of adhesion). For the citric acid passivated samples, the adhesion was slightly reduced compared to hydrochloric acid with 16.02% of adhesion related to control.
4. Discussion
Several in vitro and in vivo studies have reported the influence of dental implant surface characteristics in biofilm formation. Parameters such as surface roughness, surface free energy (SFE), wettability and sterilization mode are factors that significantly affect early colonization and, therefore, biofilm formation and maturation. In general, when the roughness increases more bacterial adhesions occur. However, the passivation films formed by titanium oxide reduce colonization due to the oxidizing character of the coats. This fact was also verified in the studies of bacteria carried out on rough surfaces by sand-blasting alumina particles on titanium disks, where in one case the entire surface was cleaned of alumina residues and in another case approximately 8% of the surface was left with alumina particles. The results were clear that the surfaces with the presence of aluminum presented less quantity of bacterial colonies [31,32,33,34].
In this work we have been able to verify with high resolution roughness equipment that the acid attacks to obtain passivation layers increase the roughness, that is, in addition to the roughness obtained by sand-blasting, the acid passivation treatment increases the roughness. However, this slight increase in roughness does not increase the bacterial colonization since it is the oxidizing effect of the oxide layer that reduces the adhesion of the bacteria on the titanium [35,36,37].
The increase in roughness obtained by the passivation process increases the specific surface of the titanium, i.e., there is a greater surface in contact with the physiological environment and therefore the release of ions is higher in the passivated materials. The barrier effect of the oxide layer (porous) does not inhibit the release of the titanium ions into the medium [38].
Between the two passivates, the one that has a higher amount of ion release is the attack with hydrochloric acid since it increases more significantly the roughness with respect to the discs treated with citric acid.
As found in other works the increase of surface roughness increases the contact angle [29,30,32]. A high value of contact angle correlates with a low value of surface free energy, which leads to a hydrophobic surface and, initially, to a lower adhesion of proteins and subsequently of bacteria. However, the antimicrobial effect of citric acid is higher than that of the hydrochloric acid. Previous studies showed that this acid is effective to reduce anaerobic pathogens related to periodontal disease [39,40,41]. The high acid concentration and low pH does not reduce the cell compatibility and in consequence acid citric treatment removes biofilms related to perimplantitis diseases without affecting the periodontal tissues [41]. The action of the citric acid reduces the pH of extracellular sites. The acidulation property of the citric acid changes the membrane permeability of bacteria, varying the hydrogen gradient between intracellular and extracellular sites. In addition, the citric acid presents an important antioxidant effect which has a fatal effect on the microbacteria [40,41,42,43]. Hydrochloric acid is not as oxidizing although it has a higher degree of acidity (strong acid) but does not affect bacteria as much as citric acid. Another important point is that the oxidizing action of citric acid lasts quite a long time and therefore it is effective in the first stages of osseointegration of the dental implant and in many cases it can form the biological seal that will prevent bacterial colonization. Once the tests were finished, the surfaces of the titanium disks were observed by means of scanning electron microscopy to observe possible pitting produced by electrochemical corrosion. Pitting was not observed in any of the samples observed, neither for those treated with hydrochloric acid nor with citric acid.
For the limitation of this study, the ion release tests were performed on titanium without bacteria. We have assumed only titanium ion was released. However, in fact, the ICP-MS is an analytical technique to measure the ions and small particles like nanoparticles in the solutions. Since we have not measured the surface morphology after immersion with bacteria, we could not confirm whether the presence of bacteria would cause any elemental increase besides ion release. This kind of chemical degradation of titanium should be studied in the future.
5. Conclusions
The passivation of rough titanium with hydrochloric acid and citric acid produces films of titanium oxide being of greater thickness than those obtained by treatment of hydrochloric acid, given the higher concentration and strong character of its acidity. In both cases, passivation causes an increase in surface roughness. The release of ions in relation to the specific surface obtained is slightly lower since the oxide layer acts as an obstacle to the release of titanium. The treatment with citric acid decreases the contact angle and causes an increase in surface energy with a high polarization and oxidizing character. These physical-chemical characteristics of the surface obtained by means of citric acid causes the bactericidal behavior as it has been proven in bacterial studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.G., R.P., and M.P.; methodology, M.P., J.V., J.N., and J.M.M.; validation, R.A.P., B.B., R.P., and M.P.; formal analysis, R.A.P., B.B., J.N., and M.P.; investigation, J.V., J.N., M.P., B.B., and J.M.M.; resources, J.G. and J.M.M.; data curation, R.A.P., B.B., and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.P., M.P., and J.G.; writing—review and editing, J.G., R.P., and M.P.; visualization, M.P. and J.G.; supervision, J.G.; project administration, J.G.; funding acquisition, J.G. and R.A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the Spanish government and the Ministry of Science and Innovation of Spain by the research project numbers RTI2018-098075-B-C21 and RTI2018-098075-B-C22, cofounded by the EU through the European Regional Development Funds (MINECO-FEDER, EU). Authors also acknowledge Generalitat de Catalunya for funding through the 2017SGR-1165 project and the 2017SGR708 project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dental Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Padros, A.; Gil, F.J. In vivo evaluation of micro-rough and bioactive titanium dental implants using histometry and pull-out tests. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshoff, J.E.; Hayakawa, T.; Van Dijk, K.; Leijdekkers-Govers, A.F.; Van der Waerden, J.P.; Jansen, J.A. Mechanical and histologic evaluation of Ca-P plasma spray and magnetron sputter-coated implants in trabecular bone of the goat. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 36, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleries, L. In Vitro Studies of Calcium Phosphate Coatings Obtained by Laser Ablation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hero, H.; Wie, H.; Jorgensen, R.B.; Ruyter, I.E. Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium produced by isostatic pressing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1994, 28, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, K.; Klein, C.P.; Wolke, J.G.; Blieck-Hogervorst, J.M. Plasma sprayed coatings of calcium phosphate. In CRC Handbook of Bioactive Ceramics. Calcium Phosphate and Hydroxyapatite Ceramics; Yamamuro, T., Hench, L., Wilson, J., Eds.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; Volume II, pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.; Condrate, S.R.; Hoelzer, D.T.; Fischman, G.S. Interfacial characterisation of plasma-spray coated calcium phosphate on Ti6Al4V. J. Mater. Sci. Med. 1998, 9, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, T.; Miyaji, F.; Kim, H.M. Preparation of bioactive Ti and its alloys via simple chemical surface treatment. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlen, T.; Wihelmsen, W. Passive behaviour of titanium. Electrochim. Acta 1986, 31, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Manzanares-Céspedes, M.C.; Sevilla, P.; Nart, J.; Manzanares, N.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Boyd, S.K.; Rodríguez, D. Evaluation of bone loss in antibacterial coated dental implants: An experimental study in dogs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violant, D.; Galofré, M.; Nart, J.; Teles, R.P. In vitro evaluation of a multispecies oral biofilm on different implant surfaces. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 9, 035007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Rodriguez, D.; Haapasalo, M. Antibacterial coatings on titanium surfaces: A comparison study between in vitro single-species and multispecies biofilm. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5992–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Guillem-Marti, J.; Sevilla, P.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Rodriguez, D. Anhydride-functional silane immobilized onto titanium surfaces induces osteoblast cell differentiation and reduces bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 59, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.G.; Delgado, L.M.; Manero, J.M.; Javier Gil, F.; Rodríguez, D. Silver deposition on titanium surface by electrochemical anodizing process reduces bacterial adhesion of Streptococcus sanguinis and Lactobacillus salivarius. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ström, G.; Fredericsson, M.; Stenius, P. Contact angles, work of adhesion, and interfacial tension at a dissolving hydrocarbon surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 119, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annarelli, C.C.; Fornazero, J.; Cohen, R.; Bert, J.; Besse, J.L. Colloidal protein solutions as a new standard sensor for adhesive wettability measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 213, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morra, M.; Cassinelli, C. Bacterial adhesion to polymer surfaces: A critical review of surface thermodynamic approaches. J. Biomater. Sci.-Polym. Ed. 1997, 9, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Rao, K.H. Analysis of different approaches for evaluation of surface energy of microbial cells by contact angle goniometry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 341–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teughels, W.; Van Assche, N.; Sliepen, I.; Quirynen, M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 17 (Suppl. 2), 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgers, R.; Gerlach, T.; Hahnel, S.; Schwarz, F.; Handel, G.; Gosau, M. In vivo and in vitro biofilm formation on two different titanium implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2010, 21, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htet, M.; Madi, M.; Zakaria, O.; Miyahara, T.; Xin, W.; Lin, Z.; Kasugai, S. Decontamination of anodized implant surface with different modalities for peri-implantitis treatment: Lasers and mechanical debridement with citric acid. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Gil, F.J.; Fonseca, C.; Barbosa, M.; Planell, J.A. The effect of shot blasting and heat treatment on the fatigue behavior of titanium for dental implant applications. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1961, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Fernández-Calderón, M.C.; Pérez-Giraldo, C.; Manero, J.M.; Albericio, F.; Gil, F.J.; Rodríguez, D. Covalent immobilization of hLf1-11 peptide on a titanium surface reduces bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. Acta biomaterialia. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3522–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Yu, K.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Rodriguez, D. Antibacterial properties of hLf1–11 peptide onto titanium surfaces: A comparison study between silanization and surface initiated polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2014, 16, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagno, A.; Di Bello, C. Surface treatments and roughness properties of Ti-based biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegueroles, M.; Aparicio, C.; Bosio, M.; Engel, E.; Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Altankov, G. Spatial Organization of Osteoblast Fibronectin-Matrix on Titanium Surface—Effects of Roughness, Chemical Heterogeneity, and Surface Free Energy. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5:2009. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.F. Titanium for medical applications. In Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications; Brunette, D.M., Tengvall, P., Textor, M., Thomsen, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ratner, B.D. A perspective on titanium biocompatibility. In Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications; Brunette, D.M., Tengvall, P., Textor, M., Thomsen, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, F.J.; Rodriguez, A.; Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Padulles, E.; Juarez, A. Effect of the oral bacteria on the mechanical behavior of titanium dental implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Impl. 2012, 27, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Buser, D.; Schenk, R.K.; Steinemann, S.; Fiorellini, J.P.; Fox, C.H.; Stich, H. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegueroles, M.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Planell, J.A.; Gil, F.J.; Aparicio, C. Adsorption of fibronectin, fibrinogen and albumin on TiO2: A kinetics, structural changes, and competition study. J. R. Soc. Interface Biointerfaces 2012, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillem, J.; Delgado, L.; Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Pegueroles, M.; Herrero, M.; Gil, F.J. Fibroblast adhesion and activation onto micro-machined titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, A.; van Oosten, M.A.; Schurch, E.; Land, N.P. The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1987, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.C.; Llama-Palacios, A.; Fernández, E.; Figuero, E.; Marín, M.J.; León, R.; Blanc, V.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M. An in vitro biofilm model associated to dental implants: Structural and quantitative analysis of in vitro biofilm formation on different dental implant surfaces. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu-Yuan, C.D.; Eganhouse, K.J.; Keller, J.C.; Walters, K.S. Oral bacterial attachment to titanium surfaces: A scanning electron microscopy study. J. Oral Implantol. 1995, 21, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Tonetti, M.S. Risk factors for osseodisintegration. Periodontol 2000 1998, 17, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzmann, N.U.; Berglundh, T. Definition and prevalence of peri-implant diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35 (Suppl. 8), 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhe, J.; Meyle, J.; Group D of the European Workshop on Periodontology. Peri-implant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35 (Suppl. 8), 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.G.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Lima, C.V.; Barao, V.A.R. Citric acid reduces oral biofilm and influences the electrochemical behavior of titanium: An in situ and in vitro study. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, W.J.; Lee, M.H.; Bae, T.S.; Lee, S.J.; Gay, J.; Loch, C. Anodisation increases integration of unloaded titanium implants in sheep mandible. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 857969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, M.; Velasco, F.; Ginebra, M.P.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C. Regenerating bone via multifunctional coatings: The blending of cell integration and bacterial inhibition properties on the Surface of biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2019, 11, 36449–36457. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).