Modeling of Surfactant-Enhanced Drying of Poly(styrene)-p-xylene Polymeric Coatings Using Machine Learning Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Set 1: Coating of 2021 μm initial coating thickness having poly(styrene), p-xylene, and TPP, 4.95%, 95.05%, and 0%, respectively.
- Set 2: Coating of 2011 μm initial coating thickness having poly(styrene), p-xylene, and TPP, 5.02%, 94.46%, and 0.52%, respectively.
- Set 3: Coating of 1999 μm initial coating thickness having poly(styrene), p-xylene, and TPP, 5.03%, 93.95%, and 1.02%, respectively.
- Set 4: Coating of 2005 μm initial coating thickness having poly(styrene), p-xylene, and TPP, 5.02%, 93.47%, and 1.51%, respectively.
- Set 5: Coating of 2009 μm initial coating thickness having poly(styrene), p-xylene, and TPP, 4.99%, 93.01%, and 2.00%, respectively.
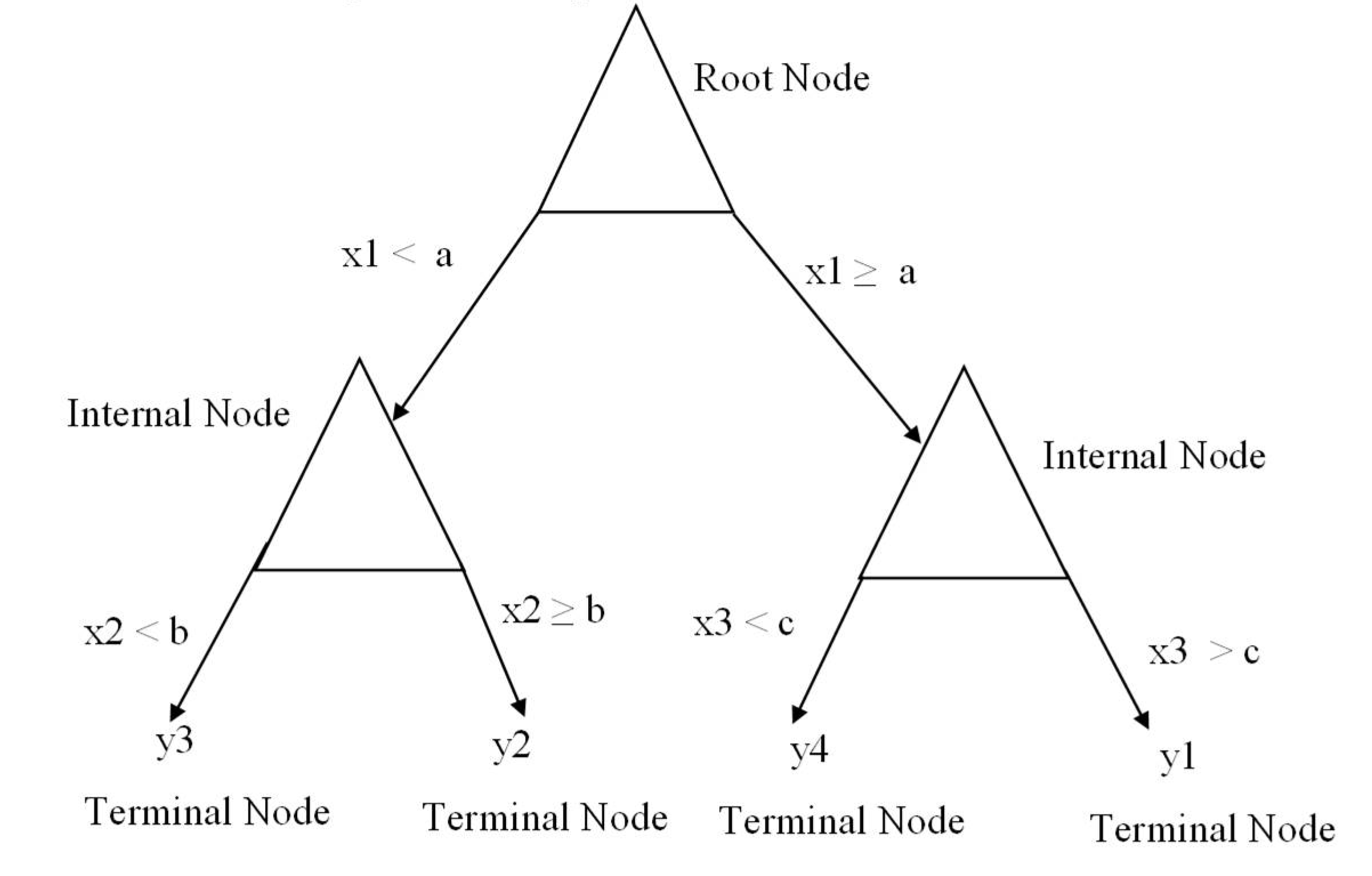
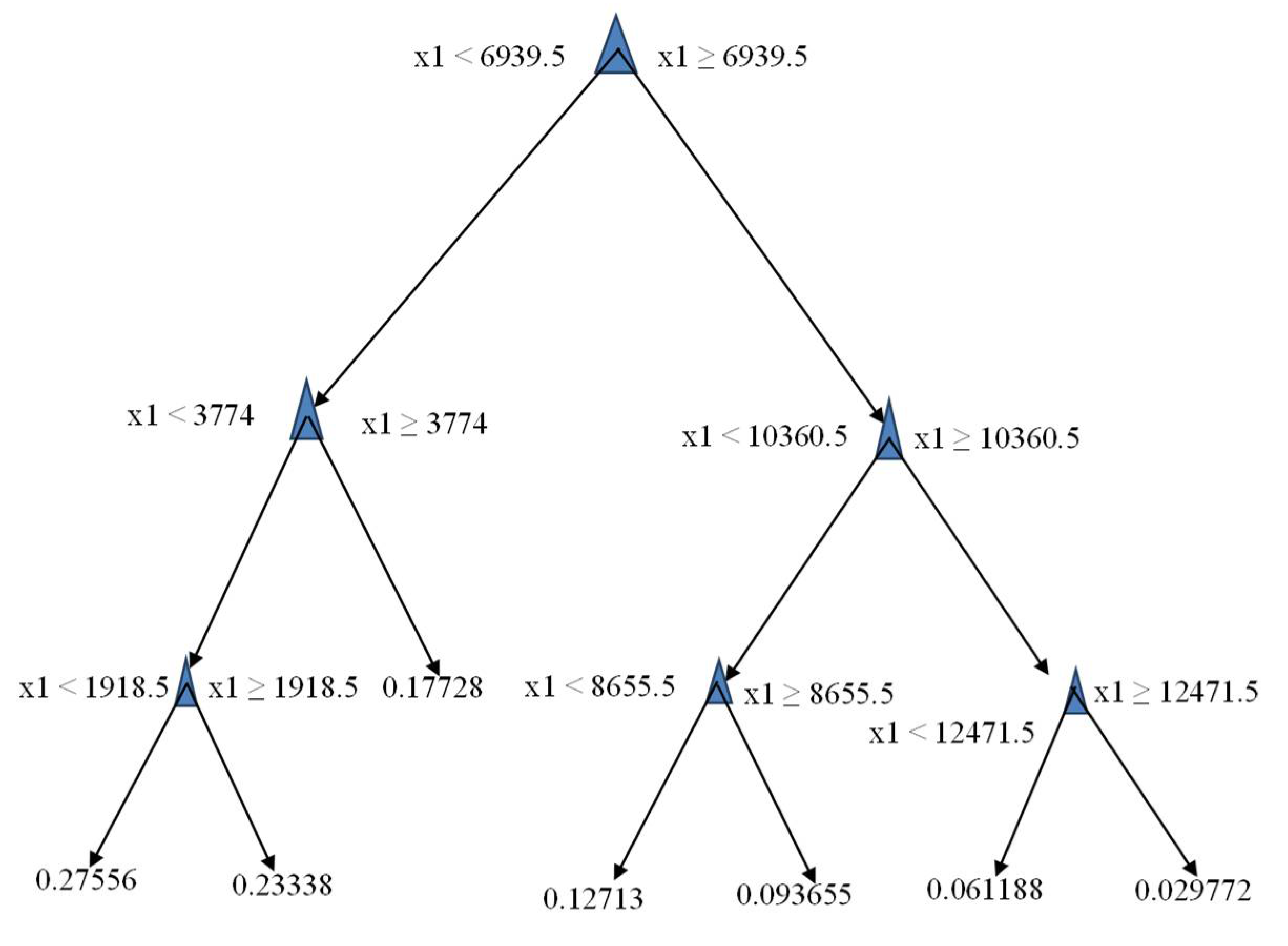
2. Modeling Based on Machine Learning Technique: Regression Tree Model
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Average of predicted values for leaf C | |
| C | Any one of the leafs for the tree |
| J | Numerical response |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| N | Number of data points/number of observations/number of samples |
| R | Matrix |
| SSE | Sum of squared errors |
| TPP | triphenyl phosphate |
| x | Input data (N×M matrix) |
| y | corresponding output data (N×1 matrix) |
| Yfit1 | Model predicted values for the unseen inputs (not used in training) |
| Data set | |
| Number of inputs/number of predictors |
References
- Fahlman, M.; Salaneck, W.R. Surfaces and interfaces in polymer-based electronics. Surf. Sci. 2002, 500, 904–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikada, Y. Surface modification of polymers for medical applications. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.K.; Thapliyal, D.; Sharma, J.; Verros, G.D. Glassy polymers—Diffusion, sorption, ageing and applications. Coatings 2021, 11, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiya, T.; Kobayashi, W.; Okuzono, T.; Doi, M. Controlling the drying and film formation processes of polymer solution droplets with addition of small amount of surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15460–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Fabiani, I.; Lesage de la Haye, J.; Schulz, M.; Liu, Y.; Lee, M.; Duffy, B.; D’Agosto, F.; Lansalot, M.; Keddie, J.L. Enhanced water barrier properties of surfactant-free polymer films obtained by macroraft-mediated emulsion polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11221–11232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Tsavalas, J.; Sundberg, D. Water whitening of polymer films: Mechanistic studies and comparisons between water and solvent borne films. Progress Org. Coat. 2017, 105, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortona, O.; D’Errico, G.; Paduano, L.; Sartorio, R. Ionic surfactant–polymer interaction in aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 2604–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeaufort, F.; Voilley, A. Effect of surfactants and drying rate on barrier properties of emulsified edible films. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 30, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, E.; Nyström, B.; Lindman, B. Polymer−surfactant interactions in dilute mixtures of a nonionic cellulose derivative and an anionic surfactant. Langmuir 2001, 17, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus-Smyth, A.; Bain, C.D.; Varga, I.; Campbell, R.A. Effects of bulk aggregation on pei–sds monolayers at the dynamic air–liquid interface: Depletion due to precipitation versus enrichment by a convection/spreading mechanism. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6103–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizri, G.; Lagerge, S.; Kamyshny, A.; Major, D.T.; Magdassi, S. Polymer–surfactant interactions: Binding mechanism of sodium dodecyl sulfate to poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 320, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, M.; Han, B. Study of interaction between sodium dodecyl sulfate and polyacrylamide by rheological and conductivity measurements. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1498–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, L.B.; Sovilj, V.J.; Katona, J.M.; Milanovic, J.L. Influence of polymer–surfactant interactions on o/w emulsion properties and microcapsule formation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, S.; Scanu, L.; Raghavan, S.R.; Khan, S.A. Influence of binary surfactant mixtures on the rheology of associative polymer solutions. Langmuir 2008, 24, 7797–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakbari, N.; Ebrahimi, M.; Mobarakeh, H.; Khorasani, M. Effect of surfactant type and concentration on surfactant migration, surface tension, and adhesion of latex films. J. Macromol. Sci. 2014, 53, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Scharfer, P.; Kind, M.; Schabel, W. Influence of non-volatile additives on the diffusion of solvents in polymeric coatings. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, O.; Zana, R. Interactions between water-soluble polymers and surfactants: Effect of the polymer hydrophobicity. 1. Hydrophilic polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 1996, 12, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, A.C.; Hu, J.Y. Effects of surfactant concentration on polymer-surfactant interactions in dilute solutions: A computer model. Langmuir 1989, 5, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Alexandridis, P. Drying of films formed by ordered poly(ethylene oxide)−poly(propylene oxide) block copolymer gels. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meconi, G.M.; Ballard, N.; Asua, J.M.; Zangi, R. Adsorption and desorption behavior of ionic and nonionic surfactants on polymer surfaces. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 9692–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, M.; Shioda, K.; Masuda, K.; Toei, R. Drying mechanism of coated film of polymer solution. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1974, 7, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.; Kumari, C.R.T. Effect of anionic surfactant on the thermo acoustical properties of sodium dodecyl sulphate in polyvinyl alcohol solution by ultrasonic method. E J. Chem. 2011, 8, 741971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, E.; Huber, G.; Hoffmann, H. Surfactant aggregation in the presence of polymers. Langmuir 1987, 3, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, M.; Mawatari, H.Y.Y.; Kage, H. Enhanced solvent drying in surfactant polymer blend coating. In Proceeding of the e 14th International Coating Science and Technology Symposium, Marina del Rey, CA, USA, 7–10 September 2008; pp. 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.; Kind, M.; Cairncross, R.; Schabel, W. Diffusion in multi-component polymeric systems: Diffusion of non-volatile species in thin films. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2009, 166, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Sharma, J.; Arya, R.K.; Ahuja, S.; Agnihotri, S. Surfactant enhanced drying of water based poly(vinyl alcohol) coatings. Progress Org. Coat. 2018, 125, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, I.; Sharma, J.; Ahuja, S.; Kumar Arya, R. Optimization of sodium dodecyl sulphate loading in poly(vinyl alcohol)-water coatings. Progress Org. Coat. 2019, 127, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.K.; Kaur, H.; Rawat, M.; Sharma, J.; Chandra, A.; Ahuja, S. Influence of plasticizer (triphenyl phosphate) loading on drying of binary coatings: Poly(styrene)-p-xylene coatings. Progress Org. Coat. 2021, 150, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhamb, S.; Enekvist, M.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Kontogeorgis, G.M. A review of computer-aided design of paints and coatings. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2020, 27, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.M.R.; Cheruku, S.; Geereddy, S.R. Process modeling and parameter optimization of surface coatings using artificial neural networks (anns): State-of-the-art review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 2764–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, İ.; Arslan, E.; Kızıltaş, E.Ç.; Çavdar, K. Development of a prediction method of rayleigh damping coefficients for free layer damping coatings through machine learning algorithms. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 166, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honrao, S.J.; Yang, X.; Radhakrishnan, B.; Kuwata, S.; Komatsu, H.; Ohma, A.; Sierhuis, M.; Lawson, J.W. Discovery of novel li sse and anode coatings using interpretable machine learning and high-throughput multi-property screening. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ravichandran, R.; Chen, K.; Patnaik, P. Application of machine learning to solid particle erosion of aps-tbc and eb-pvd tbc at elevated temperatures. Coatings 2021, 11, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siang, T.W.; Firdaus Akbar, M.; Nihad Jawad, G.; Yee, T.S.; Mohd Sazali, M.I. A past, present, and prospective review on microwave nondestructive evaluation of composite coatings. Coatings 2021, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Tremmel, S. Current trends and applications of machine learning in tribology—A review. Lubricants 2021, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Li, X. Development of models predicting biodegradation rate rating with multiple linear regression and support vector machine algorithms. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tušek, A.J. Application of multivariate regression and artificial neural network modelling for prediction of physical and chemical properties of medicinal plants aqueous extracts. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2020, 16, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, M.; Arabali, P.; Grasley, Z.; Bullard, J.W.; Jalal, H. Behavior assessment, regression analysis and support vector machine (svm) modeling of waste tire rubberized concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrougui, K.; Karim, G.; Mercatoris, B.; Khemis, C.; Roua, A.; Chehaibi, S. Prediction of organic potato yield using tillage systems and soil properties by artificial neural network (ann) and multiple linear regressions (mlr). Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, E.; Moradi, R.; Afroozeh, A.; Alizadeh, A.; Nilashi, M. A new approach for prediction of graphene based isfet using regression tree and neural network. Superlattices Microstruct. 2019, 130, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, C.; Lando, G.; Malegori, C.; Oliveri, P.; Sammartano, S. Prediction of water solubility and setschenow coefficients by tree-based regression strategies. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 282, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegler, C.H.; Renz, M.J.; Brink, G.E.; Ruark, M.D. Assessing the importance of plant, soil, and management factors affecting potential milk production on organic pastures using regression tree analysis. Agric. Syst. 2020, 180, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.; Stone, C. Classification and Regression Trees, 1st ed.; Routledge: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984; pp. 237–251. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]

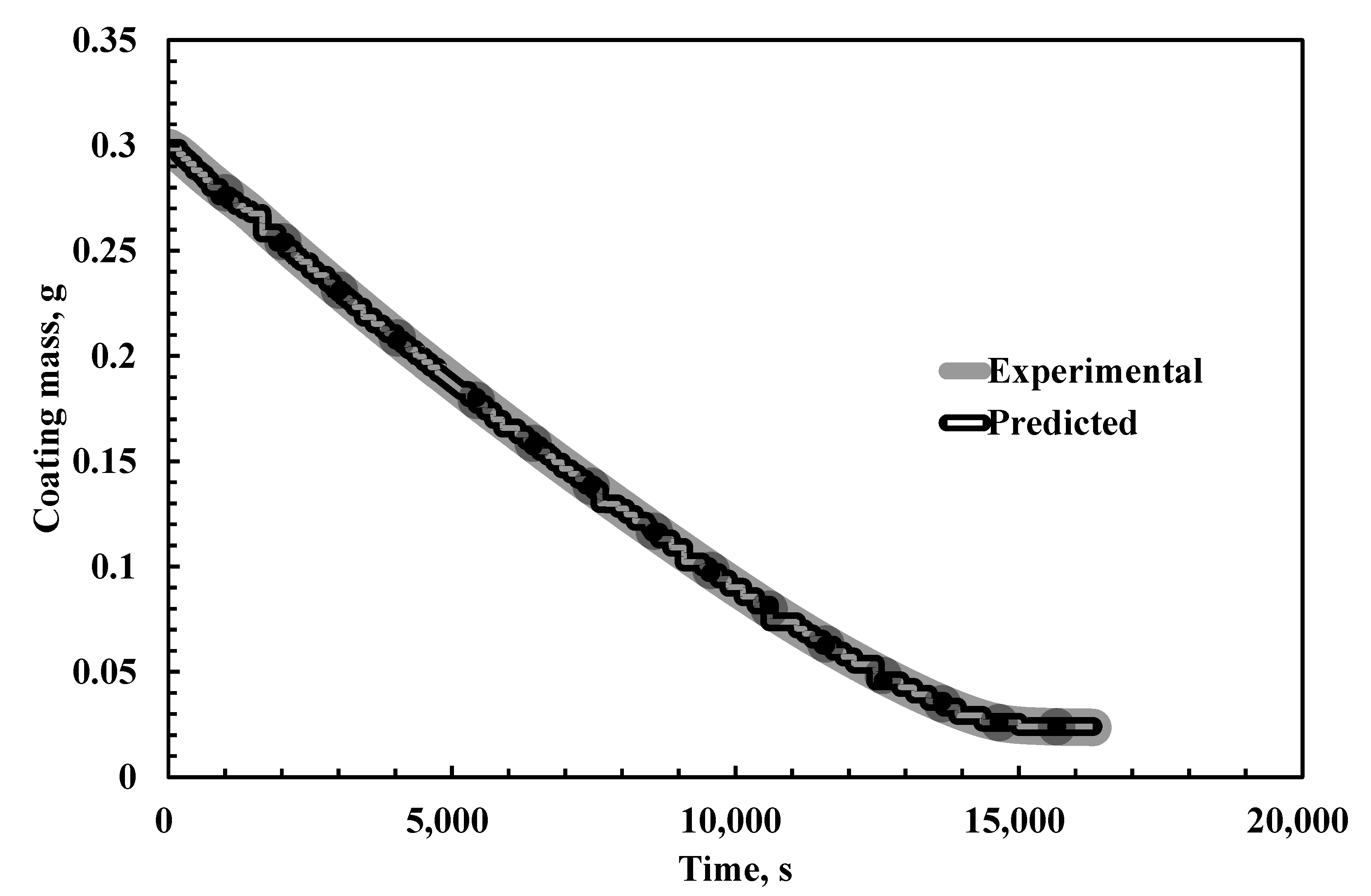
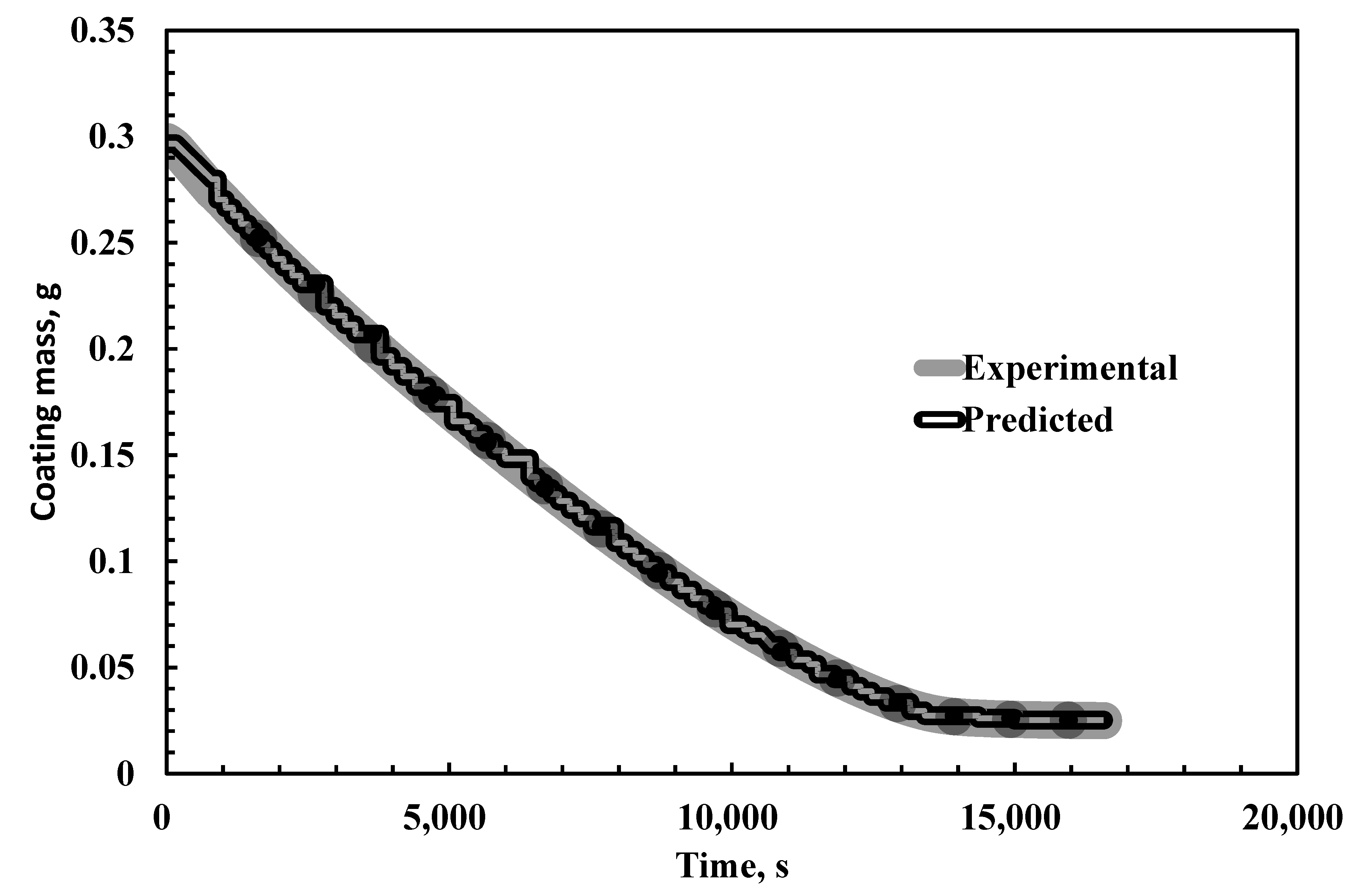
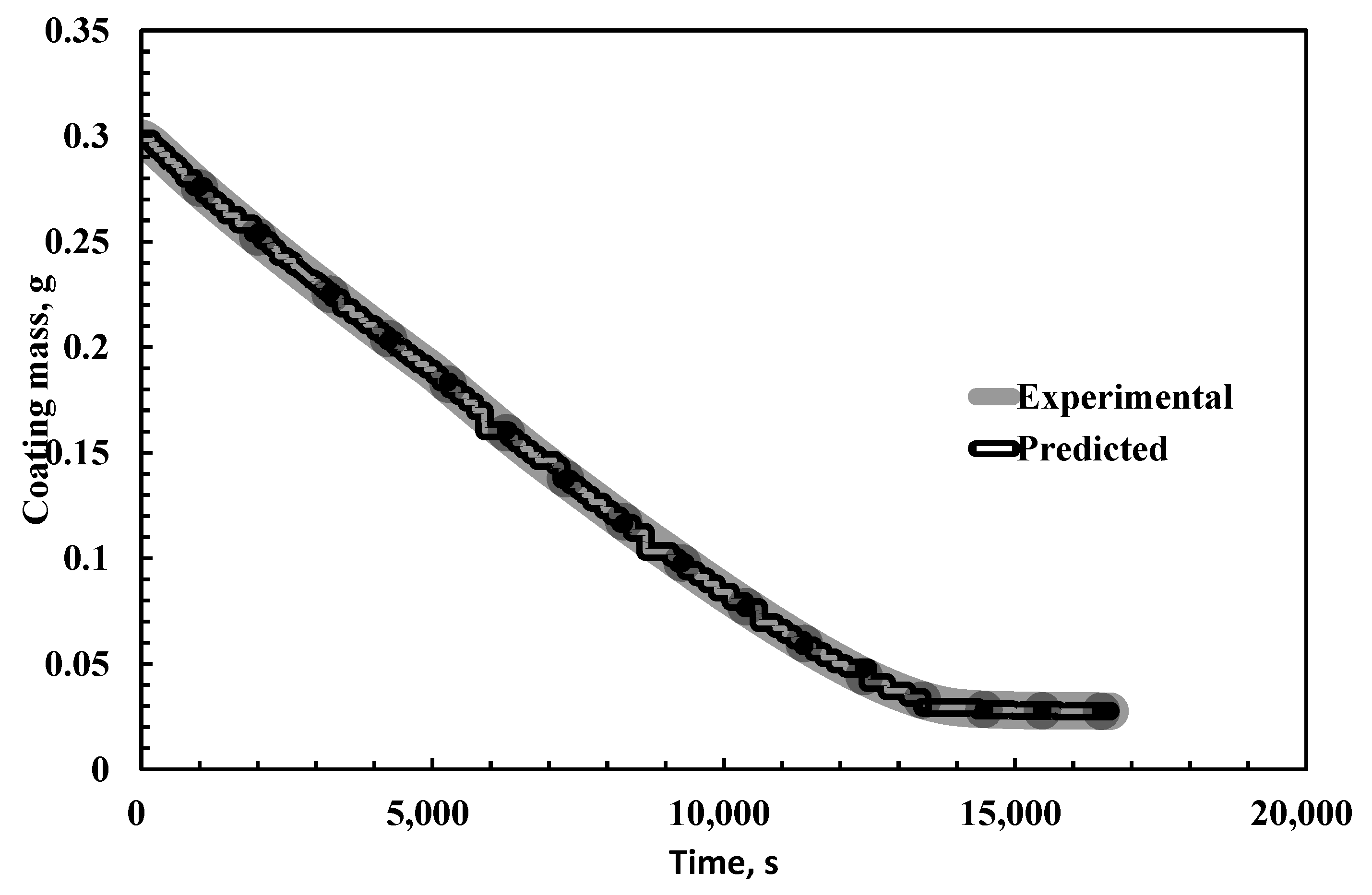
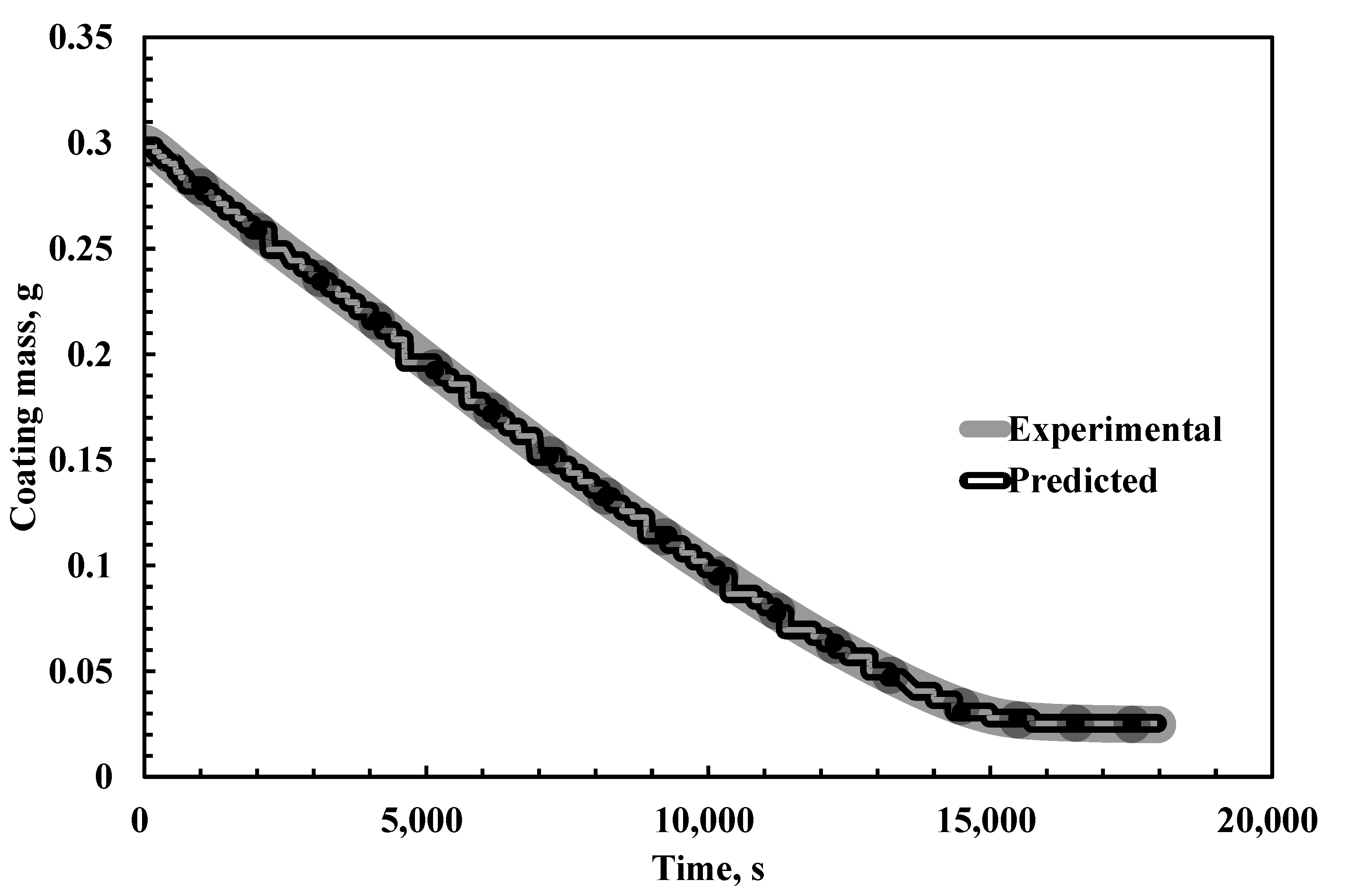
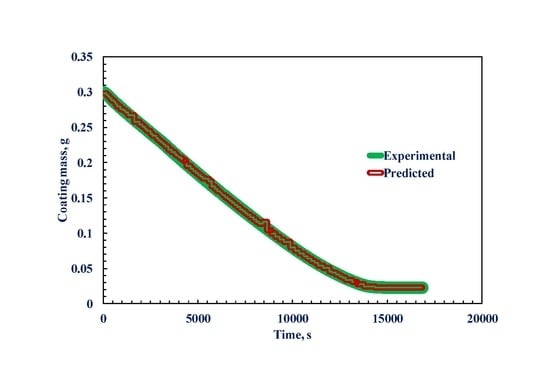
| Time, s | Experimental Weight of the Coating, g [28] | Model Predicted Weight of Coating, g | % Absolute Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 460 | 0.28964 | 0.28821 | 0.4944 |
| 465 | 0.28951 | 0.28821 | 0.4497 |
| 470 | 0.28938 | 0.28821 | 0.4050 |
| 475 | 0.28925 | 0.28821 | 0.3603 |
| 515 | 0.28819 | 0.28821 | 0.0062 |
| 520 | 0.28806 | 0.28821 | 0.0514 |
| 525 | 0.28793 | 0.28821 | 0.0965 |
| 530 | 0.2878 | 0.28821 | 0.1417 |
| 885 | 0.27895 | 0.28000 | 0.3779 |
| 890 | 0.27883 | 0.28000 | 0.4211 |
| 895 | 0.27871 | 0.28000 | 0.4644 |
| 900 | 0.27859 | 0.28000 | 0.5076 |
| 1665 | 0.26092 | 0.25835 | 0.9834 |
| 1670 | 0.26081 | 0.25835 | 0.9417 |
| 1675 | 0.2607 | 0.25835 | 0.8999 |
| 1680 | 0.26058 | 0.25835 | 0.8542 |
| 1805 | 0.25775 | 0.25835 | 0.2344 |
| 1810 | 0.25764 | 0.25835 | 0.2772 |
| 1815 | 0.25753 | 0.25835 | 0.3200 |
| 1820 | 0.25741 | 0.25835 | 0.3668 |
| 2451 | 0.24335 | 0.24473 | 0.5682 |
| 2456 | 0.24324 | 0.24473 | 0.6137 |
| 2461 | 0.24313 | 0.24473 | 0.6592 |
| 2466 | 0.24302 | 0.24473 | 0.7048 |
| 2471 | 0.24291 | 0.24473 | 0.7504 |
| Time, s | Experimental Weight of the Coating, g [28] | Model Predicted Weight of Coating, g | % Absolute Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.29862 | 0.29865 | 0.0096 |
| 35 | 0.29855 | 0.29865 | 0.0330 |
| 40 | 0.29847 | 0.29865 | 0.0599 |
| 45 | 0.2984 | 0.29865 | 0.0833 |
| 800 | 0.28184 | 0.28000 | 0.6514 |
| 805 | 0.28173 | 0.28000 | 0.6126 |
| 810 | 0.28162 | 0.28000 | 0.5737 |
| 815 | 0.28152 | 0.28000 | 0.5384 |
| 1526 | 0.26616 | 0.26768 | 0.5703 |
| 1531 | 0.26604 | 0.26768 | 0.6156 |
| 1536 | 0.26591 | 0.26768 | 0.6648 |
| 1541 | 0.26579 | 0.26768 | 0.7103 |
| 3371 | 0.22324 | 0.22327 | 0.0122 |
| 3376 | 0.22313 | 0.22327 | 0.0615 |
| 3381 | 0.22302 | 0.22327 | 0.1108 |
| 3386 | 0.22291 | 0.22327 | 0.1602 |
| 5792 | 0.17156 | 0.16992 | 0.9579 |
| 5797 | 0.17146 | 0.16992 | 0.9001 |
| 5802 | 0.17136 | 0.16992 | 0.8423 |
| 5807 | 0.17126 | 0.16992 | 0.7844 |
| 15,765 | 0.02383 | 0.02401 | 0.7727 |
| 15,770 | 0.02383 | 0.02401 | 0.7727 |
| 15,775 | 0.02382 | 0.02401 | 0.8150 |
| 15,780 | 0.02382 | 0.02401 | 0.8150 |
| 15,785 | 0.02382 | 0.02401 | 0.8150 |
| Time, s | Experimental Weight of the Coating, g [28] | Model Predicted Weight of Coating, g | % Absolute Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 140 | 0.29497 | 0.29664 | 0.5666 |
| 145 | 0.29486 | 0.29664 | 0.6041 |
| 150 | 0.29475 | 0.29664 | 0.6416 |
| 155 | 0.29463 | 0.29664 | 0.6826 |
| 160 | 0.29451 | 0.29664 | 0.7237 |
| 165 | 0.29439 | 0.29664 | 0.7647 |
| 4947 | 0.17258 | 0.17446 | 1.0913 |
| 4952 | 0.17247 | 0.17446 | 1.1558 |
| 4957 | 0.17236 | 0.17446 | 1.2203 |
| 4962 | 0.17225 | 0.17446 | 1.2850 |
| 5177 | 0.16751 | 0.16581 | 1.0121 |
| 5182 | 0.1674 | 0.16581 | 0.9471 |
| 5187 | 0.16729 | 0.16581 | 0.8820 |
| 5192 | 0.16718 | 0.16581 | 0.8167 |
| 11,399 | 0.05119 | 0.05154 | 0.6759 |
| 11,404 | 0.05112 | 0.05154 | 0.8138 |
| 11,409 | 0.05105 | 0.05154 | 0.9520 |
| 11,414 | 0.05098 | 0.05154 | 1.0906 |
| 11,419 | 0.05092 | 0.05154 | 1.2097 |
| 15,156 | 0.02545 | 0.02520 | 1.0000 |
| 15,161 | 0.02545 | 0.02520 | 1.0000 |
| 15,166 | 0.02545 | 0.02520 | 1.0000 |
| 15,171 | 0.02544 | 0.02520 | 0.9611 |
| 15,176 | 0.02544 | 0.02520 | 0.9611 |
| 15,181 | 0.02544 | 0.02520 | 0.9611 |
| Time, s | Experimental Weight of the Coating, g [28] | Model Predicted Weight of Coating, g | % Absolute Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.29896 | 0.29865 | 0.1041 |
| 5 | 0.29885 | 0.29865 | 0.0674 |
| 10 | 0.29878 | 0.29865 | 0.0440 |
| 15 | 0.29878 | 0.29865 | 0.0440 |
| 20 | 0.29875 | 0.29865 | 0.0339 |
| 1821 | 0.25632 | 0.25835 | 0.7936 |
| 1826 | 0.2562 | 0.25835 | 0.8408 |
| 1831 | 0.25609 | 0.25835 | 0.8841 |
| 1836 | 0.25598 | 0.25835 | 0.9274 |
| 1841 | 0.25586 | 0.25835 | 0.9748 |
| 1926 | 0.25394 | 0.25404 | 0.0397 |
| 1931 | 0.25383 | 0.25404 | 0.0831 |
| 1936 | 0.25372 | 0.25404 | 0.1265 |
| 1941 | 0.25361 | 0.25404 | 0.1699 |
| 1946 | 0.25349 | 0.25404 | 0.2173 |
| 1951 | 0.25338 | 0.25404 | 0.2608 |
| 3331 | 0.22327 | 0.22327 | 0.0013 |
| 3336 | 0.22316 | 0.22327 | 0.0480 |
| 3341 | 0.22305 | 0.22327 | 0.0974 |
| 3346 | 0.22295 | 0.22327 | 0.1423 |
| 14,495 | 0.0284 | 0.02816 | 0.8315 |
| 14,500 | 0.02839 | 0.02816 | 0.7966 |
| 14,505 | 0.02838 | 0.02816 | 0.7616 |
| 14,510 | 0.02838 | 0.02816 | 0.7616 |
| 14,515 | 0.02837 | 0.02816 | 0.7266 |
| Time, s | Experimental Weight of the Coating, g [28] | Model Predicted Weight of Coating, g | % Absolute Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 0.28801 | 0.28625 | 0.6128 |
| 605 | 0.2879 | 0.28625 | 0.5749 |
| 610 | 0.28778 | 0.28625 | 0.5334 |
| 615 | 0.28767 | 0.28625 | 0.4954 |
| 620 | 0.28756 | 0.28625 | 0.4573 |
| 2081 | 0.25686 | 0.25870 | 0.7182 |
| 2086 | 0.25676 | 0.25870 | 0.7574 |
| 2091 | 0.25665 | 0.25870 | 0.8006 |
| 2096 | 0.25655 | 0.25870 | 0.8399 |
| 2101 | 0.25645 | 0.25870 | 0.8792 |
| 2321 | 0.25197 | 0.24954 | 0.9642 |
| 2326 | 0.25187 | 0.24954 | 0.9249 |
| 2331 | 0.25177 | 0.24954 | 0.8855 |
| 2336 | 0.25167 | 0.24954 | 0.8462 |
| 2341 | 0.25157 | 0.24954 | 0.8067 |
| 5838 | 0.17955 | 0.17776 | 0.9969 |
| 5843 | 0.17945 | 0.17776 | 0.9418 |
| 5848 | 0.17934 | 0.17776 | 0.8810 |
| 5853 | 0.17924 | 0.17776 | 0.8257 |
| 16.941 | 0.02516 | 0.02536 | 0.7775 |
| 16.946 | 0.02516 | 0.02536 | 0.7775 |
| 16.951 | 0.02516 | 0.02536 | 0.7775 |
| 16.956 | 0.02516 | 0.02536 | 0.7775 |
| 16.961 | 0.02515 | 0.02536 | 0.8176 |
| 16.966 | 0.02515 | 0.02536 | 0.8176 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arya, R.K.; Sharma, J.; Shrivastava, R.; Thapliyal, D.; Verros, G.D. Modeling of Surfactant-Enhanced Drying of Poly(styrene)-p-xylene Polymeric Coatings Using Machine Learning Technique. Coatings 2021, 11, 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121529
Arya RK, Sharma J, Shrivastava R, Thapliyal D, Verros GD. Modeling of Surfactant-Enhanced Drying of Poly(styrene)-p-xylene Polymeric Coatings Using Machine Learning Technique. Coatings. 2021; 11(12):1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121529
Chicago/Turabian StyleArya, Raj Kumar, Jyoti Sharma, Rahul Shrivastava, Devyani Thapliyal, and George D. Verros. 2021. "Modeling of Surfactant-Enhanced Drying of Poly(styrene)-p-xylene Polymeric Coatings Using Machine Learning Technique" Coatings 11, no. 12: 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121529
APA StyleArya, R. K., Sharma, J., Shrivastava, R., Thapliyal, D., & Verros, G. D. (2021). Modeling of Surfactant-Enhanced Drying of Poly(styrene)-p-xylene Polymeric Coatings Using Machine Learning Technique. Coatings, 11(12), 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121529