Titanium-Nitride Coating Does Not Result in a Better Clinical Outcome Compared to Conventional Cobalt-Chromium Total Knee Arthroplasty after a Long-Term Follow-Up: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
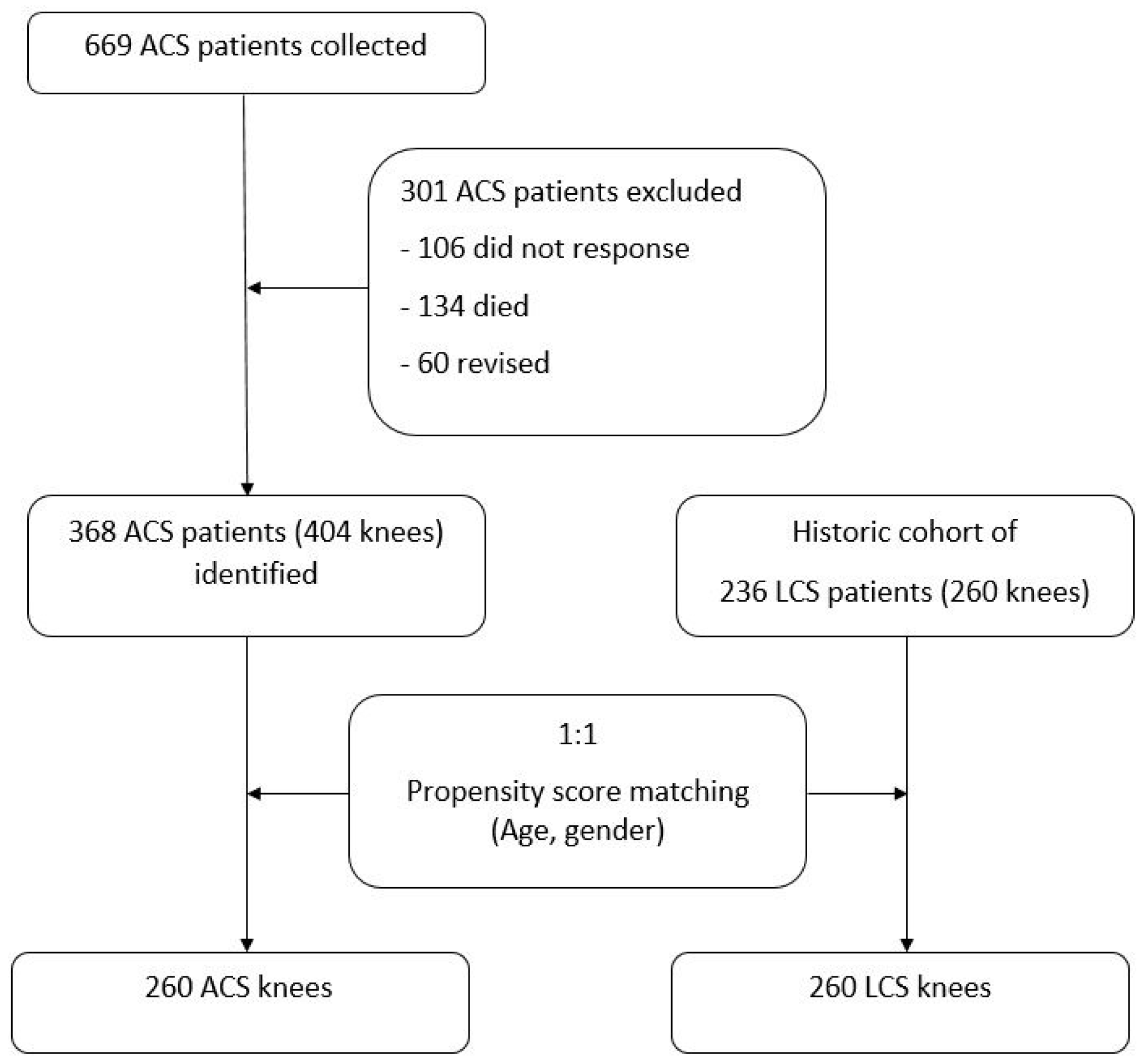
2.1. Sample Size
2.2. Outcome Measurements
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
The Overall Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pabinger, C.; Lothaller, H.; Geissler, A. Utilization rates of knee-arthroplasty in OECD countries. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkiewicz, A.; Petersson, I.F.; Bjork, J.; Hawker, G.; Dahlberg, L.E.; Lohmander, L.S.; Englund, M. Current and future impact of osteoarthritis on health care: A population-based study with projections to year 2032. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabinger, C.; Berghold, A.; Boehler, N.; Labek, G. Revision rates after knee replacement. Cumulative results from worldwide clinical studies versus joint registers. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, G.; Wright, J.; Coyte, P.; Paul, J.; Dittus, R.; Croxford, R.; Freund, D. Health-related quality of life after knee replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1998, 80, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hove, R.P.; Brohet, R.M.; van Royen, B.J.; Nolte, P.A. No clinical benefit of titanium nitride coating in cementless mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, D.; Wagner, E.R.; Larson, D.R.; Davis, M.P.; Pagnano, M.W.; Sierra, R.J. No Increased Risk of Knee Arthroplasty Failure in Patients with Positive Skin Patch Testing for Metal Hypersensitivity: A Matched Cohort Study. J. Arthroplasty 2016, 31, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, R.; Reinders, J.; Kretzer, J.P. What’s next? Alternative materials for articulation in total joint replacement. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, G.; Rothwell, A.; Frampton, C. The low contact stress mobile-bearing total knee replacement: A prospective study with a minimum follow-up of ten years. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2009, 91, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, K.J.; Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Ong, K.; Chiu, V.; Vail, T.P.; Berry, D.J. The epidemiology of revision total knee arthroplasty in the United States. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, A.; Brockett, C.; Williams, S.; Hatto, P.; Burton, A.; Isaac, G.; Fisher, J. Comparison of wear of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular cups against surface-engineered femoral heads. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2008, 222, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostlund, T.; Albrektsson, B.; Albrektsson, T.; McKellop, H. Wear of ion-implanted pure titanium against UHMWPE. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallab, N.J.; Vermes, C.; Messina, C.; Roebuck, K.A.; Glant, T.T.; Jacobs, J.J. Concentration- and composition-dependent effects of metal ions on human MG-63 osteoblasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallab, N.J.; Caicedo, M.; Epstein, R.; McAllister, K.; Jacobs, J.J. In vitro reactivity to implant metals demonstrates a person-dependent association with both T-cell and B-cell activation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Hove, R.P.; Sierevelt, I.N.; van Royen, B.J.; Nolte, P.A. Titanium-Nitride Coating of Orthopaedic Implants: A Review of the Literature. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 485975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N. Corrosion of Metallic Biomaterials: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, V.P.; Laaksonen, I.; Matuszak, S.J.; Connelly, J.W.; Muratoglu, O.; Malchau, H. Mid-term changes in blood metal ion levels after Articular Surface Replacement arthroplasty of the hip. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99 (Suppl. SB), 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraudi, A.; Catalani, S.; Montesi, M.; Stea, S.; Sudanese, A.; Apostoli, P.; Toni, A. Detection of cobalt in synovial fluid from metal-on-metal hip prosthesis: Correlation with the ion haematic level. Biomarkers 2013, 18, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.; Brewer, J.M.; Grant, M.H. Effect of chromium and cobalt ions on primary human lymphocytes in vitro. J. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 8, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltit, F.; Assiri, A.; Garbuz, D.; Duncan, C.; Masri, B.; Greidanus, N.; Wang, R. Adverse reactions to metal on polyethylene implants: Highly destructive lesions related to elevated concentration of cobalt and chromium in synovial fluid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallab, N.; Merritt, K.; Jacobs, J.J. Metal sensitivity in patients with orthopaedic implants. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2001, 83, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wicklund, B.H.; Gustilo, R.B.; Tsukayama, D.T. Prosthetic metals interfere with the functions of human osteoblast cells in vitro. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1997, 339, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzynski, J.; Gil, J.A.; Goodman, A.D.; Waryasz, G.R. Hypersensitivity to Orthopedic Implants: A Review of the Literature. Rheumatol. Ther. 2017, 4, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermes, C.; Kuzsner, J.; Bardos, T.; Than, P. Prospective analysis of human leukocyte functional tests reveals metal sensitivity in patients with hip implant. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2013, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carossino, A.M.; Carulli, C.; Ciuffi, S.; Carossino, R.; Thyrion, G.D.Z.; Zonefrati, R.; Brandi, M.L. Hypersensitivity reactions to metal implants: Laboratory options. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapaj, L.; Rozwalka, J. Retrieval analysis of TiN (titanium nitride) coated knee replacements: Coating wear and degradation in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fabry, C.; Zietz, C.; Baumann, A.; Ehall, R.; Bader, R. High wear resistance of femoral components coated with titanium nitride: A retrieval analysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 2630–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobel, F.; Ulbricht, S.; Hein, W.; Bernstein, A. Radiological mid-term results of total knee arthroplasty with femoral components of different materials. Z. Orthop. Unfall. 2008, 146, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Metcalf, B.; Makovey, J.; Bennell, K.L.; March, L.; Hunter, D.J. The influence of weather on the risk of pain exacerbation in patients with knee osteoarthritis—A case-crossover study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedslund, G.; Hagen, K.B. Does rain really cause pain? A systematic review of the associations between weather factors and severity of pain in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pain 2011, 15, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielgut, I.; Leitner, L.; Kastner, N.; Radl, R.; Leithner, A.; Sadoghi, P. Sports Activity after Low-contact-stress Total Knee Arthroplasty—A long term follow-up study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegner, Y.; Lysholm, J. Rating systems in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1985, 198, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, N.; Buchanan, W.W.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Campbell, J.; Stitt, L.W. Validation study of WOMAC: A health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Insall, J.N.; Dorr, L.D.; Scott, R.D.; Scott, W.N. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1989, 248, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hoenig, J.M.; Heise, D.M. The Abuse of Power: The Pervasive Fallacy of Power Calculations for Data Analysis. Am. Stat. 2001, 55, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thienpont, E. Titanium niobium nitride knee implants are not inferior to chrome cobalt components for primary total knee arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2015, 135, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.; Metcalfe, A.; Woodnutt, D. Medium-term outcome of titanium nitride, mobile bearing total knee replacement. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2014, 80, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry (2019). National Joint Replacement Registry. Annual Report 2019. Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. Available online: https://aoanjrr.sahmri.com/annual-reports-2019 (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- National Joint Registry for England and Wales (2018). National Joint Registry. 15th Annual Report 2018. National Joint Registry for England and Wales. Available online: http://www.njrcentre.org.uk (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Amstutz, H.C.; Campbell, P.; Kossovsky, N.; Clarke, I.C. Mechanism and clinical significance of wear debris-induced osteolysis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 276, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoghi, P.; Liebensteiner, M.; Agreiter, M.; Leithner, A.; Bohler, N.; Labek, G. Revision surgery after total joint arthroplasty: A complication-based analysis using worldwide arthroplasty registers. J. Arthroplasty 2013, 28, 1329–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverland, D. Patient satisfaction following TKA: Bless them all! Orthopedics 2010, 33, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, E.; Pawasarat, I.; Lindsay, A.; May, L.; Azzam, K.; Joshi, A.; Parvizi, J. Limitations of the Knee Society Score in evaluating outcomes following revision total knee arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liow, R.Y.; Walker, K.; Wajid, M.A.; Bedi, G.; Lennox, C.M. The reliability of the American Knee Society Score. Acta Orthop. Scand. 2000, 71, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loth, F.L.; Liebensteiner, M.C.; Giesinger, J.M.; Giesinger, K.; Bliem, H.R.; Holzner, B. What makes patients aware of their artificial knee joint? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermans, E.J.; van der Pas, S.; Schaap, L.A.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; Zambon, S.; Peter, R.; Siviero, P. Self-perceived weather sensitivity and joint pain in older people with osteoarthritis in six European countries: Results from the European Project on OSteoArthritis (EPOSA). BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, J.; Aoyama, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Okumura, S.; Takahashi, K.; Funakubo, M.; Mizumura, K. Artificially produced meteorological changes aggravate pain in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 354, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, J.; Inagaki, H.; Kusui, M.; Yokosuka, M.; Ushida, T. Lowering barometric pressure induces neuronal activation in the superior vestibular nucleus in mice. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrend, H.; Zdravkovic, V.; Bosch, M.; Hochreiter, B. No difference in joint awareness after TKA: A matched-pair analysis of a classic implant and its evolutional design. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 2124–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient Characteristics | ACS (n = 404) | LCS (n = 260) | p | Matched ACS (n = 260) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 65.6 ± 8.2 | 65.8 ± 11.3 | 0.775 | 66.5 ± 9.1 | 0.423 |
| Sex (F:M) | 275:129 | 209:51 | <0.001 | 209:51 | 0.999 |
| – | ACS (n = 260) | LCS (n = 260) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| KSS Pain (mean ± SD) | 82.6 ± 15.6 | 70.8 ± 21.9 | p < 0.001 |
| KSS Function (mean ± SD) | 61.9 ± 25.4 | 71.1 ± 29.1 | p = 0.011 |
| WOMAC (mean ± SD) | 79.9 ± 15.2 | 81.3 ± 14.6 | p = 0.453 |
| VAS (mean ± SD) Pre-operative Post-operative Change in VAS | |||
| 7.7 ± 1.2 | 6.9 ± 1.8 | p < 0.001 | |
| 2.9 ± 2.0 | 1.4 ± 1.8 | p = 0.002 | |
| 5.6 ± 2.3 | 4.4 ± 3.3 | p < 0.001 | |
| TAS (mean ± SD) Pre-operative Post-operative Change in TAS | |||
| 2.9 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.5 | p = 0.256 | |
| 2.6 ± 1.1 | 2.2 ± 1.5 | p = 0.001 | |
| 0.3 ± 1.4 | 0.6 ± 1.7 | p = 0.072 | |
| Meteoro-sensitivity (yes) | 150 (58%) | 54 (21%) | p < 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hauer, G.; Leitner, L.; Ackerl, M.C.; Klim, S.; Vielgut, I.; Ehall, R.; Glehr, M.; Leithner, A.; Sadoghi, P. Titanium-Nitride Coating Does Not Result in a Better Clinical Outcome Compared to Conventional Cobalt-Chromium Total Knee Arthroplasty after a Long-Term Follow-Up: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Coatings 2020, 10, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050442
Hauer G, Leitner L, Ackerl MC, Klim S, Vielgut I, Ehall R, Glehr M, Leithner A, Sadoghi P. Titanium-Nitride Coating Does Not Result in a Better Clinical Outcome Compared to Conventional Cobalt-Chromium Total Knee Arthroplasty after a Long-Term Follow-Up: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Coatings. 2020; 10(5):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050442
Chicago/Turabian StyleHauer, Georg, Lukas Leitner, Marc C. Ackerl, Sebastian Klim, Ines Vielgut, Reinhard Ehall, Mathias Glehr, Andreas Leithner, and Patrick Sadoghi. 2020. "Titanium-Nitride Coating Does Not Result in a Better Clinical Outcome Compared to Conventional Cobalt-Chromium Total Knee Arthroplasty after a Long-Term Follow-Up: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis" Coatings 10, no. 5: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050442
APA StyleHauer, G., Leitner, L., Ackerl, M. C., Klim, S., Vielgut, I., Ehall, R., Glehr, M., Leithner, A., & Sadoghi, P. (2020). Titanium-Nitride Coating Does Not Result in a Better Clinical Outcome Compared to Conventional Cobalt-Chromium Total Knee Arthroplasty after a Long-Term Follow-Up: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Coatings, 10(5), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050442





