Abstract
Biocompatible and bio-based materials are an appealing resource for the pharmaceutical industry. Poly(glycerol-adipate) (PGA) is a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer that can be used to produce self-assembled nanoparticles (NPs) able to encapsulate active ingredients, with encouraging perspectives for drug delivery purposes. Starch is a versatile, inexpensive, and abundant polysaccharide that can be effectively applied as a bio-scaffold for other molecules in order to enrich it with new appealing properties. In this work, the combination of PGA NPs and starch films proved to be a suitable biopolymeric matrix carrier for the controlled release preparation of hydrophobic drugs. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) was used to determine the size of drug-loaded PGA NPs, while the improvement of the apparent drug water solubility was assessed by UV-vis spectroscopy. In vitro biological assays were performed against cancer cell lines and bacteria strains to confirm that drug-loaded PGA NPs maintained the effective activity of the therapeutic agents. Dye-conjugated PGA was then exploited to track the NP release profile during the starch/PGA nanocomposite film digestion, which was assessed using digestion models mimicking physiological conditions. The collected data provide a clear indication of the suitability of our biodegradable carrier system for oral drug delivery.
1. Introduction
Nanostructured polymers are finding increasing use in pharmaceutical research for the development of drug delivery systems. Nano-delivery systems can be achieved with natural or synthetic polymers, however, synthetic polymers often have critical drawbacks, such as a lack of biodegradability and biocompatibility, with implications of inflammation and toxicity [1]. In this regard, poly(glycerol adipate) (PGA) is a valid synthetic solution. PGA is an enzymatically synthesized polymer that has been shown to be a green, biodegradable, and biocompatible macromolecule. It has an amphiphilic balance within the repetitive unit that aids with the production of self-assembled nanoparticles (NPs) by nanoprecipitation in water [2]. Moreover, the PGA suitability for drug delivery carrier development has previously been explored. For example, PGA was used as a drug delivery device of indomethacin. In particular, the polymer was grafted with the drug producing a novel composite. This grafted PGA could self-assemble into NPs and act as a drug “cargo” for a controlled delivery system [2,3,4].
Oral drug delivery systems are an important strategy to achieve more effective formulations, especially those concerning poorly bioavailable drugs, such as Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) class II compounds, which are defined as highly permeable but poorly aqueous soluble molecules [5]. In this case, the role of the carrier systems is to increase the apparent water solubility of the drug in order to improve its bioavailability. This process can be limited by an earlier instability of the carrier, causing an unwanted drug precipitation in the body fluids before it can reach the proper site of absorption [6]. The combination of nanostructured drug carriers with polymeric matrices could represent an innovative and effective approach to overcome this limitation.
Interestingly, the NPs produced with PGA show high-stability when embedded in complex polymeric semi-crystalline matrices [3]. One example of these matrices is starch, the most abundant polysaccharide on the earth [7,8,9]. Starch is a polymer composed of two macro-molecules: amylose and amylopectin. Amylopectin is a much larger branched polymer than amylose and represents approximately 75% of starch. Amylose instead is a linear polymer composed by α-(1-4) linked glucose units [8,10]. Recently, it was demonstrated that starch is a suitable vector for the transport of PGA NPs [3]. It was proposed that starch could trap NPs in its crystalline phase after producing the casted films, which should allow a more controlled release of a drug. Furthermore, starch films produced with and without NPs stimulated the growth of intestinal cells.
For all these reasons, we sought to develop a novel oral drug delivery system consisting of native barley starch blended with PGA NPs in order to obtain a biocompatible nanocomposite to improve the apparent water solubility of drugs.
Kinase inhibitors (KIs) are a class of drugs whose application in cancer treatment is constantly growing. Indeed, 49 KIs have been approved by the FDA over the last 20 years [11,12] and more than 2000 clinical trials evaluating these compounds are ongoing [13]. KIs, blocking specific enzymatic pathways that are hyper activated in tumors, have paved the way for better tolerated and targeted cancer therapies [14]. Although small molecule KIs can generally be orally administered [12] with remarkable advantages for patient treatment, they are often affected by a poor pharmacokinetic profile. This can lead to variations in plasma concentration, insufficient levels of the drug at the site of action, variability in systemic response, and other hardly controllable answers that can compromise the efficacy of therapy [15]. For these reasons, many strategies, such as the preparation of prodrugs, polymeric NPs, or liposomes, have been already developed or are under investigation in order to overcome this KI intrinsic limit [16].
Schenone et al. have reported a wide library of potent KIs endowed with a pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine scaffold [17,18]. Many of these compounds are active on different cancer cell lines, and some also showed activity in in vivo mouse models [19,20]. Among the members of this library, compound SI214 (Figure 1a) is a potent Src inhibitor (Ki = 90 nM) and possesses a considerable antiproliferative effect on the SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma cell line (IC50 = 80 nM). Despite these promising biological data, SI214 has low solubility in water (0.12 g/mL), which prevents its oral administration [21]. It has been successfully demonstrated that solid dispersions of pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine analogous containing an hydrophilic polymer as inert carrier possess an increased apparent water solubility due to enhanced interactions between the hydrophilic polymeric chain and the hydrophobic drug scaffold leading. It was further shown that the polymer–drug interactions led to the nano-microaggregates of the formulations assembling themselves [22]. For this reason, we selected SI214, as a pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine model, for the following study.
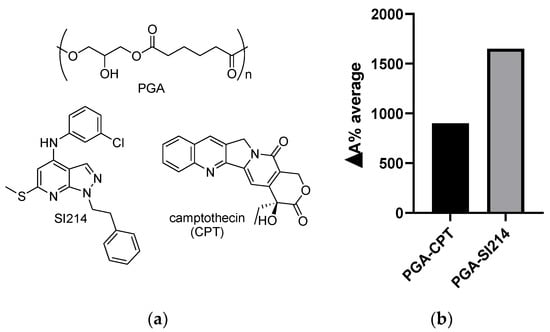
Figure 1.
(a) Poly(glycerol-adipate) (PGA) (above), SI214, and Camptothecin (CPT) (below) structures; (b) ΔA% average of the two nano-formulations calculated against the pure drugs in water.
Furthermore, evidence shows that the pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine nucleus can be a valuable scaffold to develop antimicrobial agents [23,24,25] and thus we additionally evaluated this compound against a series of strains of S. aureus and E. coli.
To further validate our work, we extended the in vitro evaluation to Camptothecin (CPT) (Figure 1a), a topoisomerase I inhibitor, whose activity as anticancer agent is confirmed [26] and efficacy as antimicrobial drug has been recently investigated [27]. CPT, as with SI214, suffers from low solubility in water and, in addition, is characterized by poor stability [28,29].
Therefore, in the present study, starch/PGA nanocomposites were characterized for the oral drug-delivery of SI214 and CPT molecules as anticancer and antimicrobial agents. A systematic study of encapsulation, via solubility enhancement UV-vis evaluation, was performed and showed that the NPs increased the apparent solubility in water of the drugs of several order of magnitudes compared to the pure drugs. Then, the stability profile of starch-NP nanocomposites was evaluated upon exposure to conditions mimicking the human gastrointestinal (GI) environment: the PGA was grafted with a fluorophore (Cy5) and the NP release from the matrix starch was monitored in a dynamic in vitro model simulating the human digestion. The formulations tuned the release of the NPs, demonstrating the feasibility of our novel system as an edible nanocomposite.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All the chemicals used in this work were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA) unless otherwise stated. Altia Industrial (Koskenkorva, Finland) kindly supplied the barley starch. Caco-2 human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA), and were used between passages 30-35 and HCT116 colorectal cancer cells were obtained from AMS Biotechnology (Abingdon, UK). S. aureus (SA01, SA02) and E. coli (EC07, EC19) bacteria were obtained from AMS Biotechnology (Europe). The PrestoBlue cell viability assay was purchased by Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Compound SI214 was synthesized as previously described [21]. CPT was purchased from Cambridge Bioscience (Cambridge, UK).
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. PGA and Cy5-PGA Synthesis
PGA was enzymatically synthesized from divinyl adipate and glycerol in tetrahydrofuran (THF) at 40–45 °C by a lipase immobilized on acrylic beads (Novozyme 435), as described by Sagnelli et al. [3]. PGA-Cy5 (PC) conjugate was synthesized via the direct coupling of amino-Cy5 to the free carboxylic end group of the polymer by carbonyldiimidazole mediated reaction. After purification via multistep precipitations and dialysis, against a mixture of water and methanol, the degree of coupling was assessed by UV-vis measurement.
2.2.2. PGA NP Preparation and Characterization by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
PGA NPs were produced by the solvent displacement technique, also called nanoprecipitation [30]. We used acetone (2 mL) as an organic solvent to dissolve the polymer and ultrapure water (10 mL) as a non-solvent system to achieve the NP formation. The PGA polymer (15 mg) dissolved in acetone was dropped into the water (1.5 mg/mL PGA in the aqueous medium) under constant magnetic stirring (550 rpm) at Room Temperature (RT) (19 °C). The mixture was left overnight in a fume hood while being agitated to let evaporate the organic phase. Blue PGA NPs were produced in the same way, but with a 1:5 (w/w) mixture of PC and PGA, in order to reach a total final polymer concentration of 1.5 mg/mL in water. Likewise, the drug loaded NPs were obtained with the same nanoprecipitation technique, dissolving both the polymers and the drug in the organic phase. In this case, the drug was in a 1:5 (w/w) ratio respect to PGA.
The different formulations in ultrapure water (1.5 mg/mL) were characterized by DLS (Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). Measurements in triplicate were used to calculate average intensity particle size distributions.
2.2.3. Casting of Films
The films were prepared in order to reach a final starch surface density of 10 mg/cm2, taking into account the native water content (%w) of starch [3]. The blue PGA NPs were 3% of starch (dry weight, d.w.). The starch was suspended in ultrapure water and the mixture was heated under magnetic stirring in an oil bath at 95 °C for ≈20 min, until complete starch melting was achieved. Then, the solution was rapidly cooled in an ice bath up to a temperature of 50 °C before mixing a proper volume of NPs and perform the casting. For the negative control (blank), an equal volume of ultrapure water with respect to the NPs suspension was mixed to the 50 °C starch solution. The films were prepared by casting in teflon-coated petri dishes and dried at 50 °C in a ventilated oven.
2.2.4. In vitro Static Digestion of Starch/Blue PGA Nanocomposites
A simplified static in vitro digestion method was used, as reported by Sagnelli et al. [31]. Simulated Salivary Fluid (SSF: 15.1 mM KCl, 13.6 mM NaHCO3, 0.75 mM CaCl2, pH 7), Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF: 6.9 mM KCl, 47.2 mM NaCl, 12.5 mM NaHCO3, 0.075 mM CaCl2, pH 2), and Simulated Intestinal Fluid (SIF: 6.8 mM KCl, 38.4 mM NaCl, 85 mM NaHCO3, 0.3 mM CaCl2, pH 7) were used to mimic the physio-chemical human gut conditions, and they were freshly prepared before use. Starch/blue PGA nanocomposites and plain starch films (negative control) were cut into small pieces in order to simulate the oral mastication. A total of 0.5 g (dry weight, d.w.) of chopped and SSF at a 1:2 (w:w) ratio was incubated under shaking conditions (170 rpm) at 37 °C for 1 min. An equal volume of SGF supplemented with fungal lipase (in SGF 60 IU/mL) and porcine pepsin (in SGF 1200 IU/mL) was added to the bolus to mimic the gastric phase (incubation for 30 min, at 37 °C, at 170 rpm shaking speed). In the intestinal phase, SIF solution with pancreatic α-amylase (in SIF 200 IU/mL) as porcine pancreatin 8X (L3126 Sigma-Aldrich) was added at a 1:1 (v:v) ratio with respect to the chyme volume, and the samples were incubated for 17 h (37 °C, 170 rpm shaking speed). Triplicate aliquots (70 µL) were taken at different time points (0, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 17 h) and replaced with an equal volume of fresh SIF. The collected aliquots were dropped in 70 µL of 99% ethanol and snap frozen in liquid N2 to interrupt the digestion [31].
2.2.5. Dynamic Digestion
A dynamic in vitro model called The Smallest Intestine (TSI) was used, as described by Cieplak et al. [32]. Briefly, the TSI allows us to modulate the physiochemical conditions (pH, bile, and gastric enzymes) through the human stomach and small intestine (SI), exploiting dialysis to simulate absorption and using a consortium of SI bacteria to simulate a healthy ileal microbiota. Five stirred batch-like reactors useable in parallel constitute the whole TSI unit, and each reactor (with a working volume of 12 mL) mimics one person’s SI. Specifically, the reactors are able to simulate the stomach, duodenum, jejunum, and ileum passage under controlled conditions (temperature, pH, anaerobic environment). The stomach passage (fasted state, pH = 2) was simulated as lined out previously [32] for 30 min using 1 g of nanocomposite (starch/blue PGA films or plain starch films as negative control). After 30 min in stomach conditions, the duodenum step started (30 min), followed by the jejunum (300 min) and ilium (120 min) passage [32].
Simulated Salivary Fluid (SSF), simulated gastric fluid (SGF), and simulated intestinal fluid (SIF) [30] devoid of sodium bicarbonate were used to mimic the electrolyte composition and osmotic pressure occurring in the human GI tract, as reported by Cieplak et al. [32]. The experiment was conducted in fasted state at 37 °C. The TSI reactors were filled with 1.4 mL SSF (PH 7), 2.3 mL of SGF (pH 3) and pepsin solution (pepsin activity of 2000 U/mL in the final volume), 1.4 mL of water, and 1 g of nanocomposite (starch/blue PGA films or plain starch films as negative controls). After 30 min, 4.5 mL of SIF, 10 μL of 0.6 M CaCl2, pancreatic juice as a mixture of SIF and porcine pancreatin 8X (trypsin activity of 40 U/mL in the final volume), and the bile solution (4 mM bile acids in the final volume) were added to simulate the duodenum. During the duodenal passage, a pH steady increment from 6 to 6.8 was achieved. Dialysis cassettes (Slide-A-Lyser G2, ThermoScientific) with a cut-off of 10 kDa were used to simulate the absorption of electrolytes, small nutrients, and bile during jejunal digestion, and the pH was elevated from 6.8 to 7.2. Fresh SIF (pH 7.2) supplemented with SI microbiota (107 CFU/mL in the reactor) was added with a chyme to SIF ratio of 50:40 (v/v) to simulate the ileum stage (pH 7.2). During the 7 h digestion, duplicate samples (70 µL) were taken at different time points for two biological replicates and the negative control (Stomach: 0 min, 30 min; Duodenum: 60 min; Jejunum: 180 min, 300 min; Ileum: 420 min). The collected samples were dropped in one volume of 99% ethanol and snap frozen in liquid N2 to interrupt the digestion.
2.2.6. NP Release Profile Evaluation
Aliquots collected during the static/dynamic digestion experiments were defrosted in ice and then centrifuged at 4000 rpm and 4 °C for 10 min. The supernatants were plated in 96 well plates and the UV absorbance at 650 nm was recorded. The calibration curve of blue PGA NPs was constructed and used to calculate the cumulative percentage release of NPs over time.
2.2.7. Cell Culture Conditions
Cells were routinely cultured in a growth medium at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in 75 cm2 culture flasks until 70% confluency was achieved. The Caco-2 cell growth medium consisted of Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplied with 10% (v/v) Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS), and 2 mM L-glutamine. HCT116 cells were cultured in McCoy’s 5a medium containing 10% (v/v) FBS.
2.2.8. Cytotoxicity of Study Formulations
The PrestoBlue cell viability assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was performed to assess NP cytotoxicity via the measurement of cellular metabolic activity. The Caco-2 cells were seeded at 1 × 104 cells/well in 96 well plates and HCT116 cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 104 cells/well. The cells were cultured for 24 h prior to assaying. Formulations were applied to cells in a growth medium containing 10% (v/v) FBS at NP concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL. Triton X-100 (TX-100) applied at 1% (v/v) was used as a cell death (positive) control and a vehicle control containing no NPs used as a negative control. After 48 h of exposure, the cells were washed twice with warm PBS and 100 µL 10% (v/v) PrestoBlue reagent diluted in a phenol red free medium applied per well for 60 min. The resulting fluorescence was measured at 560/600 nm (λex/λem). Relative metabolic activity was calculated by setting values from the negative control as 100% and positive control values as 0% metabolic activity.
2.2.9. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
The in vitro antimicrobial activity of study formulations was performed against two strains of gram-positive S. aureus (SA01, SA02) and two strains of gram-negative E. coli (EC07, EC19) bacteria. The MIC was determined via broth microdilution assay. Formulations were prepared at a concentration of 1000 µg/mL in Luria Bertani (LB) broth, and free drug was prepared at a concentration of 250 µg/mL in LB broth. An overnight culture was grown from a single colony in 10 mL LB broth at 37 °C in an incubator at 180 rpm overnight. A subculture was prepared by diluting the overnight culture 1:100 and then 1:20 in LB broth and was finally adjusted to 5 × 106 CFU/mL by optical density at 600 nm. A two-fold dilution series of 50 µL of test solution was added into U-bottom 96 well plates followed by the addition of 50 µL of bacteria subcultures. Positive (without test compound) and negative (without bacteria or test compound) were included in all experiments. MIC values were defined as the lowest concentration of test compound that showed no visible growth after overnight incubation at 37 °C.
2.2.10. Molecular Dynamics simulations (MD)
The models and forcefield parameters for the study of the interactions were developed as follows: first, the structures of the drugs and dimers of the polymers (PGA, PGA-Me) were created using ChemDraw3D. The structures were submitted to the online Automated Topology Builder (ATB) tool [33,34] that provided appropriate parameters for use with the GROMOS54a7 [35,36] force-field. The systems were composed by placing a dimer and a single drug molecule in a box and solvating the system (SPC water model [37]). After solvation, the atoms were relaxed by 10,000 steps of EM with the steepest descent algorithm followed by an equilibration via NVT ensembles at 298 K (V-rescale thermostat) for 100 ps and then in an NPT ensemble at 1 bar (Berendsen barostat). Bonds to hydrogen atoms were constrained to allow a time step of 2 fs. All of the MD simulations were run with the same barostat and thermostat under PBC. Long-range electrostatics were treated with PME [38,39].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. NPs’ Formation and Drug Water Solubility Enhancement
PGA, PGA-CTP, and PGA-SI214 NPs were formulated via simple nanoprecipitation technique, using acetone as the organic phase. A DLS screening assay and zeta potential analysis were performed in order to fully characterize the NPs (Table 1).

Table 1.
Size distribution, polydispersity index, and zeta potential data of the produced nanoparticles (NPs).
Both bare and loaded PGA NPs showed comparable sizes (range size: 172.3–184.1 nm), and a very narrow size distribution (PdI < 0.033). These data indicated a similar packaging for plain PGA and PGA-SI214 or PGA-CPT (Figure 1a) and a good quality of NPs, respectively. Furthermore, the negative surface charge of NPs (negative zeta potential), due to the free OH of the PGA, conferred NPs stability in an aqueous environment [40,41,42].
Analysis of the variation of the absorbance between the free drugs in water and their PGA formulation was assessed by UV-vis spectroscopy [22] and revealed an enhancement of the apparent water solubility of both compounds after encapsulation (Figure 1b).
PGA-SI214 exhibited a higher ΔA% than PGA-CPT. This is likely because SI214 is able to form more interactions with PGA than CPT, as supported by DLS study that showed a higher contraction of the size for the pyrazolo-pyrimidine derivative compared to the alkaloid (size of PGA-SI214 < size of PGA-CPT).
3.2. All Atom Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
All atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are attracting attention in the polymer-based drug delivery field as a tool to enlighten the interactions taking place at an atomistic level [43,44,45]. Our 10 ns MD simulations for the interactions between the dimers of PGA and the two drugs were used to evaluate the distance between the moieties and the possible formation of hydrogen bonds. Multiple H-bond formation was observed in the PGA-SI214 simulation (Figure 2a,b), while no H-bonding formation was observed in the PGA-CPT simulation (Figure 2c,d). These preliminary computational data can be used to corroborate the different experimental enhanced apparent water solubilities of the two drugs when formulated with the polymer (Figure 1b). In fact, as can be seen from Figure 1b, SI214 ΔA% improved twofold compared to the CPT, hinting to a better interaction between the polymeric chains and the KI drug.
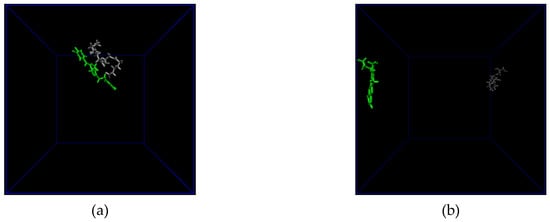
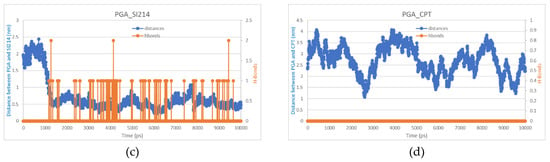
Figure 2.
(a) The final configuration of the PGA dimer (grey) and the SI214 molecule (green) after a 10 ns all atom Molecular Dynamics simulation; (b) distance (blue) and H-bonds (orange) between PGA and SI214; (c) the final configuration of the PGA dimer (grey) and the CPT molecule (green) after a 10 ns all atom Molecular Dynamics simulation; (d) distance (blue) and H-bonds (orange) between PGA and CPT.
3.3. Bioactivity of the Loaded NPs against Cancer Cells and Bacteria
The biological activity of the loaded NPs dissolved in an aqueous solution was tested against two intestinal cancer cell lines (i.e., Caco-2 and HCT116 cells) and different strains of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The application of the drug-loaded PGA- NPs to Caco-2 intestinal cells induced cell death, as determined by the loss of cellular metabolic activity, confirming the delivery of the encapsulated agents (Figure 3a). It can be noted that both formulations elicited similar levels of cytotoxicity, with PGA-SI214 and PGA-CPT reducing cell metabolic activity to 72.1% ± 7.5% and 68.1% ± 1.4%, respectively.
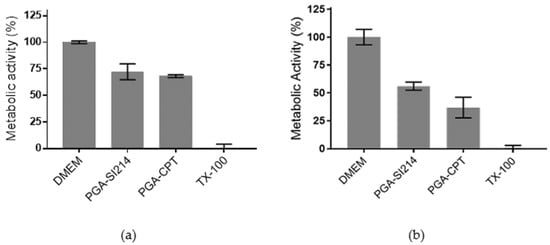
Figure 3.
In vitro cytotoxicity of study formulations on Caco-2 (a) and HCT116 (b) intestinal epithelial cells. Formulations were applied to cells at a polymer concentration of 0.5 mg/mL diluted in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) containing 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) for 48 h. A total of 1% (v/v) Triton X-100 (TX-100) was used as the positive cell death control. Caco-2 and HCT116 cells were seeded on 96 well plates at a density of 1 × 104 and 2 × 104 cells/well, respectively, and were cultured for 24 h prior to assaying. Metabolic activity was assessed using the PrestoBlue assay. The data represent mean ± S.D. (n = 3).
Slightly enhanced results were observed for HCT116 cells. In vitro data demonstrated that both SI214 and CPT formulated with PGA were cytotoxic, inducing a reduction of the metabolic activity of 56% and 36%, respectively (Figure 3b). The higher activity demonstrated by both compounds in HCT116 cells may be explained by the expression of oncogenes in this cell line that are absent in Caco-2 cells, such as mutant KRAS and PIK3CA genes [46,47,48]. These gene mutations may subsequently confer HCT116 cells increased susceptibility to treatment with a Src tyrosine KI and CPT [49,50,51].
Then, to evaluate if SI214 and CPT could be developed as antimicrobial agents, we tested against 2 strains of gram-positive S. aureus (SA01, SA02) and 2 strains of gram-negative E. coli (EC07, EC19) bacteria. The two compounds have been assayed both as free drugs dispersed in water and drug-loaded PGA NPs. As can be noted in Table 2, no activity was detected for drugs suspended in water, while the same Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) values have been calculated for both encapsulated compounds towards S. aureus and E. coli, respectively.

Table 2.
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC).
In particular, PGA-SI214 and PGA-CPT were 2-fold more potent against the two strains of E. coli than those of S. aureus, suggesting a screening of PGA-drug NPs against a panel of gram-negative bacteria as a possible continuation of this work.
3.4. Film Formation and NPs Entrapment
The suitability of barley starch film as bio-based coating polymer for PGA NPs has been previously reported [3]. Tests performed on Caco-2 cells using film extracts proved the starch/PGA nanocomposite biocompatibility. In fact, no cell membrane damage was detected, and the cell metabolic activity seemed to be increased by the free starch content of the extracts.
Prior to the preparation of the films, the stability of PGA NPs was assessed at 50 °C by DLS, to ensure NPs integrity during the film drying process. The monitoring of the NPs’ size at 50 °C over 24 h did not show significant changes in the NP dimension (data not shown), proving the PGA NPs’ suitability for the nanocomposite film preparation. Moreover, the PGA NPs stability in the starch matrix was previously showed by Sagnelli et al. [3].
3.5. Blue-NPs’ Release from Film in Different Buffers
The starch/PGA nanocomposite films were characterized via a static in vitro method simulating the physiochemical conditions of the human gut to evaluate the NP release profile over time as a cumulative percentage. As shown in Figure 4, because of the mild hydrolysis of the starch matrix in both SSF and SGF, only a minimal release of 8.4% was detected at the time of the SIF addiction (t0).
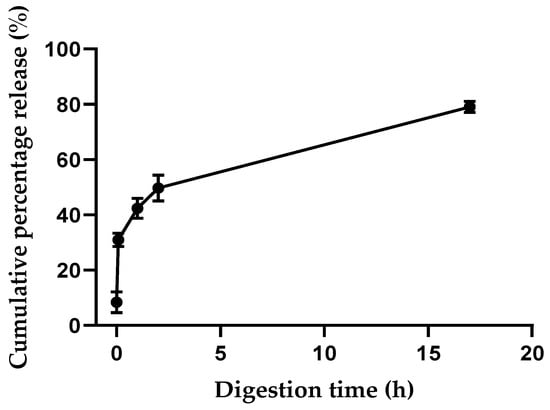
Figure 4.
Release of PGA-Cy5 (PC) conjugate during in vitro static digestion.
The small intestine represents the major site for absorption [52], and thus the starch matrix appears to be a useful bio-scaffold to preserve the integrity of the biodegradable PGA NPs to the site of interest, hampering PGA degradation in the oral–gastric tract. Indeed, PGA NPs are susceptible to degradation by the different digestive enzymes that cause the polymer breakdown. Additionally, PGA NPs are short-lived at the acidic pH of SGF [3,42]. In particular, Swainson et al. reported that the acidic pH of SGF caused PGA NPs instability, and an important swelling in terms of PGA NP hydrodynamic size was observed in the presence of lipase, suggesting degradation [42]. The PGA NP degradability by lipase was further proved by Sagnelli et al., who reported a tenfold increment in NP size after a 3 h incubation with lipase with respect to the enzyme-free NP control [3]. Undoubtedly, it is necessary to have complete drug retention in stable NPs to ensure that the active principle perseveres its solubilized state until reaching the absorption site in the small intestine. Drug absorption through the intestine mucous membrane is commonly achieved once the polymeric micelles release their active content in the gut environment [5]. In this regard, a biphasic NPs release pattern was detected during the simulated intestinal digestion (Figure 4), with an early 42% burst release of PGA NPs in the first hour. Then, a zero-order-like release phase seemed to take place, reaching a total release of 79% after 17 h. The gradual drug release in the small intestine fluids from loaded PGA NPs could reasonably take place once NPs were free from the starch matrix, as the biodegradability of the PGA NP was extensively shown by Swainson et al. [42] using lipase, pancreatin, and other digestive enzymes.
3.6. Digestion Model of the Edible Film
To further validate our results, the stability profile of our nanocomposite was evaluated using the TSI, a dynamic method that simulates the physicochemical conditions found in the human gut. Dynamic models have the advantage over static models to better mimic the physiological changes occurring through the different sections of the human GI tract, e.g., the dynamic variation of pH or the absorption process. The TSI reported by T. Cieplak et al. [32] is a small volume in vitro model working under controlled temperature and anaerobic conditions. The TSI is able to simulate the stomach, duodenum, jejunum, and ileum passages (Figure 5) using simulated gastric fluids containing digestive enzymes and the addition/absorbtion of bile salts and inoculation with a representative gut microbiota consurtium along the process.
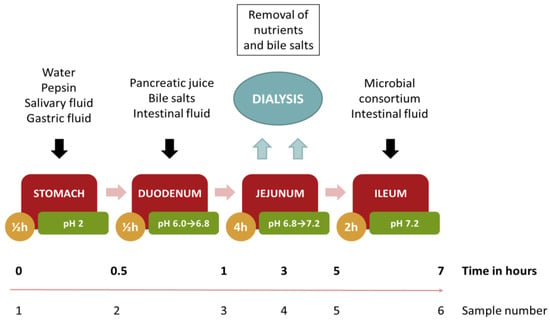
Figure 5.
Flow chart detailing the simulated dynamic digestion by the The Smallest Intestine (TSI) model.
During the gastric phase, the Starch/PGA film was incubated with SSF and SGF containing pepsin. The PC absorbance level in this phase was negligible (Figure 6), confirming that the nanocomposite was stable in this acidic environment (pH 2).
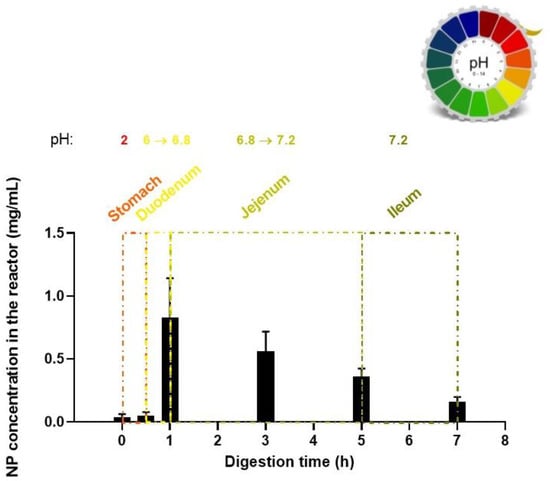
Figure 6.
Release of PC conjugate during in vitro dynamic digestion.
At the end of the gastric digestion, the chyme met the SIF, the bile salts, and the pancreatic juice. After 30 min of duodenal digestion, the apparent NP concentration reached 0.83 ± 0.31 mg/mL (≈ 28% respect to the total NP content of the film) because of the sensitivity of the starch films to the intestinal alpha-amylase. A NP concentration of 0.53 ± 0.16 mg/mL (≈ 18% respect to the total NP content of the film) was detected in the jejunum after 2 additional hours of digestion, and at the end of the jejunal phase the level of NPs was 0.36 ± 0.06 mg/mL (≈ 12% respect to the total NP content of the film). The NP concentrations during the jejunal phase were the result of the dynamic balance between different processes. On one side, the starch bio-scaffold degrades under the action of glycoside hydrolases with a consequent increase in NP level; on the other, the NPs are impaired due to the presence of different peptidases, bile salts, and lipase and the subsequent dialyzation of the degraded polymer fraction. After 7 h of total digestion, an absorbance related to 0.16 ± 0.04 mg/mL of NPs was detected in the jejunum, the intestinal site where antimicrobial drugs can start to exert their activity. In the future, different cross-linking levels of the starch matrix have to be tested to tune the NP release rate in the different GI tracts, in agreement with the activity and the site of action/absorption of the encapsulated active agent.
Interestingly, it should be noted that the data variability decreased for the time points after the duodenum phase. This variation in data variability levels could represent a further insight into NP breakdown. Indeed, multiple PC degradation by-products may differently result in shifts and shape variation in the UV-Vis absorbance peak influencing the data variability, as already reported in literature for a comparable dye-PGA conjugate [42]. This phenomenon should be mainly relevant at the end of the duodenum phase, as the initial burst releases a multitude of PC sub-products, which are produced by NP degradation and retained in the duodenum. Only after reaching the jujenum were the PC sub-products dialyzed, limiting their influence on the absorbance behavior.
The ability of the starch bio-scaffold to avoid the NP impairment in the gastric tract, despite the acidic pH and the protease activity, was herein demonstrated. Our nanocomposite system can so improve the bioavailability of class II therapeutic agents, avoiding their precipitation in the GI fluids and allowing their progressive release in the intestinal environment.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we developed PGA/starch nanocomposites as bio-polymeric matrix carriers for the controlled release of hydrophobic drugs. In particular, the polymeric formulations of two drugs (i.e., SI214 and CPT) with low solubility in water in their native form have been tested against different cancer and bacterial cell lines after dissolution in an aqueous medium. Interestingly, PGA-SI214 and PGA-CPT showed a certain activity as both antineoplastic and antibacterial drugs. This efficacy can be attributed to the enhanced apparent water solubility of formulated drugs compared to drugs alone, as confirmed by UV-vis spectroscopy analysis. PGA NPs were subsequently embedded in starch films to tune the release of the NPs. Indeed, the evidence shows that in vivo NP release is quite difficult to regulate. The starch matrix preserved the integrity of the biodegradable PGA NPs until the site of interest, hampering PGA degradation in the oral–gastric tract. This behavior has been studied by means of static/dynamic in vitro digestion models. Overall, we developed an innovative drug delivery system suitable for oral administration. Moving forward from this proof-of-concept study, it would be interesting to next explore the high-throughput screening of a panel of compounds to identify potent anticancer and/or antibacterial drugs in cell assays, with in an vivo evaluation of the most promising inhibitors in the PGA/starch bio-polymeric matrix.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.S.; Formal analysis, I.D.S.; Investigation, A.V., A.K.P., R.C., C.S., B.C., V.T., R.R.J., F.M. and D.S.; Project administration, D.S.; Supervision, V.T. and S.M.H.; Visualization, R.C., I.D.S. and D.S.; Writing – original draft, A.V. and A.K.P.; Writing – review & editing, A.V., A.K.P., R.C., S.S., F.M. and D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Ioanna Danai Styliari thanks the EPSRC EP/N025075/1 for funding. Domenico Sagnelli thanks the Danish council of research (7026-00060B). Amanda K. Pearce would like to thank the European Research Council for funding (grant number 615142). Silvia Schenone and Francesca Musumeci thanks the Italian MIUR project PRIN 2017 (2017SA5837_004). Robert Cavanagh thanks the EPSRC for funding (EP/N006615/1).
Acknowledgments
Laboratory technician Denitsa Vladimirova Stefanov, University of Copenhagen, is acknowledged for highly skilled technical assistance carrying out the TSI in vitro upper gastrointestinal tract simulation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, L.S.; Kost, J.; Yan, F.; Spiro, R.C. Hydrogels from biopolymer hybrid for biomedical, food, and functional food applications. Polymers (Basel) 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swainson, S.M.E.; Styliari, I.D.; Taresco, V.; Garnett, M.C. Poly (glycerol adipate) (PGA), an enzymatically synthesized functionalizable polyester and versatile drug delivery carrier: A literature update. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagnelli; Cavanagh; Xu; Swainson; Blennow; Duncan; Taresco; Howdle Starch/poly (glycerol-adipate) nanocomposite film as novel biocompatible materials. Coatings 2019, 9, 482. [CrossRef]
- Taresco, V.; Creasey, R.G.; Kennon, J.; Mantovani, G.; Alexander, C.; Burley, J.C.; Garnett, M.C. Variation in structure and properties of poly(glycerol adipate) via control of chain branching during enzymatic synthesis. Polymer (Guildf) 2016, 89, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, G.; Satturwar, P.; Jones, M.C.; Furtos, A.; Leroux, J.C. Polymeric micelles for oral drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, R.C.; Geraldes, D.C.; Beraldo-De-Araújo, V.L.; Costa, J.S.R.; Oliveira-Nascimento, L. Pharmacokinetic aspects of nanoparticle-in-matrix drug delivery systems for oral/buccal delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthan, T.; Hoover, R. Barley starch: Production, properties, modification and uses. Starch 2009, 601–628. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, S.; Bertoft, E. The molecular structures of starch components and their contribution to the architecture of starch granules: A comprehensive review. Starch/Staerke 2010, 62, 389–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnelli, D.; Hebelstrup, K.H.; Leroy, E.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Guilois, S.; Kirkensgaard, J.J.K.; Mortensen, K.; Lourdin, D.; Blennow, A. Plant-crafted starches for bioplastics production. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, A.; Engelsen, S.B. Helix-breaking news: Fighting crystalline starch energy deposits in the cell. Trends Pant Sci 2010, 15, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA-Approved Protein Kinase Inhibitors/US Food and Drug Administration Approved Small Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Available online: http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:http://www.brimr.org/PKI/PKIs.htm (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Search of: Kinase Inhibitors | Recruiting, Not yet Recruiting, Active, not Recruiting, Enrolling by Invitation Studies - List Results - ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=kinase+inhibitors&Search=Apply&recrs=b&recrs=a&recrs=f&recrs=d&age_v=&gndr=&type=&rslt= (accessed on 21 October 2019).
- Bhullar, K.S.; Lagarón, N.O.; McGowan, E.M.; Parmar, I.; Jha, A.; Hubbard, B.P.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Kinase-targeted cancer therapies: Progress, challenges and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbrink, M.; Nuijen, B.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Variability in bioavailability of small molecular tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharmacokinetic Considerations and Challenges in Oral Anticancer Drug Therapy | Perspective Article | Pharmaceutical Journal. Available online: https://www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/research/perspective-article/pharmacokinetic-considerations-and-challenges-in-oral-anticancer-drug-therapy/20206478.article?firstPass=false (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Matteoni, S.; Abbruzzese, C.; Matarrese, P.; De Luca, G.; Mileo, A.M.; Miccadei, S.; Schenone, S.; Musumeci, F.; Haas, T.L.; Sette, G.; et al. The kinase inhibitor SI113 induces autophagy and synergizes with quinacrine in hindering the growth of human glioblastoma multiforme cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallacara, A.L.; Passannanti, R.; Mori, M.; Iovenitti, G.; Musumeci, F.; Greco, C.; Crespan, E.; Kissova, M.; Maga, G.; Tarantelli, C.; et al. Identification of a new family of pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives as multitarget Fyn-Blk-Lyn inhibitors active on B- and T-lymphoma cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 181, 111545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintori, C.; Fallacara, A.L.; Radi, M.; Zamperini, C.; Dreassi, E.; Crespan, E.; Maga, G.; Schenone, S.; Musumeci, F.; Brullo, C.; et al. Combining X-ray crystallography and molecular modeling toward the optimization of pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines as potent c-Src inhibitors active in vivo against Neuroblastoma. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, M.; Tintori, C.; Musumeci, F.; Brullo, C.; Zamperini, C.; Dreassi, E.; Fallacara, A.L.; Vignaroli, G.; Crespan, E.; Zanoli, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines active in vivo on the Bcr-Abl T315I mutant. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5382–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, M.; Brullo, C.; Crespan, E.; Tintori, C.; Musumeci, F.; Biava, M.; Schenone, S.; Dreassi, E.; Zamperini, C.; Maga, G.; et al. Identification of potent c-Src inhibitors strongly affecting the proliferation of human neuroblastoma cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5928–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.; Sicilia, G.; Alazzo, A.; Singh, N.; Musumeci, F.; Schenone, S.; Spriggs, K.A.; Burley, J.C.; Garnett, M.C.; Taresco, V.; et al. Water solubility enhancement of pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives via miniaturized polymer-drug microarrays. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.M.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Soltan, M.K.; Abo-Kul, M.E. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of newly synthesized 4-substituted-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakavoli, M.; Bagherzadeh, G.; Vaseghifar, M.; Shiri, A.; Pordel, M.; Mashreghi, M.; Pordeli, P.; Araghi, M. Molecular iodine promoted synthesis of new pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives as potential antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Taylor, G.E.; Ellsworth, K.; Harris, G.; Painter, R.; Silver, L.L.; Young, K. Novel pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-based inhibitors of Staphlococcus aureus DNA polymerase III: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, Y.; Leo, E.; Zhang, H.; Marchand, C. DNA topoisomerases and their poisoning by anticancer and antibacterial drugs. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Luo, J.; Qiu, W.; Cai, L.; Anjum, S.; Li, B.; Hou, M.; Xie, G.; Sun, G. Inhibitory effect of camptothecin against rice bacterial brown stripe pathogen acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae RS-2. Molecules 2016, 21, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, T.G.; Mi, Z. The structural basis of camptothecin interactions with human serum albumin: Impact on drug stability. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.R.; Magnusson, J.P.; Watson, S.; Grabowska, A.M.; Wilkinson, R.W.; Alexander, C.; Pritchard, D. Camptothecin prodrug block copolymer micelles with high drug loading and target specificity. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 5320–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule formation by interfacial polymer deposition following solvent displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnelli, D.; Chessa, S.; Mandalari, G.; Di Martino, M.; Sorndech, W.; Mamone, G.; Vincze, E.; Buillon, G.; Nielsen, D.S.; Wiese, M.; et al. Low glycaemic index foods from wild barley and amylose-only barley lines. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplak, T.; Wiese, M.; Nielsen, S.; Van De Wiele, T.; Van Den Berg, F.; Nielsen, D.S. The Smallest Intestine (TSI) - A low volume in vitro model of the small intestine with increased throughput. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malde, A.K.; Zuo, L.; Breeze, M.; Stroet, M.; Poger, D.; Nair, P.C.; Oostenbrink, C.; Mark, A.E. An Automated force field Topology Builder (ATB) and repository: Version 1.0. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 4026–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziara, K.B.; Stroet, M.; Malde, A.K.; Mark, A.E. Testing and validation of the Automated Topology Builder (ATB) version 2.0: Prediction of hydration free enthalpies. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2014, 28, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, N.; Eichenberger, A.P.; Choutko, A.; Riniker, S.; Winger, M.; Mark, A.E.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. Definition and testing of the GROMOS force-field versions 54A7 and 54B7. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geerke, D.P.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. Force field evaluation for biomolecular simulation: Fenthalpies of solvation of polar and apolar compounds in various solvents. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hermans, J. Interaction models for water in relation to protein hydration. In Intermolecular Forces: Proceedings of the Fourteenth Jerusalem Symposium on Quantum Chemistry and Biochemistry Held in Jerusalem, Israel, April 13-16, 1981; Pullman, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N·log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordhan, D.; Swainson, S.M.E.; Pearce, A.K.; Styliari, I.D.; Lovato, T.; Burley, J.C.; Garnett, M.C.; Taresco, V. Poly(glycerol adipate): From a functionalized nanocarrier to a polymeric-prodrug matrix to create amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushrida, A.; Elhuni, I.; Taresco, V.; Marciani, L.; Stolnik, S.; Garnett, M.C. A simple and efficient method for polymer coating of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swainson, S.M.E.; Taresco, V.; Pearce, A.K.; Clapp, L.H.; Ager, B.; McAllister, M.; Bosquillon, C.; Garnett, M.C. Exploring the enzymatic degradation of poly(glycerol adipate). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira Do, J.; Foralosso, R.; Yilmaz, G.; Mastrotto, F.; King, P.J.S.; Xerri, R.M.; He, Y.; Van Der Walle, C.F.; Fernandez-Trillo, F.; Laughton, C.A.; et al. Poly(triazolyl methacrylate) glycopolymers as potential targeted unimolecular nanocarriers. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 21155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, R.; Booth, J.; Alexander, C.; Garnett, M.C.; Laughton, C.A. Multiscale modeling of drug-polymer nanoparticle assembly identifies parameters influencing drug encapsulation efficiency. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, E.R.; Taresco, V.; Al-Hachami, W.A.; Booth, J.; Treacher, K.; Tomasi, S.; Alexander, C.; Burley, J.; Laughton, C.A.; Garnett, M.C. In silico screening for solid dispersions: The trouble with solubility parameters and χFH. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4654–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brattain, M.G.; Fine, W.D.; Khaled, F.M.; Thompson, J.; Brattain, D.E. Heterogeneity of malignant cells from a human colonic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leibovitz, A.; Stinson, J.C.; McCombs, W.B.; McCoy, C.E.; Mazur, K.C.; Mabry, N.D. Classification of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 4562–4569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknæs, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.R.; Winter, P.S.; Lin, K.H.; Nussbaum, D.P.; Cakir, M.; Stein, E.M.; Soderquist, R.S.; Crawford, L.; Leeds, J.C.; Newcomb, R.; et al. A Landscape of therapeutic cooperativity in KRAS mutant cancers reveals principles for controlling tumor evolution. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk, N.; Mathy, A.; Boerrigter, L.; Ruijter, H.; Tielen, I.; de Jong, D.; Baas, P.; Burgers, S.; Nederlof, P. EGFR and KRAS mutations as criteria for treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Retro- and prospective observations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Young Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, E.J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 inhibition and sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation in camptothecin-induced human colon cancer cell death. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Washington, N.; Washington, C.; Wilson, C.W. Physiological Pharmaceutics, Barriers to Drug Absorption, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis Series in Pharmaceutics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).