The Surface Characterisation of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Modified via the Direct Sputter Deposition of Calcium Phosphate Thin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate Preparation
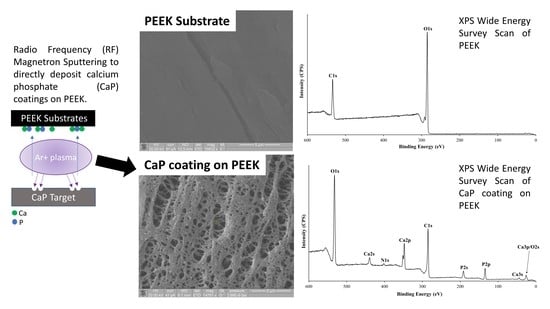
2.2. RF Magnetron Sputter Deposition
2.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
2.4. Time of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToFSIMS)
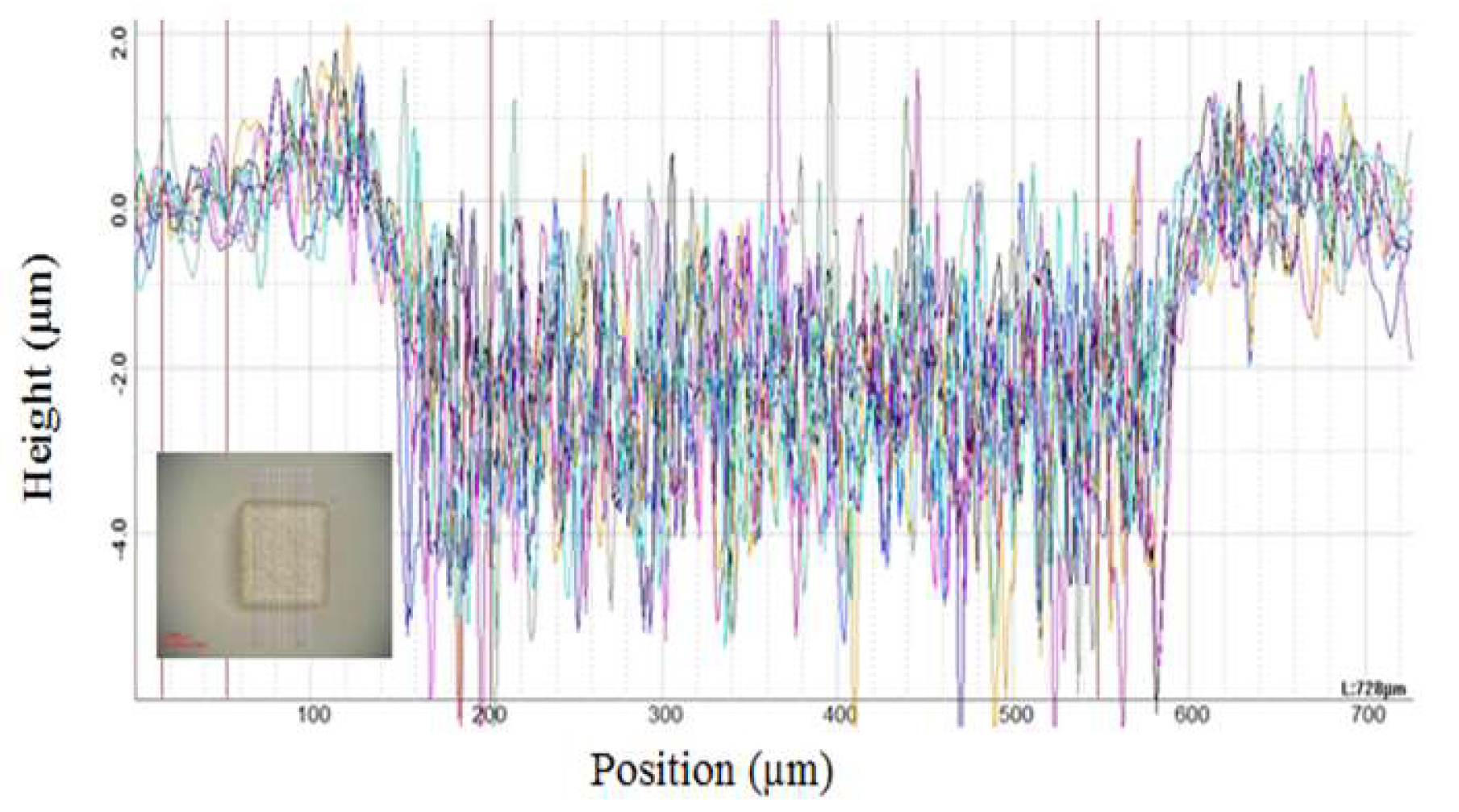
2.5. Optical Profilometry
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy Experimental Parameters
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SEM Analysis of Time Deposition Study
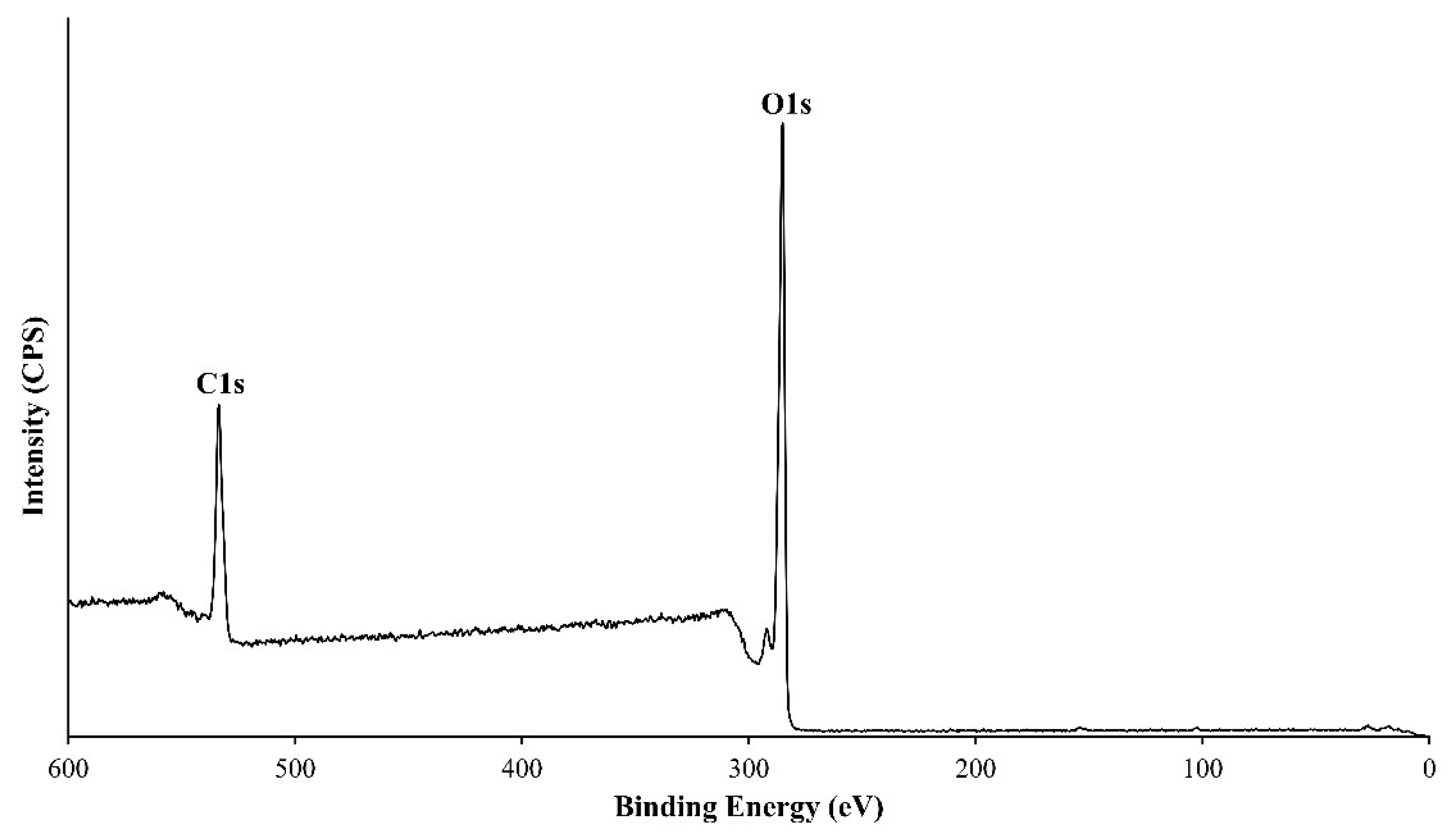
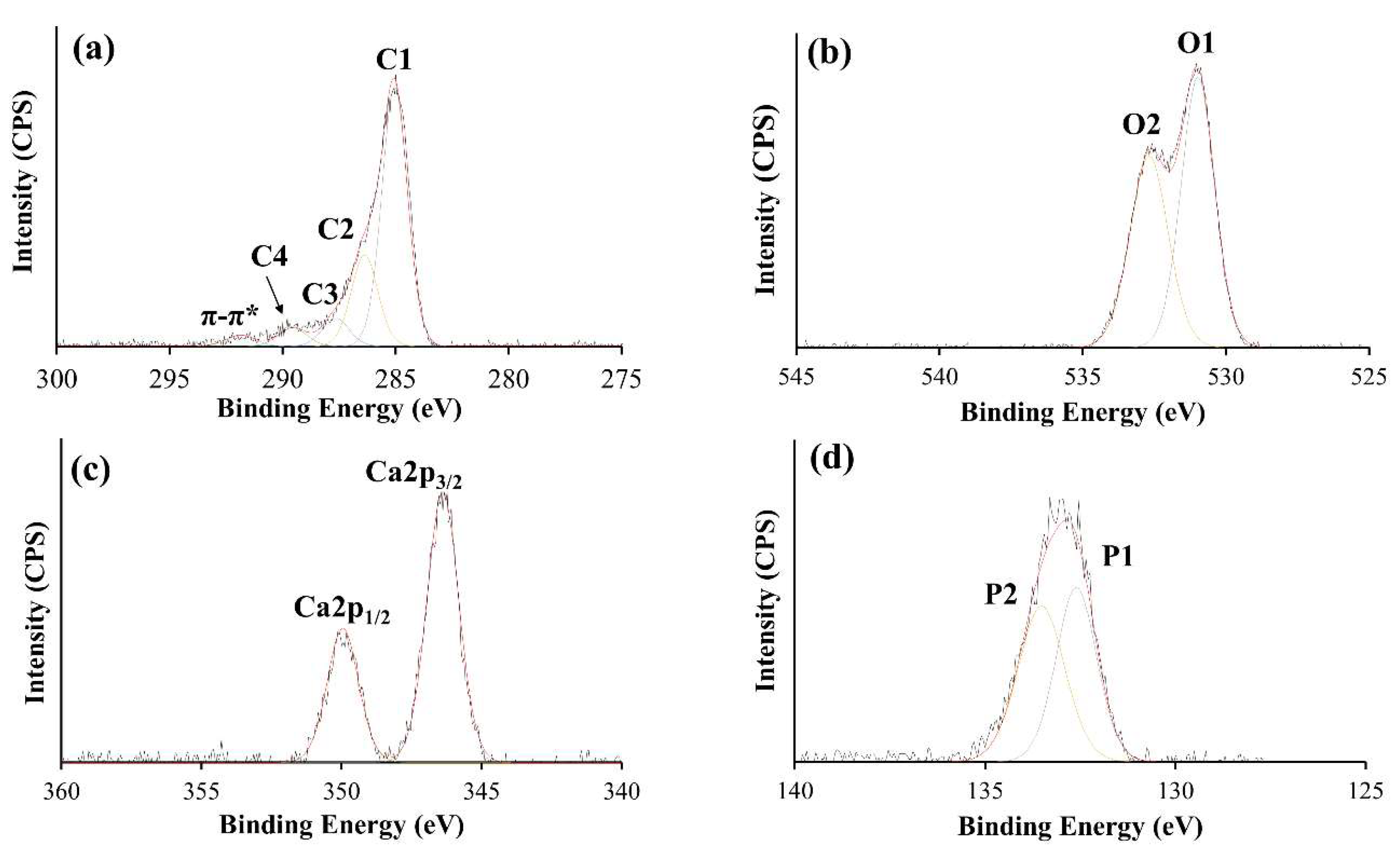
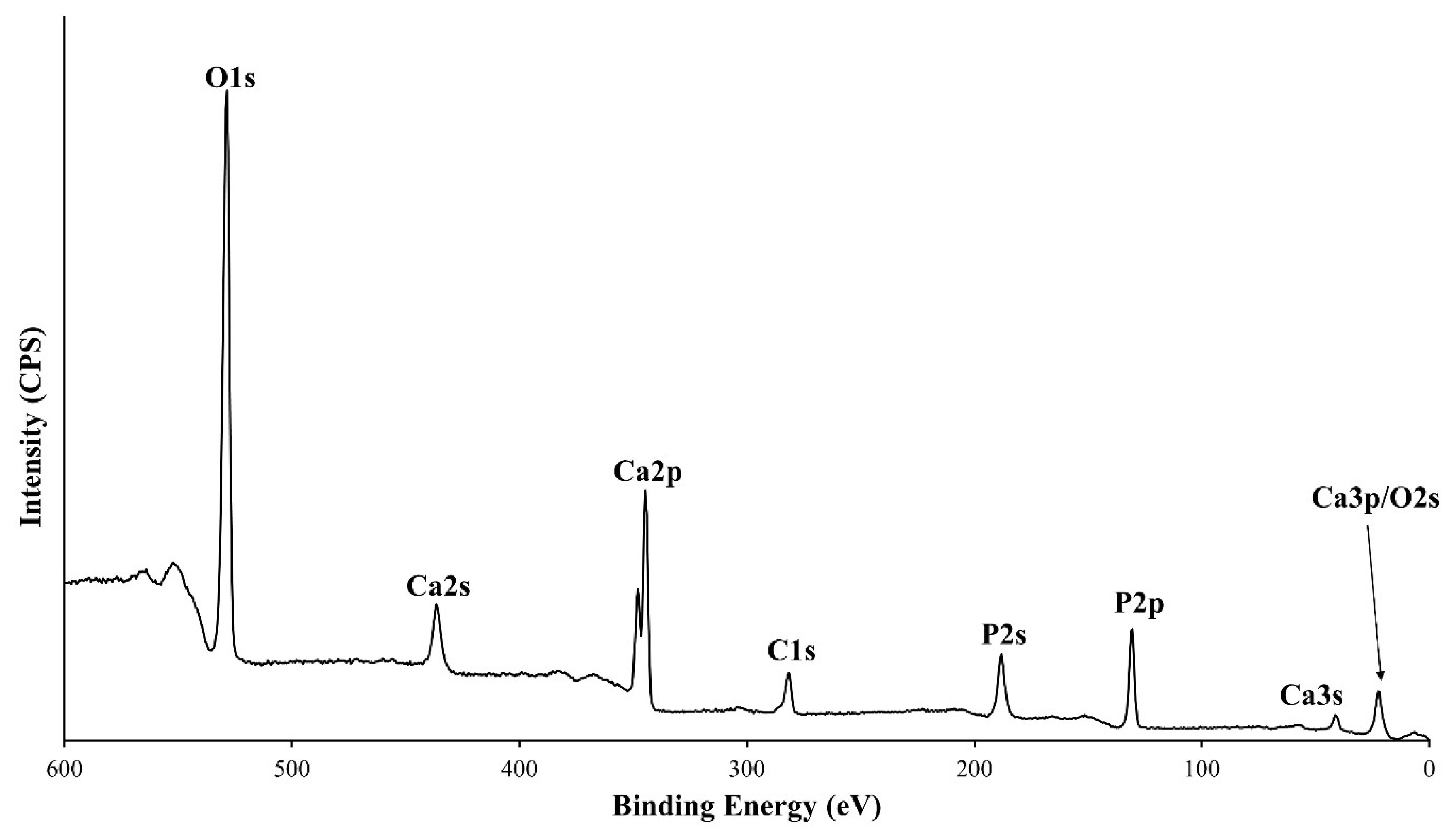
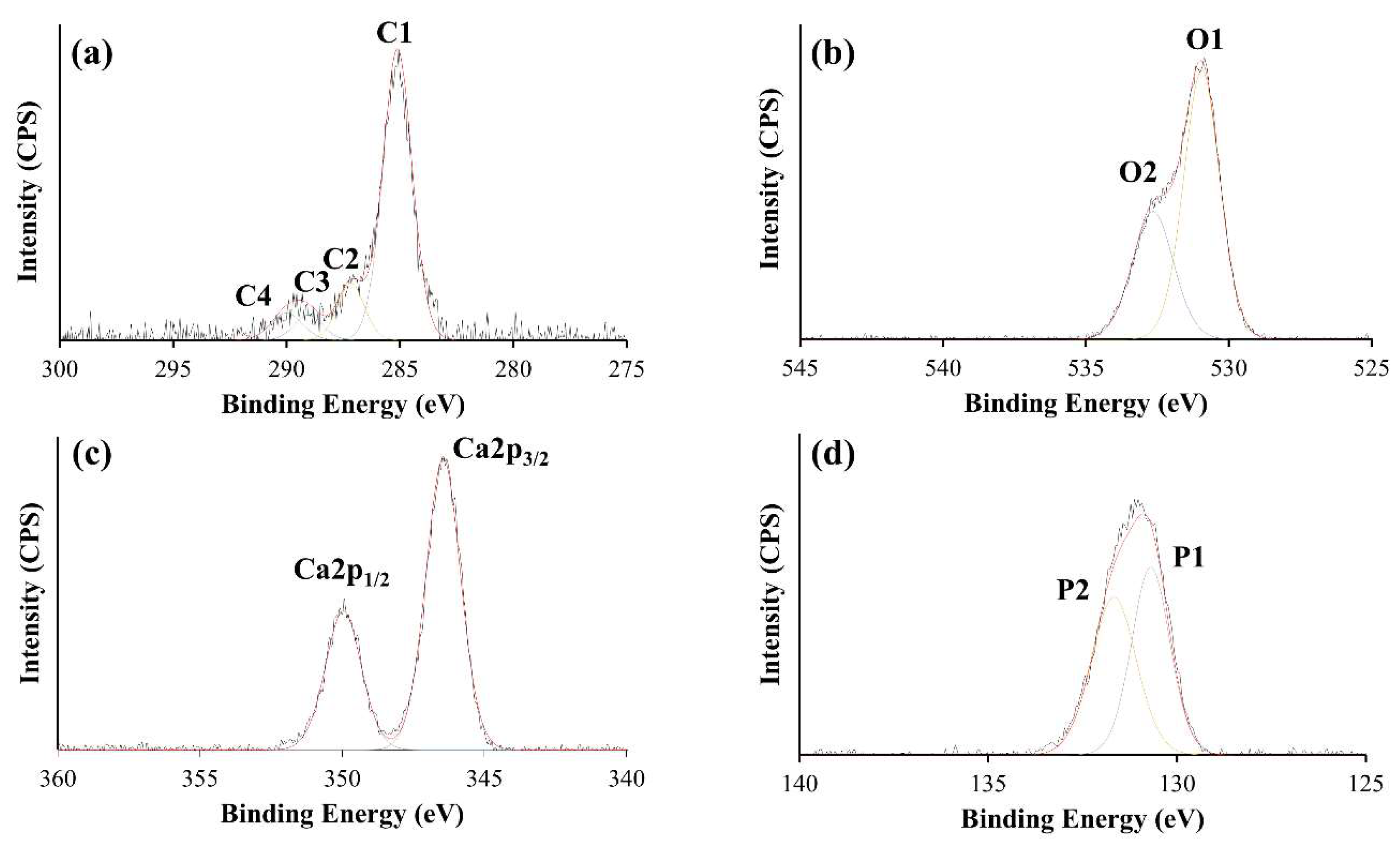
3.2. XPS Analysis
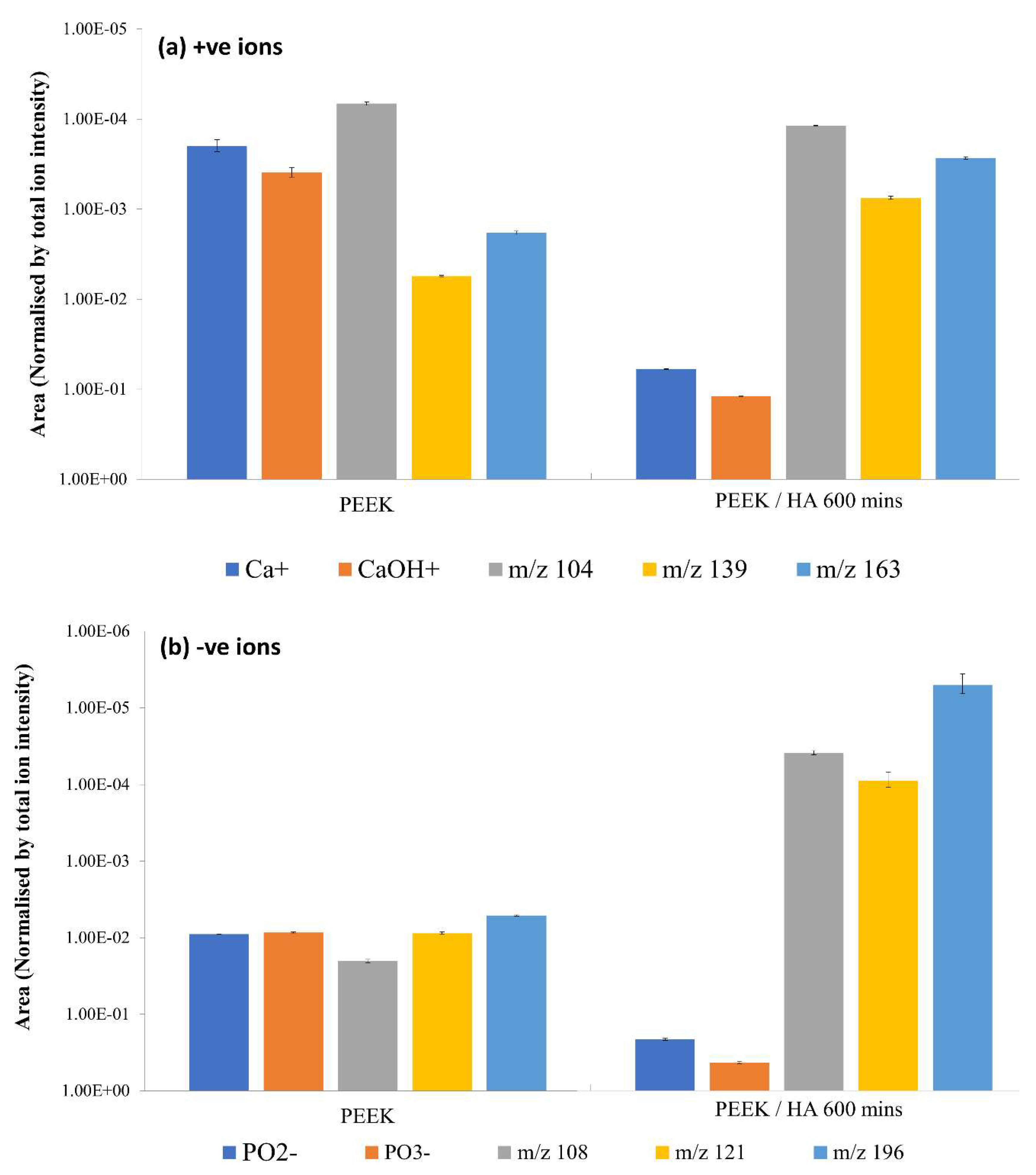
3.3. ToFSIMS Study
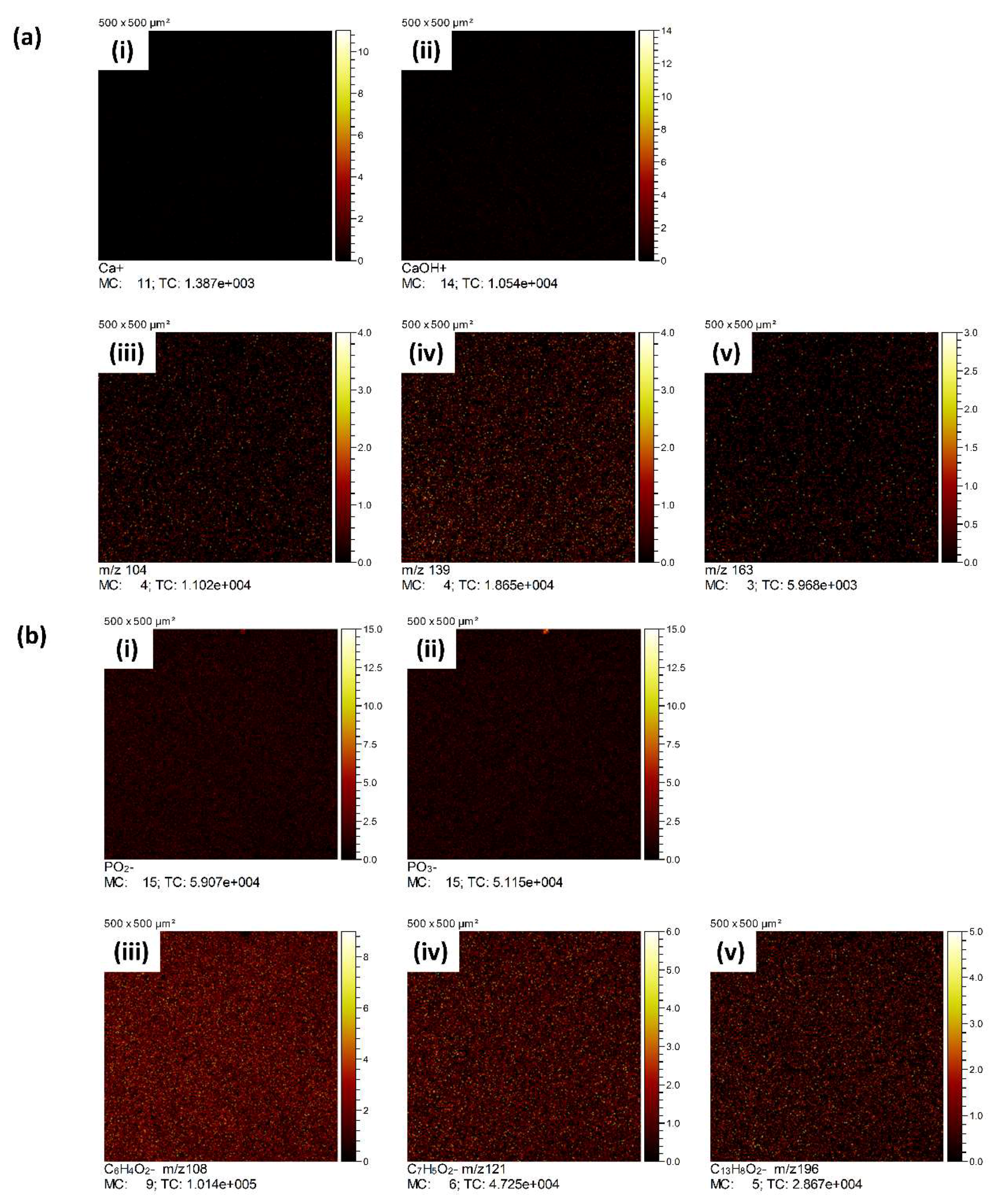
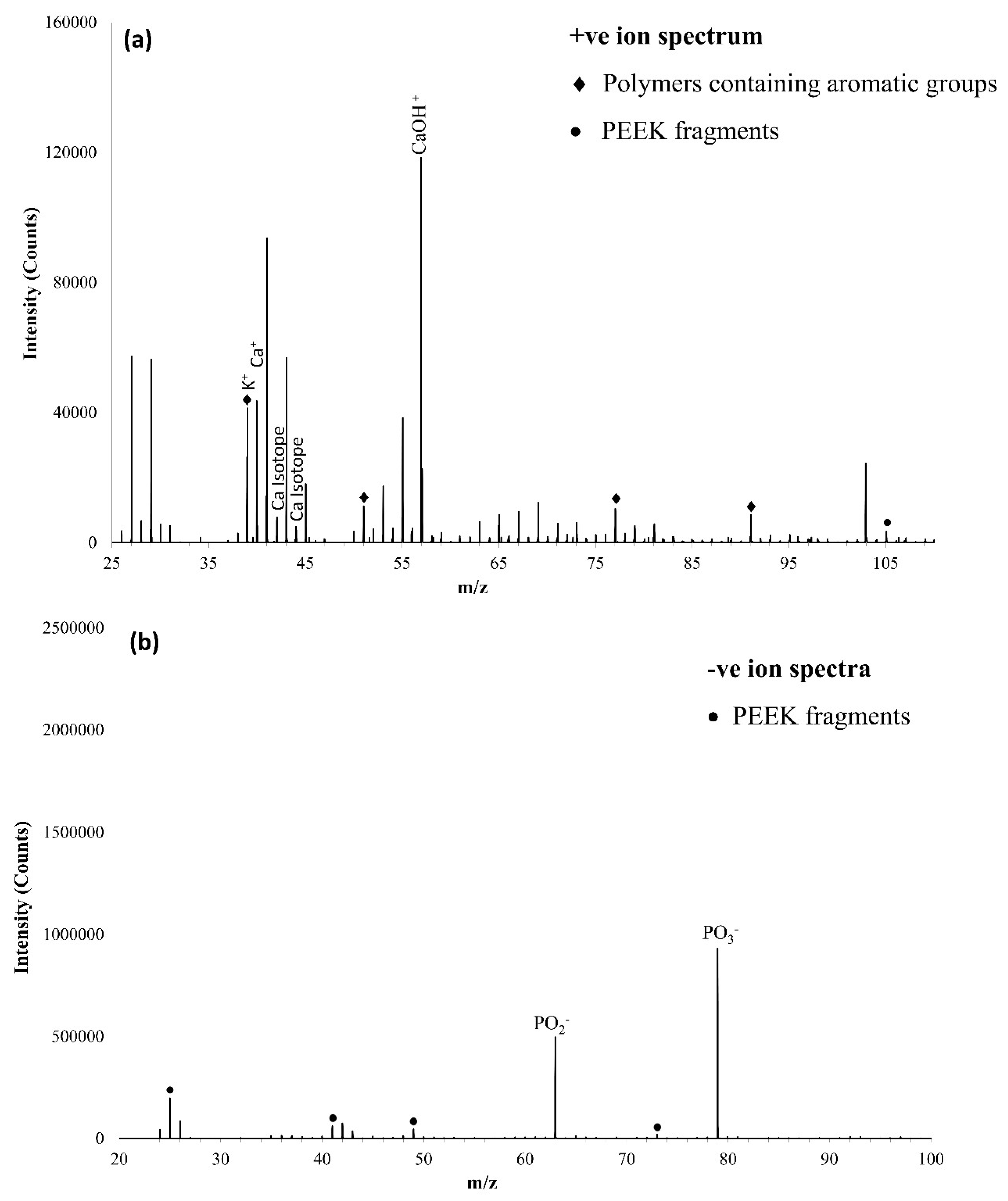
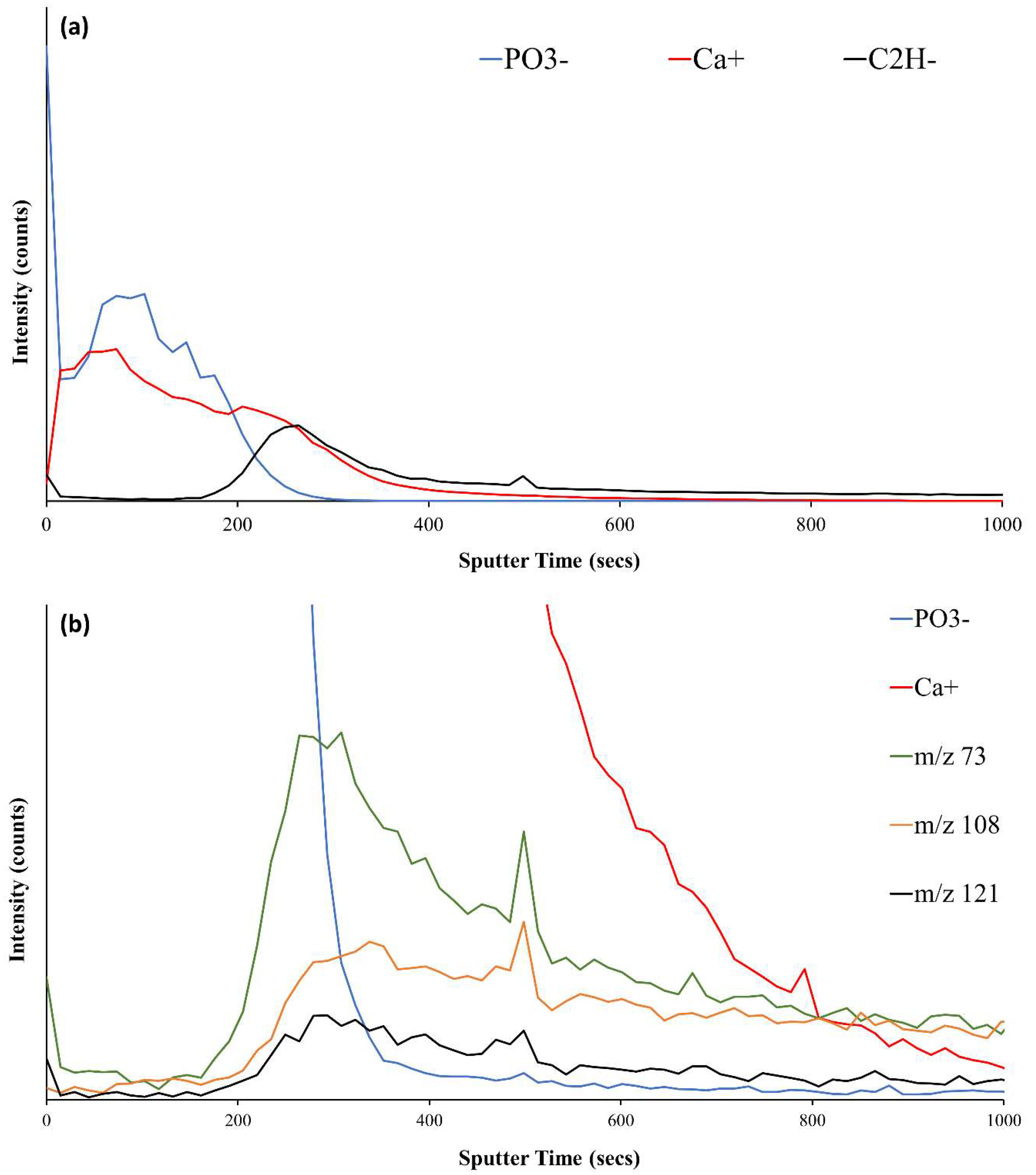
3.3.1. ToFSIMS Analysis of PEEK
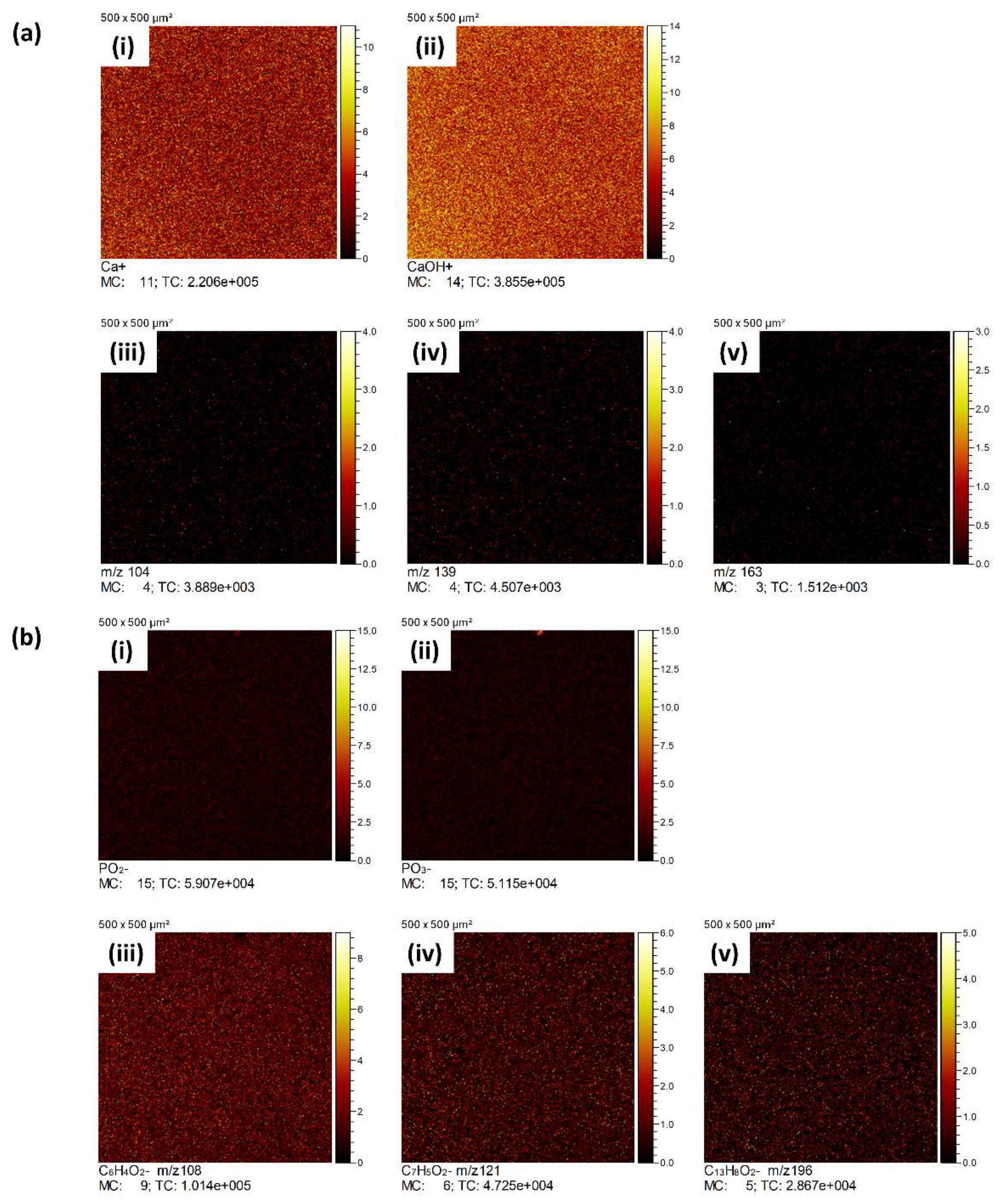
3.3.2. ToFSIMS Analysis of CaP Deposited onto PEEK over Time
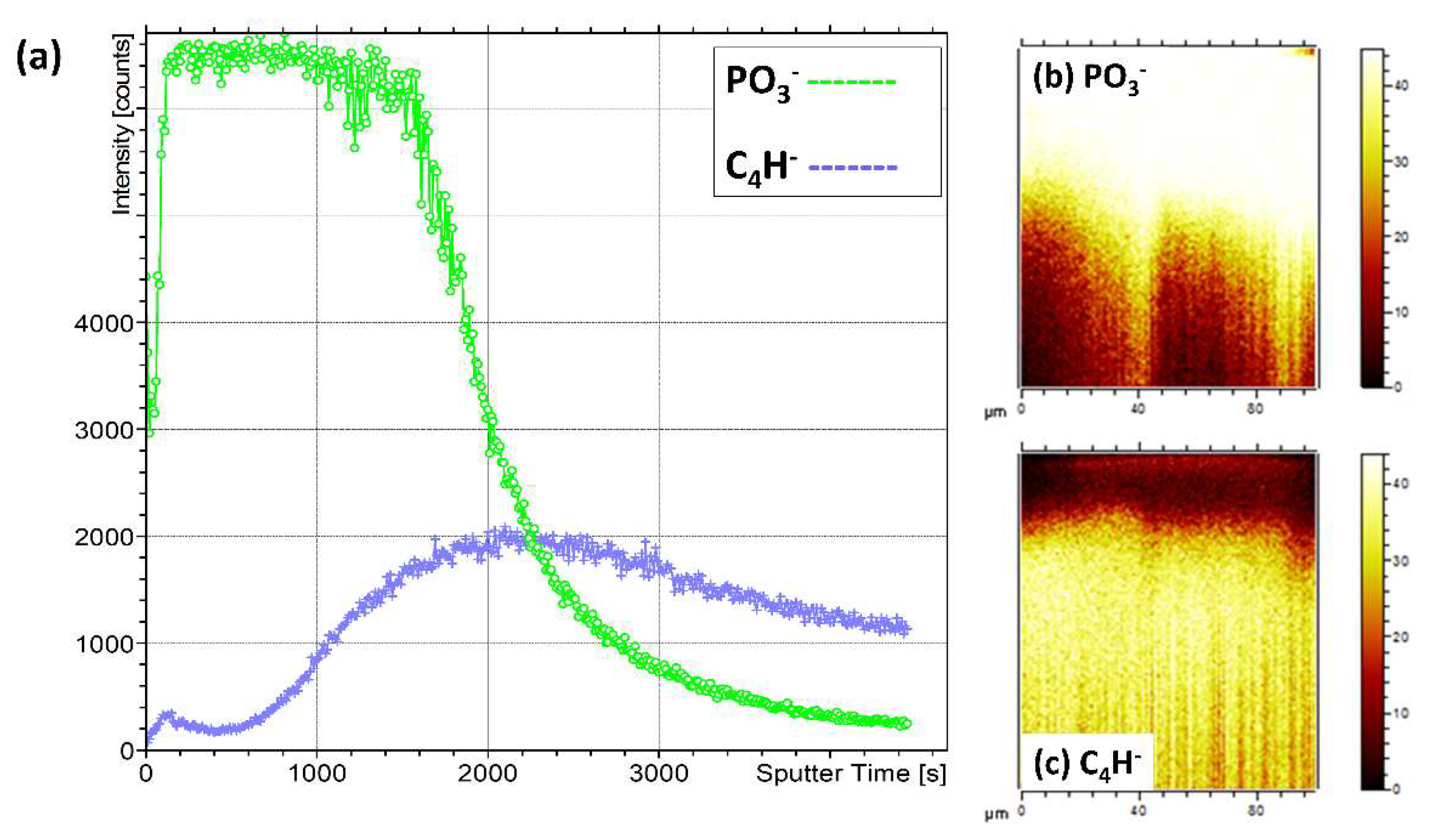
3.3.3. ToFSIMS Depth Profile of CaP Sputter Coated PEEK (HA600)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabiei, A.; Sandukas, S. Processing and evaluation of bioactive coatings on polymeric implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. A 2013, 101, 2621–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.W.; Kirch, M.; Birchler, F.; Eckert, K.L.; Mayer, J.; Wintermantel, E.; Sittig, C.; Pfund-Klingenfuss, I.; Textor, M.; Spencer, N.D.; et al. Surface activation of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and formation of calcium phosphate coatings by precipitation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1997, 8, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, A.R.; Rutledge, L.; Randolph, L.D.; Meenan, B.J. Strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings deposited via a co-deposition sputter technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 46, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloria, A.; Manto, L.; Santis, R.D.E.; Ambrosio, L. Biomechanical behavior of a novel composite intervertebral body fusion device. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2008, 6, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gloria, A.; Russo, T.; D’Amora, U.; Santin, M.; Santis, R.; De Ambrosio, L. Customised multiphasic nucleus/annulus scaffold for intervertebral disc repair/regeneration. Connect. Tissue Res. 2019, 61, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, R.M.; Correia-Pinto, J.L.; Reis, R.C.; Duarte, A.R.C. Advancing spinal fusion: Interbody stabilization by in situ foaming of a chemically modified polycaprolactone. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kane, C.; Duffy, H.; Meenan, B.J.; Boyd, A.R. The influence of target stoichiometry on the surface properties of sputter deposited calcium phosphate thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 203, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storrie, H.; Stupp, S.I. Cellular response to zinc-containing organoapatite: An in vitro study of proliferation, alkaline phosphatase activity and biomineralization. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5492–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.B.; Campbell, C.T.; Graham, D.J.; Ratner, B.D. Surface characterization of hydroxyapatite and related calcium phosphates by XPS and TOF-SIMS. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aina, V.; Bergandi, L.; Lusvardi, G.; Malavasi, G.; Imrie, F.E.; Gibson, I.R.; Cerrato, G.; Ghigo, D. Sr-containing hydroxyapatite: Morphologies of HA crystals and bioactivity on osteoblast cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolke, J.G.C.; Van Der Waerden, J.P.C.M.; De Groot, K.; Jansen, J.A. Stability of radiofrequency magnetron sputtered calcium phosphate coatings under cyclically loaded conditions. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.D.; Xu, S.; Cai, J.W.; Jiang, N.; Lu, J.H.; Ostrikov, K.N.; Diong, C. Structure, bonding state and in-vitro study of Ca–P–Ti film deposited on Ti6Al4V by RF magnetron sputtering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 20, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolbasov, E.N.; Rybachuk, M.; Golovkin, A.S.; Antonova, L.V.; Shesterikov, E.V.; Malchikhina, A.I.; Novikov, V.; Anissimov, Y.; Tverdokhlebov, S. Surface modification of poly (l-lactide) and polycaprolactone bioresorbable polymers using RF plasma discharge with sputter deposition of a hydroxyapatite target. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tverdokhlebov, S.I.; Bolbasov, E.N.; Shesterikov, E.V.; Antonova, L.V.; Golovkin, A.S.; Matveeva, V.G.; Petlin, D.; Anissimov, Y. Modification of polylactic acid surface using RF plasma discharge with sputter deposition of a hydroxyapatite target for increased biocompatibility. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 329, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tverdokhlebova, S.I.; Bolbasova, E.N.; Shesterikova, E.V.; Malchikhinaa, A.L.; Novikovb, V.A.; Anissimovc, Y.G. Research of the surface properties of the thermoplastic copolymer of vinilidene fluoride and tetrafluoroethylene modified with radio-frequency magnetron sputtering for medical application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socol, G.; Macovei, A.M.; Miroiu, F.; Stefan, N.; Duta, L.; Dorcioman, G.; Mihailescu, I.; Petrescu, S.; Stan, G.; Marcov, D.; et al. Hydroxyapatite thin films synthesized by pulsed laser deposition and magnetron sputtering on PMMA substrates for medical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2010, 169, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Tyurin, A.I.; Pirozhkova, T.S.; Shuvarin, I.A.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M.; Chaikina, M.; Surmenev, R.A. Fabrication and physico-mechanical properties of thin magnetron sputter deposited silver-containing hydroxyapatite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.; Verhoeven, J.; Marée, C.H.M.; Habraken, F.H.P.M.; Jansen, J.A. Study of the influence of oxygen on the composition of thin films obtained by r.f. sputtering from a Ca5(PO4)3 OH target. Thin Solid Film. 1997, 304, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.R.; Rutledge, L.; Randolph, L.D.; Mutreja, I.; Meenan, B.J. The deposition of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.R.; O’Kane, C.; Meenan, B.J. Control of calcium phosphate thin film stoichiometry using multi-target sputter deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 233, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Durand, D.; Chassenieux, C.; Jyotishkumar, P. Handbook of Biopolymer-Based Materials: From Blends and Composites to Gels and Complex Networks; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Guide to Charge Control and Charge Referencing Techniques in X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; ASTM Standard E 1523-03; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, P.C.; Blundell, D.J. X-ray data for poly (aryl ether ketones). Polymer 1980, 21, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.W.; Hauert, R.; Ernst, K.H.; Wintermantel, E. Surface analysis of chemically-etched and plasma-treated polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for biomedical applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1997, 96, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, P.; Sadras, B.; Decobert, F.; Arefi-Khonsari, F.; Amouroux, J. Enhancement of the adhesive bonding properties of PEEK by excimer laser treatment. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 1998, 18, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comyn, J.; Mascia, L.; Xiao, G.; Parker, B.M. Plasma-treatment of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for adhesive bonding. Spec Issue honour Dr K.W. Allen Occas his 70th Birthd. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 1996, 16, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneuse-Boxus, C.; Poleunis, C.; De-Ro, A.; Adriaensen, Y.; Bertrand, P.; Marchand-Brynaert, J. Surface functionalization of PEEK films studied by time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Surf. Interface Anal. 1999, 27, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawson, D.J.; Ameen, A.P.; Short, R.D.; Denison, P.; Jones, F.R. An investigation of the surface chemistry of poly (ether etherketone). I. The effect of oxygen plasma treatment on surface structure. Surf. Interface Anal. 1992, 18, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamson, G.; Briggs, D. High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers; The scienta ESCA300 Database; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lub, J.; van Vroonhoven, F.C.M.; van Leyen, D.; Benninghoven, A. Static secondary ion mass spectrometry analysis of polycarbonate surfaces. Effect of structure and of surface modification on the spectra. Polymer 1988, 29, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louette, P.; Bodino, F.; Pireaux, P.P. Poly (ether ether ketone) (PEEK) XPS reference core level and energy loss spectra. Surf. Sci. Spectra 2005, 12, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuccini, C.; Torricelli, P.; Sima, F.; Boanini, C.; Ristoscu, C.; Bracci, B.; Socol, G.; Fini, M.; Mihailescu, I.; Bigi, A. Strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings synthesized by pulsed-laser deposition: In vitro osteoblast and osteoclast response. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, B.D.; Park, D.S.; Choi, J.J.; Ryu, J.; Yoon, W.H.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.-W.; Ahn, C.-W.; Kim, H.-E.; Yoon, B.-H.; et al. Osteoconductive hydroxyapatite coated PEEK for spinal fusion surgery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutreja, I. Controlled Dissolution of CaP Thin Films via Surface Engineering; Ulster University: Coleraine, Ireland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Almasi, D.; Izman, S.; Assadian, M.; Ghanbari, M.; Abdul Kadir, M.R. Crystalline ha coating on peek via chemical deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Leng, Y.; Weng, L.T. Characterization of chemical inhomogeneity in plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.C.; Ciliberto, E.; Fragal’a, I.; Spoto, G. Surface and bulk study of calcium phosphate bioceramics obtained by Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 1996, 116, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Grubova, I.Y.; Chernozem, R.V.; Krause, B.; Baumbach, T.; Loza, K.; Epple, M. RF magnetron sputtering of a hydroxyapatite target: A comparison study on polytetrafluorethylene and titanium substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, B.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jansen, J.A.; Vredenberg, A.M. Radio frequency magnetron sputtering deposition of calcium phosphate coatings: Monte Carlo simulations of the deposition process and depositions through an aperture. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.; Schaeken, H.; Wolke, J.; Jansen, J. Influence of annealing temperature on RF magnetron sputtered calcium phosphate coatings. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Mauli Agrawal, C.; Ong, J.L. Effect of post-deposition heating temperature and the presence of water vapor during heat treatment on crystallinity of calcium phosphate coatings. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 5131–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolke, J.G.C.; De Groot, K.; Jansen, J.A. In vivo dissolution behavior of various RF magnetron sputtered Ca-P coatings. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 39, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Z.; Chen, C.Z.; Yu, H.J.; Zhang, S.J. Application of magnetron sputtering for producing bioactive ceramic coatings on implant materials. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmenev, R.A. A review of plasma-assisted methods for calcium phosphate-based coatings fabrication. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2035–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harton, S.; Stevie, F.; Ade, H. Secondary ion mass spectrometry depth profiling of amorphous polymer multilayers using O2+ and Cs+ ion bombardment with a magnetic sector instrument. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2006, 24, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shin, M.; Brison, J.; Castner, D. ToF-SIMS depth profiling of trehalose: The Effect of analysis beam dose on the quality of depth profiles. Surf. Interface Anal. 2011, 43, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Evdokimov, K.E.; Pichugin, V.F.; Peitsch, T.; Epple, M. The influence of the deposition parameters on the properties of an rf-magnetron-deposited nanostructured calcium phosphate coating and a possible growth mechanism. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3600–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, E.O.; Mello, A.; Farina, M.; Rossi, A.M.; Rossi, A.L. Nanoscale analysis of calcium phosphate films obtained by RF magnetron sputtering during the initial stages of deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 279, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample Name | Deposition Time (min) | Pressure (Pa) | Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA10 | 10 | 2 | 150 |
| HA30 | 30 | 2 | 150 |
| HA60 | 60 | 2 | 150 |
| HA150 | 150 | 2 | 150 |
| HA300 | 300 | 2 | 150 |
| HA450 | 450 | 2 | 150 |
| HA600 | 600 | 2 | 150 |
| Deposition Time (min) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deposition Time (min) | 30 | 60 | 150 | 300 | 450 | 600 | |
| 10 | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 30 | - | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 60 | - | - | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 150 | - | - | - | - | *** | - | |
| 300 | - | - | - | - | *** | - | |
| 450 | - | - | - | - | - | *** | |
| Deposition Time (Min) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deposition Time (min) | 30 | 60 | 150 | 300 | 450 | 600 | |
| 10 | - | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 30 | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 60 | *** | *** | *** | ** | |||
| 150 | - | *** | - | ||||
| 300 | *** | - | |||||
| 450 | *** | ||||||
| Deposition Time (Min) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deposition Time (min) | 30 | 60 | 150 | 300 | 450 | 600 | |
| 10 | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 30 | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 60 | * | *** | *** | *** | |||
| 150 | ** | *** | *** | ||||
| 300 | * | ** | |||||
| 450 | - | ||||||
| Elements | Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA10 | HA60 | HA300 | HA600 | |
| O 1s (%) | 36.01 ± 0.48 | 44.91 ± 0.75 | 53.12 ± 0.78 | 58.46 ± 0.07 |
| C 1s (%) | 53.43 ± 0.53 | 37.85 ± 1.12 | 25.83 ± 0.59 | 14.63 ± 0.28 |
| Ca 2p (%) | 4.78 ± 0.11 | 7.87 ± 0.32 | 9.50 ± 0.29 | 12.47 ± 0.23 |
| P 2p (%) | 5.77 ± 0.25 | 9.38 ± 0.20 | 11.54 ± 0.16 | 14.43 ± 0.37 |
| Ca/P ratio | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 0.84 ± 0.03 | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 0.86 ± 0.04 |
| O/C ratio | 0.69 ± 0.02 | 1.23 ± 0.06 | 2.06 ± 0.08 | 4.0 ± 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, S.; Rutledge, L.; Acheson, J.G.; Meenan, B.J.; Boyd, A.R. The Surface Characterisation of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Modified via the Direct Sputter Deposition of Calcium Phosphate Thin Films. Coatings 2020, 10, 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111088
Hussain S, Rutledge L, Acheson JG, Meenan BJ, Boyd AR. The Surface Characterisation of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Modified via the Direct Sputter Deposition of Calcium Phosphate Thin Films. Coatings. 2020; 10(11):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111088
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Shahzad, Leanne Rutledge, Jonathan G. Acheson, Brian J. Meenan, and Adrian R. Boyd. 2020. "The Surface Characterisation of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Modified via the Direct Sputter Deposition of Calcium Phosphate Thin Films" Coatings 10, no. 11: 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111088
APA StyleHussain, S., Rutledge, L., Acheson, J. G., Meenan, B. J., & Boyd, A. R. (2020). The Surface Characterisation of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Modified via the Direct Sputter Deposition of Calcium Phosphate Thin Films. Coatings, 10(11), 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111088