Abstract
Spray pyrolysis of an aqueous solution of iron nitrate, proceeded with reduction of the product in hydrogen, gave iron powder with micron-sized hollow particles. Coating these iron particles with SiO2 through tetraethyl orthosilicate hydrolysis prevented interparticle electrical contacts and suppressed DC percolation. This material shows a high ferromagnetic resonance frequency of 18 GHz, low permittivity, and weighs 20% less than common carbonyl iron. Potential microwave applications are for inductors and electromagnetic interference shielding designs.
1. Introduction
The technology of ultrasonic spray pyrolysis has been known since the end of the last century []. It consists of the drying and thermal decomposition of aerosol drops. Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis allows micron-sized powders of metal oxides [] and metals [,,] to be produced. An ultrasonic atomizer sputters the initial salt solution that undergoes high temperatures. As a result, hollow microspheres are usually formed [,]. The reason for the “hollowness” of the particles is the balance between the high evaporation rate of the solvent from the droplet [] and the diffusion rate of the components of the droplet, e.g., ions, metal clusters, etc. []. Both the metal oxides and metals, when an additional reduction stage is implemented, can be produced starting from the metal salt solution. However, the list of metals that have already been studied is limited and further extension is of interest.
Recently, the synthesis of nickel oxide [] and metallic cobalt [,] by the spray pyrolysis technique was reported. It was shown that changes in the frequency of ultrasonic atomization and the concentration of the initial salt solution regulates the particle size of the final product [,]. In these papers, nitrate solutions of the Ni and Co (10 wt.%) at 1000 °C were applied as precursors. The frequency of the ultrasonic generator was 1.7 MHz in the experiment with nickel oxide [] and 1.7–2.2 MHz in the case of Co [,]. The typical diameter of the microspheres of nickel oxide and cobalt oxide was 5–7 μm and 1.5 μm [,], respectively. The difference in size can be explained by the influence of the frequency of the aerosol generator as well as by differences in surface activity of nickel and cobalt nitrate solutions. In the papers [,], cobalt oxide was reduced to the metal in the presence of hydrogen. This two-stage method allows the control of the properties of the product both at a first stage—synthesis of the metal oxide—and at a second stage—reduction of the metal oxide to the metal. For example, elemental composition, morphology, and particle size of oxides (NiO, Co3O4) may be controlled by changing the conditions of the ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. The final particle size, porosity, and purity of the metal can be controlled by changing the temperature during the reduction process.
There are no publications existing in the literature on the synthesis of iron powders using the described two-stage method. Fine iron powders are widely used for magnetic resonance imaging [], ferrofluids [], and electromagnetic compatibility [,].
It is known that the use of nano-sized magnetic metals (Fe, Co, and Ni) is limited due to uncontrolled oxidation, aggregation [,,], and spontaneous combustion when exposed to air []. An effective way to protect these metals from oxidation is to encapsulate chemically-active particles into an inorganic protective shell. A core-shell structure is therefore formed [,]. Silica, SiO2, may be used as a protecting material [,]. The “Metal@SiO2” core-shell microparticles not only possess improved chemical stability but also show advanced electromagnetic properties since the dielectric diamagnetic shell physically prevents interparticle contacts [,]. However, since the process of deposition of the shell on the metal particles is highly substrate-dependent, extensive studies are required for each new powder material.
This paper reports the preparation of hollow iron microspheres via ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Once obtained, the iron particles were coated with a protective SiO2 coating. Morphology, particle size distribution, chemical composition, and static magnetic properties of the final product were studied. For these purposes, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Mössbauer spectroscopy were applied. Complex microwave permeability (μ′ + i·μ″) and permittivity (ε′ + i·ε″) were measured by the Nicolson–Ross technique with the use of coaxial waveguide.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Iron Powder
Nanostructured iron microspheres were prepared using the two-stage method. First, an ultrasonic powder dispenser (Mist Maker, Ontario, CA, USA) was applied to the Fe(NO3)3 water solution (10 wt.%) to create an aerosol. The aerosol was then introduced into a tube furnace Nabertherm RT 50/250/13 (Naberterm GmbH, Lilienthal, Germany), where iron (III) nitrate was subjected to heat treatment at 1000 °C. High temperatures caused chemical decomposition following the reaction (1):
4Fe(NO3)3 → 2Fe2O3 + 12NO2 + 3O2
The product, which was iron (III) oxide, “Fe2O3”, was collected on a filter and then reduced in a furnace Carbolite HZS 12/600E (CARBOLITE GERO, Neuhausen, Germany) at a temperature of 400 °C with hydrogen. Finally, the metal was passivated in N2 for 12 h.
2.2. Core-Shell Fe@SiO2 Preparation
A thin SiO2 shell on the surface of the iron particles was prepared by hydrolysis of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) in a water–ethanol mixture [,,,,,,]. First, ethanol and TEOS sequentially were added to the iron powder, in a flask. The flask was placed in an ultrasonic bath, where for 5 min the solution was subjected to ultrasonic treatment and constant mechanical stirring. After half an hour, aqueous ammonia NH4OH was added. Ethanol, TEOS, and NH4OH were measured out at a volume proportion of 10:1:1, respectively. The resulting mixture was subjected to ultrasonic treatment for 2 h with additional mechanical stirring every 15 min. In the end, Fe@SiO2 precipitate was decanted using an external magnet and washed with ethanol until transparency of the liquid. The powder was dried for 24 h at 60 °C. The yield of the SiO2 was 10% by weight.
2.3. Analysis Techniques
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was carried out using a Difray 401 diffractometer (JSC Scientific Instruments, Saint Petersburg, Russia). The Bragg–Brentano geometry was applied. XRD was measured from 14° to 140° 2θ with 0.01° 2θ steps. Cr Kα1+α2 radiation (λ = 22,909 Å) was applied.
Mössbauer spectroscopy was studied in transmission geometry and at 78 K. A constant acceleration Mössbauer spectrometer Ms-1104 Em (Kordon, Rostov-na-Donu, Russia) and a 57Co source (Ritverc, 10 mCi) were applied. A UnivemMS 9.08 program was used to decompose the measured spectra. The isomer shifts were determined relative to the α-Fe spectrum at room temperature.
The morphology of the particles was studied using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) LEO EVO-50 XVP microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) equipped with an Oxford Instruments X-Act 10 mm device (Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK) for energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Particle size distribution was measured from the SEM-images. For this purpose, several SEM images were applied. Diameters of approximately 800 to 1000 particles were measured and used in the calculations. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed using a Jeol Jem-1400 microscope (Jeol, Tokyo, Japan); a copper grid with a carbon layer was applied.
Magnetic hysteresis was measured using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) at room temperature. The samples were cold-pressed (52 MPa) discs, 3 mm in diameter, 1 mm in height. Complex microwave permeability and permittivity were measured in a standard 7/3 coaxial airline by the Nicolson–Ross–Weir method [,] in the frequency range of 0.1–20 GHz. For the measurement, composites with paraffin wax as dielectric matrix were mixed with the obtained particles, and samples of toroidal form were prepared to fill the cross-section of the coaxial waveguide.
3. Results and Discussion
Three powder products were obtained sequentially in this study. The first step, spray pyrolysis, resulted in a fine powder of iron oxide, “Fe2O3”. Since this was just an intermediate product and no chemical properties were of interest, XRD analysis was not applied for the study of the “Fe2O3”. However, this intermediate product clearly showed as typical for this synthetic technique of hollow structure of particles, when observed in SEM. In the second step, iron oxide “Fe2O3” was reduced to iron, “Fe”, which was the primary goal of the paper. The third step was a modification of the “Fe” particles with a thin SiO2 shell, “Fe@SiO2”, carried out both for an increase in chemical stability and a decrease in interparticle conductivity when mixed with dielectric matrix to form composite material.
3.1. X-ray Analysis
XRD phase analysis (Figure 1) showed that the “Fe” sample contained α-Fe and Fe3O4 phases. The reflections of α-Fe were located at (110) 68.842° 2θ and (200) 106.199° 2θ, respectively. The lattice constant was 2.8633(3) Å, which coincided with the tabular value for the α-Fe, which is 2.867 Å (JCPDS card No. 65-4899). The crystallite size was 20 nm, which was calculated using the Scherrer formula []. The reference intensity ratio (RIR) technique [] was applied for the semi-quantitative phase analysis. The reference standard was Corundum. The following tabular values were used for calculations: I/Ic (α-Fe) = 10.77, JCPDS card No. 65-4899, and I/Ic (Fe3O4) = 5.03, JCPDS card No. 75-33. The RIR calculations showed that the α-Fe content was 95 wt.%, and Fe3O4 was 5 wt.% (≈ 11 at.%). It is noteworthy that the typical uncertainty of the RIR method normally as big as 10%–20%, was even bigger in this particular case, since the diffraction was measured using Cr radiation, but the I/Ic tabular values were given for Cu radiation. XRD results showed no presence of crystalline forms of SiO2, for the Fe@SiO2 sample.
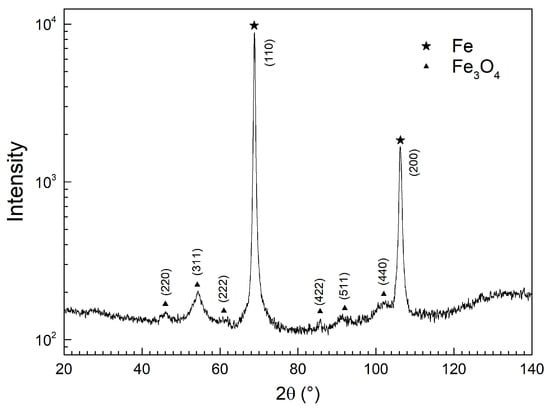
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction of the synthesized “Fe” powder. Intensity is given in logarithmic scale.
3.2. Mössbauer Spectroscopy
The Mössbauer spectra were recorded at RT and 78 K (Figure 2). They consist of two subspectra, which are better resolved at 78 K (Figure 2b). The major subspectrum includes two sextet components with the hyperfine parameters (Isomer Shifts (ISs) of ~0 mm/s; quadrupole splitting (ΔEQ) of ~0 mm/s, and hyperfine magnetic fields (Hf) of ~33 T at RT and IS ~0.1 mm/s, ΔEQ = 0 mm/s, Hf ~ 33.8 T at 78 K) corresponding to metal Fe0. The sextet with broad lines reflects the non-uniform surrounding of Fe atoms in the metal phase, presumably because of different structural defects. The sextet components of the second minor subspectrum are characterized by higher hyperfine field values (Hf ~ 36–44 T at RT and Hf ~ 37–50 T at 78 K) than that for metal Fe0. According to their isomer shifts, a part of them of ~11 at.% with Is ~ 0.24–0.4 mm/s at RT and Is ~ 0.3–0.45 mm/s at 78 K corresponds to Fe3+, while an another part of ~5–6 at.% corresponds to Fe2+ (Is ~ 0.9 mm/s at 78 K) []. This correlates well with the data of XRD phase analysis, which shows Fe3O4 presence, containing both Fe2+ and Fe3+ cations. Despite the components of oxide subspectra being notably broad, overlapping with Fe0 components and of low intensities, the total area can be estimated from the 78 K spectrum as ~15–17 at.%.
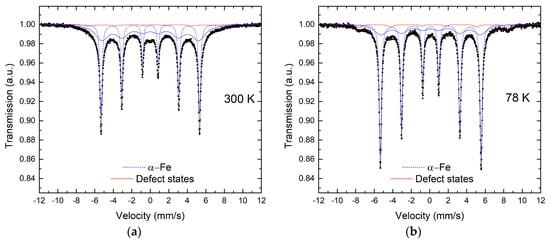
Figure 2.
Mössbauer spectrum measured of the synthesized “Fe” powder at (a) room temperature (RT) and (b) 78 K.
According to the results of semi-quantitative XRD, the fraction of the oxide phase is 11 at.%. The quantity of oxide phase established through the Mossbauer measurements (15–17 at.%) was higher than that calculated from the XRD data. This was because X-ray diffraction measured only a crystalline fraction of the specimen while the gamma-resonance is sensitive additionally to disordered matter.
3.3. SEM Analysis
The SEM images showed that the particles of all three products, “Fe2O3” (Figure 3a,d), “Fe” (Figure 3b,e), and “Fe@SiO2” (Figure 3c,f) were spherical with approximate diameter of 1 μm. The spherical shape is typical for powders, obtained with the spray pyrolysis technique [,]. The oxide reduction process did not change the average particle size. These spherical particles showed clearly a visible hollow structure (Figure 3). The thickness of “the wall” was about 0.25 of the particle diameter. The reduction of “Fe2O3” to “Fe” resulted in a porous structure (Figure 3), but the size and the “hollowness” of the particles were never affected. It can also be observed that the particles of the “Fe” powder were inhomogeneous, meaning polycrystalline, which is in accordance with the XRD data.
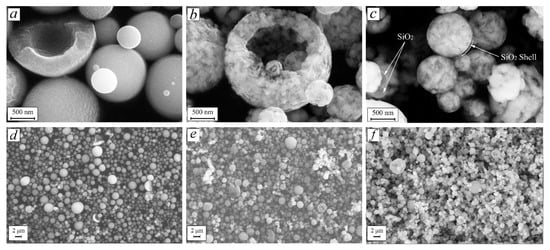
Figure 3.
Scanning electron microscopy images: (a,d) “Fe2O3”, (b,e) “Fe”, and (c,f) “Fe@SiO2” particles.
A very thin—sub-50 nm—shell was also observed in the SEM images of the “Fe@SiO2” sample (Figure 3). Local EDX analysis, which was measured from the “Fe@SiO2” sample, confirmed the presence of Si. The silicon to iron ratio was estimated at 15/85 at.%. Both the core-shell “Fe@SiO2” particles and individual SiO2 spheres presented in the powder, which was in accordance with reference []. The Fe particles have a porous structure (Figure 3b). After coating, the porous morphology of the iron particles can still be distinguished through a thin SiO2 layer (Figure 3c). Pure SiO2 particles appear as semi-transparent spheres, which is opposed to the complicated nano-structure of Fe@SiO2 particles.
The particle size distribution for the “Fe” and “Fe@SiO2” samples is given in Figure 4. The size range was 0.1–2 μm, the maximum of the both distributions was at 0.6 μm. Individual SiO2 particles influenced the particle size distribution contributing to the region of 0.2–0.6 μm.
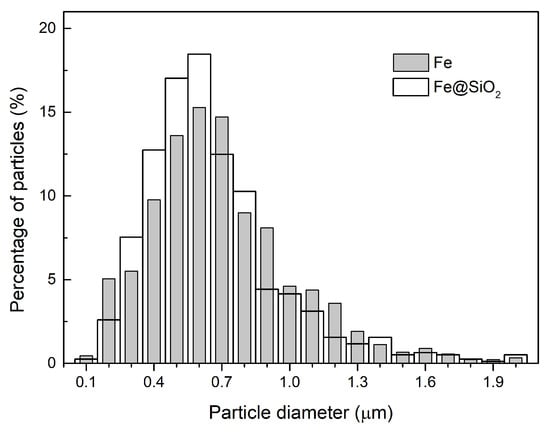
Figure 4.
Particle size distribution measured from the SEM images of the “Fe” and “Fe@SiO2” powders.
The size of the obtained iron particles was lower than those previously reported for Co and Ni [,]. The factors that influence the size of the aerosol droplets during atomization are as follows: frequency of ultrasonic treatment, the concentration of the initial salt solution, and the surface activity of the initial salt. Since the concentration of iron nitrate solution was identical to concentrations of cobalt and nickel nitrate solutions applied in refs. [,], the difference in particle size of the resulting product was probably caused by a different ultrasonication regime and the surface activity of the chemicals.
3.4. TEM Analysis
The SiO2 shell appeared as a semi-transparent layer on a surface of non-transparent iron cores. The difference in transparency was due to the difference in electron density of these two materials. TEM images showed that the SiO2 coating was uniform and of 20 nm thickness on the iron particle surface (Figure 5). Individual SiO2 particles were also observed in the TEM images which was in accordance with the SEM analysis.
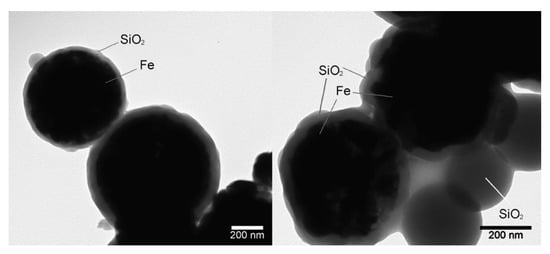
Figure 5.
Transmission electron images of the “Fe@SiO2” particles.
3.5. Magnetic Properties
The saturation magnetization (MS) of the “Fe” and “Fe@SiO2” samples was 184 ± 9 emu/g and 157 ± 12 emu/g, respectively. The measurement results are presented in Figure 6.
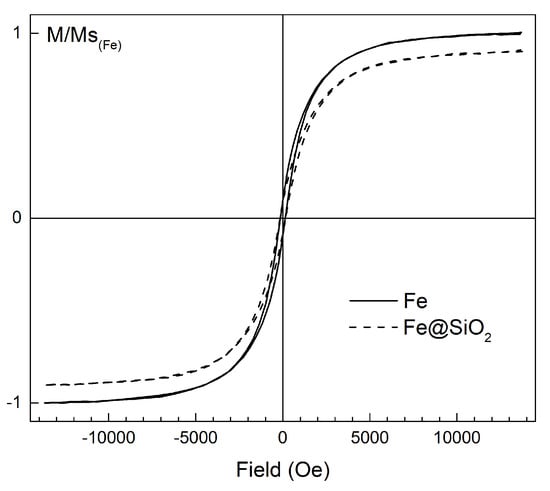
Figure 6.
Normalized hysteresis loops measured from the “Fe” and “Fe@SiO2” cold-pressed samples.
The saturation magnetization for carbonyl iron (CI) ranges from 190 to 250 emu/g [,]. CI is usually considered as widespread commercially available etalon of pure iron powder. According to [], the MS value depends on the size of the magnetic particles and is 190 ± 8 emu/g for purses 2–5 microns in size. As was reported earlier, the chemical process of the deposition of the SiO2 onto the surface of iron particles did not influence the chemical state of the iron []. Since the only reason for the decrease of ~15% in the MS value of the “Fe@SiO2” powder in comparison with the MS of the pure “Fe” powder was the substitution of iron with some of the mass of the diamagnetic phase, the fraction of the SiO2 shell was estimated at 15 wt.%. This value roughly equals 25 vol.%, taking into account the density of amorphous silica of 2.10 g/cm3 [] and the measured 6.1 g/cm3 density of the hollow microspheres through displacement of liquid. According to EDX results, the volume fraction of SiO2 is 16 wt.%.
The coercivity HC of the hollow Fe particles was 157 ± 11 Oe, which was higher than that of carbonyl iron (3–20 Oe [,]). The high HC value was probably caused by the presence of the oxidized surface and defect nanostructure of the particles. According to [], high HC values (250–400 Oe) are typical for cobalt ferromagnetic particles obtained by the spray pyrolysis technique.
The value of the measured pycnometric density for the “Fe” sample (6.1 g/cm3) is lower than for CI (7.8 g/cm3, this value was measured under exactly the same conditions as the density of the “Fe” powder) which gives a potential advantage when used in composites with a large portion of magnetic filler due to lower weight of composite.
3.6. Microwave Measurements
The microwave permeability (μ′ + i·μ″) and permittivity (ε′ + i·ε″) of the composites with a wax matrix and a filler mass fraction of 33, 50, and 66 wt.% were measured. The results are given in Figure 7 and Figure 8 for the “Fe” and “Fe@SiO2” samples, respectively. The complex microwave permeability of the composites was similar for both “Fe” and “Fe@SiO2” particles. The permeability of the composites with “Fe@SiO2” particles was lower by approximately 14% than composites with “Fe” particles (Figure 9, Table 1). This was due to the presence of the diamagnetic phase, SiO2.
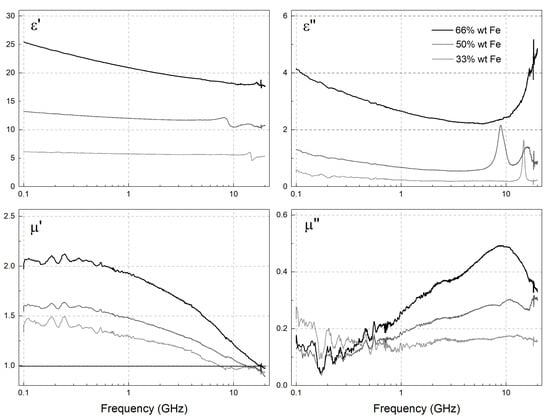
Figure 7.
The measured frequency dependences of microwave permeability (μ′ + i·μ″) and permittivity (ε′ + i·ε″) of the composites comprising the paraffin wax matrix and the “Fe” powder.
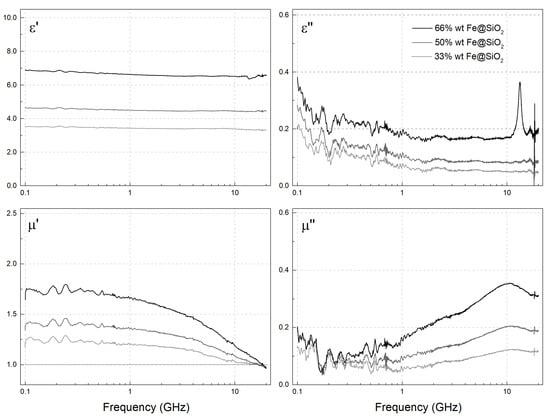
Figure 8.
The measured frequency dependences of microwave permeability (μ′ + i·μ″) and permittivity (ε′ + i·ε″) of the composites comprising the paraffin wax matrix and “Fe@SiO2“powder.
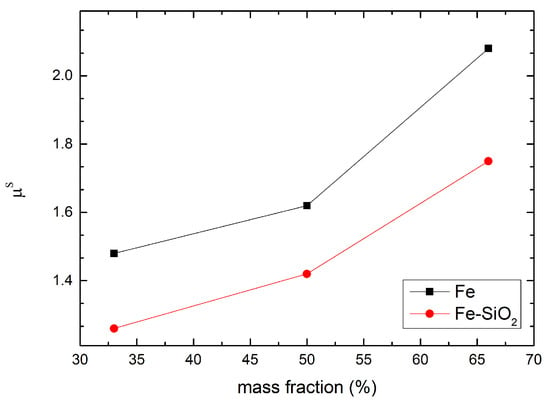
Figure 9.
Static real permeability (μs) dependences on the filler concentration for the “Fe”-wax and the “Fe@SiO2”-wax composites.

Table 1.
Static real permeability (μs) for the “Fe”-wax and the “Fe@SiO2”-wax composites.
The maximum of the imaginary part of the permeability for composites with both types of particles was around 10 GHz. For composites with “Fe” particles, the maximum was at a slightly lower frequency.
The permeability of the composites with “Fe@SiO2” particles increased proportionally with the increase of concentration of the particles (Figure 9) which meant there was no significant magnetic interaction between the particles at these volume fractions of inclusion particles. The permeability of composites with “Fe” particles appeared to increase non-proportionally with the increase of volume fraction. The maximum of the imaginary part of the composites with “Fe” particles shifts slightly to lower frequencies with the increase of volume fraction. This means that for composites with “Fe” particles there is a noticeable dipole–dipole interaction between particles.
The permittivity was clearly higher for composites with “Fe” particles with noticeable frequency dependence of complex permittivity which indicated some conductivity of the composites, especially for higher volume concentration of particles. The dielectric loss tangent was much higher for composites with “Fe” particles.
The probable cause for such a difference in frequency dependences of complex permittivity is a more effective agglomeration of the particles in “Fe” composites. The particles in “Fe@SiO2” composites are isolated which prevents them from forming conduction paths in agglomerates and they have a minimum distance from each other due to the SiO2 layer. The SiO2 layer also somewhat reduces the magnetic interaction between particles in composites.
Some of the samples demonstrated clear resonance behavior of the imaginary part of the permittivity at frequencies around 10 GHz and higher with corresponding frequency dependence on the real part. Such a resonance effect can be attributed to emerging higher-order modes (TE11 in this case) on the boundary of the sample in the coaxial waveguide with subsequent resonance absorption of electromagnetic energy []. Although these losses are attributed to a real loss of energy in the coaxial waveguide with a sample, they are not inherent to the effective properties of the samples.
At frequencies below 1 GHz, there were noticeable systematic errors that were at the same frequencies for all samples regardless of the concentration. These errors were due to the fact that samples had little reflection at these frequencies. One possibility to reduce such errors is to increase the length of the samples but there is a trade-off with other effects: the resonance on higher-order modes and half-wavelength resonance—the longer the sample with the same parameters, the lower the frequencies of these resonances. The error arises from the fact that at these frequencies very little energy reflects from the sample and because the Nicolson–Ross method needs both complex reflection and transmission coefficients in order to calculate complex permeability and permittivity, otherwise small residual calibration errors become significant.
Concerning the comparison between quantitative and semi-quantitative evaluations of the chemical composition of the studied samples, carried out using different analytical techniques, the following was revealed. Studying the “Fe” powder, the quantitative estimation of the “ordered” oxide phase, Fe3O4, was established at 5 wt.% through XRD measurements. This value may be converted to 11 at.% of iron. For the same sample, the quantity of “disordered”, or metastable oxide phase was found to be 15–17 at.%. These two values match well. Investigating the “Fe@SiO2” powder, quantity of the “SiO2” phase was found to be 15 wt.% according to the difference in saturation magnetization between Fe and Fe@SiO2. At the same time, the true value was estimated at 15 at.% (which is roughly equal to 17 wt.%). These two values also coincided well.
4. Conclusions
Iron powder of hollow particles with an average diameter of 0.6 μm was synthesized by a spray pyrolysis method proceeded by reduction in hydrogen. Due to oxidation with atmospheric oxygen, this iron powder contained 11–17 at.% of the oxide phase according to the semi-quantitative XRD and Mössbauer spectroscopy. The density of this powder as it was estimated through the pycnometric experiment was by 20% lower than that of commercial carbonyl iron.
A uniform SiO2 coating of sub-50 nm thickness on the metal surface was obtained by hydrolysis of tetraethyl orthosilicate in water–alcohol solution. The SiO2 shell physically prevented percolation by eliminating the effective conductivity of the composites with the paraffin wax matrix. The SiO2 content was estimated at 15–16 wt.% taking into account saturation and magnetization EDX data. The obtained powders, “Fe” and “Fe@SiO2”, are suitable for cold pressing, unlike the commercial carbonyl iron.
The saturation magnetization of the “Fe” powder fits in the range of values typical for commercial carbonyl iron. But, the coercivity of the powder particles was moderately high (157 ± 11 Oe). The SiO2 coating effectively reduced the real and imaginary permittivity when measured in composites with paraffin wax. The resulting material may possibly be applied for electromagnetic compatibility solutions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M., E.K., and A.K.; methodology, S.M., E.K., and A.K.; software, A.N.; validation, S.M., E.P., and M.H.; formal analysis, A.K., A.N., and S.M.; investigation, A.K., S.M., A.N., D.P., P.Z., K.P., and D.F.; resources, A.K., and S.M.; data curation, A.K., A.N., and S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K. and A.N.; writing—review & editing, S.M., A.K., D.F., and D.P.; visualization, A.K. and A.N.; supervision, S.M.; project administration, S.M. and A.K.; funding acquisition, S.M. and M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The reported study was funded by RFBR and NSFC according to the research project No. 20-52-53020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guild, C.; Biswas, S.; Meng, Y.; Jafari, T.; Gaffney, A.M.; Suib, S.L. Perspectives of spray pyrolysis for facile synthesis of catalysts and thin films: An introduction and summary of recent directions. Catal. Today 2014, 238, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, B.K.; Ergun, C. Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide particles using spray pyrolysis technique. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürmen, S.; Stopić, S.; Friedrich, B. Synthesis of nanosized spherical cobalt powder by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Mater. Res. Bull. 2006, 41, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrinaki, G.; Lorentzou, S.; Karagiannakis, G.; Rattenbury, M.; Woodhead, J.; Konstandopoulos, A.G. Parametric synthesis study of iron based nanoparticles via aerosol spray pyrolysis route. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 115, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurmen, S.; Ebin, B.; Stopić, S.; Friedrich, B. Nanocrystalline spherical iron–nickel (Fe–Ni) alloy particles prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and hydrogen reduction (USP-HR). J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahemi Ardekani, S.; Sabour Rouh Aghdam, A.; Nazari, M.; Bayat, A.; Yazdani, E.; Saievar-Iranizad, E. A comprehensive review on ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique: Mechanism, main parameters and applications in condensed matter. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 141, 104631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudin, A.; Shatrova, N.; Khaydarov, B.; Kuznetsov, D.; Dzidziguri, E.; Issi, J.-P. Synthesis of hollow nanostructured nickel oxide microspheres by ultrasonic spray atomization. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 98, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiyastuti, W.; Wang, W.-N.; Lenggoro, I.W.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Simulation and experimental study of spray pyrolysis of polydispersed droplets. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Hagura, N.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Design of a highly ordered and uniform porous structure with multisized pores in film and particle forms using a template-driven self-assembly technique. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatrova, N.; Yudin, A.; Levina, V.; Kuznetsov, D.; Novakova, A.; Dzidziguri, E.; Perov, N.; Issi, J.-P. Characteristics of Co3O4 and cobalt nanostructured microspheres: Morphology, structure, reduction process, and magnetic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 99, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatrova, N.; Yudin, A.; Levina, V.; Dzidziguri, E.; Kuznetsov, D.; Perov, N.; Issi, J.-P. Elaboration, characterization and magnetic properties of cobalt nanoparticles synthesized by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis followed by hydrogen reduction. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 86, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Okuyama, K. Progress in developing spray-drying methods for the production of controlled morphology particles: From the nanometer to submicrometer size ranges. Adv. Powder Technol. 2011, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Nanosized polymer particle-facilitated preparation of mesoporous silica particles using a spray method. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 1040–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.; Ferguson, P.; Feindel, K.W.; Hermans, I.F.; Callaghan, P.T.; Meyer, C.; Slocombe, A.; Su, C.-H.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Yeh, C.-S.; et al. Simple synthesis and functionalization of iron nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4206–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.J.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zhong, W.; Wu, X.L.; Zou, W.Q.; Du, Y.W. Synthesis and magnetic properties of Fe/SiO2 nanocomposites prepared by a sol–gel method combined with hydrogen reduction. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 419, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, R.; Huang, Z.; Kang, F.; Gu, J. Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of FeCo alloy particles/graphite nanoflake composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivkovic, I.; Murk, A. Extraction of dielectric and magnetic properties of carbonyl iron powder composites at high frequencies. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, M.F.; Corrias, A.; Paschina, G. FeCo–SiO2 nanocomposite aerogels by high temperature supercritical drying. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Mulvaney, P. The assembly of coated nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7312–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.W.; Neo, C.P.; Ding, J. Model design on calculations of microwave permeability and permittivity of Fe/SiO2 particles with core/shell structure. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2014, 75, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ni, X.; Zheng, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. Preparation of Fe (core)/SiO2 (shell) composite particles with improved oxidation-resistance. Mater. Res. Bull. 2006, 41, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gu, H.; Xu, B. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: Design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maklakov, S.S.; Lagarkov, A.N.; Maklakov, S.A.; Adamovich, Y.A.; Petrov, D.A.; Rozanov, K.N.; Ryzhikov, I.A.; Zarubina, A.Y.; Pokholok, K.V.; Filimonov, D.S. Corrosion-resistive magnetic powder Fe@SiO2 for microwave applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 706, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, S.-L.; Lee, H.-C.; Bae, Y.-S.; Kim, M.-B.; Lee, K.; Lee, C.-H. Monodisperse Fe3O4/Fe@SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles with enhanced magnetic property. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 293, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Fu, L.; Li, S.; Dravid, V.P. Silica encapsulation and magnetic properties of FePt nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 290, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Long, J.; Chen, X. Tunable synthesis of SiO2-encapsulated zero-valent iron nanoparticles for degradation of organic dyes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pon-On, W.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Tang, I.-M.; Jongwattanapisan, P.; Krishnamra, N.; Hoonsawat, R. Encapsulation of magnetic CoFe2O4 in SiO2 nanocomposites using hydroxyapatite as templates: A drug delivery system. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 131, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, W.; Luo, F. Electromagnetic property of SiO2-coated carbonyl iron/polyimide composites as heat resistant microwave absorbing materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 375, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuchang, Q.; Wancheng, Z.; Shu, J.; Fa, L.; Dongmei, Z. Microwave electromagnetic property of SiO2-coated carbonyl iron particles with higher oxidation resistance. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2011, 406, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, A.M.; Ross, G.F. Measurement of the intrinsic properties of materials by time-domain techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1970, 19, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, W.B. Automatic measurement of complex dielectric constant and permeability at microwave frequencies. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.L. The scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, C.R.; Snyder, R.L. RIR-measurement and use in quantitative XRD. Powder Diffr. 1988, 3, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menil, F. Systematic trends of the 57Fe Mössbauer isomer shifts in (FeOn) and (FeFn) polyhedra. Evidence of a new correlation between the isomer shift and the inductive effect of the competing bond T–X (→ Fe) (where X is O or F and T any element with a formal posit. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1985, 46, 763–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehring, R. Pharmaceutical particle engineering via spray drying. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 999–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semisalova, A.S.; Perov, N.S.; Stepanov, G.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Strong magnetodielectric effects in magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombard, A.J.F.; Joekes, I.; Alcântara, M.R.; Knobel, M. Magnetic susceptibility and saturation magnetization of some carbonyl iron powders used in magnetorheological fluids. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 416, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, B.; De, G.; Ganguli, D. Dense silica microspheres from organic and inorganic acid hydrolysis of TEOS. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2000, 272, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, O.; Shoushtari, M.Z.; Ackland, K.; Stamenov, P. The structural, magnetic and microwave properties of spherical and flake shaped carbonyl iron particles as thin multilayer microwave absorbers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 428, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Duan, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Guo, J. Microwave absorption properties of one thin sheet employing carbonyl–iron powder and chlorinated polyethylene. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, D.A.; Rozanov, K.N.; Koledintseva, M.Y. Influence of higher-order modes in coaxial waveguide on measurements of material parameters. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Signal Integrity and Power Integrity (EMC, SI & PI), Long Beach, CA, USA, 30 July–3 August 2018; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).